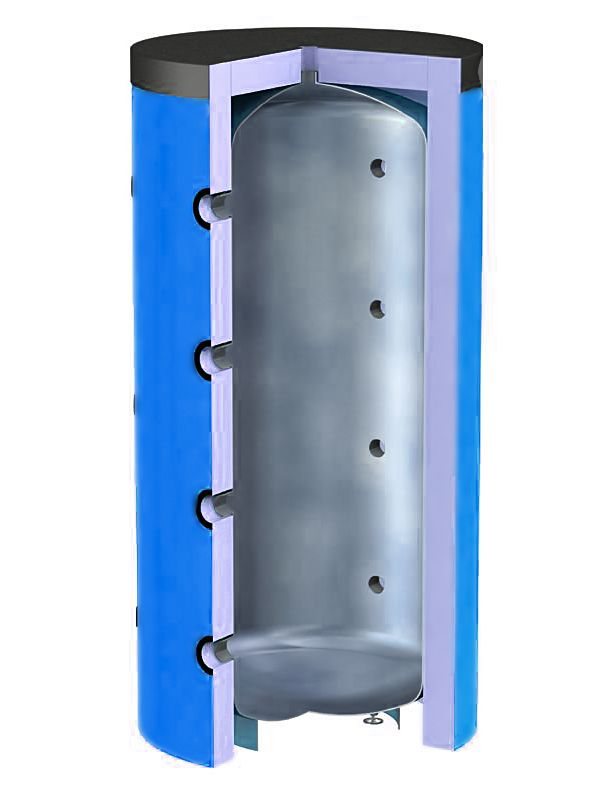
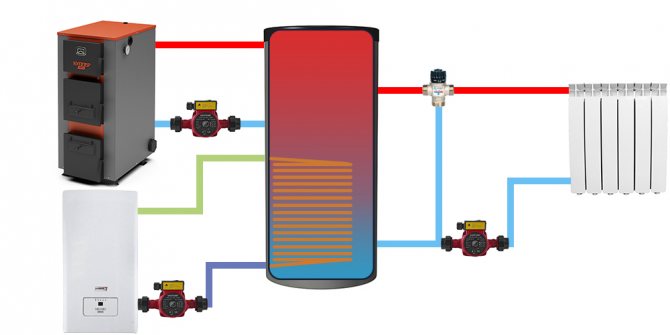
Features of installing heat accumulators
All installation work is carried out according to a previously approved project in accordance with the recommendations of the heating equipment manufacturer.
In this case, the features of the installation work should be taken into account:
- The surface of the storage tank must be insulated from heat loss without fail.
- Thermometers should be installed on pipelines through which water circulates (outlet and inlet).
- Accumulator tanks with a volume of more than 500 liters in most cases do not pass through the doorway. In such cases, you should use collapsible structures or install several batteries of a smaller volume.
- At the lowest point of the tank, the installation of a drainage channel will not interfere. It comes in handy when you have to completely drain the water.
- It is advisable to install strainers on the pipelines through which water enters the tank. They will prevent large inclusions from getting inside (scale from welding, minerals that have got into the system, etc.).
- If an air exhaust valve is not provided in the upper part of the container, then it should be installed at the upper point of the outlet pipe.
- A pressure gauge and a safety valve must be installed on the line next to the battery.
If you are the owner of a solid fuel boiler and have not yet purchased a heat storage device, think about it. You will not only extend the life of your heating equipment, but also significantly save on fuel.
TOP-2: HAJDU PT 300

Overview
The newest of the latest developments in the TOP-10 is given the 2nd place. The device stores heated water for a closed heating system. Compatible with boilers using various types of fuel for operation, with heat pumps and solar panels.
A floor-standing indirect heating water heater is connected to heating equipment, to gas boilers, for example. Water heats up during operation, accumulates in the tank and is used for domestic needs.
These boilers are installed directly on the floor and work together with other equipment, also installed on the floor or mounted on the wall.
Like the models already described, the model is needed to equalize the time difference in the accumulation and use of heat. The volume of the tanks can vary in the range of 300-1000 liters.
Parameters
- Country - Hungary;
- Height - 1595 mm;
- Weight - 87 kg;
- Tank with a volume of 300 liters.
Device
The heat exchanger is not included in the package of the buffer tank. No anti-corrosion layer is applied to the inner surface, which is why the tank can only be filled with water for heating.
Shroud
Artificial leather was chosen for its production. The dimensions of the device are such that they allow it to pass through the doorway without any problems.
Thermal insulation
Its quality is spoken of as exceptionally high. Thanks to this, the heat is stored in the accumulator for several days, which ensures uniform heating of the home.
Features of the
- Can be used for closed heating;
- Allows you to install heating elements;
- Easy to use and install.
- Simple installation and maintenance
- Renewable energy use
- Complies with European safety requirements
- Supplied without heat exchanger.
The cost
Functionality of heat accumulators
The principle of operation of the equipment is that during the operation of the boiler, part of the heat is used to heat the coolant from the additional tank. The connected tank has good thermal insulation and perfectly retains the received heat.After the boiler is turned off, the water in the heating system cools down, and the control devices turn on the pump supplying hot water from the storage tank.
These cycles continue as long as the water temperature in the additional tank remains high enough. The total operating time of the system without turning on the boiler depends on the volume of the additional tank. In practice, it allows you to heat rooms from several hours to 2 days.
The heat accumulator performs the following functions:
- It accumulates heat coming from the system boiler and releases it over time to heat the rooms in the room.
- Prevents the possibility of boiler overheating by taking away excess heat from the exchanger.
- Allows you to easily combine different heating devices (electric, gas, solid fuel) into a common system.
- Helps to improve the performance of heating equipment, reducing fuel consumption and improving efficiency.
- In systems with solid fuel boilers, it allows you to exclude constant monitoring of the state of heating equipment. Heating the coolant in an additional tank, homeowners can forget about the need to constantly load fuel into the boiler.
- It is a source of hot water for domestic needs.
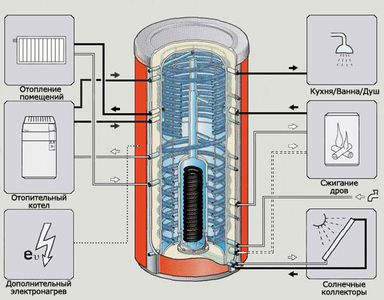
Heating system diagram
How profitable a heating system with a heat accumulator can be considered with this example.
Suppose that a 10 kW boiler is installed in the heating system. Every 3 hours it is necessary to load firewood. This does not fit into the plans of the homeowners in any way. In order to lengthen the intervals between loads, it is necessary to use a boiler with a higher capacity. But in this case, boiling of the coolant is possible, since the system will not have time to take away all the generated heat.
Connecting a heat accumulator with a capacity of about 200 liters solves the problem easily. The equipment allows to accumulate 110 kW of energy provided that the boiler is fully and frequently loaded. Subsequently, the accumulated heat will maintain a comfortable room temperature for about 10 hours. Boiler loading with fuel is not needed all this time.
Benefits of using a heat storage device
The peculiarity of the operation of solid fuel boilers is that the highest efficiency of fuel combustion is obtained in the nominal power mode. In this case, the coolant often heats up more than is required.


Excess heat can be stored using a storage tank to be used after stopping the boiler. The principle of operation is as follows:
- during the operation of the boiler, after the coolant has reached the desired temperature, the liquid is heated in an additional container;
- the accumulator tank, which has reliable thermal insulation, retains the incoming heat;
- after stopping the boiler and cooling the coolant in the system, the hot liquid from the heat accumulator is directed by the pump to the heating system.
If necessary, the boiler is started several times at high power until the required degree of water heating in the tank. After that, the heating system can function without turning on the boiler, as long as a sufficient temperature of the heating medium remains.

Depending on the volume of the heat accumulator and the area of the heated house, this process can last up to two days. In addition to the ability to reduce the frequency of regular fuel loads, the storage tank provides other advantages:
- retention of excess heat for later use;
- protection of the boiler from overheating;
- the possibility of parallel use of heating boilers of different types;
- increase in boiler efficiency;
- extending the service life of heating equipment;
- reduced fuel consumption;
- heating water for domestic needs.
Advice! The use of a backup storage tank reduces the limitation on hot water use during peak hours.
What is a heat accumulator buffer capacity and its purpose.
The purpose of the heat accumulator (TA) will be easier to describe using several example tasks.
The first task. The heating system is built on the basis of a solid fuel boiler. It is not possible to constantly monitor the temperature of the coolant at the supply and toss up firewood in time, as a result of which the supply temperature either exceeds the one we need, then it drops below the norm. How to maintain the required coolant temperature?
The second task. The house is heated with an electric boiler. Electricity supply is two-tariff. How to reduce energy costs by reducing energy consumption during the day and increasing at night?
The third task. There is a heating system in which heat is generated by heat generators operating on various types of fuel and energy - for example. gas, electricity, solar energy (solar collectors), earth energy (heat pump). How to ensure their efficient operation without loss of generated heat, when there is no need for it, while providing the house with heat during peak energy consumption?
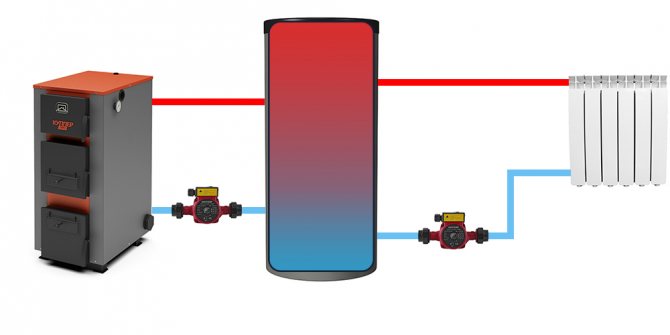
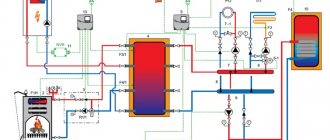
Not going too deeply into the theory of heat engineering, for all problems a solution suggests itself in the form of installing a buffer tank in the system, which would serve as a reservoir for the coolant and in which its temperature would be maintained at a given level. It is precisely such a buffer capacity that a heat accumulator is. To solve these problems, the heat accumulator is usually included "in the break" of the system with the formation of the boiler and heating circuits. A conventional diagram of the inclusion of a heat accumulator in the heating system is shown in the figure below.
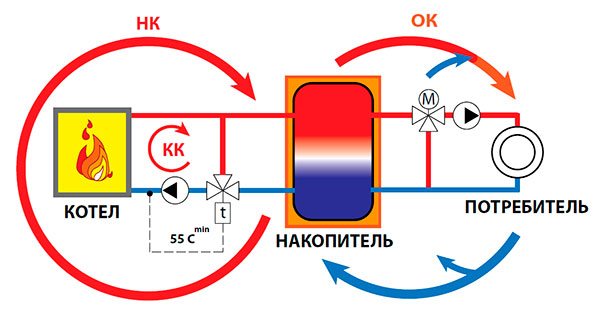

Fig. Schematic diagram of switching on a buffer tank (heat accumulator)
The various ways of connecting the buffer tank to the heating system can be found in the article "Heat accumulator connection diagrams".
Currently, heat accumulators are most often used in heating systems with solid fuel boilers. In these systems, the use of a heat accumulator makes it possible to load fuel less often, to provide a comfortable supply of heat regardless of fluctuations in the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the boiler. Often, buffer tanks are installed with electric boilers to save money due to a reduced night rate and in combined systems with the simultaneous use of solid fuel and electric boilers. A heat accumulator (TA) is useful in systems and with gas boilers, especially when the minimum heat output of the boiler exceeds the heat load of the facility. Due to the longer periods of "loading" of the TA (heating of the coolant), it is possible to avoid the "clock" of the boiler.
In addition to being used as a buffer tank, the TA performs the function of a low loss header. This property of the heat accumulator is especially in demand in systems with heat generators operating on different types of energy (including alternative). As a rule, these heat sources operate on special heat carriers that do not allow mixing with other types, require a unique temperature and hydraulic regime, which is often incompatible with the heating circuit modes (radiator, underfloor heating). For example, the temperature range of a heat pump is usually
5 ° C, and in the heat distribution loop the temperature range can be much larger (10-20 ° C). To separate the circuits, the heat accumulator can be equipped with additional built-in heat exchangers.
What is a buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler
A buffer tank (also a heat accumulator) is a tank of a certain volume filled with a coolant, the purpose of which is to accumulate excess heat power and then distribute them more rationally in order to heat a house or provide hot water supply (DHW).
What is it for and how effective is it


Most often, the buffer tank is used with solid fuel boilers, which have a certain cyclicity, and this also applies to long-burning TT boilers. After ignition, the heat transfer of the fuel in the combustion chamber rapidly increases and reaches its peak values, after which the generation of thermal energy is extinguished, and when it dies out, when a new batch of fuel is not loaded, it stops altogether.
The only exceptions are bunker boilers with automatic feed, where, due to a regular uniform supply of fuel, combustion occurs with the same heat transfer.
With such a cyclicity, during the period of cooling or attenuation, thermal energy may not be enough to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house. At the same time, during the period of peak heat output, the temperature in the house is much higher than the comfortable one, and part of the excess heat from the combustion chamber simply flies out into the chimney, which is not the most efficient and economical use of fuel.
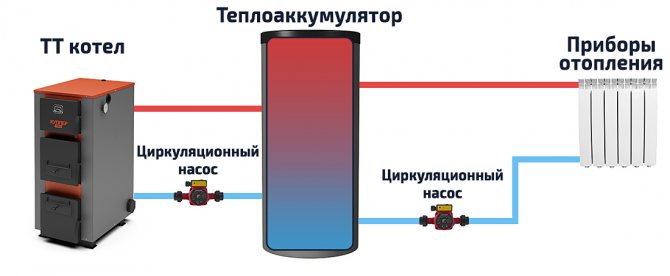

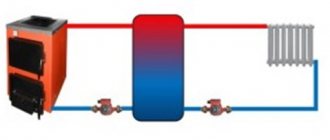
A visual diagram of the buffer tank connection, showing the principle of its operation.
The efficiency of the buffer tank is best understood on a specific example. One m3 of water (1000 l), when cooled by 1 ° C, releases 1-1.16 kW of heat. Let us take as an example an average house with a conventional masonry of 2 bricks with an area of 100 m2, the heat loss of which is approximately 10 kW. A 750 liter heat accumulator, heated by several tabs to 80 ° C and cooled to 40 ° C, will give the heating system about 30 kW of heat. For the aforementioned house, this is equal to 3 additional hours of battery heat.
Sometimes a buffer tank is also used in combination with an electric boiler, this is justified when heating at night: at reduced electricity tariffs. However, such a scheme is rarely justified, since in order to accumulate a sufficient amount of heat per night for daytime heating, a tank is needed not for 2 or even 3 thousand liters.
Device and principle of operation
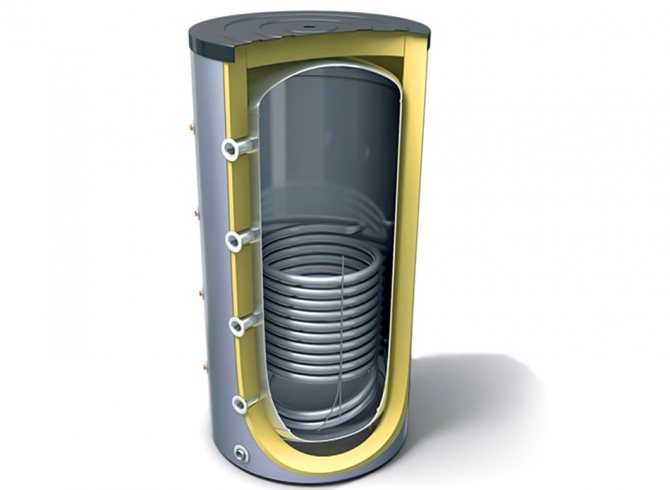


The heat accumulator is a sealed, as a rule, vertical cylindrical tank, sometimes additionally thermally insulated. He is an intermediary between the boiler and the heating devices. Standard models are equipped with a tie-in of 2 pairs of nozzles: first pair - boiler supply and return (small circuit); the second pair - the supply and return of the heating circuit, divorced around the house. The small circuit and the heating circuit do not overlap.
The principle of operation of a heat accumulator in conjunction with a solid fuel boiler is simple:
- After firing up the boiler, the circulation pump constantly pumps the coolant in a small circuit (between the boiler heat exchanger and the tank). The boiler supply is connected to the upper branch pipe of the heat accumulator, and the return to the lower one. Thanks to this, the entire buffer tank is smoothly filled with heated water, without a pronounced vertical movement of warm water.
- On the other hand, the supply to the heating radiators is connected to the top of the buffer tank, and the return is connected to the bottom. The heat carrier can circulate both without a pump (if the heating system is designed for natural circulation), and forcibly. Again, such a connection scheme minimizes vertical mixing, so the buffer tank transfers the accumulated heat to the batteries gradually and more evenly.
If the volume and other characteristics of the buffer tank for a solid fuel boiler are correctly selected, heat losses can be minimized, which will affect not only fuel economy, but also the comfort of the furnace. The accumulated heat in a well-insulated heat accumulator is retained for 30-40 hours or more.
Moreover, due to a sufficient volume, much larger than in the heating system, absolutely all the released heat is accumulated (in accordance with the boiler efficiency). Already after 1-3 hours of the furnace, even with complete damping, a fully "charged" heat accumulator is available.
Types of structures
| Photo | Buffer tank device | Description of distinctive features |
| Standard, previously described buffer tank with direct connection at the top and bottom. | Such designs are the cheapest and most commonly used. Suitable for standard heating systems where all circuits have the same maximum allowable operating pressure, the same heat carrier, and the temperature of the water heated by the boiler does not exceed the maximum allowable for radiators. |
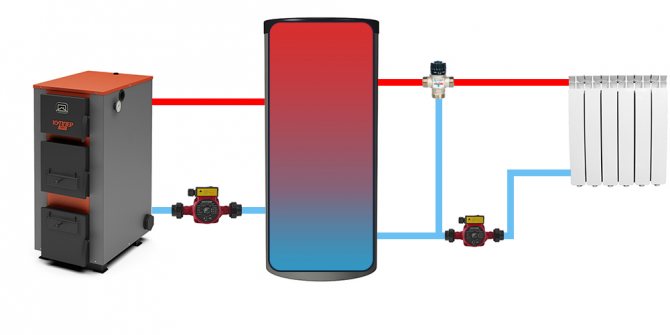
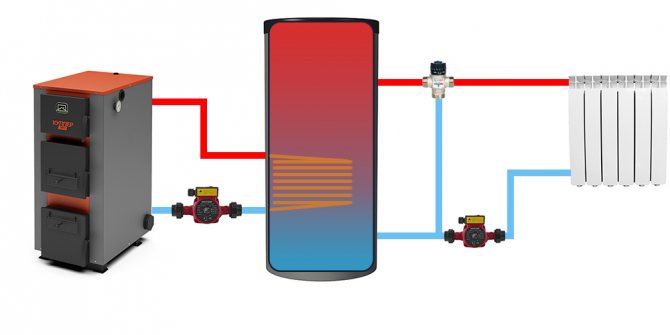
| Buffer tank with an additional internal heat exchanger (usually in the form of a coil). | A device with an additional heat exchanger is necessary at a higher pressure of a small circuit, which is unacceptable for heating radiators. If an additional heat exchanger is connected with a separate pair of nozzles, an additional (second) heat source can be connected, for example, TT boiler + electric boiler. You can also separate the coolant (for example: water in the additional circuit; antifreeze in the heating system) | |
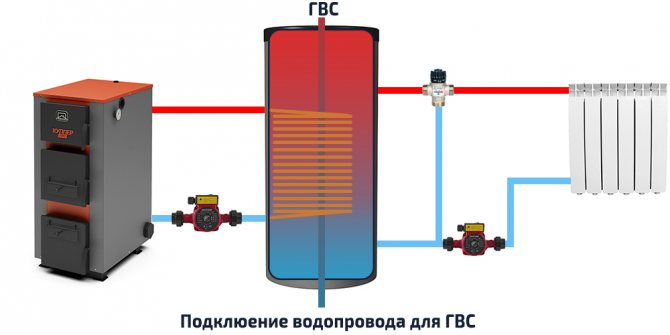
| Storage tank with an additional circuit and another circuit for DHW. The heat exchanger for hot water supply is made of alloys that do not violate sanitary standards and requirements for water used for cooking. | It is used as a replacement for a double-circuit boiler. In addition, it has the advantage of almost instantaneous hot water supply, while a double-circuit boiler requires 15-20 seconds to prepare it and deliver it to the point of consumption. |
| The design is similar to the previous one, however, the DHW heat exchanger is not made in the form of a coil, but in the form of a separate internal tank. | In addition to the benefits described above, the internal tank removes the limitations in hot water capacity. The entire volume of the DHW tank can be used for unlimited simultaneous consumption, after which time is required for heating. Usually, the volume of the internal tank is enough for at least 2-4 people bathing in a row. |
Any of the above types of buffer tanks can have a larger number of pairs of nozzles, which makes it possible to differentiate the parameters of the heating system by zones, additionally connect a water heated floor, etc.
How to calculate the volume of a heat accumulator
If desired, it is easy to find methods for calculating the volume of a heat accumulator on the Internet, but none of them suited me.
Some "experts" recommend multiplying the maximum power of the existing boiler in kilowatts by some coefficient, and this coefficient on different sites differs twice or more - from 25 to 50. In my opinion, this is complete nonsense. Simply because the result obtained has nothing to do with your particular home, or your wishes for how often you want to heat the boiler.
A normal technique takes into account all factors: the climate in your area, and the thermal insulation of the house, and your ideas about comfort. In an amicable way, this calculation will also need to be carried out many times for different temperature conditions, and select the maximum volume of the heat accumulator. And, by the way, the power of the boiler in the correct method is obtained as a result of calculations, and not according to the principle "what it was, it was delivered like this." But all this is quite complicated, and is more suitable for boiler rooms, and not for private households.
I did it much easier. I did the calculation of the heat accumulator for a solid fuel boiler as follows.
- It is necessary to estimate the amount of heat required by the house per day. This is the most difficult and responsible part of the job. Again, you can delve into the calculations (in textbooks for construction universities, you can find all the necessary techniques). But, if possible, it is easier and more reliable to carry out a direct measurement - simply by heating the house in cold weather and measuring the amount of fuel used. My house is relatively small - a little less than 100 sq. m, and quite warm. Therefore, it turned out that at an outside temperature of about 0 degrees, to maintain a comfortable temperature, 50 kW * h is required with a solid margin, for - 10 degrees - 100 kW * h, for - 20 degrees - 150 kW * h.
- Choosing a boiler is very simple. The most common boilers have a power of about 25 kW and from one maximum load give this power for about 3 hours. Therefore, one kindling gives about 75 kWh of heat. For zero temperature, therefore, even one full load will be too much for me. And for -20 degrees, it will be enough to heat 2 times a day. I was quite satisfied with this option.
- Now the actual volume of the heat accumulator. The heat capacity of water is 4.2 kJ per liter per degree. the maximum temperature in the heat accumulator is 95 degrees, the comfortable temperature of the water in the heating system is 55 degrees. That is, 40 degrees of difference. In other words, 1 liter of water in a heat accumulator can store 168 kJ of heat, or 46 Wh. And 1000 liters, respectively - 46 kWh. It follows that in order to keep the heat from one full load of the boiler, I need a heat accumulator for 1500 liters. This is all with a margin. In fact, it takes a little less, but after studying the prices for buffer tanks, I decided to ignore this.
This calculation means that in severe frosts I have to heat the boiler twice a day, and in very severe frosts three times. Moreover, this should be done evenly throughout the day: in the morning and evening or in the morning, at the beginning of the evening and before bedtime. And when there is no big frost, I fire the boiler only once - at any time of the day.
Of course, if you put an even larger heat accumulator, you can make your life even more comfortable. But here we already have to face the fact that a large barrel needs a lot of space.
Advantages and disadvantages
A heating system with a heat accumulator, in which a solid fuel plant serves as a heat source, has a lot of advantages:
- Improving the comfort conditions in the house, since after the fuel has burned out, the heating system continues to heat the house with hot water from the tank. There is no need to get up in the middle of the night and load a portion of firewood into the firebox.
- The presence of a container protects the boiler water jacket from boiling and destruction. If the electricity is suddenly cut off or the thermostatic heads installed on the radiators cut off the coolant due to reaching the desired temperature, then the heat source will heat the water in the tank. During this time, the electricity supply may resume or the diesel generator will be started.
- The supply of cold water from the return pipeline to the red-hot cast-iron heat exchanger after a sudden start of the circulation pump is excluded.
- Heat accumulators can be used as hydraulic dividers in the heating system (hydraulic arrows). This makes the operation of all branches of the circuit independent, which gives additional savings in thermal energy.
The higher cost of installing the entire system and the requirements for the placement of equipment are the only disadvantages of using storage tanks. However, these investments and inconveniences will be followed by minimal operating costs in the long term.
We recommend:
How to make heating in a private house - a detailed guide How to choose an expansion tank for a heating system How to choose and connect a membrane expansion tank
Calculation of the capacity of the heat accumulator
The calculation methodology can be different depending on the application scheme. Here is a rough calculation chart:
- Determination of the maximum fuel load. For example, the firebox holds 20 kg of firewood. 1 kg of firewood is able to release 3.5 kWh of energy. Thus, when burning one bookmark of firewood, the boiler will give 20 3.5 = 70 kWh of heat. The time it takes for a complete bookmark to burn can be determined empirically or calculated. If the boiler output is, for example, 25 kW 70: 25 = 2.8 h.
- Heat carrier temperature in the heating system. If the system is already installed, it is enough to measure the temperature at the inlet and outlet and determine the heat loss.
- Determination of the desired download frequency. For example, loading is possible in the morning and in the evening, but there is no way to service the boiler during the day and night.
Calculation of the heat accumulator
If, for an hour, the heat loss of a room, for example, is 6.7 kW, then per day it will be 160 kW. In this example, this is slightly more than two fuel fillings. As it was defined above, one tab of firewood burns for about 3 hours, releasing 70 kWh of thermal energy.
The need for heating the house is 6.7 3 = 20.1 kWh, the storage tank reserve will be 70-20.1 = 49.9, that is, approximately 50 kWh. This energy will be enough for a period of 50: 6.7 - this is about 7 hours. This means that two full snacks and one incomplete one are required per day.

Based on these calculations, having considered several options, we stop at this: at 23 o'clock, an incomplete load is made, at 6.00 and 18.00 - full. If you draw a graph of the charge level of the heat accumulator, you can see that the maximum charge falls on 60 kWh at 9 am.
Since 1 kWh = 3600 kJ, the reserve should be 60 3600 = 216000 kJ of thermal energy. The temperature reserve (the difference between the maximum water indicator and the required flow rate) is 95-57 = 38 ° С. Heat capacity of water 4.187 kJ. Thus, 216000 / (4.18738) = 1350 kg. In this case, the required volume of the heat accumulator will be 1.35 m3.
The considered example gives a general idea of how the storage tank capacity is calculated. In each individual case, it is necessary to take into account the peculiarities of the heating system and the conditions of its operation.
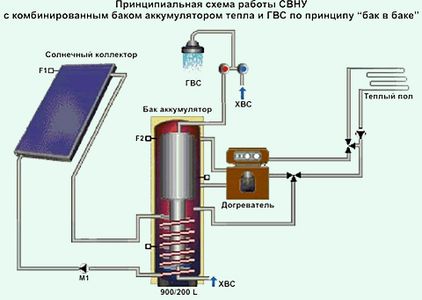

Features of installing a heat accumulator
Before installing the equipment, a detailed design must be drawn up. It is necessary to take into account all the requirements of manufacturers of heating equipment. When installing the storage tank, the following rules must be observed:
- The surface of the container must have reliable thermal insulation.
- Thermometers should be installed at the inlet and outlet to monitor the temperature of the water.
- Bulky tanks most often do not fit into the doorway. If it is not possible to bring in the tank before the end of construction, you will have to use a collapsible version or several smaller tanks.
- A coarse filter is desirable on the inlet pipe.
- A safety valve and a pressure gauge should be installed near the tank. There should also be an air vent valve in the tank itself.
- It must be possible to drain the water from the tank.
The use of a heat accumulator in a system with a solid fuel boiler increases the efficiency of the heat generator and its service life, and also allows more economical fuel consumption. Possibility of less frequent loading of fuel makes the use of the heating boiler more convenient for the consumer. The calculation of the required capacity of the storage tank should take into account the type of boiler, the characteristics of the heating system and the conditions of its operation.
Despite the simplicity of the device, and the obvious benefits of using heat accumulators, this type of equipment is not yet very common. In this article we will try to talk about what a heat accumulator is and the advantages that it brings with its use in heating systems.
Heat accumulator connection diagram
The way of connecting the heat accumulator to the heating system is given on page 19 of the "Stropuva" boiler passport. The buffer tank is connected according to the following principle:
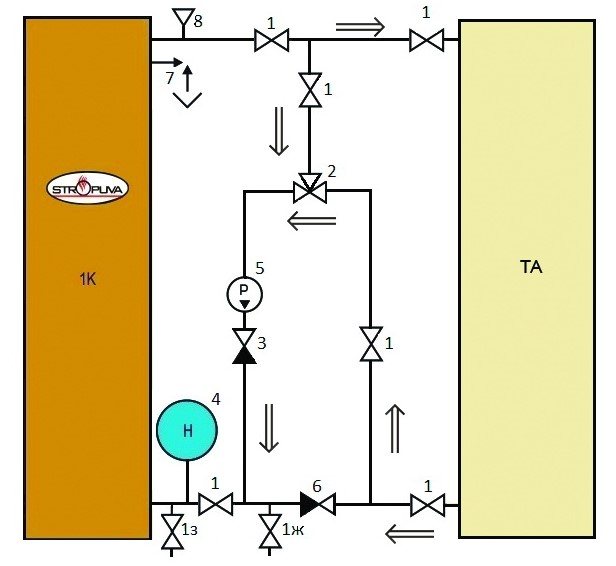

The boiler circuit is always connected to the heat accumulator in parallel, that is, the supply pipe is connected from the top, and the return pipe is connected from the bottom. At the same time, in order to prevent the supply of cold coolant to the boiler, the circuit is equipped with an admixture block (mixing unit).
The mains pump circulates the heating medium in the system, and the boiler circuit pump serves to pump the return flow into the boiler.For normal loading of the heat accumulator and simultaneous heating of the radiators, the coolant flows inside the buffer tank must move horizontally. To be able to control this process, temperature sensors are installed at both return inputs to the tank. The flow regulation is carried out manually using a balancing valve. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the temperature at the inlet of the return to the tank is lower than at the outlet.
Application of heat accumulators
There are several methods for calculating the volume of a tank. Practical experience shows that, on average, 25 liters of water are required for each kilowatt of heating equipment. The efficiency of solid fuel boilers, which includes a heating system with a heat accumulator, increases to 84%. By leveling the combustion peaks, up to 30% of energy resources are saved.
When using tanks for domestic hot water supply, there are no interruptions during peak hours. At night, when the needs are reduced to zero, the coolant in the tank accumulates heat and in the morning again provides all the needs in full.
Reliable thermal insulation of the device with foamed polyurethane (polyurethane foam) helps to maintain the temperature. Additionally, it is possible to install heating elements, which helps to quickly "catch up" the desired temperature in case of emergency.
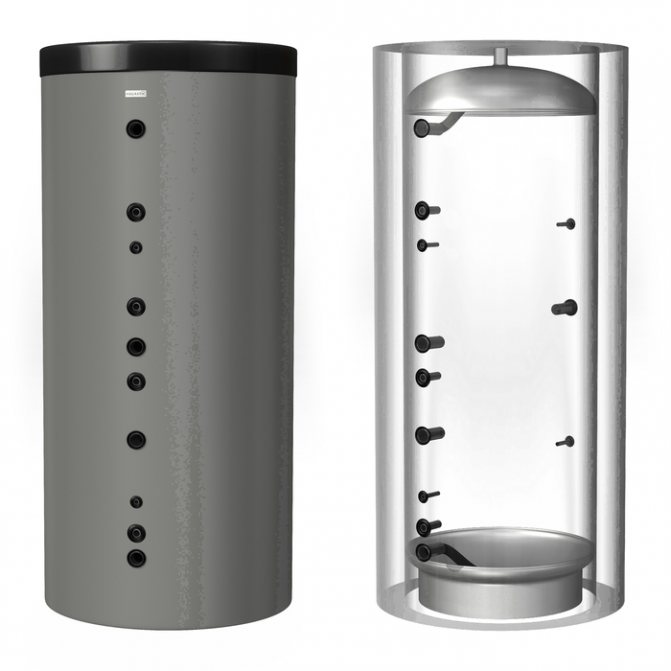
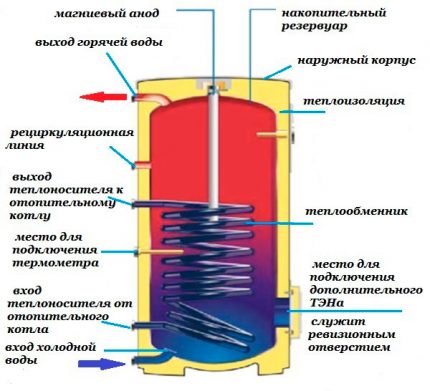
Sectional view of the heat accumulator
Heat storage is recommended in cases:
- great need for hot water supply. In a cottage, where more than 5 people live, and two bathrooms are installed, this is a real way to improve living conditions;
- when using solid fuel boilers. Accumulators smooth the operation of heating equipment in the hour of the greatest load, take away excess heat, preventing boiling, and also increase the time between filling solid fuel;
- when using electric energy at separate tariffs for daytime and nighttime;
- in cases where solar or wind batteries are installed to store electrical energy;
- when using circulation pumps in the heat supply system.
This system is perfect for rooms heated with radiators or underfloor heating. Its advantages are that it is able to store energy from different sources. The combined power supply system allows you to choose the most optimal option for generating heat for a given period of time.
Features of the design of the heat accumulator
The device is a cylindrical container made of stainless steel or black steel. The dimensions of the container depend on its volume, which varies from several hundred to tens of thousands of liters. Due to the large volumes, such a device is difficult to place in an existing boiler room, so it often has to be completed. There are models both with factory thermal insulation and containers without it.
When installing the heat accumulator, it must be borne in mind that the thickness of the insulation is 10 cm. After it, a leather casing is put on the top of the tank. Inside the tank there is a coolant, which, when fuel is burned in the boiler, heats up quickly and retains heat for a long time due to a layer of insulation. After stopping the operation of the boiler, the accumulator gives off its heat to the room, heating it. For this reason, the boiler will not need to be fired up as often as before.


According to their design, the capacities of the heat accumulator are:
- with a boiler located inside. This design was created to provide housing with hot water from an autonomous source;
- with one or two heat exchangers;
- empty (no coolant).
Threaded holes are provided for connecting the storage device to the boiler and the heating system of the house.
Varieties of heat storage models
All buffer tanks perform almost the same function, but have some design features.
Manufacturers produce storage units of three types:
- hollow (without internal heat exchangers);
- with one or two coilsensuring more efficient operation of equipment;
- with built-in boiler tanks small diameter, designed for the correct operation of an individual hot water supply complex for a private house.
The heat accumulator is connected to the heating boiler and the communication wiring of the home heating system through the threaded holes located in the outer casing of the unit.
How does a hollow unit work?
The device, which has neither a coil nor a built-in boiler inside, belongs to the simplest types of equipment and is cheaper than its more "sophisticated" counterparts.
It is connected to one or several (depending on the needs of the owners) power supply sources through central communications, and then through the 1 ½ branch pipes it is wired to the points of consumption.
It is planned to install an additional heating element operating on electrical energy. The unit provides high-quality heating of residential real estate, minimizes the risk of overheating of the coolant and makes the operation of the system completely safe for the consumer.


When a residential building already has a separate hot water supply system and the owners do not plan to use solar heat sources to heat the room, it is advisable to save money and install a hollow buffer tank, in which the entire usable area of the tank is given to the coolant, and is not occupied by coils
Heat storage unit with one or two coils
A heat accumulator equipped with one or two heat exchangers (coils) is a progressive version of equipment for a wide range of applications. The upper coil in the structure is responsible for the selection of thermal energy, and the lower one carries out intensive heating of the buffer tank itself.

A device equipped with heat exchangers has a higher price than a hollow unit, but the costs are justified here. The device significantly expands the functionality of the system and makes its work much more efficient
The presence of heat exchange units in the unit allows you to receive hot water for domestic needs around the clock, to heat the tank from the solar collector, to warm up the house paths and to use the useful heat as efficiently as possible for any other convenient purposes.
Internal boiler module
The heat accumulator with a built-in boiler is a progressive unit that not only accumulates the excess heat generated by the boiler, but also ensures the supply of hot water to the tap for domestic purposes.
The internal boiler tank is made of stainless alloy steel and equipped with a magnesium anode. It reduces the hardness of the water and prevents the formation of limescale on the walls.


The owners choose the appropriate volume of the buffer tank on their own, but experts say that there is no practical sense in buying a tank less than 150 liters.
The unit of this type is connected to various energy sources and works correctly with both open and closed systems. It controls the temperature level of the operating heat carrier and protects the heating complex from overheating of the boiler.
Optimizes fuel consumption and reduces the number and frequency of downloads. Compatible with all solar collectors and can function as a substitute for a hydraulic pointer.
Background
It so happened that some time ago I bought a private house at some distance from civilization. The distance from civilization is mainly determined by the fact that there is no gas there at all. And the permitted power of the electrical connection does not provide the technical ability to heat the house with electricity.The only real source of heat in winter is the use of solid fuels. In other words, the house was equipped with a stove, which the former owner heated with wood and coal.
If someone has experience using the stove, then he does not need to be explained that this activity requires constant monitoring. Even in not too cold weather, it is impossible to put firewood in the stove once and “forget” about it. If you put too much wood on, the house will get hot. And after the fuel burns out, the house will cool down quickly anyway. Willy-nilly, to maintain a comfortable temperature, you need to constantly add a little firewood. And in severe frosts, the oven cannot be left unattended even for 3-4 hours. If you don't want to wake up in a cold room in the morning, be kind enough to go to the stove at least once a night ...
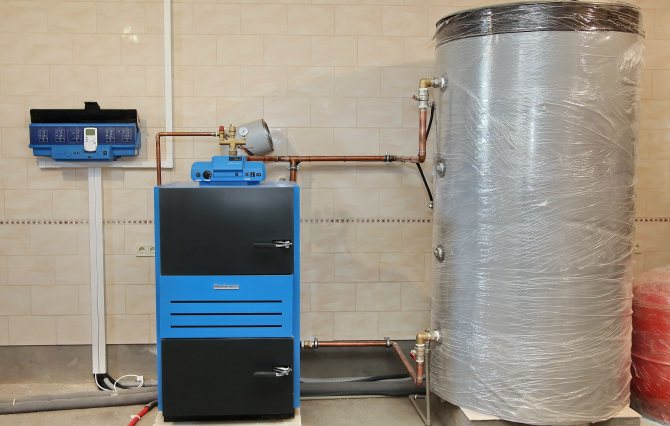
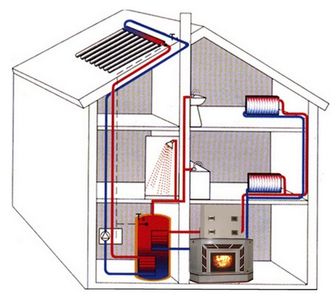
Of course, I had no desire to work as a fireman. And so I immediately began to think about a more convenient way of heating. Of course, if it was impossible to use gas or electricity, only a modern solid fuel heating system could become this way, consisting of a solid fuel boiler, a heat accumulator and the simplest automation for turning on and off the recirculation pump.
Why is a modern boiler better than a conventional stove? It takes up much less space, you can put more fuel in it, it provides better combustion of this fuel at maximum load, and theoretically it can be used to leave most of the heat in the house, and not be released into the chimney. But unlike a stove, a solid fuel boiler is practically impossible to use without a heat accumulator. I am writing about this in such detail, because I know many people who have tried to heat a house with such boilers, connecting them directly to heating pipes. They didn't do anything good.
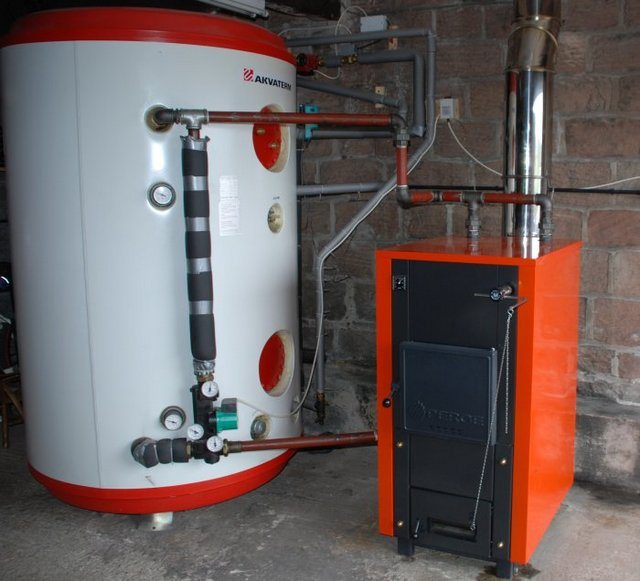
What is a heat accumulator or, as it is also called, a buffer tank? In the simplest case, it is just a large barrel of water, the walls of which have good thermal insulation. The boiler heats up the water in this barrel in two to three hours of its operation. And then this hot water circulates through the heating system until it cools down. As it cools down, the boiler needs to be fired up again. The simplest heat accumulator can be easily done by any welder. But I, after a short thought, abandoned this idea and bought a ready-made one. Since I live in Ukraine, I turned to and never regretted it: here accumulation tanks are made professionally and very efficiently.
Depending on the volume of the heat accumulator, the power of the boiler and how much heat the house needs, the boiler does not have to be heated constantly, but once or twice a day, or even once every two or three days.
Calculation of the volume of the buffer tank of the boiler
The most optimal solution to this problem will be the assignment of its implementation to heating engineers. Calculation of the volume of the heat accumulator for the entire heating system of a private house requires taking into account various factors known only to them. Despite this, preliminary calculations can be done independently. For this, in addition to general knowledge of physics and mathematics, you will need a calculator and a blank sheet of paper.
We find the following data
:
- boiler power, kW;
- active fuel combustion time;
- thermal power of heating the house, kW;
- Boiler efficiency;
- temperature in the supply pipe and "return".
Let's consider an example of preliminary calculation. The heated area is 200 m 2. The time of active combustion of the boiler is 8 hours, the temperature of the coolant during heating is 90 ° C, in the return circuit is 40 ° C. The estimated thermal power of the heated rooms is 10 kW. With such initial data, the heating device will receive 80 kW (10 × 8) of energy.
We calculate the buffer capacity of a solid fuel boiler by the heat capacity of water
:
where: m is the mass of water in the tank (kg); Q is the amount of heat (W); ∆t is the difference between the temperature of the water in the supply and return pipes (° С); 1.163 is the specific heat capacity of water (W / kg ° С) ...


Calculation of the buffer capacity of a solid fuel boiler
Substituting the numbers in the formula, we get 1375 kg of water or 1.4 m 3 (80,000 / 1.163 × 50). Thus, for a heating system of a house with an area of 200 m 2, it is necessary to install a TA with a capacity of 1.4 m 3. Knowing this figure, you can safely go to the store and see which heat accumulator is acceptable.
Dimensions, price, equipment, manufacturer are already easily identifiable. Comparing the known factors, it is not difficult to make a preliminary selection of a heat accumulator for a home. This calculation is relevant in the case when the house is built, the heating system has already been installed. The result of the calculation will show whether it is necessary to disassemble the doorways due to the dimensions of the TA. After evaluating the possibility of installing it in a permanent place, the final calculation of the heat accumulator for the solid fuel boiler installed in the system is made.
After collecting data on the heating system, we perform calculations using the formula
:
where: W is the amount of heat required to heat the coolant; m is the mass of water; c is the heat capacity; ∆t is the temperature of water heating;
In addition, you need the value of k - the efficiency of the boiler.
From formula (1) we find the mass: m = W / (c × ∆t) (2)
Since the boiler efficiency is known, we refine formula (1) and obtain W = m × c × ∆t × k (3) from which we find the updated mass of water m = W / (c × ∆t × k) (4)
Let's consider how to calculate a heat accumulator for a home. A 20 kW boiler is installed in the heating system (indicated in the passport data). The fuel tab burns out in 2.5 hours. To heat a house, you need 8.5 kW / 1 hour of energy. This means that during the burning out of one bookmark, 20 × 2.5 = 50 kW will be obtained
Space heating will consume 8.5 × 2.5 = 21.5 kW
Excess heat produced 50 - 21.5 = 28.5 kW is stored in the TA.
The temperature to which the coolant is heated is 35 ° C. (The temperature difference in the supply and return pipes. Determined by measurement during operation of the heating system). Substituting the sought values into formula (4), we obtain 28500 / (0.8 × 1.163 × 35) = 874.5 kg
This figure means that in order to store the heat generated by the boiler, it is necessary to have 875 kg of heat carrier. To do this, you need a buffer tank for the entire system with a volume of 0.875 m 3. Such lightweight calculations make it easy to choose a heat accumulator for heating boilers.
Advice. For a more accurate calculation of the volume of the buffer tank, it is better to contact a specialist.