Heat retention requirements for private houses and apartments have increased significantly. Many people resort to additional finishing of attic floors, external walls due to the constant increase in the cost of energy carriers.
In recent years, enough materials have appeared that can significantly improve heat conservation in a private house or apartment. They also have a number of other properties, making them generally an excellent alternative to major renovations.
Varieties and description
Materials with different mechanical properties are offered for the choice of consumers.
Ease of installation and properties largely depend on this. According to this indicator, they are distinguished:
- Foam blocks... They are made of concrete with special additives. As a result of a chemical reaction, the structure is porous.
- Plates. Building materials of various thicknesses and densities are made by pressing or gluing.
- Cotton wool. It is sold in rolls and has a fibrous structure.
- Granules (crumb). Loose heaters with foam substances of various fractions.
Various substances can be used as raw materials for insulation. They all fall into two categories:
- organic based on peat, reeds, wood;
- inorganic - made of foamed concrete, minerals, asbestos-containing substances, etc.
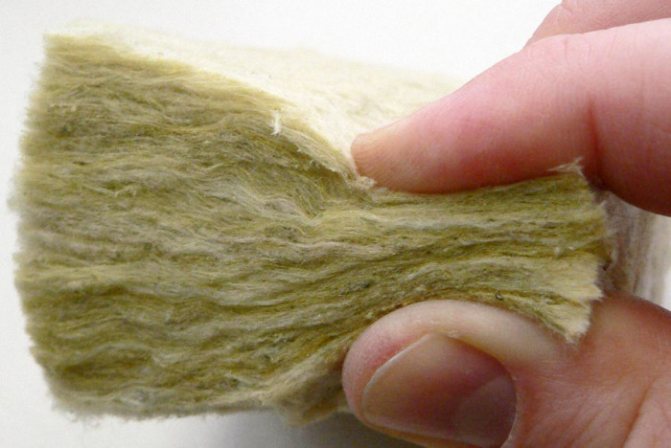
Basalt wool
This insulation is obtained by melting basalt rocks with the addition of auxiliary components. The result is a material with a fibrous structure and excellent water repellency. The insulation is non-flammable and completely safe for health. In addition, basalt has excellent performance for high-quality sound and heat insulation. It can be used for insulation both outside and inside the house.

In the photo - basalt wool for insulation
When installing basalt wool, you must wear protective equipment. This includes gloves, a respirator, and goggles. This will protect the mucous membranes from the ingress of cotton wool debris. When choosing basalt wool, the Rockwool brand is very popular today. In the article you can find out which is better: basal or mineral wool.
During the operation of the material, you do not have to worry that the plates will be compacted or caked. And this speaks of the excellent properties of low thermal conductivity, which do not change over time.
Basic properties
The effectiveness of a material largely depends on three main characteristics. Namely:
- Thermal conductivity... This is the main indicator of the material, expressed by a coefficient, calculated in watts per 1 square meter. Depending on the level of heat retention, a different amount of insulation is required. It is significantly influenced by the rate of moisture absorption.
- Density. An equally important characteristic. The higher the density of the porous material, the more efficiently heat will be retained inside the building. In most cases, it is this indicator that is decisive when choosing a heater for walls, floor slabs or roofs.
- Hygroscopicity. Resistance to moisture is very important. For example, basement floors, which are located in damp places, it is important to insulate with a material with the lowest hygroscopicity, which is, for example, plastic form.
It is necessary to pay attention to a number of other indicators. This is resistance to mechanical damage, temperature extremes, flammability and durability.
Thermal conductivity characteristics of foam
In order to consider such a characteristic as the thermal conductivity of foam, let's first figure out what the thermal conductivity of materials is, in principle. Thermal conductivity is a quantitative characteristic of a body's ability to conduct heat.
This is the amount of thermal energy (Watt) that any material is able to conduct through itself (meter), at a certain temperature (C) for a certain time. It is designated - λ and is expressed in W / m • С.
We will determine the optimal dimensions of this insulation based on its heat-conducting characteristics. There are many different insulation materials on the building materials market. Polyfoam, as we already know, has a very low thermal conductivity, but this value depends on the grade of the material.
For example, polystyrene grade PSB-S 50 has a density of 50 kg / m3. Thus, its thermal conductivity is 0.041 W / m • С (data are indicated at 20-30 С). For polystyrene grade PSB-S 25, the value will be 0.041 W / m • C, and for grade PSB-S 35 - 0.038 W / m • C. The quoted values of the thermal conductivity coefficients are indicated for foam of the same thickness.
The thermal conductivity of the foam is most noticeable when comparing the values with other thermal insulation materials. For example, a 30-40 mm foam sheet is similar to the volume of mineral wool several times larger, and a sheet thickness of 150 mm replaces 185 mm of expanded polystyrene. Of course, there are materials that have a lower coefficient. These include penoplex. 30 mm of foam can replace 40 mm of foam, under similar conditions.


Comparison of key indicators
To understand how effective a particular insulation will be, it is necessary to compare the main indicators of materials. This can be done by reviewing Table 1.
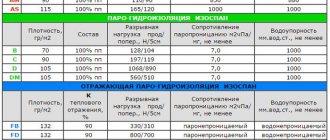
| Material | Density kg / m3 | Thermal conductivity | Hygroscopicity | Minimum layer, cm |
| Expanded polystyrene | 30-40 | Very low | Average | 10 |
| Plastiform | 50-60 | Low | Very low | 2 |
| Penofol | 60-70 | Low | Average | 5 |
| Styrofoam | 35-50 | Very low | Average | 10 |
| Penoplex | 25-32 | low | low | 20 |
| Mineral wool | 35-125 | Low | High | 10-15 |
| Basalt fiber | 130 | Low | high | 15 |
| Expanded clay | 500 | High | Low | 20 |
| Aerated concrete | 400-800 | High | High | 20-40 |
| Foam glass | 100-600 | Low | low | 10-15 |
Table 1 Comparison of thermal insulation properties of materials
Of these types, the leader in the rating is foam plastic. The material has undeniable advantages, including an affordable cost.
At the same time, many prefer plastic form, mineral wool or aerated concrete. This is due to individual preferences, installation features and some physical properties.
What does thermal conductivity depend on?
The ability of expanded polystyrene boards to retain heat depends mainly on two factors: density and thickness. The first indicator is determined by the number and size of air chambers that make up the structure of the material. The denser the slab, the higher thermal conductivity she will have.
Density dependence
In the table below you can see exactly how the thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam depends on its density.
| Density (kg / m3) | Thermal conductivity (W / mK) |
| 10 | 0.044 |
| 15 | 0.038 |
| 20 | 0.035 |
| 25 | 0.034 |
| 30 | 0.033 |
| 35 | 0.032 |
The above background information, however, is likely to be useful only to home owners who have been using expanded polystyrene foam to insulate walls, floors or ceilings for quite some time. The fact is that in the manufacture of modern brands of this material, manufacturers use special graphite additives, as a result of which the dependence of thermal conductivity on the density of the plates is practically reduced to naught. You can verify this by looking at the indicators in the table:
| Brand | Thermal conductivity (W / mK) |
| EPS 50 | 0.031-0.032 |
| EPS 70 | 0.033-0.032 |
| EPS 80 | 0.031 |
| EPS 100 | 0.03-0.033 |
| EPS 120 | 0.031 |
| EPS 150 | 0.03-0.031 |
| EPS 200 | 0.031 |
Dependence on thickness
Of course, the thicker the material, the better it retains heat. In modern polystyrene foam, the thickness can vary between 10-200 mm.For this indicator, it is accepted classified into three large groups:
- Plates up to 30 mm. This thin material is usually used to insulate partitions and interior walls of buildings. Its thermal conductivity does not exceed 0.035 W / mK.
- Material up to 100 mm thick. Expanded polystyrene of this group can be used for cladding both external and internal walls. Such plates retain heat very well and are successfully used even in regions of the country with a harsh climate. For example, a material with a thickness of 50 mm has a thermal conductivity of 0.031-0.032 W / Mk.
- Expanded polystyrene with a thickness of more than 100 mm. Such overall slabs are most often used for the manufacture of formwork when pouring foundations in the Far North. Their thermal conductivity does not exceed 0.031 W / mK.
Calculation of the required material thickness
It is quite difficult to accurately calculate the thickness of polystyrene foam required for warming a house. The fact is that when performing this operation, a lot of various factors should be taken into account. For example, such as the thermal conductivity of the material chosen for the construction of insulated structures and its type, the climate of the area, the type of cladding, etc. However, it is still possible to roughly calculate the required thickness of the slabs. For this you will need the following reference data:
- indicator of the required thermal resistance of the enclosing structures for a given region;
- thermal conductivity coefficient of the selected brand of insulation.
The calculation itself is made according to the formula R = p / k, where p is the thickness of the foam, R is the thermal resistance index, k is the thermal conductivity coefficient. For example, for the Urals, the R index is 3.3 m2 • ° C / W. For example, EPS 70 grade material with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.033 W / mK is selected for wall insulation. In this case the calculation will look like this:
- 3.3 = p / 0.033;
- p = 3.3 * 0.033 = 100.
That is, the thickness of the insulation for external enclosing structures in the Urals should be at least 100 mm. Typically, homeowners in cold regions sheathe walls, ceilings and floors with two layers of 50 mm styrofoam. In this case, the plates of the upper layer are positioned so that they overlap the seams of the lower one. Thus, you can get the most effective insulation.
Application features
Before deciding on the materials for finishing a private house or apartment, it is necessary to correctly calculate the thickness of the layer of a particular insulation.
You should also adhere to the following recommendations:
- For horizontal surfaces (floor, ceiling), you can use almost any material. The use of an additional layer with high mechanical strength is mandatory.
- It is recommended to insulate basement floors with building materials with low hygroscopicity. Increased humidity must be taken into account. Otherwise, the insulation, under the influence of moisture, will partially or completely lose its properties.
- For vertical surfaces (walls), it is necessary to use plate-and-sheet materials. Bulk or roll will sag over time, so you need to carefully consider the method of fastening.
Comparison of the characteristics of heaters
To begin with, we will provide the main characteristics of thermal insulation materials that you should pay attention to when choosing them. Comparison of heaters according to these characteristics should be made based on the purpose and characteristics of the room to be insulated (presence of open fire, humidity, natural conditions, etc.). We have arranged the main characteristics of insulation in the order of their importance.
Thermal conductivity... The lower the thermal conductivity, the less the insulation layer is required, which means that your insulation costs will be reduced.
Moisture permeability... Less moisture permeability reduces the negative impact of moisture on the insulation during subsequent use.
Fire safety... The material should not support combustion and emit poisonous vapors, but be self-extinguishing.
Profitability... Insulation should be affordable for a wide range of consumers.
Durability... The longer the period of use of the insulation, the cheaper it costs to the consumer during operation and does not require frequent replacement or repair.
Environmental friendliness... The material for thermal insulation must be environmentally friendly, safe for human health and the environment. This characteristic is important for living quarters.
Material thickness... The thinner the insulation, the less the living space of the room will be “eaten up”.
Material weight... Less weight of the insulation will give less weighting of the insulated structure after installation.
Soundproofing... The higher the sound insulation, the better the protection of living quarters from street noise.
Ease of installation... The moment is important enough for those who like to make repairs in the house with their own hands.
Installation of various types
When choosing this or that material for better preservation of heat in a house or apartment, you need to take into account the features of its installation. The complexity and set of tools for installation work largely depends on the form of thermal insulation. Namely:
- expanded clay. It is used exclusively for floors and floors. You need an entrenching tool and additional building materials (screed or boards). You will also need a waterproofing layer in the form of roofing felt or other similar material.
- mineral wool... Correct installation involves the use of a hand tool to secure the frame. Mineral wool is very easy to install in pre-prepared cells, but uniform fastening is required over the entire plane. A waterproofing layer on top of the insulation is a prerequisite for long-term operation. Can be used for vertical and horizontal surfaces.
- Styrofoam. Plates are attached to the surface with dowels with "dimes". Among the necessary tools are a screwdriver, a hammer drill, a construction knife and a dowel. The shape of the building material and its light weight allow even independently performing the entire volume of work in a short period of time.
- foam glass... For a tight connection with the surface, mechanical fasteners or solutions (cement, mastics and other adhesives) are used. The choice depends on the material of the walls. Blocks are very popular, but there are also slabs and granules in the assortment.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool is a material based on basalt fiber.
Mineral wool may not be used everywhere, since it has a lower temperature limit. For example, this insulation cannot be used in a refrigerator compartment.
Under the influence of low temperatures, mineral wool becomes brittle and deformed, which is unacceptable for insulation. Here, as a comparison of thermal conductivity heaters shows, the advantage is on the side of expanded polystyrene, which does not have a lower temperature limit.


As for the upper temperature limit, it all depends on the mechanical stress during exposure to high temperatures and the duration of this exposure. If you are interested in the thermal conductivity of heaters, the table on our website will help you in obtaining information about this. In particular, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of mineral wool is given there.
Mineral wool allows steam and moisture to pass through. This significantly reduces its thermal insulation properties. Also, the accumulation of moisture contributes to the development of mold and mildew, rodents begin to settle in the insulation, putrefactive bacteria, etc.
Also, mineral wool insulation is hygroscopic, which is why it is necessary to erect ventilated walls and a roof. In some cases, this leads to a large expenditure of funds.
Mineral wool insulation is 1.5-3 times heavier than its counterpart from expanded polystyrene. Hence the higher cost of transporting it. Also, the minus is that such insulation can be used only when the foundation of the structure, which is insulated with it, is strong enough. Of course, it is more difficult to carry out loading and unloading and construction and installation work using a large amount of insulation.


Thermal conductivity of heaters - comparative table
Saline solution. Alcohol based paint. Water based emulsions and paints. Ammonia, propane or butane. Paraffin vegetable oils and animal fats. Application Penoplex 50 mm is used in hinged facade technology. It is effective for insulating the subfloor of a sauna and bathhouse.
Included in pitched roof sandwich set. Laying on walls indoors is done with a low-density view, using a frame, or wet plaster technology. When forming the foundation, it serves as a formwork. Compression resistance and tightness provide the design reliability required by the standard.
Lay under the blind area, protect the walls from freezing in the winter season. The facade of the foundation is finished using the wet plaster technology with the use of insulation. Designed for laying under the roadway - a technology to prevent soil swelling at low temperatures. In permafrost conditions, it prevents soil shrinkage from thawing of the top layer, under the laid bed of asphalt or concrete slabs. In this and the previous type of work, a high-strength insulation penoplex is used. Lay it inside the loggia on the floor or wall from the side of the window adjacent to the street.
Tile or wallpaper is applied to it.