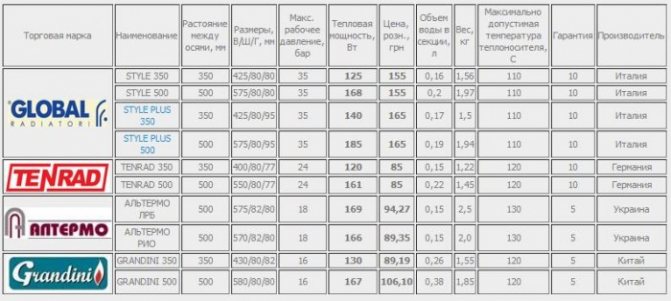
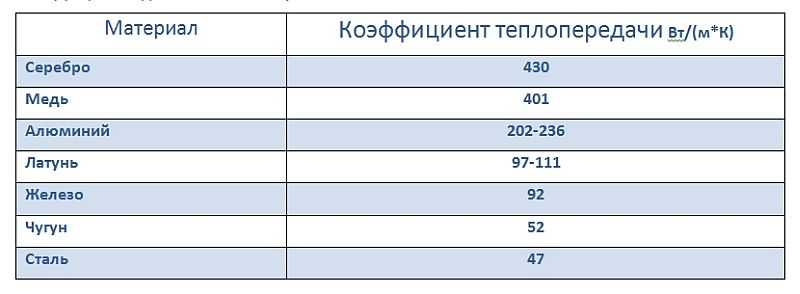
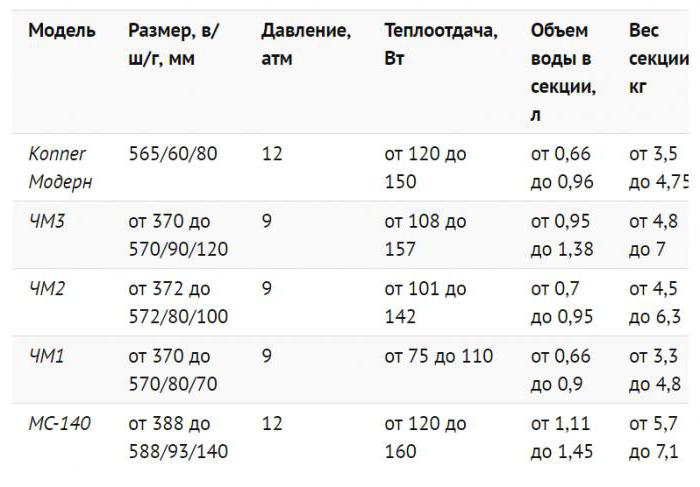
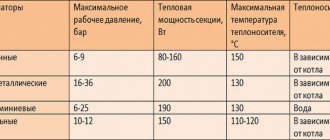
Leading classification
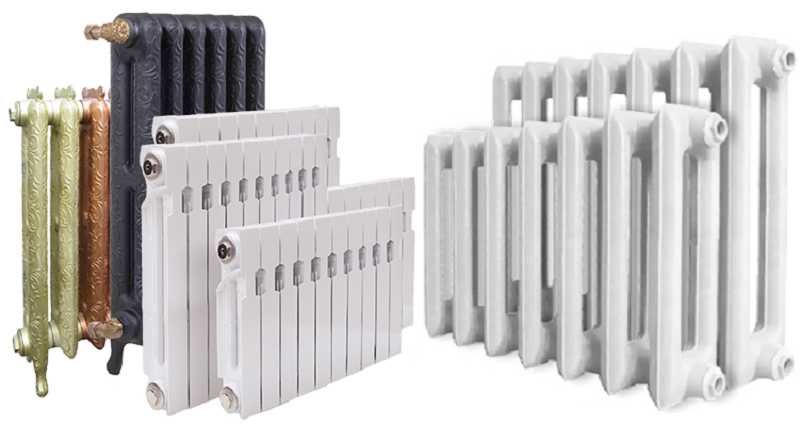
This will depend on the type and quality of the material used in the manufacture of the radiators. The main varieties are:
- cast iron;
- bimetal;
- made of aluminum;
- of steel.

Each of the materials has some disadvantages and a number of features, therefore, to make a decision, you will need to consider the main indicators in more detail.
Made of steel
They function perfectly in combination with an autonomous heating device, which is designed to heat a substantial area. The choice of steel heating radiators is not considered an excellent option, since they are not able to withstand significant pressure. Extremely resistant to corrosion, light and satisfactory heat transfer performance. Having an insignificant flow area, they rarely clog. But the working pressure is considered to be 7.5-8 kg / cm 2, while the resistance to possible water hammer is only 13 kg / cm 2. The heat transfer of the section is 150 watts.


Steel
Made of bimetal
They are devoid of the disadvantages that are found in aluminum and cast iron products. The presence of a steel core is a characteristic feature, which made it possible to achieve colossal pressure resistance of 16 - 100 kg / cm 2. The heat transfer of bimetallic radiators is 130 - 200 W, which is close to aluminum in terms of performance. They have a small cross-section, so over time, there are no problems with pollution. The significant disadvantages can be safely attributed to the prohibitively high cost of products.


Bimetallic
Made of aluminum
Such devices have many advantages. They have excellent external characteristics, moreover, they do not require special maintenance. They are strong enough, which allows you not to fear water hammer, as is the case with cast iron products. The working pressure is considered to be 12 - 16 kg / cm 2, depending on the model used. The features also include the flow area, which is equal to or less than the diameter of the risers. This allows the coolant to circulate inside the device at a tremendous speed, which makes it impossible for sediment deposition on the surface of the material. Most people mistakenly believe that too small a cross section will inevitably lead to a low heat transfer rate.


Aluminum
This opinion is erroneous, if only because the level of heat transfer from aluminum is much higher than, for example, that of cast iron. The cross section is compensated by the ribbing area. Heat dissipation of aluminum radiators depends on various factors, including the model used and can be 137 - 210 W. Contrary to the above characteristics, it is not recommended to use this type of equipment in apartments, since the products are not able to withstand sudden temperature changes and pressure surges inside the system (during the run of all devices). The material of an aluminum radiator deteriorates very quickly and cannot be recovered later, as in the case of using another material.
Made of cast iron
The need for regular and very careful maintenance. The high inertness rate is almost the main advantage of cast iron heating radiators. The heat dissipation level is also good. Such products do not heat up quickly, while they also give off heat for a long time. The heat transfer of one section of a cast-iron radiator is equal to 80 - 160 W. But there are a lot of shortcomings here, and the following are considered to be the main ones:
- Perceptible weight of the structure.
- Almost complete lack of ability to resist water hammer (9 kg / cm 2).
- A noticeable difference between the cross-section of the battery and the risers. This leads to a slow circulation of the coolant and a fairly rapid pollution.

Heat dissipation of heating radiators in the table
Steel batteries
Old steel radiators have a fairly high thermal power, but at the same time they do not retain heat well. They cannot be disassembled or added to the number of sections. Radiators of this type are susceptible to corrosion.
Currently, steel panel radiators have begun to be produced, which are attractive because of their high heat output and small dimensions compared to sectional radiators. The panels have channels through which the coolant circulates. The battery can consist of several panels, in addition, it can be equipped with corrugated plates that increase heat transfer.
The thermal power of steel panels is directly related to the dimensions of the battery, which depends on the number of panels and plates (fins). The classification is carried out depending on the radiator fins. For example, Type 33 is assigned to three-plate heaters with three plates. The range of battery types is 33 to 10.
Self-calculation of the required heating radiators is associated with a large amount of routine work, so manufacturers began to accompany products with tables of characteristics, which were formed from the records of test results. This data depends on the product type, installation height, inlet and outlet temperature of the heating medium, target room temperature and many other characteristics.
Formulas for calculating the power of the heater for various rooms
The formula for calculating the power of the heater depends on the height of the ceiling. For rooms with a ceiling height
- S is the area of the room;
- ∆T - heat transfer from the heater section.
For rooms with a ceiling height> 3 m, calculations are carried out according to the formula
- S is the total area of the room;
- ∆T - heat transfer from one section of the battery;
- h - ceiling height.
These simple formulas will help to accurately calculate the required number of sections of the heating device. Before entering data into the formula, determine the real heat transfer of the section using the formulas given earlier! This calculation is suitable for an average temperature of the incoming heating medium of 70 ° C. For other values, the correction factor must be taken into account.
Here are some examples of calculations. Imagine that a room or non-residential premises has dimensions of 3 x 4 m, the ceiling height is 2.7 m (the standard ceiling height in Soviet-built city apartments). Determine the volume of the room:
3 x 4 x 2.7 = 32.4 cubic meters.
Now let's calculate the thermal power required for heating: we multiply the volume of the room by the indicator required to heat one cubic meter of air:
Knowing the real power of a separate section of the radiator, select the required number of sections, rounding it up. So, 5.3 is rounded up to 6, and 7.8 - up to 8 sections. When calculating the heating of adjacent rooms that are not separated by a door (for example, a kitchen separated from a living room by an arch without a door), the areas of the rooms are summed up. For a room with a double-glazed window or insulated walls, you can round down (insulation and double-glazed windows reduce heat loss by 15-20%), and in a corner room and rooms on high floors add one or two sections "in reserve".
Why doesn't the battery warm up?
But sometimes the power of the sections is recalculated based on the real temperature of the coolant, and their number is calculated taking into account the characteristics of the room and installed with the necessary margin ... and it is cold in the house! Why is this happening? What are the reasons for this? Can this situation be corrected?
The reason for the decrease in temperature may be a decrease in the water pressure from the boiler room or repairs from neighbors! If, during the repair, a neighbor narrowed the riser with hot water, installed a "warm floor" system, began to heat a loggia or a glazed balcony on which he arranged a winter garden - the pressure of hot water entering your radiators will, of course, decrease.
But it is quite possible that the room is cold because you installed the cast iron radiator incorrectly. Usually, a cast-iron battery is installed under the window so that the warm air rising from its surface creates a kind of thermal curtain in front of the window opening. However, the back side of the massive battery heats not the air, but the wall! To reduce heat loss, glue a special reflective screen on the wall behind the heating radiators. Or you can buy decorative cast-iron batteries in a retro style, which do not have to be mounted on the wall: they can be fixed at a considerable distance from the walls.
General provisions and algorithm for thermal calculation of heating devices
The calculation of heating devices is carried out after the hydraulic calculation of the pipelines of the heating system according to the following method. The required heat transfer of the heating device is determined by the formula:
, (3.1)
where is the heat loss of the room, W; when several heating devices are installed in a room, the heat loss of the room is distributed equally between the devices;
- useful heat transfer from heating pipelines, W; determined by the formula:
, (3.2)
where is the specific heat transfer of 1 m of open-laid vertical / horizontal / pipelines, W / m; taken according to the table. 3 appendix 9 depending on the temperature difference between the pipeline and air;
- total length of vertical / horizontal / pipelines in the room, m.
Actual heat dissipation of the heater:
, (3.4)
where is the nominal heat flux of the heating device (one section), W. It is taken according to the table. 1 appendix 9;
- temperature head equal to the difference of the half-sum of the temperatures of the coolant at the inlet and outlet of the heating device and the temperature of the room air:
, ° С; (3.5)
where is the flow rate of the coolant through the heating device, kg / s;
- empirical coefficients. The values of the parameters depending on the type of heating devices, the flow rate of the coolant and the scheme of its movement are given in table. 2 applications 9;
- correction factor - the method of installation of the device; taken according to the table. 5 applications 9.
The average water temperature in the heater of a one-pipe heating system is generally determined by the expression:
, (3.6)
where is the temperature of the water in the hot line, ° C;
- cooling of water in the supply line, ° C;
- correction factors taken according to table. 4 and tab. 7 applications 9;
- the sum of heat losses of the premises located before the considered premises, counting along the direction of water movement in the riser, W;
- water consumption in the riser, kg / s / is determined at the stage of hydraulic calculation of the heating system /;
- heat capacity of water, equal to 4187 J / (kggrad);
- coefficient of water flow into the heating device. It is taken according to the table. 8 applications 9.
The flow rate of the coolant through the heating device is determined by the formula:
, (3.7)
Cooling of water in the supply line is based on an approximate relationship:
, (3.8)
where is the length of the main line from the individual heating point to the calculated riser, m.
The actual heat transfer of the heating device must be no less than the required heat transfer, that is. The inverse ratio is allowed if the residual does not exceed 5%.
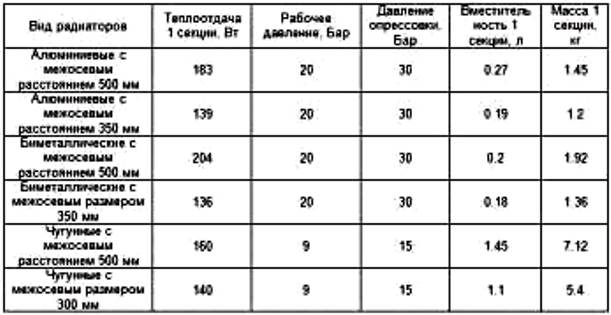
Comparison of heating radiators by heat transfer: table
Below is a comparative table of heat dissipation of batteries made of various materials. It will help you navigate the market for these devices.
You just need to remember that in order to effectively warm up the room, you need not only to choose the type of radiator and its connections, but also to calculate the length of the device (the number of sections) depending on the heated area.
The comparison table looks like this.
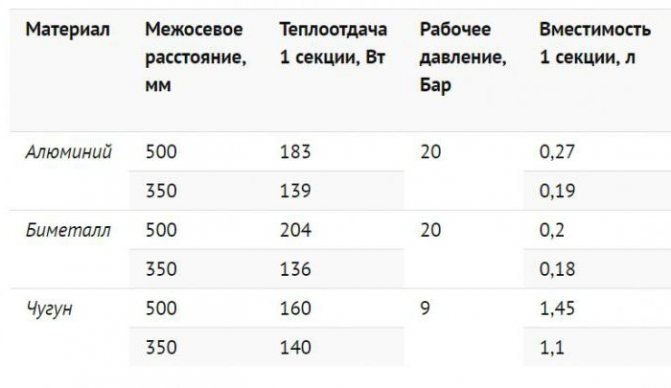

Characteristics and features
The secret of their popularity is simple: in our country there is such a coolant in centralized heating networks that even metals dissolves or erases. In addition to a huge amount of dissolved chemical elements, it contains sand, rust particles that have fallen off pipes and radiators, “tears” from welding, bolts forgotten during repairs, and a lot of other things that got inside it is not known how. The only alloy that does not care about all this is cast iron. Stainless steel also copes well with this, but how much such a battery will cost is anyone's guess.


MS-140 - an undying classic
And one more secret of the popularity of the MC-140 is its low price. It has significant differences from different manufacturers, but the approximate cost of one section is about $ 5 (retail).
Advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators
It is clear that a product that has not left the market for many decades has some unique properties. The advantages of cast iron batteries include:
- Low chemical activity, which ensures a long service life in our networks. Officially, the warranty period is from 10 to 30 years, and the service life is 50 years or more.
- Low hydraulic resistance. Only radiators of this type can stand in systems with natural circulation (in some, aluminum and steel tubulars are still installed).
- High temperature of the working environment. No other radiator can withstand temperatures above +130 o C. Most of them have an upper limit of +110 o C.
- Low price.
- High heat dissipation. For all other cast iron radiators, this characteristic is in the "disadvantages" section. Only in MS-140 and MS-90 thermal power of one section is comparable to aluminum and bimetallic ones. For MS-140, heat transfer is 160-185 W (depending on the manufacturer), for MS 90 - 130 W.
- They do not corrode when the coolant is drained.


MS-140 and MS-90 - the difference in section depth
Some properties under some circumstances are a plus, under others - a minus:
- Large thermal inertia. While the MC-140 section warms up, it may take an hour or more. And all this time the room is not heated. But on the other hand, it is good if the heating is turned off, or an ordinary solid fuel boiler is used in the system: the heat accumulated by the walls and water maintains the temperature in the room for a long time.
- Large cross-section of channels and collectors. On the one hand, even a bad and dirty coolant will not be able to clog them in a few years. Therefore, cleaning and flushing can be carried out periodically. But because of the large cross-section in one section, more than a liter of coolant is "placed". And it needs to be "driven" through the system and heated, and this means extra costs for equipment (more powerful pump and boiler) and fuel.
"Pure" disadvantages are also present:
Great weight. The mass of one section with a center distance of 500 mm is from 6 kg to 7.12 kg. And since you usually need from 6 to 14 pieces per room, you can calculate what the mass will be. And it will have to be worn, and also hung on the wall. This is another drawback: complicated installation. And all because of the same weight. Brittleness and low working pressure. Not the most pleasant characteristics
For all the massiveness, cast iron products must be handled carefully: they can burst on impact. The same fragility leads to not the highest working pressure: 9 atm
Pressing - 15-16 atm. The need for regular staining. All sections are only primed. They will need to be painted often: once a year or two.


Thermal inertia is not always a bad thing ...
Application area
As you can see, there are more than serious advantages, but there are also disadvantages. Putting it all together, you can define the scope of their use:
- Networks with a very low quality of the heat carrier (Ph above 9) and a large amount of abrasive particles (without mud collectors and filters).
- In individual heating when using solid fuel boilers without automation.
- In natural circulation networks.
What determines the power of cast iron radiators
Pig-iron sectional radiators are a proven way of heating buildings for decades. They are very reliable and durable, however there are a few things to keep in mind. So, they have a slightly small heat transfer surface; about a third of the heat is transferred by convection. First, we recommend watching about the advantages and features of cast iron radiators in this video.
The area of the section of the MC-140 cast-iron radiator is (in terms of the heating area) only 0.23 m2, weight 7.5 kg and holds 4 liters of water. This is quite small, so each room should have at least 8-10 sections. The area of the section of a cast-iron radiator should always be taken into account when choosing, so as not to hurt yourself. By the way, in cast-iron batteries the heat supply is also somewhat slowed down. The power of a section of a cast iron radiator is usually about 100-200 watts.
The working pressure of a cast iron radiator is the maximum water pressure it can withstand. Usually this value fluctuates around 16 atm. And heat transfer shows how much heat is given off by one section of the radiator.
Often, manufacturers of radiators overestimate the heat transfer. For example, you can see that cast iron radiators heat transfer at a delta t 70 ° C is 160/200 W, but the meaning of this is not entirely clear. The designation "delta t" is actually the difference between the average air temperatures in the room and in the heating system, that is, at a delta t 70 ° C, the heating system's work schedule should be: supply 100 ° C, return 80 ° C. It is already clear that these figures do not correspond to reality. Therefore, it will be correct to calculate the heat transfer of the radiator at a delta t 50 ° C. Nowadays, cast-iron radiators are widely used, the heat transfer of which (more specifically, the power of the cast-iron radiator section) fluctuates in the region of 100-150 W.
A simple calculation will help us to determine the required thermal power. The area of your room in mdelta should be multiplied by 100 W. That is, for a room with an area of 20 mdelta, a 2000 W radiator is needed. Be sure to keep in mind that if there are double-glazed windows in the room, subtract 200 W from the result, and if there are several windows in the room, too large windows or if it is angular, add 20-25%. If you do not take these points into account, the radiator will work ineffectively, and the result is an unhealthy microclimate in your home. You should also not choose a radiator by the width of the window under which it will be located, and not by its power.
If the power of cast iron radiators in your home is higher than the heat loss of the room, the devices will overheat. The consequences may not be very pleasant.
- First of all, in the fight against the stuffiness arising due to overheating, you will have to open windows, balconies, etc., creating drafts that create discomfort and illness for the whole family, and especially for children.
- Secondly, due to the highly heated surface of the radiator, oxygen burns out, the humidity of the air drops sharply, and even the smell of burnt dust appears. This brings special suffering to allergy sufferers, since dry air and burnt dust irritate the mucous membranes and cause an allergic reaction. And this also affects healthy people.
- Finally, the incorrectly selected power of cast iron radiators is a consequence of uneven heat distribution, constant temperature drops. Radiator thermostatic valves are used to regulate and maintain the temperature. However, it is useless to install them on cast-iron radiators.
If the thermal power of your radiators is less than the heat loss of the room, this problem is solved by creating additional electric heating or even a complete replacement of heating devices. And it will cost you time and money.
Therefore, it is very important, taking into account the above factors, to choose the most suitable radiator for your room.
Cast iron batteries


The cast-iron type of heaters has many differences from the previous, above-described radiators. The heat transfer of the type of radiator under consideration will be very low if the mass of the sections and their capacity are too large.At first glance, these devices seem completely useless in modern heating systems. But at the same time, the classic "accordions" MS-140 are still in high demand, since they are highly resistant to corrosion and can last a very long time. In fact, MC-140 can really last more than 50 years without any problems. Plus, it doesn't matter what the coolant is. Also, simple batteries made of cast iron material have the highest thermal inertia due to their enormous mass and spaciousness. This means that if you turn off the boiler, the radiator will still remain warm for a long time. But at the same time, cast iron heaters do not have strength at the proper operating pressure. Therefore, it is better not to use them for networks with high water pressure, as this can entail huge risks.
Advantages and disadvantages of cast iron radiators
Cast iron radiators are made by casting. The cast iron alloy has a homogeneous composition. Such heating devices are widely used both for central heating systems and for autonomous heating systems. The sizes of cast iron radiators may vary.
Among the advantages of cast iron radiators are:
- the ability to use for a coolant of any quality. Suitable even for heat transfer fluids with a high alkali content. Cast iron is a durable material and it is not easy to dissolve or scratch it;
- resistance to corrosion processes. Such radiators can withstand the coolant temperature up to +150 degrees;
- excellent heat storage properties. An hour after the heating is turned off, the cast iron radiator will radiate 30% of the heat. Therefore, cast iron radiators are ideal for systems with irregular heating of the coolant;
- do not require frequent maintenance. And this is mainly due to the fact that the cross-section of cast iron radiators is quite large;
- long service life - about 50 years. If the coolant is of high quality, then the radiator can last a century;
- reliability and durability. The wall thickness of such batteries is large;
- high heat radiation. For comparison: bimetallic heaters transfer 50% of the heat, and cast iron radiators - 70% of the heat;
- for cast-iron radiators, the price is quite acceptable.
Among the disadvantages are:
- great weight. Only one section can weigh about 7 kg;
- installation should be carried out on a previously prepared, reliable wall;
- radiators must be painted. If after a while it is necessary to paint the battery again, the old layer of paint must be sanded. Otherwise, heat transfer will decrease;
- increased fuel consumption. One segment of a cast iron battery contains 2-3 times more liquid than other types of batteries.
Bimetallic radiators
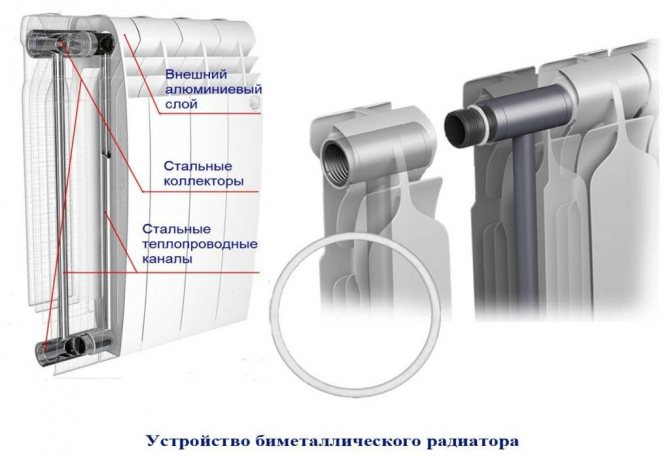

Based on the indicators of this table for comparing the heat transfer of various radiators, the type of bimetallic batteries is more powerful. Outside, they have a ribbed body made of aluminum, and inside a frame with high strength and metal pipes so that there is a coolant flow. Based on all indicators, these radiators are widely used in the heating network of a multi-storey building or in a private cottage. But the only drawback of bimetallic heaters is the high price.
Connection method
Not everyone understands that the piping of the heating system and the correct connection affect the quality and efficiency of heat transfer. Let us examine this fact in more detail.
There are 4 ways to connect a radiator:
- Lateral. This option is most often used in urban apartments of multi-storey buildings. There are more apartments in the world than private houses, so manufacturers use this type of connection as a nominal way to determine the heat transfer of radiators. A factor of 1.0 is used to calculate it.
- Diagonal.Ideal connection, because the heating medium passes through the entire device, evenly distributing heat throughout its volume. Usually this type is used if there are more than 12 sections in the radiator. A multiplying factor of 1.1–1.2 is used in the calculation.
- Lower. In this case, the supply and return pipes are connected from the bottom of the radiator. Typically, this option is used for hidden pipe wiring. This type of connection has one drawback - heat loss is 10%.
- One-pipe. This is essentially a bottom connection. It is usually used in the Leningrad pipe distribution system. And here it was not without heat loss, however, they are several times more - 30-40%.
Calculation of devices for the heat loss of the room
The thermal indicators of the installed devices are determined from the calculation of the heat loss in the room. The standard value of the heat required per unit volume of the heated room, which is assumed to be 1 m3, is:
- for brick buildings - 34 W;
- for large-panel buildings - 41 W.
The heating medium temperature at the inlet and outlet and the standard room temperature differ for different systems. Therefore, to determine the real heat flow, the temperature delta is calculated using the formula:
Dt = (T1 + T2) / 2 - T3, where
- T1 - water temperature at the system inlet;
- T2 - water temperature at the outlet of the system;
- T3 is the standard room temperature;
Important! The nameplate heat transfer is multiplied by a correction factor, determined depending on Dt.
To determine the amount of heat that is needed for a room, it is enough to multiply its volume by the standard power value and the coefficient of accounting for the average temperature in winter, depending on the climatic zone. This coefficient is equal to:
- at -10 ° C and above - 0.7;
- at -15 ° C - 0.9;
- at -20 ° C - 1.1;
- at -25 ° C - 1.3;
- at -30 ° C - 1.5.
In addition, a correction for the number of outer walls is required. If one wall goes out, the coefficient is 1.1, if two - we multiply by 1.2, if three, then we increase by 1.3. Using the radiator manufacturer's data, it is always easy to select the right heater.
Remember that the most important quality of a good radiator is its durability in operation. Therefore, try to make your purchase so that the batteries will last you the required amount of time.
gopb.ru
How to correctly calculate the real heat transfer of batteries
You must always start with the technical passport that is attached to the product by the manufacturer. In it, you will definitely find the data of interest, namely, the thermal power of one section or a panel radiator of a certain standard size. But do not rush to admire the excellent performance of aluminum or bimetallic batteries, the figure indicated in the passport is not final and requires adjustment, for which you need to calculate the heat transfer.
You can often hear such judgments: the power of aluminum radiators is the highest, because it is well known that the heat transfer of copper and aluminum is the best among other metals. Copper and aluminum have the best thermal conductivity, this is true, but heat transfer depends on many factors, which will be discussed below.


The heat transfer prescribed in the passport of the heater corresponds to the truth when the difference between the average temperature of the coolant (t supply + t return flow) / 2 and in the room is 70 ° C. With the help of a formula, this is expressed as follows:
For reference. In the documentation for products from different companies, this parameter can be designated in different ways: dt, Δt or DT, and sometimes it is simply written “at a temperature difference of 70 ° C”.
What does it mean when the documentation for a bimetallic radiator says: the thermal power of one section is 200 W at DT = 70 ° C? The same formula will help to figure it out, only you need to substitute the known value of room temperature - 22 ° С into it and carry out the calculation in the reverse order:
Knowing that the temperature difference in the supply and return pipelines should not be more than 20 ° С, it is necessary to determine their values in this way:
Now you can see that 1 section of the bimetallic radiator from the example will give off 200 W of heat, provided that there is water in the supply pipeline heated to 102 ° C, and a comfortable temperature of 22 ° C is established in the room. The first condition is unrealistic to fulfill, since in modern boilers heating is limited to a limit of 80 ° C, which means that the battery will never be able to give the declared 200 W of heat. Yes, and it is a rare case that the coolant in a private house is heated to such an extent, the usual maximum is 70 ° C, which corresponds to DT = 38-40 ° C.
Calculation procedure
It turns out that the real power of the heating battery is much lower than that stated in the passport, but for its selection you need to understand how much. There is a simple way for this: applying a reduction factor to the initial value of the heating power of the heater. Below is a table where the values of the coefficients are written, by which it is necessary to multiply the passport heat transfer of the radiator, depending on the value of DT:
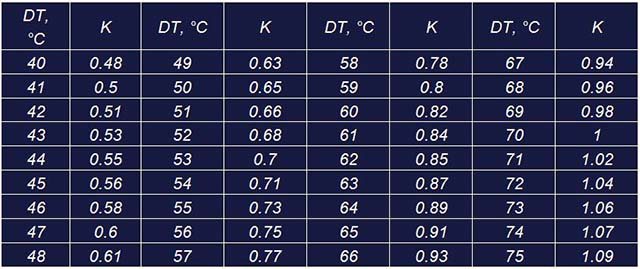

The algorithm for calculating the real heat transfer of heating devices for your individual conditions is as follows:
- Determine what should be the temperature in the house and the water in the system.
- Substitute these values into the formula and calculate your real Δt.
- Find the corresponding coefficient in the table.
- Multiply the nameplate value of the radiator heat transfer by it.
- Calculate the number of heating devices required to heat the room.
For the above example, the thermal power of 1 section of a bimetallic radiator will be 200 W x 0.48 = 96 W. Therefore, to heat a room with an area of 10 m2, you will need 1 thousand watts of heat or 1000/96 = 10.4 = 11 sections (rounding always goes up).
The presented table and the calculation of the heat transfer of the batteries should be used when the Δt is indicated in the documentation, equal to 70 ° С. But it happens that for different devices from some manufacturers, the power of the radiator is given at Δt = 50 ° C. Then it is impossible to use this method, it is easier to collect the required number of sections according to the passport characteristics, only take their number with a one and a half stock.
For reference. Many manufacturers indicate the values of heat transfer under such conditions: supply t = 90 ° С, return t = 70 ° С, air temperature = 20 ° С, which corresponds to Δt = 50 ° С.
What it is?
At its core, bimetallic heating is a mixed type of construction that was able to embody the advantages of an aluminum and steel heating system.
It is on these elements that the radiator device is based:
which consists of 2 cases - external (aluminum) and internal (steel).

Heater,- Thanks to the strong inner shell made of steel, the body of the structure is not afraid of the effects of strong hot water, it can withstand even high pressure and gives excellent indicators of the strength of the connection of each section of the radiator into a single battery.
- Housing made of aluminum perfectly transfers and dissipates heat in the air, does not corrode outside.
To confirm what kind of heat transfer from bimetallic heating radiators, a comparative table was created. The closest and strongest competitor is a radiator made of CG cast iron, aluminum AL and AA, steel TS, but the BM bimetallic radiator has the best heat transfer rates, good operating pressure and corrosion resistance.
Interestingly, almost all tables contain information from manufacturers about the level of heat transfer, which are reduced to the standard in the form of a radiator height of 0.5 m and a temperature difference of 70 degrees.
But in fact, everything is much worse, since recently 70% of manufacturers indicate the heat transfer of thermal power per section and per hour, i.e. data may vary significantly. This is done on purpose, the data is not specifically cited to simplify the perception of the buyer, so that he does not have to calculate the data about a particular radiator.
Heat dissipation of the radiator which means this indicator
The term heat transfer means the amount of heat that the heating battery transfers to the room over a certain period of time. There are several synonyms for this indicator: heat flow; thermal power, power of the device. The heat transfer of heating radiators is measured in Watts (W).Sometimes in the technical literature you can find the definition of this indicator in calories per hour, with 1 W = 859.8 cal / h.
Heat transfer from heating batteries is carried out through three processes:
- heat exchange;
- convection;
- radiation (radiation).
Each heating device uses all three heat transfer options, but their ratio differs from model to model. Earlier it was customary to call radiators devices in which at least 25% of thermal energy is given as a result of direct radiation, but now the meaning of this term has expanded significantly. Now, convector-type devices are often called this way.


The best batteries for heat dissipation
Thanks to all the calculations and comparisons carried out, we can safely say that bimetallic radiators are still the best in heat transfer. But they are quite expensive, which is a big disadvantage for bimetallic batteries. Next, after them are aluminum batteries. Well, the last in terms of heat transfer are cast iron heaters, which should be used in certain installation conditions. If, nevertheless, to determine a more optimal option, which will not be entirely cheap, but not entirely expensive, and also very effective, then aluminum batteries will be an excellent solution. But again, you should always consider where you can use them and where you can't. Also, the cheapest, but proven option, remains cast-iron batteries, which can serve for many years, without problems, providing homes with heat, even if not in such quantities as other types can do.
Steel appliances can be classified as convector-type batteries. And in terms of heat transfer, they will be much faster than all of the above devices.
Technical characteristics of cast iron radiators
The technical parameters of cast iron batteries are related to their reliability and endurance. The main characteristics of a cast iron radiator, like any heating device, are heat transfer and power. As a rule, manufacturers indicate the power of cast iron heating radiators for one section. The number of sections can be different. As a rule, from 3 to 6. But sometimes it can reach 12. The required number of sections is calculated separately for each apartment.
The number of sections depends on a number of factors:
- area of the room;
- room height;
- number of windows;
- floor;
- the presence of installed double-glazed windows;
- corner placement of the apartment.
The price per section is given for cast iron radiators, and may vary depending on the manufacturer. The heat dissipation of batteries depends on what kind of material they are made of. In this regard, cast iron is inferior to aluminum and steel.
Other technical parameters include:
- maximum working pressure - 9-12 bar;
- the maximum temperature of the coolant is 150 degrees;
- one section holds about 1.4 liters of water;
- the weight of one section is approximately 6 kg;
- section width 9.8 cm.
Such batteries should be installed with the distance between the radiator and the wall from 2 to 5 cm. The installation height above the floor should be at least 10 cm. If there are several windows in the room, the batteries must be installed under each window. If the apartment is angular, it is recommended to carry out external wall insulation or to increase the number of sections.
It should be noted that cast iron batteries are often sold unpainted. In this regard, after purchase, they must be covered with a heat-resistant decorative compound, and must be stretched first.
Among domestic radiators, the model ms 140 can be distinguished. For cast iron heating radiators ms 140, the technical characteristics are given below:
- heat transfer of the MS 140 section - 175 W;
- height - 59 cm;
- the radiator weighs 7 kg;
- the capacity of one section is 1.4 liters;
- section depth is 14 cm;
- section power reaches 160 W;
- section width is 9.3 cm;
- the maximum temperature of the coolant is 130 degrees;
- maximum working pressure - 9 bar;
- the radiator has a sectional design;
- pressure test is 15 bar;
- the volume of water in one section is 1.35 liters;
- Heat-resistant rubber is used as the material for the intersection gaskets.
It should be noted that the ms 140 cast iron radiators are reliable and durable. And the price is quite affordable. This is what determines their demand in the domestic market.
Features of the choice of cast iron radiators
To choose which cast-iron heating radiators are best suited for your conditions, you must take into account the following technical parameters:
- heat transfer. Choose based on the size of the room;
- radiator weight;
- power;
- dimensions: width, height, depth.
To calculate the thermal power of a cast-iron battery, one must be guided by the following rule: for a room with 1 outer wall and 1 window, 1 kW of power per 10 sq.m. is needed. the area of the room; for a room with 2 outer walls and 1 window - 1.2 kW .; for heating a room with 2 outer walls and 2 windows - 1.3 kW.
If you decide to buy cast-iron heating radiators, you should also take into account the following nuances:
- if the ceiling is higher than 3 m, the required power will increase proportionally;
- if the room has windows with double-glazed windows, then the battery power can be reduced by 15%;
- if there are several windows in the apartment, then a radiator must be installed under each of them.
Modern market
Imported batteries have a perfectly smooth surface, they are of higher quality and look more aesthetically pleasing. True, their cost is high.
Among domestic counterparts, cast iron radiators konner can be distinguished, which are in good demand today. They are distinguished by a long service life, reliability, and fit perfectly into a modern interior. Cast iron radiators konner heating in any configuration are produced.
- How to pour water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular floor-standing gas boiler of Russian production
- How to properly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed-type heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes in case of malfunction
Recommended reading
2016–2017 - Leading portal for heating. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying of site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement entails legal liability. Contacts
What you need to consider when calculating
Calculation of heating radiators
Be sure to take into account:
- The material from which the heating battery is made.
- Its size.
- The number of windows and doors in the room.
- The material from which the house is built.
- The side of the world in which the apartment or room is located.
- The presence of thermal insulation of the building.
- Type of piping routing.
And this is only a small part of what must be taken into account when calculating the power of a heating radiator. Do not forget about the regional location of the house, as well as the average outdoor temperature.
There are two ways to calculate the heat dissipation of a radiator:
- Regular - using paper, pen and calculator. The calculation formula is known, and it uses the main indicators - the heat output of one section and the area of the heated room. Coefficients are also added - decreasing and increasing, which depend on the previously described criteria.
- Using an online calculator. It is an easy-to-use computer program that loads specific data about the dimensions and construction of a house. It gives a fairly accurate indicator, which is taken as the basis for the design of the heating system.
For a common man in the street, both options are not the easiest way to determine the heat transfer of a heating battery. But there is another method, for which a simple formula is used - 1 kW per 10 m² of area. That is, to heat a room with an area of 10 square meters, you will need only 1 kilowatt of thermal energy.Knowing the heat transfer rate of one section of a heating radiator, you can accurately calculate how many sections need to be installed in a particular room.
Let's look at a few examples of how to correctly carry out such a calculation. Different types of radiators have a large size range, depending on the center distance. This is the dimension between the axes of the lower and upper manifold. For the bulk of heating batteries, this indicator is either 350 mm or 500 mm. There are other parameters, but these are more common than others.
This is the first thing. Second, there are several types of heating devices made of various metals on the market. Each metal has its own heat transfer, and this will have to be taken into account when calculating. By the way, everyone decides for himself which one to choose and install a radiator in his home.
What affects the heat transfer coefficient
- Heat carrier temperature.
- The material from which the heating batteries are made.
- Correct installation.
- Installation dimensions of the device.
- The dimensions of the radiator itself.
- Connection type.
- Design. For example, the number of convection fins in steel panel radiators.
With the temperature of the coolant, everything is clear, the higher it is, the more heat the device gives off. The second criterion is also more or less clear. Here is a table where you can see what kind of material and how much heat it gives off.
| Heating battery material | Heat dissipation (W / m * K) |
| Cast iron | 52 |
| Steel | 65 |
| Aluminum | 230 |
| Bimetal | 380 |
Let's face it, this illustrative comparison says a lot, from it we can conclude that, for example, aluminum has a heat transfer rate almost four times higher than cast iron. This makes it possible to reduce the temperature of the coolant if aluminum batteries are used. And this leads to fuel savings. But in practice, everything turns out differently, because the radiators themselves are made in different shapes and designs, besides, their model range is so huge that there is no need to talk about exact numbers here.
Heat transfer depending on the temperature of the coolant
For example, we can cite the following spread in the degree of heat transfer from aluminum and cast-iron radiators:
- Aluminum - 170-210.
- Cast iron - 100-130.
First, the comparative ratio has plummeted. Secondly, the range of spread of the indicator itself is quite large. Why does this happen? Primarily due to the fact that manufacturers use different shapes and wall thicknesses of the heater. And since the model range is quite wide, hence the heat transfer limits with a strong run-up of indicators.
Let's look at several positions (models), combined into one table, where the brands of radiators and their heat transfer rates will be indicated. This table is not a comparative one, we just want to show how the heat output of the device changes depending on its design differences.
| Model | Heat dissipation |
| Cast iron M-140-AO | 175 |
| M-140 | 155 |
| M-90 | 130 |
| RD-90 | 137 |
| Aluminum RIfar Alum | 183 |
| Bimetallic RIFAR Base | 204 |
| RIFAR Alp | 171 |
| Aluminum RoyalTermo Optimal | 195 |
| RoyalTermo Evolution | 205 |
| Bimetal RoyalTermo BiLiner | 171 |
| RoyalTermo Twin | 181 |
| RoyalTermo Style Plus | 185 |
As you can see, the heat transfer of heating radiators largely depends on the model differences. And there are a huge number of such examples. It is necessary to draw your attention to one very important nuance - some manufacturers in the product passport indicate the heat transfer of not one section, but several. But all this is written in the document. It is important here to be careful not to make a mistake when carrying out the calculation.
Connection type
I would like to dwell on this criterion in more detail. The thing is that the coolant, passing through the internal volume of the battery, fills it unevenly. And when it comes to heat transfer, then this very unevenness greatly affects the degree of this indicator. To begin with, there are three main types of connections.
- Lateral. Most often used in city apartments.
- Diagonal.
- Lower.
If we consider all three types, then we select the second (diagonal), as the basis of our analysis. That is, all experts believe that this particular scheme can be taken for such a coefficient as 100%. And this is actually the case, because the coolant according to this scheme passes from the upper branch pipe, going down to the lower branch pipe installed on the opposite side of the device. It turns out that hot water moves diagonally, evenly distributed throughout the entire internal volume.
Heat dissipation depending on the model of the device
Lateral connection in this case has one drawback. The coolant fills the radiator, but the last sections are poorly covered. That is why heat loss in this case can be up to 7%.
And the bottom connection diagram. Let's face it, not entirely effective, heat loss can be up to 20%. But both options (side and bottom) will work effectively if they are used in systems with forced circulation of the coolant. Even a small amount of pressure will create a head that is enough to bring water to each section.
Correct installation
Not all ordinary people understand that a heating radiator must be installed correctly. There are certain positions that can affect heat dissipation. And these positions in some cases must be strictly followed.
For example, the horizontal landing of the device. This is an important factor, it depends on it how the coolant will move inside, whether air pockets will form or not.
Therefore, advice to those who decide to install heating batteries with their own hands - no distortions or displacements, try to use the necessary measuring and control tools (level, plumb line). The batteries in different rooms must not be installed on the same level, this is very important.
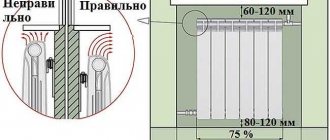
And that is not all. Much will depend on how far from the boundary surfaces the radiator will be installed. Here are just the standard positions:
- From the windowsill: 10-15 cm (an error of 3 cm is permissible).
- From the floor: 10-15 cm (3 cm error is acceptable).
- From the wall: 3-5 cm (error 1 cm).
How can an increase in error affect heat transfer? It makes no sense to consider all the options, we will give an example of several main ones.
- Increasing the error in the distance between the window sill and the device to a larger side reduces the heat transfer rate by 7-10%.
- Reducing the error in the distance between the wall and the radiator reduces heat transfer by up to 5%.
- Between the floor and the batteries - up to 7%.
It would seem that some centimeters, but it is they that can reduce the temperature regime inside the house. It seems that the decrease is not that big (5-7%), but let's compare all this with fuel consumption. It will increase by the same percentage. It won't be noticeable in one day, but in a month, but for the entire heating season? The amount immediately rises to astronomical heights. So it is worth paying special attention to this.
otepleivode.ru