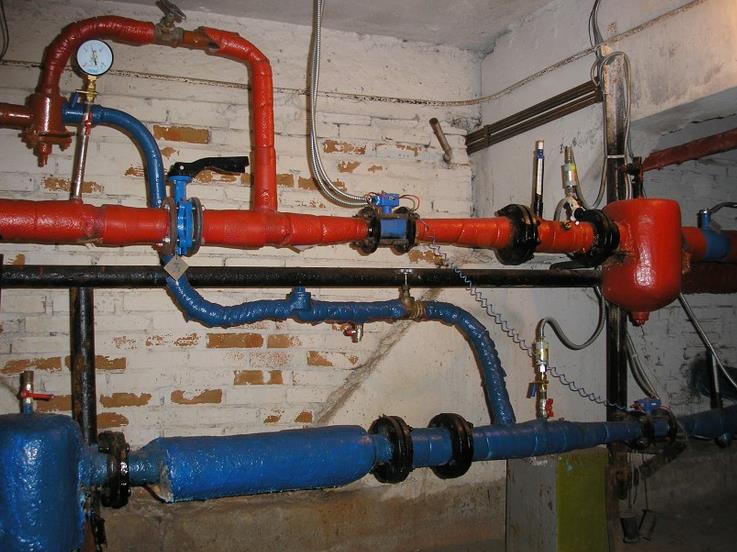
How to organize heating of a specific building, the owner decides for himself. If we are talking about a private residential building, then the most common heating option is a closed system with forced circulation. Compared with an open one, it has a number of significant advantages, therefore, it is more widespread, regardless of the dimensions of the structure, its purpose, the complexity of the contour configuration and the parameters of the component parts.
What is a closed heating system with forced circulation, what are the advantages, what are the features of such a scheme - all these questions can be answered in this article.
Open system
But before considering its specifics, you should understand the terminology. It is because of ignorance of some of the nuances that people who do not have professional training are often confused in the definitions. The fact is that not everyone understands the fundamental difference between a closed heating system (CL) and an open (OS) one.
Forced movement of the coolant (its circulation) can be organized in both. In order to avoid substitution of concepts in the future, you should immediately answer a number of questions.
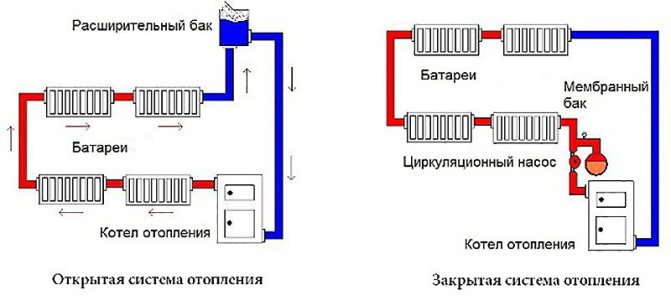
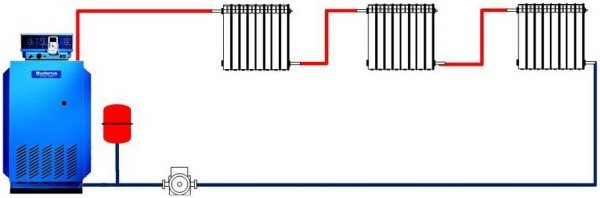
What is the difference between ZS and OS? Any liquid expands when heated. Since the coolant is water (less often - antifreeze or its analogs), it is necessary to somehow compensate for the increase in pressure in the pipes, otherwise the depressurization of the system cannot be avoided. For this, an expansion tank is included in the circuit. In the OS, it is open, and the pressure is regulated by the atmosphere.
Closed heating system
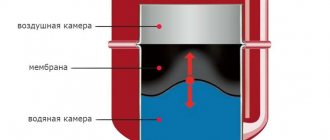
In a closed circuit, it is completely sealed, and its internal diaphragm (membrane) is responsible for compensating for expansion.
What is the meaning of forced circulation? The movement of liquid does not occur due to the pressure difference at the outlet and inlet of the heat generator (as they say, by gravity), but is carried out by a pump, which is one of the constituent parts of the circuit.
Comparing various systems, one can see that each has both advantages and disadvantages, although the ES with forced circulation has much more advantages. Its significant drawback is only in one - "binding" to the industrial / voltage. When it is turned off, the pump and the boiler will "stand up".
On a note! When choosing just such a heating option, it is necessary to foresee in advance how to organize an alternative power supply. Therefore, the cost estimate should immediately include the cost of purchasing an autonomous power source.
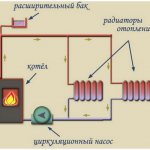
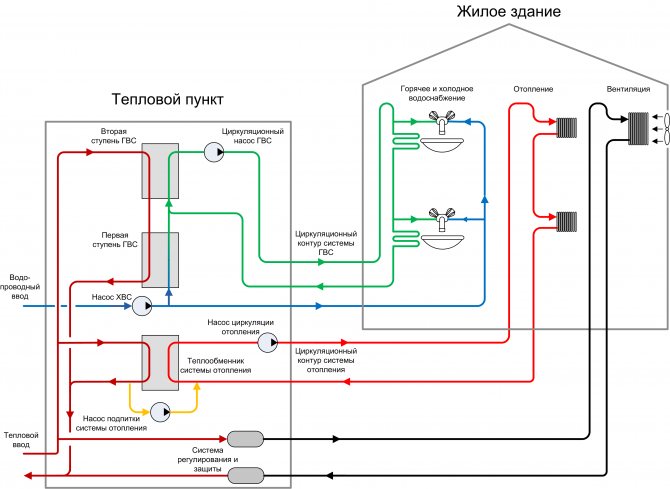
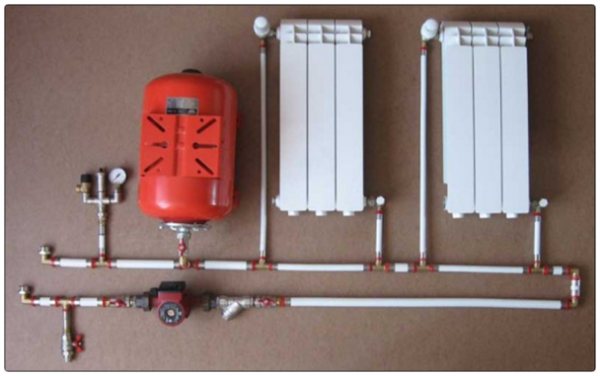
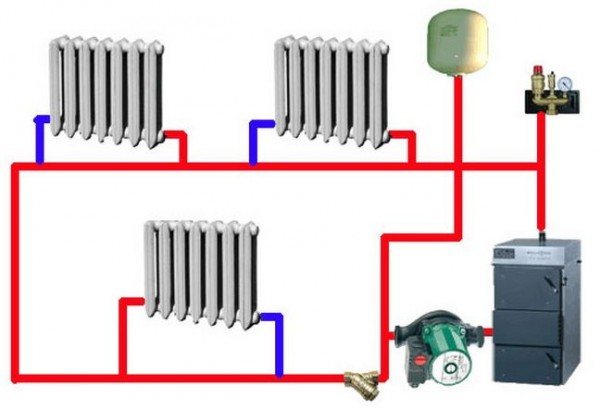
Scheme composition
As you can see from the figure, its main parts are:
- 1 - heat generator (boiler of any type);
- 6 - membrane tank;

- radiators and pipe system;
- 9 - water pump.
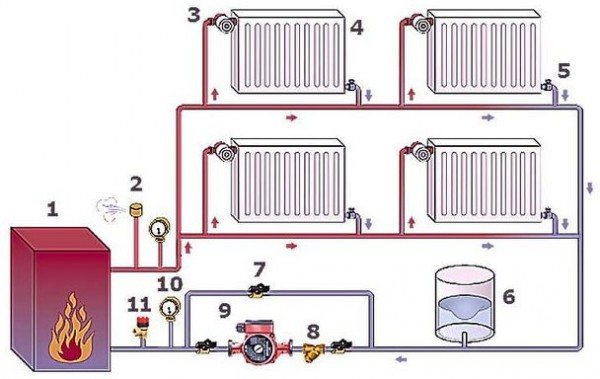

On a note! It is advisable to install the pump at the boiler inlet (at the end of the line). In this case, it will pump the already cooled coolant, which means that the service life of the product will slightly increase.
Additional elements - valves, valves, sensors (pressure, temperature) and a number of others. The need for their installation is determined by the design features of the boiler and the specifics of the circuit to be installed (its diagram).

Open heating system
In an open heat supply system, an expansion tank is required, since the heated water expands. The expansion tank serves to receive excess water during expansion and return it to the system when it cools down, as well as to remove water in case of an excessive volume. The tank is not completely sealed, therefore water evaporates as a result of which it is necessary to constantly renew its level.An open heating system does not use a pump. The system is pretty simple. Consists of pipes, steel expansion tank, radiators and boiler. Diesel, gas and solid fuel boilers are used, except for electric ones.
In an open heating system, water circulates slowly. Therefore, the pipes during operation must
warm up gradually to avoid damaging them and boiling the coolant. This can lead to premature wear of the equipment. If heating is not used in winter, then the water from the system must be drained, in order to avoid freezing of the pipeline.
In order for the circulation of the coolant to be carried out at the required level, it is necessary to install the heating boiler in a lower place in the system, and in the highest place to install expansion tank, for example, in the attic. In winter, the expansion tank must be insulated. When installing the pipeline in an open heating system, it is required to use a minimum number of turns, shaped and connecting parts.
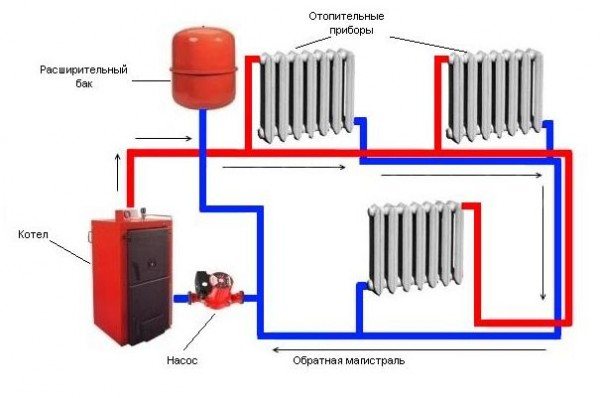
How the system works
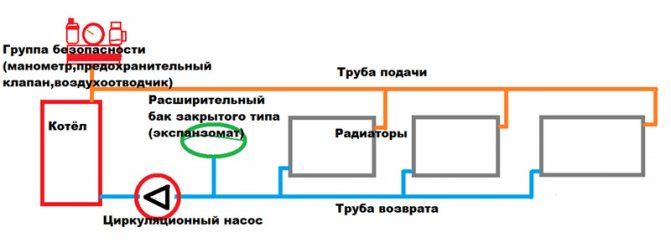
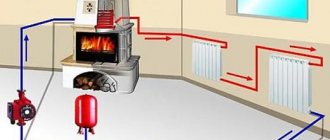
It is easy to understand from the picture. The direction of movement of the coolant is shown by arrows.
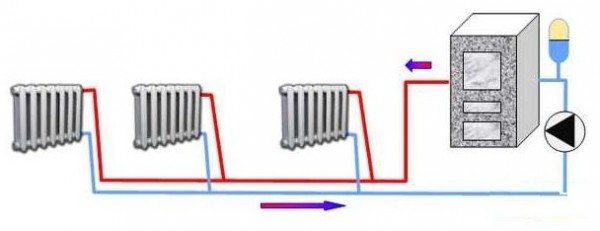

From the boiler outlet, water heated to the required temperature passes through the pipe system through all the batteries installed in the circuit, giving them thermal energy. Since the system is closed, the liquid returns back. This circulation is provided by the pump. In the heat exchanger, the cooled heat carrier is heated, and it again goes into the circuit. This process is continuous, and all parameters of the system are controlled by the boiler automation. In principle, nothing complicated.
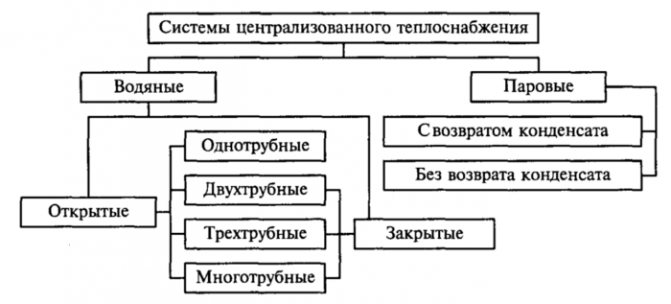
Classification of heat supply systems
There are the following types of heat supply schemes.
By the amount of heat generated, centralized and decentralized types of heat supply are classified. In centralized systems, one source of heat energy supplies several buildings. In a decentralized system, each building or group of houses, individual rooms, generate heat independently.
The classification of decentralized types of heat supply divides them into individual ones, when each apartment is heated independently and local ones - where the heat source heats the entire apartment building.
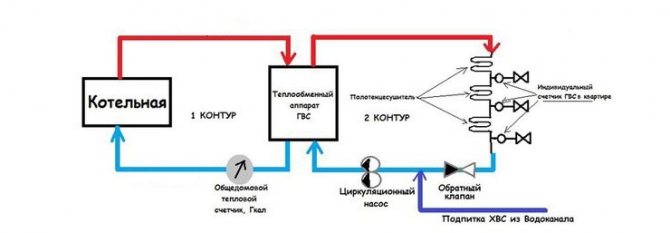
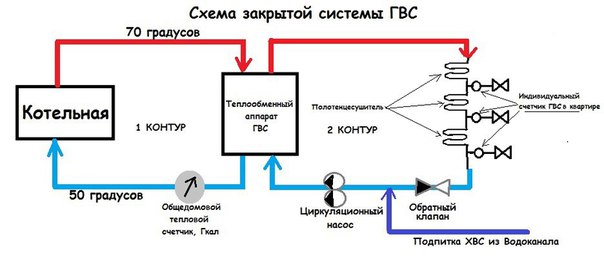
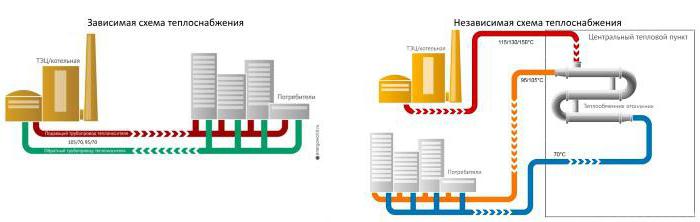
According to the method of connection to networks, dependent and independent types of heat supply systems are classified. Dependent - when the coolant (liquid or steam) is heated in the boiler room and, passing through the pipeline network, enters the radiators of the heated room. Independent - liquid from the heating network passes through the heat exchanger and heats the heating medium of the house (the coolant that heats up in the boiler room does not enter the heating system of the house).
According to the method of the device for hot water supply and water heating, open and closed types of heat supply are distinguished.


Open heating system
In an open heat supply circuit, water heated in a boiler room is used simultaneously in hot water supply and as a heat carrier for heating devices. The constant consumption of water for the needs of hot water supply leads to the need for regular replenishment of the heating network. Due to the use of water in hot heat supply, its temperature should be 65-70 degrees. This scheme is very outdated, it was widely used in the USSR.
Advantages and disadvantages of open heating
Advantages of an open type of coolant supply:
- a minimum of equipment, as the use of heat exchangers is not required;
- due to the fact that the water temperature is lower, losses during transportation along heating mains over long distances are less than in a closed system.
Disadvantages of an open circuit:
Dirty water.Due to the long length of the heating main, the liquid entering the hot water supply pipelines contains a large amount of dirt, rust, which it collects on the way from the boiler room to the consumer. Due to the long length of heat supply pipelines, the water in the tap may have an unpleasant odor and color and may not comply with sanitary standards. The installation of water treatment devices in every home will require significant financial costs.
The high demand for hot water during peak hours leads to a noticeable pressure drop in the pipelines. Because of this, it forces resource-supplying enterprises to install additional booster pumps and automation to control the pressure in the system. Otherwise, a drop in pressure will lead to a smaller amount of coolant passing through the heaters in the apartments, and as a result, a decrease in the air temperature in the premises.
High liquid losses from the thermal system are forcing the installation of massive water treatment plants in boiler houses, thermal power plants and other energy-producing enterprises, which purify river water from salts and other impurities.
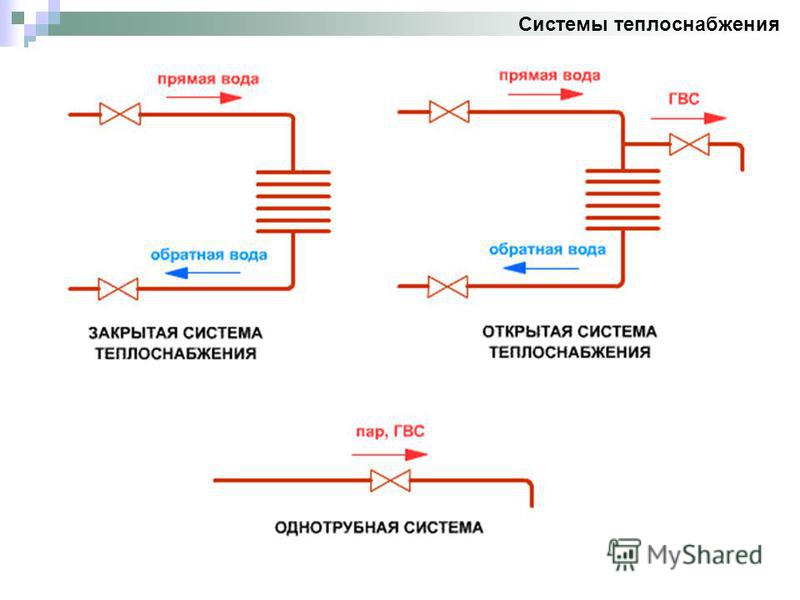

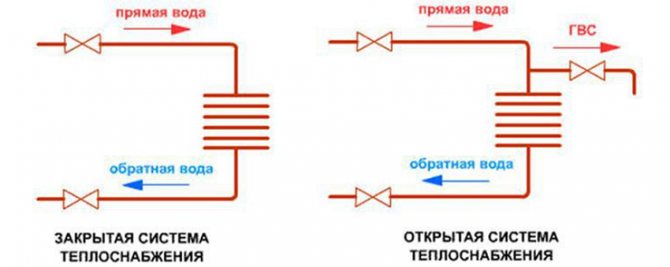
Differences between open and closed water supply schemes
In a closed system, unlike an open one, the liquid used as a heat carrier circulates through the pipelines without leaving them. For hot water supply, drinking tap water is used, which is heated by a coolant in special devices (heat exchangers) installed in houses or central heating points. In closed circuits, the water temperature in the heating main ranges from 120 to 140 degrees, and fluid losses are absent or minimal.
Pros of a closed circuit:
- for hot water supply, clean tap water is connected, in contrast to an open circuit, which meets all sanitary and hygienic standards without impurities and unpleasant odors;
- there is no need to install additional pumps and devices for automatic control of parameters at heat supply enterprises, since the pressure in the heating network is constant and does not depend on the consumption of hot water;
- it is not necessary to install additional water treatment plants at boiler houses and other heat supply sources, because the circulating liquid is already desalinated and contains a minimum amount of impurities;
- energy-saving effect achieved by adjusting the required temperature of heat supply at heat points, carried out in automatic mode.
The disadvantages of this heating system include expensive equipment and automation required for the installation of energy exchange points, where the temperature of heating tap water is regulated.
The second drawback is the high temperatures of the heat carriers in the main heating mains and, as a result, high heat losses. This drawback has now lost its relevance due to the use of the technology of thermal insulation of pipes with polyurethane foam, which provides the strength of the insulating coating and effective protection against heat losses.

Varieties of a closed system
Since the consideration of the features of various schemes is not directly related to the topic of the article, we note only some of their main differences.
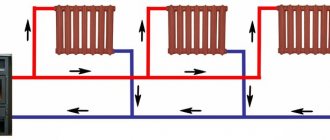
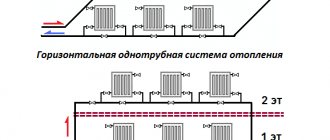
Single pipe

As can be seen from the figure, all radiators are included in the circuit sequentially (the so-called "Leningrad"). The disadvantage is that the last battery in the chain will be significantly colder than the first. Therefore, such circuits are mounted in relatively small buildings. An obvious plus is the lower consumption of materials (first of all, pipes).
Two-pipe

This scheme allows for more uniform heating of all rooms without exception. But the cost of its installation is slightly higher.However, it is precisely such a heating circuit device that is considered the most acceptable for a private house, especially if it has quite a lot of rooms and 2 - 3 floors.
There are a number of other features of closed-type systems - for piping (vertical, horizontal), installing a membrane tank (read more about the accumulator), and so on. But these are already separate topics, and those who are interested in a specific option will be able to familiarize themselves with it on our website. We will summarize what has been said.
Features of pipe routing
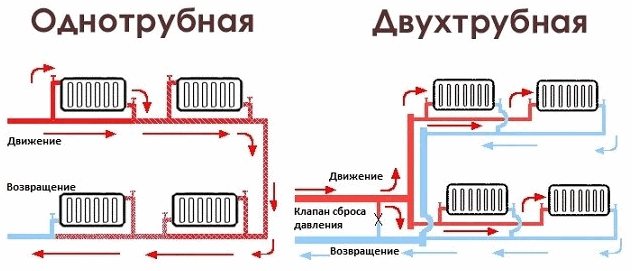

Layout of elements in a one-pipe and two-pipe system
Depending on the location of the main pipe, the technology for connecting the batteries, the supply risers, the wiring technology is selected.
One-pipe method
With one-pipe wiring, a horizontal and vertical scheme is used. Laying pipes horizontally excludes the regulation of the amount of water, therefore bypasses are additionally used. The vertical arrangement of the highway is typical for high-rise buildings.
Two-pipe method
Two-pipe intake of wiring provides for the supply of two lines to one radiator - for supplying warm water and removing cold water. The following schemes can be implemented in an apartment or house:
- gravity - the circulation of warm water is carried out in a natural way;
- classical - a dead-end system;
- annular - the coolant moves along the way;
- radial - heat is supplied from the distributor to the radiators on an individual basis.
The two-pipe system is suitable for underfloor heating, where heating circuits are assigned the role of batteries, and pipes and a comb with a mixer are mains.
Heating pipes
Currently, domestic ones are in disrepair. Due to the high wear and tear of communications, it is cheaper to replace pipes for heating mains with new ones than to engage in permanent repairs.
It is impossible to immediately renew all the old communications in the country. During the construction or overhaul of houses, new pipes are installed to reduce heat losses by several times. Pipes for heating mains are made using a special technology, filling the gap between the steel pipe located inside and the shell with foam.
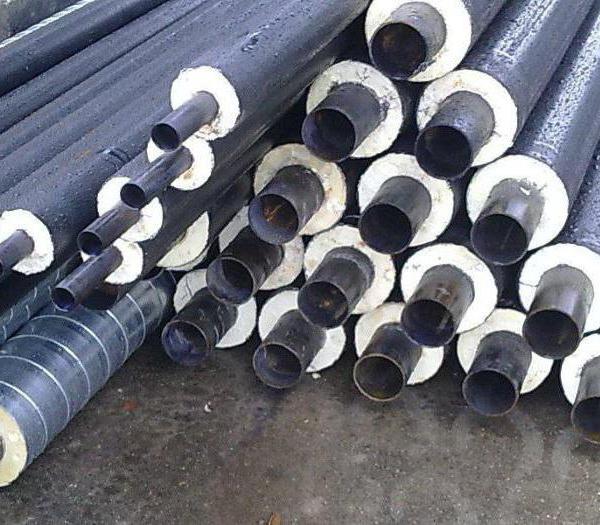


The temperature of the transported liquid can reach 140 ° C.
The use of polyurethane foam as thermal insulation allows you to keep heat much better than traditional protective materials.
Features of the functioning of the forced heating system
The heating circuit, in which the fuel circulates naturally, is as simple as possible. In such a chain, the coolant is heated in the boiler and, in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, rushes up the riser. Having reached the radiators, the carrier gives off part of the thermal energy, its temperature decreases. Under the pressure of the newly arriving doses of heat, the cooled fuel is lowered back into the boiler to repeat the cycle.
Such an elementary scheme has significant drawbacks, especially in conjunction with a one-pipe type of wiring:
- Heat is distributed unevenly: in rooms that are located next to a heat supply source (boiler), the temperature is higher than in those that are at a greater distance from it.
- A system with natural circulation consumes a significant amount of heating material, which is not in favor of its rationality. The arrangement of two-pipe distribution allows to partially neutralize these problems.
The efficiency of a forced circulation heating circuit is due to the inclusion of a pump in it. Its function is to give the fuel movement along the heating main at a higher speed. The value of this indicator is in direct proportion to the temperature of the heated rooms.
The presence of a circulation pump in the heating system gives it undeniable advantages:
- profitability. It is associated both with the rational use of heat resources, and with reasonable financial costs for the purchase of small diameter pipes;
- ergonomics. Lightweight design allows you to hide its elements in the walls, under the floor, etc.;
- the possibility of functioning in heating projects of any complexity with a different combination of heating equipment. The heating circuit may include radiators, heat curtains, and heated floors. The main concern when designing a forced circulation heating system is the uninterrupted supply of electricity, since it is electricity that is designed to drive the pump. Therefore, it is a good idea to take care of a backup power supply.
Drawing up a heat supply scheme
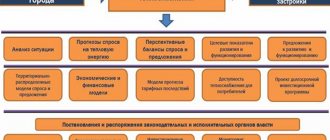
The heat supply scheme is a pre-design document, which reflects the legal relations, the conditions for the functioning and development of the heat supply system for the urban district, settlement. In relation to it, the federal law includes certain norms.
- for settlements are approved by the executive authorities or local government, depending on the size of the population.
- There must be a single heat supply organization for the corresponding territory.
- The diagram indicates energy sources with an indication of their main parameters (load, work schedules, etc.) and the radius of action.
- The measures for the development of the heat supply system, the conservation of excess capacity, the creation of conditions for its uninterrupted operation are indicated.

Heat supply facilities are located within the boundaries of the settlement in accordance with the approved scheme.
Selection of a circulation pump


A quality pump for a forced circulation heating system must meet the criteria:
- energy saving;
- simplicity and reliability in operation.
Power characteristics are determined by the dimensions of the living space that needs to be heated. For example, for heating an area of 250 square meters, a circulation pump with a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters / h and a pressure of 0.4 atm is required. In addition, the choice of equipment is influenced by calculations from the heating system design. These include:
- material of pipes intended for installation and their diameter;
- total footage of the circuit;
- the number of heating appliances;
- type of coolant.
Self-selection of a pump can cause a number of difficulties, so it is best to get advice from a competent specialist on this issue.
The need to comply with the slope of pipes
When installing a heating system with forced circulation of the coolant, it is not necessary to comply with the requirements for the slope of the pipes. Heating mains are installed in a straight line or with an insignificant slope in relation to the drain. This will make it easier to drain the coolant before carrying out repair work or when a situation arises when the system will have a long downtime.
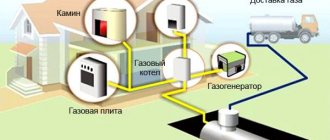
Choosing a heating boiler correctly
manufactures heating boilers suitable for installation in both types of systems. However, there are certain nuances of choice:
- For an open system, it is recommended to choose a boiler that operates on gas or wood. It must be placed in a separate room, where the floor is covered with non-combustible material.
- In a closed circuit, it is allowed to install the boiler on any type of fuel - gas, wood, coal, diesel fuel. The most profitable option is a gas appliance.
In both cases, the system can be single or double-circuit and be supplemented with a boiler to provide residents with hot water.
Each of the heating systems of a private house has certain advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when choosing equipment. Proper installation is a prerequisite for the normal functioning of heating.