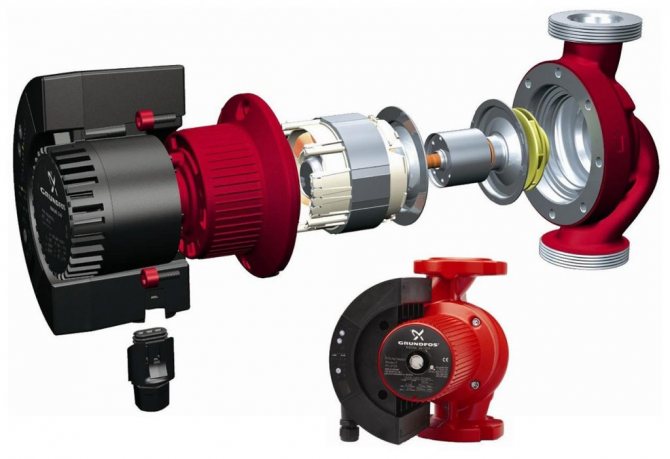
devices with a wet dry rotor, advantages and disadvantages
For pumping liquid, many use a rotary circulation pump.
A rotary pump is a mechanism that is used to pump various liquid masses in large volumes. On the modern market, you can find a variety of types of these devices, which differ in the principle of operation, design and price. Each buyer can choose for himself exactly the device that he needs.
The content of the article
Working principle and dignity
The principle by which rotary pumping equipment works is to pump liquid from the inner chamber of the mechanism by pushing it out by the rotor. This is due to a decrease in the working space of the chamber, where the pumped mass first enters. Moving parts of the rotor changes the volume of the chamber and thus carries out the pumping.
The main advantages of a rotary pump are uniform fluid supply and high speed of frequency of movements.
The main element of the rotor is a hollow disc, which rotates to adjust the pumped mass from the suction to the outlet. If it is necessary to pump liquids containing solids, then, as a rule, the unit is equipped with one disc. It rotates rather slowly, but thereby reduces the likelihood of breakdowns and increases the life of the pump. However, there are often devices equipped with several disks.
Advantages:
- Quite uniform fluid supply;
- The presence of a reverse stroke, which makes it possible to use the device as a hydraulic motor apparatus;
- Highest possible efficiency due to the absence of valves in the design;
- High speed of frequency of movements.
As for the disadvantages, they lie in the rather high cost of such equipment and sensitivity to the pumped liquid - it should not contain abrasive particles and too aggressive chemicals that can violate the integrity of the device.
If you choose by brands, then Grundfos pumps ("Grundfos") are very popular, which are distinguished by their quality and high performance, due to which they are in demand all over the world.
Varieties of products
When deciding which pump is better to choose, you should understand the types of such devices and the principles of their operation.
Rotary lobe pumps are either linear or rotary
A rotary pump is:
- Translational - it has more compact dimensions and gearing inside. There are slide and piston. The former are rather cumbersome, but at the same time they can pump fluids from great depths. The latter are also divided into two types: radial and axial. The latter run mainly in parallel and are equipped with swash plates and discs. Torsion from the engine is transmitted using a special connecting rod located inside the piston. The former move only in the radial direction.
- Rotational - in this case, the device is "powered" by electricity. More precisely, electricity powers the electric motor, which transfers power to the rotor itself. The shaft begins to rotate and, in contact with the teeth of the disc, sets it in motion.
Rotary pumps are more common among consumers and are divided into devices with wet and dry rotor. "Wet" people basically work with a working fluid inside them. And the "dry" ones can be launched without having anything inside them.
Glandless circulation pump
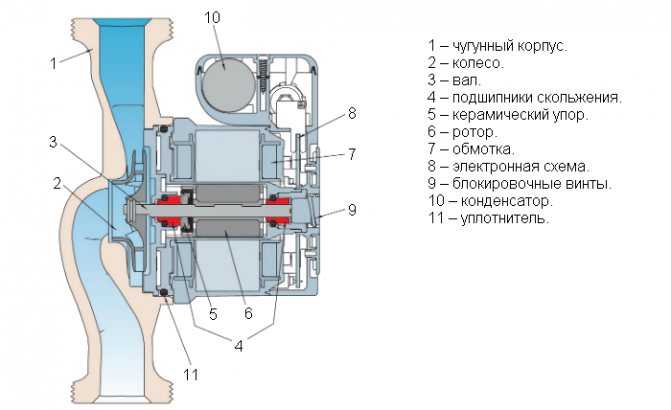
A circulating pump has something in common with drainage pumps.Regardless of the rotor type, the housing is often made of brass, stainless steel, cast iron or bronze. The rotor is made of either ceramic or stainless steel. The impeller with blades is located on the rotor shaft itself.
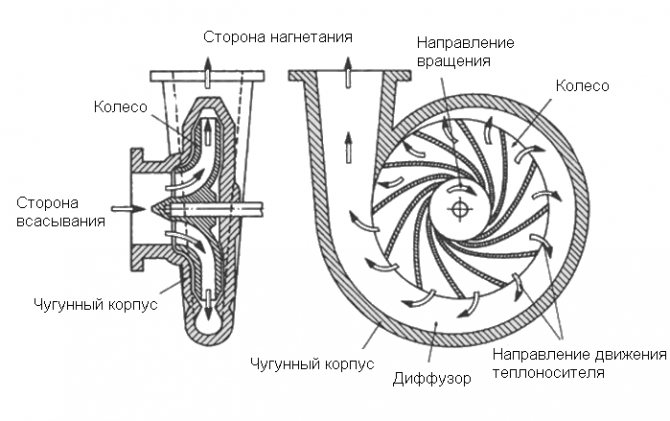
The principle of operation is to create a centrifugal force inside the device. Rotating, the rotor makes the blades move quickly, lowering the pressure in the working chamber. This increases the flow of liquid into the container. Then the pumped water increases the pressure in the tank and, thanks to this differential, is pushed out.
As for the device with a wet rotor, its peculiarity lies in the fact that the impeller blades are in the pumped liquid. At the same time, all electrical equipment of the device is reliably sealed and separated from direct contact with water.
A circulating pump with a wet rotor is in demand today.
Advantages of a wet rotary pump:
- Due to its presence in a wet environment, the pump does not overheat;
- The liquid absorbs all vibration sounds of the device, which makes it virtually noiseless;
- The unit is lightweight and compact;
- It can work for a long time without stopping;
- Easy to install, maintain and repair.
The disadvantages of such devices include only low efficiency, so such equipment is rarely used on long pipelines where good performance is needed.
Dry rotor unit and its features
The peculiarity of this type of pump is that it works without contact with the pumped liquid. The main advantage of such a pump is that such equipment has a very high efficiency, which can reach 80%.
But despite this, such devices have disadvantages:
- Quite a high level of noise emitted during operation;
- Demanding in the pumped medium - there should be no debris or air bubbles.
In this case, "dry" rotor systems are divided into vertical and horizontal (cantilever). In the first, the engine is located vertically, and the pipes are on the same axis. In the second, the motor is in a horizontal position, and the pipes are perpendicular to each other.
Thus, rotary circulation pumps are excellent for pumping various liquids. Depending on what mass will be distilled, you should choose a pump with a dry or wet rotor.
Pump electrical engineering
Usually, asynchronous electric motors are used as a power unit, connected to a network with a voltage of 220 V. The average current strength is 0.12-0.18 A. The basis for connections is a complex of a terminal box, a frequency switch and cable connections. In the device of Wilo circulation pumps from the Star-RS line, it also provides for condensate drainage and two-way cable connection with a blocking current protection system.

But it is far from always possible to implement a full range of devices for electrical protection on the basis of the pump itself. Therefore, external devices will also play a significant role in organizing the power supply system. At a minimum, a voltage stabilizer and a short-circuit protection system should be provided - of course, grounding requirements cannot be ignored. What is more important, in networks with periodic power outages, it will not be superfluous to think over the issue of providing backup power to the circulation pump. Devices for solving such problems are presented in a wide range - from external batteries (accumulators) to stand-alone generators. The choice of specific equipment depends on the conditions and operating conditions of the pump. If we are talking about a private house, where the power supply is interrupted in exceptional cases, then you can choose a battery of the corresponding volume with regular energy support.But in conditions of an acute shortage of electricity at remote sites, it is better to use a generator unit running on gasoline or diesel fuel with an auto-start system. By the way, the operation of low-power pumps up to 30 W for a couple of days can be supported by car batteries, but this option should be used only in extreme cases.
principle of operation. Variable speed pumps
Glandless pump design
IN wet rotor pumps
the rotor of a special electric motor is immersed in the pumped medium. A spacer sleeve integrated into the motor housing protects the stator coil. This bushing is made of non-magnetic high alloy steel. The shaft is made of stainless steel and rotates in graphite bearings. The shaft sleeve is stationary. The medium pumped through the system under pressure simultaneously cools it and reduces friction in the bearings.
Installing a glandless pump in a direct or return line ensures fast and intensive movement of water. As a result, it becomes possible to use pipelines with a smaller cross-section. This leads to lower costs for the heating system. This also means that there will now be significantly less water in the lines of the system. The heating system can react more quickly to temperature fluctuations and is easier to adjust.
Features of the
A distinctive feature of the impeller of a centrifugal pump is the radial movement of water. The shaft driving the impeller in rotation is made of stainless steel; shaft bearings are made of sintered carbon or ceramic material. The rotor of the motor, mounted on the shaft, rotates in the water. Water lubricates the bearings and cools the motor.
The energized stator of the motor is surrounded by a separating sleeve. It is made of non-magnetic stainless steel or carbon fiber and has a wall thickness of 0.1 to 0.3 mm.
For special applications such as water systems, fixed speed pump motors are used.
If a glandless pump is used, for example, in a heating circuit, and therefore is intended to supply heat energy to a radiator, it must adapt to the changing thermal load of the building. Thermostatic radiator valves installed in front of the heating surfaces determine the flow rate of the pump.
Pump heating system
In order to reduce energy consumption, it is necessary that the motors of pumps with a wet rotor constantly change the speed. The speed can be changed manually using switches. It is also possible to organize an automation system by installing switching equipment and control devices, which will be triggered depending on time, pressure difference or temperature.
Since 1988, there have been designs with built-in electronic devices that provide stepless speed control.
First fully electronic glandless pump with integrated infinitely variable speed control
Glandless pumps, depending on the size and the required output power of the pump, operate on a 1 ~ 230 V ~ or 3 ~ 400 V three-phase mains supply.
Glandless pumps are quiet and, due to their design, have no shaft seals.
The design of the current generation of glandless rotor pumps is based on a modular principle. Depending on the size and required output of the pump, the modules are assembled in different configurations. Thus, any repairs that might be required can be done with less labor by simply replacing the part with a spare.
An important quality of this type of pump is their ability to independently evacuate air during commissioning.
Installation methods
Glandless pumps are supplied with threaded connections up to R 1¼. Larger pumps have flange connections. These pumps can be installed in the pipeline horizontally or vertically without building a foundation.
As mentioned earlier, the bearings of such a pump are lubricated with a working fluid. It also serves as a coolant for the electric motor. Therefore, liquid must be constantly circulating through the separating bowl.
If it is necessary to heat large rooms with a total area of several hundred square meters, the pressure in the autonomous heating system with natural circulation (about 0.6 MPa) created by the heating heater is usually insufficient.
To solve this problem, you can go in two ways: 1. Build a closed system using large-caliber pipes, which are not cheap. 2. Turn on the circulation pump in the system.
The second option is more economically feasible. Thanks to the improvement in the circulation of the coolant in the system, the heating efficiency increases significantly.


Circulation heating pumps are divided into two types: 1.With wet rotor.
They are used in the heating system of private households, where the length of the pipelines is not so great. The rotor of the pump, equipped with an impeller, rotating inside the housing, accelerates the movement of the coolant. The fluid inside which the rotor rotates cools and lubricates the mechanism. When installing a "wet" pump, pay attention to the horizontalness of the shaft, then there will always be water inside the casing. Advantages of pumps with a wet rotor: - practically silent; - stepless switching of the rotor speed; - reliability in operation; - long service life; - no need for maintenance; - ease of repair and adjustment of the pump;
- relative cheapness. Disadvantages: - low efficiency (no more than 50%)


2.With dry rotor.
They are used in long-distance heating systems. O-rings are installed between the electric motor and the working part of the rotor, the service life of which is 3 years. There is no contact between the rotor and the coolant. Advantages: - high efficiency - about 80%; Disadvantages: - high noise level, and therefore they are installed in a separate room equipped with sound insulation; - the need to control the absence of suspended particles in the coolant and dust in the air surrounding the engine in order to avoid damage to the surfaces of the sealing rings, which can cause their damage and leakage.
When choosing the type and model of a circulation pump for a heating system, one should also take into account their performance, operating conditions, features of the coolant (its viscosity and density), the manufacturer's recommendations and requirements for the installation and quality characteristics of the pumped liquid.
Today, you rarely find a home heating system built according to the classical gravitational scheme. A circulation pump for heating is used almost everywhere. This device is useful and functional, but reduces the overall requirements for the accuracy of the pipeline network design. At the same time, without a forced circulation source, it is impossible to operate such technologically advanced heating systems in a private house or apartment as underfloor heating.
Circulation pump device - implementation of the standard scheme centrifugal machine
... The main structural units include:
- pump housing;
- a rotor transmitting rotation from the engine shaft to the turbine unit;
- a turbine impeller with inclined blades, which is also called an impeller;
- means of sealing, isolation from water or heat carrier;
- basic electrical circuit that switches operating modes and monitors engine parameters.
Circulation pumps can have different body shapes and the location of the branch and inlet pipes. This is done so that the device can be easily installed, maintained in the operating conditions for which it was designed. In particular, the selection of the pump can be made by the type of connection: with a flange, threaded connection, nut.
The circulating pump has small size
... It is often built directly into the inner cavity of the housing of household gas heating boilers. Safety devices can be assembled with the pump. The small dimensions of the blower are easy to understand when considering the purpose of the circulation pumps. They do not require record-breaking fluid delivery. In fact, they literally move the water horizontally.
The task of circulation pumps is to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipelines.
If a collector group for a warm floor is considered, the blower is busy creating a very small volume flow as such, since there are no significant gravitational forces in this type of heating circuit.
The principle of operation of the circulation pump
several
How to install a circulation pump for heating correctly?
All nuts required for installation and rubber sealing rings are always included with the pump.
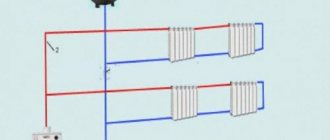
Pay attention to the correct position of the pump as shown in the figure:
Correct installation of the circulation pump for heating
That is, the pump shaft must be horizontal, no matter how you "turn" the body.
With a vertical shaft arrangement, the pump loses about 30% of its capacity.
The pump must be accessible for service or replacement.
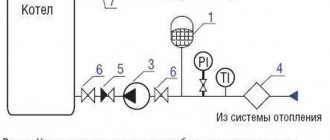
In front of the pump (from the side of the coolant movement) we put a coarse filter. And in case it is necessary to replace the pump or clean the filter, ball valves are installed on both sides.
You can also read about manipulations with the pump when you first turn it on in the article about starting the heating system.
Now about the pump piping. An example of piping with metal pipes is shown in the photo:
Circulation pump installed in the heating system
It is likely that initially it was a heating system made of steel pipes, with natural circulation, that is, without a pump. Subsequently, a pump was added, for which they made a bypass branch (bypass), the device of which is clearly visible in the photo.
In the event of a power outage or a pump malfunction, the tap on the straight pipe is opened and the system works with natural circulation. In other cases, the coolant goes along the bypass branch, being driven by a circulation pump, which results in energy savings, as mentioned at the beginning of this article.
what it is and how it works. Rotary pumps.
In this article, we tried to collect all the possible principles of pump operation. Often, in a wide variety of brands and types of pumps, it is quite difficult to understand without knowing how this or that unit works. We tried to make it clear, as it is better to see once than hear a hundred times. In most descriptions of the operation of pumps on the Internet, there are only sections of the flow path (at best, the schemes of operation in phases). This does not always help to understand exactly how the pump functions. Moreover, not everyone has an engineering education. We hope that this section of our website will not only help you in choosing the right equipment, but also broaden your horizons.
For a long time, the task was to lift and transport water. The earliest devices of this type were water-lifting wheels. It is believed that they were invented by the Egyptians. The water-lifting machine was a wheel, around the circumference of which jugs were attached.The lower edge of the wheel was lowered into the water. When the wheel rotated around the axis, the jugs scooped up water from the reservoir, and then at the top of the wheel, the water was poured from the jugs into a special receiving tray. use human or animal muscular strength to rotate the device.
Archimedes (287–212 BC), the great scientist of antiquity, invented a screw water-lifting device, later named after him. This device lifted the water with the help of a screw rotating inside the pipe, but some of the water always flowed back, since in those days effective seals were unknown. As a result, the relationship between screw tilt and feed was derived. When working, it was possible to choose between a large volume of raised water or a higher lift. The more the screw is tilted, the greater the feed height with a decrease in capacity.
The first piston pump for extinguishing fires, invented by the ancient Greek mechanic Ctesibius, was described as early as the 1st century BC. e. These pumps, by right, can be considered the very first pumps. Until the beginning of the 18th century, pumps of this type were rarely used, because made of wood, they often broke. These pumps were developed after they began to be made of metal. With the onset of the industrial revolution and the advent of steam engines, piston pumps began to be used to pump water from mines and mines. Currently, the piston
Where is the best place to install a circulation pump?
It is best to install a pump for heating on the return line, in front of the boiler. Why? For two reasons.
First. With this installation, the pump operates at lower temperatures, which will result in a longer service life.
The second reason. Air can collect at the top of the boiler (especially in floor standing boilers). If the pump is in supply, it pulls the coolant out of the boiler, which creates a vacuum in the upper part, and here the boiler can boil. When the pump is in front of the boiler, it pushes water into the boiler, and no air space is created at the top of the boiler, the boiler is completely filled.
(Actually, this rule is uniquely suitable only for simple heating systems in which there are only radiators and only in one building; but for complex combined heating systems, most likely, you will have to install a distribution manifold, and circulation pumps - for each circuit separately ... but the task of this article is a general acquaintance with pumps for heating, so we will not go deeper. Whoever is interested or needs it, refer to the boiler connection diagrams.)
Differences between pumps with "wet" and "dry" rotor
07.01.2014
It was believed by many that for domestic use it is necessary to take circulation pumps with a wet rotor. Dry rotary circulation pumps were used for industrial use.
It was believed that dry rotor pumps are oversized and noisy. However, large manufacturers began to produce more and more household models of circulation pumps with a dry rotor.
The industry uses dry rotor circulation pumps.
In the domestic version, circulation pumps with a wet and dry rotor are used. For industrial needs, pumps with a wet rotor are not used, since they can be produced with a power of up to 3 kW and they are not widely used.
Advantages of circulation pumps with a dry rotor of industrial design: the quality of the coolant is not important for them, they have good maintainability. The downside of these pumps is that they are large, make a lot of noise, so they are installed in separate rooms and consume a lot of electricity.
As for the domestic version of the pump with a dry rotor, its advantages:
has a higher efficiency;
the purity of the coolant is not important for him;
has good maintainability, and spare parts are cheaper than pumps with a wet rotor;
in size, it almost does not differ from the wet-rotor analogue.
The downside is a lot of noise during operation and the need for regular replacement of the mechanical seal.
The disadvantages of circulation pumps with a dry rotor are the advantages for a pump with a wet rotor: noiselessness, no mechanical seal. The disadvantage is that the quality of the coolant is of great importance during operation. The worse the quality of the pumped liquid, the faster the pump can fail.
Considering all the pluses and minuses of the considered pumps, we can draw the appropriate conclusions. If the quality of the coolant is not important to you, then it is better to choose a pump with a wet rotor, but it is not known what will happen to the rest of the heating system.
If you want everything to work smoothly, it is better to use a dry rotor motor, but you need to take care of the quality of the coolant.
As for the noise, everyone decides for himself, because the pump does not come into sight so often. The efficiency is not so important, since the difference in percentage is small, but the absence of the need to replace the mechanical seal is a big plus.
However, maintenance should be carried out regularly together with an inspection of the entire heating system by a specialist.
What are the benefits of using a circulation pump?
In systems with natural circulation of the heating medium, a circulation pump is not needed. However, if such a pump is installed in an old system of large-diameter pipes, then there will be gas savings of 20 ... 30 percent! Agree, it's nice.
Where does this savings come from?
Thanks to the circulation pump, the coolant circulates in the system faster and, accordingly, returns to the boiler faster. That is, the coolant does not have time to give up all the heat, it returns to the boiler heated, and the load for the boiler is less, because it is necessary to heat up the coolant less in order to send it back to the heating devices.
what it is and how it works. Positive displacement rotary pumps.
A rotary lobe pump is a positive displacement pump with rotary or rotational and reciprocating movement of the working bodies, regardless of the nature of the movement of the pump driving link. Thus, the obligatory movement is rotational.
According to the classification, the main representatives of this group of pumps are gear, vane, radial piston and axial piston.
It is important that the company builds industrial equipment and installations, that the pump is durable, so that its parts do not wear out frequently and are easy to maintain. A manufacturer of paints, varnishes and specialty chemicals was looking for an efficient pump for pumping parquet and tile adhesives. Until now, piston diaphragm pumps have been used for this purpose. However, the efficiency of these pumps decreases as the viscosity increases. Moreover, their use is associated with very high energy costs.
Due to poor experience with diaphragm pumps, the chemical industry was interested in rigorously testing an alternative pump. Due to the very demanding press environment, a rotary safety pump with double-acting sliding seal is installed. The pump is added to the pump using a thermosyphon system. Protect pumps from glue from mixer to tank or reservoir. When pumping out the medium to empty the tank, the embossing should be done with minimal pulsation and uniformity.
Gear pumps.
Using the example of a gear pump, we will consider the features of the working process of all rotary pumps.
These pumps (fig. 11.9) are most often made in the form of a pair of identical gears with involute engagement, enclosed in a housing.
All rotary pumps consist of three parts: stator (stationary part of the pump), rotor and displacers.
Otherwise, there may be interference.The customer was very pleased with the company's rotary lobe pump and after extensive testing, he bought it. The significant cost savings were an important benefit. Benefit from our many years of experience and knowledge in the manufacture of positive displacement pumps.
The stator consists of a recyclable polygonal profile and insert it into an elastomer. The advantage of this new technology is less than breakout force, higher efficiency, longer life
Circulation pumps from different manufacturers
In addition to Grundfos and Wilo, DAB pumps can be found:
This is also a German company.
From our "Asian friends" you can find Sprut pumps:
Speroni seems to be made in Italy:
Russian Dzhileks:
(in any case, the inscriptions on it are great and mighty, but this does not guarantee that it is produced entirely in Russia, there is a possibility of a "Chinese trace")
These pumps have a lower price than the German ones, but not necessarily because of the inferior quality, it is just that the labor in China is cheaper. And the processing of the outer cast-iron surfaces is slightly less smooth, which, as you understand, does not affect the operation of the pump itself.
what it is and how it works.
The use of rotary pumps is associated with the need to pump a large volume of liquid. There are several types of rotary lobe pumps, differing in the principle of operation and design features. We will consider the main types of rotary pumps and their design further.
Rotary lobe pumps operating principle and characteristics
The principle of operation of a rotary pump consists in transporting liquid by placing it in a chamber, from which it is pushed out using rotational and translational manipulations. The main working mechanism of these pumps is the rotor. In relation to its design, rotary lobe pumps are divided into different types.
Some people apologize to government officials for these misappropriations, claiming that their wages are too low. How can illegal activities be honestly justified? If the landlord steals goods, even ten dollars worth, they will probably be dead.
If the salaries of civil servants are too low, then they need to be adjusted to market value minus the amount of additional benefits they receive, such as increased risk, housing subsidies, etc. their privileged position in government should not be a reason to ignore illegal activities, especially those involving important material resources for the poor. Low wages should never be used as an excuse to explain theft and dishonesty.
The working mechanism of rotary pumps constantly rotates, but despite this, the principle of operation of this equipment is individual and not similar to dynamic pump options. In the process of pumping liquid, it enters the chamber, and its displacement is carried out using the discharge pipe.
They are more common where there is no transparency in government spending. In contrast to the previous situation, where the pit is digested using local labor, and when the pump is fully utilized using local materials, the leak is more difficult to conceal and therefore more difficult to achieve.
Governments and local business people will also have more reason to identify gaps in an alternative technology solution and protect against its use. Like most things in life, a wire rope pump isn't perfect. There are some restrictions on its use. These include limited water depth and possible water pollution.
Inside the working chamber of the rotary pump, a closed-type space is created, to restrict which movable and stationary parts of the device are used. In the process of work, this space changes in volume.In the process of moving parts of the movable type, the working chamber changes in size, thus pumping the working fluid.
While the wireline pump is effective for shallow wells, it is less effective for deep decks. Unfortunately, it is not easy to predict how deep this might be good for a wireline pump to operate. The inability to predict this is due to the use of local materials for the manufacture of the pump, which do not have universal standards. Both the diameter and thickness of the valves, for example, affect the depth of the well where the pump can be used. Since the inner tubes and leather may have different thicknesses, and since the valves are handcrafted by local craftsmen, they are not uniform.
Depending on the main movement in a rotary pump, they are of two types - rotary rotation and rotary intake. The first option is based on the exceptional rotation of the moving parts in the pump, while the second is based on a combination of both rotation and inflow.
Rotary rotary pumps are of gear and screw type. The first option is distinguished by the presence of a working chamber, the body of which remains stationary, and the gears move in a certain direction. The working chamber changes in size precisely due to the movement of the gears. This version of the pumps can have both external and internal gearing.
If the valve is too thin and flexible, oh
Installing the pump
By the time of installation, both the place of operation and the unit itself must be prepared. As for the first condition, you must be ready to connect the pipe with shut-off valves in front of the connection points for shutting off the water. The pump, in turn, must be thoroughly flushed and checked for structural integrity. Tapping is carried out using a coupling and a lock nut with sealing materials. To increase the reliability of the control loop, a bypass is sometimes provided in the mounting device of the circulation pump. This is a crawler on the equipment placement circuit, which is a section of the pipeline running parallel to the critical technological zone and performing the function of a backup route for the delivery of the coolant. On the same section, you can install additional functional equipment such as filters, air vents and just shut-off valves.