According to fire safety rules, the arrangement around stoves, fireplaces and fuel boilers should be carried out using refractory special materials that can simultaneously protect a residential or utility building (bathhouse) from possible fire hitting the walls, and at the same time not harm health.
Any stove or fireplace heats up to create a favorable home atmosphere, they radiate a strong heat, which in turn can be a source of ignition or fire. Therefore, it is important to carefully choose the right materials when arranging a heat source in a house, bathhouse or basement when it comes to a fuel boiler.
Types of materials
Refractory materials can be roughly divided according to the method of heat transfer:
- Heat-reflecting - aimed at reflecting infrared radiation into the interior of the room;
- Preventing loss due to their physical and chemical properties.
On the video of refractory materials for walls around ovens:
But all of them can also differ in the type of raw materials from which they are produced:
- With organic ingredients, for example, polystyrene foam materials, although their refractory index is very low, they are best suited for walls near furnaces with low heating;
- Inorganic - This is an extensive class of non-combustible materials for insulation of walls of various fire resistance, including very flammable ones, such as wooden floors. These include stone and basalt wool, pressed into large slabs, fiberglass wool, lightweight cellular concrete slabs with fire retardant impregnations, honeycomb plastics, foamed perlite or vermiculite, polypropylene. However, such a beautiful decorative thing as Leroy Merlin plastic sheet is definitely not suitable.
- Mixed type - these include asbestos-cement refractories, asbestos-lime or silica, foamed from a variety of inorganic substances.
Basic requirements for refractory materials
Many suburban buildings are erected from wood, whether it is a cylinder or frame house, without a stove or fireplace it is difficult to survive the frosty winter, therefore they are very careful about their arrangement, and such materials are chosen around the stoves so that they are:
- Effectively and reliably prevented any attempt at fire;
- Environmentally friendly, so that when heated, they do not emit harmful substances into the home air.
What is the composition of the kiln plaster solution that exists and is most often used, the information from this article will help to understand.
But what are the dimensions of the standard kiln brick, you can see here.
You may also be interested in knowing what kind of brick is used for laying stoves.
For walls around ovens
A long time ago, people used asbestos sheets to cover the walls around stoves, but it turned out to be very harmful to health and the environment - its microparticles can get into the lungs or settle on things, which leads to serious ailments, and when heated, they are also released carcinogenic substances. Therefore, the best materials can be considered:
Fire resistant gypsum board. can serve as the basis for wall cladding around hot-heated stoves, and for decoration you can use porcelain stoneware tiles of the most unusual colors.
Sheets have the following characteristics:
- Fire-resistant indicator - up to 30 minutes of resistance to fire;
- Does not ignite until 1 hour of time even after the formation of a fire center;
- Slab parameters - 120 x 250 x 1.25;
- On the front and back sides, gypsum-treated cardboard, inside there are fiberglass threads that will resist fire;
- The ends of the sheets are covered with cardboard material, along them there is a mating chamfer;
- Fasteners can be carried out both on adhesives and on self-tapping screws.
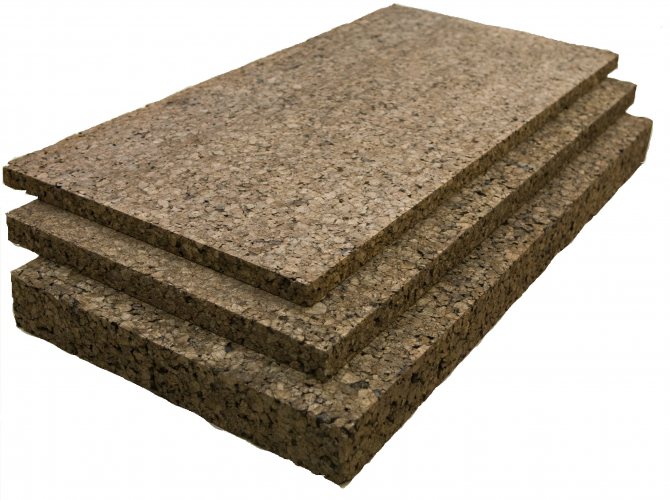
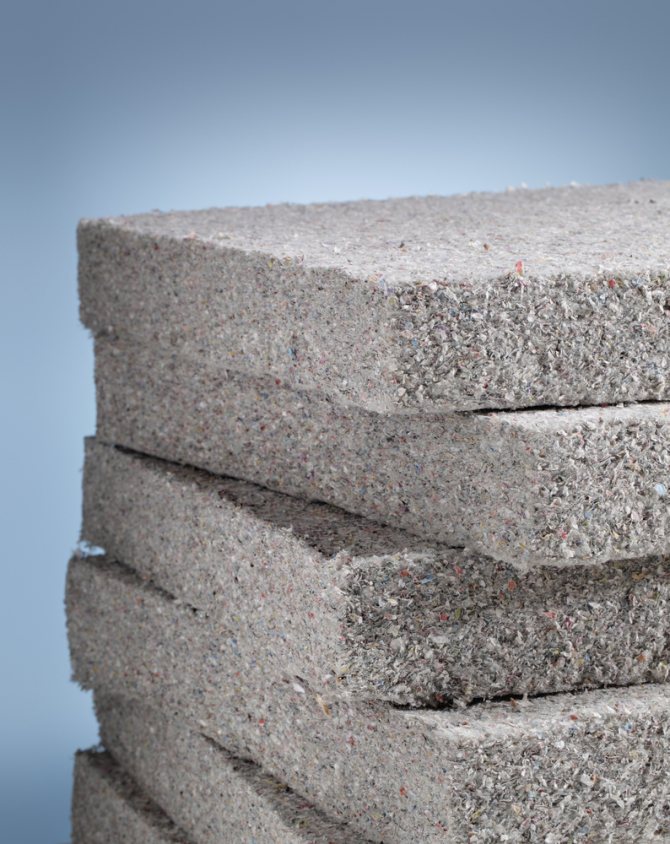
Refractory minirite slabs. The material is distinguished by excellent heat-resistant properties, it is made exclusively from environmentally friendly substances, including:
- Compositions of white or gray cement make up up to 90% of the total material;
- Mineral fiber materials included;
- Fiber reinforcement plates are used for strength and durability.
Asbestos fiber is absolutely excluded from the composition, which improves the quality of the material for the home stove. It is easy to fix it to the wall with screws close to the wall itself; for reliability, you can mount 2 sheets of minirite each. Note! Leave a small distance during installation, as the material may increase in size when heated. For other walls, you can choose a similar decorative brick finish.
Protective stainless sheets - a little expensive, but reliable refractory material, with which you can protect not only the walls of the house, but also the basement, when installing a heating boiler. But in order to provide the greatest protection, special fiberglass with thermal protective properties should be laid under the stainless steel - the structure will reliably protect the house from any attempts to start a fire. Choose a substrate carefully so that there are no harmful phenolic resins in it; when heated, they release substances that are too hazardous to health.
Heat Resistant Basalt Fiber Material, pressed into mats - is distinguished by hygroscopicity, a high degree of resistance to fire, can remain unchanged at temperatures up to 900 degrees Celsius.
Superisol sheets for wall insulation - a practical and versatile thermal insulation material, with a low specific weight and excellent strength and durability.
Wall insulation with heat-resistant terracotta tiles... The main advantage is the complete environmental friendliness of the material, they do not contain any chemical coloring compositions, they have excellent vapor permeability and fireproof properties. Glazed ceramic tiles for interior wall cladding also look beautiful.
For wall decoration under the boiler
A gas or steam boiler is very hot in order to provide heat transfer to the house at the desired temperature of the carrier. Therefore, experts recommend equipping the walls with porcelain stoneware tiles with a high degree of fire resistance. The characteristics are the most reliable - it can withstand high temperatures without visible signs of fire.
It is also allowed to use sheets of fibers impregnated with gypsum, installation is very easy by sticking on walls, but plastic panels for brick for interior wall decoration are not recommended, since they do not meet fire safety requirements.
Recently, a sheet of xylolite fiber has begun to gain popularity, since it meets all environmental properties in terms of purity and the absence of any harmful emissions, even at elevated temperatures of about 1000 degrees. Also, the material is very flexible, these properties allow you to sheathe the most curved wall surfaces. It can perfectly withstand humid and damp air, its main characteristics do not change.
Differences between Izolona PPE and NPE
The differences between these two types of Izolon are also visible to the naked eye, moreover, they have different areas of application. Externally, Izolon NPE has larger cells and is less elastic to the touch. It is undesirable to use it with a point load, since cells filled with air can burst, depriving the material of its sound-absorbing and heat-insulating properties.Large cells contribute to the formation of a rather uneven surface of the material, which can complicate the process of gluing and subsequent leveling of the surface.
Most often, this type of Izolon is used when carrying out packing work, as well as when it is necessary to create an amortization pad. Due to the simpler production method, NPE is an order of magnitude cheaper than polyethylene foam with a crosslinked molecular base.
PPE costs a little more, but its technical characteristics benefit a lot. It is more durable and elastic, better adapted to ambient temperature extremes and mechanical stress, and it is also more durable. This material has a perfectly smooth surface, making it easier to install. When gluing the material, several times less glue is spent than when installing the PSE.
Manufacturers and prices
- Basalt fiber panels cost of 1 sq. meter - from 390 to 690 rubles, depending on the decor of the front side, produced by ESCAPLAT;
Roll refractory nonwoven fabric - cost of 1 running meter from 112 rubles, production of OgneuporEnergoHolding, LLC, Moscow;
- Non-flammable composition for plastering walls with a volume of 20 liters at a price of 410 rubles a bucket, produced by a company from Perm.
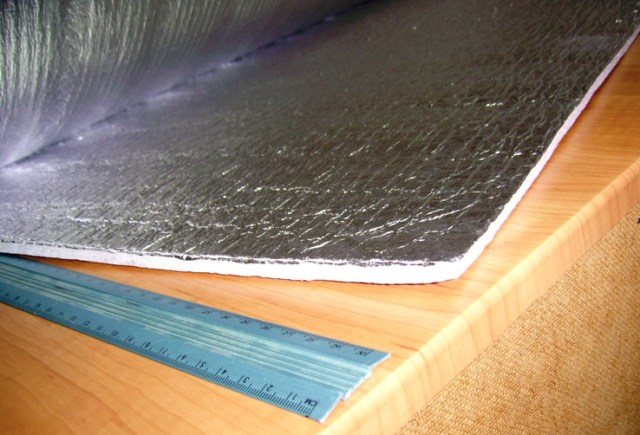
Reflective insulation is a roll-up material that consists of a base layer and a reflective layer. The latter is represented by a foil with a high reflectance from 90%. Any insulating material with good physical and mechanical properties can be taken as a basis, and reinforced meshes are used to enhance the qualities.
Styrofoam
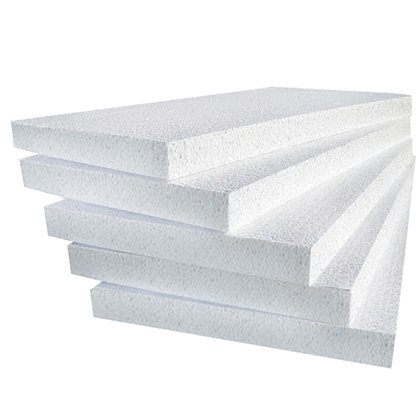

Polyfoam with external insulation must be covered with plaster - the material is afraid of ultraviolet radiation
The most famous inorganic insulation is polystyrene foam. It is an inexpensive material with high efficiency, which is usually used for wall insulation. Positive characteristics include:
- Low cost. The cost of manufacturing thermal insulation is minimal, and it is required less than other heat insulators.
- Ease of installation.
- Versatility. Suitable for thermal insulation of different parts of the house.
- High efficiency.
- Small coefficient of thermal conductivity.
- Virtually no moisture absorption.
- Good insulation.
- Resistant to alcohols, alkalis.
- Environmentally friendly.
Polyfoam has a vapor permeability coefficient of 0.05 mg. Operated at temperatures from -60 ° C to + 80 ° C. It has a cellular structure and does not absorb liquid well.
Disadvantages:
- Flammability. At the stage of industrial production, ingredients that increase fire resistance are added to the insulation foam, but it is still considered combustible.
- Deformation of characteristics during prolonged exposure to temperatures above 80 ° C. It is not recommended to put in saunas and other buildings with high temperatures.
- Rodents can damage the insulation.
Despite its shortcomings, polystyrene has established itself as a high-quality insulation for home and summer cottages. Thermal insulation sheet material is used for walls and floors. The roll view is used for pipes.
Principle of operation
To understand the principle of operation of such insulation, consider the main methods of transferring heat from one coating to another:


Thus, heat loss is inevitable. It turns out that in order to create the effect of thermal insulation, it is necessary to minimize heat loss from radiation. But traditional TIMs are not able to protect a building from this type of heat transfer.And the optimal material was found - foil insulation, known for its reflective and low emitting ability.
Reflective insulation works on all heat transfer processes: radiation, convection and heat conduction, inhibiting heat loss.
Insulation recommendations
It is best to carry out insulation work in the summer, when the air humidity is minimal.
Walls for insulation in the room must be perfectly dry. You can dry them after additional plastering, finishing work to level the surfaces using construction hair dryers and heat guns.
Stages of surface insulation:
- Cleaning the surface from decorative elements - wallpaper, paint.
- Treatment of walls with antiseptic solutions, priming of the surface with deep penetration into the layers of plaster.
- In some cases, when installing polystyrene foam and electric heating elements, the walls are pre-leveled using waterproof bathroom plaster.
- Installation of insulation should be carried out in accordance with the instructions prescribed by the manufacturer for this type of material.
- Installation of a protective partition for applying the final finish, or covering the surface with a construction mesh, plastering it.
- Creation of a single composition with the overall design of the room.
Insulating the walls inside the house is one of the most effective ways to protect your home from the penetration of cold and the negative effects of condensation, the main thing is to observe the technological sequence of stages. More details about the technology of insulating a home from the inside can be found in this material.
Nuances of use
So, there are several nuances of using such heaters:
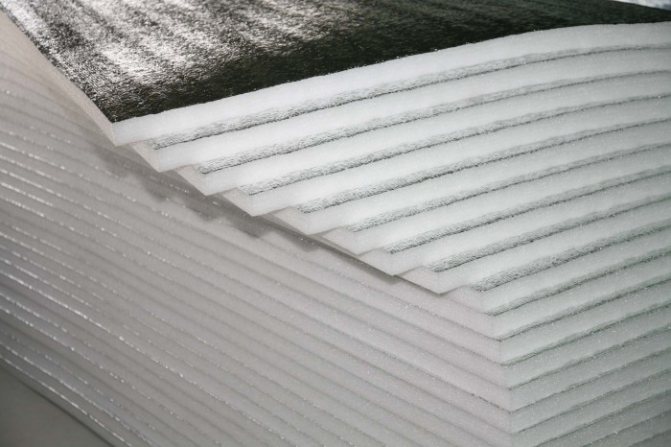


- deposited aluminum spraying on a polyethylene or lavsan film does not reflect infrared heat waves;
- a thick layer of foil is needed for the radiation to really reflect;
- for weak heat waves, a thin sprayed layer of 20-30 angstroms is enough;
- it is impossible to determine the thickness of the layer by eye.
The vapor permeability of foil-clad TIM is 0.001 mg / m * h * Pa. The technical resistance parameter must be indicated in the documentation of the reflecting TIM. In the absence of it, this means that the material has not been tested for reflectivity, which means that it cannot be used as insulation.
Scope of application
Reflective thermal insulation is applicable to all surfaces without dirt and dust, suitable for complex structures with corners, bends and drops. Insulation of walls from the outside can be maximized by creating an air gap of 20 mm on the foil side.
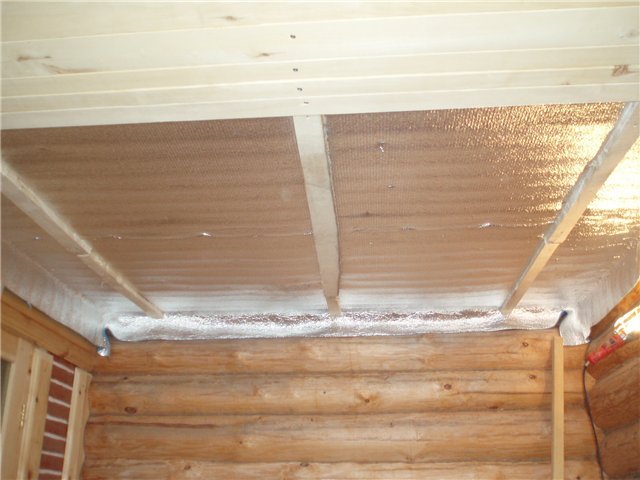


The material is effective for multi-storey and one-storey frame houses, while this will increase the resistance of the walls without increasing their volume. Installation is carried out end-to-end without overlaps, and the seams are glued with foil tape.
Application from the inside
If you want to insulate the room from the inside, then there are two options. The first option is to make 2 air gaps between the outer wall and the material, between the insulation and the cladding (for example, drywall). In this case, TIM with double foil is used.
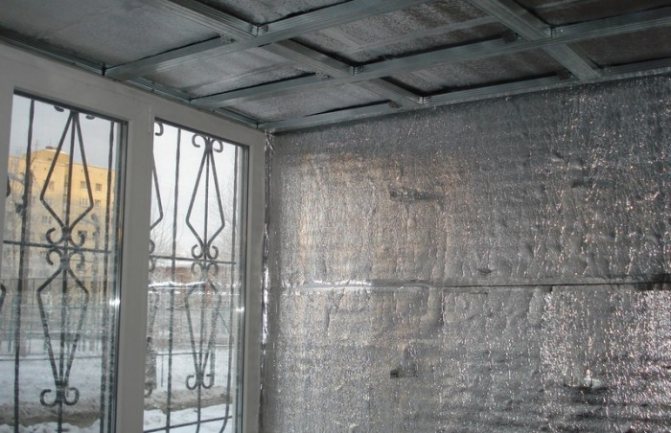


The second option is to create one gap between the outer wall and the insulation, for which a material foil on one side is used. The foil is turned inside the room.
Roof insulation
Reflective TIMs mounted on the roof provide not only thermal insulation, but also vapor insulation. The under-roof space is also protected from moisture.
The reflective film is especially effective when insulating the ceiling of the bath.
Piping and ventilation
For pipes, insulation with double-sided foil is required. If the pipes have a diameter less than 159 mm, then it is possible not to create an air gap between the TIM and the pipe. If the pipes have a larger diameter, then the gap is required. The air gap is set up as follows:
Advantages and disadvantages
The performance characteristics of such material are as follows:
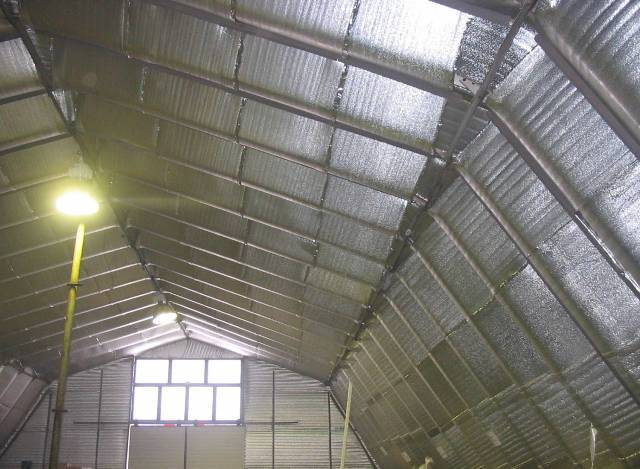


- for production, polyethylene and foil are used, which are acceptable for the food industry, and therefore the material meets hygienic standards;
- polished aluminum foil reflects up to 97%, emitting no more than 5% of thermal energy;
- a layer of air bubbles in polyethylene foam provides additional thermal resistance, which does not transmit heat according to the principle of thermal conductivity;
- insulation is fireproof, non-flammable and refers to hardly flammable materials;
- low weight and compactness of rolls make it convenient to transport and store them;
- reducing heat loss reduces heating costs, the cost of thermal insulation of the room in comparison with the cost of other materials.
Minuses
Reflective insulation has the following disadvantages. Firstly, its softness - the lack of rigidity makes it impossible to finish the insulation with plaster and wallpaper. Secondly, fastening is easy only with materials on an adhesive basis (type C), and for the installation of other models, you will have to stock up on adhesive.
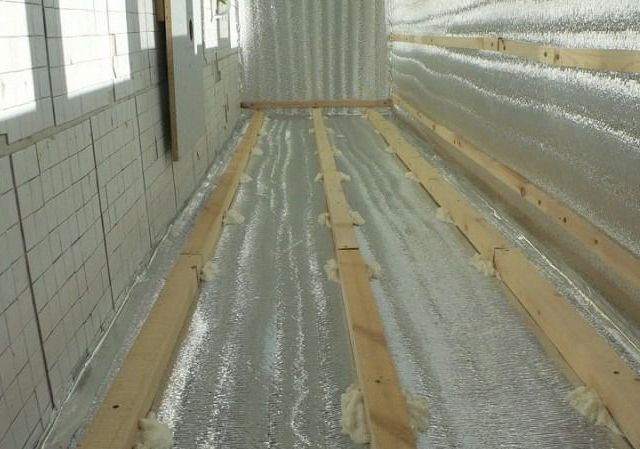


Thirdly, nailing the material degrades the thermal insulation qualities. Finally, when insulating external walls, it can only be used as an additional layer that reflects heat and protects against moisture.
The most popular brands of such insulation today are Porileks NPE-LF, Ekofol and Penofol, BestIzol. Manufacturers Ursa, Isover and Rockwool produce reflective insulation based on mineral wool of various densities and thicknesses. The modern market offers foil-clad TIM in the form of mats and cylinders, with which it is convenient to insulate pipelines.
BestIsol
BestIzol is a vapor, heat and sound insulation material with a reflective ability, in the production of which closed cell polyethylene foam and aluminum foil are used. The thickness of polyethylene foam can vary from 2 to 10 mm, and the thickness of the foil - from 7 to 14 mm, depending on the brand.


There can be several modifications:
- type A - polyethylene foam with one-sided foil;
- type B - with double-sided foil;
- type C - foil is applied on one side, and glue with a layer of anti-adhesive material on the other.
This type of reflector is effective not only for insulating residential buildings, but also for insulating ships, ventilation ducts, vans, and metal structures.


Lightness and strength allows this TIM to be built into metal structures by fixing it to the frame. This will not require additional expenses for the construction of temporary structures, gratings for securing the insulation.
Aluminum tape
Adhesive tape is used for seams of reflective insulation elements. Types F-20 and F-30 are foils with a thickness of 20 and 30 microns, respectively, with an adhesive coating and permanent stickiness. Protection of the adhesive layer is provided by a material with anti-adhesive characteristics.
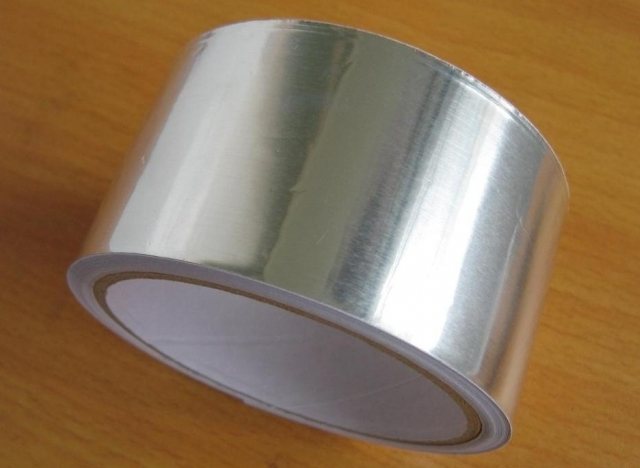


FL-50 type - combined of 20 µm aluminum foil and 20 µm polyethylene film also with adhesive application and anti-adhesion material. In addition to foil, film and glue, the reinforced adhesive tape contains a fiberglass mesh. The characteristics of aluminum tape are as follows:
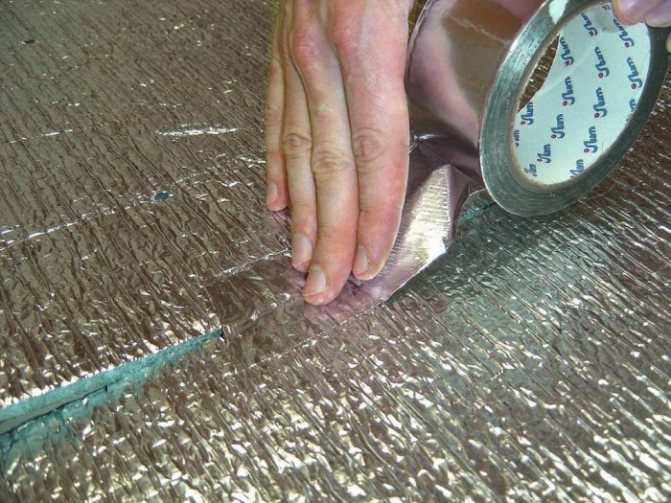


- high strength, wear resistance and reflection of UVF rays and infrared rays, which makes it effective;
- durability of the adhesive layer, which gives a high-quality connection;
- the material can be used at temperatures up to 350С;
- has high moisture resistance.
Thermal insulation products
An analysis of the experience of various countries in solving the problem of energy saving shows that one of the most effective ways to solve it is to reduce heat losses through the enclosing structures of buildings and structures, as well as in industrial equipment and heating networks. This can be achieved by using highly efficient thermal insulation products.The list of tasks for the solution of which thermal insulation products are used is very wide. This is the insulation of facades, roofs, floors, ceilings and basements of buildings, various types of communications and pipelines.
Thermal insulating products are those that have low thermal conductivity and are intended for thermal insulation of building structures of residential, industrial and agricultural buildings, surfaces of production equipment and units (industrial furnaces, turbines, pipelines, refrigerator chambers). Thermal insulation products are characterized by a porous structure and, as a consequence, low density (no more than 600 kg / m3) and low thermal conductivity (no more than 0.18 W / (m * ° C).
The efficiency and scope of use of thermal insulation products in specific building structures are determined by their technical characteristics, including the following main parameters: thermal conductivity, density, compressibility, water absorption, vapor permeability, fire resistance, frost resistance, biostability and the absence of toxic emissions during operation.
The main technical characteristic of thermal insulation materials is thermal conductivity, i.e. the ability of a material to transfer heat. To quantitatively determine this characteristic, the thermal conductivity coefficient is used, which is equal to the amount of heat passing in 1 hour through a sample of material with a thickness of 1 m and an area of 1 m2 at a temperature difference on opposite surfaces of 1 ° C. Thermal conductivity is expressed in W / (m K) or W / (m degree Celsius). In this case, the value of thermal conductivity of thermal insulation materials depends on the density of the material, type, size, location of pores, etc. Also, the temperature and humidity of the material have a strong effect on thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity increases sharply when insulating materials are moistened, since the thermal conductivity of water is 0.58 W / (m ° C), that is, approximately 25 times higher than that of air. When the moistened heat-insulating material freezes, its thermal conductivity further increases, since the thermal conductivity of ice is 2.32 W / (m ° C), i.e., 100 times more than air in fine pores. Obviously, it is very important to protect thermal protection in structures and equipment from moisture, especially in the event of possible subsequent freezing of moisture. In a number of materials, especially fibrous ones, the thermal conductivity with an increase in the average density first sharply decreases, and then increases approximately proportionally to the increase in the average density of the material. This can be explained by the fact that at a very low average density and a large number of large pores, thermal conductivity increases with convection. With increasing density, the proportion of heat transfer by conduction increases.
Thus, it can be stated that thermal conductivity is the most important technical characteristic of thermal insulation products. The thermal resistance of the fence R (term), m2K / W directly depends on it
The most characteristic feature of heat-insulating materials is their high porosity, since the air in the pores has a lower thermal conductivity than the surrounding substance in a condensed state (solid or liquid). The porosity of thermal insulation materials is up to 90% and even up to 98%, and super-thin fiberglass has a porosity of up to 99.5%. Meanwhile, such structural materials as heavy cement concrete have a porosity of up to 9 ... 15%, granite, marble - 0.2 ... 0.8%, ceramic bricks - 25 ... 35%, steel - 0, wood - up to 70%. Since porosity directly affects the value of the average density, thermal insulation materials are usually distinguished not by porosity, but by average density.
Fire resistance is a very important property of thermal insulation products, especially when used to insulate industrial equipment operating at high temperatures.They characterize the refractoriness of materials by technical and economic limiting temperatures of use. The technical temperature is understood as the temperature at which the material can be operated without changing the technical properties. The economic limiting temperature of application is determined not only by the temperature resistance of the material, but also by its other indicators - thermal conductivity, cost, installation conditions, etc. Some materials with increased thermal conductivity are irrational, for example, to be used for high-temperature insulation, despite their high technical limiting application temperature.
Compressibility is the ability of a material to change its thickness under a given pressure. Compressibility materials are soft M: deformation of over 30%, semi-rigid RV: deformation of 6-30%, hard F: deformation of no more than 6%. Compressibility is characterized by the relative deformation of the material in compression under the action of a specific load of 0.002 MPa. The soft insulating materials allow air to pass through so well that air movement has to be prevented by using a separate windscreen. Rigid products, in turn, have good air tightness and do not need any special measures. They can also be used as windscreens.
Water absorption significantly impairs thermal insulation properties and reduces strength and durability. Closed cell materials such as foam glass have low water absorption (less than 1%). To reduce water absorption, for example, in the manufacture of mineral wool products, hydrophobic additives are often introduced, which make it possible to reduce the sorption moisture during operation.
Gas and vapor permeability is taken into account when using heat-insulating material in enclosing structures. Thermal insulation should not impede the air exchange of living quarters with the environment through the outer walls of buildings. In the case of high humidity in industrial premises, the thermal insulation is protected from moisture by means of reliable waterproofing installed from the "warm" side. Thermal insulation materials with communicating open pores allow a significant amount of water vapor to pass through, almost as much as air. Due to their low resistance to vapor permeability, they are almost always dry; vapor condensation is mainly observed in the next layer on the colder side of the enclosure. To avoid condensation of water vapor, the warm side must be more vapor tight than the cold side and also airtight.
The fire hazard of building materials is determined by the following fire-technical characteristics: flammability, flammability, flame spread over the surface, smoke-generating ability and toxicity. According to SNiP 21-01-97 "Fire safety of buildings and structures" building materials are divided into non-combustible (NG) and combustible (G). Combustible building materials are divided into four groups: G1 (slightly combustible), G2 (moderately combustible), G3 (normally combustible), G4 (highly combustible).
Thermal insulation products are classified according to the type of the main raw material, shape and appearance, structure, density, stiffness and thermal conductivity.
By the type of the main raw materials, thermal insulation products are divided into:
- organic - obtained by the processing of non-business wood and woodworking waste (fiberboards and chipboards), agricultural waste (straw, reeds, etc.), peat (peat plates), etc., as well as plastics (polyethylene foam, expanded polystyrene, foam glass, foamed plastics, porosity, honeycomb, etc.). A characteristic feature of most organic thermal insulation products is low fire resistance, therefore they are usually used at temperatures not exceeding 100 ° C, as well as with additional structural protection with non-combustible materials (plaster facades, three-layer panels, walls with cladding, facing with gypsum board, etc.)
- inorganic - made on the basis of mineral raw materials (rocks, slag, glass, asbestos).This group includes mineral wool and glass wool and products made from them, some types of lightweight concrete based on porous aggregates (expanded perlite and vermiculite), cellular heat-insulating concrete, foam glass, asbestos and asbestos-containing materials, ceramic, etc. These materials are used as for thermal insulation of building structures and for insulation of hot surfaces of industrial equipment and pipelines.
- mixed - used as assembly ones, made on the basis of asbestos (asbestos cardboard, paper, felt), mixtures of asbestos and mineral binders (asbestos diatomaceous, asbestos-rubble, asbestos-lime-silica, asbestos-cement products) and on the basis of expanded rocks, perlite (vermiculite).
In terms of structure, thermal insulation materials are classified into fibrous (mineral wool, glass - fibrous), granular (perlite, vermiculite), cellular (products from aerated concrete, foam glass).
In terms of density, thermal insulation products are divided into especially light (especially low density) with a density of 15 ... 75 kg / m3, light (low density) - 100 ... 175, medium density - 200 ... 350 and dense - 400 ... 600 kg / m3.
In terms of rigidity, thermal insulation products are divided into soft semi-rigid, rigid, increased rigidity and hard. For the industrialization of construction work, rigid, large-sized thermal insulation products are increasingly used. A measure of the stiffness is the value of their compressibility or relative compression deformation. At a specific load of 0.02 MPa, rigid materials have a relative compression of up to 6%, semi-rigid - 6 ... 30 and soft - more than 30%. In materials of increased rigidity and solid at a specific load of 0.04 and 0.1 MPa, respectively, the relative compression should not exceed 10%.
In terms of thermal conductivity, thermal insulation materials are divided into classes: A - low thermal conductivity up to 0.06 W / (m- ° C), B - medium thermal conductivity - from 006 to 0.115 W / (m- ° C), B - increased thermal conductivity - from 0.115 up to 0.175 W / (m ° C).
According to their intended purpose, heat-insulating products are heat-insulating-construction (for warming building structures) and heat-insulating - assembly (for thermal insulation of industrial equipment and pipelines).
In terms of shape and appearance, they distinguish between piece and bulk thermal insulation materials. Piece materials include various types and shapes of products. They can be flat - bricks, mats, blocks, slabs; shaped - cylinders, segments, shells; and corded - cords, harnesses. The use of piece materials improves the quality of thermal insulation and reduces labor costs. Bulk materials include powdery, fibrous and granular loose materials. They are used for filling voids in frame walls, in interfloor ceilings. But over time, they cake, thicken and their thermal insulation properties decrease. Some powders, mixed with water, are used for the preparation of mastic insulation (sovelite, magnesite "newel", asbesurite), which is used mainly for sealing joints between heat-insulating products.
Organic thermal insulation products.
Organic thermal insulation materials, depending on the nature of the feedstock, can be conditionally divided into two types: materials based on natural organic raw materials (wood, woodworking waste, peat, annual plants, animal hair, etc.), materials based on synthetic resins, the so-called thermal insulation plastics.
Organic thermal insulation materials can be rigid and flexible. The rigid ones include wood-based, fibreboard, fibrolite, arbolite, reed and peat, and flexible - construction felt and corrugated cardboard. These insulating materials are characterized by low water and biological resistance.
Wood fiber insulation boards are obtained from wood waste, as well as from various agricultural waste (straw, reeds, fire, corn stalks, etc.). Fiber boards are produced with a length of 1200-2700, a width of 1200-1700 and a thickness of 8-25 mm. According to their density, they are divided into insulating (150-250 kg / m3) and insulating-finishing (250-350 kg / m3). The thermal conductivity of insulating boards is 0.047-0.07, and of insulation-finishing boards is 0.07-0.08 W / (m- ° C). Chipboards are produced in single and multi-layer. For example, in a three-layer board, the porous middle layer consists of relatively large chips, and the surface layers are made of flat thin chips of the same thickness. Light slabs with a density of 250 ... 500 kg / m3 and a thermal conductivity of 0.046 ... ... 0.093 W / (m ° C) are used for thermal insulation purposes. Semi-heavy and heavy slabs with a density of 500 ... 800 and 800 ... 1000 kg / m3 and a bending strength of 5 ... 35 MPa, respectively, are used as a finishing and structural material.
Fiberboard has high sound insulation properties. Along with insulating boards, insulation and finishing boards are used, having a front surface painted or prepared for painting.
Reed slabs, or simply reeds, are used for thermal insulation of the enclosing structures of HI class buildings, in the construction of low-rise residential buildings, small industrial premises, in agricultural construction. It is a heat-insulating material, pressed from reed stalks in the form of slabs, which are then fastened with galvanized steel wire. Depending on the location of the reed stalks, slabs are distinguished with a transverse (along the short side of the slab) and a longitudinal arrangement of the stems. According to the bulk density of the slab, three grades are distinguished: 175, 200 and 250 with a bending strength of at least 0.18-0.5 MPa, a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.06-0.09 MPa, and a moisture content of no more than 18% by weight ... Reed slabs are produced with a length of 2400-2800, a width of 550-1500 and a thickness of 30-100mm.
Peat insulation products are made in the form of slabs, shells and segments. The raw material for their production is low-decomposed high-moor peat, which has a fibrous structure, which favors the production of high-quality products from it by pressing. Plates are made with dimensions 1000x500x30 mm by pressing in metal molds of peat mass with additives (or without them) and followed by drying at a temperature of 120-150 ° C. Peat insulating plates by bulk density are divided into M 70 and 220 kg / m3 with a tensile strength of pa bending - 0.3 MPa, thermal conductivity coefficient in dry condition 0.06 W / m- ° С, humidity not more than 15%.
Peat thermal insulation products are used for thermal insulation of building envelopes of the 3rd class and surfaces of industrial equipment with operating temperatures from -60 to +100 ° С.
Cement-fibrolite boards are heat-insulating and heat-insulating-structural material obtained from a hardened mixture of Portland cement, water and wood wool. Wood wool plays the role of a reinforcing frame in fiberboard. In appearance, thin wood shavings up to 500 long, 4-7 wide, 0.25-0.5 mm thick are prepared from non-commercial coniferous wood on special wood-wool machines. By volumetric mass, cement-fiberboard plates are divided into M 300, 350, 400 and 500 with a bending strength, respectively, not less than 0.4 0.5, 0.7 and 1.2 MPa, a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.09-0, 15W / m- ° С, water absorption - no more than 20%. The length of the slabs is 2000-2400, the width is 500-550, the thickness is 50, 75, 100 mm.
Fiberboard slabs based on Portland cement are used as heat-insulating, heat-insulating-structural and acoustic material for walls, partitions, ceilings and coatings of buildings.
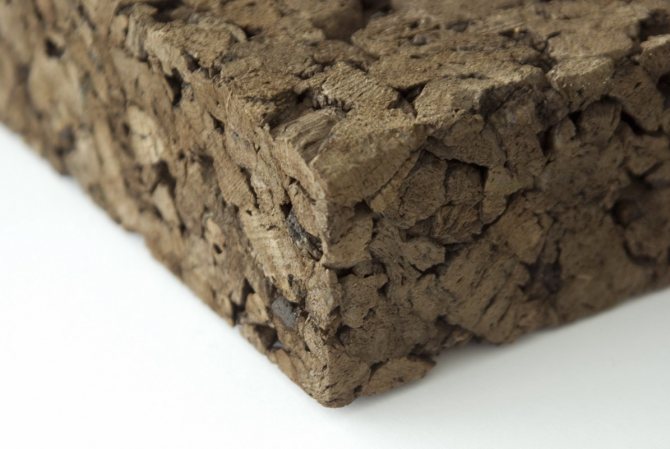
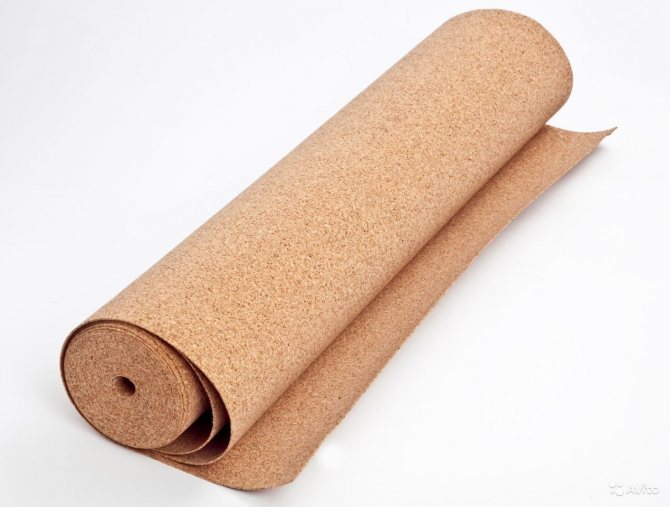
Cork heat-insulating materials and products (plates, shells and segments) are used for thermal insulation of building envelopes, refrigerators and surfaces of refrigeration equipment of pipelines at a temperature of insulated surfaces from minus 150 to plus 70 ° C, for insulating ship hulls.They are made by pressing crushed cork chips, which are obtained as a waste in the production of closures from the bark of cork oak or the so-called velvet tree growing in the Far East Territory, in the Amur Region and on Sakhalin. Due to its high porosity and the presence of resinous substances, cork is one of the best thermal insulation materials. Cork heat-insulating materials and products by volumetric weight in a dry state are divided into M 150-350 with a bending strength of 0.15-0.25 MPa, respectively, a coefficient of thermal conductivity in a dry state at a temperature of 25 ° C-0.05-0.09 W / m- ° C.
The positive properties of the plates also include the fact that they do not burn, smolder with difficulty, are not susceptible to infection by house fungus and are not destroyed by rodents. Cork materials are packed in cages with a volume of 0.25-0.5 m3 and stored in a dry, closed room, and transported in covered wagons.
Thermal insulation products based on polymers in the form of gas-filled plastics and products, as well as mineral wool and glass wool products, are produced on a polymer binder.
Porization of polymers is based on the use of special substances that intensively emit gases and swell the polymer softened when heated. Such intumescent substances can be solid, liquid and gaseous.
Plates, shells and segments of porous plastics are used for thermal insulation of building envelopes and surfaces of industrial equipment and pipelines at temperatures up to 70 ° C. bending not less than 0.1-0.2 MPa, thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.04 W / m ° С, humidity - not more than 2% by weight. The same products on emulsion polystyrene by volumetric weight have M 50-200 bending strength, respectively - not less than 1.0-7.5 MPa, thermal conductivity coefficient - not more than 0.04-0.05, humidity not more than 1% mass. Porous plastic plates are made with a length of 500-1000, a width of 400-700, and a thickness of 25-80 mm.
Depending on the structure, thermal insulation plastics can be divided into two groups: foamed plastics and cellular plastics.
Foam plastics are cellular plastics with low density and the presence of non-communicating cavities or cells filled with gases or air.
Foam plastics are porous plastics, the structure of which is characterized by interconnecting cavities. Of greatest interest for modern industrial construction are polystyrene foam, polyvinyl chloride foam, polyurethane foam and mipora.
Insulating and insulating - finishing boards are used for heat and sound insulation of walls, ceilings, floors, partitions and ceilings of buildings, acoustic insulation of concert halls and theaters (suspended ceilings and wall cladding).
Inorganic insulation products.
Inorganic thermal insulation products include piece, roll, cord, loose materials and products with a fibrous and cellular structure, intended for insulation, mainly of enclosing structures and structures: mineral wool, glass fiber, foam glass, expanded perlite and vermiculite, asbestos-containing thermal insulation products, cellular concrete, etc.
Mineral wool is a fibrous thermal insulation material obtained from silicate melts. The raw materials for its production are rocks (limestones, marls, diorites, etc.), waste from the metallurgical industry (blast furnace and fuel slags) and the building materials industry (broken clay and silicate bricks). Depending on the density, mineral wool is classified into grades 75, 100, 125 and 150. Mineral wool is fragile, and a lot of dust is generated during its installation, therefore, the wool is granulated, i.e.o turn into loose lumps - granules. They are used as heat-insulating backfill for hollow walls and ceilings. The mineral wool itself is, as it were, a semi-finished product from which a variety of heat-insulating mineral wool products are made: felt, mats, semi-rigid and rigid plates, shells, segments, etc.
Distinctive features of mineral wool products are high heat and sound insulating ability, resistance to temperature deformations, chemical and biological resistance, environmental friendliness and ease of installation. But the most valuable property of mineral wool, which distinguishes it from other heat-insulating materials, is incombustibility.
According to fire safety requirements, mineral wool products belong to the class of non-combustible materials (NG). Moreover, they effectively prevent the spread of flame and are used as fire insulation and fire protection. Also, mineral wool products can be used in very high temperatures. Mineral fibers are able to withstand temperatures above 1000 ° C. Even after the binder breaks down at a temperature of 250 ° C, the fibers remain intact and bound together, maintaining strength and creating fire protection.
Mineral wool is used for thermal insulation of both cold (up to -200 ° C) and hot (up to + 600 ° C) surfaces, most often in the form of products - felt, mats, hard and hard plates, shells, segments. Mineral wool is also used as a heat-insulating backfill for hollow walls and coatings, for this it is granulated (turned into loose lumps).
Mineral raw materials are used to produce mineral wool mats, semi-rigid and rigid slabs, as well as shells, segments, cylinders and other products. Mineral wool stitched mats are manufactured with a length of 2000, a width of 900-1300 and a thickness of 60 mm. By volumetric weight in a dry state, mats are produced M 150, the coefficient of thermal conductivity in a dry state is not more than 0.046 W / m- ° C. Thermal insulation mats based on mineral fibers are designed for thermal insulation of building structures, industrial equipment and pipelines of heating networks. The domestic industry produces several types of mineral wool mats. Mineral wool stitched mats are used for thermal insulation of building envelopes and surfaces of industrial equipment and pipelines at temperatures up to 400 ° C.
Glass wool is a material consisting of randomly arranged glass fibers obtained from molten raw materials. The raw material for the production of glass wool is a raw material mine for glass melting (quartz sand, soda ash and sodium sulfate) or glass breakage.
Depending on the purpose, they produce textile and heat-insulating (staple) fiberglass. The average diameter of the textile fiber is 3-7 microns, and the heat-insulating fiber is 10-30 microns.
Glass fibers are considerably longer than mineral wool fibers and are characterized by greater chemical resistance and strength. The density of glass wool is 75-125 kg / m3, thermal conductivity is 0.04-0.052 W / (m / ° C), the maximum temperature for using glass wool is 450 ° C.
Currently, our industry produces six kinds of glass fiber products. These are mainly slabs and mats.
Thermal insulation products made of fiberglass are used in "wet" type external insulation systems, in hinged ventilated facades, in systems with insulation on the inside of the enclosing structure, in systems with insulation inside the enclosing structure. For glass wool products, the maximum application temperature is about 450 ° C.
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material of a cellular structure. The raw material for the production of foam glass products (slabs, blocks) is a mixture of finely crushed glass broken with gassing (ground limestone).
Foam glass has a number of valuable properties that distinguish it favorably from many other heat-insulating materials: foam glass porosity 80-95%, pore size 0.1-3 mm, density 200-600 kg / m3, thermal conductivity 0.09-0.14 W / ( m, / (m * ° С), the ultimate compressive strength of the foam glass is 2-6 MPa. In addition, the foam glass is characterized by water resistance, frost resistance, fire resistance, good sound absorption, it is easy to handle with a cutting tool. Foam glass in the form of plates 500 long, 400 wide and 70-140 mm thick are used in construction to insulate walls, ceilings, roofs and other parts of buildings, and in the form of semi-cylinders, shells and segments - to insulate heating units and heating networks, where the temperature does not exceed 300 ° C. In addition, foam glass serves as sound-absorbing and at the same time finishing material for audiences, cinemas and concert halls.
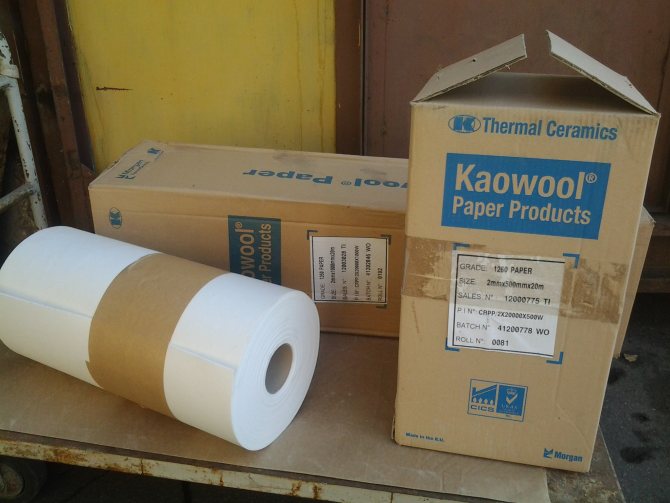
Materials and products made of asbestos fiber without additives or with the addition of binders include asbestos paper, cord, fabric, plates, etc. Asbestos can also be part of the compositions from which various heat-insulating materials are made (sovelite, etc.). In the materials and products under consideration, the valuable properties of asbestos are used: temperature resistance, high strength, fiber, etc.
Smooth asbestos paper is used as heat-insulating gaskets when insulating pipelines. Corrugated paper is used for the production of cellular asbestos cardboard, asbestos cardboard is used for thermal insulation of pipelines with operating temperatures up to 500 ° C, as well as for coating wood and other flammable objects and products in order to increase fire resistance. In the form of slabs, asbestos cardboard is used for thermal insulation of flat surfaces, in the form of semi-cylindrical tires - for insulation of pipelines, asbestos cord - for thermal insulation of industrial equipment and heat pipelines. In the absence of organic fiber in the composition of the cord, it can be used at temperatures up to 500 ° C, in the presence of fiber - no more than 200 ° C, Asbestos-magnesia powder is used for thermal insulation of industrial equipment at temperatures up to 350 ° C. The powder is used not only in the form of bulk thermal insulation, but also for the preparation of mastics, plates, segments.
Aluminum foil (alfol) is a new heat-insulating material, which is a tape of corrugated paper with aluminum foil glued on the crest of the corrugations. This type of heat-insulating material, unlike any porous material, combines the low thermal conductivity of the air trapped between the sheets of aluminum foil with the high reflectivity of the surface of the aluminum foil itself. Aluminum foil for thermal insulation purposes is produced in rolls up to 100 mm wide and 0.005-0.03 mm thick.
The practice of using aluminum foil in thermal insulation has shown that the optimal thickness of the air gap between the foil layers should be 8-10 mm, and the number of layers should be at least three. The density of such a layered structure made of aluminum (foil 6-9 kg / m3, thermal conductivity - 0.03 - 0.08 W / (m * C).
Aluminum foil is used as reflective insulation in heat-insulating layered structures of buildings and structures, as well as for thermal insulation of surfaces of industrial equipment and pipelines at a temperature of 300 ° C.
Heat-insulating concretes are also widely used in domestic construction - gas-filled (aerated concrete, aerated concrete, aerated concrete) and based on lightweight aggregates (expanded clay concrete, perlite concrete, polystyrene concrete, etc.). This is facilitated by the simplicity of the technology, which makes it possible to produce foam concrete directly on the construction site, as well as the availability of raw materials and a relatively low cost.However, despite the fact that foam concretes, due to their high fire resistance, can be used for fire barriers and similar structures, their thermal insulation properties, in comparison with the materials listed above, are significantly lower.
The use of heat-insulating materials in construction makes it possible to increase the degree of industrialization of work, since they provide the possibility of manufacturing large-sized prefabricated structures and parts, reduce the mass of structures, reduce the need for other building materials (concrete, brick, wood, etc.), reduce fuel consumption for heating buildings, reduce heat loss in industrial units. Thermal insulation materials provide adequate comfort in living quarters, improve working conditions in production, and reduce the incidence of injuries.
A good effect is provided by the use of heat-insulating materials for the insulation of heating units, technological equipment and pipelines, which makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption by reducing heat loss.
It is considered very important to use heat-insulating materials in various refrigeration installations to reduce cold losses (the cost of obtaining a unit of cold is about 20 times higher than that of a unit of heat).
Due to their high porosity, many thermal insulation products have the ability to absorb sound, which allows them to be used also as acoustic materials to combat noise.
You can purchase heat-insulating construction products on our website.
The company offers a wide range of thermal insulation products of various brands at competitive prices.
The main types of insulation
Modern thermal insulation materials for use in construction and repair are divided into many varieties: industrial and household, natural and artificial, flexible and rigid thermal insulation materials, etc.
For example, in terms of form, modern thermal insulation is divided into samples such as:
In terms of structure, the following types of thermal insulation are distinguished with their own unique feature:
By the type of raw materials, such products of various quality classes are distinguished:
- Organic, natural or natural insulation materials are cork bark, cellulose wool, expanded polystyrene, wood fiber, foam plastic, paper granules, peat. These types of building insulation materials are used exclusively indoors to minimize high humidity. However, natural building thermal insulators are not fireproof.
- Inorganic thermal insulation materials - rocks, fiberglass, foam glass, mineral wool insulation, foamed rubber, aerated concrete, stone wool, basalt fiber. A good heat insulator from this category is characterized by a high degree of vapor permeability and fire resistance. Insulation with a product with water-repellent additives is especially effective.
- Mixed - perlite, asbestos, vermiculite and other insulation made of foamed rocks. They are distinguished by the best quality and, of course, increased cost. These are the most expensive brands of the best thermal insulation materials. Therefore, premises are covered with such insulation much less often than with more economical materials.
If you need to make thermal insulation of the pipeline in the wall, then special "sleeves" of high density are used for this.
Determining the best product depends not only on the price. They are chosen for their quality characteristics, ergonomic properties and environmental friendliness.
Which is better: Izolon, Penofol or Splen
In addition to Izolon, thermal insulation materials such as Penofol and Splen are very popular in the construction market. It can be difficult for an ordinary buyer to figure out what their fundamental differences are, and which material is better, because outwardly they look almost the same.
Penofol is a foamed polyethylene, which is covered on one or both sides with a dense foil, which is necessary to reflect solar energy. Experts say that Penofol is somewhat inferior in performance to foil-clad Izolon, which has a higher density, better heat and sound insulation properties, has a smooth surface and is more durable. In addition, modern Penofol is made from gas-foamed polyethylene, which is less durable than foil-clad Izolon made from Izolon PPE.
Splenna is a polyethylene foam with a sticky layer, thanks to which the material is easily adhered to the surface. It is identical to Izolon and performs the same functions, but it can cost a little more than a simple Izolon. The cost of a self-adhesive Izolon with a foil base will be higher than that of Splen without a foil layer. Spleen is used most often for soundproofing a car.
What parameters should you pay attention to when choosing?
The choice of quality thermal insulation depends on many parameters. The methods of installation, and the cost, and other important characteristics, which are worth dwelling on in more detail, are taken into account.
Choosing the best heat-saving material, you must carefully study its main characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity. This coefficient is equal to the amount of heat that in 1 hour passes through 1 m of an insulator with an area of 1 m2, measured by W. The thermal conductivity index directly depends on the degree of surface moisture, since water passes heat better than air, that is, the raw material will not cope with its tasks.
- Porosity. This is the proportion of pores in the total volume of the heat insulator. The pores can be open or closed, large or small. When choosing, the uniformity of their distribution and appearance are important.
- Water absorption. This parameter shows the amount of water that can be absorbed and retained in the pores of the heat insulator in direct contact with a humid environment. To improve this characteristic, the material is subjected to hydrophobization.
- Density of thermal insulation materials. This indicator is measured in kg / m3. Density shows the ratio of mass to volume of a product.
- Humidity. Shows the amount of moisture in the insulation. Sorption humidity indicates the balance of hygroscopic humidity in conditions of different temperature indicators and relative humidity.
- Water vapor permeability. This property shows the amount of water vapor passing through 1 m2 of insulation in one hour. The unit of measurement for steam is mg, and the temperature of the air inside and outside is taken as the same.
- Resistant to biodegradation. A heat insulator with a high degree of biostability can withstand the effects of insects, microorganisms, fungi and in high humidity conditions.
- Strength. This parameter indicates the impact on the product will have transportation, storage, installation and operation. A good indicator is in the range from 0.2 to 2.5 MPa.
- Fire resistance. All parameters of fire safety are taken into account here: the flammability of the material, its flammability, smoke-generating ability, as well as the degree of toxicity of combustion products. So, the longer the insulation resists the flame, the higher its fire resistance parameter.
- Heat resistance. The ability of a material to resist temperatures. The indicator demonstrates the level of temperature, after reaching which the material's characteristics, structure will change, and its strength will also decrease.
- Specific heat. It is measured in kJ / (kg x ° C) and thus demonstrates the amount of heat that is accumulated by the thermal insulation layer.
- Frost resistance. This parameter shows the ability of the material to tolerate temperature changes, freeze and thaw without losing its main characteristics.
When choosing thermal insulation, you need to remember about a whole range of factors.It is necessary to take into account the main parameters of the insulated object, conditions of use, and so on. There are no universal materials, since among the panels, bulk mixtures and liquids presented on the market, it is necessary to choose the type of thermal insulation that is most suitable for a particular case.
How to choose insulation for your home
Our rating contains the most popular types of insulation. Before considering it, let us briefly touch on the main parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing:
- Thermal conductivity
... The indicator informs about the amount of heat that can pass through different materials under the same conditions. The lower the value, the better the substance will protect the house from freezing and save money on heating. The best values are 0.031 W / (m * K), the average values are 0.038-0.046 W / (m * K). - Vapor permeability
... It implies the ability to let moisture particles pass through (breathe) without retaining it in the room. Otherwise, excess moisture will be absorbed into the building materials and promote mold growth. Heaters are divided into vapor-permeable and impermeable. The value of the former ranges from 0.1 to 0.7 mg / (ppm Pa). - Shrinkage.
Over time, some heaters lose their volume or shape under the influence of their own weight. This requires more frequent fixing points during installation (partitions, clamping strips) or use them only in a horizontal position (floor, ceiling). - Mass and density.
The insulation characteristics depend on the density. The value varies from 11 to 220 kg / m3. The higher it is, the better. But with an increase in the density of the insulation, its weight also increases, which must be taken into account when loading building structures. - Water absorption (hygroscopicity).
If the insulation is directly exposed to water (accidental spillage on the floor, roof leakage), then it can either withstand it without harm, or deform and deteriorate. Some materials are not hygroscopic, while others absorb water from 0.095 to 1.7% of the mass in 24 hours. - Operating temperature range
... If the insulation is laid in the roof or directly behind the heating boiler, next to the fireplace in the walls, etc., then maintaining the elevated temperature while maintaining the properties of the material plays an important role. The value of some varies from -60 to +400 degrees, while others reach -180 ... + 1000 degrees. - Flammability
... Household insulation materials can be non-flammable, low-flammable and highly flammable. This affects the protection of the building in the event of accidental fire or intentional arson. - Thickness.
The section of the layer or roll insulation can be from 10 to 200 mm. This affects how much space is required in the structure for its placement. - Durability
... The service life of some heaters reaches 20 years, and others up to 50. - Simplicity of styling.
Soft insulation can be cut with a little extra and they will tightly fill a niche in the wall or floor. Solid insulation needs to be cut exactly to size so as not to leave "cold bridges". - Environmental friendliness.
Implies the ability to release vapors into a dwelling during operation. Most often these are binder resins (of natural origin), so most materials are environmentally friendly. But during installation, some species can create an abundant dust cloud, harmful to the respiratory system, and prick hands, which will require protection with gloves. - Chemical resistance.
Determines whether it is possible to lay plaster over the insulation and paint the surface. Some species are completely resistant, others lose from 6 to 24% of their weight upon contact with alkalis or acidic environment.
Materials for the manufacture of thermal insulation [edit | edit code]
For the manufacture of thermal insulation that prevents thermal conductivity, materials are used that have a very low coefficient of thermal conductivity - heat insulators
... In cases where thermal insulation is used to retain heat inside the insulated object, such materials may be called
heaters
... Heat insulators are characterized by a heterogeneous structure and high porosity.
To date, thermal insulation materials based on aerogels have the lowest thermal conductivity coefficients (0.017 - 0.21 W / (m • K)).
Types of insulation and their properties
If you do not know how to choose thermal insulation, first of all it is worth referring to its classification. Thermal insulation materials are distinguished by the type of basic raw material, shape and appearance, structure, density, stiffness, thermal conductivity, and application.
By the type of raw materials, thermal insulation is:
- Organic - based on wood and peat raw materials. Differs in low biostability, is susceptible to negative effects of moisture. Possesses high soundproofing characteristics.
- Inorganic - based on various types of mineral raw materials (rocks, slags, asbestos). Low hygroscopic, frost-resistant, sound-absorbing.
- Plastic - based on various synthetic resins.
In shape and appearance:
- Rigid slab, shell, segment, brick, cylinder. It is convenient for cladding various surfaces with a simple shape.
- Flexible - mat, harness, cord. It is used for winding pipelines.
- Loose - cotton wool, vermiculite, perlite sand. Effective in filling various cavities.
- Fibrous - fiberglass, mineral wool.
- Granular - perlite, vermiculite.
- Cellular - foam glass, cellular concrete.
- Classes from 15 to 600. Thermal insulation materials of lower density are used for internal premises, for external thermal insulation - higher.
- soft - wool (mineral, glass, kaolin, basalt);
- semi-rigid - a slab of spatula fiberglass with a synthetic binder;
- rigid - a plate of mineral wool with a synthetic binder;
- increased rigidity;
- solid.
- class A - low thermal conductivity, up to 0.06 W / (m- o C);
- class B - average thermal conductivity, 0.06-0.115 W / (m- o C);
- class B - increased thermal conductivity, 0.115-0.175 W / (m- o C)
- For thermal insulation of building structures (building).
- For thermal insulation of pipelines and industrial equipment (assembly).