Author: Kolesnikov Yuri Fedorovich, heat and power engineer
The stove is erected once, and you need to heat it all the time, on the one hand. On the other hand, the design of the furnace is largely, if not completely, determined by the type of fuel used. And its availability depends significantly on the reserves of local resources in the region. So the stove is danced from the fuel.
Modern heating technology allows you to burn to carbon dioxide, water and ash everything that, in principle, can burn, and something that, in principle, cannot burn. This is not just a joke. What can you expect from burning fuel in a stove? And how simple and efficient can a stove be on such and such, or such and such types of fuel? It depends on its properties:
- Aggregate state - solid, liquid, gaseous;
- Specific calorific value, or heat of combustion;
- Specific cost;
- Combustion rates;
- Combustion temperatures;
- Ability to water up;
- Ash content;
- Content of higher organic compounds;
- Sulfur content;
- Activity.
Solid, liquid or gas?
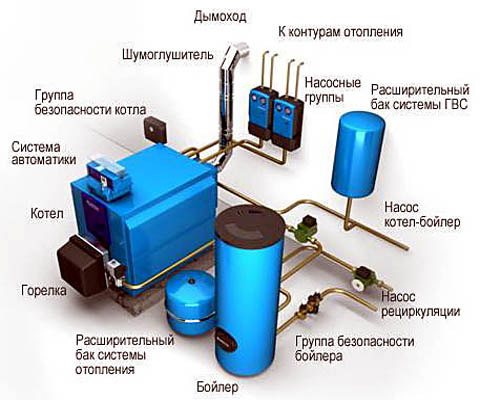
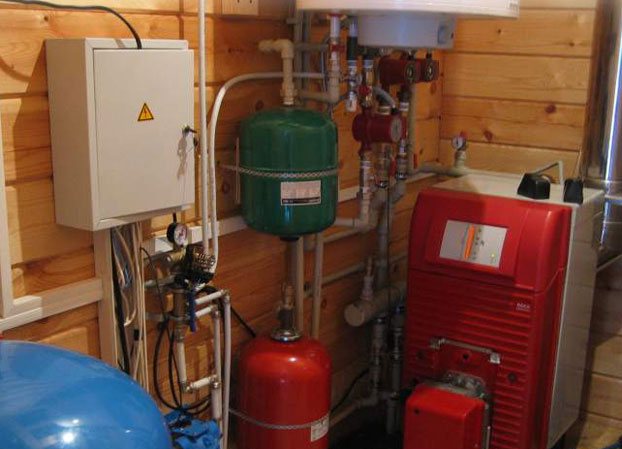
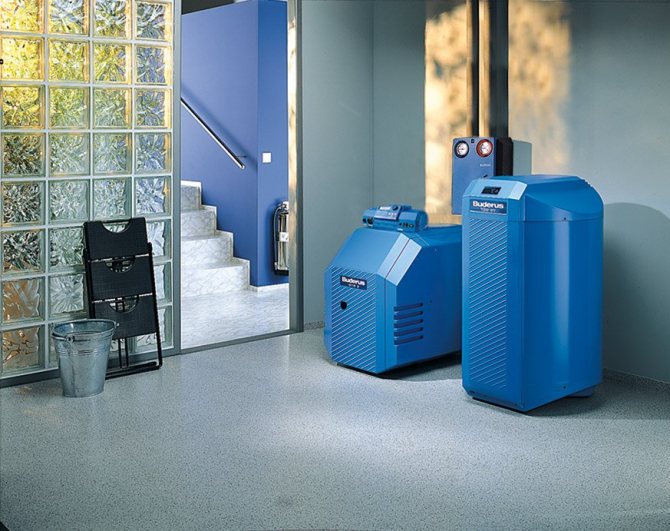
Mini-boiler room diagram
Upon careful consideration (for which, unfortunately, there is no place here), in terms of the totality of qualities, natural gas and liquid fuels still turn out to be the best. But it is better not to try to make a stove for them on your own: without industrial equipment and well-established technology, an experienced heating engineer will not undertake this either. More precisely, all the more it will not undertake, knowing what's what.
And there is a nuance: since this fuel gives off heat almost instantly, you cannot do with one stove. A complex set of equipment is also needed for incineration. For an example, see fig. scheme of a mini-boiler room. It costs a lot, and it is economically (and environmentally) justified for households with a living area of more than 120-150 sq. m.
Note: The efficiency of even a small gas or fuel oil boiler with automation reaches 90% or more. Almost all losses in centralized boiler houses are due to pipelines.
A homemade stove can be heated and supplied with hot water up to 60-100 sq. m. residential. More - the complexity of the work and costs increase so much that it turns out to be cheaper and easier to install a double-circuit gas boiler. If, of course, there is a gas supply. In this case, you need to focus on the lowest of the indicated values; with bottled gas - for higher education.
An exception is a pyrolysis (more precisely, a gas-generating) furnace for working off or dark heating oil. It is easy to do it yourself, in compliance with safety conditions. But the heated area is up to 40-60 sq. m, the extraction of heat for hot water supply is difficult, and the device of a full-flow hot water circuit is hardly possible. Those. field of application - a garage, a summer residence, a small residential building, provided that the stove is in the annex.
Note: pyrolysis oil is not a fuel for pyrolysis ovens. It is a product of rapid (50-30 s) oxygen-free pyrolysis of woodworking waste at a temperature of about 600 degrees. The pyrolysis oil is quite heavily watered, has an acidic reaction, i.e. chemically aggressive components in its composition and contains up to 2% or more sulfur. It is burned in industrial boilers and furnaces using a special burner.
Advantages and disadvantages
Liquid fuel heating units, like any other technical device, have their own advantages and disadvantages. To make the right choice and know what to be prepared for, you need to familiarize yourself with them.


Oil heating boiler
Advantages of liquid fuel boilers:
- the possibility of using as heaters for residential buildings, enterprises, non-residential premises;
- independence from the central heating system;
- the operation of the device is automated;
- lack of smell and noise during operation;
- reliability;
- very high efficiency (about 95%);
- safety.


Oil fired boilers have many advantages
Disadvantages of liquid fuel boilers:
- the need for a storage facility for fuel - a special container is required;
- high cost of equipment;
- the need to equip a boiler room - an individual room for installing the device;
- chimney installation;
- relatively high cost of liquid fuel.


Diesel heating of a private house
Heat of combustion and cost
The formal content of this paragraph does not require special explanations: kilocalories or joules. It can only be recalled that 1 kcal = 4.3 kJ. That is, if the heat of combustion is 10,000 kcal / kg, then in joules it will be 43,000 kJ / kg or 43 MJ / kg for solid fuel. For gaseous - kilocalories or kilo / mega joules per cubic meter. For liquid, reference books are given either per kilogram or per liter / cubic meter.
The heat of combustion of commonly used fuels ranges from 1,800 kcal / kg (waste wood: alder, willow, rotten raw brushwood) to almost 11,000 kcal / kg (polyethylene and other organic polymers), which in megajoules will be from 7.74 MJ / kg to 47.14 MJ / kg for polyethylene.
A nuance is already revealed here: you can completely burn everything, but the price of a kilogram is different! Therefore, we do this:
- We make a heat engineering calculation of the heating capacity of the room.
- We give it a 10-20% margin for hot water supply.
- We give to the received another 50% margin for abnormal cold.
- The obtained value is DIVIDED by the efficiency of the selected furnace.
- According to the obtained required heat power of the furnace and the specific heating value of the fuel, we determine its mass / volumetric consumption.
- By multiplying the consumption by the cost, we get the unit cost of heating.
- We repeat the procedure for different stoves and fuels until we reach the minimum price.
Note: heating devices with an efficiency less than the threshold 70% can be ignored. Even if we personally have a purple ecology on the yellow side, there will be additional taxes and fines somewhere else. Required.
How to determine quality heating oil
Only laboratory analysis will give an unambiguous answer. When delivering diesel fuel, stove brands can be roughly distinguished from automobile brands by the following features:
- oil products for boiler houses have a darker color, as they are less purified;
- during short-term storage, a precipitate forms in heating oil (this can be noticed if you pour the liquid into a transparent container and wait a little).
It is not necessary to determine the quality of petroleum products "by eye" if you cooperate with trusted suppliers. sells fuel with delivery and guarantees their compliance with standards. We provide passports and certificates for petroleum products, we offer favorable terms of cooperation. Call the number listed on the website for more information.
Combustion rate
In home-made stoves without complex automation, a clear correspondence is observed: the faster the fuel burns, the lower the efficiency of the stove can be achieved and the more complex its design is. The reason is simple: without technological tricks inaccessible to the home-builder, it is difficult to catch a large amount of heat released at once and send it into the room, or into the water heater, before it flies out into the pipe. Therefore, it makes sense only to make a homemade stove on slowly burning fuel - solid, oils, oil sludge, etc. Or a slow-burning furnace, where the combustion process is artificially slowed down.
In terms of combustion rate, coal is distinguished among solid fuels. He has it very uneven as it burns. In the beginning, when gasification is in progress, the flame rages.And then, when pure carbon (amorphous carbon, coke) remains, slow smoldering begins. And it is not so easy to make a furnace with high efficiency in either combustion mode.
Other solid fuels for furnaces and boilers
This group includes fuel briquettes and pellets made from wood waste, as well as natural resources - coal and peat.
Let's see them briefly in order.
Fuel briquettes and pellets
In any woodworking industry, a large amount of small waste remains - sawdust, shavings, wood chips, removed bark, etc. Once upon a time, their utilization became even a considerable problem - it was useless to burn tons of this quite suitable for use raw materials. Over time, technologies have been developed that make it possible to make substitutes for the usual firewood from such waste.
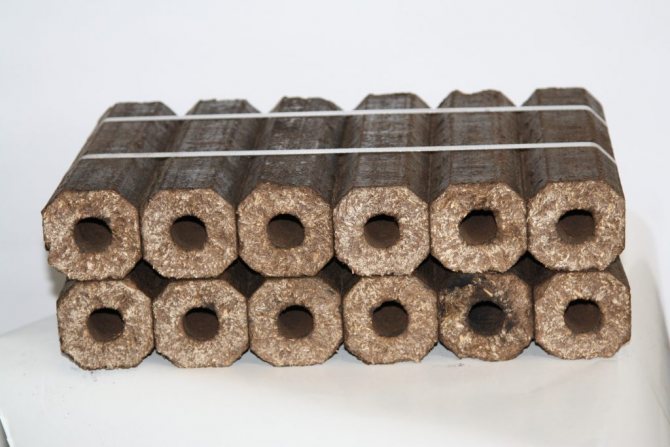
- Fuel wood briquettes have been used abroad for a long time. In our area, the attitude towards them was initially wary, but now many homeowners consider them as the main type of fuel for their heating equipment.
There are several varieties of such briquettes on sale.
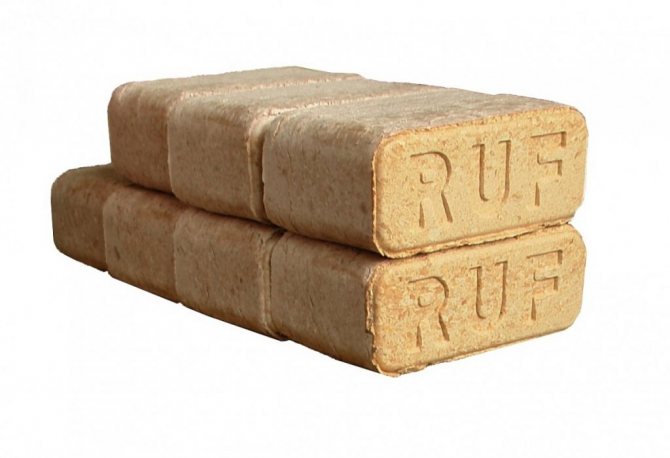
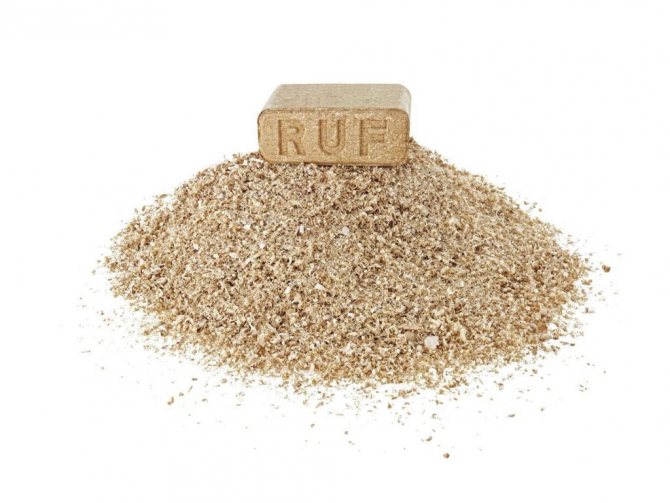
RUF briquettes, which have a characteristic shape of neat bricks, are very convenient in transportation, storage, loading into the furnace. Perhaps they can be attributed to the most popular today.


Very convenient and high performance RUF fuel briquettes.
There is nothing superfluous in their composition, except for crushed sawdust. No binders are used in production. In the process of pressing, a natural sticky substance that is part of cellulose - lignin, is activated. Briquettes perfectly "keep their shape", do not crumble, and after combustion they leave a minimum amount of waste.
You may be interested in information on how to make a heat accumulator for a solid fuel boiler
Video: How to choose the right RUF fuel briquette?
Briquettes, which are often called "Eurowood", are closer to the classic forms. Many companies are engaged in their production, for example, the Pini Kay brand is in good demand.
The briquettes are given a shape close to the cylinder, but nevertheless with a "cut", like a pencil - it is easier to store them this way, and they will not "scatter" on the floor. The through channel in the center provides an increase in the combustion area.
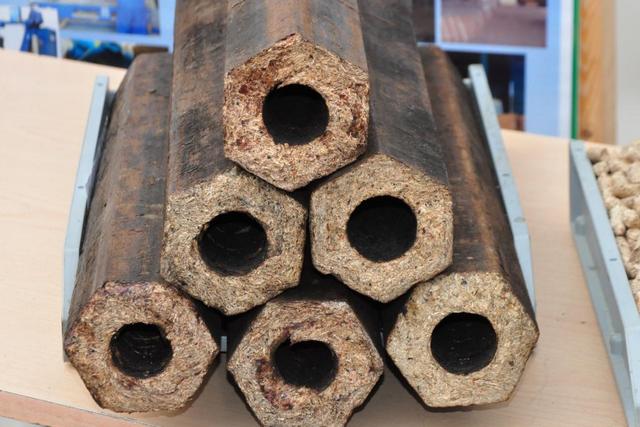


Fuel briquettes from pressed wood waste "Pini Kay", or, as they are often called - "Eurowood".
Such briquettes undergo a special surface heat treatment, which makes them perfectly protected even from direct contact with water.
TO merits wood fuel briquettes can be safely attributed to the following:
- Good duration of uniform burning with equally high heat transfer throughout the entire cycle (more than that of ordinary firewood).
- Briquettes burn almost without residue - solid waste does not exceed 1 ÷ 3% of the volume of fuel stored in the combustion chamber. Ash, by the way, is a good fertilizer for a personal plot.
- Very little smoke production. Moreover, the smoke is practically odorless. In general, due to the absence of third-party components, such fuel can be classified as non-harmful to the environment.
- Convenience of transportation and storage. By the way, briquettes at the place of their storage practically do not leave garbage.
TO disadvantages we attribute the following:
- The cost of briquettes is quite affordable, but some owners, who are accustomed to firewood or who have the opportunity to stock up on firewood almost for free, have a different opinion on this matter.
- The heat from briquettes is less than from hardwood firewood - in the bath they are of little use as a fuel.
- They complain about their inability to create a “live” comfortable atmosphere, which is typical for a wood-burning stove.
- You need a certain skill in using them. For ignition, it is often necessary to use special flammable liquids.
- If the storage rules are not followed, they are able to gradually lose strength - to crumble.
- Pellets - these are also, in fact, pressed briquettes, only of miniature sizes. During their production, shredded wood waste is passed through a special die-extruder, and the output is "sausages" - cylinders with a diameter of 6 ÷ 10 mm and a length of 10 ÷ 40 mm. No binders - pressing is ensured again due to the presence of lignin.
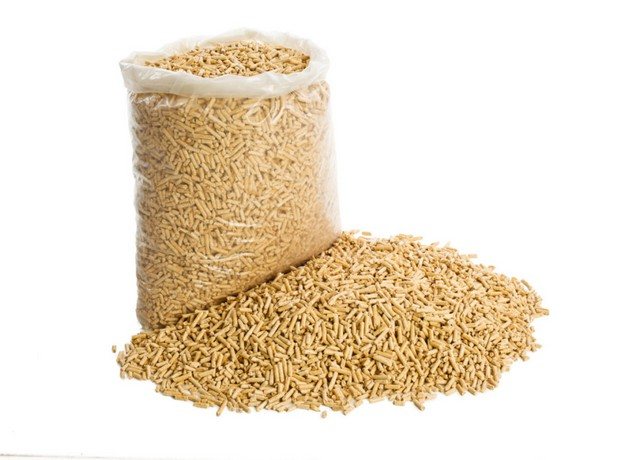


After drying, finished pellets are packed in moisture-proof bags and in this form are sold.
In principle, all the advantages and disadvantages inherent in fuel briquettes are also characteristic of pellets. But there is also a peculiarity - they are not suitable for every boiler or stove, simply because of the specific miniature shape of the granules. Either you will have to fail some modernization of the existing unit, or you will have to acquire a suitable model.
But on the other hand, modern pellet boilers are equipped with a loading hopper and an automatic metering system for feeding fuel into the combustion chamber. This means that intervention in the operation of heating equipment becomes more rare - frequent loads are not required.
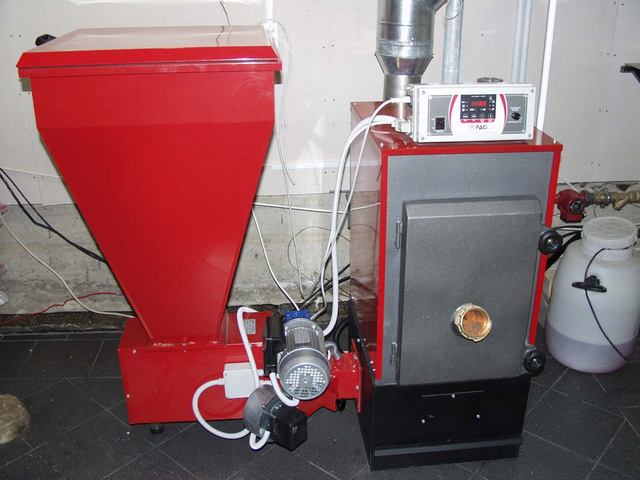


Heating boiler with an automatic pellet feeding system from the hopper to the combustion chamber
The use of pellets is becoming more and more popular. This may be confirmed by the fact that home craftsmen have already mastered the independent manufacture of units for the production of pellets at home. A find for those who have free access to woodworking waste!
Pellet boiler prices
pellet boilers
Coal as a solid fuel
Information on the classification of this type of solid fuel and its characteristics deserves a separate article, and it will be included in the next work plan. In the meantime - just about some aspects of the use of coal in solid fuel furnaces and boilers.
First of all, this fuel is still not universal. More precisely, not every unit is capable of working with it. That is, before considering the option of using coal as the main source of energy, you should once again make sure that such a possibility is separately specified in the passport of the device.
It's all about the features of this fuel - it is an unstable chemical composition of different brands, difficult ignition, high heat transfer and a very significant amount of non-combustible waste (slag), sometimes reaching 45% of the load volume.
Three types of coal are used as fuel - brown coal, stone coal of various subspecies, and anthracite.
- Brown coal is the youngest from a geological point of view. Its calorific value is small, it gives a lot of slag, so it is usually not even seriously considered. In addition, its transportation and storage is a very risky business, since biochemical processes have not yet subsided in it, and under certain conditions (high humidity), it is impossible to exclude the processes of discussion, turning into smoldering and spontaneous combustion.
- Bituminous coal is used most often. He has a very complex classification, but it can be noted that long-flame grades (WPC) are well suited for furnaces or boilers. Low-caking coals have lower heat transfer and higher ash content, and their use is less cost-effective. From lean coals, up to 45% of slag remains, and they are difficult to ignite. But the low price and rather good heat transfer still make them in demand for boilers with a pronouncedly good draft.
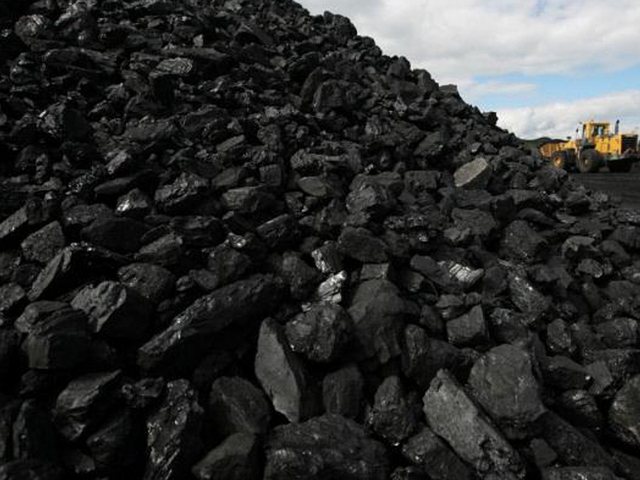


In the illustration - long-flame WPC coal of coarse fraction
- Anthracite has the highest calorific value. It is also characterized by a minimum amount of slag, low smoke generation.But it does not find wide application in household heating systems, and, interestingly, precisely because of its main advantage.
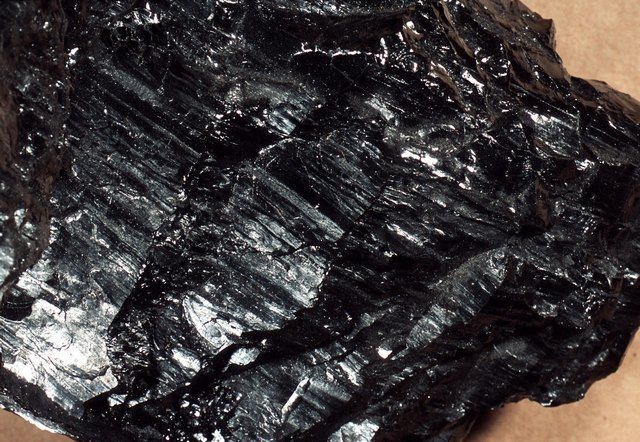


Anthracite - the highest calorific value, and for the same reason - serious restrictions on the use in boilers and stoves of domestic heating systems
The fact is that the use of anthracite is allowed only in those models of boilers or furnaces for which this is specially stipulated. Not every unit is able to cope with the high combustion temperatures of anthracite - you can simply "kill" expensive equipment with ill-conceived actions. And the "second side of the coin" - only in such special heating units the possibility of maximum use of the energy potential of this coal is thought out. Otherwise, its use becomes unprofitable, and the efficiency of the furnace or boiler drops sharply.
You may be interested in information on how long-burning solid fuel boilers work.
At the end of the section, we also present a plate with the calorific value of types of solid fuels alternative to firewood. Peat briquettes are also indicated there. But, as can be seen from the indicators, the energy efficiency from them is small, even worse than that of brown coal. And it hardly makes sense to use them for home heating, if it is possible to use any other type of solid fuel.
| Solid fuel type | Average calorific value of the mass by mass (kWh / kg) | Average calorific value of fuel by storage measures (kW / t) |
| Anthracite | 8.1 | 8100 |
| Charcoal | 8.6 | 8600 |
| Coal | 6.2 | 6200 |
| Brown coal | 4.2 | 4200 |
| Fuel briquettes, pellets | 5.6 | 5600 |
| Peat briquettes | 3.4 | 3400 |
Combustion temperature
This is a double-edged sword. One end - the higher the temperature, the easier it is to achieve complete combustion and high efficiency. On the other hand, again, it becomes more difficult to extract and direct the heat where needed; due to the large temperature gradient, it strives to fly into the pipe. Therefore, the design of the furnace becomes more complicated. In addition, high temperature combustion requires expensive heat-resistant materials.
In general, the lower the combustion temperature, the simpler and more efficient the stove is. Gnarled home-made designs on smoldering at 600 degrees (slow-burning furnaces) can give an efficiency of more than 85%. It is difficult to achieve an efficiency of more than 75% from a wood / coal stove (800-900 degrees) in an amateur design, and it often turns out that the construction shown in the video with pride burned out or cracked before the end of the heating season.
Note: the maximum combustion temperature achievable in home-made structures is about 1100 degrees; these are pyrolysis and gas generating furnaces. Above - without special steels and refractories, only a few test furnaces will withstand.
The principle of operation of a coal boiler
To figure out how to properly heat a boiler, you first need to consider its device and understand how such equipment works. The device of any coal boiler includes two main compartments. The upper compartment is a firebox in which the process of converting solid fuel into thermal energy takes place. The lower compartment is designed to collect ash and slag that remain after coal combustion. The compartments are separated by a ductile iron grill.
A rather sophisticated automation can be built into the design of the boiler, which makes it possible to adjust the operation of the system in such a way that the draft is regulated independently, without the need for constant intervention. In the absence of automation, the boiler works by natural circulation. The first category of devices is much more convenient, but they also cost an order of magnitude more expensive than simple boilers.
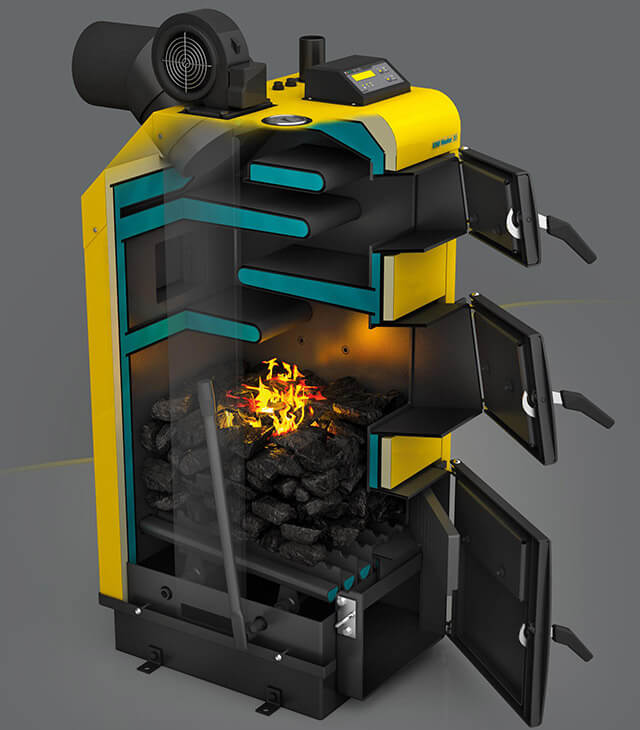


Automation works according to very simple principles. To ensure the combustion process, the boiler needs oxygen, which, in the presence of automation, is supplied by the fan.An increase in the amount of oxygen in the furnace accelerates the combustion process, and a decrease in the intensity of air supply leads to the opposite effect - the fuel burns more slowly and produces less heat.
The temperature regime of the boiler is regulated by a special sensor, which allows programming the operation of the device. When a certain temperature is reached, the sensor turns off the fan, as a result of which the fuel combustion rate decreases. The falling temperature forces the automation to restart the oxygen supply and resume active combustion.
Water cut
Watering the fuel removes heat not only and not so much for the evaporation of water. At high temperatures in the presence of a catalyst - carbon - even more energy is spent on the chemical reduction of water and the combination of the released oxygen with atmospheric nitrogen. The water content of the fuel in percent by weight is designated as W.
The ability of the fuel to absorb moisture, firstly, reduces its heat of combustion. For firewood - twice or more with an increase in humidity from 20% to 50%. Watered fuel oil can also be explosive. And barely wet brown coal ignites spontaneously, so it is not transported from the mining sites, thermal power plants on brown coal are built near mining pits.
A furnace operating on watered liquid fuel must be equipped with a special burner and a fuel preparation system. Solid fuel - a complex smoke path in which the reduced components and oxidized nitrogen do not cool down before decaying to the original ones and giving back heat.
Coal


It is a natural mineral that has formed over millions of years in various layers of soil from wood and other plants. People learned how to mine this fossil a long time ago and understood its value as an energy carrier.
Depending on the grade, coal has a very high calorific value, about 6800-8350 kcal / kg. Therefore, it is the most high-calorie solid fuel. However, it is not devoid of significant drawbacks. First of all, this is a price that is significantly higher than that of firewood. Its cost can be compared with some types of briquettes, but, at the same time, burning coal pollutes the environment. High ash content requires very frequent boiler maintenance, and the ash itself requires disposal.
Before deciding which coal is better to heat, let's look at the coal and the calorific value:
- Brown coal - up to 4177 kcal / kg. It is rarely used in private homes due to the complexity of storage and the high probability of spontaneous combustion.
- Rocky coal - 5097-6700 kcal / kg. The most common type of fuel in private households due to its properties, including storage safety.
- Antarcytes - 5800-6500 kcal / kg. Industrial type of coal.
Peat


Fossil formed by the decomposition of plant residues under conditions of limited oxygen availability and high humidity. It is mined in swampy areas, then briquetted and dried. The calorific value is 3511-4492 kcal / kg.
This fuel has long been widely used both for heating private households and in production. Affordability and ease of storage allows it to compete with firewood and coal.
Activity
Fuel activity is a conditional parameter. It characterizes the ability of a fuel to ignite and burn on its own.
The fuel that flashes from a spark is considered to be extremely active, and the combustion zone immediately spreads over its entire surface. Highly active fuel requires a small amount of fire, or with the help of a wick, but then in the open air quickly and over the entire surface flares up. Medium active requires ignition with more active fuel and does not completely burn out without additional measures (joke, turn) or pressurization in the open air. Low-level fuel combustion can only take place in special devices after ignition.
Fuel activity depends little on its calorific value, but much more on the state of aggregation, boiling point (for liquid fuel) and the degree of fineness (dispersion) for solid fuel. For example, gasoline and ethyl alcohol are extremely active at room temperature. In diesel fuel at room temperature, the torch goes out, but, sprayed with a nozzle, it flashes itself at 90 degrees in the open air. Wood in the form of firewood is moderately active, in the form of dry shavings it is highly active, and in the form of sawdust it is very weakly active.
Note: according to TU, the flash point of summer diesel fuel is 62 degrees. But this is in a closed crucible.
Oil fuel burners for boilers
|
| Oil burners |
Combined burners "gas-diesel fuel", "gas-fuel oil" are more expensive than specialized liquid fuel burners, but they can provide uninterrupted heat supply when changing the type of fuel, for example, when a house is gasified over time. Such burners require adjustment separately for each type of fuel, they have a device - mechanical or electronic, that regulates the air-fuel ratio in the feed mixture, and the fuel oil-gas burners are equipped with a fuel oil heater.
Actually, oil burners are divided into:
- burners with spray nozzles, including steam-mechanical nozzles;
Preparation for kindling
For coal heating equipment to be safe and effective, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- If the boiler or stove is rarely used (for example, seasonally), then before using it, make sure that there are no cracks in the masonry. Even small cracks in the structure of the stove are a wide path for the release of carbon monoxide into the room, where it can seriously harm the people present there. To get rid of this problem, all cracks must be covered with a mixture of sand and clay before melting a solid fuel boiler.
- Before melting the boiler with coal, you need to inspect it visually. There should be no flammable objects near the heating equipment. The inner surfaces of the structure must be cleaned. It is advisable to wipe the firebox with a dry cloth so that the burning dust does not emit an unpleasant odor that gets into the room.
- Coal stoves need to be heated several times a day, and the duration of each kindling should not be more than two hours (in more detail: "How to heat a stove with coal and which coal is better"). Dry coal of the middle fraction is best suited for heating.
- To ignite coal equipment, you cannot use various flammable waste and liquids such as kerosene. In addition, the stove must be supervised during combustion, especially if there are animals or children in the house.

The described moments are not particularly difficult and make it possible to make the operation of boiler equipment safe.