Household and industrial stoves, fireplaces and chimneys perform their intended functions with the correct selection of material for their manufacture. Fireclay refractory bricks can successfully cope with a long-term high-temperature load, the production technology of which includes special methods of processing selected mineral raw materials.
There are several brands of heat-resistant brick products that differ in composition, some consumer properties, and sizes. When planning the construction of a stove, construction of a sauna, a fireplace, you need to deal with the assortment, make an order correctly, so as not to get into a mess.
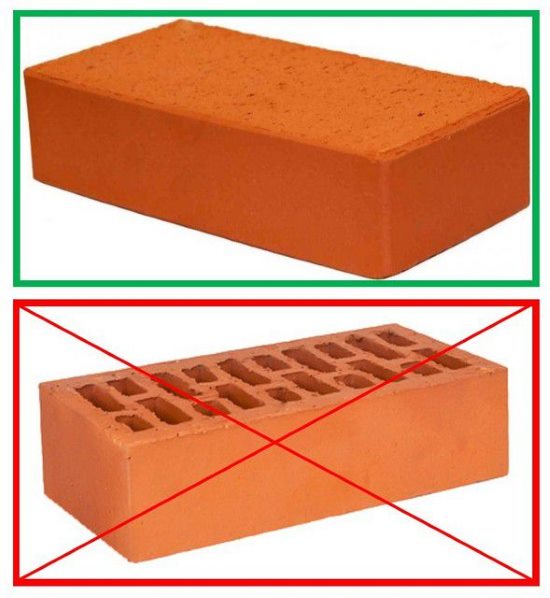
Which brick can not be used
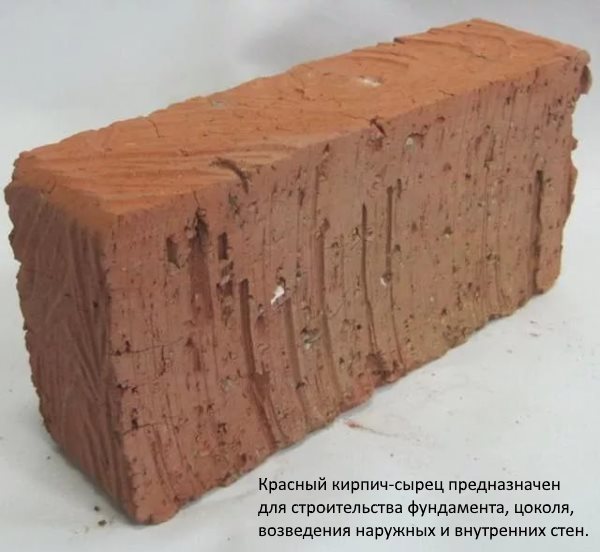

First, you need to decide what you should definitely not buy. A lot of complaints appear in all sources of information on the usual red brick raw. The claims are not entirely clear, because unfired products were not originally intended to be used as refractory bricks for fireplaces and any furnaces.
The structure resulting from the simplified formation of the raw mix and conventional drying allows moisture to easily penetrate. A brick made in this way, with temperature extremes, easily collapses, begins to crumble, does not meet the requirements for refractory materials.
Brick products made of silicates are highly hygroscopic; moreover, these products have low heat capacity and resistance to temperature extremes. Even with a sufficient thickness of the stove or fireplace masonry, silicates can quickly deteriorate, rendering the structure unusable.


It is not recommended to use a limestone brick made using the hyper-pressing technology as a heat-resistant material. When heated, limestone undergoes decarboxylation, as a result of which carbon dioxide is released. The resulting massif easily absorbs moisture, loses its mechanical strength, plasticity, quickly collapses during shrinkage and operation.


A large number of brick products are made by slip casting, during which the semi-liquid mass of the raw mixture is poured into molds and heated well. The resulting products have beautiful, precise shapes, suitable for outdoor decoration of ovens. The main part of the refractory masonry from slip bricks cannot be made due to the low mechanical strength.
How to choose quality oven bricks?
Before purchasing the material, it is important to study the characteristics, pros and cons. There are several positions for assessing quality:
- Appearance. You should pay attention to the size and shape, compare several copies from the same batch. No crumbling or debris is allowed.
- Color uniformity. A black or deep brown tint that appears on the garment indicates excessive scalding. A very light shade on the cut appears as a result of insufficient heat treatment.
- Sound. When tapping on a quality stone, a clear sound is heard. A muffled sound indicates a violation of the production technology.
- Internal structure of the heater. Splitting one specimen, the stove-maker estimates the porosity and density. The structure should be uniform and not crumble.
There are a huge number of fire-resistant stones on the building materials market, which have their pros and cons. It is better to take into account the advice of an experienced stove-maker in order to choose the right brick. Even an old brick will help not to violate the technology and invest in the budget.If the block keeps its shape well and has not been previously exposed to fire, it can be useful for laying some areas.
What bricks can be used


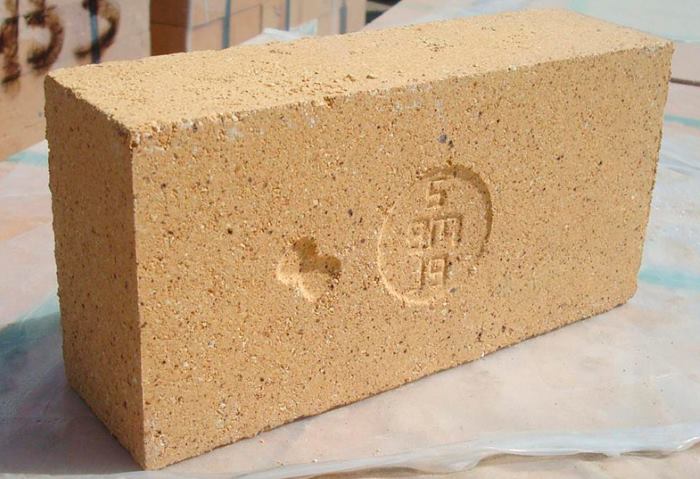
The intensive development of the construction services market has led to the emergence of a huge number of material manufacturers. Bricks are made by many enterprises, but a limited number of products have good fire-resistant properties.
Among the mandatory steps in the process of manufacturing refractory bricks, the following should be noted:
- the use of high-quality natural raw materials, including the best grades of clay;
- careful observance of the ratio of solid mass of a certain moisture content to the volume of added water;
- compliance with the mode of molding and firing, in accordance with the regulatory requirements of a particular technology;
- obtaining a homogeneous structure of the entire parallelepiped that does not contain air cavities.


The walls of the furnace are exposed to maximum heating, so they are laid out of fireclay refractory bricks... Some stove-makers make a firebox from quartz products.
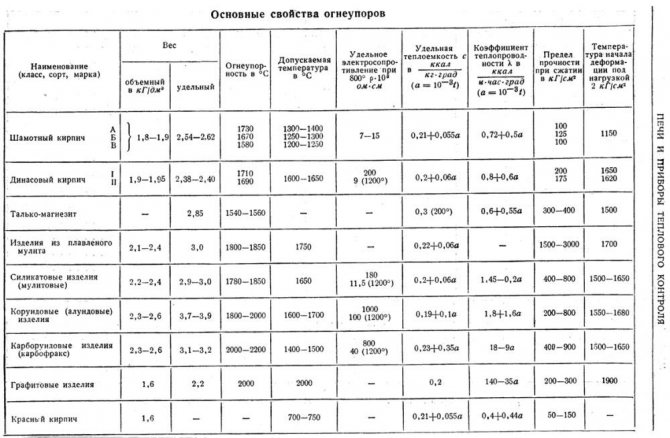
Table 1. Technical parameters of refractory bricks
| Indicator | Normal value for a given brick grade | ||||||
| SHAK | SHA | SB | ШВ | SHUS | PB | PV | |
| Refractoriness, ° C | 1730 | 1690 | 1650 | 1630 | 1580 | 1670 | 1580 |
| Porosity of products,% | 23 | 24 | 24 | — | 30 | 24 | — |
| Tensile strength, N / mm2 | 23 | 20 | — | 22 | 12 | 20 | 15 |
| Content of additives | |||||||
| Al2 O2 | 33 | 30 | 28 | 28 | 28 | — | — |
| Al2 O3 | — | — | — | — | — | 14 — 28 | 14 — 28 |
| SiO2 | — | — | — | — | — | 65 — 85 | 65 — 85 |
The master determines the required thickness of refractory bricks for the stove in each case, based on the quality of the fuel that will be used, the size of the stove or fireplace, and the area of the room as a whole.
The layers directly adjacent to the firebox, chimney channels are usually laid out of refractory ceramic bricks, which have sufficient heat resistance for these zones.


The facing surface of the furnace is mainly used for interior decoration, does not bear a significant thermal load, therefore, the requirements for its refractory qualities are very sparing.
The upper part of the chimneys above the roof is in specific conditions. Smoke that has not yet been completely cooled comes out through the internal channels, while outside the structure may be surrounded by frosty air.


Therefore, for the internal masonry of the chimney, refractory bricks are used, and the outside of the chimney is protected by masonry made of a material with minimal thermal conductivity. This approach will eliminate the formation of condensation and increase the durability of the outer part of the chimney.
Types of refractory bricks


A special material with pronounced refractory qualities is used both in everyday life and in production, especially in metallurgy and foundry. What is the classification of such a brick, depending on the raw materials from which it is made:
- Quartzite - brick, for the production of which fine-grained enriched quartz sand and certain types of clay are used. The mixed and formed mixture is subsequently fired in tunnel kilns;
- The main refractory or dinas is more than 90% composed of silicas associated with lime. The molded products are fired at a temperature of 1460 degrees Celsius and used for the construction of industrial furnaces: open-hearth, glass-making, for coke burning. In everyday life, such products are used extremely limitedly;
- Carbonaceous or graphite refractory is characterized by a rich dark color due to the inclusion of carbonaceous components, in particular graphite, in the molding mixture. Due to the specificity of its use in everyday life, it also did not receive distribution;
- Fireclay bricks are made on the basis of refractory clay - kaolin, and to improve certain operational qualities, additives are introduced into the formulation: zirconium, corundum and others. Due to the optimal ratio of price and high consumer qualities, it is very widely used in everyday life, in furnace construction.Withstands temperatures up to 1600 degrees, is resistant to open flames, is well processed into chamotte grits, which are used as part of a refractory mortar for laying and repairing sauna stoves. It differs in light color, from sandy to cream in the interpretations of shades, depending on the raw materials and the characteristics of the firing.
Main factors
When choosing a material, it is useful to know and take into account its basic characteristics, so that later when working, there are no unpleasant surprises.
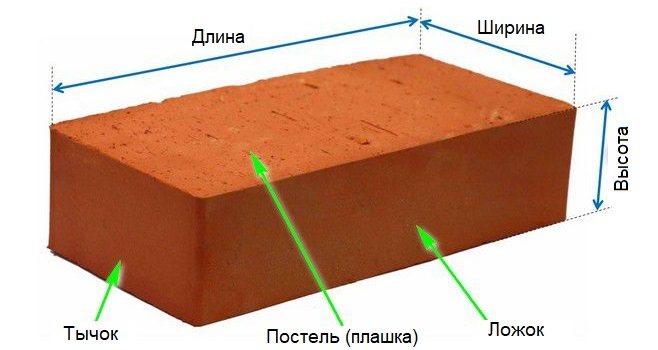

Shape and dimensions
For laying out stoves, chimney ducts, fireplaces, bricks of several standard sizes are used, in which three main indicators appear: the length of a large platform (bed or dice), its width and the height of the parallelepiped.
Table 2. Common typical sizes of refractory bricks
| Kind of brick | Frequently used type designation | Dimensions, mm | Size designation | ||
| Length (L) | Width (W) | Height (B) | |||
| Normal format brick (single) | KO | 250 | 120 | 65 | 1 nf |
| Brick of "Euro" standard | KE | 250 | 85 | 65 | 0.7 NF |
| Thickened brick | KU | 250 | 120 | 88 | 1.4 NF |
| Single modular brick | KM | 288 | 138 | 65 | 1.3 NF |
| Thickened brick with horizontal voids | KUG | 250 | 120 | 88 | 1.4 NF |
Most often, they use a brick of the usual normal format, which is called single and denoted by the letter abbreviation KO.
Brick that meets European standards is very similar to ordinary domestic ones. The difference lies in a slightly smaller die width (by about a third). This format is designated by the abbreviation KE.


A brick for a kiln, the height of which is exceeded by 20% compared to the usual format, is called thickened, denoted by the abbreviation KU. The rest of the parameters of such products correspond to the products of KO.
Modular brick KM is much less common in stove masonry, with the height and width of the die (bed) increased by 5-10% in relation to KM.
Special types of products are produced to decorate the arched finishes of stoves and fireplaces, external figured elements. Wedge-shaped shapes with tapered edges or ends are popular. The outer surfaces are sometimes decorated with bricks with curly curves.
Resistance to mechanical stress
An unconditional requirement for stove masonry is high strength, which is primarily due to the characteristics of each brick product. The value of the maximum mechanical load is indicated in the marking next to the letter M.


The number informs about the amount of kilograms that 1 cm2 of a brick bar can withstand without consequences. For ordinary stoves and fireplaces, a strength of 200 kg / cm2 is sufficient; for large massive structures, you can buy products with increased strength, up to a maximum of 250 kg / cm2. It makes no sense to buy even more durable products for laying stoves, they are more expensive, they are designed for ordinary load-bearing walls, and when heated, they can release synthetic additives specially introduced into the raw materials.
Frost resistance
The requirement for resistance to negative temperatures can be surprising, since we are talking about stoves. However, frost resistance is an important indicator for chimneys, stoves and fireplaces in summer buildings, which is indicated in the marking with the letter F. The number next to it indicates the permissible number of freezing and thawing cycles. In general, frost resistance characterizes the general ability of brick products to withstand any temperature extremes.
The ability to conduct and store heat
All layers of stove masonry, from the firebox to the cladding, must have good thermal conductivity and sufficient heat capacity, otherwise the structure will be beautiful, durable, reliable, but does not fulfill the main purpose - heating the room. The optimal value of the coefficient of thermal conductivity is considered to be 0.6 W / (m · ° C).Brickwork in the attic and above may have less heat conduction capacity. In these locations, the thermal insulation properties of the material are acceptable and useful.
Ability to absorb moisture
Refractory bricks have minimal hygroscopicity, which contributes to the production of durable heat-resistant masonry. When buying, special attention should be paid to the choice of bricks for laying out the foundation of the heating structure and the chimney - areas surrounded by humid air. For the construction of furnaces, you need to purchase only products that meet the standards.
Clinker features


Brick made by clinker technology from highly melting clay grades has high strength (more than M300) and frost resistance (more than F 100).
The specific features of clinker are indispensable when laying the base layer of the foundation and the internal channel of the chimney, reaching the head, provided that the cladding is decorated with another material.
Making the main part of the stove out of clinker is an expensive and unjustified pleasure, especially since the structure will turn out to be massive and weighted.
If the owner plans to make a compact stove in the bathhouse, clinker brick will be an ideal material that will heat the space no worse than a thick-walled cast-iron "potbelly stove".