Insulation of the facade of the house, regardless of the purpose of its purpose: for permanent residence or rare visits (country house), this is a very important point in finishing, which is not recommended to be neglected. Probably, few people agree with the opinion that in a cold room a person does not feel very comfortable and most of us prefer warmth to cold. House insulation technology is constantly being improved towards the selection of the best thermal insulation materials. A wide range of products allows you to choose exactly the one that will correspond to the type of building and the technological requirements of the chosen method.
Classification of thermal insulation materials
A large number of materials act as heat insulating materials, they are all divided according to different criteria, including density:

- High, over 250 kg / m3.
- Average, in the range of 100-250 kg / m3.
- Low, less than 100 kg / m3.
All modern materials for the production of thermal insulation works have high quality characteristics, most of them are environmentally friendly. There is a wide range of such products on the market, but before buying them, you need to carefully familiarize yourself with them and their characteristics, areas of application, installation features.
All materials can be divided into three more groups:
- organic;
- inorganic;
- mixed.
By their structure, heat-insulating materials are divided into:
- fibrous;
- cellular;
- grainy.
Also, all materials can be with or without a binder. By fire resistance, they are divided into:
- Combustible.
- Fireproof.
- Hardly combustible.
Each material for thermal insulation works has a certain vapor permeability, humidity, water absorption, biostability, temperature resistance. Therefore, when choosing a particular material, you need to compare them and select the most acceptable one that meets all the requirements.
Requirements for materials
In order to choose the right material for external work, it is necessary to thoroughly study all the requirements that apply to it, regardless of which facades will be installed on: a residential or country house.
High thermal insulation performance
The higher the coefficient of thermal conductivity, the better the material will protect the building from cooling.
It's important to know
Sometimes, with sudden changes in ambient temperature in the summer, a country house with high-quality thermal insulation retains heat in cold weather and vice versa: cool on hot days.
Sometimes, with sharp changes in ambient temperature in the summer, a country house with high-quality thermal insulation retains heat in cold weather and vice versa: cool on hot days.
Vapor permeability
Thermal insulation must have high vapor permeability and allow excess moisture in the room to be discharged to the outside through it. Thus, a dacha or residential building will last a much longer period, and the air in it will be much richer and fresher.
Non-flammable
The insulation used must meet fire safety requirements. It is best to choose a non-combustible material such as mineral wool.
Environmental friendliness
It is recommended to insulate the walls of the house outside as well as inside the premises only using materials that are safe for humans. We will consider the characteristics associated with this factor and the applicability of materials for living quarters below.
Price
For many, this criterion is one of the main ones, but in this case one can recall the proverb: "A miser pays twice." Therefore, when choosing thermal insulation, it is recommended to use only certified materials, despite the fact that they can cost 10-20% more.
Mineral wool


Mineral wool is highly porous and has a high thermal insulation capacity. It is considered one of the most common materials for working in a domestic environment.
Thermal insulation works with it have the following advantages:
- ease of use;
- cheapness;
- does not burn;
- well ventilated;
- noise-insulating and frost-resistant;
- long service life.
But in addition to the obvious advantages, mineral wool also has disadvantages:
- after contact with water, it loses its heat-insulating properties;
- it is not a vapor barrier and waterproofing, therefore, additional materials will be required for insulation;
- not durable.
Additional benefits
In addition to energy-saving capabilities, such an appearance of the house facade decoration has a number of other advantages.
Fire safety
Due to the fact that such mineral fillers as perlite, vermiculite, foam glass are added to the plaster, it can be classified as NG, that is, non-combustible materials. But this does not apply to plaster with expanded polystyrene as a filler, it belongs to the G1 class.
Versatility
In addition to the fact that it performs the functions of a heat insulator, it can also serve as the finishing plaster of the facade of your house.
Frost resistance
It can be used in regions with a harsh, cold climate, as this material is not afraid of frost and can withstand temperatures up to - 60 degrees.
Moisture resistance
Compared to a conventional heat insulator such as rock wool, which absorbs moisture like a sponge, this material repels any liquid from its surface and does not allow moisture to be absorbed inside.
Glass wool and basalt slabs
Glass wool is sold in rolls. It is widely used for pipe insulation. Stronger than mineral wool. Basalt slab is a subspecies of glass wool. It is made from basalt rocks.


Its advantages:
- increased strength;
- fire resistance;
- does not deform and is durable.
Facades, panels, foundations, roofs of houses - all this is insulated with basalt slabs.
Advantages and disadvantages
The undoubted advantages of warm plaster include its versatility: buying such a mixture means solving two problems at once, these are insulation and facade finishing.
And also the advantages of this material include:
- high steam and heat insulation properties;
- high adhesive properties, if the surface is properly prepared, then the mixture is capable of covering the facade for more than 10 years;
- the possibility of finishing painting the facade in any color;
- ease of application, plaster a small house with an area of 150-200 sq. meters even without experience it is possible in a few days;
- does not require reinforcement and fastening;
- not affected by rodents and insects.
The disadvantages of this insulation include:
- the need to apply a thick layer. Manufacturers claim that 2–2.5 cm is enough, but practice shows that in fact the layer should be 2 times larger - at least 5 cm;
- relatively high price.
You can argue with the last point, because by choosing a warm mixture for the facade, there is no need to purchase fasteners that are required for insulation in the form of slabs or in rolls, as well as reinforcing mesh and final finishing.
Cork and Styrofoam


Cork is an environmentally friendly material that is popular all over the world.
Cork has many positive aspects:
- does not rot and does not settle due to its low weight;
- strong, but easy to cut;
- durable;
- in the event of a fire, it smolders, without emitting harmful substances.
But the cost of cork is quite high, so few can afford it.
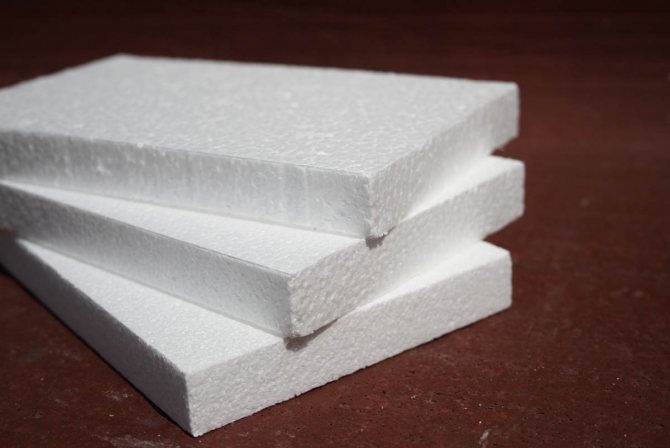
One of the most popular insulating materials is foam. You can buy it at any hardware store. The pluses of foam include:
- high thermal insulation, strength;
- practically does not absorb water;
- ease of use;
- cheapness.
Cons of Styrofoam:
- does not allow air to pass;
- with prolonged exposure to moisture, its structure collapses.
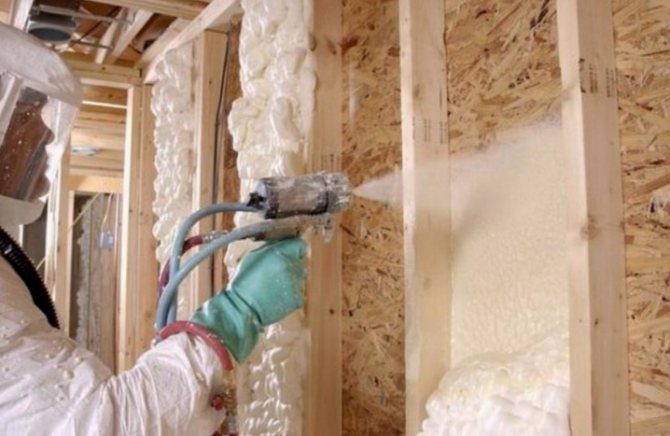
What you need to know about the thermal insulation of a frame house?
The peculiarity of frame structures is that wood and wood-based panels have a lower thermal resistance than insulating materials placed between the frame elements. Therefore, most of the heat flows through the studs, slabs, rails and beams, rather than in the areas of external walls or roof structures.

This increase in thermal conductivity is called thermal bridge. Such bridges can occur at any junction between building elements.
Many other building materials have lower thermal resistance than wood and can be important factors in thermal insulation. For example, a steel post inside the timber frame of the outer wall will create a significant thermal bridge.
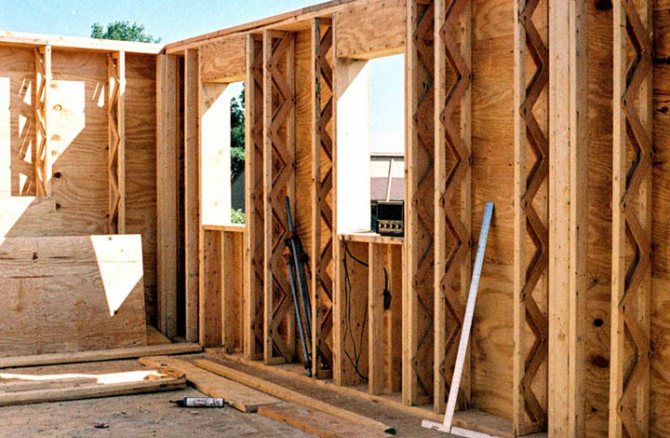


The property that describes heat loss associated with thermal bridging is its linear heat transfer. Research conducted in 2005-2007 by a team at Leeds Metropolitan University as part of a Stamford Brook field trial showed that wall cavity masonry promotes significant air movement. This air movement can transfer heat from the wall cavity to the outside, resulting in large heat losses from the building.
Therefore, when designing a future home, it is very important to consider where the thermal bridges will be located.
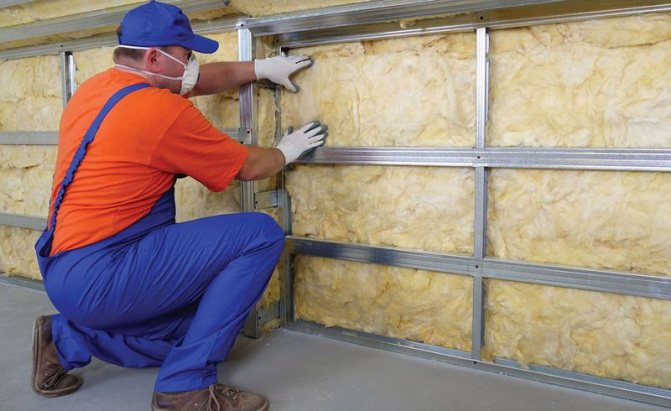
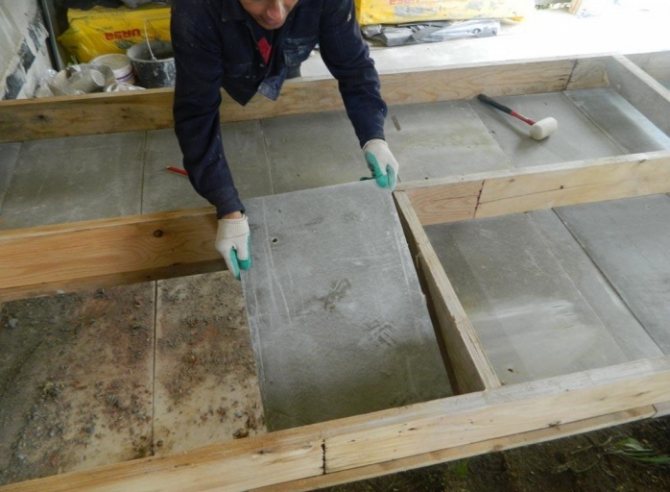
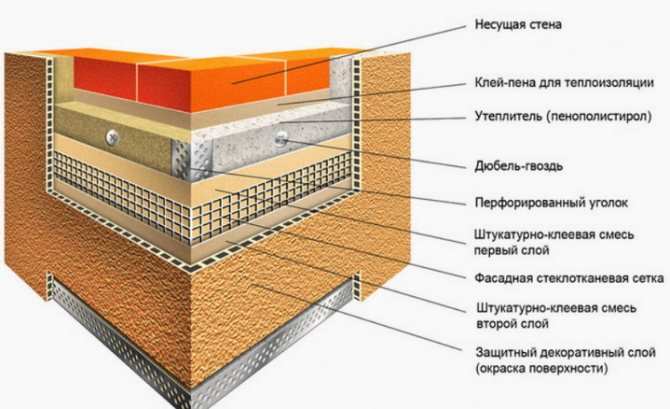
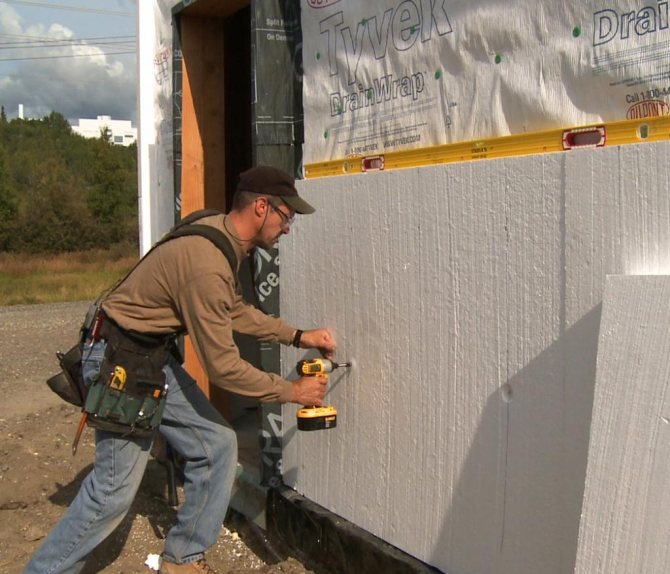
Stages of wall insulation
In order for the result to pay off, you need to take every step seriously. Otherwise, no thermal insulation will work, the appearance will be, to put it mildly, ugly. Depending on the insulation, the technology of thermal insulation work will be slightly different. Preparatory steps:
- Preparing the walls. Thorough stripping of old and peeling coatings, cleaning of cables, drains, plates and other things.
- Sealing cracks, potholes, upholstery of bumps.
Installation heat-insulating work during plastering work consists of the following processes:
- Fastening of auxiliary profiles.
- Insulation gluing and additional fixation on anchors or dowels.
- Slopes and ebb tides are attached.
- Reinforcing coating application.
- Sanding and painting.
At the same time, it is important to make intervals in the work until each layer is completely dry.
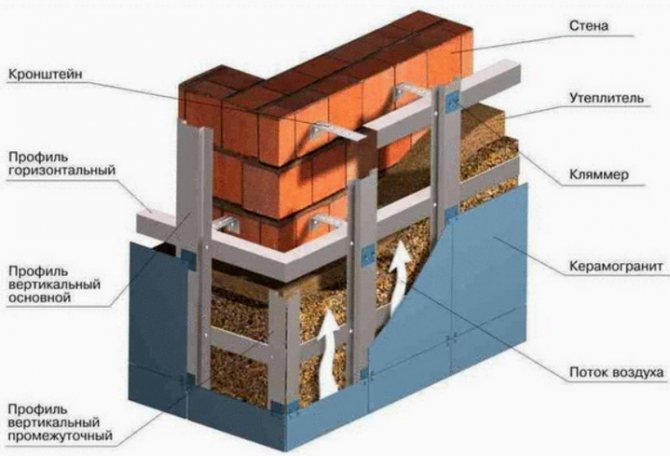
Frame systems are attached as follows:


- Subsystem axes marking.
- Division of the facade into small sections.
- Determination of reference points, installation of screws in them and tension of the cord along them.
- Installation of support elements and frame chords.
- Fastening insulation.
- The waterproofing membrane is fixed on top.
- Thermal insulation plaster for outdoor use is used as a finishing layer.
When performing internal work, all of the above materials are used. The sequence of all actions is practically the same. Thermal insulating plaster for interior work is used only as a finishing layer.
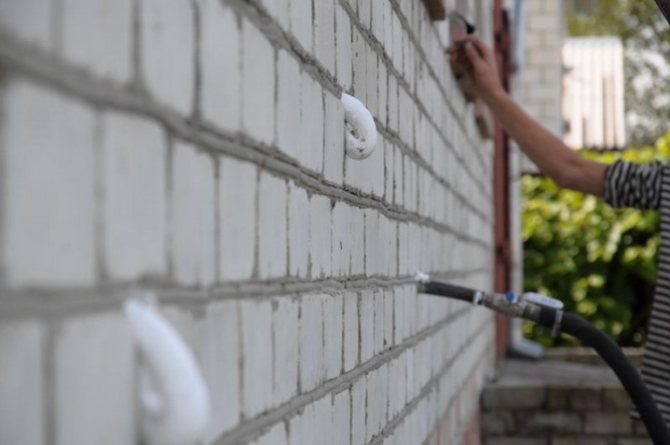
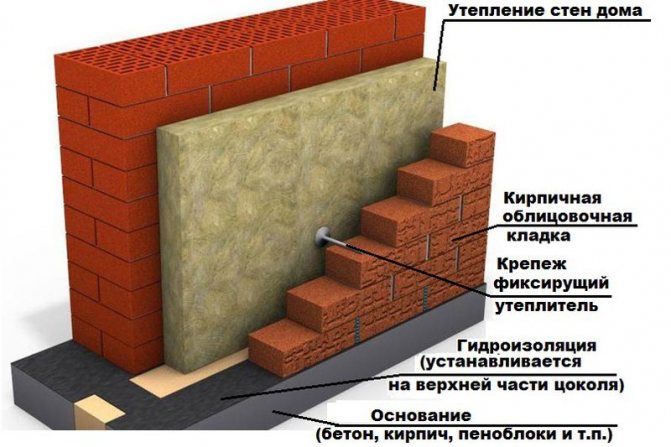
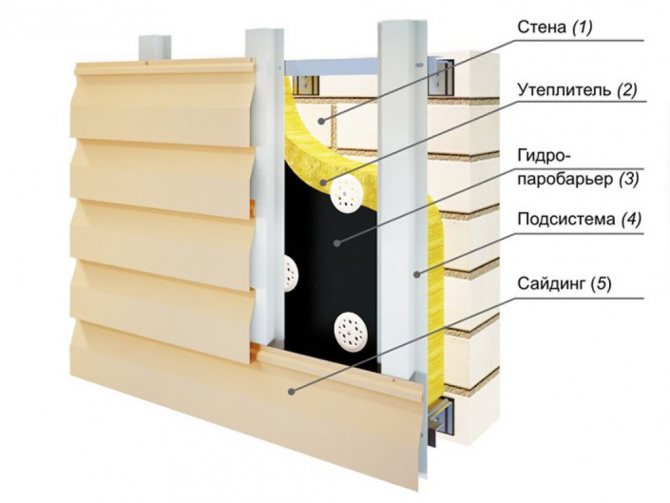
Facade insulation methods
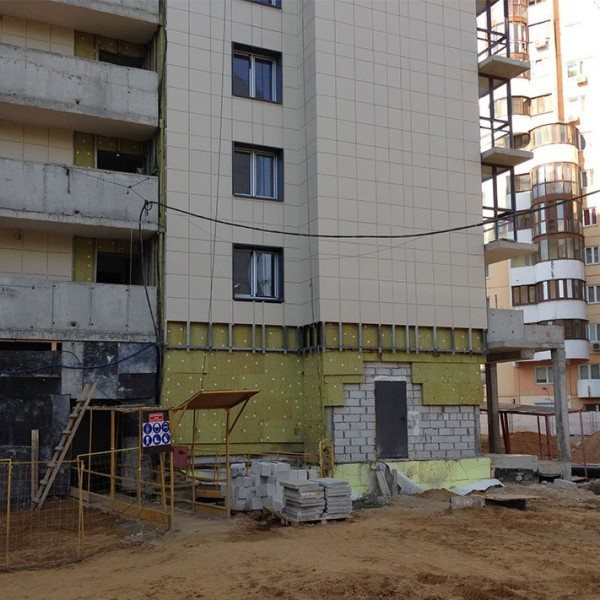


Ventilated facade at the final stage of installation

Wet facade. Insulation has been installed, the mesh and the base for the decorative coating are being installed
The question of how to insulate a house from the outside can be answered in two of the most popular ways.
- it is a ventilated facade technology;
- wet process technology.
The difference between them is very significant and consists not only in the order of actions when performing work (the installation of the second method is carried out directly on the wall of the building, and for the first one requires a crate) but also a number of other reasons:
- The materials used (both thermal insulation and facing);
- at the cost (initially, the technology of a wet facade is significantly cheaper than ventilated ones, but it should be understood that due to the maintenance-free service life and improved energy saving, ventilated facades begin to pay for themselves in 5-7 years of operation);
- the conditions of work (if the hinged structures can be mounted in any weather and climatic conditions, then the wet method requires a positive temperature and a certain air humidity).
Both methods are very different from each other. For example, as mentioned earlier: the necessary lathing for a ventilated facade is not required for the wet method, therefore, before jumping to conclusions which of these options is better, you need to fully familiarize yourself with their technology.
General norms of SNiP
Thermal insulation work can be carried out at an air temperature of +60 ° C to -30 ° C. If during work water compounds are used, then the minimum temperature value is +5 ° С.
At the base under the roof and insulation, according to the project, you need to perform:
- Sealing joints between precast panels.
- Installation of temperature and shrinkage joints.
- Installation of embedded elements.
- Plastering sections of vertical surfaces of stone structures.
Thermal insulation work must be carried out without any defects; for this, all compounds and materials must be applied evenly. After drying, each layer must be sanded.
What does all this mean for frame buildings?
Currently, framed walls usually contain acoustic wood insulation between the studs, and insulated cavity barriers around the perimeter. Thus, if you install thermal insulation between the posts, as well as in the cavity between two wall blocks, you can reduce heat loss to zero.
Achieving this goal may require a qualitative change in the current practice of frame construction. If insulation for the walls of a frame house is installed between fully sheathed walls, this can slow down the assembly process, since it will take additional time. In addition, it is quite difficult to ensure that the insulation is dry and does not move during the rest of the frame wall assembly.
The simplest solution to these problems is to use a bare wall, or use insulation for just one wall. With open (or partially open walls) insulation can be easily installed after the building is fully assembled.
Modern technologies of thermal insulation
Conventional timber frames are difficult to meet the latest thermal standards used in modern residential buildings. Fortunately, the latest thermal insulation technology offers several solutions. Prefab building owners can choose from panel options or use a technique called the "inside out" method.
Such panels are divided into 3 types:
- Custom built;
- Prefabricated, filled with polyurethane foam inside;
- Integrated panels for frame construction.


Panel construction has several advantages. Among them is an efficient installation, heat-shielding quality with several thermal bridges.
The inside out method also has a number of advantages, it is worth considering if only because this type of home insulation will cost much less. This does not require heavy equipment, all work can only be carried out with the participation of electricians and plumbers, carpenters.
The role of ventilation in house insulation
When the level of tightness of the building is estimated at less than 5 points, it is recommended to install a mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery. Thanks to this system, warm air is removed from non-residential rooms (kitchens and bathrooms), directed through a heat exchanger, which collects heat from the outgoing air and uses it to heat fresh supply air.
All this allows fresh air to penetrate inside the house, and moist (and not fresh) air remains in the source.
The ventilation system will also save on heating bills. For this installation, 100 W of electricity is sufficient for operation - this is significantly less than the thermal energy that would be needed in the absence of such a system.
Warming at the stage of building a house
So, as we noted above, the frame structure can be made of walls with high thermal insulation, with their relatively thin thickness, and such houses will be really warm.
In recent years, frame house building technologies have advanced significantly. The thickness of the outer walls can already be 90-140 mm. This provides additional space for installing insulation. Therefore, the choice of insulation for a frame house is no longer such a difficult issue.
Thermal insulation technology
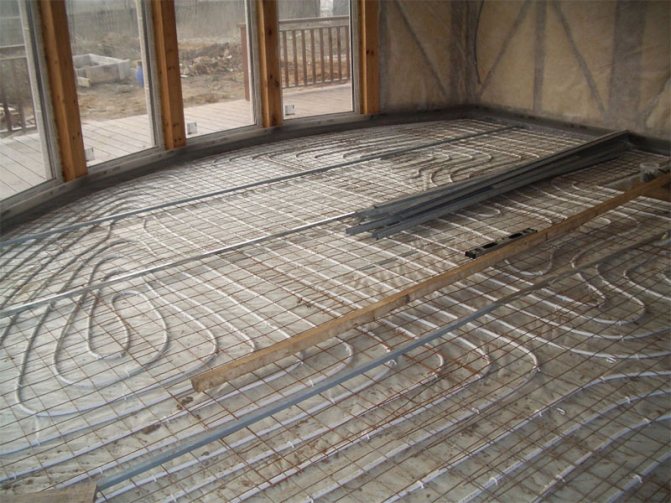
Mineral wool insulation
We will describe the technology by which thermal insulation for the ceiling is made using the example of the most common insulation - mineral wool.
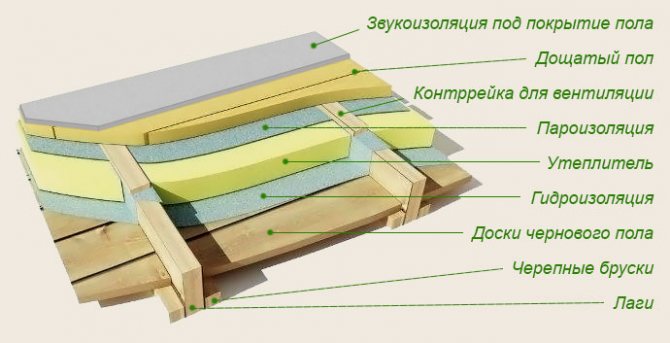
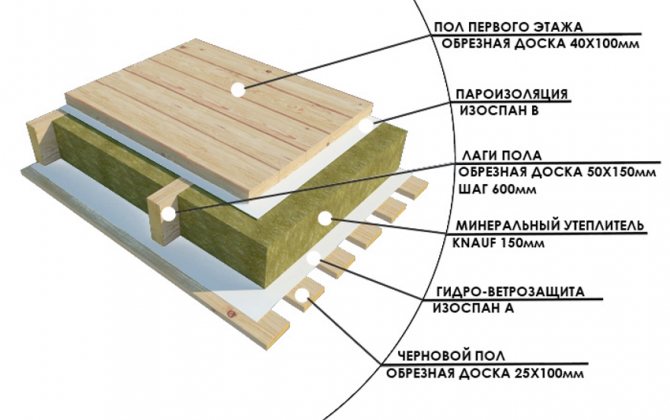
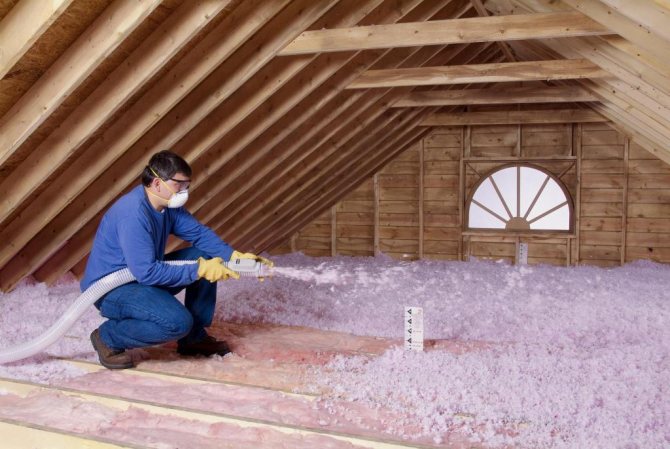
With the help of this material, you can make both external and internal insulation. We mentioned the inside earlier, and now we will consider how you can insulate the ceiling from the outside. This option is possible if there is an attic or attic in the mansion. All thermal insulation materials are placed in the intermediate space between the timber floor beams.
The work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Thoroughly clean the surface from dirt and debris.
- Lay a vapor barrier on a clean base, such as glassine (especially important when the ceiling of the bath is insulated).
- Spread the mineral wool over the glassine.
- Sheathe the top with planks, nailing them to the joists of the hardwood floor. Depending on the functional purpose of the attic, either rough edged boards or grooved ones are used. On top of the mineral wool, you can put foil or make foil insulation.


A common way to insulate a ceiling with mineral wool
If you don't know which rock wool has the best characteristics, go for the more affordable one. Although glass wool and slag wool have differences, they are not significant enough to be of fundamental importance. The main disadvantage of this material is its ability to "cake", so after a while it needs to be replaced.
Foam application
This material can be used both for external insulation from the attic side, and from the inside - under a false ceiling.
If the thermal insulation of the ceiling of a wooden house is done in the attic, then the plates are laid on the floor, after which the joints are sealed. From above, the foam is covered with boards (when the attic is intended for further use).
It is just as easy to insulate from the inside. The only difficulty is the need to temporarily dismantle the ceiling. The foam must be tightly attached to the concrete slabs and attached with liquid nails, then the suspended ceiling must be restored. This is how the upper floor of the house is insulated when it is impossible to make thermal insulation from the attic side.


Polyfoam is used for internal and external thermal insulation
Using penoplex
At present, penoplex or expanded polystyrene is increasingly used to insulate attic floors. These modern materials are robust and flexible, practical and durable. The technology for laying them is very simple. A roll or slabs (there are different packages) are laid on the attic floor in 2-3 layers. They are fastened using liquid nails, and then, (with further use of the attic), they are covered with boards.
Compared to foam, foam is more flexible and resilient, so that it is not damaged as a result of mechanical shock.Unlike mineral wool, it retains its original characteristics for a long time.


Penoplex is flexible, resilient and has a long service life.
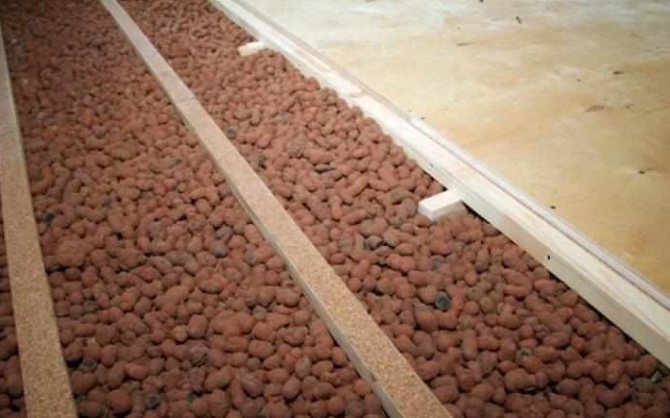
With traditional expanded clay
The popularity of this material can be envied. Despite some disadvantages, expanded clay is still in demand. It is an excellent alternative when thermal insulation of the ceiling with other materials is not possible. In terms of the ease of installation, it has no equal, because to create an insulating layer, it is enough to scatter the material on the attic floor. The main thing is to do it carefully, without missing a single gap. Of course, such insulation is inferior to the option with a minelite or penoplex, but it does not need special skills and tools.


Expanded clay can be used to insulate the most difficult surfaces
All heaters are the same for their purpose and solve the same problem. They differ only in the method of installation and the possibility of using it in specific conditions. Therefore, your personal preference will play a decisive role in this choice. Good luck!
Did you like the article? Share it
Why insulate the ceiling
If you live in a private house, then low-quality insulation of the ceiling will make itself felt sooner or later. How does it manifest itself? You can see and feel for yourself that, despite the heat-saving windows and modern renovation, the thermometer does not want to go up. Most likely, the reason lies in the ceiling, and there will be only one way out - to urgently engage in thermal insulation work.
On a note! It is necessary to pay special attention to the insulation of the ceiling, since in mansions and cottages the heat loss through it is much higher than similar losses through windows and walls.
Not so long ago, this was done mainly with the help of bulk materials, for example, expanded clay. Sometimes hay, dried herbs and the like were also used as protection. Today, the championship is given to rolled insulation and slabs. They better protect the floor from heat loss and are much more convenient to use. Next, we will tell you what to look for when choosing a material.
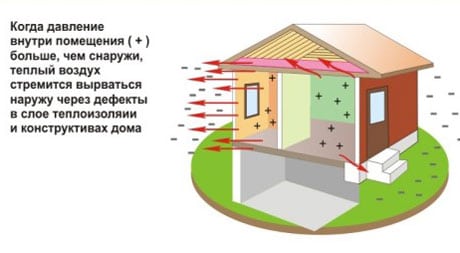

Air exfiltration is the main reason for high heat losses
Educational-methodical complex for the discipline "Technology of construction production" (p. 34)
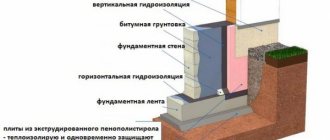
Mastics and solutions should have a working temperature of 160 ... 180 ° C. Before use, rolled materials are kept warm for at least 20 hours until they reach a temperature of 15 ... 20 ° C, slowly treated with a volatile solvent and served to the place of work in insulated containers, and hot mastics in thermoses. The backfill of the walls covered with waterproofing is carried out with thawed soil carefully with layer-by-layer compaction.
Waterproofing from emulsion mastics and cement mortars is performed only in greenhouses. Metal waterproofing can be arranged at an outside air temperature of at least - 20 ° C.
The device in winter conditions of insulation made of polymeric materials is made in accordance with special instructions.
Protective screeds and laying of protective walls can be carried out on mortars with antifreeze chemical additives.
GIR performance in greenhouses does not change the technology of applying waterproofing coatings.
10.1.4. Production technology of vapor barrier works
Vapor barrier is arranged in compliance with the requirements of waterproofing work.
When installing vapor barrier coatings, it is allowed to stick tar materials on bitumen mastics.
When installing a HIP, the use of slightly waterproof materials is allowed.
When performing work in the winter, calcium chloride and antifreeze additives are added to the bitumen mastic.
The vapor barrier coating must not have breaks. When the vapor barrier is attached to the walls, it is necessary to wind it up 10-15 cm so that the vapor barrier is connected to the waterproofing layer.
Moistening of thermal insulation during the production of vapor barrier works is not allowed. When installing pasting insulation, the overlap of adjacent panels is made 5-7 mm wide. Voids are not allowed. To drain condensate at the lowest points of the insulated surface, drain holes are arranged.
10.1.5. Thermal insulation work technology. Features of the device for thermal insulation in winter conditions
Thermal insulation is used to protect hot and cold surfaces from heat and cold losses to the environment.
Thermal insulation works (TIR) are started after completion of all construction and installation works at the facility. Thermal insulation of pipelines is made after hydraulic or pneumatic testing.
Before laying the first layer of heat-insulating material, the insulated surfaces are cleaned of dust, dirt and rust, dried, and in some cases covered with anticorrosive compounds. Surfaces are cleaned with mechanical or manual brushes, sandblasting machines, scrapers. Dust remaining on the surface is blown off with a jet of air or washed with a cloth. For the purpose of degreasing, metal surfaces are wiped first with a rag soaked in turpentine or other solvent, and then with a dry rag.
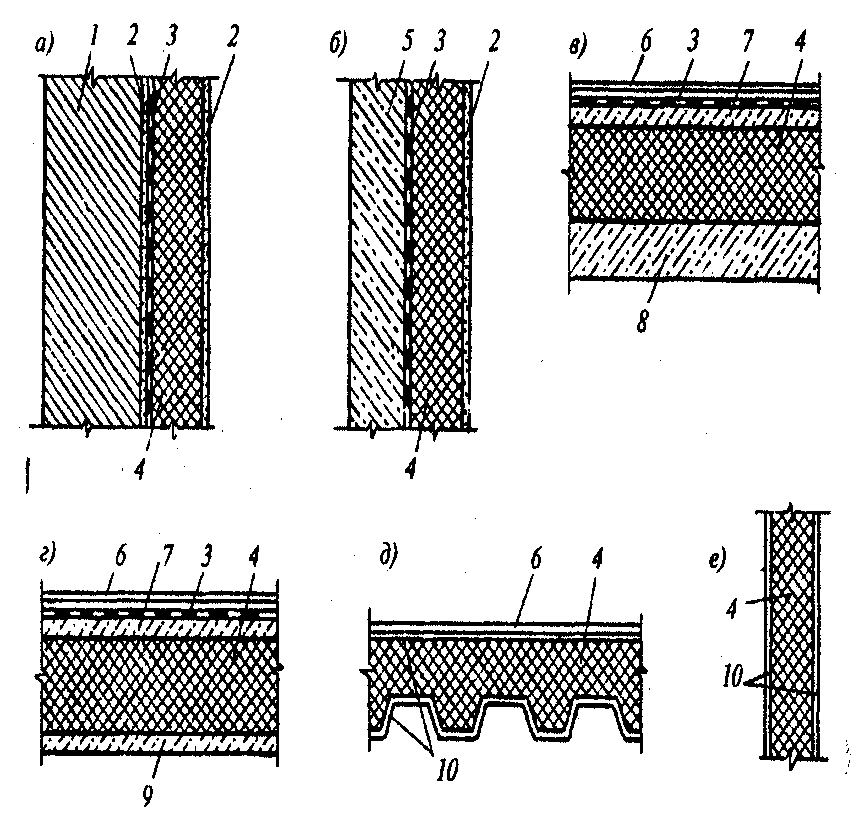
Distinguish the following types of insulation
: m
astic -
from mastics;
cast
, arranged as a result of filling the space with foam or aerated concrete;
enveloping
- from flexible materials (mineral wool, mats, strips, rolled fiberglass, etc.); s
alpine
(stuffed) - from bulk materials; of
molded products
- slabs, bricks, shells.
Mastic insulation
They are used both on cold and hot surfaces of complex configuration and are made of various powder or fibrous materials (asbestos, asbesurite, sovelite), mixed with water. The mastics are prepared by mixing all the components in a mortar mixer.
The first layer - the spray is done no thicker than 5 mm. As the layer dries, a second layer is applied, then all subsequent layers to the required thickness provided for by the project.
The mastics are applied manually or mechanically, using pneumatic blowers, directly on the insulated surface or on an asbestos gasket.
Due to the high labor intensity and the need to heat the insulated surface, the use of mastic insulation is limited.
Cast thermal insulation
used in the construction of industrial furnaces, refrigerators, with channelless laying of heating systems. It is made of foam and aerated concrete or bitumen perlite, which are laid in the formwork in layers of the design thickness and height.
For the device of cast insulation, the gunning method is also used, in which the insulation is applied over a mesh of 3 or 5 mm wire.
Enveloping thermal insulation
is made of flexible roll materials and products (mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, glass wool, etc.).
TIM is placed on an insulated surface and fixed with studs, screws, anchors. To increase its strength, the insulation can be reinforced with a metal mesh, and covered with plaster on top, pasted over and painted.
How effective reflective insulation
Foamed insulation is used in the form of polyethylene foam, sandwiched on one or both sides with polished aluminum foil. When used correctly, it is a thermal and waterproofing agent. The one-sided foil material can be self-adhesive and reflect up to 97% of the heat flux. The ability to reflect the heat of structures is also acquired after painting them with the composition "liquid foil".
Get full text
Tutors
Unified State Exam
Diploma
Backfill (rammed) thermal insulation
made of powdery or fibrous materials: perlite, mineral and glass wool, diatom and trefoil chips, vermiculite and sovelite.First, after 30-50 cm, support rings made of wire or other molded insulating products are installed, a metal mesh is pulled over these rings and a heat-insulating material is placed in the formed shape, the mesh is fixed with soft wire. The bulges of the insulation are leveled with a wooden calatushka, and plastering with a powder waterproofing material is performed on the mesh. In addition to plastering, other methods of finishing insulation are also used: pasting or sheathing with special fabrics, wrapping with roll materials.
Prefabricated thermal insulation
industrial and widely used for insulation of hot and cold surfaces. Prefabricated products are laid in strips on a dry surface or on a layer of mastic.
After the installation of all the plates and the sealing of the joints, a vapor barrier is arranged, followed by plastering on the grid.
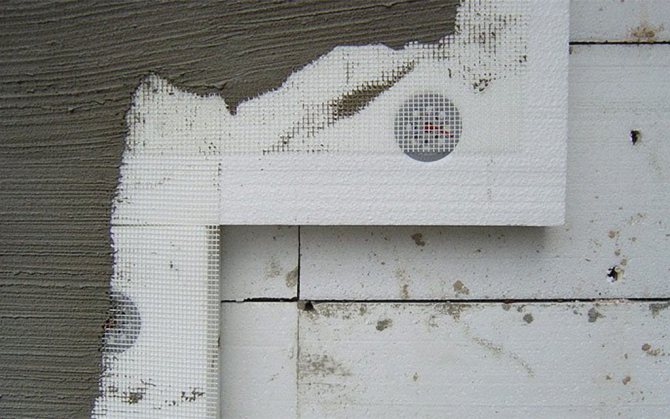
The developed building insulation technologies are widely used in modern construction. Plates made of expanded polystyrene or mineral wool are attached to the wall with plastic dowels, reinforced with fiberglass mesh and finished with a decorative plastering method.
The most effective is the method of preliminary thermal insulation of structures in the factory, that is, before their installation. At the construction site, only joint sealing and final surface finishing are performed, which improves the quality of work and ensures high labor productivity.
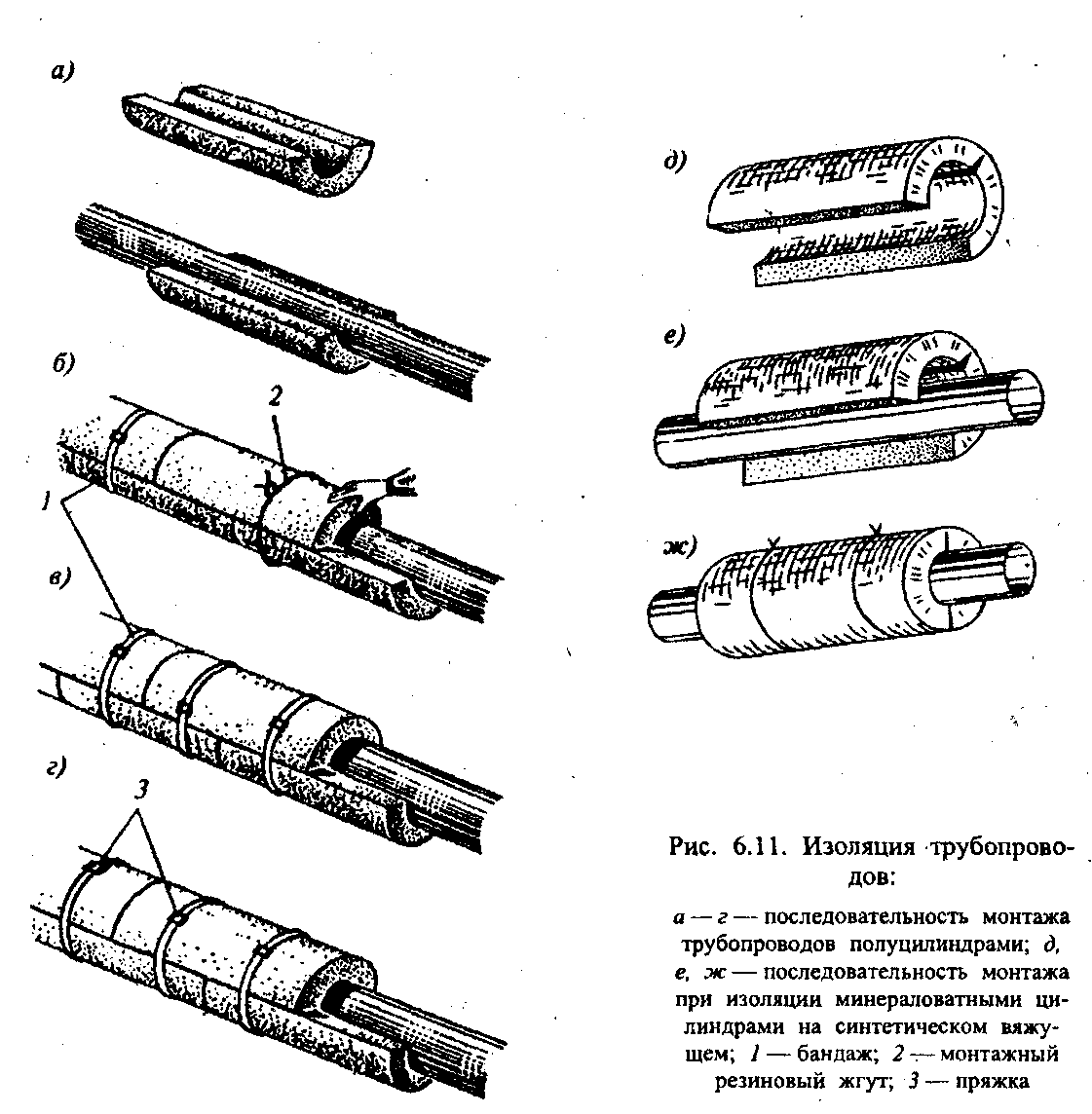
Thermal insulation with shaped (molded) products
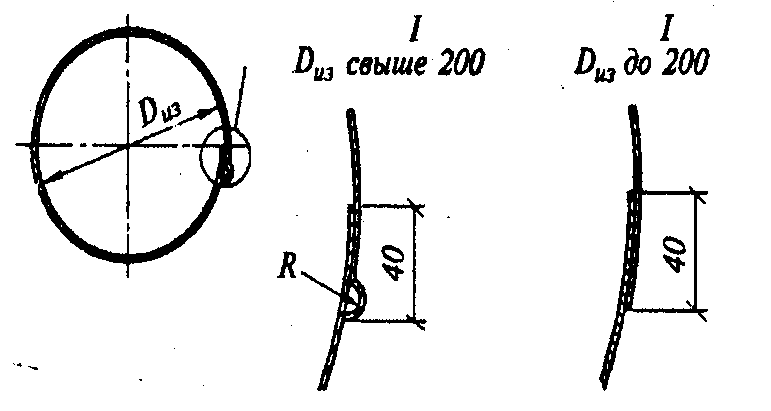
used for pipelines. Shells, segments and bricks made of diatomite or foam concrete are used as shaped elements. Perlite-concrete shells made from a mixture of expanded perlite sand, asbestos and cement with a diameter of up to 200 mm are used to insulate pipelines laid in through and non-through channels, central heating points, technical undergrounds of buildings and indoors.
Thermal insulation with plate materials
applies to both flat and curved surfaces. Before the start of the insulation, the plates are selected in thickness, then they are adjusted to the insulated surface to each other, tightly dry or on a thin layer of mastic with seams. Plates are laid in horizontal strips from bottom to top, with the bottom row being placed on a support shelf. With a high height of structures, support shelves are made every 3-4 m horizontally. Plates are laid so that fasteners (hooks, pins) pass through the seams between the plates, if necessary, holes for fastening hooks or pins are arranged in the latter in advance. The insulation is fixed horizontally or diagonally with a wire tied to the fasteners, after which it is covered with a wire mesh for subsequent plastering with a special solution or coating with other materials according to the project.
Features of the device for thermal insulation in winter conditions.
Thermal insulation works not related to wet processes are allowed to be performed at an air temperature not lower than - 20 0С. In the presence of wet processes, the device of thermal insulation is allowed only in closed rooms (greenhouses) at a temperature of at least 5 ° C.
Get full text
Drying of the mastic slows down, so the insulation is made thinner, complementing the laying of mats or molded products, which are removed in spring. Backfilling of thermal insulation, waterproofing for the winter period is arranged as temporary.
Soundproofing.
The type of sound insulation, materials for it, the layout of the room, the size and type of enclosing structures are determined by the project.
In all cases, it is necessary to seal cracks, cracks, holes. When installing the overlap, it is impossible to leave concrete plugs between the panels, pipelines released through the overlappings of elastic couplings.
The sound insulating ability of windows depends on the weight of the glass, the density of the gaps and the size of the air gap between the bindings.
Acceptance of works.
The quality of materials, surface preparation, the correctness of the compositions, the mixtures used, their temperature, the quality of the joints, the correct placement, adhesion to the insulated surface are checked.
An act is drawn up for hidden work.
When installing waterproofing, it is imperative to control the quality of the materials used, insulated surfaces, finished coatings and protective fences.
The paint waterproofing should be free from sponginess, cracks, cavities and delamination. Defects found should be cleaned out and re-covered with waterproofing material.
In the process of installing the gluing waterproofing, the size of the overlap of the panels, the placement of the joints, the strength of the sticker, the absence of ruptures and swelling of the carpet, and non-glued places are controlled.
The glued insulation is checked by applying a 2-meter strip in different directions, no more than 1 lumen (10 mm) per 1 lm is allowed.
The adhesion of the material is considered to be strong if the material breaks during the test tearing off. Places that are not firmly glued are detected by a dull sound.
| Due to the large volume, this material is spread over several pages: 34 |