All stages of the foam plastic production technology are considered. The equipment required to make this material is listed. Recommendations are given, which you must definitely familiarize yourself with before buying.
Many of us have met polystyrene foam more than once, tried it by touch, made something from it, used it in construction, for home improvement. However, not everyone knows what the technology of making foam plastic is, what are its features.
Oddly enough, but in the production of this material there is nothing super complicated. And it is noteworthy that now a lot of low-quality expanded polystyrene has appeared on the market, which is made without taking into account the relevant rules and regulations.
Some craftsmen manage to create a small production line even in a regular garage. Yes, don't be surprised.
And this must be taken into account when buying - not all Vasya Pupkins strictly adhere to the prescribed technological standards. And what standards can there be in the garage?
How is styrofoam made
Earlier we talked about what expanded polystyrene is. Remember that this material consists of numerous cells filled with air. This means that the manufacturing process must include foaming of the material.
And there is: the foaming process is one of the most important in the production of expanded polystyrene.
However, this is not all.
Stages of foam manufacturing technology
Typically, the process includes:
1. Foaming. In the course of this process, the raw material is placed in a special container (foaming agent), where, under the influence of pressure (a steam generator is used), the granules increase approximately 20-50 times. The operation is performed within 5 minutes. When the pellets have reached the required size, the operator turns off the steam generator and unloads the foam from the container.
2. Drying of the obtained granules. At this stage, the main goal is to remove excess moisture remaining on the granules. This is done with the help of hot air - it is directed from the bottom up. At the same time, for better drying, the granules are shaken. This process also does not last long - about 5 minutes.
3. Stabilization (tracking). The granules are placed in silos, where the aging process takes place. Duration of the process - 4. 12 hours (depends on the ambient temperature, the size of the granules).
Important note: the technology for the production of expanded polystyrene can exclude the 2nd stage (drying). In this case, stabilization (bedding) will last longer - up to 24 hours.
4. Baking. This step in the production of foam is often referred to as molding. The bottom line is to connect the previously obtained granules. To do this, they are placed in a special mold, after which the granules are sintered under pressure and under the action of high temperature of water vapor. Lasts approximately 10 minutes.
5. Maturation (aging). The goal is to rid the obtained sheets of expanded polystyrene from excess moisture, as well as from the remaining internal stresses. For this, the sheets are placed in an empty place in the production workshop for several days. In some cases, ripening can take up to 30 days.
6. Cutting. The produced blocks of polystyrene are placed on a special machine, on which the blocks are cut into sheets of the appropriate thickness, length, and width. This manufacturing process is performed using nichrome strings heated to a specific temperature. Accordingly, both horizontal and vertical cutting of blocks are carried out.
This is how styrofoam is made.
Of course, after the listed 6 stages, 7th stage - processing of the remaining scraps... As a result, they are mixed with other granules, which will then undergo the same processes - sintering, aging.
The equipment used in the production of expanded polystyrene is shown in the form of a table:
The choice of finishing material
What are the requirements for plaster for expanded polystyrene
The main quality of this component is the ability to penetrate the foam polystyrene structures to a sufficient depth to ensure good adhesion. Otherwise, the quality of application can be very mediocre, and the finish will begin to fall off, exposing the base of insulation.

Types of plastering compounds
For application in this direction, plastering products can be used, both for external and internal works. The latter are usually divided into two types:
- Acrylic front on polystyrene. A material with excellent vapor permeability, but at the same time with resistance to moisture. It is resistant to temperature extremes, severe frosts, sun exposure (it does not collapse, although it fades over time from ultraviolet radiation) and physical pressure, since it has elasticity. Moreover, this type of plaster is very expensive, and also rather difficult to maintain, as it absorbs dirt well. The high price, however, is offset by the high durability - up to a quarter of a century;
- Mineral. Consists of cement, lime and mineral aggregates. Environmentally friendly material that can withstand moisture, temperature extremes, precipitation and frost. At the same time, it has high vapor permeability, excellent adhesion and an affordable price. As a disadvantage, it is worth noting a lower durability (about 10 years), as well as a lack of flexibility. And if in the case of hard substrates such as concrete or brick this is not a problem, then pushing polystyrene can lead to cracks in the plaster under external influences.
Important! In general, for outdoor use, it is better to choose acrylic compounds. While environmentally friendly and non-combustible mineral plaster is suitable for interior work. Moreover, the latter can also be finished in various ways. Well, for outdoor work, if necessary, it is better to immediately pick up decorative options with the desired effect.
Foam manufacturing technology directly affects quality
As we said above, now the market is filled with a considerable amount of low-quality material. It can be produced in garages, some kind of warehouses.
But the main problem is not where the material is made (although the environment also affects quality), the main problem is not following all the rules for making foam.
What deviations can there be from the correct production of polystyrene foam?
The most varied - from poor-quality granulation to poor, inaccurate cutting of foam blocks into sheets.
Some clever people do not carry out as such stabilization, aging. For them, only the speed of production of expanded polystyrene is important.
"The more - the better - we will earn more money!"
Because of this, the characteristics of the foam are greatly deteriorated:
- it can turn out to be fragile, fragile,
- granules can be poorly connected to each other,
- density may be uneven.
It can also be due to low quality, faulty equipment that was used in production - frothers, dryers, compressors, steam generators, etc.
And further important moment: with poor manufacturing techniques, the foam can have a pungent, unpleasant odor. Such a picture is possible: they brought new sheets of expanded polystyrene home, put them in a garage or other room, etc.soon they heard that the room was filled with some kind of acrid, unpleasant smell.
Disposal and recycling
PS wastes are generated during the production of polystyrene, plus it is obsolete products. Most of the waste of polystyrene falls on foamed polymers, that is, on foamed plastics. Waste based on polystyrene can be reused in the following directions:
- Utilization of highly contaminated industrial waste.
- Disposal of high-impact polystyrene production waste
- Recycling of used products.
- Utilization of PS waste.
- Disposal of mixed waste.
Let's consider each of them in more detail.
Utilization of highly contaminated industrial waste: waste is examined, sorted, cleaned, crushed, washed and dried. Then the mass is dehydrated, finally crushed and fed to the extruder, where it is compressed, melted and gas impregnated. Then the melt is cooled, dried and granulated.


Before processing


After processing
Disposal of high-impact polystyrene production waste: injection molding, extrusion, pressing.


Foam Plastic Extruder
Recycling of used products (refer to solid waste and have the code 43414101205). In Russia, there are companies that produce polystyrene concrete, furniture, toys, insulation, foam blocks, sheets and new foam blocks from foam waste.
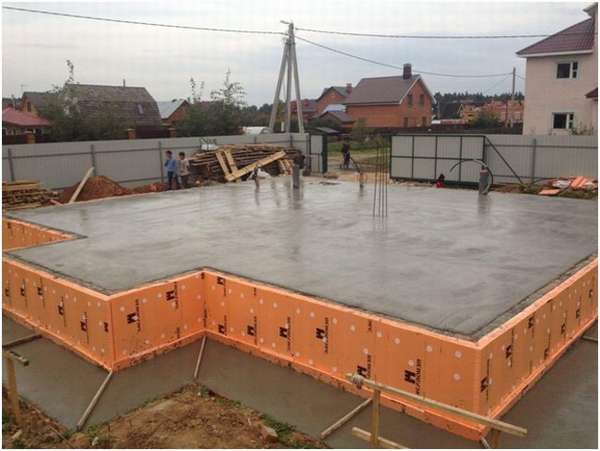


The use of products from foam waste: insulation of the foundation of the house with sheets of expanded polystyrene
Utilization of PS waste:
- mechanical processing is the grinding of secondary polystyrene and further mixing with primary granules. Benches and fences can be cast from the material obtained,
- the use of shredded polystyrene-based waste to improve the structure of soil or concrete,
- energy recovery is the incineration of waste to generate heat,
- filling in the depressions of the terrain,
- depolymerization is the catalytic production of styrene from polystyrene in order to obtain a polymer.
Disposal of mixed waste.
What the equipment for processing foam looks like, as well as some of the stages of the process itself, can be seen in the following video
Conclusions on the manufacture of foam
- The technology is quite simple, but it requires mandatory compliance with all prescribed rules and regulations.
- Material (which outwardly will be similar to quality) can be obtained even with significant deviations from the production rules. And this is used by "handicraft" firms (bad people).
Therefore: buy only products from reliable, trusted manufacturers (who monitor quality)... Check the vendors for the appropriate quality certificates.
Now you know how foam is made, you know the main features of the manufacturing technology and which material you need to give preference to. Good luck!
Foam plastic is used very widely - it is indispensable as a heat-insulating, finishing and packaging material. What is he like? How is foam production carried out, what raw materials and equipment are used? Let's figure it out!
What is Styrofoam?
Foams include all types of gas-filled plastics.
Distinctive features of the material:
- porous structure, which consists of closed cells;
- low level of density;
- high sound and heat insulation properties.
The group of foamed plastics includes:
- polyvinyl chloride material;
- polyurethane analogue;
- urea-formaldehyde foam;
- phenol-formaldehyde material;
- polystyrene analog.
Expanded polystyrene is the most common material. I will describe its production. Expanded polystyrene was created in 1951 by the German company BASF. Then he received the brand name "styrofoam".
Foam plastic for its main purpose is a heat-insulating material. It is 98% air.The gas is contained in many small, thin-walled polystyrene foam cells.
What kind of raw materials are used?
Expandable polystyrene is used as a raw material for polystyrene:
- It is obtained by means of suspension type styrene polymerization.
- The process takes place with the addition of a pore-forming substance, which is a mixture of isopentane and pentane. The volume of the mixture in the material is 5-6%.
- If the foam is intended for construction, then 1% of a fire retardant is added to the raw material. These are usually bromine compounds.
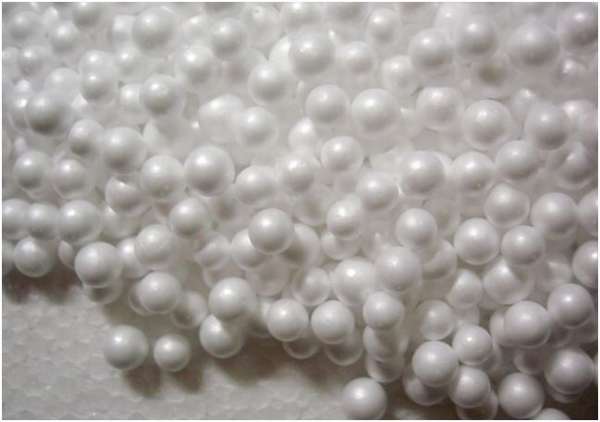
Polystyrene is produced in the form of granules. These spherical particles are treated with antistatic agents. They prevent the accumulation of electric charges by the material during its transportation. Also, processing improves the manufacturability of raw materials. Polystyrene granules in Russian denote PSV (expandable polystyrene).
Manufacturers differ in brands, types of foam and raw materials. Therefore, before purchasing the material, read its symbol in the technical documentation.
- EPS (expandable polystyrene), expandable polystyrene. This is the international designation for granules. FS (self-extinguishing polystyrene) Is another possible marking.
- PSB (suspended non-pressed polystyrene foam) Is the Russian designation for polystyrene.
PSB-S (suspended self-extinguishing foam polystyrene) - another version of the Russian marking.
After such a designation, there is a digital indication of the grade of material in terms of density.
Where is Styrofoam Used?
The use of foam was determined by its technical characteristics. Both molded products from expanded polystyrene and its crushed waste are used.
Foam boards are used in construction:
- For do-it-yourself insulation of facades and interiors of buildings.
- For the production of non-removable formwork.
- In sandwich panels.
- As an insulating layer inside load-bearing structures (three-layer reinforced concrete panels or blocks, layered masonry).
- As an insulating base under the screed for mastic or rolled roofs.
- For thermal insulation of floors and basements.
- As protection against freezing of the road base.
Also, foam is used:
- in shipbuilding;
- in refrigeration devices;
- when arranging pontoons and floating piers;
- as packaging for food and household appliances.
Due to the low price and easy processing, decorative foam molded products are now widely used:
- skirting boards;
- ceiling tiles;
- moldings, etc.
The use of polystyrene concrete.
A composite material made of polystyrene and cement is used:
There is a similar article on this topic - Blocks for building a house: which ones are better?
- in classic block construction;
- with monolithic construction methods;
- for insulating coatings of walls, slabs, roofs, ceilings, partitions;
- in the manufacture of facade panels and decorative elements.
At home, blocks are usually made of polystyrene concrete with a density of 250-600 kg / m3, moreover, lighter grades D 250-300 are used as thermal insulation, and from grades D 400-600 load-bearing walls and enclosing structures are erected, the main area of application is low-rise building.


Production of foam boards
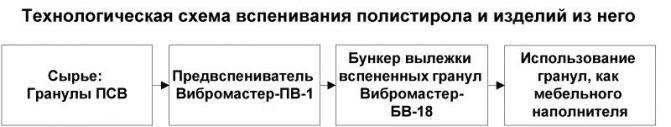
Foam production technology includes the following stages:
- Initial foaming of raw materials;
- Aging of granules;
- Their final foaming;
- Sintering of expanded polystyrene into plates.
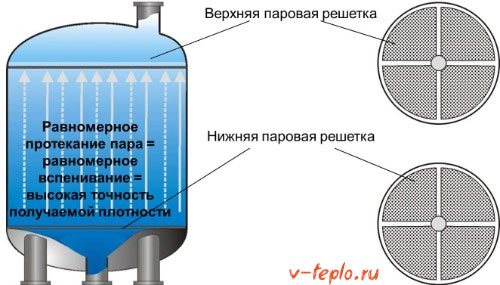
Saturated steam is used as a heat carrier in the production of foam.
Pre-foaming of granules
Pre-foaming of raw materials — this is the most important stage in the production of expanded polystyrene. It affects the quality of the final product:
- Loading granules into the pre-frother... Before that, their required volume is determined.
- Steam supply... It is supplied at a pressure of 4-6 bar.
- Foaming granules... At the same time, they increase in volume many times.
- Stopping steam... This happens when the granules reach a volume of one cubic meter.
- Unloading the pre-frother... Pneumatic delivery of the foamed granules to the dryer and then to the holding bin.
The production of foam grades of different density is influenced by:
- raw material grade, since polystyrene granules have different fractionation;
- the volume of the loaded granules;
- steam characteristics;
- the total volume of already foamed granules.
The density of the material is also influenced by the time it is in the pre-frother:
- If the time period is too longthen the granules begin to crack. Therefore, the density increases.
- If the foaming period is short, then the foam will have a significant variation in its density. Therefore, you will have to reduce the temperature by supplying a small amount of air and reduce the power supply to the pre-frother.
For the manufacture of light grades of expanded polystyrene (8-12 kg / m³), repeated foaming is used. The pellets to be loaded a second time must be well saturated with air.
The aging time of raw materials before re-foaming should be 11-24 hours. The smaller the granules, the shorter their ripening should be.
Drying and conditioning of foamed raw materials in the maturation bin
- The foamed raw materials are dried in dryers. For this, heated air is supplied to them through a perforated panel. Its temperature is + 30-35 ° C. The pellets are then cooled.
- The pre-foamed raw material is exposed to a slight vacuum. Therefore, pellets are sensitive to changes in the environment. To remove internal stress from them, they are blown out by a fan into the storage bin. There the raw materials are stabilized.
- Based on the brand of raw materials used, the conditioning time can be from 11 to 24 hours.
- The ambient temperature when holding the pellets should be + 16-20 ° C. If it is lower, then the duration of conditioning should be increased. In summer, at temperatures above +20 ° C, the holding period should be reduced.
When the foamed granules are delivered to the silos, their apparent density increases due to their collisions with the inner walls of the conveyor. This increase in density must be taken into account when determining the foaming parameters.
At the stage of holding the granules, due to the fact that the pressure inside the spheres is less than atmospheric pressure, air enters them. Pentane and water are squeezed out of the raw material until it stabilizes.
Mini-workshop for foaming polystyrene

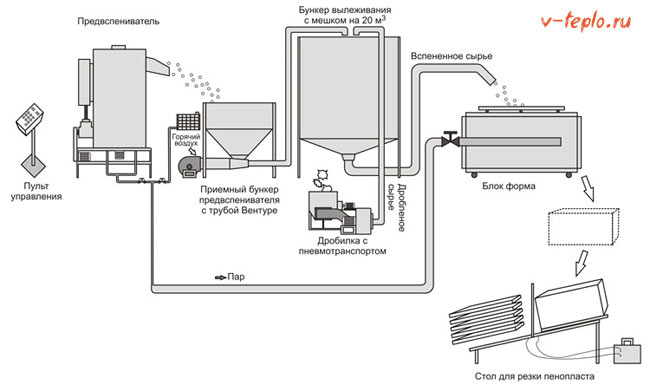
A complete set of equipment for the workshop for the production of expanded polystyrene (foam balls) consists of the following technological units:
This set of equipment is specially designed for the furniture industry.
This is how the raw materials for production (PSV granules) and the finished product look like - light, warm and balloons of expanded polystyrene used as filler for furniture:
As you know, frameless upholstered furniture is now becoming increasingly popular. At the heart of such furniture is a cover made of dense furniture fabric or leather, filled with foamed polystyrene (polystyrene) granules. Such furniture turns out to be fashionable, unusual and very inexpensive, and sitting and lying on it is warm and very comfortable.
Foamed polystyrene is also used by manufacturers of sleep products - for the production of pillows and mattresses.


Usually, manufacturers of such furniture buy ready-made foamed polystyrene in bags. We offer furniture manufacturers to reduce the cost of expanded polystyrene by starting to produce it themselves. The production is simple, clean, and does not take up much space in your workshop.
Let's consider what equipment you need for this.
Pre-foamer Vibromaster PV-8
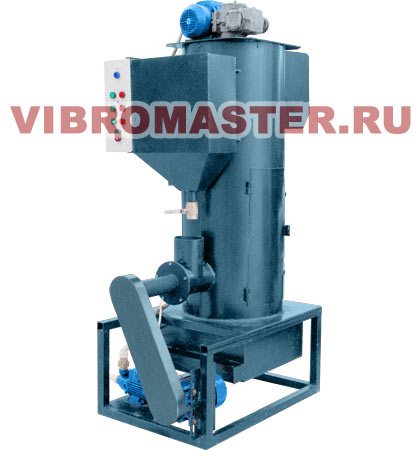


For the operation of this device, you will need an electrical connection to a three-phase 380V network and water. Foaming of granules occurs in a continuous mode. The device is easy to maintain and operates in a semi-automatic mode.The operator's task is to periodically turn on the supply of raw materials.
The price is only 129,700 rubles!
Technical characteristics Vibromaster-PV-8
| Parameter | Value |
| Productivity, up to, cubic m / shift | 8 |
| Hopper volume for granules, l | 40 |
| Chamber volume, l | 220 |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 1200x820x1920 |
| Weight, kg | 220 |
| Supply voltage, V | 220/380 |
| Electricity consumption, kW / hour | 18 |
| Number of employees, people | 1 |
Pneumatic transport VM-PT-1
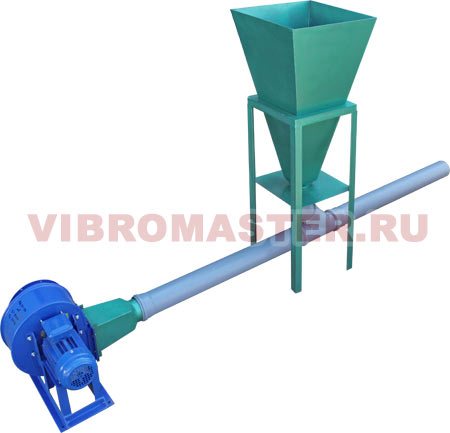


Pneumatic transport is intended for feeding expanded polystyrene (polystyrene) balls into the VM-BV-18 maturation hopper.
Equipped with a receiving hopper. After filling the bunker, the operator turns on the pneumatic transport to work. A strong air flow directs the expanded polystyrene through the pipeline into the maturation bin.
The price is only 26427 rubles!
Technical characteristics of Vibromaster-PT-1
| Parameter | Value |
| Installation productivity by air, cubic meters / hour | 1620 |
| Working area pressure, Pa | 1177 |
| Supply voltage, V | 380 |
| Power consumption, kW / hour | 1.1 |
| Weight, kg | 50 |
VM-BV-18 maturation bunker
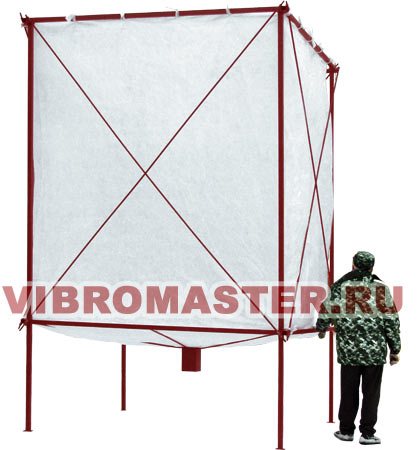


The maturing bin is needed to dry the granules after the foaming process. The bag liner of the hopper is made of "breathable" high-strength synthetic fabric of high density.
The polystyrene balls in it dry quickly and are then ready for use.
The hopper is equipped with a discharge gate at the bottom.
The price is only 28681 rubles!
Technical characteristics of Vibromaster-BV-18
| Parameter | Value |
| Bunker volume for maturing, cubic meters | 18 |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 2550x2550x4000 |
| Hopper overall dimensions, mm | 2500x2500x2900 |
| Weight, kg | 130 |
You can purchase these components separately:
- Pre-foaming device Vibromaster-PV-8 (price 129,700 rubles)
- Vibromaster-PT-1 (price 26,427 rubles)
- Vibromaster-BV-18 maturing bunker (price 28681 rubles)
Or you can buy the whole set
The price of a complete set of equipment is only 159,900 rubles!
You can also see the following sections
- Mini-workshop for polystyrene concrete
- Pre-foamer Vibromaster-PV-8
- Pneumatic transport Vibromaster-PT-1
- Vibromaster-BV-18 maturing bunker
- Concrete mixer SB-80-05
- Raw materials for polystyrene (PSV granules)
- Form for polystyrene concrete PSB-Standard
- 1-seater plastic form
- Plastic form in a metal frame, 3-seater
How to choose equipment for the production of expanded polystyrene?
If you decide to make your own styrofoam, you need to choose the right equipment for the workshop. Select the components of production equipment based on the volume of products you plan.
For example, if the required amount of material is no more than 1000 cubic meters per month, you need a line with a capacity of 40 cubic meters per shift. She will be able to give this volume of foam.
Please note that the estimated line capacity may not match the real one. It depends on the following points:
- The most important factor - the origin of raw materials: imported or domestic. On Russian pellets, the productivity may decrease slightly.
- Second nuance - the grade of foam that you will be producing. So, PSB-12 expanded polystyrene has a density of less than 12 kg per cubic meter. Therefore, it can only be obtained by double foaming. This reduces the line performance.
It is better to choose equipment for the production of foam, which has a high performance. It is not worth operating a low-power line at the limit of its capabilities, it may soon fail.
How to choose a steam generator?
The steam source is a steam generator (steam boiler). Its minimum capacity should be 1200 kg per shift. However, it is advisable to purchase a steam boiler with a higher capacity. This will make it possible to further improve the performance of the equipment.
Preparatory activities
Before proceeding with the purchase of equipment, it is necessary to prepare the appropriate premises.
For this reason, the room where the expanded polystyrene will be produced must have a high-quality ventilation system. Consequently, it is unlikely that it will be possible to establish a production workshop in a city apartment. You will need a separate room, ideally a whole shed or even a hangar in a suburban area, located as far as possible from living quarters. With this we have found out, now we will consider what exactly may be needed in the work.


Equipment for the production of foam
Necessary equipment
The minimum set of specialized equipment for the manufacture of the described material consists of:
- steam generators, as well as batteries for them;
- compensators;
- pre-frothers;
- coolers;
- receiving bins;
- cutting units;
- block forms;
- crushers.
The very process of manufacturing and selling should begin with getting to know suppliers who, by the way, can help with the search for distributors of raw materials and additional equipment. Most of the domestic market is flooded with Chinese devices. It is possible to deliver products to their destination, prepare relevant documentation for customs, etc. A separately paid specialist can visit you to set up and start the system. As for European equipment, it will cost about two to three times more, although the quality will certainly be much better.
Penoplex glue
Earlier we did a review on the brands of glue suitable for penoplex, in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information, read about it here
Purchases required for the production process
So, you have drawn up a business plan, you know what the future scope of work and the required capital investment will be, now the main thing remains for you - to purchase equipment for the production of foam plastic. The process will use the settings below.
- Accumulators or steam generators required for the normal functioning of the pre-frothers. This category also includes pneumatic conveying pipes, scales, transformers, condensation taps, and so on.

- presence / absence of a built-in steam generator, feeding dispenser, hopper;
6. Receiving hopper. This mechanism can be equipped with a fan with air heating mode, or it (the fan) can be connected to it separately. In this bunker, the raw materials are aged and dried. The devices can differ not only in terms of power, but also in terms of useful volume.
7. Table for cutting expanded polystyrene into sheets of the required thickness and dimensions.First of all, these tables vary in configuration; many modern models are additionally equipped with rangefinders, special grooving saws, transformers that warm the strings, and much more. For long elements of the profile type (such as insulation for slates, skirting boards, columns or platbands), the table can be replaced with a machine for a three-dimensional format. Control in this case is carried out by means of a special computer program.



Having found out what equipment is required, we will calculate how much it will cost approximately.
Table. The approximate cost of the equipment (if the production capacity of the workshop is 40 cubic meters per shift).
| Steam generator, 85 thousand rubles (1 pc.) | Pneumatic pipes, 24 thousand rubles (1 set) |
| Pre-frother, 80 thousand rubles (2 pcs.) | Steam accumulator, 90 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
| Receiving hopper, 15 thousand rubles (1 pc.) | Crusher, 45 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
| Heated fan, 14 thousand rubles (1 pc.) | Cutting machine, 20 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
| Bag for the maturation bunker, 8 thousand rubles (1 pc.) | Bag for bunker No. 2, 5 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
| Venturi pipes, 3 thousand rubles (2 pcs.) | Vacuum pump, 50 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
| Fan, 11 thousand rubles (2 pcs.) | Block-form, 125 thousand rubles (1 pc.) |
As you can see, all the necessary equipment for the production of polystyrene will cost about 680,000 rubles. Consequently, it is advisable to make expanded polystyrene only when it comes to rather large volumes of material. If your goal is personal consumption, then buying all this is unlikely to be profitable.
Note! Many manufacturers looking to reduce costs are purchasing used equipment. For example, in Germany, the government provides loans at 3-5 percent per annum to improve the production base. Consequently, it is more profitable for the Germans to sell units that have served four years at their current cost (minus depreciation, of course).
So, second-hand installations from or "Kurz" will cost about 70 thousand rubles, but you can get German quality, a unique coating of all iron elements and at least a five-year service life. For comparison: the cost of a Russian block-form after creating a similar coating on it increases by about 25 thousand.
Now - directly to the manufacturing process!
Output
Polyfoam can be produced from granules of various sizes and origins. There are grades of different density and thickness on the market, so take this into account when purchasing the material.
When choosing equipment for the production of expanded polystyrene plates, take into account its type, performance, completeness and level of automation. This directly affects the volume and quality of the material produced.
The video in this article will help you better understand the topic. If something remains unclear to you, ask questions in the comments.
- Expanded polystyrene foam... Raw materials are placed in a special container, where the material is treated with steam of low-boiling liquids. As a result of foaming, the granules expand in volume from 20 to 50 times. After reaching the required level of granules, the steam flow stops, and the working material is removed from the tank. The process itself takes about 4 minutes.
- Maturation... After drying, the material is sent to a special maturation bin, according to the brand (15, 25, 35 and 50), where the maturation process takes place.The time of the whole procedure takes from 4 to 12 hours, depending on the size of the granules and the environment t.
- Curing blocks... The prepared blocks are sorted by brands and stored. At first, the blocks can still give off the remaining moisture. The ripening period of the blocks takes from 12 to 30 days.
- Cutting foam blocks. On a special foam machine, string cutting of foam blocks into plates of specified dimensions is performed. Standard sizes are 20, 30, 40, 50 and 100 mm, other sizes are possible as well.
The difference in the types of polystyrene and why it should be protected
We will not write about the insulating qualities of this material, since we have already raised this issue earlier. Let us dwell on the composition - styrene granules connected together quite simply. This porous structure is extremely poor at conducting temperature. But over time, the conductivity rises as the bonds between the granules diminish. This happens due to changes in humidity, as well as exposure to direct sunlight, the ultraviolet spectrum of which has a destructive effect on the structure of the insulation. That is why such polystyrene must be protected with either a curtain wall or plaster.
There is also extruded polystyrene, which is much denser than usual. This is due to the melting of the granules. It does not break and crumble so easily, so it needs less protection, but the latter still cannot be ruled out.
There is also polystyrene concrete, which, as the name implies, is a mixture of granules of material with cement. In this case, we get durable insulation and even building material. Finishing the latter with plaster is much easier, and we will not touch on it in this article.