The principle of operation of the condensing boiler
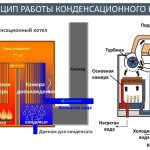
The operation of the condensing boiler is based on the principle of fuel combustion and condensation processes. When hydrocarbons are burned, water and carbon dioxide are formed during a chemical reaction. A liquid in a high-temperature environment in a short time interval turns into steam, consuming thermal energy, which can be returned by turning the steam into water.
The difficulty in creating such a system was the release of toxic substances during the combustion of gas, which created chemically active compounds that cause corrosive processes, as well as carbon dioxide. With the development of stainless steels capable of operating in this environment, these problems were no longer significant.
The operation of the condensing boiler in stages is as follows:
- Water is supplied to the boiler.
- Gas is supplied to the combustion chamber, fire is kindled.
- In the process of combustion, heat energy is released, which is transferred to the heat exchanger by a gas method and heats it and the water that circulates in it.
- Gas with a temperature above the dew point passes into a second heat exchanger, in which it is cooled by circulating water with a lower temperature.
- When the gas reaches the dew point, the released thermal energy of the vapor is transferred to the liquid.
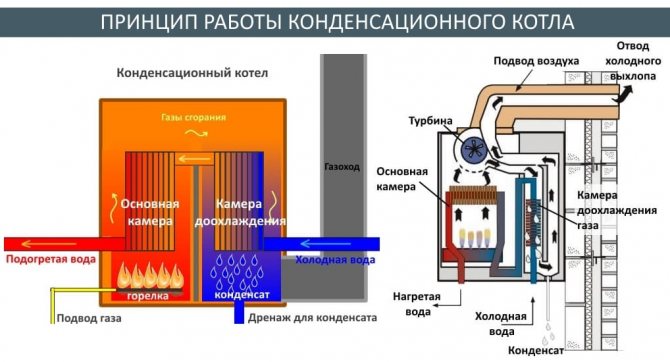
The principle of operation of the condensing boiler
The condensing boiler heat exchanger is designed to maximize the contact area between gas and coolant for increased efficiency. Its configuration also has a significant impact on efficiency.
The dependence of the volume of condensed moisture on the operating mode of the boiler is as follows: the lower the water temperature in the return circuit, the higher the condensation. However, in this case, the temperature should be at a level up to + 500C. Otherwise, the condensing boiler will operate in the normal gas mode and thus its efficiency will decrease to 5%.
For comparison: at a liquid temperature of + 40 ° C in the direct supply circuit and + 30 ° C in the reverse, the efficiency of the condensing boiler will be 108%, and at 90 ° C and 750 ° C, respectively, it will be 98%.
When operating boilers, it is necessary to observe the operating modes, and also when choosing a suitable model, its optimal heating power should be selected.
Types of boilers for heating: floor-standing, wall-mounted, condensing and others


Gas water heaters divided into several options:
- By installation option: floor and wall models. The first ones are mounted specifically on the floor, the second ones are installed on the wall.
- By the method of fuel use: convection and condensation. The heat carrier in traditional boilers is heated by the heat generated from the combustion of gas. Condensing models are equipped with a secondary type of heat exchanger, which makes it possible to extract additional volumes of heat energy.
- By type of air draft: with natural and forced draft.
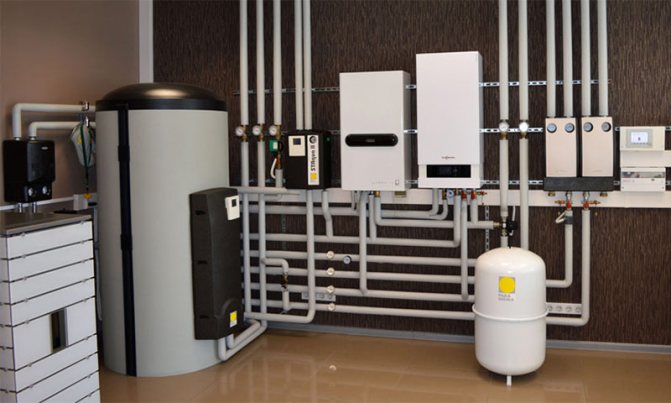
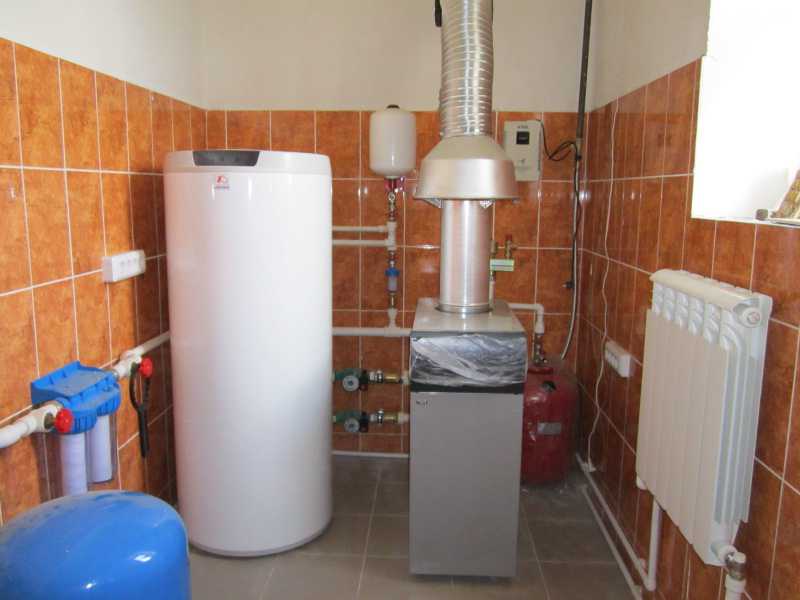
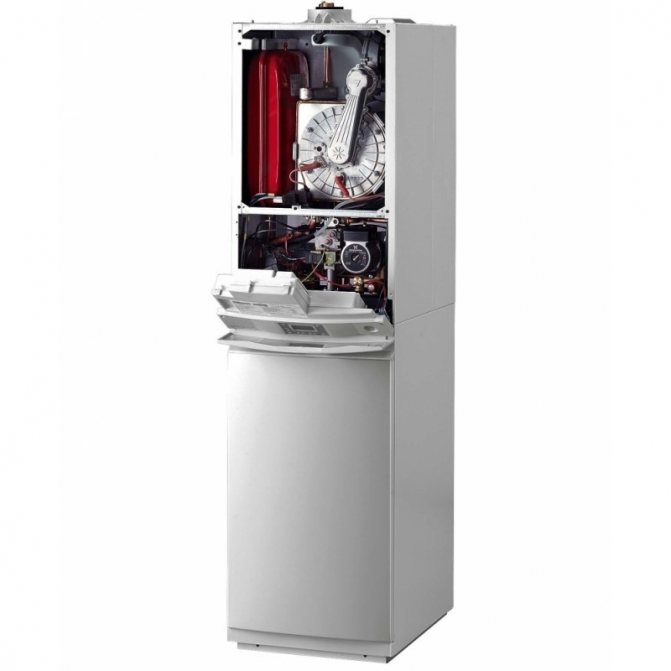
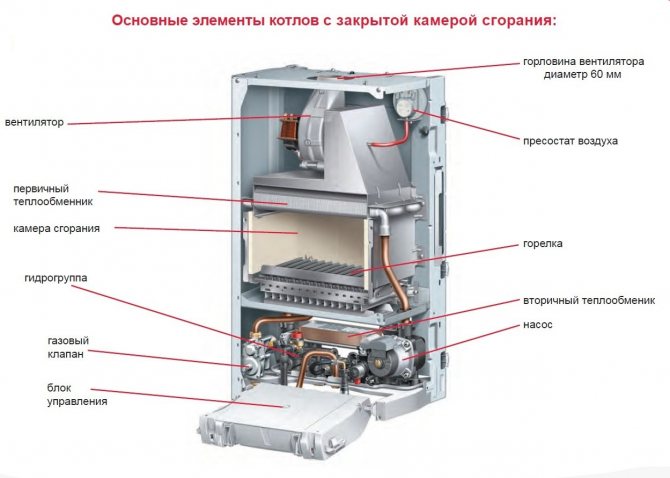
The device of the main components of the boiler
Condensing heating boilers consist of the following main components:
- a steel body in which all structural elements are located;
- a circulation pump for circulating water in the heat exchanger system;
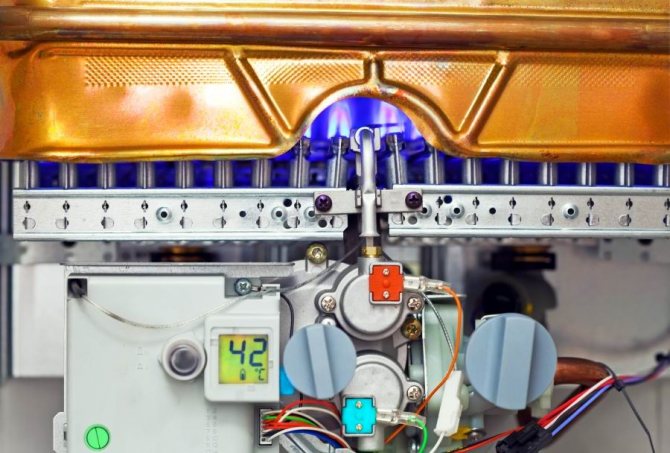
- combustion chamber, inside which burners are located;
- aftercooling chambers for the vapor-gas mixture to a temperature of + 570C;
- a fan (turbine) located above the combustion chamber, designed to mix the gas and air mixture;
- two heat exchangers: for transferring heat to water from the combustion products of the chamber and for condensation of moisture and obtaining thermal energy;
- nozzles and pipes for supplying water to the circulation system;
- condensate collection tank;
- chimney for removal of combustion products;
- control panel.
Double-circuit boiler or indirect heating boiler?
The owner of a private house or cottage almost always faces a problem with regard to obtaining hot water.
Previously, various systems for producing hot water were widely used for these purposes, but the most popular, from the point of view of practicality and economy, were primitive gas water heaters or, at best, bulky home-made indirect heating boilers.
What changed?
Gas water heaters in their design, reliability and convenience have stepped forward a lot. And, moreover, in some cases they have changed beyond recognition, turning into wall-mounted gas boilers, with an open combustion chamber that uses air from the room for combustion, or even closed, with outside air intake and forced smoke removal through a coaxial chimney. Excellent boilers working in fully automatic mode.
What is the difference between a double-circuit gas boiler and a gas water heater? The fact that in a double-circuit boiler there are two heat exchangers, one of which heats the heating medium of the heating system, and the other - water for household needs. Or they are collected in one heat exchanger, in which water from the heating system and domestic hot water move in opposite directions, then this single heat exchanger is called bithermal.
Such boilers are now very popular, they are simple, cheap and reliable. But in every seemingly ideal option, there is always a catch.
Double-circuit gas boilers have frankly weak performance in terms of generating hot water. Depending on the power, a double-circuit boiler is capable of continuously heating from 6-7 to 10-12 liters of hot water per minute at best. If the house has a kitchen sink and shower, this is quite enough. And if the family is large, there are two showers and there is also a bathtub - here it is already worth thinking, a double-circuit boiler may not be able to cope. No, one way or another it will give out the required hot water for some time, but during this time the water in the heating system may have time to cool down. In addition, if the heat exchanger is bithermal, when the boiler is switched to heating, the cooled water from the heating system will enter the heat exchanger, which is very heated by the preparation of hot water. Automation will notice an excessively large temperature difference and turn off the boiler, putting it into emergency mode until the heat exchanger cools down, and some models of gas boilers will also need to be turned on manually.
Another disadvantage of wall-mounted gas boilers that prepare water in heat exchangers is that the heat exchanger is heated directly by the burner flame. This is not a problem for a heating heat exchanger, since oxygen has already been removed from the water, the salts and minerals in the water during the initial filling have settled, the same prepared, "empty" water circulates. And the water from the water supply system used to prepare hot water carries more and more salts and minerals. Scale is inevitable. Over time, the heat exchanger needs to be flushed, and in some regions this time can be very short. Professional flushing of the heat exchanger with special chemicals is inexpensive and we successfully provide such services, but it must be done almost every year, and over time, a decent amount of money spent on flushing can accumulate.
What to do?
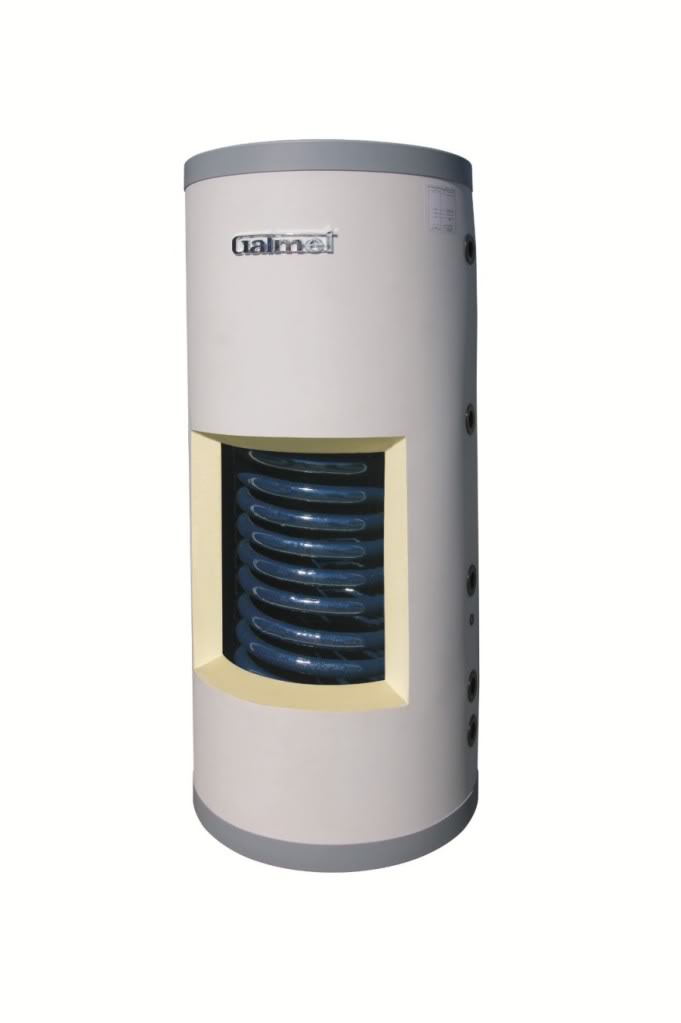
The indirect heating boiler is an ideal means of obtaining large volumes of hot water.
Removing heat from the heating circuit, powered by a separate branch from the distribution manifold, the indirect heating boiler, in a boiler-friendly mode, creates a large supply of hot water, always ready for use.High-quality thermal insulation made of solid foam or expanded polystyrene protects water from cooling for a long time. Thanks to the powerful and long heat exchangers built into the boiler tank, they are extremely efficient and capable of preparing really large volumes of water - showers, baths, and even a jacuzzi - all of which will be filled with a large, free head without overloading the boiler. In addition, in an indirect heating boiler, the water supply is heated by the heating circuit water, and not by the flame, no overheating zones are created on the walls of the heat exchanger tubes, and scale is formed much, much less!
Also, very often indirect heating boilers are equipped with an additional heating element and are able to operate without a boiler at all, during routine maintenance with the boiler or if necessary. Indirect heating boiler - hot water always. If you have a large family, several bathrooms, a bathroom, then an indirect heating boiler is your choice!
www.teplomir-nsk.ru
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of condensing boilers are the main criteria for choosing this particular design for heating systems. These include:
- environmental friendliness - the minimum amount of toxic emissions, for comparison, is on average 70% lower than gas or solid fuel;
- compact size, due to which they can be installed even in small rooms;
- low noise and absence of vibrations;
- relatively low temperature of the exhaust gases, which makes it possible to equip boilers with plastic chimneys and save finances;
- the possibility of a cascade installation, which allows heating large rooms or organizing heating systems of increased reliability;
- precise regulation of the heating power, thanks to which it is possible to change the efficiency of the condensing boiler and use it in economy modes.


Among the advantages of condensing boilers are their environmental friendliness and low noise.
When choosing, it is also important to take into account the disadvantages of boilers in order to avoid unnecessary fuel costs and ensure effective heating of the premises:
- high cost of equipment and spare parts for it;
- complex design of the heat exchanger, requiring periodic maintenance and condition monitoring;
- the need to dispose of condensate;
- high requirements for the cleanliness of indoor air;
- inefficiency of use at high temperature conditions.
That is, the disadvantages of condensing boilers are not so significant compared to their efficiency, durability, reliability and environmental friendliness, especially when they are used in residential premises.
Gas boiler operation with indirect gas
The covenik is a separate container, which can be equipped with both single-circuit and two-stage a gas boiler
... Single-stage devices are equipped with an indirect device to ensure the production of hot water supply, since these devices are designed exclusively for heat supply.
An additional tank is connected to double-circuit gas heating boilers, for example, if the volume of the built-in storage water heater or the productivity of the flow-through heat exchanger is not enough.
Pros and cons of boilers with indirect
The positive qualities of floor-standing gas boilers equipped with an indirect device are as follows:
- the probability of installing a non-volatile system;
- no need to buy real boiler.
The disadvantages of such heating devices include the following aspects:
- take up a lot of space;
- there may be difficulties when connecting the container to the boiler.


Types of condensing boilers
Condensing boilers are classified according to the following criteria:
- by type of installation: floor or wall;
- by the number of circuits: single or double circuit.
Condensing floor boilers are not only large in size, but can also be equipped with external pumps and other equipment that require a separate room for installation.They are usually single-circuit and are designed to heat large areas. Their advantages are maintainability and design simplicity.
Condensing wall-hung boilers differ from floor-standing boilers in their compact size and relatively low weight. All units and assemblies are located inside the body, there are no external elements. They are produced in one- and two-circuit design, are easy to connect, unpretentious in operation.


Floor standing single-circuit condensing boiler
Single-circuit heating boilers for space heating can be used not only in heating systems, but also for hot water supply, provided there is a boiler. They are distinguished by simplicity of design, low cost compared to a double-circuit boiler, high efficiency and heating power, economical fuel consumption.
The double-circuit condensing gas boiler is produced with a storage boiler or with a flow-through heat exchanger. It can be used for heating or heating water without the need to purchase a separate boiler. Compact, easy to install and maintain, floor or wall mounting.
Condensing boilers rating
The rating of condensing boilers is allocated by manufacturer and model, depending on the type of construction: wall-mounted or floor-standing.
The most common wall-mounted types of boilers:
- De Dietrich PMC-M 24/28 MI Plus is a double-circuit hinged boiler with cast, alloyed aluminum, a heat exchanger and a plate for connection to a hot water supply, and an 8 l expansion tank. The heating power is 6.1-24 kW, the largest heating area is 248 m 2, the weight of the structure is 29 kg.
- Ariston Genus Premium Evo 30 is an elite-class double-circuit boiler equipped with radial and plate heat exchangers, weather-dependent automation. It is calculated for a power of 3.3-30 kW and an area of premises up to 311 m 2, the weight of the structure is 35 kg.
- Viessmann Vitodens 100-W is a double-circuit boiler with a very technologically advanced Inox Radial heat exchanger and a secondary plate type for hot water supply, modulated by a Matrix burner in the range from 20% to 100%. Power range - 11-35 kW, calculated for area up to 350 m 2, weight 44 kg.
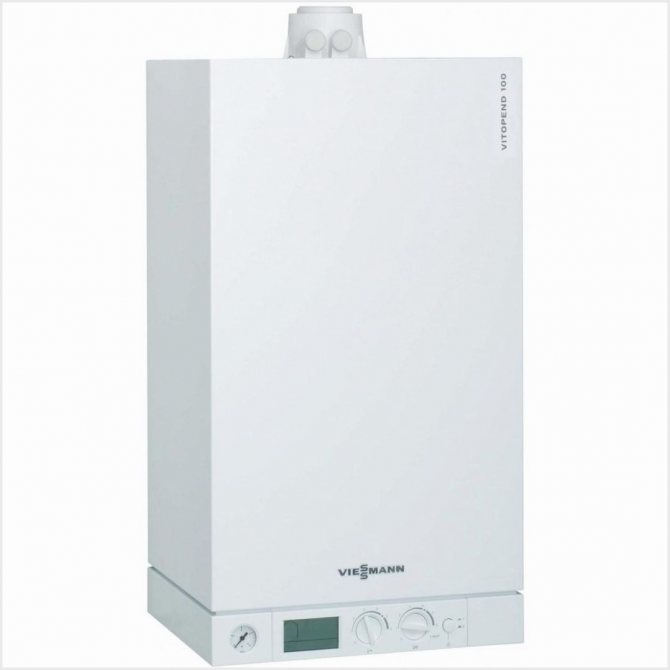


Boiler
condensing type Viessmann Vitodens 100-W
Rating of common floor boilers:
- Vaillant ecoVIT VKK INT 366 is a 34 kW single-circuit boiler designed for heating rooms up to 340 m 2. Equipped with digital control system DIA-System, electronic ignition and modulating burner. Designed for heating and hot water production.
- Viessmann Vitogas 100-F GS1D870 is a single-circuit boiler equipped with an open firebox, a reliable and durable ignition system with premixing, precise automation. Designed for a power of 29 kW and a heated area of 300 m 2.
- Buderus Logano G234 WS-38 is a 38 kW single-circuit boiler designed for heating rooms up to 380 m 2. The design is thermally insulated, supports the connection of additional automation, is durable and reliable in operation. Designed for heating and water heating for hot water supply.
The installation of condensing boilers in modern heating systems is considered quite cost-effective, even without paying attention to their high price. They are not hazardous to work, undemanding in maintenance, maintainable, productive and versatile in use. are considered an excellent alternative to direct fired boilers due to their high efficiency and economical gas consumption.
Criterias of choice
Condensing gas boiler, due to its high cost, must be chosen most carefully based on the following criteria:
- it is recommended to purchase certified equipment from well-known brands that can guarantee full compliance with the declared characteristics, as well as provide a guarantee and service;
- heating power should be enough to heat a certain area of the room, taking into account the temperature difference inside and outside buildings, as well as the length of communications with the coolant;
- installation method, depending on the amount of space and technical conditions for the operation of the boiler;
- a complete set, which may not include expensive accessories or components, without which it is impossible to connect and operate the boiler;
- functionality, methods and ease of management;
- the possibility of connecting an additional heating circuit;
- the level of gas and water consumption.
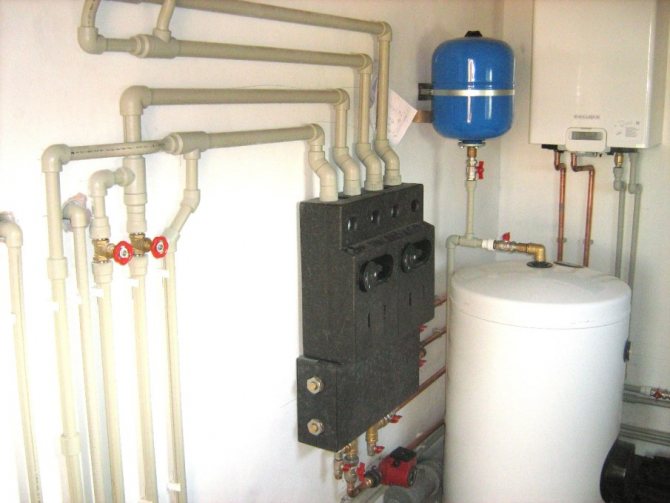
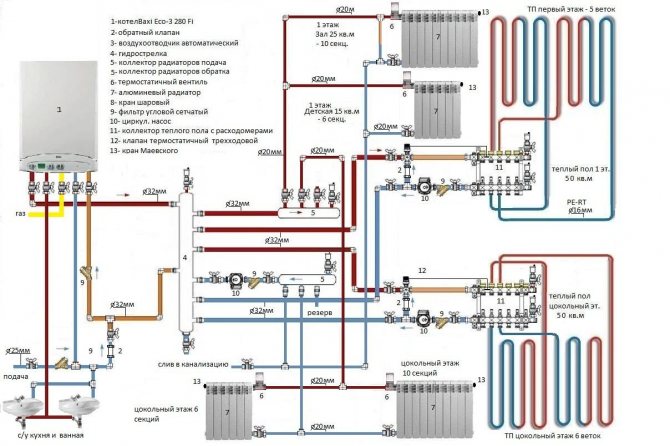
Connection diagram


A gas boiler with an indirect heating boiler, the connection diagram of which must be considered by the master, allows you to solve problems expressed in an insufficient amount of hot water. This is possible thanks to a full-fledged boiler, which has an additional electric heating insert. This solution will keep the temperature at a certain level.
To connect, you need to know that the system assumes the presence of a protective magnesium electrode, polyurethane foam insulation, a metal vessel with an enamel coating, as well as a coil that acts as a heating element. The external boiler for the boiler should be connected according to the diagram to the circulation pump.
Areas of use
The areas of application of condensing boilers are as follows:
- for heating apartments and private houses;
- for industrial purposes: heating of workshops or hot water supply;
- heating of office premises, public places.
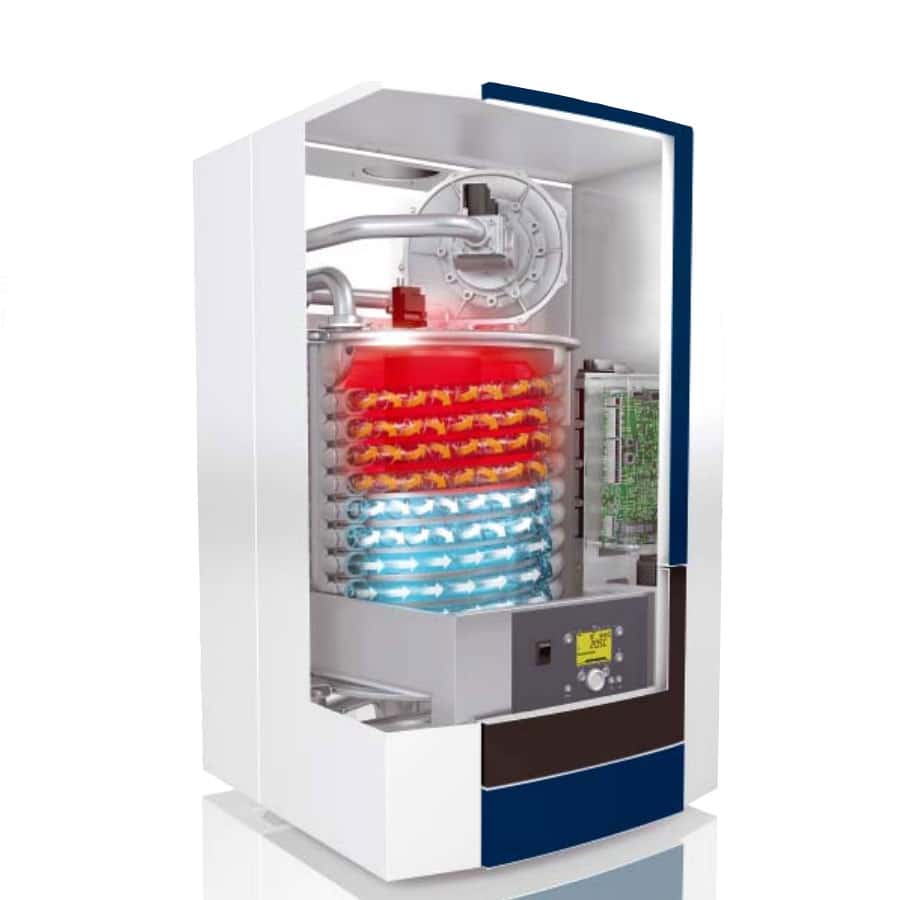


The condensing boiler is often used to heat apartments and private houses.
Reviews of gas boilers with storage type boiler


If you want to purchase a gas boiler with a boiler, then you must be guided by the volume of the external storage tank. If he is ready to give out about 14 liters of water per minute, then this, according to buyers, is considered quite a good indicator. However, this is not always enough. Suspended heat generators are limited in size, so large vessels are not installed in them. After all, it is the volume of heated water in stock that will determine the performance of the hot water supply system. In addition, consumers note that the weight of the structure with water will eventually turn out to be such that no wall can withstand it.
Choosing a gas boiler with a boiler, you can come across models that have storage tanks, but in this case, consumers claim that the dimensions of the device will be significant.
Condensing boiler installation rules and common installation errors
The installation of the condensing boiler must be carried out taking into account the following rules and requirements:
- it is recommended to choose a well-ventilated room for installing the boiler that meets all fire safety requirements: ceiling height not less than 2.2 m, room volume - from 7.5 m3, ventilation window area 0.025 m2;
- the location of the boiler must be strictly vertical;
- before mounting, it is important to mark the installation site in order to bring the necessary communications in advance and think over the installation steps;
- you need to mount the boiler on a special frame that is included in the delivery set (only for the highest class of equipment), or on a mounting plate;
- the chimney must be made of heat-resistant plastic or corrosion-resistant steel;
- the horizontal part of the chimney from the boiler should go with a slight slope towards the room;
- Condensate drainage can be organized in the following ways: to a centralized sewer system or to a separate container with subsequent disposal.
Connecting a condensing boiler without experience in carrying out such work can lead to the following errors:
- Condensate drainage is made outside the heated space. In the cold period of the year, this can be fraught with the formation of an ice plug in the tube, as a result of which the probability of failure of the boiler will increase.
- Condensate drainage is carried out into a container not intended for these purposes or is not organized at all.This is a big mistake, as the condensate can contain toxic or corrosive substances that require special disposal.
- The structure touches the heated part of easily flammable or combustible substances, which leads to a violation of fire safety rules.
- The gas connection is made without the use of special sealing gaskets, gas filters are not installed. The consequences can be as follows: gas leakage or clogging of the burner inside the combustion chamber, respectively. Operation with such errors is prohibited, as the level of explosion in the room increases.
- The angle of inclination of the boiler, which is specified in the installation requirements by the manufacturer, has not been observed. This will lead to a violation of the condensation and circulation modes, may cause an increased gas consumption or a decrease in heating power.
- Installation of a gas meter that does not correspond to the power characteristics of the boiler. In such cases, either the gas flow will be insufficient, or the meter itself will fail with the likelihood of leaks.
Features of operation
Some basic nuances of the operation of condensing boilers:
- it is forbidden to reduce the burner power below 10% of the total power, since due to constant switching on and off, it will fail much earlier than the calculated period;
- it is not recommended to increase the heating temperature at the outlet of the boiler above + 500С, as the gas consumption will significantly increase;
- condensate can be discharged into the sewer, subject to dilution in a ratio of 10: 1, and also into a septic tank, if it is neutralized.
Device
The design of floor-standing gas boilers differs only in the increased strength of units and parts. There are no fundamental differences.
The main elements are:
- Primary heat exchanger. This is the main unit in which the basic function of the boiler is performed - the heating medium is heated.
- Gas-burner. It is located directly under the primary heat exchanger and performs an equally important function - it is a source of thermal energy for heating the coolant.
- Secondary heat exchanger. Provides heating of hot water for domestic needs. There are different types of such units, designed for different performance and operating mode.
- Circulation pump. Present only in volatile installations. Provides the movement of the coolant through the system at a given speed.
- Turbocharger fan. Available only in closed boilers. Creates overpressure that forces smoke and combustion products outward.
- Gas equipment. Performs the functions of supply and timely shutdown of gas in case of emergency.
- Control board. Present only on volatile units. Performs the functions of monitoring the operation of all boiler units, ensures the stability of the heating medium heating mode, the operation of all other elements. Complete with it, a self-diagnosis system works - a network of sensors installed on all important parts of the unit and notifying the owner of any problems.
The process of functioning consists in the flow of the coolant from the return line of the heating circuit into the heat exchanger, heating it with a gas burner and supplying it to the system with the specified parameters.
At the exit from the primary heat exchanger, the coolant passes through the secondary unit, where it transfers part of the thermal energy to the water flow, heating it to the operating temperature.
Then the coolant enters the three-way valve, partially mixes with the colder return water and receives the required temperature, from which it enters the heating circuit.
Flue gases are discharged either naturally, using furnace-type traction, or under the influence of overpressure created by a turbofan. Its additional function is to provide an inflow of fresh air to support the combustion of the gas.
IMPORTANT!
The most common cycle of operation of a floor-standing gas boiler is described. There are other design options with some differences.