Why do you need thermal insulation of the base
Insulation of the foundation of a wooden house can be internal and external. In any case, thermal insulation will help prevent many of the destructive factors.
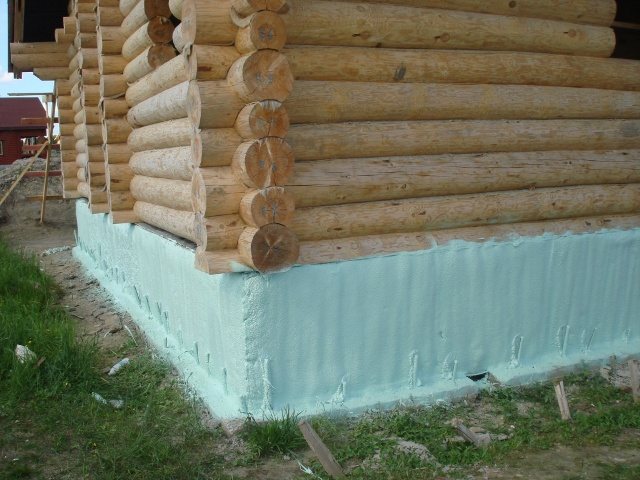

External insulation (regardless of material) protects against freezing and cold air ingress into living rooms, saving about 1/3 of electricity. In addition, the externally insulated foundation is protected from the destructive effects of moisture from the soil, which prolongs the service life of communications and the very foundation of the building.
Arrangement of thermal protection from the inside contributes to the formation of an optimal microclimate in the basement and, accordingly, in the house, creates an obstacle to the penetration of groundwater and the accumulation of condensate, which excludes the appearance of mold.
Positive aspects of basement insulation
Insulation favorably affects the preservation of heat in the room, and also provides reliable waterproofing of the foundation belt.
When performing insulation work with your own hands, significant savings are achieved, allocated for heating the building (usually, the reduction in consumption is from 30 to 50%).
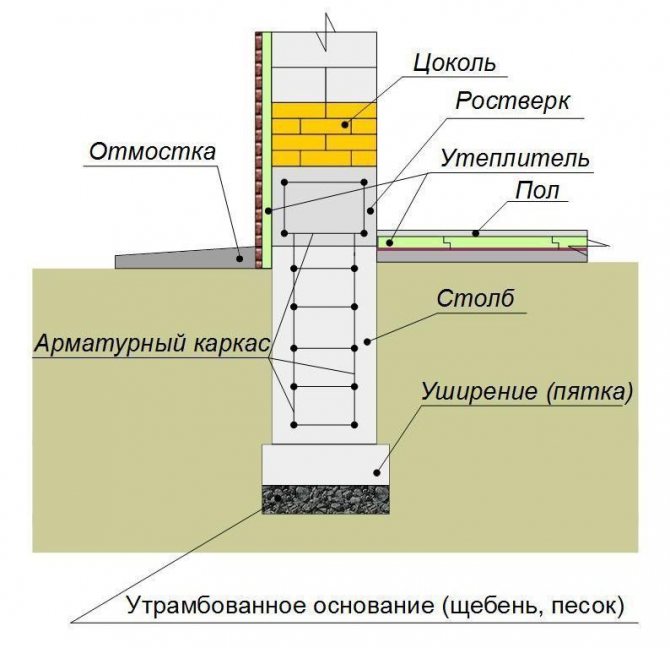

Foundation insulation design
There is a decrease or complete elimination of the impact on the structure of the forces of heaving of the soil, which develop in frosty, severe winters.
The internal temperature in the building with insulated foundations is significantly stabilized - night and day drops are excluded, which also has a beneficial effect on the safety of the foundation and the entire structure of the house.
Thermal insulation prevents the formation of condensation on buried structures and ceilings, which is guaranteed to reduce the possibility of the spread of foci of rot and mold. A layer of insulation performs the function of protecting the waterproofing from mechanical damage.
When performing insulation of foundations, their strength increases and the service life of the structure increases without the need for repair work.
Varieties of foundations and methods of their thermal insulation
Depending on the method of support on the ground, the following types of foundations can be distinguished, used for wooden buildings:
- columnar;
- monolithic;
- tape;
- pile.
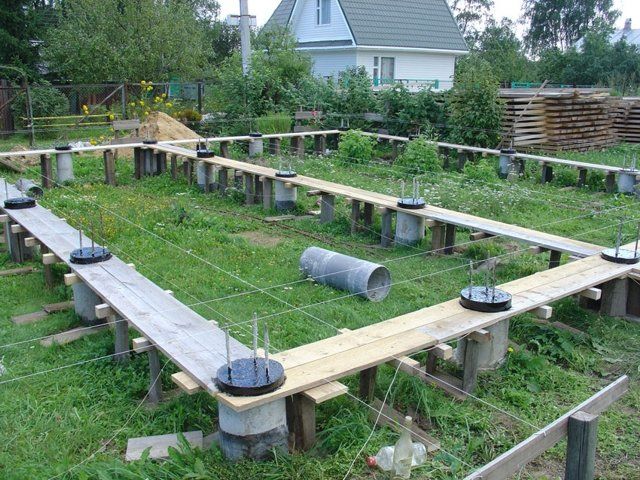


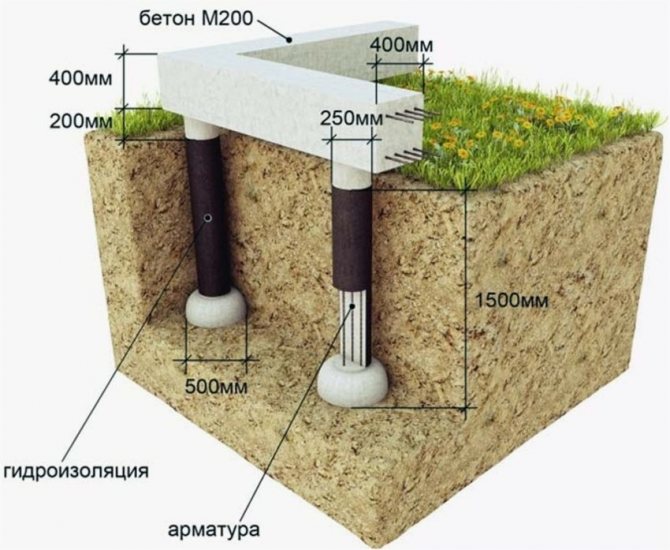
For the construction of wooden and frame houses, in most cases, shallow foundations are used. They are made of concrete or brick in the form of a strip or slab structure. It is better to insulate such a foundation from the outside. The thermal insulation layer is located at a distance of about 1.5 m, behind which a frost-free soil layer is created.
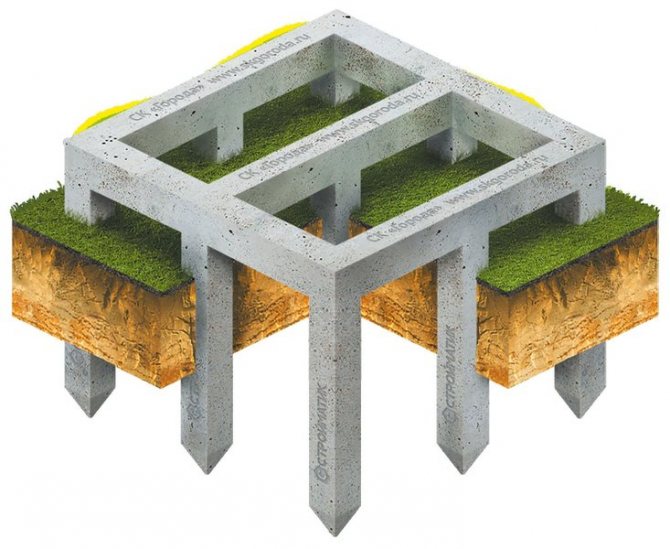
Columnar base
This type of foundation is equipped with pillars that are dug in below the freezing line by about 2 m.
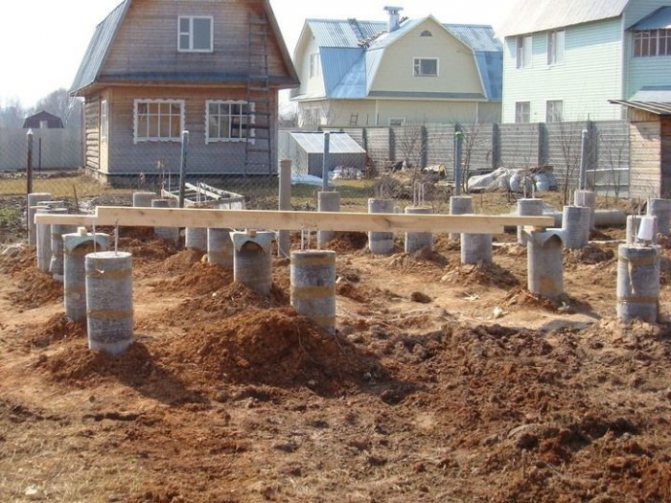


The pillars are located at all corners and intersections of the building structure, as well as in places with maximum load.
In this case, the basement is made of a large thickness and the floors are thoroughly insulated, there is no basement.
Pile structures
When making a screw base, instead of monolithic pillars, piles are used, which are screwed into the ground.


It is insulated in the same way as a columnar foundation.
Monolithic foundation
Monolithic is made in the form of a slab under the base of the house, the basement is not provided in this case.
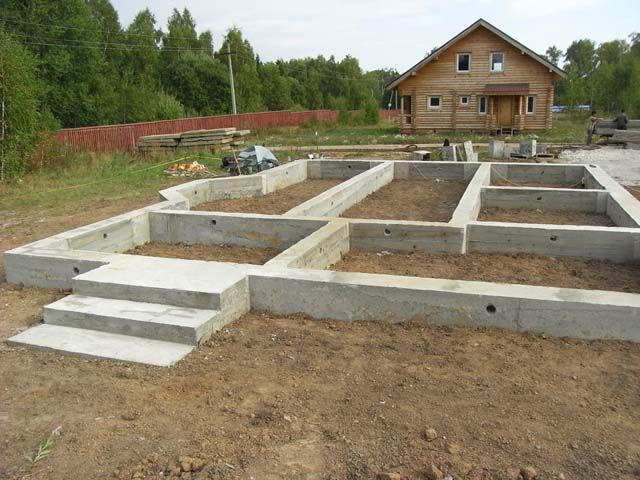


To equip its buried version, they dig a pit; for a shallow one, the top layer of soil is simply removed. Such a foundation can be insulated with any modern materials only from the outside.
Tape
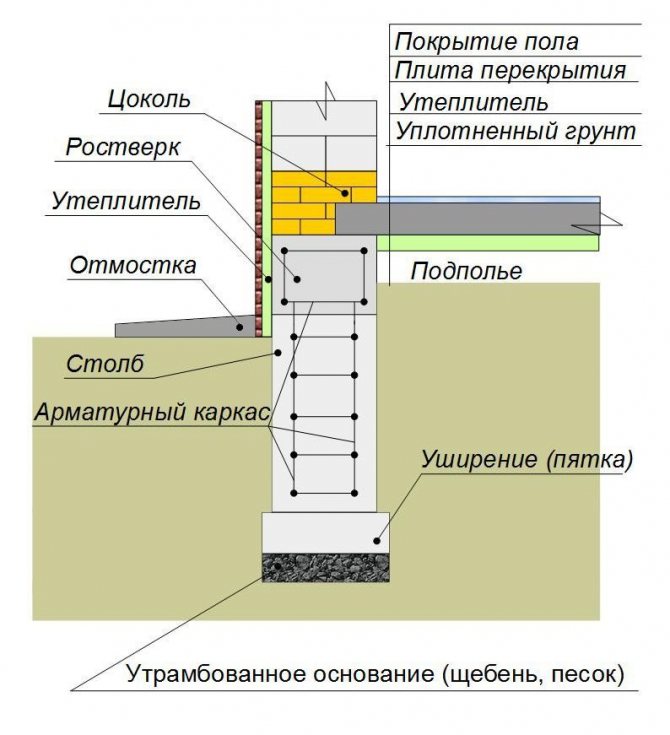
A tape-type foundation is created under the walls along the perimeter of the building, provides for a basement, it can be made from concrete blocks.
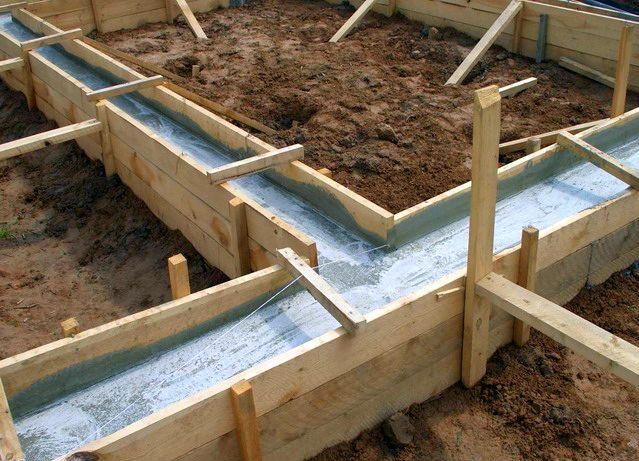


It can be insulated from the outside and from the inside without any problems.
How to insulate the foundation?
The easiest way is to insulate the columnar foundation by creating a pick-up... It is a variant of the basement of the building and protects the space between the building and the soil surface from various precipitation, freezing and wind.
Various materials can be used for picking up, influencing not only its design, but also the construction technology. Let's consider several specific options:
Wooden - from boards or from logs / beams. The sequence of work is as follows:
- dig a shallow trench (25-450 cm);
- cover it by a third with an even layer of sand or fine gravel;
- fix logs / beams with a pre-cut groove on the posts, insert boards (40-60 mm) into them so that the bottom board lies on a sandy pillow;
- cover the inner lower part with any heat-insulating material.
To install the boards in a vertical position in a pick-up, it is planned to lay logs with a groove in a prepared trench and fix the next one to the bottom of the house. Now the boards are vertically inserted into the grooves.
Sometimes it is used to lay logs in a horizontal position between the posts, similar to the construction of a log house.
Brick or masonry. When creating such a filling, as in the first case, a sole is created for its walls (a trench with a pillow). Brickwork is 1.5 bricks, and the thickness of the stone wall should be no more than 300 mm. After that, the masonry is poured with concrete mortar (up to ground level), reinforced with reinforcement.
Insulated drawers are used in houses installed on poles with a height of at least 0.75 m. After that, the columnar foundation is insulated:
- a steel frame is attached to the posts;
- any heat-insulating material is hung from the inside;
- from the outside, corrugated board is fixed on self-tapping screws;
- the gap between it and the soil is filled with gravel or expanded clay.
Important! It is not enough just to insulate the foundation - you need to make it ventilated. To do this, regardless of the type of filling made, small ventilation holes must be left in the walls on opposite sides, which are closed with special plugs in the cold season.
The choice of insulation
The most popular insulation materials for insulating the base from the outside are:
- expanded clay;
- polystyrene, polystyrene, penoplex;
- polyurethane foam.
Cotton wool
Internal insulation of the foundation of a house, as a rule, is carried out using cotton materials (mineral, glass, basalt).
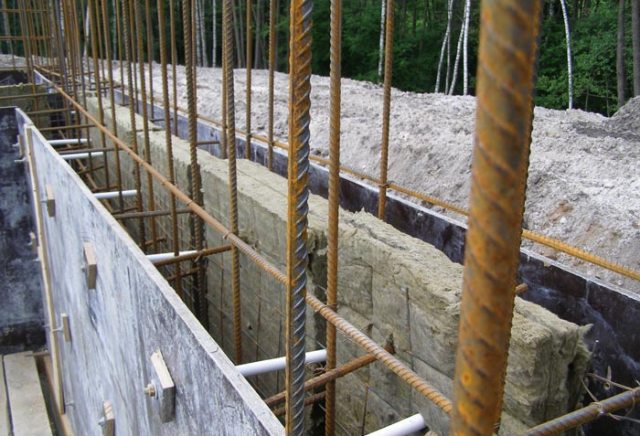


They will require double-sided waterproofing (to avoid getting wet, the appearance of lumps, the penetration of cold through the voids).
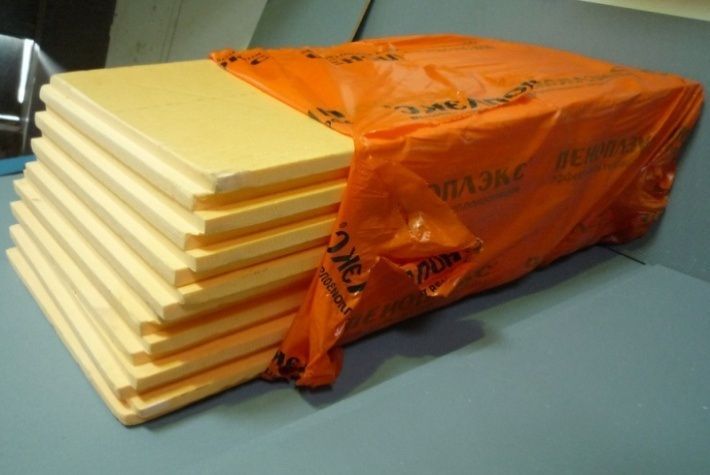
Styrofoam
Styrofoam can also be used. It is affordable, cheap, easy to install. But this is a fragile material, so you need to work with it carefully.
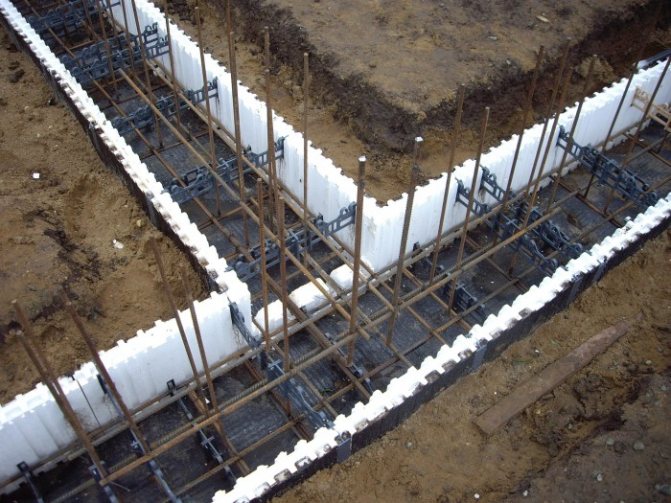


Despite its fire safety, when insulating outside, experts prefer foam, since contact with electrical wiring is excluded, and the performance characteristics of the insulation make it possible to create an effective thermal insulation system.
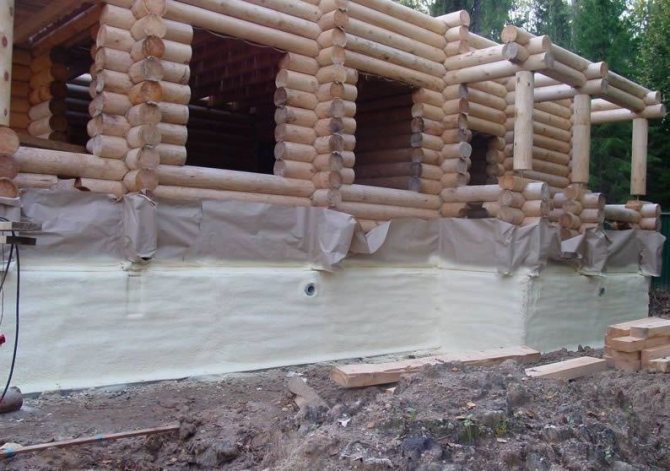
PPU
Polyurethane foam is considered a universal insulation. It is usually used as a heat insulator under floors and in basements.
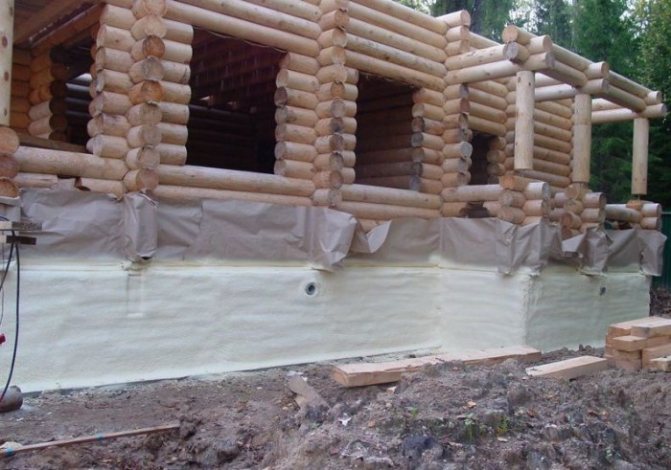


It is applied by spraying on the surface. It forms a heat-insulating layer after drying.
It does not need additional insulation, is very lightweight, and lasts a long time.
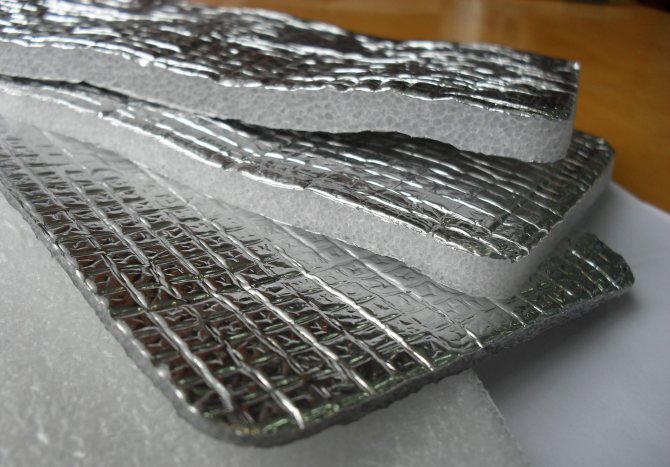
Penofol
Penofol, foamed polyethylene covered with aluminum foil, is also used to insulate the foundation. It is thin, retains heat well, protects against moisture.
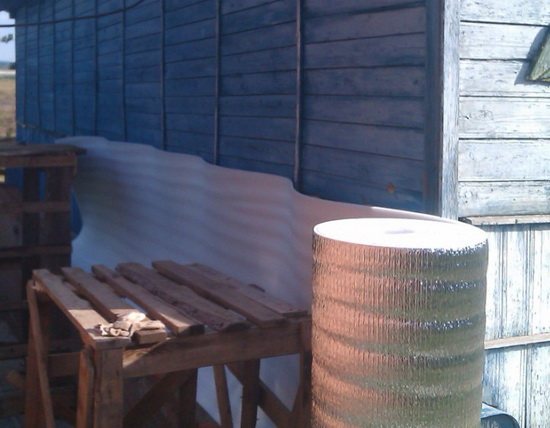


It is used as an additional material with other types of insulation.
EPS
More often, for any method of insulating the supporting base, extruded polystyrene foam is used.


It is a versatile material that has excellent moisture-repellent properties, is relatively cheap, and has a long service life.
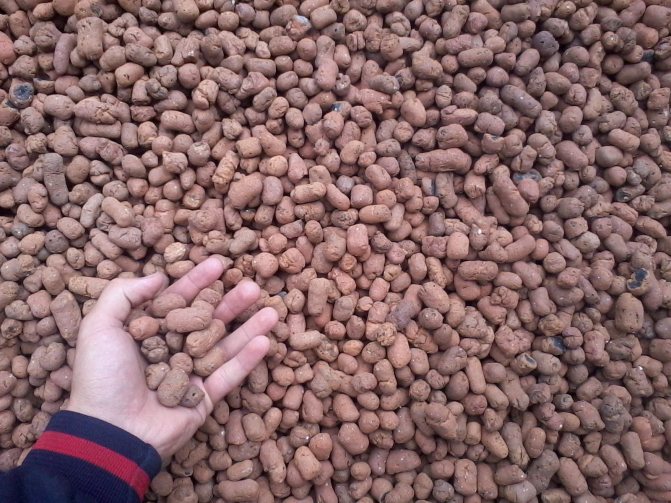
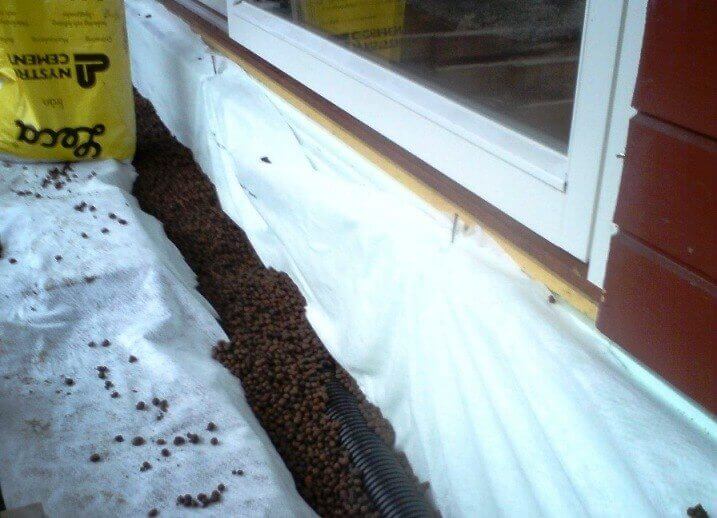
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is a good choice for insulating a shallow foundation. Due to the porous structure of the granules, it keeps heat well. It is an environmentally friendly and inexpensive material. Often thermal insulation with expanded clay is carried out outside.
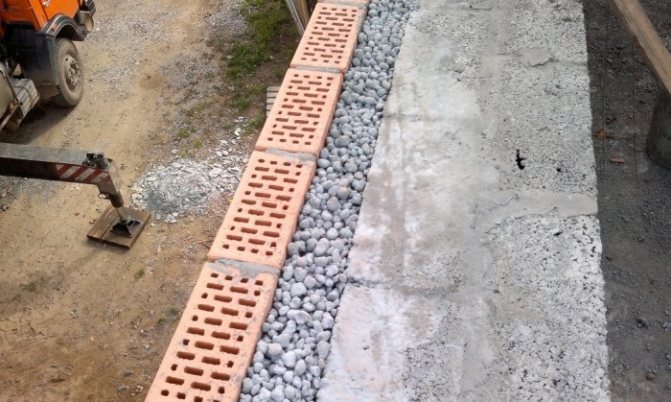


For this, the foundation is dug around the entire perimeter, cleared of the ground. After that, all cracks are eliminated in the base and waterproofing is installed. Protection against moisture can be done using a coating method, for example, with bitumen mastic or by pasting with waterproofing materials (as an option, roofing material). Insulation is poured into the trench and a concrete screed is poured.
When is it better to insulate the basement of a wooden house
The optimal period for arranging foundation insulation is considered to be the beginning of construction work, when the walls are not erected and the subfloors are not ready. But if at the construction stage heat protection was not provided, then it can be made during the operation of the building.
If there is an opportunity to choose the option of insulation, then it is better to focus on the external one. According to experts, internal insulation shifts the dew point, and the foundation is easily affected by external humidity and cold, which quickly destroy it.
The insulation layer in the basement creates increased dampness, which can be eliminated with additional ventilation, and this is an additional cost.
Another disadvantage of arranging the system from the inside is a noticeable reduction in the area of the room.
Materials for performing work on the insulation of columnar foundations


Concrete foundation structures, or laid out of rubble stone, are isolated during construction - when removing the formwork, they perform a coating waterproofing of all outer walls of the grillage (strapping beams) 2 times with bituminous compounds.
For insulation work on insulation, the following materials are used:
- Polyfoam - has a low strength, therefore it is used only for insulating the internal surfaces of foundations.
- Mineral wool - insulating material is produced in rolls and slabs (mats), wool has a high degree of water absorption. When using mineral wool for insulation work, especially in wet soils, it is necessary to provide for the laying of an additional layer of insulation from film materials.
- Expanded clay - the use of the material is an economically viable option for performing insulation, but requires additional work (making a box of boards from the inside of the foundations, followed by backfilling with a layer of expanded clay - up to 40 cm).
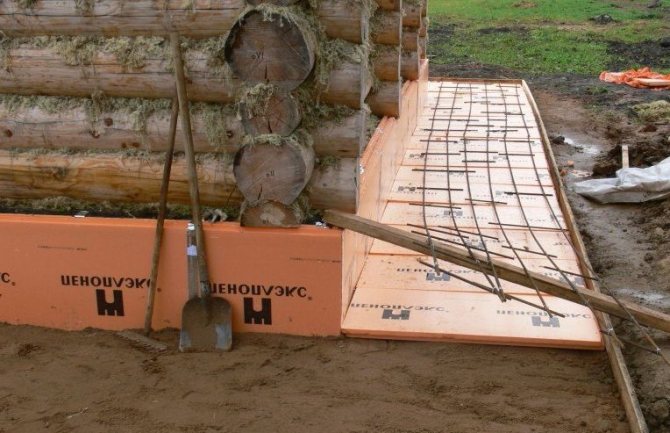
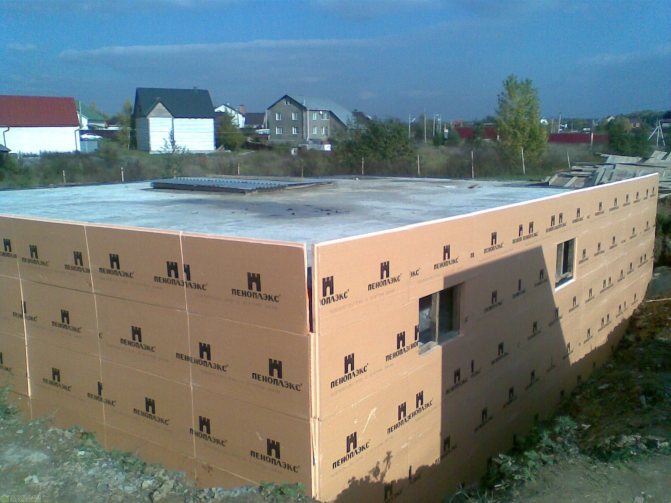
- Penoplex is a modern insulation with high technical and economic performance. The material has high strength, durability and reliability, is not damaged in conditions of high humidity and low temperatures in winter. Penoplex is not damaged by rodents, insects do not start in it. Currently, penoplex is the most suitable material for insulating buried structures. The material is produced in slabs, the thickness of which varies from 20 to 100 mm.
Features of the implementation of thermal insulation
Before arranging the insulation system, the foundation of the building in use must be completely dug out. The surface is cleaned of soil and other contaminants, damages and cracks are removed.
Waterproofing layer
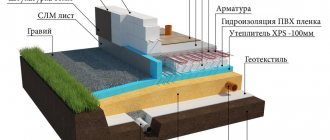
It is important to protect the base from groundwater. For this, waterproofing is performed.


Bitumen mastic, special deep penetration solutions, roofing material, liquid rubber are used as waterproofing materials.
Insulation installation
For external heat protection, foam plastic or extruded polystyrene foam plates are most often used. The insulation is installed using a special glue without organic solvents. Additionally, you can fix them using dowels with a wide head. After the glue has completely dried (after about two days), backfill the underground part of the foundation.
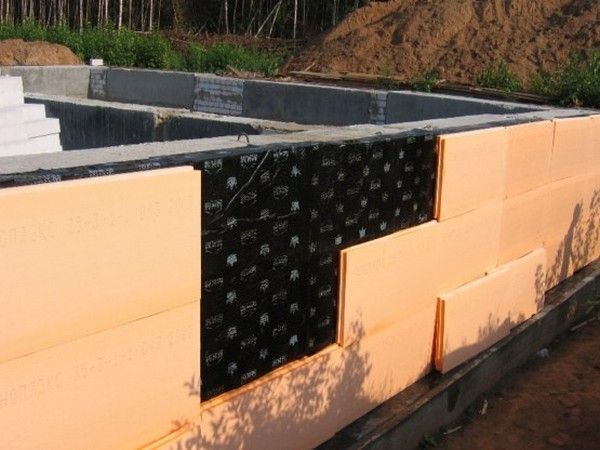


The material is attached to the base in the same way. But in the upper part it is necessary to use a non-combustible insulation, for example, mineral wool. So the plates of expanded polystyrene or polystyrene, which do not differ in high fire resistance, are separated from the wooden structures of the building.
Reinforcement and cladding
A reinforcing mesh is installed on the surface of the insulation, which is recessed into the glue solution.
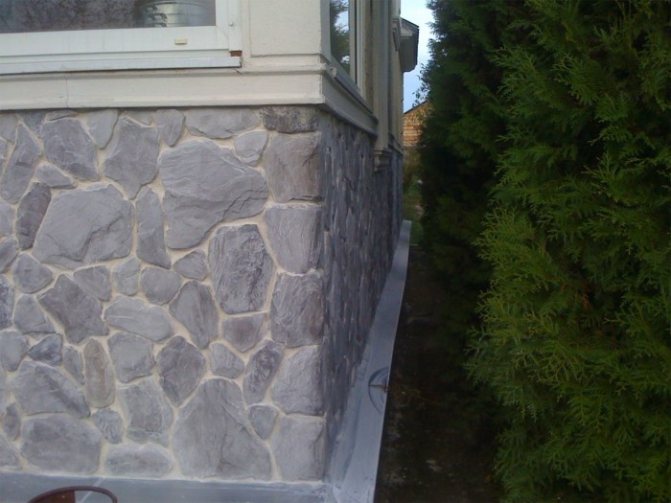


Then you can make the finishing. For this, artificial stone or brick, tiles, decorative plaster are suitable.
Ventilated facades
In the event that fibrous materials are used as a heater, after its installation, it is necessary to lay a vapor barrier layer. After that, a crate is installed, on top of which the facing material is attached.
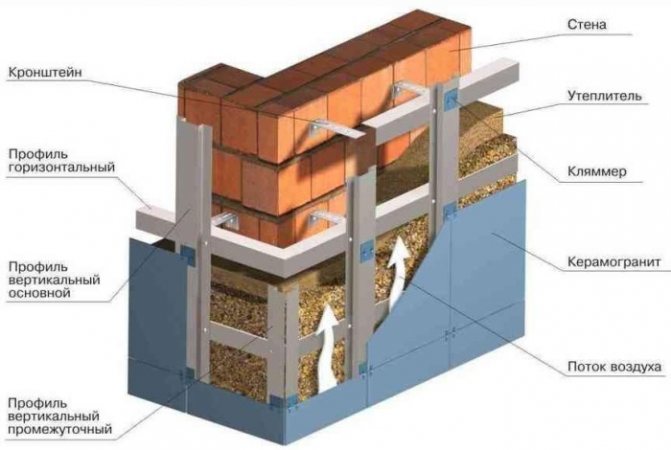

Thus, a ventilation gap is formed between the insulation and the finish, so that moisture does not accumulate in the insulation and it does not lose its properties.