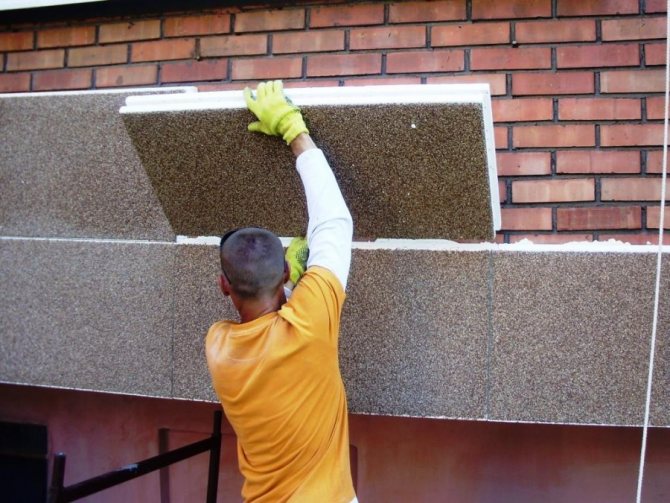
Often, the facade in a private house is one of the very last stages, when the construction has already eaten up all the money. Therefore, many decide to do it on their own, without hiring professional builders or call friends for help. The technology of work is being violated. Well, what, the neighbor has 10 years and nothing! Yes, in the best case there will be nothing, and in the worst case you will not be able to live in such a house. To avoid popular mistakes and get the job done right, learn these important rules.

Warming options
There are 2 facade insulation systems:
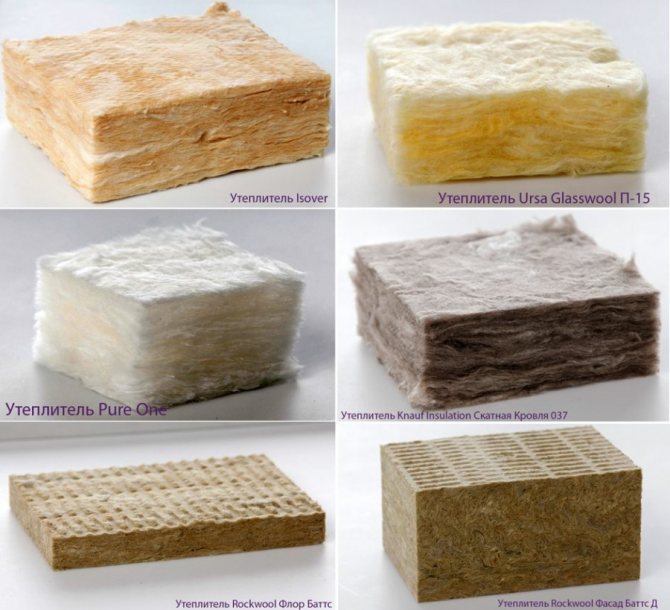
Mineral wool (WM). Mineral wool is vapor-permeable, does not burn, insulates and insulates well. Suitable for any base. Ideal, but expensive - plaster, paint and primer must be vapor-permeable.
Polyfoam (VWS or PSBS). Suitable for thermal insulation of monolithic reinforced concrete, three-layer wall concrete and reinforced concrete panels. Walls made of expanded clay concrete or solid bricks can only be insulated for dry rooms. The minimum density of foam for insulation of the facade is PSB-S25f. Everything below is suitable only for interior work, it crumbles on the street.


Extruded polystyrene foam is only suitable for insulating the basement. It is vapor-proof and well suited to protect against moisture penetration from the soil to the base of the house. Without sanding the surface of the EPSP, it has poor adhesion, the glue will not hold well.


Facade under plaster: applied technologies
Whatever material a building is constructed from, thermal insulation is required to increase its energy efficiency. According to experts, the best option is a plaster facade, as:
- choosing this technology, you can save on reducing the cost of heating and air conditioning of premises;
- you can reduce the cost of construction materials and installation work for the construction of the building by reducing the weight of the facade structure of the building;
- external insulation of the facade for plastering preserves the internal area of the premises;
- in addition to general thermal insulation, problems with the insulation of interpanel seams and their protective sealing are solved.
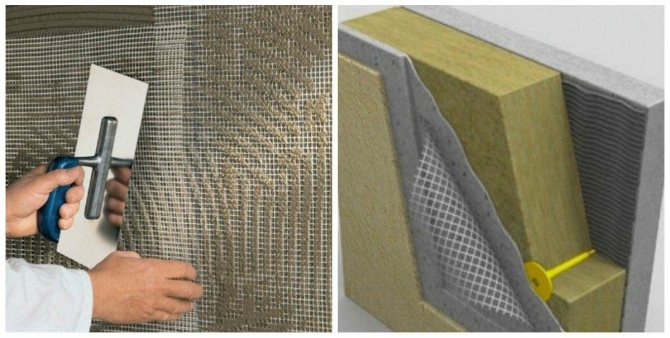

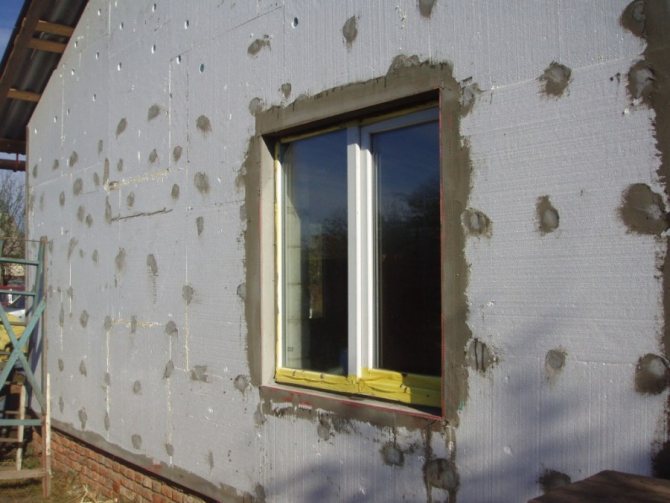
Photo 2. Preparing the facade for plastering - plaster mesh
Two-layer technology "plastering facades of stone houses"
There are several technologies for thermal insulation of buildings, when the facade plaster is applied without insulation. The finishing process for brick, block and panel houses includes the following steps:
- preliminary preparation of the external surfaces of the walls - cleaning from dust and dirt, leveling and sealing cracks and irregularities;
- application of primer mixes to increase the adhesion of plaster mixes to the base;
- if the walls have large defects and corners with significant deviations from the vertical, additional measures are taken to strengthen and strengthen the bases with a special metal mesh;
- applying a base plaster layer;
- after the first layer has completely dried, a finishing or a layer of decorative plaster is applied;
- the final stage is staining a smooth surface or hydrofibrating a structural one.


Photo 3. Preparation of walls before plastering
With this technology, the final thickness of the plaster layer does not exceed 2.5 cm.
Technology "facade without insulation for wooden buildings"
According to this technology, there is no need to choose a heater for plastering, wooden walls receive good thermal insulation and protection from external factors. This method of insulating wooden buildings has been used for a long time in regions with a temperate and cold climate.Today it is rarely used due to its complexity. The process of finishing the plaster facade of wooden houses includes the following stages:
- installation of shingles. Shingles are narrow plywood strips up to 5 mm thick and up to 20 mm wide. It is nailed in two layers in the form of a diagonal lattice with a pitch of 30 mm between the slats;
- installation of beacons. It is necessary to obtain a perfectly flat surface;
- light moistening of the shingle lathing to increase its adhesive properties;
- application of the first layer of plaster by the "throwing" method. It is carried out in order to close all cracks and irregularities, lattice cells. The thickness of the plaster layer is at least 10 mm;
- after light drying of the primer layer, the main one is applied by "throwing" and then leveling with the rule. Layer thickness 5–10 mm;
- painting a smooth surface or finishing with decorative plaster.
Plastering of the facade without insulation on wooden buildings is carried out only after its shrinkage and preliminary preparation. It consists in sealing the cracks formed with mineral wool, linen jute or wooden slats. Surface finishing is carried out from the corners, then moves along the walls. The step between the beacon strips must correspond to the size of the rule.


Photo 4. Insulation of a wooden house
Warming cake
When insulated with mineral wool, the cake is as follows:
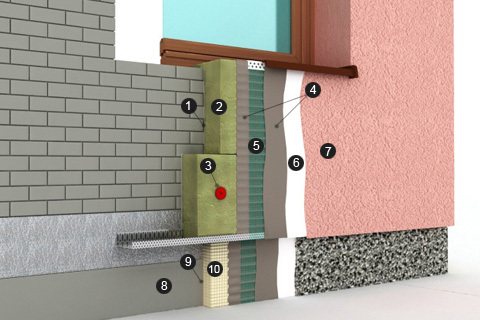

- Priming layer,
- Adhesive composition,
- Mineral wool,
- Disc dowels,
- Base layer of plaster,
- Glass network,
- Primer,
- Decorative plaster.
With foam insulation:
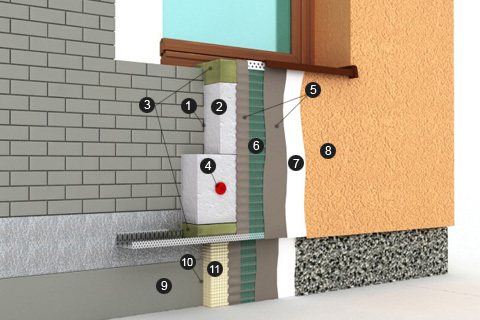

- Priming layer,
- Adhesive composition,
- Styrofoam,
- Mineral wool notch,
- Disc dowels,
- Base layer of plaster,
- Glass network,
- Primer,
- Decorative plaster.
For the base:
- Waterproofing,
- Glue,
- Extruded polystyrene foam.
General design description
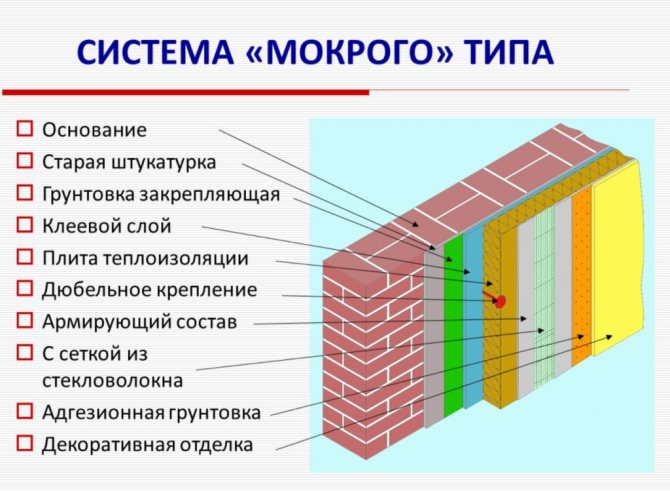

A construction of this type consists of several layers that perform a specific function:
- Kleeva. Consists of an adhesive mixture, it is on it that the quality of adhesion of the insulating material to the wall of the building depends;
- Heat insulating. Wet insulation is carried out using expanded polystyrene or mineral wool. This choice is due to the fact that these materials have low thermal conductivity, which makes it possible to perform high-quality insulation of the facade;
- Reinforced. A reinforcing alkali-resistant mesh is applied to the insulation fixed to the wall, which makes it possible to enhance the adhesion of the protective and decorative layers to the surface of the plates. Fastening is done with mineral glue;
- Protective. Priming the surface allows you to increase the durability of the entire structure;
- Decorative. Includes finishing decorative plaster, which protects the facade from the harmful effects of climatic conditions and mechanical damage. It can be used to create a facade of almost any shade.
Insulation from the inside
In no case should a residential building be insulated from the inside. This is the same as tucking a fur coat into panties. Here's an example of what happens when you insulate a house from the inside:
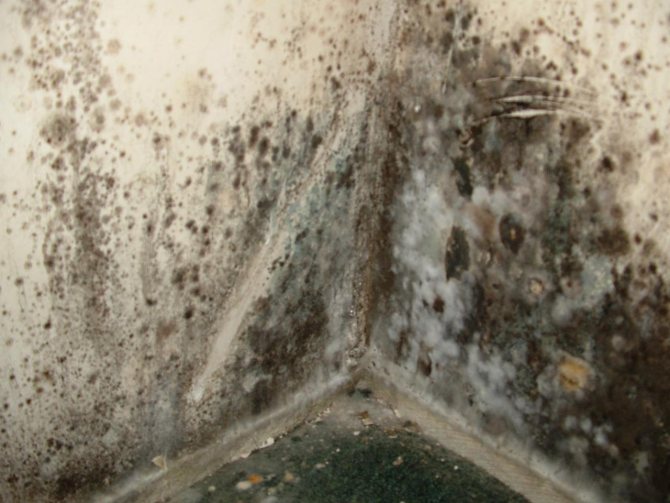


Mold and mildew have now developed in the place where the extruded polystyrene foam touches the wall. This is because the dew point has shifted inside the room. Now it is always wet there, any foundation will collapse: even brick, even concrete.
The only option when insulation from the inside is justified is on the loggia. But you need to make a good vapor barrier. There must be good ventilation in the room, otherwise it will be impossible to live in it - it will be inside like in a package.
Advantages and disadvantages
Thermal insulation of walls under the "wet facade" method is one of the cheapest options. Low cost does not allow talking about its significant disadvantages. Like any other option, insulation in this way has its pros and cons.
Benefits
- Low cost of materials and work;
- Thermal insulation of this type (external) allows you not to take away the usable area inside the building;
- The low weight of the structure does not load the foundation with unnecessary load; • a wet facade is not only insulation, but also decorative wall decoration, which allows you to transform the building;
- Warming in this way allows you to modify the surface by ordinary painting in a different color.
disadvantages
It's important to know
All the disadvantages of this type of insulation relate to the installation process. Therefore, when performing work on your own, it is extremely important to take them into account.
- Work should be carried out only at a positive ambient temperature. To be more precise - not less than +5 degrees. If it is necessary to carry out work at lower rates, it is required to mount protective polyethylene casings and the presence of a heat gun to comply with the recommended temperature regime;
- Insulation of the facade during rain is not recommended. The adhesive solution may dry unevenly, which will lead to gradual flaking;
- Direct sunlight on the surface is also not recommended;
- During strong winds, particles of dirt and dust can get on a wet facade.
Vapor barrier and waterproofing
Wet insulation stops working. Vapor barrier is often confused with waterproofing. The names are similar, and steam and hydro, unknowingly, can be attributed to moisture. What's the difference?
The vapor barrier does not allow steam to pass through. It is attached to the bottom layer under the insulation to reduce the amount of moisture that will penetrate the insulation.
Waterproofing allows steam to pass through. Waterproofing is also called breathable or diffusion membranes. They release steam from one side, but do not let the condensate drop inside. Waterproofing is attached over the insulation to release moisture that has penetrated the insulation.
If you mix up the layers or put the waterproofing on the wrong side, mold will appear, the humidity in the house will increase, it will become cold, and the corners will blacken.
Types of ventilation facades insulation: which can and cannot be used in the system
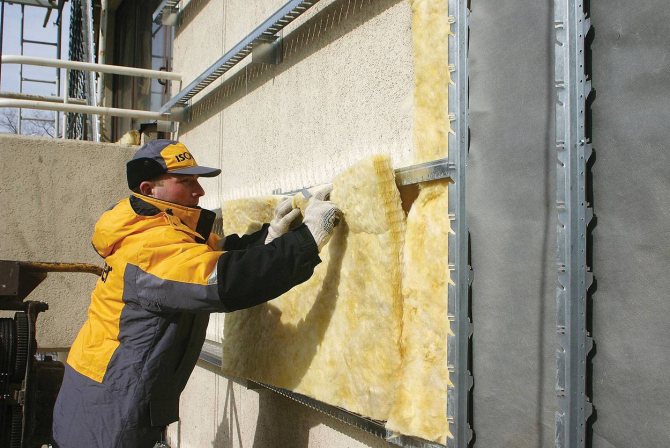


Only non-combustible materials should be used as a layer of thermal insulation. Otherwise, the presence of a ventilated gap in the event of a fire can lead to a rapid spread of fire over the entire area of the facade. Polyfoam is not used when installing ventilation facades. It burns with the release of toxic gases, poorly passes water vapor through itself, not allowing the house to "breathe", and crumbles over time.
The most effective insulation for a ventilated facade is stone wool or fiberglass slabs. They are made of environmentally friendly natural materials with heat treatment and fully comply with the requirements. Mineral insulation has a wide temperature range of application, is resistant to moisture, is not susceptible to the spread of mold and perfectly absorbs noise. They can be used separately or in combination with each other. In this case, the fiberglass layer should be internal, and the basalt fiber should be external.
Cotton wool in the form of rectangular slabs with elasticity and capable of retaining their shape throughout the entire period of operation is convenient for installation and durable. Rolled thermal insulation materials do not have these qualities. They have a low density, deform quickly and are subject to fiber weathering. They are not used when creating ventilated facades.
Primer
Don't skimp on the primer. It is inexpensive, but it increases adhesion to the surface many times over and does not allow the glue to dry out.
The primer is selected depending on the surface. Check with your purchase if the primer is suitable for your base.
For porous and rapidly absorbing walls (eg aerated concrete or loose cement-sand plaster) use a deep penetration primer. It will de-dust the surface, bind it and reduce absorbency.
If the substrate is smooth (eg monolithic concrete), a quartz sand primer should be used to improve adhesion.
The choice of insulation for a wet facade


The wet facade technology is the leader among the existing insulation methods. The advantages lie in the use of modern high-quality thermal insulation materials, the service life of some of them can reach half a century. Exterior decoration with high aesthetic characteristics guarantees the beauty of modern residential buildings and makes this technology acceptable for the restoration of architectural landmarks.
Facade heaters are divided into products from expanded polystyrene and mineral wool. Foam materials are lightweight, quick to install and have a high level of thermal protection. The main drawback of the material is its flammability. Mineral wool for a wet facade is an order of magnitude more expensive, while being more reliable in terms of performance. Plates made of this material do not burn, have a high level of vapor permeability.
The density of mineral wool for a wet facade must be at least 150 kg / m³, tensile strength - at least 15 kPa. It is recommended to give preference to the choice of basalt fiber slabs. As for the foam, for insulation work, you should choose a material of special purpose with low flammability. Experts do not advise using extruded polystyrene foam, which has low vapor permeability characteristics and has poor adhesion to the adhesive solution.
Different types of insulation boards are used in different conditions. When choosing, they are guided by the physical and chemical characteristics of the insulation, based on the specific purpose. The main characteristics that affect the preferred choice are the indicator of density, combustibility, water and thermal conductivity. It is known that a layer of mineral wool with a thickness of 1.1 cm corresponds to a foam styrene plate having a thickness of 5 cm. When insulating facades, dense insulation materials are used, which have high water-repellent properties and the ability to withstand mechanical stress.
Mineral wool for a wet facade


Mineral wool slabs are the best suited for facades. The material is distinguished by its durability, fire resistance, vapor permeability, a high level of heat and sound insulation, resistance to the effects of chemical and biological substances, environmental friendliness, and ease of installation.
Certain types of cotton wool, in particular products based on phenolic binders, are distinguished by a high level of moisture resistance. The most preferred slabs are diabase or basalt wool slabs for wet façades.
Since the strength of mineral wool should start from 15 kPa, and the material should not react with plaster, the use of fiberglass plates in this area is impractical. This is due to the fact that such mineral wool is easily destroyed in an alkaline environment and does not have sufficient tensile strength.
Fiberglass boards will begin to crumble under the influence of alkalis, which are contained in the reinforced base layer and the adhesive solution. The average pH of these materials is 12.5. The destruction is especially intense under the influence of strong winds. Very quickly, a wet fiberglass facade will deteriorate.
An important indicator in the selection of thermal insulation boards is the moisture absorption coefficient. It is desirable that its level be at around 15%, since moisture absorbed into the material will lead to deformation and negatively affect thermal conductivity.Slabs with a high degree of moisture absorption do not provide the required level of solidity of the facade. As a result, such a structure will not last more than two years.
The density index of the mineral wool of the wet facade should be from 150 to 180 kg / m³. Otherwise, the process of applying the finishing layer becomes more complicated and there is a risk of delamination of the thermal insulation coating of the facade.
The main disadvantage of mineral wool is hygroscopicity; when wet, the material loses at least half of its thermal insulation properties.
The technology of a wet facade on mineral wool involves the selection of slabs in such a way that the degree of vapor permeability from the first to the last (decorative) layer gradually increases. Compliance with this requirement will prevent condensation from forming in the middle of the structure. In the climatic conditions of Russia, most of the time throughout the year, the temperature indicators inside houses are much higher than outside. These conditions greatly increase the likelihood of condensation occurring.
Wet foam facade

Among the positive qualities possessed by heaters, the raw material in the production of which is expanded polystyrene, one can note the low cost, low weight of the material, high thermal and sound insulation, vapor permeability, environmental friendliness, ease of installation. Polyfoam is not afraid of moisture and dampness, therefore it is more often used for insulation outside.
The price of a wet foam facade largely depends on the brand of insulation, the denser this heat insulator, the higher its cost.
The main disadvantage of foam plates is the flammability of the material. To eliminate this drawback, manufacturers treat the insulation with special chemical agents - fire retardants. Even in the event of a fire, the spread of the fire will be stopped, the flame can extinguish itself.
Fire safety is also ensured by special inserts made of non-combustible materials, in particular, mineral wool. The use of this method has led to the emergence of a separate composite material.
Among other disadvantages of the material is the low degree of biosecurity. Insects and even rodents can settle in the foam. Plates made of expanded polystyrene are more fragile, which creates problems during the installation process, and less wear-resistant in operation.
Material for a wet facade made of expanded polystyrene must have a tensile strength of at least 100 kPa and have a density of 15 to 25 kg / m³.
The choice of material in accordance with all the requirements for it and correct installation with strict adherence to the technology of installing a wet facade for insulation guarantee its service life for 20-30 years. Repair of the decorative layer will have to be done a little more often, but the costs will be much less.
Quality material can also be identified by its appearance. Insulation granules should fit as tightly as possible to each other and have approximately the same size. Low-quality coarse-grained material absorbs an increased amount of moisture, which entails deformation and leads to a loss of thermal insulation qualities and early destruction of the facade.
The shape of the polystyrene foam insulation boards must be the same as that of a regular rectangle. The error is allowed no more than 2 mm per 1 m. Differences in the thickness of the insulation can be a maximum of 1 mm, and the deviation on the surface of the front plane should not exceed 0.5%. Otherwise, it is impossible to insulate the facade of the house without defects. A wet facade from the outside will have low aesthetic characteristics, and the service life will be reduced several times.
Mineral wool or expanded polystyrene?
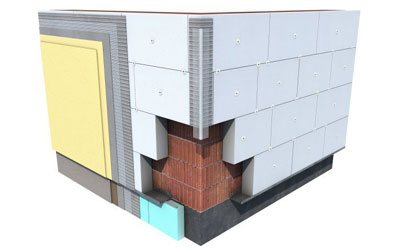

The preferred choice is made depending on how the building is insulated. Each material has its own advantages, which are in demand in a particular case.
Advantages of expanded polystyrene: - ample opportunities for creating ideal surfaces and shapes; - Convenience when applying putty; - excellent pliability of plates during processing; - lightness; - high efficiency while maintaining heat in buildings at low temperatures; - resistance to microorganisms and destructive bacteria; - the ability to self-extinguish; - increased diffuse resistance (vapor permeability); - does not cause allergic reactions; - effectively resists compaction (subsidence).
Disadvantages of expanded polystyrene: - collapses when exposed to resins, solvents and bitumen: - has a high cost; - is capable of being destroyed by mechanical action of ultraviolet radiation; - changes configuration when exposed to high temperatures; - low fire resistance (spontaneous combustion occurs at a temperature of +491 ° C); - the adhesive bond is destroyed after a couple of months. Reliable fastening is achieved only with the help of perforated corners, dowels or base planks, the number of which must strictly correspond to the technology. Otherwise, the service life is reduced from 20 years to 2 years.
Advantages of mineral wool: - environmental friendliness (natural product obtained from basalt and limestone rocks). - the material has sufficient density necessary to maintain its original shape for a long period (10 or more years); - the ability to "breathe"; - no problems with disposal; - resistance to chemical and biological effects; - fireproof (ability to withstand temperatures over 1000 ° C).
Vote
Tweet
The quality of the products depends on the raw materials. The material obtained from molten rocks is distinguished by its durability and reliability, and from blast furnace slag - by its rapid wear.
Disadvantages: - Indicators of vapor permeability of mineral wool are 6 times higher than that of expanded polystyrene. At high humidity, the mineral wool gets wet, and the heat-insulating characteristics are sharply reduced. To prevent this phenomenon in the process of its manufacture, hydrophobization is used. - Despite the high temperature threshold that exists for the fibers, at 250 ° C the binder begins to melt, which leads to the destruction of the integrity of the protective layer. - When working with mineral wool, you must use protective clothing: glasses, overalls, gloves, special shoes, respirator. If fragile and brittle fibers come into contact with the skin, irritation and itching occurs. Mineral wool dust is not excreted when it enters the lungs. With prolonged contact, allergic diseases may occur.
Mineral wool is chosen for the insulation of wooden structures and apartment buildings, paying tribute to its incombustibility. Expanded polystyrene plates significantly speed up construction and do not require the use of special protective equipment when working with them. In addition, its cost is an order of magnitude lower than the price of mineral wool.
Do you need fungi?
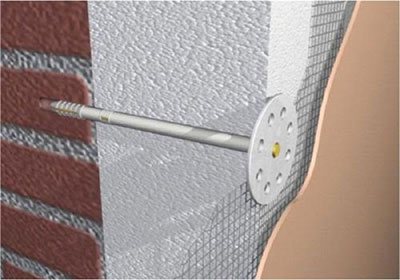
Yes, plastic dowels with a metal core (they are usually called fungi or disc dowels) are used when attaching insulation, but this is not the main fastener. It is used for wind protection and as a support during the curing of the adhesive. The plastic around the core prevents a cold bridge from appearing at the attachment point.


For good fixation, solid sheets of insulation are attached at 5-6 points. But for economy and speed of installation, the main part of the dowels holds 2 sheets at once. How this is done is shown on the model:

The efficiency of the house facade insulation system
It is generally accepted that the heat loss through the outer walls is about 40%, the rest falls on the roof, windows and foundation. In the images taken with a thermal imager, you can see the difference in temperature differences in different parts of the facade of a stone building in comparison with the temperature of the outside air.In especially critical places, the difference reaches 120 ° C. The photographs show a panel building, insulated according to the principle of "insulation inside the enclosing structure" (well masonry). In such structures, the zones of freezing are interfloor concrete ceilings. In addition to intense heat loss, condensation forms in such places, leading to corrosion in steel reinforcement, brick destruction, as well as the appearance of fungus and mold.
In the figure, you can see a thermal imager shooting the facade of a panel building before applying the thermal insulation system (photo on the left) and after (photo on the right). The dark homogeneous surface of the facade in the photo on the right indicates the absence of cold bridges and approximately the same outdoor temperature and the surface of the facade. So the effect is obvious.
Dew point
In simple terms, dew point is the ratio of temperature, humidity and pressure in the wall where condensation occurs.
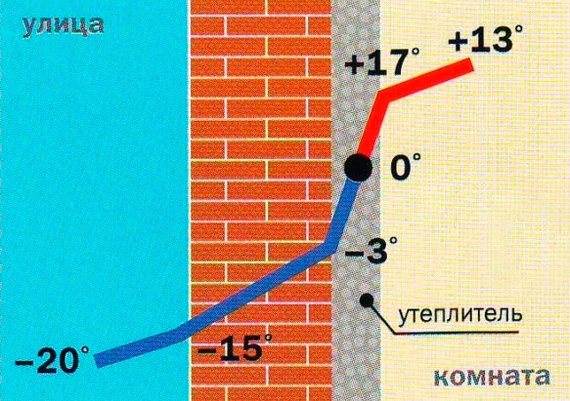

The diagram shows an error with insulation from the inside. After insulation, the wall began to freeze completely, condensation appears under the insulation. The same problem can arise if the thickness of the insulation is incorrectly calculated. The mineral wool can be squeezed out like a sponge.
The choice of materials for the device of thermal insulation with your own hands
Before proceeding to installation of a "wet facade" at the facade of the house
, you need to plan everything exactly. Do not neglect the opportunity to get professional advice at the points of purchase of building materials. Carefully study the recommendations for the production of work provided by the manufacturer of building mixtures.
House thermal insulation method Do it yourself "wet facade"
will help to significantly save on the production of work. Before proceeding with the insulation and decoration of the house, you should responsibly and thoughtfully approach the choice of building materials. All elements of the "wet facade" must work in concert, and for this it is desirable that the components are produced under the same brand and linked into a single recommendation system. The instructions will also help you correctly calculate the required amount of material.
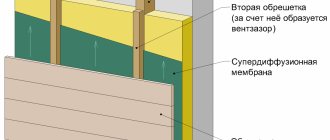
The technology of laying stone wool in the ventilation facade
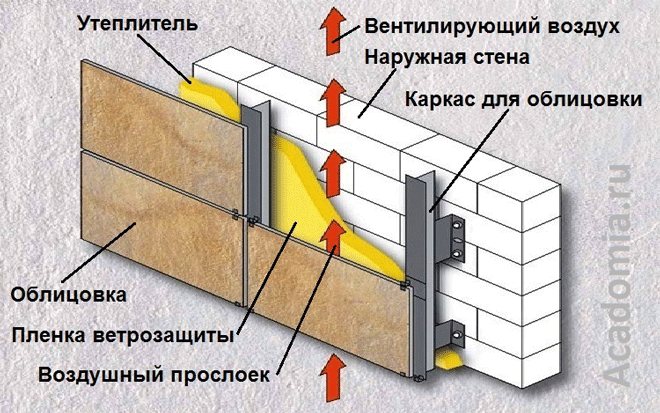

Ventilated facade installation technology with insulation
Insulating the facade with mineral wool is not difficult - it can be done even with your own hands without special skills:
- Install brackets to fix the elements of the ventilated facade.
- Fix the reference angle to the horizon to the plinth.
- Lay the insulation plates in horizontal rows, while the vertical seams should be made with a slight offset between the rows. To fix the insulation to the wall, use the dowels-umbrellas, the density of the dowels is 2 pcs / 1 plate.
- In the case of two-layer insulation of the ventilation facade: mount a windproof film - such a layer is applied in horizontal stripes, the overlap should be about 10 cm.
- The final stage - the layer of insulation is once again fixed with fungi, the density of the dowels is 5 pcs. / 1 plate.
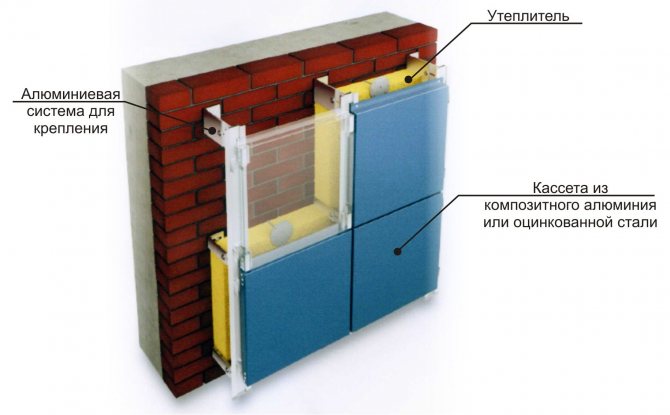
Ventilated facades - what is it
A ventilated facade is understood as a cladding system that is attached to a monolithic floor or a load-bearing wall layer using a frame made of galvanized steel, stainless steel or aluminum. The main feature of such a system is the gap between the wall and the cladding - air moves through it freely, which allows solving the problem of condensation in the structure.
For additional insulation of the building wall, a layer of insulation is included in the system - it must be non-hygroscopic. When insulating a ventilated facade, it is important to maintain a gap between the wall and the insulation of about 40 mm so that the air currents circulating between the facing material and the thermal insulation layer remove moisture from the latter. In general, the size of such a gap is standard, but in different countries the standards range from 20 to 50 mm.
The list of advantages of ventilated facades includes the following:
- Wide range of colors;
- High thermal insulation characteristics;
- The multilayer structure allows for good sound insulation, which is important for large cities;
- Natural ventilation, which relieves the materials used and the building itself from high humidity and destruction;
- Timely disposal of condensate ensures the preservation of the properties of the insulation - wall insulation with a ventilated facade reduces heat loss during the cold period for the entire period of operation;
- Durability - the service life of such a structure is 50 years;
- Fire safety;
- Operational installation, which can be done in any season of the year;
- Overheating protection during hot periods;
- The structure is repairable - partial damage can be repaired.
Do not forget about aesthetics - the facade, refined in this way, looks modern and attractive.
All these advantages are relevant only in cases where the ventilated facade is assembled in compliance with all installation rules.
Savings on glue and other components
A set of components for wet insulation of facades can be purchased as a set or formed independently. Any set includes an adhesive mixture for fixing insulation, insulation and dowels for fixing insulation, reinforcing mesh, building mixture for reinforcing insulation and plaster.
Choosing the components on their own, some craftsmen believe that the insulation does not have to be glued to the wall, but it is enough to attach it with dowels. In other cases, it is suggested to replace the adhesive mixture for the insulation with a cheap solution (for example, tile adhesive) or simply save on the application of glue.
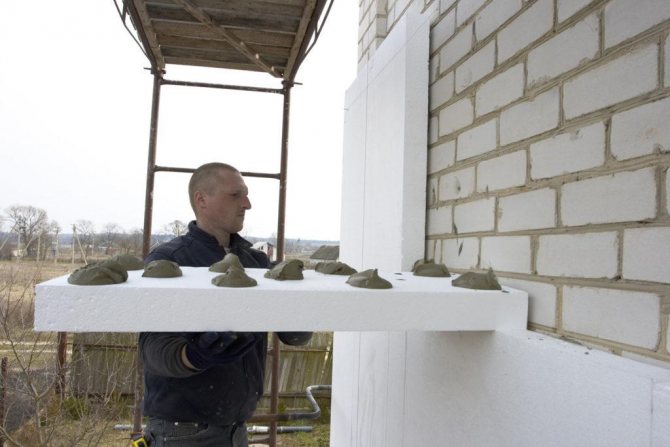


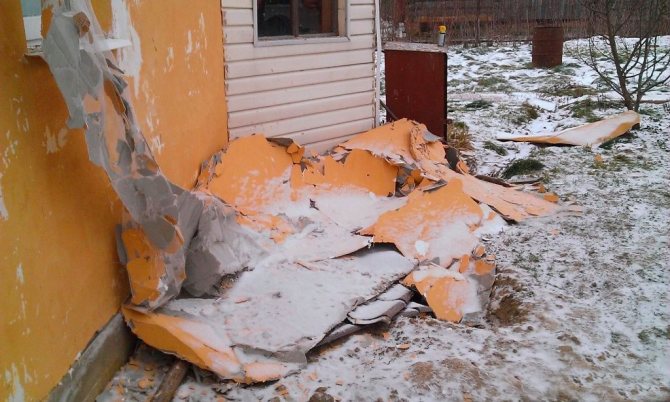
But a wall insulated in this way is likely to begin to collapse. Cracking of the plaster, peeling and tearing of thermal insulation, etc. External insulation of facades is performed for a long time, and it is better to give up saving, not to reduce the amount of glue and not to dilute it with sand.
Another problem is the wrong choice of dowels for facade systems, which must withstand the corresponding loads, changes in humidity and temperature, the influence of the external environment, etc. The choice of fasteners should be determined by the wall material, the type and thickness of the insulation. At the same time, not only the quality of the dowels, but also their quantity are important for fixing the thermal insulation.