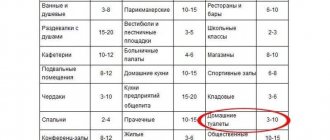
The air exchange rate in the premises of retail trade enterprises (stores)
| № | Premises | Estimated air temperature for the cold season, ° С | The rate of air exchange or the amount of air removed from the premises | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Sales areas of shops with an area of 400 m2 or less: | |||
| food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| non-food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| 2 | Sales halls of shops with an area of over 400 m2: | |||
| food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| non-food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| 3 | Cutting | 10 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | Unloading rooms | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 5 | Premises for preparing goods for sale (when placed in a separate room), picking, acceptance | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | Pantries (uncooled): | |||
| bread, confectionery; | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| gastronomy, fish, milk, fruits, vegetables, pickles, wine, beer, drinks; | 8 | — | 1 | |
| footwear, perfumery, household chemical goods, chemicals; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| other goods | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| 6.1 | Premises for the preparation of goods for sale (when placed in a separate room), picking, acceptance, expeditions | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | Premises for demonstration of new products (if placed in a separate room) | 16 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | Ironing | 16 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 9 | Waste chambers (unheated) | — | — | — |
| 10 | Room for mechanized pressing of paper waste | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| Storage rooms: | ||||
| 11 | packaging materials and inventory | 16(8) | — | 1 |
| 12 | exchange fund containers | — | — | 1 |
| 13 | containers | 8 | — | 1 |
| 14 | cleaning equipment, detergents | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| 15 | Linen | 18 | — | 0,5 |
| 16 | Workshops, laboratories | 18 | 2 | 3(2) |
| 17 | Refrigerated containment chambers: | |||
| meat, semi-finished products, gastronomy | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, confectionery, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| ice cream, dumplings, etc. | -12 | Periodically | ||
| food waste | 2 | — | 10 | |
| 18 | Air-cooled machine rooms | 5 | By calculation | |
| 19 | Water-cooled chilled chamber machine rooms | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 20 | Office premises, staff room, main cash desk, security room, ACS strong point | 18 | — | 1 |
| 21 | Dressing rooms, utility room for catering staff, dining room | 16 | — | 1 |
| 22 | Public toilets for shoppers and toilets for staff | 16 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet |
| 23 | Showers | 25 | — | 5 |
| 24 | Dispensary room (when the store is located in the underground floors) | 20 | — | 60 m3 / h per person |
| 25 | Premises for receiving and issuing orders | 12 | — | 1 |
| 26 | Glass container reception rooms | 16 | — | 1 |
| 27 | Health center | 20 | 1 | 1 |
Terms and Definitions
The following terms are used in this standard with the corresponding definitions:
3.1. bio-efluents: Contaminants from people, pets, birds, etc., such as odor, carbon dioxide, debris from the surface of the skin, hair, etc.
3.2. ventilation: Organized exchange of air in the premises to ensure the parameters of the microclimate and air purity in the serviced area of the premises within the permissible limits.
3.3. natural ventilation: Organized exchange of air in rooms under the influence of thermal (gravitational) and / or wind pressure.
3.4. mechanical ventilation (artificial): Organized exchange of air in rooms under the influence of pressure created by fans.
3.5. outdoor air: Atmospheric air taken in by the ventilation or air conditioning system for supply to the manned room and / or entering the manned room through infiltration.
3.6. supply air: Air supplied to the room by the ventilation or air conditioning system and entering the serviced room due to infiltration.
3.6. Exhaust air (outgoing): Air taken from the room and no longer used in it.
3.7. harmful (polluting) substances: Substances for which the maximum permissible concentration (MPC) has been established by the sanitary and epidemiological authorities.
3.8.harmful emissions: Streams of heat, moisture, pollutants entering the room and negatively affecting the microclimate parameters and air purity.
3.10. permissible indoor air quality (air cleanliness): Air composition in which, according to the definition of the authorities, the concentration of known pollutants does not exceed the MPC and to which more than 80% of people exposed to it have no complaints.
3.11. permissible microclimate parameters: Combinations of microclimate indicators values that, with prolonged and systematic exposure to a person, can cause a general and local feeling of discomfort, moderate tension of thermoregulation mechanisms that do not cause damage or health disorders.
3.12. odor: A sensation that occurs when gases, liquids or airborne particles are exposed to the receptors in the nasal mucosa.
3.13. infiltration: Unorganized air flow into the room through leaks in the building fences under the influence of thermal and / or wind pressure and / or due to the operation of mechanical ventilation.
3.14. concentration: The ratio of the amount (weight, volume, etc.) of one component to the amount (weight, volume, etc.) of the mixture of components.
3.15. place of permanent residence of people in the room: A place where people stay for more than 2 hours continuously.
3.16. microorganisms: Bacteria, fungi and unicellular organisms.
3.17. room microclimate: The state of the indoor environment of the room, characterized by the following indicators: air temperature, radiation temperature, movement speed and relative humidity in the room.
3.18. serviced area (living area): The space in the room, bounded by planes parallel to the fences, at a height of 0.1 and 2.0 m above the floor level, but not closer than 1.0 m from the ceiling with ceiling heating; at a distance of 0.5 m from the internal surfaces of external walls, windows and heating appliances; at a distance of 1.0 m from the distributing surface of the air distributors.
3.19. local suction: A device for capturing harmful and explosive gases, dust, aerosols and vapors at the places of their formation, connected to the air ducts of local ventilation systems and which, as a rule, is a part of technological equipment.
3.20. air purification: Removing pollutants from the air.
3.21. room that does not emit harmful substances: A room in which harmful substances are released into the air in quantities that do not create concentrations exceeding the MPC in the air of the served area.
3.22. room with constant presence of people: A room in which people are at least 2 hours continuously or 6 hours in total during the day.
3.23. premises with a massive presence of people: Premises (halls and foyers of theaters, cinemas, meeting rooms, conferences, lecture halls, restaurants, lobbies, checkout rooms, production facilities, etc.) with a permanent or temporary stay of people (except for emergencies), more than 1 person per 1 m2 of premises with an area of 50 m2 or more.
3.24. air recirculation: Admixing room air to outside air and supplying this mixture to this or other rooms.
Air exchange rate in the premises of public catering establishments
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Hall, dispensing | 16 | According to the calculation, but not less than 30 m3 / h per person. | |
| 2 | Lobby, entrance hall | 16 | 2 | — |
| 3 | Cooking shop | 16 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | Hot shop, confectionery baking room | 5 | By calculation, but not less than 100 m3 / h per person. | |
| 5 | Workshops: precooking, cold, meat, poultry, fish, processing of greens and vegetables | 18 | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | Production manager's premises | 18 | 2 | — |
| 7 | Premises for flour products and confectionery finishing, linen | 18 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | Room for cutting bread, for preparing ice cream, service, utility room | 18 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | Washing room: dining room, kitchen utensils, pans, containers | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | Director's office, office, main cash desk, rooms of waiters, staff, storekeeper | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 11 | Pantry for dry products, pantry for inventory, pantry for wine and vodka products, storage room for beer | 12 | — | 1 |
| 12 | Pantry of vegetables, pickles, containers | 5 | — | 2 |
| 13 | Reception | 16 | 3 | — |
| 14 | Engine room of refrigerated chambers with air-cooled units | By calculation | By calculation | By calculation |
| 15 | The same with water-cooled units | — | 3 | 4 |
| 16 | Repair shops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 17 | Premises of public organizations | 16 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | Refrigerated storage chambers: | |||
| meat | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| dairy products, gastronomy | 2 | — | — | |
| semi-finished products, including a high degree of readiness | 0 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, berries, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| confectionery | 4 | — | — | |
| wines and drinks | 6 | — | — | |
| ice cream and frozen fruits | -15 | — | — | |
| food waste | 5 | — | 10 | |
| 19 | Smoking room | 16 | — | 10 |
| 20 | Unloading rooms | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
Notes: 1. The air temperatures in rooms (except for refrigerated chambers) indicated in the table are calculated when designing heating systems.
2. In buffets, bars, cocktail halls, banquet halls located in separate rooms, the air ratio is taken as minus 3.
3. The air temperatures in the refrigerated chambers indicated in the table are maintained around the clock throughout the year. In chambers for the simultaneous storage of meat and fish or meat, fish semi-finished products, take temperatures ± 0 ° C; for vegetable semi-finished products +2 ° С; for storage of all products (1 chamber in the enterprise) ± 2 ° C.
Central air conditioners for ventilation of offices

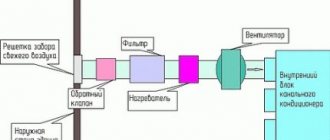
Central air conditioners are classified as industrial climatic technology. They are installed in accordance with SNiP and provide ventilation and air conditioning of office premises. In the air conditioner module, the air is brought to the required parameters of temperature and humidity. Air recirculation is carried out (mixing of waste and fresh air), including partial air recirculation. After processing, the air is supplied to the premises through the air duct system.
The advantage of central systems is the absence of internal modules. At the same time, the air conditioner itself is a rather bulky structure that requires a separate room. Air ducts are also needed quite voluminous. At the same time, the temperature throughout the building will be maintained at the same level.
Air flow rates for modulated equipment
| № | Equipment | Brand | kw | Air volume, m3 / h | |
| Exhaust | Supply | ||||
| 1 | Electric stove | PE-0.17 | 4 | 250 | 200 |
| 2 | PE-0.17-01 | 4 | 250 | 200 | |
| 3 | Electric stove | PE-0.51 | 12 | 750 | 400 |
| 4 | PE-0.51-01 | 12 | 750 | 400 | |
| 5 | Roasting cabinet | ShZhE-0.51 | 8 | 400 | — |
| 6 | ShZhE-0.51-01 | 8 | 400 | — | |
| 7 | ShZhE-0.85 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 8 | ShZhE-0.85-1 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 9 | Electric device, cooking | UEV-60 | 9,45 | 650 | 400 |
| 10 | Mobile boiler | KP-60 | — | — | — |
| 11 | Deep fryer | FE-20 | 7,5 | 350 | 200 |
| 12 | Cooking kettle with a capacity, l: | ||||
| 100 | KE-100 | 18,9 | 550 | 400 | |
| 160 | KE-160 | 24 | 650 | 400 | |
| 250 | KE-250 | 30 | 750 | 400 | |
| 13 | Steam cooking apparatus | APE-0.23A | 7,5 | 650 | 400 |
| APE-0.23A-01 | 7,5 | 650 | 400 | ||
| 14 | Electric frying pan | SE-0.22 | 5 | 450 | 400 |
| SE-0.22-01 | 5 | 450 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45-01 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| 15 | Steam table | ITU-0.84 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 |
| ITU-0.84-01 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 | ||
| 16 | Food warmer mobile | MP-28 | 0,63 | — | — |
Ventilation standards in warehouses
Warehouses are buildings designed to store certain goods and cargo. And the storage periods for the contents of the warehouse largely depend from its microclimate - temperature, mobility and humidity.
Combined and forced ventilation systems are used depending on the characteristics of the warehouse contents. Ventilation in the warehouse must completely replace air in an hour - this is a multiple of one.
For warehouses that store gasoline, kerosene, oils and volatile substances, and the staff is there temporarily, the multiplicity is 1.5-2, if it is constant - 2.5-5.
Warehouses with cylinders with liquefied gases and nitro varnishes - 0.5, when people are temporarily in it. In warehouses for storing flammable liquids, the multiplicity when people are temporarily there is 4-5, temporary - 9-10.In rooms for storing toxic substances, the hourly frequency is 5, while temporarily.
Frequency rate of air exchange in the premises of sports and recreation institutions
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Sports halls without seats for spectators (except for rhythmic gymnastics halls) | 15 | By calculation, but not less than 80 m3 / h per one practitioner | |
| 2 | Rhythmic gymnastics halls and choreographic classes | 18 | By calculation, but not less than 80 m3 / h per one practitioner | |
| 3 | Rooms for individual strength and acrobatic training, individual warm-up before the competition | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | Workshops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | Classrooms, methodological rooms, rooms for instructors and coaches, judges, press, administrative and engineering staff | 18 | 3 | 2 |
| 6 | Household premises of workers, employees of the protection of public order | 18 | 2 | 3 |
| 7 | Fire post premises | 18 | — | 2 |
| 8 | Outerwear dressing room for practitioners | 16 | — | 2 |
| 9 | Locker room (including massage rooms) | 25 | Balance taking into account showers | 2 (via showers) |
| 10 | Showers | 25 | 5 | 10 |
| 11 | Massage | 22 | 4 | 4 |
| 12 | Sanitary facilities: | |||
| common use | 16 | — | 100 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| for practicing (with dressing rooms) | 20 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| individual use | 16 | — | 25 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| 13 | Washrooms at public sanitary facilities | 16 | — | At the expense of sanitary facilities |
| 14 | Inventory at the halls | 15 | — | 1 |
| 15 | Storerooms and warehouses: | — | ||
| with the constant presence of service personnel; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| with a short stay of service personnel | 10 | — | 1 | |
| 16 | Warehouses for reagents, household chemicals and paints | 10 | — | 2 |
| 17 | Drying rooms for sportswear | 22 | 2 | 2 |
Determination of air exchange depending on the maximum permissible concentration of substances:
L = GCO2 / (UPDK-UP) (m3 / h)
Where GСО2 - the amount of released CO2, l / h, UPDC - the maximum permissible concentration of CO2 in the removed air, l / m3, UP - gas content in the supply air, l / m3.
| Standards of permissible concentration of СО2 in air, l / m3 | ||||
| In places of permanent residence of people (living rooms) | 1,0 | |||
| In hospitals and childcare facilities | 0,7 | |||
| In places of temporary residence of people (institutions) | 1,25 | |||
| In places of short-term stay of people (institutions) | 2,0 | |||
| In the outside air: | Settlements (village) | 0,33 | ||
| Small towns | 0,4 | |||
| Big cities | 0,5 | |||
Air exchange rate in the premises of a credit and financial institution
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1. | Operating and checkout rooms | 18 | Based on the assimilation of heat and moisture surpluses, but not less than twice the air exchange | |
| 2. | Shared work rooms, coin counters | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 3. | Room for meetings and negotiations | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 4. | Cashier for counting banknotes | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 5. | Computing facilities, computing center | 18 | Calculated for assimilation of heat and moisture surplus | |
| 6. | Communication room (teletype) and photocopying | 18 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 7. | Offices and receptions | 18 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 8. | Archive, pantry of forms, pantry of equipment and inventory, pantry of bank materials, room for storing personal belongings of cashiers | 18 | — | 1,5 |
| 9. | Repair shops | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 10. | Meal room, buffet | 16 | 3 | 4 |
| 11. | Room for storing weapons, loading and cleaning weapons | 16 | — | 1 |
| 12. | Boxes for collector cars | 18 | According to the design standards for parking garages | |
| 13. | Security premises with a fire station | 18 | 1 | 1,5 |
| 14. | Women's personal hygiene facilities | 23 | — | 5 |
| 15. | Sanitary facilities | 16 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet or urinal |
| 16. | Lobby | 16 | 2 | — |
| 17. | Wardrobes | 16 | — | 2 |
| 18. | Premises for placement of uninterruptible power supply sources | 16 | Calculated for assimilation of heat and moisture surplus | |
Air handling units in combination with VRF systems for the office
On large areas, the installation of duct equipment is difficult, therefore, maintenance of large buildings is carried out by supply and exhaust ventilation units for offices in combination with chiller-fan coil units and VRF systems.
The capacity of such equipment can reach 60 thousand cubic meters per hour. Ventilation and climatic equipment is installed on the roof of the building or in separate rooms.
The installation consists of many modules that are assembled depending on the needs of the enterprise and taking into account the norms of ventilation of offices. The kit may include:
- fan chamber;
- recuperator;
- noise absorber;
- mixing chamber;
- block with filters.
VRF- is a multi-zone climate system capable of maintaining the microclimate of an entire building. It is possible to differentiate the temperature in different rooms. In each room, an internal module is installed that keeps the temperature within the specified limits. There are no temperature changes typical for household air conditioners. Indoor modules can be of any type (floor, cassette, ceiling).
The chiller heats or cools the refrigerant ethylene glycol. Which is fed to the heat exchanger - fan coil unit with forced air movement. Fan coil units are located directly in the office rooms. In order for the coolant to move at a given speed, the system is complemented by a pumping station. Many offices and halls can be connected to one ventilation and air conditioning scheme. And not all at once, but as the need arises.
Air exchange rate in administrative and residential buildings
SNiP 2.09.04-87 *
| № | Premises | Temperature during the cold season | Frequency rate or volume of air exchange, m3 / h | |
| Inflow | Hood | |||
| 1. | Lobby | +16° | 2 | — |
| 2. | Heated passages | Not lower than by 6 ° C the design temperature of the rooms connected by the transitions | — | — |
| 3. | Streetwear wardrobes | +16° | — | 1 |
| 4. | Wardrobes for joint storage of all types of clothing with incomplete changing of workers | +18° | Based on the compensation of the hoods from the shower rooms (but not less than one air change in 1 hour) | According to clause 4.8 |
| 5. | Dressing rooms at showers (pre-showers), as well as with full dressing of workers a) dressing clothes | +23° | 5 | 5 |
| b) dressing rooms of home (street and home) clothes | +23° | Based on the compensation of the hoods from the shower rooms (but not less than one air change in 1 hour) | According to clause 4.8 | |
| 6. | Showers | +25° | — | 75 m3 / h for 1 shower net |
| 7. | Restrooms | +16° | — | 50 m3 / h for 1 toilet and 25 m3 / h for 1 urinal |
| 8. | Washrooms at latrines | +16° | — | 1 |
| 9. | Smokers | +16° | — | 10 |
| 10. | Rest, heating or cooling rooms | +22° | 2 (but not less than 30 m3 / h for 1 person. | 3 |
| 11. | Premises for personal hygiene of women | +23° | 2 | 2 |
| 12. | Premises for the repair of workwear | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 13. | Premises for shoe repair | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 14. | Premises for administrations, design bureaus, public organizations, with an area: a) no more than 36 m2 | +18° | 1,5 | — |
| b) more than 36 m2 | +18° | By calculation | ||
| 15. | Drying rooms for workwear | According to technological requirements within the range of 16-33 ° С | Also | |
| 16. | Dust collection rooms for workwear | +16° | « | |
Source: Administrative and domestic buildings SNiP 2.09.04-87 *
Air exchange rates in industrial premises


Local supply system in production
For buildings of an industrial type, a general exchange ventilation system is provided, the calculation of the needs of which is made based on the conditions of a specific production and the availability of a certain amount:
- heat;
- liquid or condensate;
- harmful particles.
If there is equipment with gas or vapor emissions in the room, the amount of required air exchange is calculated taking into account the emissions:
- from this equipment;
- laid communications;
- provided fittings.
All the necessary indicators are included in the technical documentation of the room, otherwise the data is taken from the actual parameters. This calculation is regulated by VSN21-77 and the corresponding SNiP.
Air exchange rate in health care facilities
| № | Name of premises | T, ° C | Air exchange rate | Room frequency category | Exhaust rate with natural air exchange | ||
| inflow | hood | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| I. | Hospitals, clinics, emergency and ambulance stations | ||||||
| 1. | Manipulation toilet for newborns | 25 | 2 | H | 2 | ||
| 2. | Manipulation with the use of chlorpromazine | 22 | 8 | 10 | D | not allowed | |
| 3. | Doctor's offices, staff rooms, rest rooms for patients using hydrotherapy and mud therapy, acupuncture rooms, discharge rooms, audiometry and anthropometry rooms, dispatch rooms for receiving calls and sending teams, a room for filling out documents, a rest room for dispatchers, doctors, paramedics, orderlies, drivers , mobile teams, medical statistics | 20 | influx from the corridor | 11 | H | 1 | |
| 4. | Angiography rooms, procedural X-ray diagnostic rooms, procedural and dressing rooms of fluorographic rooms, electrophototherapy rooms, massage | 20 | 3 | 4 | D | not allowed | |
| 5. | Undressing rooms at X-ray diagnostic rooms | 20 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 6. | Procedural for X-ray. dental pictures, washing laboratory glassware, pathological departments, control rooms of X-ray rooms and radiological departments, darkroom | 18 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 7. | Sterilization in operating rooms | 18 | — | 3 septic compartments | D | 2 | |
| 3 | aseptic departments | H | 2 | ||||
| 8. | Laboratories and rooms for the production of analyzes, rooms (rooms) for radiotelemetric, endocrinological and other research, rooms for receiving, sorting and taking samples for laboratory analyzes, assembly and washing rooms for an artificial kidney and rooms for a heart-lung machine, solution-demineralization, preparative laboratories, rooms for painting smears, weighing, colorimetric, medium cookers, material and apparatus laboratories, fixation, prescription, rooms for the preparation of dressing and operating materials and linen, control, collection and packaging of instruments, reception, disassembly, washing and drying of surgical instruments, syringes, needles , catheter, procedural rooms for treatment with neuroleptics, radio post, dictaphone center, current sterilization rooms, equipment room | 18 | — | 3 | see table. 3 | 2 | |
| 9. | Halls of medical physical culture | 18 | 50 m3 / h for one person engaged in the gym 80% | 100 % | D | ||
| 10. | Functional diagnostics rooms, rooms for sigmoidoscopy | 22 | — | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 11. | Physical therapy, mechanotherapy rooms, dental rooms, sounding rooms, rooms for deworming | 20 | 2 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 12. | Premises (rooms) for the sanitization of patients, showers, personal hygiene booths, premises for subaquatic, hydrogen sulfide and other baths (except for radon), rooms for heating paraffin and ozokerite, therapeutic swimming pools | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 13. | Premises for storing plaster bandages, plaster, museums and preparatory rooms with them in pathological departments, compressor inhalers, central linens, pantries of infected linen and bedding, pantries of household equipment, pantries for patients and ironing, instrumental and material, pantries of reagents and equipment in pathological anatomical departments, premises for the current repair of physiotherapy equipment, storage of boxes for mobile teams, the current stock of medicines, a pharmacy room, a pantry for a month's supply of medicines, a pantry of non-sterile materials and linen | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 14. | Sterilization rooms - autoclave central sterilization rooms: | 18 | by calculation | is allowed | |||
| a) clean compartment | 100 % | — | H | ||||
| b) dirty compartment | — | 100 % | D | ||||
| 15. | Premises for washing, sterilizing and storing ships, pots, washing and drying oilcloths, sorting and temporary storage of dirty linen, for storing cleaning items, premises for temporary storage of linen and solid waste contaminated with radioactive substances, pantries of acids and disinfectants, stretcher washing rooms and oilcloths, a room for drying clothes and shoes of mobile teams | 18 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| 16. | Receptions, information lobbies, dressing rooms, rooms for receiving parcels for patients, waiting room, storage rooms for warm clothes at verandas, pantries, canteens for patients, dispensers with a utility room in milk dispensing points, pantries for patients' clothes and clothes, medical archives | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 17. | Premises for processing rubber gloves, for washing and sterilizing table and kitchen utensils in pantry and canteen departments, hairdressing salons for serving patients, dummy | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 18. | Storage of radioactive substances, filling and washing in radiological departments, washing in laboratories | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | |
| 19. | Treatment rooms in rooms for static and mobile tele-gamma therapy, rooms for centralization in rooms for mobile tele-gamma therapy, procedural X-ray therapy rooms, microwave therapy rooms, ultra-high-frequency therapy rooms, thermotherapy rooms, rooms for wrapping up rooms for preparing solutions for radon sculpts, rooms for ultrasound treatment | 20 | 4 | 5 | D | » | |
| 20. | Dressing rooms and undressing rooms in hydrotherapy departments | 23 | inflow according to the balance of the exhaust from the halls with bathrooms, mud procedures | H | 2 | ||
| 21. | Corpse storage rooms | 2 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 22. | Premises for radon baths, mud treatment halls. shower room with a chair, mud treatment rooms for gynecological procedures | 25 | 4 | 5 | D | does not go down | |
| 23. | Premises for storing and reclaiming dirt | 12 | 2 | 10 | D | » | |
| 24. | Premises for dressing corpses, issuing corpses, storage rooms for funeral accessories, for processing and preparing for burial of infected corpses, premises for storing bleach | 14 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| 25. | Premises for disinfection chambers: | ||||||
| a) reception rooms; | 16 | from the clean compartment | 3 | D | » | ||
| b) dirty compartments: | from the clean compartment | 5 | D | » | |||
| c) unloading (clean) compartments | 5 | Through dirty compartments | |||||
| 26. | Hydrogen sulfide bath locks | 25 | 3 | 4 | H | not allowed | |
| 27. | Undressing rooms for hydrogen sulphide baths | 25 | 3 | 3 | H | » | |
| 28. | Room for the preparation of a solution of hydrogen sulfide baths and storage of reagents | 20 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 29. | Room for washing and drying sheets, canvases, tarps, mud kitchens | 16 | 6 | 10 | D | » | |
| 30. | Inhalation (procedural) | 20 | 8 | 10 | D | ||
| 31. | Sectional | 16 | — | 4 | D | 4 | |
| 32. | Gateways in front of the newborn wards | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 33. | Premises for discharge of puerperas and irradiation of children with a quartz lamp | 22 | — | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 34. | Bathrooms | 20 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet and 20 m3 for 1 urinal | D | 3 | |
| 35. | Washrooms | 20 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 36. | Enema | 20 | — | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 37. | Gateways in boxes and semi-boxes of infectious wards | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 38. | Small operating rooms | 22 | 10 | 5 | H | 1 | |
| 39. | Premises for hospital pharmacies (see section General self-supporting pharmacies) | ||||||
| Vivariums5) | |||||||
| 40. | Quarantine room for the entry of cars with animals. Reception with a warm vestibule | 16 | 1 | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 41. | Washing for dogs, cats, miniature pigs with bathtub and circular shower | 22 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 42. | Hot air dryer for dogs and miniature pigs | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 43. | Premises for keeping laboratory animals: 6) | ||||||
| a) mice | 20:22 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| b) hamsters | 20 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| c) guinea pigs | 14:16 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| d) rabbits7) | 5 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| e) dogs (with walking) | 14 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| f) cats | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| g) sheep (with access to the walk) | 5 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| h) dwarf pigs | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| i) roosters | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| 44. | Staff room | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 45. | Cell and inventory warehouse | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 46. | Examination of sick animals and disinfection | 20 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | |
| 47. | Large animal isolator | 15 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | |
| 48. | Premises for storage and preparation of disinfectants (with a fume hood) | 18 | according to technologists | D | 3 | ||
| 49. | Storing feed and bedding | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| Disinfection and washing department | |||||||
| 50. | Cleaning and washing inventory: | ||||||
| a) for manual washing; | 16 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | ||
| b) with a machine wash: | |||||||
| rough cleaning room | 16 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | ||
| washing | 16 | 5 | 6 | D | 2 | ||
| 51. | Sterilization and drying of equipment | 18 | by calculation | H | not allowed | ||
| 52. | Storing clean cages, racks, containers, feeders, stretchers, bedding | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 53. | Loading into cages of feed, water, bedding | 18 | — | 3 | D | 1 | |
| 54. | Temporary storage of animal corpses | 2:4 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| Department of keeping experimental animals | |||||||
| Block for keeping small laboratory rodents (mice, rats, guinea pigs) in conditions excluding the penetration of pathogenic flora8) Rooms of the barrier zone. | |||||||
| 55. | Compulsory sanitary inspection | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | not allowed | |
| 56. | Putting on sterile clothing: | 1 | |||||
| - clean area | 25 | by calculation | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 25 | » | D | » | |||
| 57. | Sterilization with steam autoclave | 18 | » | D | » | ||
| 58. | Germicidal hydraulic sluice: | 18 | 3 | H | » | ||
| - clean area | 18 | 3 | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 18 | 3 | D | » | |||
| 59. | Germicidal air lock | 18 | by calculation | H | » | ||
| Barrier area premises3) | |||||||
| 60. | Premises for keeping animals SViB and conducting experiments: | ||||||
| a) for mice | 20:22 | 15 | 10 | OCH | » | ||
| b) for rats | 18 | 15 | 10 | OCH | not allowed | ||
| c) for guinea pigs | 14:16 | 15 | 10 | OCH | » | ||
| 61. | Room for experiments | 20 | OCH | » | |||
| 62. | Staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 63. | Warehouse for sterile equipment, feed, bedding | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 64. | Distribution and distribution of feed | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 65. | Sterilizing water | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| Unit for keeping laboratory animals under normal conditions | |||||||
| 66. | Premises for keeping laboratory animals (except for rams) | on items 50a: 50i | |||||
| 67. | Rooms for experiments | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 68. | Surgical section premises: | ||||||
| a) preoperative with sterilization | 18 | 1 | 2,5 | H | not allowed | ||
| b) operating room, postoperative room, intensive care room for recovering animals | 20:22 | by calculation | OCH | — | |||
| 69. | Premises for infecting animals and working with them: | ||||||
| a) premises for toxicological studies | 18 | ||||||
| b) premises for infecting animals (manipulation, boxes for control animals) | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | ||
| c) personnel and specialists | 18 | — | 1,.5 | H | » | ||
| d) storage of clean: inventory, feed, bedding | 18 | — | 1 | D | » | ||
| e) waste collection | 10 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| Department of Veterinary Services | |||||||
| 70. | Doctor's office | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | |
| 71. | Sectional | 16 | 3 | 3 | D | » | |
| 72. | Laboratory diagnostics with an autopsy box | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | » | |
| 78. | Storage of medicines | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | not allowed | |
| 74. | Sick animal isolation unit: | ||||||
| a) room for patients with a gateway | on paragraphs 50a-50i | ||||||
| b) storage of feeders, cages, inventory, storage of bedding and feed | 10 | — | 1 | D | » | ||
| c) staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | ||
| d) cleaning items with a tap, ladder and drying | 10 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| Feed preparation department | |||||||
| 75. | Preparation of vegetables from the washing machine, preparation of grain mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 76. | Digestive hall | 16 | by calculation | » | |||
| 77. | Washing-kitchen utensils | 18 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 78. | Sterilization of feed | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | » | |
| 79. | Refrigerated food chamber | 2-4 | — | — | D | » | |
| II. General self-supporting pharmacies | |||||||
| 80. | Public service halls | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | 3 | |
| 81. | Work rooms or isolated work areas in the service hall, forwarding rooms for receiving and placing orders from the attached institution, prescription | 18 | 2 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 82. | Assistant, aseptic, defective, gateway; billet and filling with a sluice, seaming and control-marking sterilization-autoclave, sterilization distillation | 18 | 4 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 83. | Packaging, control and analytical room, washing, sterilization solutions, distillation and sterilization room, cocktail, unpacking | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 1 | |
| 84. | Premises for the preparation of dosage forms under aseptic conditions | 18 | 4 | 2 | OCH | not allowed | |
| 85. | General stock storage rooms: | ||||||
| a) medicinal substances, finished medicinal products, including thermolabile and medical supplies; dressings | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 1 | ||
| b) medicinal plant materials | 18 | 3 | 4 | D | 3 | ||
| c) mineral waters, medical glass and recyclable shipping containers, glasses and other optical items, auxiliary materials, clean dishes | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | ||
| d) poisonous drugs and drugs | 18 | — | 3 | D | 3 | ||
| 86. | Flammable and flammable liquids | 18 | — | 10 | D | 5 | |
| 87. | Disinfectants and acids, disinfection with sluice | 18 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| 88. | Administrative premises | on PP. 13, 19, 20, 25, 26, 44 of this table | |||||
| 89. | Refrigeration machine room | 4 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 90. | Electrical control room | 15 | — | 1 | |||
| SANITARY-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STATIONS (SES) | |||||||
| Radiological group | |||||||
| 91. | Laboratory room | 18 | 3 | 5 | D | not allowed | |
| 92. | Bacteriological group Premises for doctors and laboratory assistants study rooms | 18 | — | 1,5 | H | » | |
| 93. | Room for serological research, sowing, rooms for express diagnostics | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 94. | Boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | |
| 95. | Preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | |
| 96. | Entomology premises for helminthological research, environment | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 97. | Washing rooms | ||||||
| a) without washing machine | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) with a washing machine | 18 | 3 | 5 | D | » | ||
| 98. | Sterilizing autoclave | 18 | — | 3 | D | not allowed | |
| 99. | Thermal rooms | At the request of the technology The internal air temperature is provided by the technological equipment | |||||
| 100. | Rooms for receiving registration, sorting and issuing test results | 18 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| Virology Department and Laboratory of the Department of Highly Dangerous Infections | |||||||
| 101. | Rooms for the identification of respiratory, enteric viruses, for the preparation of tissue culture | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| d) boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| e) pre-boxes for preparation of tissue culture | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| 102. | Room for the identification of arboviruses: | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| 103. | Rooms for bacteriological research, rooms for processing traps and preparing baits, | 18 | 3 | 6 | D | » | |
| 104. | Rodent infestation rooms (bioassay) | 18 | 8 | 10 | D | » | |
| 105. | Corridors | 18 | By the balance of the branch | H | » | ||
| Dairy kitchens | |||||||
| 106. | Brewhouse | 5 | By calculation | D | » | ||
| 107. | Mashed potatoes workshop | 16 | 3 | H | » | ||
| 108. | Packing milk and juices | 16 | 2 | 3 | D | » | |
| 109. | Sterilization of finished products | ||||||
| a) "clean zone" | 16 | 6 | — | H | not allowed | ||
| b) "dirty zone" | 16 | — | 4 | D | » | ||
| 110. | Washing flasks | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 111. | Milk intake | 16 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| 112. | Biolact preparation | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 113. | Filtration and milk filling room | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 114. | Premises for heat treatment of milk and preparation of milk mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 115. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 116. | Room for the preparation of lactic acid products and lactic acid mixtures: | ||||||
| a) room for the preparation of starter cultures | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | ||
| b) kefir shop | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| c) shop for acidophilic milk | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| d) thermostatic | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | ||
| 117. | Premises for the preparation and packaging of cottage cheese | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 118. | Premises for the preparation of fruits, fruits, vegetables | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 119. | Premises for the preparation of fruit and vegetable mixtures | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 120. | Premises for preparation of fish, meat, preparation of fish and meat dishes | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 121. | Laboratory | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | » | |
| 122. | Premises for receiving containers for finished products | 16 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 123. | Premises for receiving raw materials | 16 | 3 | — | D | » | |
| 124. | Washing and sterilization room | 20 | 4 into the "clean" zone inflow | 6 exhaust - through the "dirty" area | D | » | |
| 125. | Washing kitchen utensils | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 126. | Washing room: | ||||||
| a) milk pipelines | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) inventory | 20 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 127. | Expedition loading | 16 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 128. | Refrigeration machinery room | 16 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| 129. | Temporary storage room | 12 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| milk | periodic ventilation | ||||||
| 130. | Dry food pantry | 12 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 131. | Pantry of vegetables and fruits | 4 | 4 (per day) | 4 (per day) | D | » | |
| 132. | Premises for storing and receiving containers | 12 | 4 | 6 | D | 1 | |
| 133. | Pantry of household equipment | 12 | 2 | 2 | D | » | |
| 134. | Linen | 16 | 2 | 1 | D | » | |
| 135. | Material pantry | 12 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| 136. | Chilled food waste chamber with a vestibule | 2 | — | 10 | D | not allowed | |
| 137. | Service and utility rooms | under section I of this table | |||||
| Donor point | |||||||
| 138. | Breast milk pumping room | 22 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 139. | Sterilization room | 18 | — | 3 | H | » | |
| 140. | Filtration and milk filling | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 141. | Heat treatment | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 142. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | |
| Milk distribution points | |||||||
| 143. | Handout | 16 | 2 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 144. | Refrigerating chamber (for finished products) | 2 | Periodic ventilation | ||||
| 145. | Premises for receiving and storing dishes from the population | 12 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 146. | Cashbox | 18 | — | 1 | H | » | |
| 147. | Pantry of disinfectant solutions and cleaning equipment | 16 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| Sauna | |||||||
| 148. | Expected | 18 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 149. | Corridor | 18 | — | 2 | H | ||
| 150. | Dressing room | 22 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 151. | Shower room | 22 | — | 8 | D | ||
| 152. | Steam room10) | 100/80 (85/80) | — | 5 | D | ||
| 153. | Cooling room inside the sauna | 1 | — | 4 | D | ||
| 154. | Restroom | 26 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 155. | Massage room | 25 | — | 4 | D | ||
| 156. | Solarium | 23 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 157. | Restroom | 22 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet | D | ||
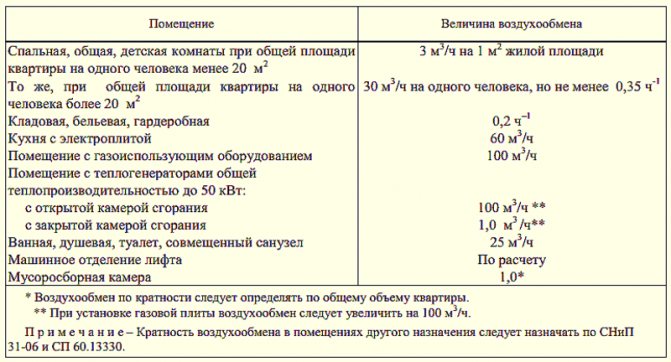
Air exchange rate in the premises of preschool organizations
| Premises | t ° (С) -not lower | Air exchange rate per hour | |||
| In IA, B, D climatic regions | In other climatic regions | ||||
| inflow | hood | inflow | hood | ||
| Reception, playroom nursery group cells | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Reception, play junior, middle, senior group cells | 21-23 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Bedrooms of all group units | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Dressing nursery groups | 22-24 | — | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Dressing preschool groups | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Medical premises | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Halls for muses. and gymnastics | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Walking verandas | not less than 12 | by calculation, but not less than 20 m3 per 1 child | |||
| Hall with pool bathroom | not less than 29 | ||||
| Locker room with shower pool | 25-26 | ||||
| Heated passages | not less than 15 | ||||
Values for different buildings
In order for people in a particular room to feel as comfortable as possible, it is necessary to observe the air exchange rates provided for by building codes and rules. They differ significantly for different buildings, so you should approach their selection with the utmost responsibility. Only in this case it is possible to achieve the desired result and create ideal conditions in the room for finding people.

For all residential buildings, it is required to ensure not only artificial, but also natural air flow. If one of them is not enough, then the use of the combined option is allowed. In this case, it is also necessary to ensure the removal of stagnant oxygen. This can be done by arranging ventilation ducts. from the following premises
:
- bathroom;
- restroom;
- kitchen.
The multiplicity of air exchange in a dwelling is indicated in SNiP 2.08.01−89. According to these norms, the indicator should be like this
:
- A separate room in the apartment (bedroom, children's room, playroom) - 3.
- Bathroom and private toilet - 25 (with a combined arrangement, the value should be 2 times more).
- Dressing room and washroom in the hostel - 1.5.
- Kitchen with electric stove - 60.
- Kitchen with gas equipment - 80.
- Corridor or lobby in an apartment building - 3.
- Ironing, drying, laundry in the hostel - 7.
- Pantry for storing sports equipment, personal and household items - 0.5.
- Elevator machine room - 1.
- Staircase - 3.
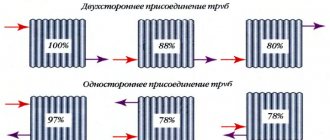
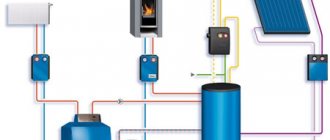
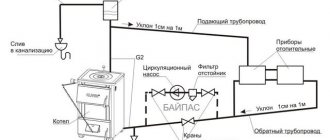
Calculation of air exchange in the boiler room (detailed analysis)
In office centers
The size of the air exchange rate index for administrative buildings and offices is much larger than for residential premises. This is due to the fact that the ventilation and air conditioning system must efficiently cope with heat emissions emanating not only from workers, but also from various office equipment. If the ventilation system is properly equipped, it is possible to improve the health and productivity of employees.
The main system requirements
:
- filtration, humidification, heating or cooling of air before it is supplied to the room;
- ensuring a constant supply of a sufficient volume of fresh oxygen;
- arrangement of an exhaust and supply ventilation system;
- the use of equipment that will not create a lot of noise during the air exchange process;
- the most convenient arrangement of installations for the convenience of carrying out repair and preventive measures;
- the ability to adjust the parameters of the ventilation system and adapt its operation to changing weather conditions;
- the ability to provide high-quality air exchange with minimal energy consumption;
- the need to have small dimensions.
For the correct setting of the air conditioning and ventilation system, it is necessary to accurately calculate the multiplicity and compare it with the norms of SNiP 31-05-2003, which envisage such importance
:
Production workshops
It is especially important to ensure good air exchange in industrial premises, where people work in the most harmful conditions. To reduce the negative impact on their health, it is necessary to properly equip the ventilation system and calculate the air exchange rate
On totals influenced by several main factors
:
The working capacity of an office worker directly depends on the indoor climate. According to medical research, the air temperature in the office should not exceed 26 degrees, while in practice, in buildings with panoramic windows and an abundance of equipment, it can go over 30 degrees. In the heat, the reaction of employees is dulled, fatigue increases. The cold also affects the ability to work badly, causing drowsiness and lethargy. Lack of oxygen and high humidity create unbearable conditions for employees, lowering labor productivity, and hence the profitability of the enterprise.
To maintain the optimal temperature and humidity conditions, an office ventilation system is installed.