Polyfoam and its features
Polyfoam is a class of materials that are foamed (cellular) plastics (gas-filled plastics). Since the bulk of the foam is gas, the density of the foam is significantly lower than the density of its feedstock (polymer). This determines the relatively high heat-insulating (convection flows are practically impossible in a single cell) and sound-insulating (thin and relatively elastic partitions of the cells - a poor conductor of sound vibrations) properties of materials of this class.

Foams were obtained from almost all the most widely used plastics (polymers), therefore the most famous materials of this class are: polyurethane foams, PVC foams, phenol-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde foams and polystyrene foam.
Depending on the composition of the raw material and the technology of its processing, it is possible to produce polystyrene of different density, mechanical strength, resistance to various types of impact. These factors determine the choice of a specific type of foam for use in certain conditions and purposes.
In domestic conditions, a person most often encounters such a type of foam as pressless expanded polystyrene (was invented by BASF in 1951). Styrofoam granules (PSV / EPS) are produced by polymerizing styrene with the simultaneous addition of a pore-forming agent (pentane). Polyfoam PSB-S (expanded polystyrene, styrofoam) is a well-known heat-insulating material, 98% consisting of gas enclosed in microscopic thin-walled polystyrene cells. Content
Formwork cost and average market prices
| Appearance | Name | Dimensions, mm. | Thermal insulation thickness, mm. | Price (per sq. M.) |
| Series 25 (one-piece) | ||||
| Main wall block | Length - 1250 Width - 250 Height - 250 | internal - 50 external - 50 | From 490 rub. | |
| Wall end block | From 500 rubles. | |||
| Corner wall block (left / right) | Length - 700/450 Width - 250 Height - 250 | From 500 rubles. | ||
| Wall swivel block | Length - 700 Width - 250 Height - 250 | From 500 rubles. | ||
| Series 30 (one-piece) | ||||
| Main wall block | Length - 1250 Width - 300 Height - 250 | internal - 50 external - 100 | From 560 rub. | |
| Wall end block | From 570 rub. | |||
| Corner wall block (left / right) | Length - 1250/500 Width - 300 | From 570 rub. | ||
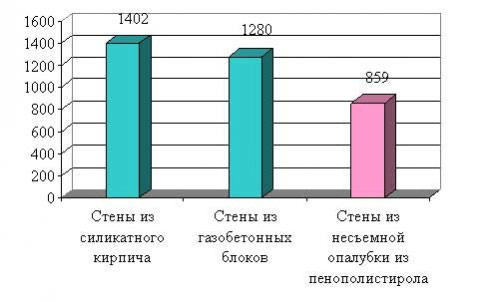

Comparative cost for 1 m2
Let's consider it in more detail using the example of popular manufacturers. First, let's find out: what explains this cheapness? First of all, the production process is not associated with special costs, because of which the price may rise slightly only due to increased demand in a particular region of the country.
Thus, it produces a wide range of expanded polystyrene blocks at the following prices:
- straight blocks - from 490 rubles;
- straight blocks 5 cm thick - about 800 rubles;
- 10 cm corner products - the same amount;
- jumpers and all sorts of plugs - somewhere around 25 rubles.
Note! These are Moscow prices. If we take, for example, Blagoveshchensk, then there such blocks will generally cost about 300-350 rubles apiece.
Fixed formwork made of expanded polystyrene is often constructed from blocks produced by Samara. The cost of its products starts from 780 rubles; products are distinguished not only by high quality, but also by the ideal combination of foam and plastic.
The most expensive blocks are products from Technoblok, faced with artificial stone.They cost about 1800-2500 rubles per square. Be that as it may, the costs will still be less than if any other building material was used.
Foam thermoblocks
To date, the most effective and fastest way to build your own house while making a minimum of effort and money is to use foam thermoblocks.


Working with this type of material is not a big problem, on the contrary, it is even a pleasure. Since these blocks are lightweight, it is not physically difficult to work with them. But there is also a downside to the technology, these blocks must be poured with concrete, which is a very laborious process. But first things first.
I will not delve into the details that it is necessary to correctly break the site and diagonals for the future house, as well as to dig and pour concrete into a solid foundation. Consider the construction of these blocks
Block dimensions 1000x300x300 inside it is hollow with transverse stiffeners. The wall thickness of the block is 50 mm, it is also necessary to purchase end caps in the kit to highlight the slopes of doors and windows. The design also includes special grooves that are located at the top and bottom of the block, representing the so-called daddy mama, which fit tightly to each other, which allows you to achieve a perfectly smooth wall surface. Also, these grooves prevent the flow of liquid concrete through the gaps between the blocks. Installation of blocks is carried out as follows
On a well-displayed zero - the basement is installed two rows of blocks (it is through such a distance that concrete must be poured, otherwise the wall can move out) it is also important to correctly determine the number of blocks on one or another wall so that they fit into the dressing and at the same time they are small overrun. After placing the first row of blocks, it is advisable to pull them together with a knitting wire in order to provide them with greater rigidity and protect them from the formation of cracks. Then, using a punch, we drill holes in the foundation in the lower position, perpendicular to the foundation, right through the block, 100 mm deep. Reinforcement 1200 mm long is hammered into these holes at a distance of 2 - 3 meters from each other, by the way, this must be done at the corners of the building. Then the second row of blocks is exposed, putting them on the fittings, and at the same time fastening them together with wire. The result is two rows of blocks with reinforcement sticking out of them. This entire structure is poured with concrete. Every two rows, it is necessary to lay the reinforcement flat along the perimeter, fastening it together. After the concrete hardens to the vertically protruding reinforcement, another batch of rods of the same length (1200 mm) is attached with the help of a wire. Blocks with dressing are put on again and the procedure is repeated. Thus, the walls of the required height are driven out, I had to see buildings of three floors built in this way.
What are the proportions of foam chips with cement
Grouting the screed will put stress on the ceiling slabs. This is very bad, so in order to significantly reduce it, you need to add foam crumbs to the cement mixture. An important aspect is to increase heat and sound insulation at the same time.


Before adding the crumb to the cement, it must be treated with a special solution.
You can use this crumb:
- crushed, obtained by crushing foam pieces;
- primary, specially manufactured for use in mortars.
The first type has a cheaper cost than the second.
What is the proportion of foam crumb cement for concrete mortar? It's pretty simple:
- from 4 to 5 buckets of small foam crumbs;
- 1 part of cement grade M 500;
- 2 parts of coarse sand;
- 1 part water.
Use a concrete mixer to mix all components.It will take you no more than 5 minutes, and the result will be a slightly dry mixture, rather than resembling buckwheat in appearance.
Concrete with crumbs - negative points
As already mentioned, a mixture of a solution with a light filler (foam crumbs) has a high level of sound insulation and thermal insulation. In addition, this material is not porous and does not absorb moisture.
But foam balls, interacting with cement mortar and sand, do not differ in durability. The action of oxygen causes their destruction. They will completely collapse in about 20 years.
That is why concrete with the presence of foam crumbs must be plastered. In addition, such material as polystyrene does not differ in absolute harmlessness. Since the foam balls, in cooperation with sand and cement, become non-flammable, when heated, they simply melt and release toxic gas at the same time.
Instructions for the preparation of concrete with foam crumbs
First, you need to load sand and cement into the concrete mixer. After that, fill in the crumb. At this stage, you should mix the components and only then add water. The proportions of foam crumbs with cement must be taken into account so that later the mixture does not crumble. After mixing all the components, add water and bring the solution to a homogeneous state.
The finished product will have the following characteristics that positively distinguish it from pure concrete:
- Decreased heat conduction;
- Lightening weight, with the ability to reduce the load on the foundation;
- Improving sound insulation;
- Significant cost reduction.
But, despite all the advantages, the strength of this product is clearly not enough. In order for this indicator to be normal, it is necessary to maintain the ratio of foam crumbs and other components.
Foundation
The foundation is the most important part of the building. This is the foundation of your home. It must be performed correctly and with high quality in order to avoid in the future many difficulties and problems that may arise both during the construction phase and during the operation of the building. The type of foundation is determined in accordance with the recommendations of geodetic surveys in the "spot" of the building, as well as taking into account the specifics of the project and the development of the designer.

The depth of the foundation should reach the depth of soil freezing in this region, for the Kiev region this figure is 100-120 cm.
Before pouring concrete, it is necessary to fill the entire area under the foundation with an interlayer of river sand and crushed stone, according to the design solution. This is done to drain rainwater from under the foundation. There are also a number of operations required to properly lay the foundation, but we will not describe them in detail as they are similar to traditional construction techniques.
The only important difference is that the wall made of thermoblocks (if we compare it with a brick wall of 2 bricks) is not 50 cm thick, but 25 and weighs not 980 kg, but 360 kg, respectively, the foundation can be much thinner. For the wall of Thermohouse, it is quite enough that the foundation is 30 cm thick, and not 60 cm, as it would be in a brick house. This is quite enough to withstand the required load, plus considerable savings in materials and earthworks. Before erecting the walls, it is necessary to level the foundation with mortar and waterproof the entire area.
Benefits
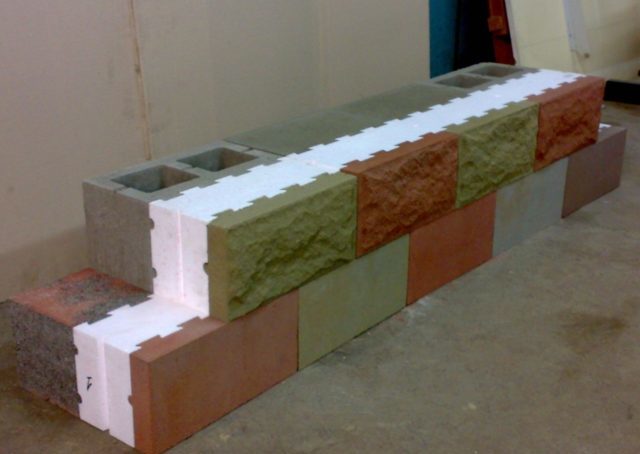
Due to its "layering", any multi-block has a number of advantages over any traditional building materials. First, strength. All layers of the multiblock are fastened together not only with bonding solutions, but also with strong reinforcing rods. This achieves high strength and durability of the multilayer structure.


Secondly, lightness.It has already been noted above that due to the special composition of the supporting part, the multilayer block has a much lower weight compared to traditional materials. Accordingly, their dimensions will be small. A modern building, built of multilayer blocks, has a thickness of the outer walls of the order of 3-3.5 cm. Therefore, such a structure does not require digging a deep and fortified foundation.
Thirdly, thermal insulation. Modern heat-retaining materials allow the structure to have high insulating characteristics. For comparison, the thickness of the usual insulation, laid on the finished walls of the house, will be at least 2-4 cm.The thickness of the entire wall, made of multilayer building blocks, will be only about 3.5 cm. And in such a room it will be as warm and comfortable as and in standard heat-insulated buildings.
Moisture insulation and resistance
Modern thermal insulation materials are sensitive to steam and moisture. Constant contact with a humid environment gradually destroys the insulating layer and reduces its performance. In multiblocks, the layer is reliably protected by cladding. The outer layer is designed in such a way that the thermal insulation retains its properties for many years.


They are also resistant to corrosion, mildew and mildew. The three-in-one design consists of chemically inert substances that interact weakly with aggressive environments.
In addition, the special properties of the raw materials that make up the building block make the environment inside it unsuitable for the reproduction of microorganisms.
Climate and convenience
Buildings erected using multi-layer blocks will serve for many years even in the most difficult climatic conditions. Concrete blocks retain their performance characteristics in a wide temperature range, and special technologies for creating a facing layer make it resistant to various mechanical damage.
Thermohouse walls
After all the foundation work is completed, you can proceed to the construction of the walls of the thermal house. An important point is that on the first day, only one row of fixed formwork blocks (thermoblocks) is installed along the entire perimeter of the foundation, i.e. 25 cm in height. Then you should carefully measure the distances (length of walls, diagonals, corners) of the exposed row. With the help of a level, it is necessary to make sure that all formwork blocks are aligned, both vertically and horizontally. This is necessary so that during further construction the wall does not lead to the side and there are no deviations from the project.
Before pouring concrete, it is necessary to lay sewer and ventilation pipes and reinforce the wall. The reinforcement should not be removed from the foundation, as this will break the waterproofing between the foundation and the wall of the house. A reinforcement cage is laid along the perimeter of the entire building in the first row of thermoblocks. It consists of 4 rods of reinforcement interconnected (the distance between the rods is 10 cm). The same frame should be laid in each corner of the building of the thermal house, in the places of window and door openings and in the last row of blocks in front of the floor panel (sometimes in the last two rows). Reinforcement is done on the basis of a project, and it is rather difficult to give a monosyllabic answer to exactly how this process takes place. The diameter of the reinforcement and the step of reinforcement (vertical and horizontal) are calculated by the designer, and depends on the number of storeys of the house and the loads on the walls. After all the preparatory work has been done, concrete can be poured. The concrete should be poured up to the level of the upper edge of the thermoblock lintel. Until the concrete has completely hardened, you need to check again whether the blocks are aligned horizontally and vertically and, if necessary, correct them.After the first row of permanent formwork blocks has been poured with concrete, the entire structure must be left until the next day in order for the concrete to gain sufficient strength for further construction.
The next day, you can erect 4 more rows of thermoblocks (height 1 m) and so on in the following days, until the moment when you need to lay down the floor panel. Before covering a floor with a floor panel, the wall must stand for 12 days to achieve the required strength.
Heat block - characteristics, features, scope
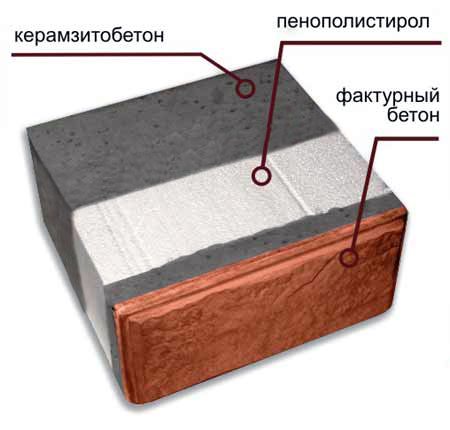
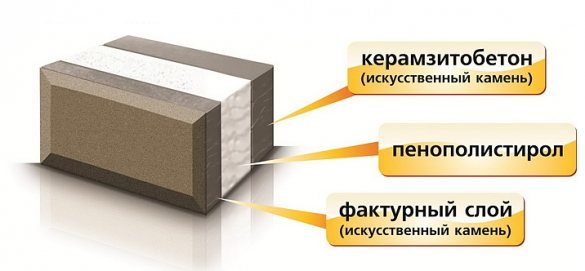
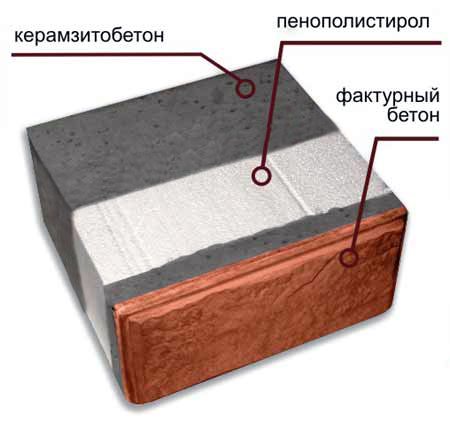
The heat-efficient block, or heat block for short, consists of three layers:
- Structural (bearing) - porous block of expanded clay concrete with a density of 1300-1500 kg / mᶟ.
- Thermal insulation - expanded polystyrene (PPS) or extruded polystyrene foam (EPS), 150-200 mm thick.
- Facing (decorative) - a thin block of expanded clay concrete or concrete (on average 50 mm), characterized by increased density, strength and frost resistance; the surface imitates figured or smooth brick, natural stone.

Heat blocks are produced by two methods - vibrocasting or vibrocompression:
- Vibration casting - an insert made of insulation is installed in the matrix, the liquid solution is poured into the mold and processing is carried out on a vibrating table until the block is completely compacted.
- Vibrocompression - the solution in the form of a vibrating press with an installed liner is poured semi-dry, the block is simultaneously exposed to vibration and pressure.
The blocks produced by the vibrocompression method are placed in a thermal chamber for finishing after molding, the vibrated ones dry naturally.
The layers are connected to each other not only due to adhesion - manufacturers use special bonds, it can be metal-reinforced plastic, fiberglass or basalt rods. Heat blocks are also produced with additional voids in the structural layer, reinforcement is installed in them during the masonry process and the solution is poured.
The facing layer can be either the original, gray color, or multi-colored, almost any shade can be ordered from the factory.
The main advantages of the blocks include minimal thermal conductivity, due to which a wall with a thickness of 30-40 cm does not need additional insulation, and the presence of a finishing layer. The facade immediately turns out to be decorative and does not require cladding, plastering or various hinged screens. In addition, the bearing part of the block made of lightweight concrete significantly reduces the weight of the structure, making it possible to dispense with a strip foundation. As for the speed of construction, also attributed to the pluses of the material, it is inherent in other block categories and to a greater extent depends on the skill of the performers. The same can be said about the minimum consumption of the solution - a thin seam is typical for wood concrete, gas silicate or warm ceramics, and whether it will be possible to do it this way depends on the master and the geometry of the blocks.
Walls
After all the foundation work is completed, you can start building the walls. An important point is the fact that on the first day, only one row of thermoblocks is installed along the perimeter of the foundation, i.e. 25 cm in height (photo 1).


Then you should carefully measure the distances (length of walls, diagonals, corners) of the exposed row. Using the level, you need to make sure that all blocks are aligned, both vertically and horizontally. This is necessary so that during further construction the wall does not lead to the side and there are no deviations from the project. During the installation of the first row, the architecture of the whole floor is formed, therefore it is important to take into account in the right places the slopes of door and window openings, the junction of the internal walls, install sewer and ventilation pipes inside the thermoblocks (if provided by the project), as well as lay fittings.
We do not recommend using welding equipment when installing fittings, as this is unacceptable in monolithic construction.
The walls should be reinforced on the basis of design calculations, taking into account the loads that will affect the wall, therefore, only a designer participating in the development of the project, or a specialist of Valkyria LLC can give an unambiguous answer about what the reinforcement step will be, and the diameter of the reinforcement. We will introduce you only to the principle of wall reinforcement. A reinforcement cage is laid horizontally along the perimeter of the entire building in the first row of blocks. It consists of 4 rods of reinforcement interconnected (the distance between the rods is 10 cm). The same frame, only vertically, should be laid in every corner of the building, in the places of window and door openings and in the last row of blocks, before laying the floor panel (sometimes in the last two rows). After completing all the above operations, you can start concreting.
The concrete should be poured up to the level of the upper edge of the thermoblock lintel. Until the concrete has completely hardened, you need to double-check whether the blocks are aligned horizontally and vertically and, if necessary, correct them. After the concrete has been poured into the first row of blocks, the structure must be left until the next day so that the concrete gains sufficient strength for further construction.
On the second day, you can put another 4-6 rows of thermoblocks (height 1-1.5 m) and pour concrete. Often in individual construction (if two or three workers are involved) in the manufacture of concrete directly at the construction site, the workers do not have time to prepare the required amount of concrete and pour 2-3 rows of blocks (50-75 cm) per day, which is not a violation of construction technology. It's just that the speed of building the walls will decrease slightly.
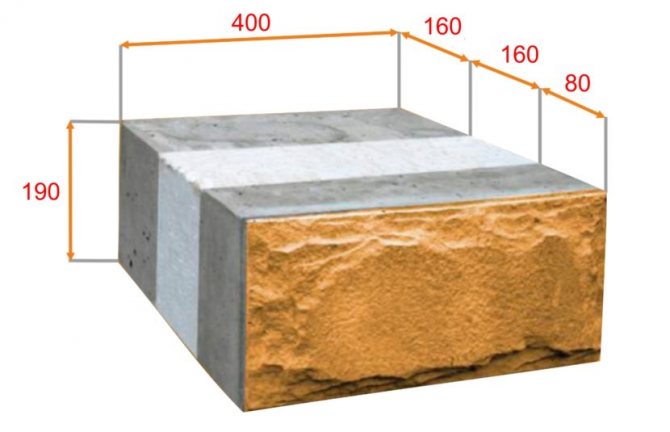
"Thermodom" is not a definition from a science fiction novel. Of course, it sounds a little incomprehensible and puzzling. But if you look at it, everything is extremely simple. Foam blocks for construction are used for construction such houses from expanded polystyrene blocks... This construction method is called the permanent formwork method. In this article, we will look at the technology of building a thermal house. First of all, let's talk about the blocks themselves. The blocks are hollow "boxes" made of polystyrene: 95 cm long, 25 cm wide and 25 cm high for a wall block. The dimensions for the wall unit are 95x13x25 cm.
Such blocks are produced (see video production of polystyrene foam blocks) from expanded polystyrene by industrial conveyor production. One production line can produce about 120 blocks per shift.
Advantages of polystyrene foam blocks
* Blocks are not hygroscopic - i.e. they do not absorb moisture, they are resistant even to direct and prolonged exposure to moisture. * Blocks are excellent noise isolators. * Double - outer and outer - foam layer provides excellent thermal insulation. * Blocks "breathe", ie they slowly let air through. This makes them resistant to fungal diseases and rotting. * Blocks are lightweight, lightweight. * Blocks are convenient and easy to mount and handle.
Disadvantages of polystyrene foam blocks
* Blocks do not withstand high temperatures. The limiting temperature is 90 ° C. * Blocks are fire hazardous. Additional fire safety measures are required. * Blocks are easy to damage. Despite the apparent strength, the block is easy to pierce even with a finger. It is necessary to putty the walls.
In addition, some argue that expanded polystyrene, like any "chemistry", is not environmentally friendly and even harmful. I cannot categorically refute this fact. There are various requirements, GOST and norms, including sanitary, polystyrene foam blocks fully comply with them. But sometimes it's hard to convince a person of something that would seem obvious. The psychological factor is at work here.Although polystyrene has been widely used for a long time for interior decoration and insulation of buildings.
The cost of the polystyrene foam block about 4-5 USD In principle, this is a normal price. For comparison, you can calculate the total construction costs, for example, from bricks. Thermodom provides you with a wall ready for finishing, both inside and outside the house. In the decoration, you can use almost any material: putty, bark beetle plaster, wallpaper, paint, siding, etc. In a house built of brick, you will need to plaster and putty at least the internal walls, and even insulate the surfaces with the same foam, which will be even more expensive.
Thus, you should not be afraid of the high price, because it already includes ready-made, finished, insulated walls. Is it profitable? Yes, I think so!
At the moment, GOST allows the construction of thermal houses up to 15 meters high, which is already 4-5 floors.
How to build a thermohome Tools and materials:

* expanded polystyrene blocks * reinforcement 12 * tying wire * concrete mixer * sand * cement * crushed stone
Ready-made 600 grade cement can be used if desired.
* Construction from expanded polystyrene blocks is very similar to assembling a constructor - you assemble blocks into walls, joining them groove into groove, and shifting them horizontally and vertically with reinforcement. * After driving 4-5 rows, pour liquid concrete, tapping on the sides of the blocks with your palm (this will make the concrete more dense). * Then collect 4-5 more rows and repeat the process.
Of course, the number of rows is dictated by the overall dimensions of the building. If the building is small, then 4-5 rows around it will not take long to fill, and if the building has many piers and load-bearing walls, then the number next to it for filling is reduced. Here you should practice, calculate your strength, how much you pour at a time, how much concrete.
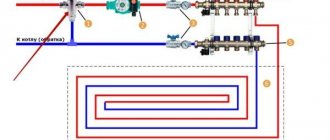
Installation of water supply, sewerage, electrical wiring and other systems is carried out by laying pipes for water and sewerage and corrugated hoses for wiring directly into the walls of the building.
How I built a house from heatblocks
One of the craftsmen of our portal with the nickname Skazochnik14 posted a detailed description of the construction of a house from a heat block and his feelings from its operation in the topic of the same name.
At first I did not know what to build a house from, but by chance I saw a house made of heat blocks, I liked the material. I drove to that construction site, asked, and decided to build a house from a heating block. Firstly, the house should turn out to be very warm, secondly, savings on finishing work outside, the heat block is already beautifully tiled, and thirdly, savings on work on facade insulation and painting.
In production, calculations were made on the basis of the project, the craftsman ordered wall, corner blocks and quarters, chose a color, for the basement - concrete slabs with a texture like blocks, with fastening on dowels. The promised deadline was a month, in reality they did not meet even two, the blocks instead of October were ready only in May. From the pros - no storage problems, one hundred thousand penalties and free shipping. Of the minuses - different parties differed in the shade of the cladding, the gamut was the same, but the saturation was different, I had to solve this problem during the masonry process. In order to save additional money, we bought all the lumber in the winter (board 150 × 150 and inch).
Foundation - insulated tape 1 meter deep with compacted sand bed and crushed stone pillow, insulation with PSB plates. In the outgoing construction season, a base of expanded clay concrete was laid out and left to winter.
Box - the walls began to be erected in May, since the foundation was not initially tied to the wall material, the thickness of the seam on different walls was from 5 to 10 mm. This led to difficulties with the masonry mixture - the purchased glue for foam concrete was not designed for such fluctuations, so they began to mix it with cement, and the seams were also foamed with polyurethane foam. The addition of cement showed itself as efflorescence on the masonry.

Increasingly, residents of the private sector are faced with the question: how best to insulate their homes? They know from their own experience how damp and uncomfortable in a cold room.
Traditionally, during the construction and thermal insulation of buildings, insulation was carried out in three stages:
- a capital wall was erected;
- insulation was installed;
- outside finishing was carried out.
It was important to choose the right characteristics of the heat-shielding composition. A frivolous attitude towards solving this problem led to significant heat losses, and, consequently, an increase in the cost of heating the house. For developers, this was a serious problem, which was solved by modern material - blocks with cladding and insulation. They harmoniously combine a power array, heat-insulating gasket and decorative trim. Most recently, builders dreamed of such a product, but today the dream has become a reality.
Would you like to know in detail what are veneered composites? Consider the structure, characteristics, properties, scope of this promising building composite.


Manufacturers offer new materials that simplify the process of building an insulated house
Thermal house construction technology
Construction technology "Termodom" is the technology of the so-called "fixed formwork", which means: the construction of the walls of a house built from blocks made of high-quality expanded polystyrene, the inner space of the blocks is filled with concrete and reinforced. Thus, a very strong concrete wall is obtained, reinforced vertically and horizontally, and insulated on both sides, resulting in a "thermos" effect. This, in turn, allows you to significantly reduce the cost of heating and cooling the internal space of the house. The walls of a house designed and made using the Termodom technology are much stronger than capital brick walls 38 cm thick. The cost of installing interfloor ceilings on walls erected using the termodom technology is much lower than the cost of installing similar ceilings on walls erected from any other material. The cost of building a thermal house box is one third cheaper than building a brick box. Specially developed construction technology and construction of the foundation under the walls using the termodom technology allows you to reduce the cost of building the foundation, basements and basements.
Heat transfer and lack of seasonality in construction.
Construction technology "Termodom" (termodom) is universal and suitable for almost all climatic zones and does not depend on the season. The construction of a thermal house is possible both in winter and in summer, and the temperature of the external environment will not affect either the appearance or the durability of the walls. It is cool in the house, built according to the "Termodom" technology, and warm in cold weather. That is, regardless of the climate and season, such a house is always a comfortable warm home. Expanded polystyrene is an excellent thermal insulator. In winter, it makes sense to start heating with a thermal house at a temperature of -2 ° C or -3 ° C, and in warmer weather, the heat emitted by household appliances will be enough to maintain a comfortable temperature. Thermodom (termodom) in winter does not cool down as quickly as a brick building, and perfectly stores heat.
Structural strength and number of storeys of buildings.

Recently, more and more often, customers prefer the construction of a private cottage from thermoblocks, but in principle, the Termodom technology is also suitable for projects of apartment buildings up to nine floors high, as well as for kindergartens, hospitals, schools, technical rooms, workshops, office buildings , etc. As for strength, a nail driven into a polystyrene wall and a dowel planted withstands a load of about 70 kg. The walls themselves are much thinner, lighter and at the same time durable and warm.According to the standard, the thermo house serves for more than 120 years, but in practice, if the construction is carried out in strict accordance with the technology, then the 120-year period is far from the limit. Turnkey construction of Thermohouse has been used for a long time in the world and has become widespread in Europe, USA and Canada.
Aeration and resistance to microorganisms.
Expanded polystyrene walls of houses and cottages built according to the "Turnkey Thermodom" technology not only "breathe", but at the same time they are resistant to moisture, which increases their thermal insulation properties. Many other materials accumulate moisture, which gradually leads to a decrease in their quality, which requires an increase in heating costs and maintaining a comfortable indoor microclimate. Firstly, excessive humidity negatively affects the health of people and animals living in such a house, in addition, it provokes increased energy consumption for heating, which can cause the formation of fungus and gradually destroy the walls of the building, especially as a result of temperature differences. Such problems are not terrible for expanded polystyrene, even with prolonged high humidity and when the temperature rises to + 90 ° C. The chemical composition of such blocks does not contain absolutely any elements that fungi and other microorganisms can feed on.
Construction time and ease of construction.
From an engineering point of view, the weight of a foam block structure is much less than that of a brick - about three times. Therefore, you can completely safely use a lightweight foundation structure and be glad that the construction of such a house or cottage will take much less time than you expected.
Thermal house construction: Expanded polystyrene.
Expanded polystyrene is a light gas-filled material of the foam plastic class based on polystyrene, its derivatives (polymonochlorostyrene, polydichlorostyrene) or copolymers of styrene with acrylonitrile and butadiene. The method for the production of expanded polystyrene was obtained back in 1928, and after 9 years in 1937 its industrial production was established. Since then, the method of producing expanded polystyrene has undergone a number of changes due to regional differences in the concepts of the development of the chemical industry.
Expanded polystyrene is a fairly common material, and its scope is not limited only to the construction of houses, cottages and other objects. Expanded polystyrene has found wide application in industry - the production of packaging material for household appliances and decorative elements, food packaging and disposable dishes, insulated containers for food and energy-absorbing elements in the automotive industry.
Expanded polystyrene is used where environmental friendliness and harmlessness as a material play an important role. Regardless of the ambient temperature, expanded polystyrene does not emit any substances harmful to health, and that is why even hospitals and kindergartens can be built from expanded polystyrene blocks. For the construction of houses using the "Termodom" technology, a special, hardly flammable expanded polystyrene foam is used, which guarantees its complete fire safety.
Negative characteristics of expanded polystyrene
According to its parameters, expanded polystyrene is not very suitable for wood, since it does not breathe, while wood has such a need. This material is also unacceptable to use for the installation of roofs with rafter systems made of wood. The surface of the blocks can be destroyed by the sun and heat. However, if we are talking about walls, then the base of the PPS plates can be covered with a layer of plaster, which is applied to a special steel mesh, in some cases the traditional painting method is used.
Despite its versatility, expanded polystyrene is not recommended for internal insulation.
Pros of expanded polystyrene
- high rigidity;
- the ability to undergo heavy loads;
- good thermal performance;
- not saturated with moisture;
- frost resistance;
- long service life.
Cons of expanded polystyrene
- destroyed by the sun;
- not recommended for use with internal insulation;
- cannot be fixed to wooden walls.
Let's summarize?
All of the above factors convince you of the correct choice of this wall material. As a result, the developer saves not only during construction, but also during the operation of housing.
In addition, the variety of textures and colors of multilayer blocks allows you to implement any exterior solution. Neither fire, nor water, nor bioorganisms are afraid of such a structure. It is truly a “house of the XXI century” because it: relatively cheap, heat-efficient, environmentally friendly, durable, non-flammable.
Call us at any time and buy multi-layer blocks or order the construction of a typical house at the best price. Choose a cottage or summer cottage that is suitable for the cost in the catalog and let such housing become your happy family nest.
Expanded polystyrene blocks are the result of the efforts of scientists from the German chemical company BASF, who tried to combine various properties and characteristics in one material.
Polystyrene concrete block D300
Light and warm blocks made of foamed polystyrene concrete for home are actively used today in modern construction. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the basic information about the material - its characteristics, sizes, pros and cons of use - in this article.
Areas of use of the structure
Fixed formwork made of expanded polystyrene in the construction process is an obvious saving not only in time, but also in material costs. As a rule, savings in the construction of buildings using this technology averages 40 percent.
Note! This is largely due to the fact that the cost of expanded polystyrene as a building material is quite low. In addition, non-removable structures made of it eliminate the need for additional manipulations related to strengthening and thermal insulation of walls.
If we compare this technology with traditional brickwork, then the material aspect of the issue is very important. And after analyzing the prices of building materials, it becomes obvious that building a house with fixed formwork is more economical. For example, as of last year, the cost of one wall erected using this technology cost the developer about 1 thousand rubles per square meter. For comparison: the cost of a silicate brick wall was then somewhere around 1.8 thousand per square. Aerated concrete walls were cheaper, but foam is still the most profitable option.