- Problems of the movement of the coolant in the heating system
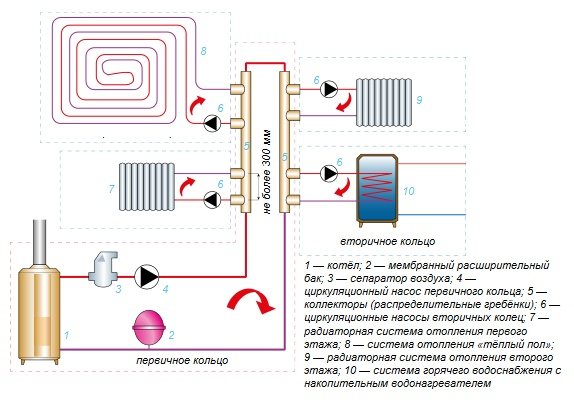
- What is the primary ring in a heating system?
- What is the secondary ring in the heating system?
- How to make the coolant go into the secondary ring?
- Selection of circulation pumps for a combined heating system with primary-secondary rings
- Primary-secondary rings with hydraulic arrow and manifold
To understand how does the combined heating system work, you need to deal with such a concept as "primary - secondary rings". This is what the article is about.
Problems of the movement of the coolant in the heating system
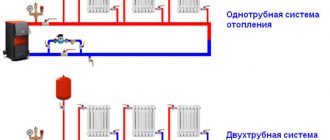
Once in apartment buildings, heating systems were two-pipe, then they began to be made one-pipe, but at the same time a problem arose: the coolant, like everything else in the world, seeks to go along a simpler path - along a bypass pipe (shown in the figure with red arrows), and not through a radiator that creates more resistance:
To force the coolant to go through the radiator, they came up with the installation of narrowing tees:
At the same time, the main pipe was installed with a larger diameter than the bypass pipe. That is, the coolant approached the narrowing tee, ran into a lot of resistance and, willy-nilly, turned to the radiator, and only a smaller part of the coolant went along the bypass section.
According to this principle, a one-pipe system is made - "Leningrad".
Such a bypass section is made for another reason. If the radiator fails, then while it is removed and replaced with a serviceable one, the coolant will go to the rest of the radiators along the bypass section.
But this is like history, we are returning "to our days."
Horizontal and vertical riser?
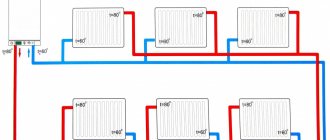
The horizontal system involves connecting radiators to a single riser, which is best located outside residential premises: in the corridor or on the staircase. The main advantage of this option is saving pipes and lower installation costs. The disadvantages include some difficulties in operation and a tendency to form air jams in the system. To bleed them, Mayevsky taps are usually installed on radiators. A horizontal structure is used most often in one-story buildings of a large area.
The horizontal arrangement of the system saves on pipes and installation. However, such a system has a tendency to airing, which requires the installation of additional equipment, for example, Mayevsky cranes
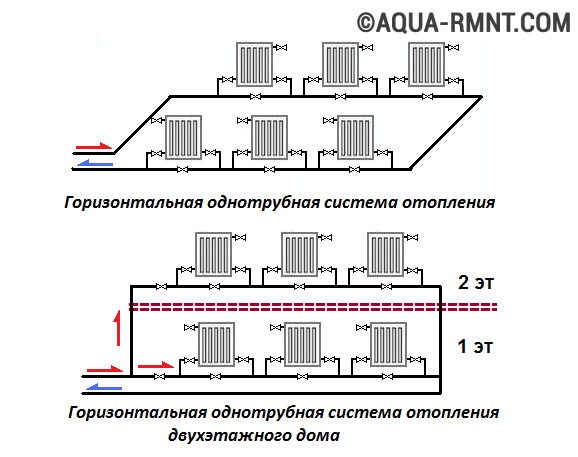
When arranging a vertical system, all heating devices are supplied to the vertical riser. This method allows you to connect separately each floor of a multi-storey building. The main advantage is that no air locks are formed during operation. However, the arrangement of the vertical version of the system will cost a little more than the horizontal one.

The vertical design is not prone to the appearance of air jams during operation, but it is more expensive to equip
How to make the coolant go into the secondary ring?
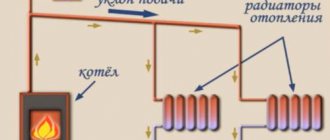
But not everything is so simple, but you need to deal with the node, circled by a red rectangle (see the previous diagram) - the place of attachment of the secondary ring. Because the pipe in the primary ring is most likely of a larger diameter than the pipe in the secondary ring, so the coolant will tend to the section with less resistance. How to proceed? Consider the circuit:
The heating medium from the boiler flows in the direction of the red arrow "supply from the boiler". At point B, there is a branch from the supply to the underfloor heating. Point A is the entry point for the underfloor heating return into the primary ring.
Important! The distance between points A and B should be 150 ... 300 mm - no more!
How to "drive" the coolant in the direction of the red arrow "to the secondary"? The first option is a bypass: reducing tees are placed in places A and B and between them a pipe of smaller diameter than the supply.
The difficulty here is in calculating the diameters: you need to calculate the hydraulic resistance of the secondary and primary rings, bypass ... if we miscalculate, then there may be no movement along the secondary ring.
The second solution to the problem is to put a three-way valve at point B:
This valve will either completely close the primary ring, and the coolant will go directly to the secondary. Or it will block the way to the secondary ring. Or it will work as a bypass, letting in part of the coolant through the primary and part through the secondary ring. It seems to be good, but it is imperative to control the temperature of the coolant. This three-way valve is often equipped with an electric actuator ...
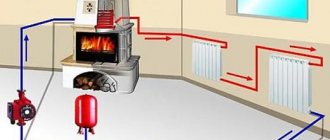
The third option is to supply a circulation pump:
The circulation pump (1) drives the coolant along the primary ring from the boiler to ... the boiler, and the pump (2) drives the coolant along the secondary ring, that is, on the warm floor.
Solution to the problem
To solve this problem, an example of a hydraulic resistance solution is chosen. This formula shows that the losses generated in the circuit are directly proportional to the coefficient of circulating friction and double internal speed. Also, the allowable losses in the opposite direction are proportional to the size of the diameter of the inner pipe, which is multiplied by 2 the acceleration of free fall. In the previous case with the hydraulic pipe, the pipe size was increased to keep the pressure inside to a minimum. What if we try to resize the pipe?
After research, it turned out that during the reduction of the gap near the pipeline to significant values, then the resistance of the hydraulics automatically decreases. At the end of these actions, the circulation pumps will become free from each other. Then it turns out that two identical expressions in their composition turn out to be the same. But there is still a difference between the two options.
When using the hydraulic tube, the equipment will perform three main functions. When a person wants to apply the method of primary-secondary rings to the heating system, then to solve this issue, the separator and the deslimer are equipped separately, according to their own views or need.
It is because of this, when a pair of circulation pumps is equipped at once in the structure, then the method of close tees is used. When using this technology, any of the three hydraulic pumps will start to work freely from their neighbor.
Strapping options
There are 4 main and most common ways:
- with natural circulation,
- with forced,
- collector classic,
- on primary-secondary rings.
To understand which layout is best for a particular case, you need to understand the principle of each.
1. Natural circulation stroke. This option is the simplest. Here, as the name implies, there is no pump, and the coolant moves along the highway due to physical laws. All settings are set manually, and you also need to monitor the operation of the system. In order for such heating to work properly, some tips must be taken into account:
- the pipe must have a large inner diameter (from 32 mm),
- the boiler is installed below the radiators,
- the slope of the pipes must be at least 5 mm along the flow of the coolant,
- the minimum number of pipe turns so as not to interfere with the natural flow of fluid in the line.
Typically, this method is used in settlements with power outages.
2. Forced circulation.This type of strapping is the most common. It has many benefits. One of the most important is adjusting the temperature of each battery. The principle of forced circulation is that the coolant can flow through the line at high speed, thanks to the pump. The only drawback of this option is the dependence of the pump on electricity. When it is turned off, the pump also stops working. However, there are 2 ways to solve this problem:
- installation of a bypass pipeline (bypass), which will enable the system to switch to natural circulation;
- arrange a high-quality emergency scheme, thanks to which it will be possible to dump excess heat;
- install an autonomous power supply system (uninterruptible power supply).
Thus, the disadvantage of this wiring is solved inexpensively and quickly.
3. Collector wiring. Although this heating option is the most expensive and difficult to install, it is the most efficient, convenient and energy-saving. Its essence is that all pipes from the boiler pass through a special device called a collector. This unit contains various valves, taps, air vents, measuring devices, and so on. There is a separate wiring from the collector to other devices. There are a number of advantages that come with this method:
- Each heating element is controlled separately from the manifold box, which makes it possible to turn off any one without disrupting the operation of the entire line.
- The temperature is the same throughout the line.
Collector wiring greatly simplifies the supervision and maintenance of the heating system.
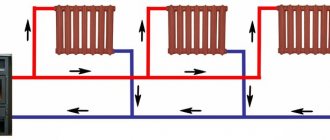
4. Strapping on primary-secondary rings. This method is more often used in buildings where there are many consumers. More than one circulation pump is used here. The essence of the work of this wiring is as follows: pumps are connected to the small circuit where the heated coolant is located, which, if necessary, take this water to the consumer. There are 2 types of circuits connected to the boiler:
- Mixing. Here, the temperature of the coolant is influenced by how much the damper is open.
- Straight. In this case, the liquid is heated from the burner.
There are also 2 ways to connect circuits:
- Two-way connection, when the heating medium is supplied by pumps.
- In a three-way connection, each circuit has a separate tap and is connected to a boiler in which the coolant is heated.
However, one should not forget about the emergency scheme. It is necessary in those homes where boilers depend on electricity. When the light is turned off, the heating will continue to work, thanks to the emergency circuit. There are 4 options for such a scheme.
- Cold water is supplied from the mains.
- The pump switches to an additional power source (e.g. battery). When using this option, it is important not to forget to monitor the charging of this source.
- Installation of an additional circuit with natural circulation. This small circuit removes heat after the pump is turned off.
- Simultaneous use of two circuits. When the electricity-dependent branch stops working, the natural circulation circuit continues to heat the room.
Choosing a suitable scheme, you need to be guided by the type of boiler, access to electricity and the funds allocated for additional devices.
The principle of the organization of the beam scheme
One of the central elements of the beam system is the collector assembly. If you are going to make heating in a house with several floors, then the collector should be located at each level.
During installation, the collectors are placed in a collector cabinet, where a convenient system for the location of this element is provided for subsequent maintenance or adjustment.
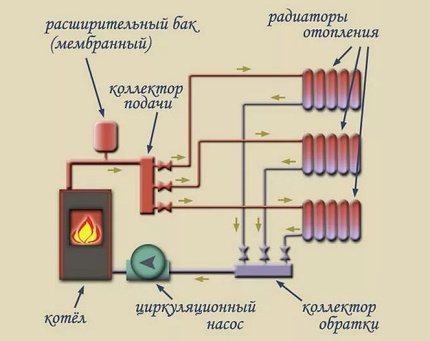

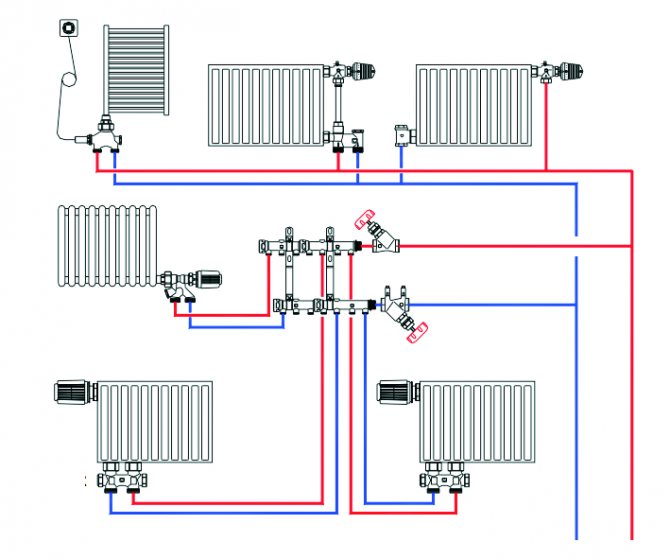
The beam wiring is used for one- and two-pipe systems.The first option assumes that the supply and collection of the coolant is carried out by one collector. The second option involves the use of two collectors for supply and return
The indisputable advantage of the radiant system is the minimum number of connections, which has a positive effect on the hydraulic stability of the entire heating system. The central working body is the boiler.
To ensure high efficiency and safety, the owner needs to take into account the power of the unit, the consumption of thermal energy by heating devices and the heat loss of the system. This must be done regardless of what type of fuel the boiler is running on.
An increase in the length of the pipeline when creating a beam wiring is fraught with a slight increase in heat loss, which must also be taken into account for the balance of capacities.

In a single-pipe radial distribution of heating circuits, the supply of the coolant prepared for heating the devices is carried out by the same collector, which collects the return flow and sends it to the boiler (+)
Choosing a circulation pump
Beam piping is used mainly in horizontal circuits with a lower coolant supply. It requires a circulation pump that stimulates the movement of heated water through multiple branches.
The controlled circulation of the heating medium makes it possible to reduce the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the heating circuit. As a result, it is possible to increase the efficiency of heating, making the system more compact and less material-intensive.


When selecting and installing a circulation pump, you need to take into account a number of features, using which you can achieve high efficiency of the entire system.
This unit is selected for several important parameters, including:
- productivity, m3 / hour;
- head height, m.
In order to choose the right circulation pump for these parameters, it is necessary to take into account the diameter of the pipes, their length and height relative to the level of the pumping unit. When drawing up a project for the installation of a heating system, these parameters are calculated in advance.
Circulation pump installation rules
Adhering to the recommendations below, you can milk high efficiency and safety of heating:
- circulating pumps with a wet rotor are installed so that the shaft has a horizontal position;
- the device with a thermostat should not be close to hot surfaces (radiator or boiler) so that the readings are not distorted;
- as a rule, it is installed on the return section of the pipeline due to lower temperatures. Modern models can also be installed in the supply line, withstanding high temperature conditions;
- the heating circuit must be equipped with an air bleed mechanism. If not, then the pump must have an air vent;
- should be located as close to the expansion tank as possible;
- before installing the pump, it is recommended to flush the system to remove solid inclusions;
- fill the system with water before starting the pump;
To avoid becoming a victim of excessive noise, select the pump in accordance with the performance of the heating system.
Is it possible without a pump?
Of course, you can save money and not buy a pump, air vents for bleeding air, sensors, etc. But the natural circulation ray system requires compliance with several not very convenient conditions.
Experts recommend this option in extremely rare cases. Firstly, you will need to install wide diameter pipes. Secondly, the expansion vessel must be installed at the highest point of the object.

To save on components, you can do without a pump, but this is possible only if a number of conditions are met and only for small buildings
This option is suitable for a summer residence or other modest-sized object, providing enough heat.The choice between natural circulation and forced circulation should be made at the design stage.
Choosing a distribution manifold
This device is also called a manifold. Serves to supply the coolant to each heating device (warm floor, radiator, convector, etc.). Through the collector, the return flow also flows out, which then enters the boiler or is again mixed into the circuit to regulate the temperature.
The manifold can support from 2 to 12 circuits. Some vendors offer even more branches for complex projects.
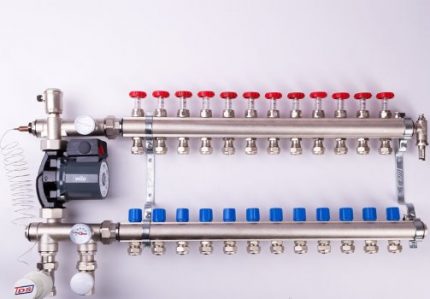

The distribution manifold is the main transport terminal, which serves to distribute the heating medium in the right amount for each room or heater
The combs are often equipped with additional shut-off and thermostatic elements. They allow you to adjust the optimal flow rate of the heating agent for each heating branch. The presence of air vents guarantees a more efficient and safer operation of the system.