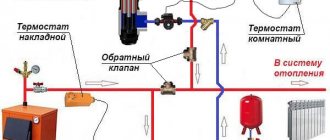
When designing and installing a heating system, the question always arises - what diameter of the pipeline to choose.
The choice of the diameter, and hence the throughput of the pipes, is important, because it is necessary to ensure the speed of the coolant in the range of 0.4 - 0.6 meters per second, which is recommended by specialists. In this case, the required amount of energy (the amount of coolant) must be supplied to the radiators.
It is known that if the speed is less than 0.2 m / s, then air congestion will stagnate. A speed of more than 0.7 m / s should not be done for reasons of energy saving, since the resistance to fluid movement becomes significant (it is directly proportional to the square of the speed), moreover, this is the lower limit for the occurrence of noise in pipelines of small diameters.
What pipes should be used for the heating system?
Polypropylene pipes are divided into several types, which have their own technical characteristics, and they are designed for different conditions. Suitable for heating grades PN25 (PN30), which withstand an operating pressure of 2.5 atm at a liquid temperature of up to 120 degrees. FROM.
Wall thicknesses are given in the tables.
For heating, polypropylene pipes are now used, which are reinforced with aluminum foil or fiberglass. The reinforcement prevents significant expansion of the material when heated.
Many experts prefer pipes with internal fiberglass reinforcement. Such a pipeline has recently become the most widely used in private heating systems.
Classification of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes can differ not only in cross-section and size shown in the table, but also in resistance to environmental pressure and technical parameters.
There are several types of pressure classification:
- N10 - this type of pipes is used most often if it is necessary to organize a warm floor or water supply (only if the maximum water heating temperature is 450). The outer diameter of polypropylene pipes is up to 100 mm, the inner diameter is 85 mm.
- PN16 - is not used very often, because the maximum pressure on the pipe walls should be no more than 1.7 MPa. A suitable option for organizing water supply (with water heating up to 600).
- РN20 - pipe thickness up to 17.8 mm, maximum pressure on pipe walls 2.1 MPa. Such pipes are in demand for water supply systems (water can be heated in this case up to 750).
- РN25 - working pressure is 2.3 MPa (reinforced with aluminum foil along the entire perimeter). The most common type of polypropylene pipes, because it is possible to heat the liquid in them up to 900.
Various materials are classified according to the composition of raw materials:
- PPRС - the raw material for such pipes is a random copolymer. Their main advantage is temperature stability (range from -1600 to +13500), as well as a high level of resistance to shock loads.
- PPH - for the manufacture of such pipes, additional additives are used - nucleators and antistatic agents, which increases the strength of the structure. They are used for the organization of ventilation, drainage, etc., are not used for heating systems.
- PPB - the main components of raw materials for such pipes are hypo-polymer micromolecules, thanks to which they can also be used for cold water supply.
- PPs - considered a high grade polymer. Possesses a high level of resistance to overheating, loads, sufficiently strong and durable.
Selection of the diameter of the heating pipeline
Pipes are available in standard diameters, from which you need to make a choice. Typical solutions have been developed for the selection of pipe diameters for heating a house, guided by which, in 99% of cases, you can make the optimal correct choice of diameter without performing a hydraulic calculation.
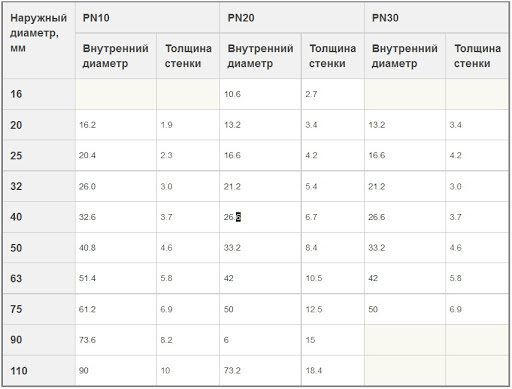
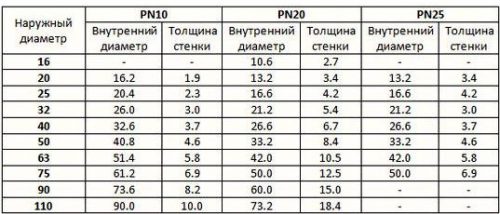
Standard outer diameters of polypropylene pipes are 16, 20, 25, 32, 40 mm. The inner diameter of pipes of grade РN25 corresponding to these values is 10.6, 13.2, 16.6, 21.2, 26.6 mm, respectively.
More detailed information on the outer diameters, inner diameters and wall thickness of polypropylene pipes is given in the table.
Pressure classification
In the marking of PP products, the designation N25, N10, etc. is found. This indicator makes it possible to assess the resistance of the material to the pressure of the liquid passing through the line.
Yulia Petrichenko, expert
There are the following types of polypropylene pipes:
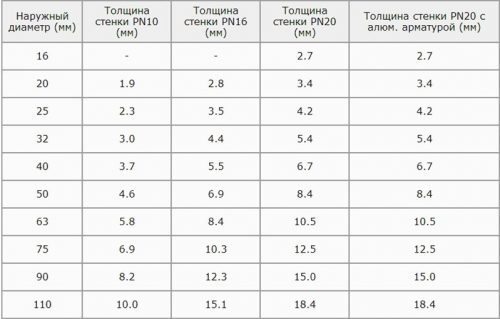
- N10 (РN10) - with a working pressure on the wall of 1.0 MPa and a polymer thickness of 1.9 to 10 mm. They are used for arranging underfloor heating, cold water supply with heating up to +45 degrees. Diameter of polypropylene pipes of this type: outer - 20 ... 110 mm, inner - 16 ... 90 mm.
- PN16 is a rarely used type of product with a wall pressure of 1.6 MPa. Suitable for supplying cold and hot water with liquid heating up to +60 degrees.
- N20 (РN20) - polypropylene lines with a working pressure on the wall of 2.0 MPa and a product thickness of 16 ... 18.4 mm. The most demanded material for the device of hot and cold water supply with a liquid heating temperature up to 80 degrees. Execution: outer diameter - 16 ... 110 mm, inner diameter - 10.6 ... 73.2 mm.
- N25 (PN25) - polypropylene pipe with a working pressure on the wall of 2.5 MPa and reinforcement with aluminum foil. Ideal for heating systems, hot water supply with a heating medium temperature up to +95 degrees. Due to the multilayer structure, products of this type have increased resistance to shock and heat loads. Version: inner diameter of polypropylene pipes PN25 - 13.2 ... 50 mm, outer diameter - 21.2 ... 77.9 mm.
Currently, there is a variant of reinforcing the line made of polypropylene with fiberglass. This allows you to avoid delamination of water lines during operation, and during installation - loss of time for cleaning the sections during welding. Systems with fiberglass mesh reinforcement are the most preferable, as they provide quick installation, resistance to deformation, and extended service life without repairs.
What diameters what to connect
We need to ensure the supply of the required thermal power, which will directly depend on the amount of the supplied coolant, but the speed of fluid movement should remain within the specified limits of 0.3 - 0.7 m / s
Then there is such a correspondence of the connections (for polypropylene pipes, the outer diameter is indicated):
- 16 mm - for connecting one or two radiators;
- 20 mm - for connecting one radiator or a small group of radiators (radiators of "normal" power within 1 - 2 kW, maximum connected power - up to 7 kW, the number of radiators up to 5 pcs.);
- 25 mm - for connecting a group of radiators (usually up to 8 pcs., Power up to 11 kW) of one wing (arm of a dead-end wiring diagram);
- 32 mm - for connecting one floor or a whole house, depending on the thermal power (usually up to 12 radiators, respectively, the thermal power is up to 19 kW);
- 40 mm - for the main line of one house, if there is one (20 radiators - up to 30 kW).
Let's consider the choice of the pipe diameter in more detail, based on the previously calculated tabular correspondences of energy, speed and diameter.
Classification of pipes
There are tables of diameters of polypropylene pipes. Several varieties of PP pipes should be distinguished.
PPB
This marking corresponds to impact resistant pipes.Most often they are used to equip floor heating and cold water transportation systems.

PPH
Traditionally, these include PP pipes whose diameters are of great importance. They are used in ventilation systems and for transporting cold water, as they are sensitive to high temperatures.
PPR
Such pipes are considered the most popular because they are distinguished by their versatility. They are not afraid of high temperatures, therefore they can be used even in hot water supply systems and for heating (read: "Advantages of polypropylene pipes for hot water and operating rules").


It is worth noting that all of the above pipes are a type of polyethylene pipes. Depending on the additives, polypropylene can be flexible and heat resistant.
Selection of pipes by capacity
It can be seen from the table that at a speed of 0.4 m / s approximately the following amount of heat will be supplied through polypropylene pipes of the following outer diameter:
- 4.1 kW - inner diameter about 13.2 mm (outer diameter 20 mm);
- 6.3 kW - 16.6 mm (25mm);
- 11.5 kW - 21.2 mm (32 mm);
- 17 kW - 26.6 mm (40 mm);
And at a speed of 0.7 m / s, the values of the supplied power will already be about 70% higher, which is not difficult to find out from the table.
How much heat do we need?
What determines the dimensions of polypropylene pipes?
The parameters of polypropylene pipes directly depend on the volume of liquid that will be in the pipes and its temperature. Also, do not forget about the pressure that the liquid will exert on the walls of the system. In order to select the appropriate pipes for a particular design, it is best to use the data from the table.


The dimensions of polypropylene pipes depend on their purpose, that is, what tasks they will perform. Despite the fact that the diameters of polypropylene pipes differ slightly from each other, compared to analog products, this difference is quite diverse.
As soon as the permeability of the pipeline being built is calculated, it is possible to determine exactly what size of pipes will be needed for these purposes.
In principle, the size of the products under consideration depends on many factors, from their purpose to the load of the liquid that will circulate inside them, so when choosing the size of the pipes, you need to take into account all sorts of factors so that the system works fully and is durable. The inner diameter of polypropylene pipes, the table of which was presented above, is also an important factor when choosing the right product.
How much heat should the pipeline supply
Let us consider in more detail, using an example, how much heat is usually supplied through the pipes, and select the optimal diameters of the pipelines.
There is a house with an area of 250 square meters, which is well insulated (as required by the SNiP standard), so it loses heat in the winter by 1 kW from 10 square meters. To heat the whole house, an energy supply of 25 kW (maximum power) is required. For the first floor - 15 kW. For the second floor - 10 kW.
Our heating scheme is two-pipe. A hot coolant is supplied through one pipe, and the cooled one is discharged through the other to the boiler. Radiators are connected in parallel between the pipes.
On each floor, the pipes branch out into two wings with the same heat output, for the first floor - 7.5 kW each, for the second floor - 5 kW each.
So, from the boiler to the interfloor branching, 25 kW comes in. Therefore, we need main pipes with an internal diameter of at least 26.6 mm so that the speed does not exceed 0.6 m / s. Suitable for 40mm PP pipe.
From the interfloor branching - along the first floor to the branching on the wings - 15 kW is supplied. Here, according to the table, for a speed of less than 0.6 m / s, a diameter of 21.2 mm is suitable, therefore, we use a pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
7.5 kW goes to the wing of the 1st floor - an inner diameter of 16.6 mm is suitable, - polypropylene with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
For each radiator, the power of which does not exceed 2 kW, you can make a branch with a pipe with an outer diameter of 16 mm, but since this installation is not technologically advanced, pipes are not popular, more often a 20-mm pipe with an inner diameter of 13.2 mm is installed.
Accordingly, we accept a 32mm pipe on the second floor before branching, a 25mm pipe on the wing, and we also connect radiators on the second floor with a 20mm pipe.
As you can see, it all comes down to a simple choice among the standard diameters of commercially available pipes. In small home systems, up to a dozen radiators, in dead-end distribution schemes, polypropylene pipes are mainly used 25 mm - "on the wing", 20 mm - "on the device". and 32 mm “to the boiler line”.
Features of the choice of other equipment
The diameters of the pipes can also be selected according to the conditions of the hydraulic resistance for atypically long pipelines, at which it is possible to go beyond the technical characteristics of the pumps.
But this can be for production workshops, but in private construction it practically does not occur.
For a house up to 150 square meters, according to the conditions of the hydraulic resistance of the heating radiator system, a pump of type 25 - 40 (pressure 0.4 atm) is always suitable, it can also be suitable up to 250 square meters in some cases, and for houses up to 300 square meters ... - 25 - 60 (head up to 0.6 atm).
The pipeline is designed for maximum capacity. But the system, if ever, will work in this mode, it will not be for a long time. When designing a heating pipeline, it is possible to take such parameters that at the maximum load, the speed of the coolant is 0.7 m / s.
In practice, the speed of the water in the heating pipes is set by a pump that has 3 rotor speeds.
In addition, the supplied power is regulated by the temperature of the coolant and the duration of the system's operation, and in each room it can be regulated by disconnecting the radiator from the system using a thermal head with a pressure valve.
Thus, with the diameter of the pipeline, we ensure that the speed is within the range of up to 0.7 m at maximum power, but the system will generally work with a lower speed of fluid movement.
Differences in polypropylene pipes for raw materials used
PPR... If the products have this marking, then random copolymer of polypropylene was used for their production, which provides thermal stability. Products with this marking can be used for lines intended for transporting hot liquids, and for cold ones. Basically, this brand is used for the installation of underfloor heating.
PPH. Additives are added to the raw materials that provide higher strength to the products. This brand of simple polypropylene products is used mainly for the installation of cold water supply systems.
PPB... This marking indicates that a complex polypropylene block copolymer was used for the production. High strength fittings are made from this brand.
PPs. Products with similar designations are used to supply hot liquid. An excellent option for installing heating mains.
Corrugated pipe can be bought here https://ingplast.ru/element/gofrirovannaya-truba-ecopal-dn-od-0110/
Required data for calculation
The main task of heating pipes is to deliver heat to the heated elements (radiators) with minimal losses. From this we will build on when choosing the correct pipe diameter for heating a house. But in order to calculate everything correctly, you need to know:
- pipe length;
- heat loss in the building;
- power of elements;
- what kind of piping will be (natural, forced, one-pipe or two-pipe circulation).
The next point, after you have all the above data on hand, you will need to sketch a general diagram: how, what and where it will be located, what heat load each heating element will bear.
Then you can begin to calculate the required cross-section of the pipe diameter for heating the house. You should also be careful when buying:
- metal-plastic and steel pipes are marked according to the size of the inner diameter, there are no problems;
- but polypropylene and copper ones - in the outer diameter. Therefore, we need to either measure the inner diameter ourselves using a caliper, or subtract the wall thickness from the outer diameter of the pipe for heating the house.
Do not forget about this, because we need exactly the "inner diameter of the pipe for heating the house" in order to calculate everything correctly.

Choosing a diameter for your heating
Do not count on the fact that you will be able to choose the right pipe diameter for heating your house right away. The point is that you can get the desired efficiency in different ways.
Now in more detail. What is most important in having the right heating system? The most important thing is uniform heating and delivery of liquid to all heating elements (radiators).
In our case, this process is constantly supported by a pump, thanks to which, for a specific time period, the liquid moves through the system. Therefore, we can choose from only two options:
- buy pipes of a large cross-section and, as a result, a low flow rate of the coolant;
- or a pipe of small cross-section, naturally, the pressure and the speed of fluid movement will increase.
Logically, of course, it is better to choose the second option for the diameter of pipes for heating a house, and for the following reasons:
- when laying pipes externally, they will be less noticeable;
- when laying internally (for example, in a wall or under the floor), the grooves in the concrete will be more accurate and easier to hammer;
- the smaller the diameter of the product, the cheaper it is, of course, which is also important;
- with a smaller pipe cross-section, the total volume of the coolant also decreases, thanks to which we save fuel (electricity) and reduce the inertia of the entire system.
And working with a thin pipe is much easier and easier than with a thick one.
If a house or apartment is being settled
When creating a project for a standard private house or apartment, there is no need for precise calculations. The number of plumbing fixtures will be minimal, while the difference in prices for pipes of various diameters will differ minimally, which will practically not affect the budget.
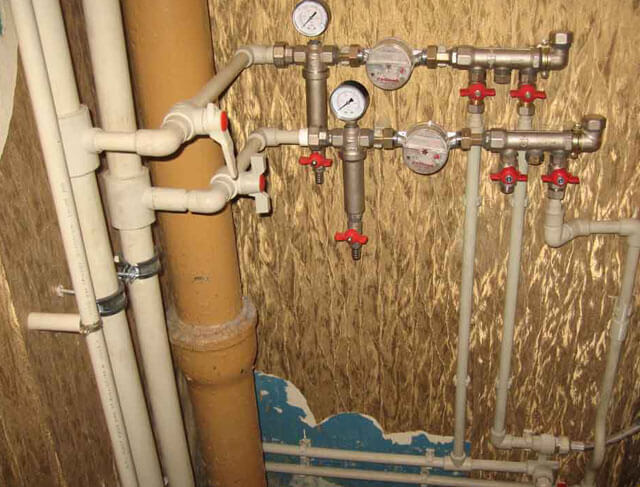


If you look at the mixer hose, you can see how small their diameter is, that is, through what minimum holes water enters the sink. Given that the cross-section of the polypropylene pipe will be much larger, it will always be enough, since this particular hose will be the bottleneck in this case. That is, the patency of the entire system will rest against its narrowest point.
That is why the owners of private houses and apartments do not carry out complex calculations, but simply purchase a polypropylene pipe with a cross section of 20 mm, while saving their precious time. In the overwhelming majority of cases, with a standard number of washbasins, sinks, bathtubs and other plumbing fixtures, such a pipe will suffice with a large margin.
conclusions
We hope everyone figured out what diameter polypropylene pipes are measured by. Their selection will not be difficult. As practice shows, it is often possible to simply purchase the simplest and cheapest pipe - as a result, you will get a high-quality and properly functioning water utility.
The formula for calculating the diameter of a pipe for heating a house
For example, we will select a cross-section for a copper pipe in direct proportion to how powerful the radiators are.
All pipes are manufactured in accordance with GOST. Consequently, all diameters are known in advance, as well as the amount of useful heat that they can pass through themselves, depending on the section and pressure.
Therefore, it is not necessary to calculate every time that which has long been calculated and recorded in special tables. All that is required is simply to find a table with data suitable for you and use it to choose the diameter of the pipe for heating the house.
How were these tables created? It's very simple. Take this formula for calculating the diameter of the pipe, count, and write down the result, and so on for all sections:
D = √ (354 * (0.86 * Q / ∆t) / V)
Wherein:
V is the velocity of the liquid in the pipe (m / s); Q is the required amount of heat for heating (kW); ∆t is the difference between reverse and direct feed (C); D - pipe diameter (mm).
You can try to calculate everything yourself.
It is known that in individual heating systems the coolant moves at a speed of 0.2-1.5 m / s. It is also known that the ideal speed should be in the range of 0.3-0.7 m / s.
If the speed is higher than the optimal values, then the noise increases, and if it is less, then air jams may appear. For this, there are already ready-made tables. In them, we choose the speed that suits us.
There are tables for copper, polypropylene, metal and metal-plastic pipes. They have ready-made solutions for working in medium and high temperatures. For clarity, let's look at specific examples.
Operational and technical parameters of PP pipes
- For gas pipelines (gas mains, ventilation ducts and systems), diameters of polypropylene pipes in millimeters: 10.0; 15.0; 20.0; 25.0; 32.0; 40.0; 50.0; 65.0; 80.0; 90.0; 100.0; 125.0; 150.0; 160.0; 200.0; 225.0; 250.0; 300.0; 400.0; 500.0; 600.0.
- For water pipelines (plumbing with hot or cold water, heating systems, sewer lines) the dimensions of polypropylene pipes in mm: 16.0; 20.0; 25.0; 32.0; 40.0; 50.0; 63.0; 75.0; 90.0; 110.0; 125.0; 160.0; 180.0; 225.0; 250.0; 280.0; 315.0; 400.0; 500.0; 630.0; 800.0; 1000.0; 1200.0.
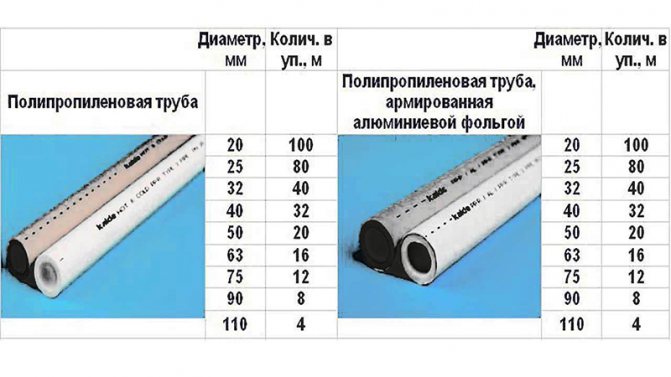

Parameters of polypropylene pipes
The use of polypropylene pipes increases the reliability of the line, since they can completely replace steel pipes that rust over time. Another plus is that the diameter of polypropylene pipes for water supply or gas pipelines is smaller than that of steel products, and the operating time is longer. So, a steel pipe ⌀ 17 mm is replaced by a PP product ⌀ 10 mm, a metal pipe 43.2 mm - plastic ⌀ 32 mm. The tables show the dimensions and diameters of the running products PN10 for cold water during operation under the following conditions: liquid temperature 200C, working pressure 10 atm, capacity for the indicated dimensions for 4-meter sections:
| Product size in millimeters | Dn, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Capacity, liters per running meter |
| 20 x 1.9 | 20 | 1,9 | 0,206 |
| 25 x 2.3 | 25 | 2,3 | 0,327 |
| 32 x 3.0 | 32 | 3,0 | 0,531 |
| 40 x 3.7 | 40 | 3,7 | 0,834 |
| 50 x 4.6 | 50 | 4,6 | 1,307 |
| 63 x 5.8 | 63 | 5,8 | 2,075 |
| 75 x 6.9 | 75 | 6,9 | 2,941 |
| 90 x 8.2 | 90 | 3,2 | 4,254 |
| 110 x 10.0 | 110 | 10,0 | 6,362 |
Pipes PN16 for hot water supply, operating temperature 60 ° С, pressure 10 atm, lengths of 4 meters:
| Size, mm | Dn, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Capacity, liters per running meter |
| 20 x 2.8 | 20 | 2,8 | 0,206 |
| 25 x 3.5 | 25 | 3,5 | 0,327 |
| 32 x 4.5 | 32 | 4,4 | 0,531 |
| 40 x 5.6 | 40 | 5,5 | 0,834 |
| 50 x 6.9 | 50 | 6,9 | 1,307 |
| 63 x 8.7 | 63 | 8,6 | 2,075 |
| 75 x 10.24 | 75 | 10,3 | 2,941 |
| 90 x 12.5 | 90 | 12,3 | 4,254 |
| 110 x 15.2 | 110 | 15,1 | 6,362 |
Where Dn is the inner diameter of the product.
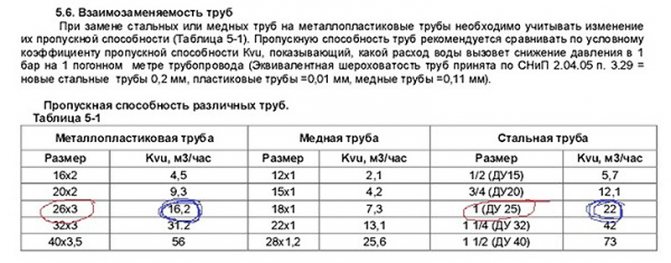

Interchangeability table for steel and PP products
From PP pipes are mounted:
- Ventilation pipelines and routes. For the smooth movement of air flows:
- high strength of pipes is not needed;
- the track can be mounted on light plasterboard partitions or on a suspended ceiling frame, since the polypropylene pipe weighs little;
- for ventilation, you will need polypropylene pipes ⌀ 10-12.5 mm and up to 500 cm long.
- Sewerage and stormwater drainage, which require high tightness of the connections. Sealing rubber rings are used at the joints.
- Internal sewerage system: ⌀ 40 mm, 50 mm, 110 mm; length of products - 30-200 mm.
- External sewer main: length up to 500 cm; ⌀ 150 mm and more. Products of larger diameters and dimensions (⌀ 600 mm, length 10 m) should be laid in trenches using special equipment.
- Hot water or cold water supply lines ⌀ 16-110 mm, length 500 cm.
- Heating pipelines. The required diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating is 20-75 mm, the length can be different.
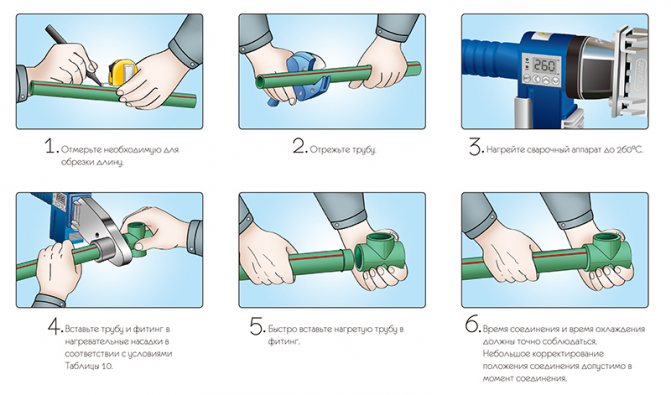

Sequence of assembly of PP-tracks
The price for PP-products is determined depending on:
- class of polypropylene. The most expensive pipe is type III;
- the diameter of polypropylene pipes, the table of which is presented above, - the larger it is, the higher the cost;
- the presence of wall reinforcement;
- manufacturing company.
The approximate cost of some pipes for one running meter:
- PPR # 20 - 35 rubles;
- PPR No. 25 Fiber - 45 rubles;
- PP-Fiber - fiberglass-reinforced pipe - 45 rubles;
- Ekoplastik PPR No. 20 - 40 rubles;
- PP-ALUX, reinforced with aluminum - 55 rubles;
- Ekoplastik PPR Fiber Basalt Plus with fiberglass reinforcement - 99 rubles.
Calculation of the diameter for a two-pipe heating system
We will count on the example of a simple house with two floors. We have two wings on each floor. A two-pipe heating system with the following parameters will be installed in the house itself:
- total heat loss - 36 kW;
- loss on the 1st floor - 20 kW;
- loss on the 2nd - 16 kW;
- polypropylene pipes installed;
- system operation in 80/60 mode;
- temperature - 20 C.
Below is a table (a), based on the data of which, we will determine the desired pipe diameter. Cells with the best (optimal) fluid velocity are marked in green in the table.
We count. Through the section of the pipe that connects the first fork and the boiler, the entire volume of liquid passes, therefore, all the heat, and this is 38 kW. Let's determine which pipe to take here.
We take our table, look for the corresponding line in it, then go through the green cells and look up. What do we see? And we see that with such parameters, two options are suitable for us: 50 and 40 mm. Naturally (as described above), we choose a smaller pipe diameter for heating a house of 40 mm.
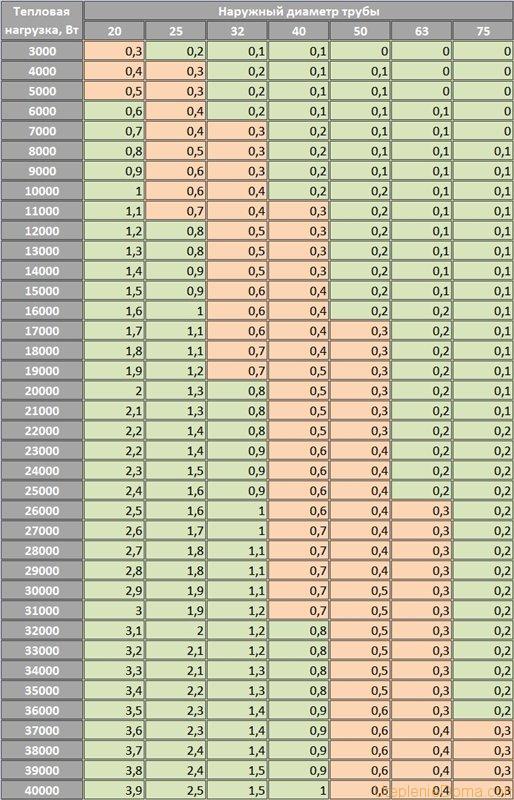

Next, we look at the fork that divides the movement of the coolant into the second and first floors (16 and 20 kW). Again, we look at the values in the table and we find that a pipe diameter of 32 mm is needed in both directions.
We have two wings on each floor. The path is also split into two branches. We consider the first floor:
20 kW / 2 = 10 kW per wing
Second floor by analogy:
16 kW / 2 = 8 kW per wing
Again, we take our table and determine that in these areas we need a pipe with a cross section of 25 mm. It is also clearly seen from the table that we use such a diameter until the load drops to 5 kW, then we will use pipes of 20 mm.
Important! From personal experience, I can say that it is better to switch to a pipe diameter of 20 mm when the heat load is not 5 kW, but 3 kW.
In such a simple way, we calculated all the diameters of the pipe for heating the house of the polypropylene pipes we need for a two-pipe heating system.
For the return water supply, you do not need to calculate anything, everything is much simpler there: you do all the wiring with pipes of the same diameter as for the direct supply. As you can see, there is nothing complicated. All you need is a good, appropriate table.
Some nuances of calculating the diameter for metal pipes
If you decide that you will use metal pipes for the heating system, then you need to take into account that they lose heat. In small areas, this is almost invisible.
But on extended systems, it can happen that the very last heating elements in the chain are cold or slightly warm. This is also a consequence of the wrong choice of the pipe diameter. Fortunately, heat loss can be easily calculated:
q = k * 3.14 * (tv-tp) q - heat loss per meter (W / s); k is the heat transfer coefficient (W * m / s); tв - temperature of hot supplied water (С); tp - ambient temperature (C).
Let's take a pipe with a diameter of 40 mm. Let's say the wall is 1.4 mm thick. Material - steel. Let's calculate:
q = 0.272 * 3.15 * (80 - 22) = 49 W / s
Here is another proof of why you need to take the diameter of a pipe for heating a house with a smaller diameter. After all, it is clear that the thicker the pipe, the more heat we will lose.
And in this example, we got losses of almost 50 W per 1 meter of distance. And if the system is quite extended, then you can lose all the heat.
But don't be discouraged! Such accurate calculations are needed only for multi-storey residential buildings. For individual heating systems, everything is simpler: the calculations are rounded up and this gets a certain margin.
Where to get tables?
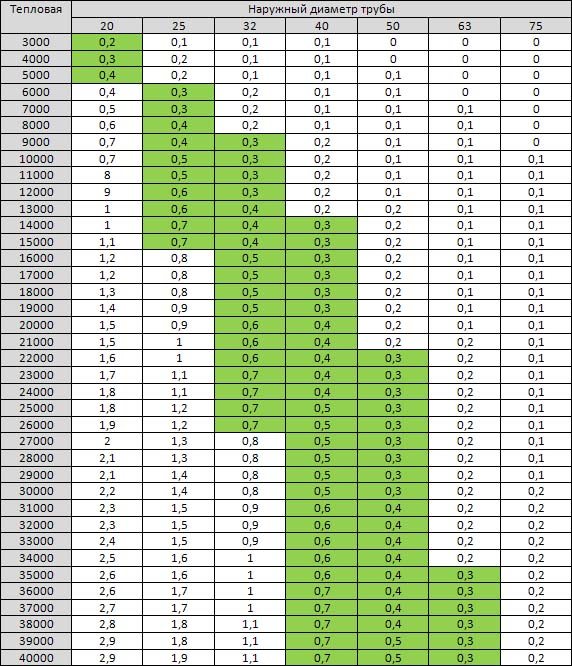

Everything is simple here. Usually, all detailed tables with all the necessary data can be viewed (or downloaded for yourself) on the websites of pipe manufacturers. But sometimes there are no tables.
You can get out of this situation as follows. If there are no tables for the outer diameter, then take it for the inner one, and calculate using it. Yes, there will be inaccuracies, but, as experience shows, for forced circulation they are absolutely insignificant and permissible.
Having analyzed a huge number of already installed and perfectly working systems, experts noticed a certain pattern in the choice of the pipe section. It is mainly suitable for small stand-alone systems.
In private houses, the pipes that come out of the boiler are most often one-half and three-quarters in size. Such a pipe diameter for heating a house is used before the first fork, and at each next one, the section is reduced by exactly one step.
But this method is applicable only for apartments and one-story houses, for high-rise buildings, alas, you have to calculate everything very carefully.
If we have a private house or apartment, autonomous heating for no more than 5-8 radiators and 2-3 forks, we can easily calculate everything ourselves. We need to know how powerful each heating point is, the heat loss in the room and a good table for selecting the pipe diameter.
However, as it has already become clear, trust experienced specialists to calculate a complex multi-level system with numerous joints and forks. Well, if you still decide to do everything yourself, then at least read articles such as ours and consult with experts.
How to choose the right pipes of the required diameter
In cases where heating is carried out in a private house or cottage, the pipes must be selected taking into account the fact that the diameter will not change only when there is a direct connection to the central heating system. In the case of an autonomous pipe system, any size (different diameter and length) can be used, depending on the preferences of the owner of the house.
Related article: How to wash glue from mice off the floor: expert advice
When choosing the necessary blanks, you need to take into account all the features, especially when it comes to a natural heating system, where the ratio of the cross section to the pump power will not be a primary feature. This fact is attributed to the advantages of this heating system.
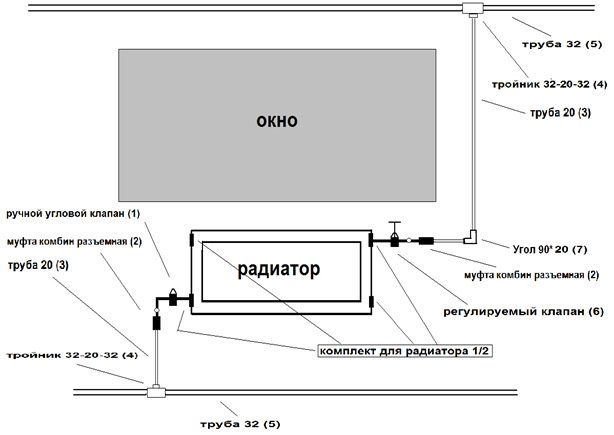

Pipe installation diagram.
The disadvantage of such a system is the small radius of action and the high cost of large elements used in this case.
To ensure the efficiency of the system, it is necessary to maintain a certain level of pressure in it, which allows the water moving inside to overcome all obstacles in its path. Resistances (obstacles) can be in the form of water friction against walls, a drain or a tap and a heating device. The most interesting thing is that the resistance and the speed with which water will flow depends on the length and diameter of the pipeline. With a high water velocity, a small cross-section and a long pipeline, the level of resistance on the path of the water increases.
How to choose the right pipe diameter for heating a house - table and calculations
It is not difficult for a professional to calculate the optimal cross-section of the pipeline. Practical experience + special tables - all this is enough to make the right decision. But what about an ordinary homeowner?
Indeed, many people prefer to install the heating circuit on their own, but at the same time they do not have a specialized engineering education. This article will be a good tip for those who need to decide on the diameter of the pipe for heating a private house.
There are several nuances that you need to pay attention to:
- Firstly, all the data obtained on the basis of calculations using the formulas is approximate. Various rounding of values, averaged coefficients - all this makes a number of corrections to the final result.
- Secondly, the specifics of the operation of any heating circuit has its own characteristics, therefore, any calculations give only approximate data, "for all cases."
- Thirdly, pipe products are produced in a certain range.The same applies to diameters. The corresponding values are located in a certain row, with a gradation by value. Therefore, you will have to select the denomination that is closest to the calculated one.
Based on the foregoing, it is advisable to use the practical recommendations of professionals.
All Du - in "mm". In brackets - for systems with natural circulation of the heat carrier.
- The common pipe of the line is 20 (25).
- Taps to batteries - 15 (20).
- With a one-pipe heating system - diameter 25 (32).
But these are general parameters of the contour that do not take into account its specifics. More precise values are shown in the table.
What is taken into account when choosing a pipe diameter
Heat generator power. It is taken as a basis and is determined individually for each building. What does the owner focus on when purchasing a boiler?
The total area of all heated premises. This is what the manager at the point of sale will definitely clarify if the buyer has questions about this item.
On a note! It is generally accepted that in order to ensure high-quality heating of a house, it is necessary to adhere to the following ratio - 1 m2 / 0.1 kW. But if we take into account the peculiarities of the climate, the sparing mode of operation of the unit (so as not to "drive" it to the limit), then about 30% should be added. It turns out - 1 / 1.3.
Coolant speed. If it is less than 0.25 m / s, then there is a risk of airing the system, the formation of traffic jams on the highway. Exceeding the value of 1.5 is fraught with "noise" in the line.
This is especially noticeable when the pipes are metal, and even laid in an open way. But in any case, the movement of the coolant along the route will be well monitored.
Practice has proven that for a private building (with an autonomous heating circuit), one should focus on an indicator in the range from 0.3 to 0.7. This is the optimal value for any system.
Loop configuration. In private houses, during its installation, as a rule (regardless of the scheme), all "threads" are put on the collector. Each of them is "loaded" on a certain number of radiators.
It makes no sense to purchase pipes of the same diameter for all lines, given that the larger the section of the workpiece, the higher the price of 1 running meter.
Pipe diameter. The outer one does not play a special role, since products from various materials have differences in wall thickness. This parameter only indicates the convenience of fastening the product. Inner diameter - about the throughput of the route. It is he who is decisive.
On a note! It is customary to operate with the averaged value of the section size (nominal diameter). It is this parameter that is used in the calculations.
It is customary to designate pipe diameters in inches. For us, this is an unusual (not metric) system, so you should know the rules for converting values. The ratio of inch to centimeter is ½.54 (or 25.4 mm). Pipe material - metal-plastic, steel, PP, PE.
The specifics of the structure. First of all, this refers to the effectiveness of its thermal insulation - from what materials it is mounted, by what method, and so on.
Classification and selection
Nowadays, the production provides a significant selection of plastic pipes. To understand all the abundance, you need to have an understanding of the rules for their application. The main thing in this is to be able to classify products by their application and section.
Polypropylene pipes are divided into:
- PN 20 (having high shockproof strength) - they are used for the equipment of ventilation systems, water pipes, floors with water heating. They are, as a rule, large in diameter and do not withstand cold well (become brittle);
- PN 10 (have normal strength) - suggest a wide range of applications, therefore they are in demand among buyers. They are resistant to sudden changes in temperature, which allows them to be equipped with a plumbing system, and used when arranging floors with warm water heating;
- PN 25 (reinforced, that is, provided with various inclusions of aluminum or fiberglass foil) - are distinguished by the greatest indestructibility and durability. They go well for laying outdoor systems and communications, with centralized heating, when supplying compressed air. These pipes, as a rule, are cost-effective, but also win-win in operation.
Numerical designations (10, 20, 25) indicate the limit of permissible pressure (in kg / cm2) in pipes.

What do the diameters of polypropylene pipes say?
Judging by the application, the diameters of the pipes have different indicators, but in all pipes they are internal and external.
It will be interesting: How not to make mistakes when soldering plastic pipes
External ones indicate their ability to solve various construction problems:
- Pipes with a relatively small cross-section (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 75 mm) are very convenient in the equipment of heating communications, when laying water pipes and drainage systems in private buildings, as well as apartments. In this case, the supply of hot water will be provided by 20 mm products; pipes with a diameter of 25 mm will fit on the risers. Arrangement of a warm floor will turn out well from pipes of 16-18 mm cross-section. They bend easily, so they can be shaped to the desired shape;
- 80, 90, 100, 110, 125, 160, 200, 250, 315 - mm are also suitable for water supply and drainage systems, replacing cast iron pipes with a similar external section used for these purposes. 200 mm are used in the construction of large buildings where a significant number of people are expected to stay (shops, clinics, hotels, etc.);
- Products with a cross section of 400 mm and more are suitable for pumping water in large volumes, as well as for ventilation systems.
Which of them is better to use in one case or another is easiest to find out from special tables. However, for private construction, such complex and meticulous costs do not apply. In fact, for such buildings, polypropylene pipes with a 20-25 mm cross section are usually used.
Note that all of the above refers to the selection of this important part of the communications, given their diameter. But when purchasing pipes for a particular purpose, it is important to study their operational boundaries, in particular to ask what temperature and pressure can withstand, installation features, type of connection, etc.
Throughput of various pipe diameters
In addition to all this, the pipes still differ in passability. Actually, the inner diameter of polypropylene pipes determines the amount of liquid that this or that product can pass it in a certain fraction of time. But the size of the external section does not play a role here. But it, and therefore the thickness of the walls of the pipe, speaks of how strong it is and is able to cope with pressure.

The ratio of both cross-sections of plastic pipes is usually as follows:
- The outer 16 mm corresponds to the inner 10 mm section;
- 20mm - 15mm;
- 63mm - 50mm;
- 125mm - 100mm.
Calculation of the throughput capacity of the pipe section is very important when equipping water supply in high-rise buildings. After all, the slightest miscalculation, which will lead to the use of communications with a smaller cross-section of pipes, can lead to the fact that at the peak of the greatest water consumption (for example, in the evening), it simply will not reach the upper floors.