Heating equipment and engineering systems | No.4 (54) ‘2011
Often, when building chimneys, mistakes are made that can be very expensive and even lead to irreparable consequences. Moreover, the homeowner notices flaws sometimes too late, when he begins to experience certain inconveniences when using the stove or fireplace. People have to spend money on timely elimination of emerging problems or overhaul of the smoke channel, because its improper operation is quite capable of causing a fire.
Most often, mistakes made in the selection, design and installation of flue gas evacuation systems lead to a disruption of draft or destruction of the walls of the chimney, which may cause a fire in the adjacent building structures. The reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon can be very different.

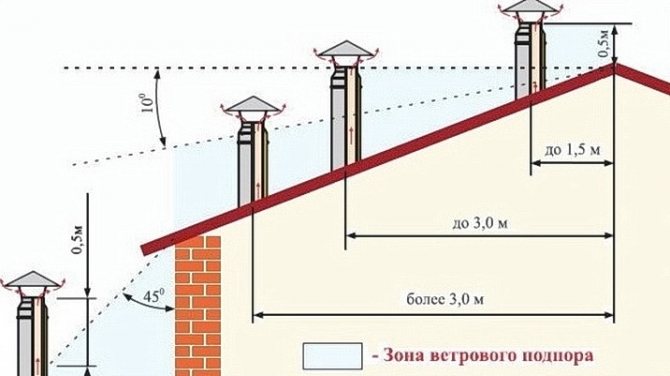
Regardless of the material from which the chimney is made, the cut of the pipe must rise above the outer surface of the roof to a height recommended by regulatory documents - SNiP 41-01-2003, paragraph 6.6.12; the head of the structure is crowned with a deflector, which quite effectively protects the channel from atmospheric precipitation and increases the traction force due to the suction of smoke using wind energy
Where the wind goes, there is smoke
Violation of the draft in the chimney is either its insufficient or excessive force. In both cases, the stove or fireplace will no longer meet the expectations of its owners: the fuel will ignite and go out poorly, and the firebox will smoke. The reasons for this situation may be:
• too low height of the entire chimney or that part of it that rises above the roof of the house; • incorrectly selected section of the chimney duct: if the passage is too narrow, the entire mass of the gases formed is not provided, and if the passage is too wide, the walls of the chimney heat up worse, turbulence may occur, and cold street air may form reverse flows; • insufficient insulation of the pipe; • excessive length or angle of inclination of chimney sections deviating from the vertical, especially in the upper part of the duct; • Lack of air required for normal combustion: an additional supply duct should have been provided in the chimney design.


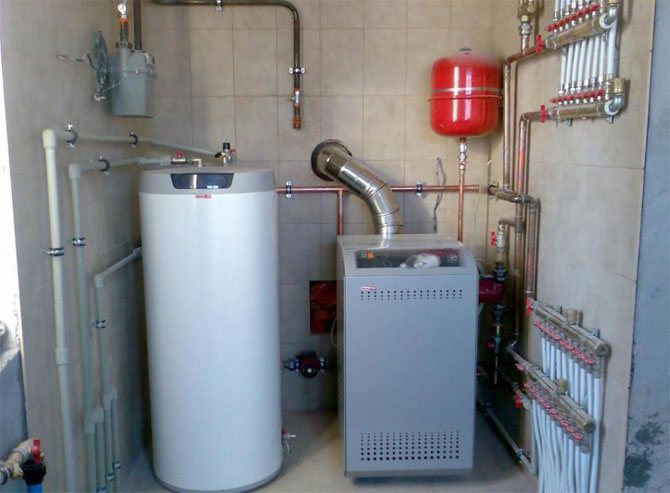
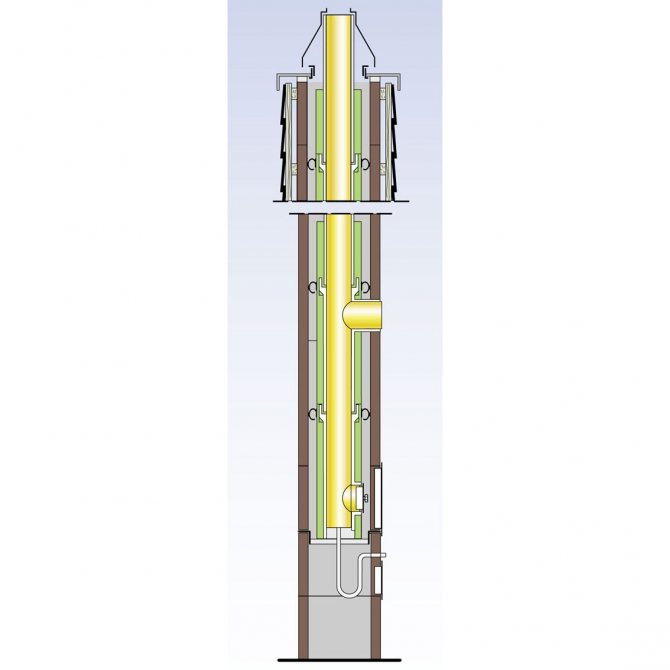
Flue gas evacuation and combustion air supply in modern low-temperature boilers are organized using coaxial gas ducts
With an insufficient height of the chimney above the roof, the draft often overturns - this is due to the wind. At the ridge of the roof, turbulences of the air flow appear, which is directed downward and, if the chimney outlet is located on the leeward slope, is capable of blowing flue gases back into the chimney.
To prevent blowing out, its end part must: • rise not less than 0.5 m above a flat roof, as well as a ridge or parapet of a pitched structure, if it is not more than 1.5 m above them; • be located not lower than a ridge or parapet, if it is from 1.5 to 3 m to them; • be above (or at the level) of a line drawn from the ridge downward at an angle of 10 ° to the horizon, if the pipe is more than 3 m away from the ridge.


A special fan installed inside the chimney will provide the necessary traction force, and the device, mounted in the form of a nozzle on the top of the chimney, will also play the role of a deflector
The vacuum in the chimney required to create good draft depends on its height. The minimum allowable value of this parameter is 5–5.5 m from the grate of the furnace to the upper cut of the pipe.Such requirements are easy to take into account in the process of building a one- or two-story house, however, their observance is fraught with some difficulties when installing a fireplace on the upper attic floor: the height of the ceilings and attic may be insufficient.
Good draft also depends on a correctly calculated chimney cross-sectional area, selected in accordance with the power of the heat generator. At a low temperature of exhaust gases, for example, in the case of using modern low-temperature boilers, electric smoke exhausters are used to increase the efficiency of the smoke channel, installed at the upper end of the structure and representing a fan, the blades of which are mounted on a vertical axis. The device forcibly removes the combustion products from the pipe, increasing the vacuum in the pipe and thereby providing the required traction force.
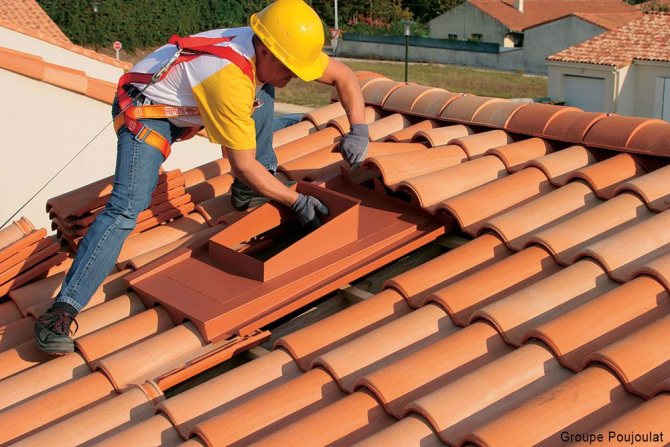


To protect the places where the roof passes through the chimney, special linings are used
Alternatively, insufficient efficiency of the chimney operation can be observed due to too rapid cooling of flue gases: this happens especially often in the cold season with poor thermal insulation of the pipe walls. By the way, sometimes, to restore the necessary thrust, it is enough to insulate a relatively small section of the structure in its upper part.
Inadmissible deviations of the duct from the vertical are also a source of problems in smoke evacuation. According to the norms, when using wood-burning heat generators, they can be no more than 30 ° in areas up to 1 m long. Such restrictions are associated with an increased fire hazard of such foci, and good traction serves as a certain protection against the ignition of nearby objects and structures.


The main tools of a chimney sweep are a metal ball on a string and a brush-brush. The special brush with a split handle cleans the chimney most effectively
It happens that in winter it blows from a non-working fireplace, pulls cold, that is, frosty air comes into the room from the street. This happens when the outer chimney cap is located below the end of the ventilation hood. Sometimes because of too large and poorly insulated attic. But the main reason is the lack of a properly organized air flow into the rooms, which leads to a decrease in pressure inside the house compared to the outside. The laws of physics are implacable: compensation of the resulting drop is achieved in the simplest and most affordable way, that is, through the chimney.
Excessive draft in the pipe leads to too fast and ineffective combustion of fuel: often this process is accompanied by active and very dangerous emission of sparks over the roof. However, adjusting the position of the slide gate will help to cope with this unpleasant phenomenon.
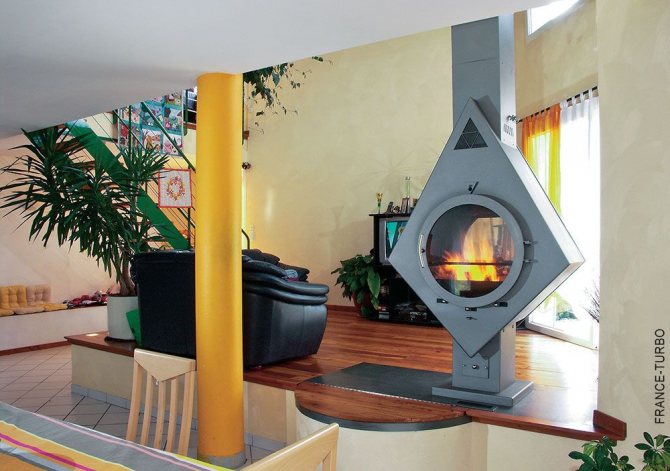


France-Turbo technology: turbine electric motor inside the flue duct
Top-mounted chimneys
This type is one of the most common. It gained its popularity due to its simple design, and also due to the fact that a variety of materials can be used for its construction. According to the principle of orientation in space, packing pipes are divided into vertical and horizontal. The first type is found much more often, however, it has two main disadvantages. Firstly, the combustion products are removed at a high speed, therefore the heat transfer of the chimney is very low, and secondly, if the construction technology is not followed, a slight smoke of the room is possible. The second type, unlike the first, has a high heat transfer, since the combustion products stay longer in the outlet channels, but it is more difficult to care for it due to the fact that a lot of soot settles in it, which must be cleaned out regularly.
We offer a video on how to install a Sandwich chimney.
For every fireman
Taking into account the high thrust force characteristic of direct-flow chimneys of fireplaces with an open hearth, in order to avoid ignition of the roof, especially made of combustible materials, it is recommended to equip the chimney heads with spark arresters. For the same reasons, according to the standards, the distance from the outer surfaces of brick or concrete chimney ducts to rafters, battens and other flammable roof parts should be at least 130 mm, and from ceramic pipes without and with thermal insulation - 250 and 130 mm respectively. In places where chimneys made of bricks of ceilings made of combustible materials pass through, the distances between them are normalized. For unprotected structures, it is chosen at least 500 mm, and for protected structures - at least 380 mm. In this case, we are talking about the construction of cutting, which is typical for brick chimney structures. But for modern modular chimney systems (steel sandwich type with an inner layer of basalt wool, ceramic concentric, etc.) there are no clear standards, so when installing them there is nothing left to do but follow the instructions of the manufacturers.


The soot deposited on the walls of the chimneys interferes with the normal flue gas discharge and can ignite, causing a fire.
It is possible to connect stoves to chimneys using chimneys with a length of no more than 0.4 m.At the same time, a distance of at least 0.5 m from the top of this element to the ceiling made of combustible materials must be maintained in the absence of ignition protection and at least 0.4 m - if available. According to the same standards, the bottom of the connector in question is removed from the combustible floor by 0.14 m or more. The chimneys are, of course, made of non-combustible materials.
Material compliance
Modern heating boilers are characterized by high thermal efficiency: almost all gas, liquid-fuel and even solid-fuel models have an efficiency of at least 84%, and usually exceeds 90%, and condensation models are the "champions" in this area.


Steel and ceramic chimney systems inside buildings are placed in shafts, the presence of which is recommended at the design stage of the house
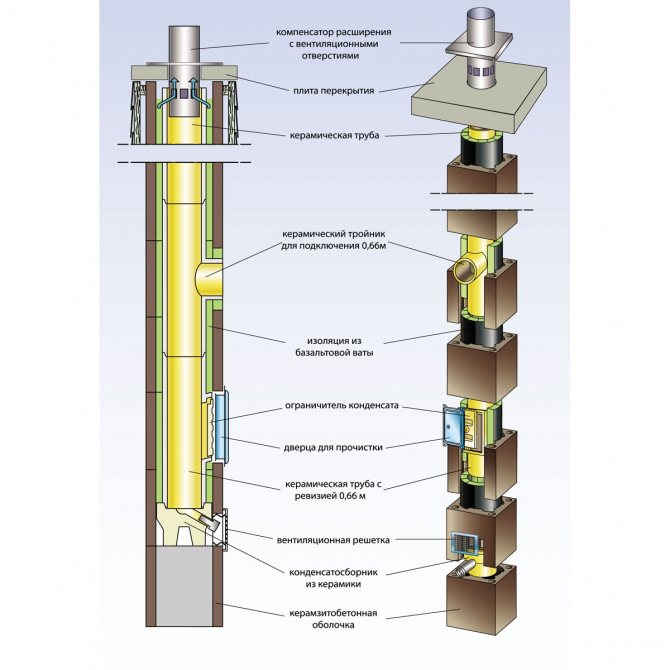
Such performance has a beneficial effect on the environment: due to a more complete combustion of fuel, the level of harmful emissions into the atmosphere is minimized, which also helps to save energy resources and money for the user. However, the inevitable consequence of this technical perfection is the low temperature of the flue gases, which can be as low as 100–120 ° C. It not only causes a deterioration in draft, but also leads to the formation of condensate with its settling on the walls of the chimney due to the presence of water vapor in the exhaust smoke. At its initially low temperature, liquid condensation still occurs inside the chimney: if the latter did not have time to warm up or was not initially insulated, then the process in question proceeds especially quickly. By settling on the walls of the channel, water dissolves the inorganic substances present in the combustion products and turns into an extremely aggressive mixture of sulfuric and nitric acids.
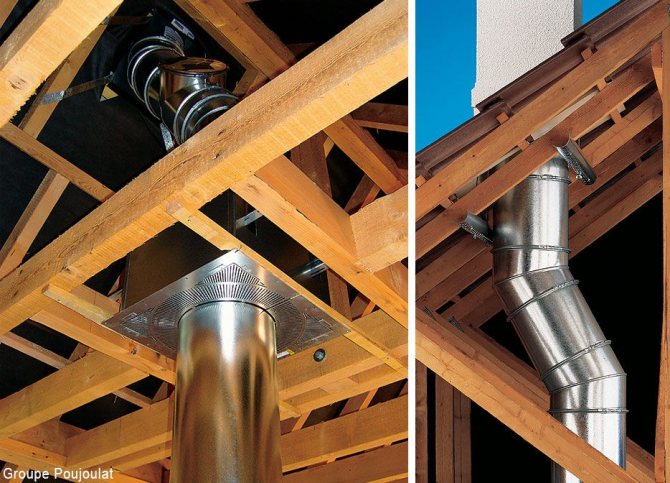


The chimney should be insulated from structures made of combustible materials. According to the standards, the chimney can deviate from the vertical at an angle of up to 30 ° with a section length of no more than 1 m
Condensate can form in large enough quantities, because when burning 1 m³ of natural gas, which is widely used as fuel for domestic heating boilers, about 2 liters of liquid are released, in the form of steam carried away from the furnace along with flue gases.Brick chimneys turned out to be extremely vulnerable to this effect: the mentioned acids corrode the surface of the brick, penetrate into the masonry, destroy the chimney, and then the decoration of the house, plaster, concrete. For this reason, such designs, which have proven themselves well when used with traditional stoves and fireplaces, are practically not suitable for modern boiler equipment without some refinement. Here, chimneys made of modern materials should be used, specially designed for low-temperature heating units. The most widespread are steel pipes - single-walled, which in this case are mounted inside a brick chimney, and double-walled "sandwich" type with an interlayer in the form of a mineral non-combustible insulation made of basalt fiber. Ceramic concentric flues and polymer systems are also produced for these purposes. There are even glass chimney designs. By the way, all of the listed materials are designed for a certain range of operating temperatures and can not always be used with stoves or fireplaces, the heat from which is unacceptably high.
To avoid the difficulties and inconveniences associated with an extraordinary repair of the chimney, you should initially select the flue system, taking into account the correspondence of the characteristics of the heat generator and the materials of the chimney.


When installing the pipe on the facade of the building, the fixing brackets are installed with a step of 2.5 m
For the manufacture of chimneys, leading manufacturers use stainless steel 1.4571, the good anti-corrosion properties of which are provided by a high chromium content, as well as additives based on molybdenum and nickel. The smooth polished surface of stainless steel chimneys reduces the aerodynamic resistance of the line, minimizes the possibility of soot deposition and facilitates the rapid removal of condensate, which in most such systems flows down the pipe base, is discharged to the firebox through a siphon, neutralizer or directly, and then discharged into the sewer.
Chimneys made of stainless steel, depending on their quality, are suitable for all types of fuels and combustion systems. According to the recommendations of the developers, they can be used both at operating temperatures of up to 600 ° C, and in tandem with condensing boilers, where the exhaust gases are cooled below the dew point. According to Russian regulations, modular two-layer prefabricated chimneys made of stainless steel with a layer of thermal insulation made of non-combustible material may be exposed to temperatures not exceeding 500 ° C. It should be noted that in a chimney or chimney, it rises to 1000 ° C only when soot is ignited, and in normal cases it does not exceed the already mentioned 600 ° C.
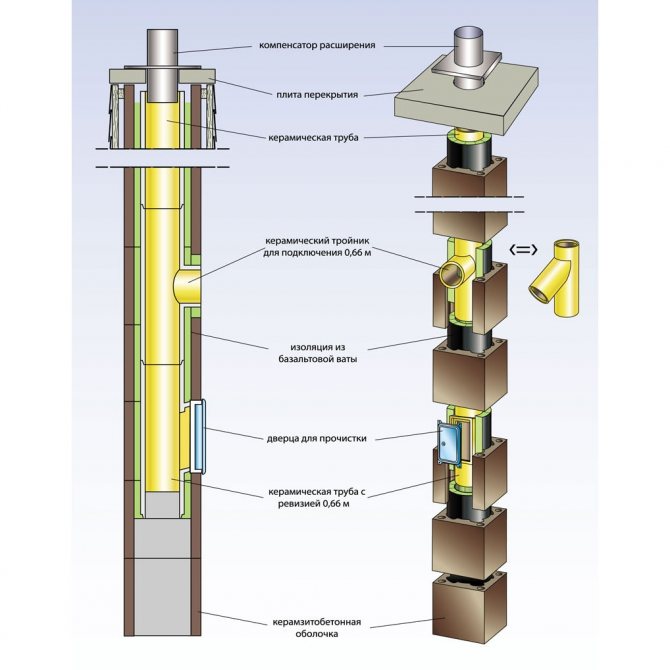
In double-walled systems, a heat-insulating material enclosed between the inner and outer layers reduces the heat loss of flue gases through the walls of the chimney, preventing them from cooling below the dew point, and condensation does not occur. To prevent smoke from penetrating through the wall of the structure, that is, water does not condense from its outer side, modern chimneys are made in a gas-tight design.


Openings in the chimney head and a deflector with a mechanical turbine serve to increase the draft in the duct
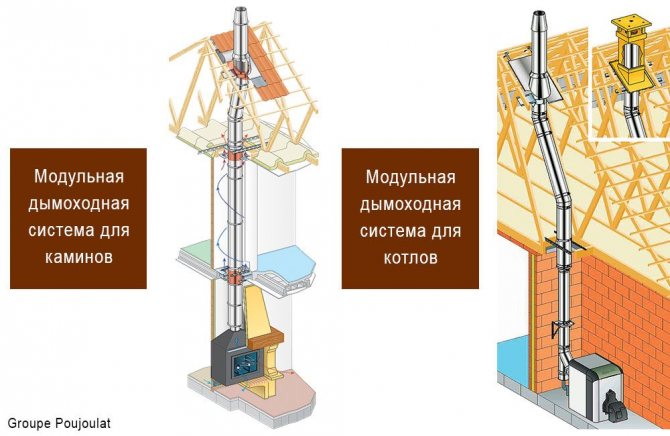
Double layer steel chimneys
The Russian market is offered by Schiedel, Jeremias, Raab and Rosinox (Germany), Fineline (Hungary), Camin Wierer (Italy) and others. Among the Russian manufacturers of similar products, Elits can also be mentioned.
Leading chimney manufacturers recommend the LAS (air-gas) system for apartment heating in multi-storey buildings. In this case, the flue gases are removed through the inner pipe, and the air required for fuel combustion is supplied to the boiler through the channel between it and the walls of the shaft.The use of LAS makes it possible to operate gas heating units in a mode independent of air exchange in the room, that is, this approach is most consistent with the requirements of SNiP 41-01-2003 (clause 6.2.2), which prescribe installing heat generators in apartments exclusively with closed combustion chambers. These products, manufactured from polymer materials, are offered on the Russian market, in particular, by the Viessmann company.
Condensing boilers, which are becoming more and more popular, make good use of the latent heat of flue gases, the temperature of which, as a result, drops to such an extent that condensation in the chimney cannot be ruled out, even with good thermal insulation of the latter. Fineline recommends the use of Furanflex polymer liner, which has a one-piece structure, as a means of combating corrosion of the inner walls of chimney pipes. This device is suitable for protecting brick and steel ducts of any length, and its installation is carried out without breaking the wall. At the same time, polymers do not withstand high temperatures, which is why they cannot be used to remove flue gases from stove and fireplace inserts.
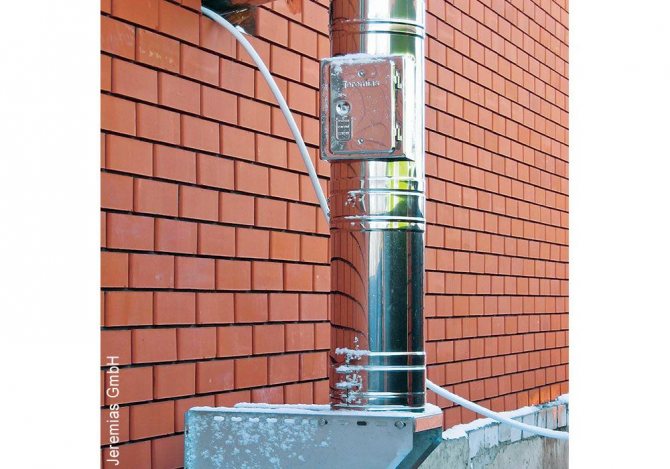


When installing a steel chimney at the exit of the structure from the wall, it is necessary to install additional fasteners, moreover, the elbows and bends are not supporting elements, they cannot be pressed against the outer surfaces of the building
Resistance to moisture and chemically aggressive environment is the main advantage of modern ceramic chimney systems, which are suitable for work with any type of heating equipment. Made of high quality technical ceramics, the chimney is immune to moisture, acids and temperature extremes, withstands up to 1250 ° C. Such chimneys are mounted from ceramic blocks, and a reliable gas-tight connection is provided by the very design of the channel in combination with a special sealant. The disadvantages of such systems are their relatively large mass, volume, and high cost.
Wall type chimneys
A pipe of this type consists of one or more interconnected channels, which are arranged according to the type of ventilation. Installation of a wall chimney is carried out directly in the wall itself. By its design features, this type of chimney is best suited for fireplaces that are used exclusively for aesthetic purposes.
Root chimney
For stoves, the purpose of which is to heat the house, it is better not to use a wall-type chimney, since it contributes to the removal of not only combustion products, but also heat into the street.
Hot topic
In stoves and fireplaces, the temperature of the exhaust gases is quite high, and therefore it is most reasonable to use brick or concrete chimneys with them, which, of course, does not exclude the possibility of using steel or clay structures. In principle, asbestos-cement analogs are also suitable, but in accordance with the norms, the flue gases in this case should not be heated above 300 ° C. It is advisable to provide for each stove a separate chimney duct, but it is possible to connect two stove inserts to one chimney if they are located on the same floor. When connecting chimneys, they should provide for incisions with a height of at least 1 m from the bottom of the joint.
If stoves are allowed to be placed only in one- or two-storey buildings, and for heat generators on each floor there must be a chimney, then solid fuel fireplaces with closed fireboxes can be installed even in multi-storey residential and public buildings. At the same time, they must be connected to the collective smoke exhaust system through an air seal with a length of at least 2 m, which excludes the spread of combustion products.


Chimneys made of technical ceramics are resistant to moisture and acids, as well as temperatures up to 1250 ° C
Errors in the construction of brick chimneys may also relate to the quality and characteristics of the masonry or the choice of bricks. In this case, you cannot use its slightly burnt wall or partition varieties. The thickness of the masonry joints should not exceed 5 mm, and the installation of the bars on the edge is not allowed. Significant miscalculations include the stepped shape of the inclined sections of the channel, which leads to the formation of eddies and a decrease in thrust. Inaccurate splitting of bricks, improper preparation of the mortar, the presence of voids in masonry joints and double vertical joints - all this causes problems during the operation of brick chimneys.
When constructing such structures, the use of hollow or porous bricks is not allowed. Only refractory ceramic products are used for masonry of furnaces and fireplaces, as well as chimneys. The technology of their production provides for firing at a temperature of 1300-1350 ° C, while the color of the finished product is different - from almost white to light brown, more often - straw with brown blotches. Taking into account the design features of furnace furnaces of various types, straight and wedge-shaped (end and ribbed) refractory bricks are produced.
The condition of the brick chimney must be periodically monitored: to simplify this task, the structures are whitewashed, since black soot, indicating the presence of cracks and flue gas leaks, is clearly visible on the light surface.

Why do you need a chimney?
All stove chimneys are equipped according to a certain technology, which takes into account many nuances. At the same time, many people do not attach due importance to chimneys, since they think that their functions are only in the removal of combustion products.
However, in practice, stove flues regulate many processes, namely:
- output of carbon monoxide gases to the street;
- regulation of the speed of movement of smoke through the chimney;
- additional heat transfer and heating of the wall bordering the chimney.
The design of the chimney may differ in each case. It can be simple in shape, or it can be made according to the principle of an air maze. The second option is more difficult to implement, however, it contributes to a significant increase in the efficiency of heating the room. This is due to the fact that hot smoke stays in the chimney longer, so it has time to give off more heat. A low speed is ideal so that condensation does not form on the pipe walls.
see also
- Heating equipment and engineering systems | # 3 (53) ‘2011 Pellet boilers Wood-fired heat generators capable of operating in automatic mode, having an efficiency of over 90% and requiring ash pan cleaning no more than twice a year - is this possible? Quite. And in this case we are talking about pellet boilers, which managed to gain quite wide popularity in Western countries ...
- Heating equipment and engineering systems | # 2 (52) ‘2011 Managed Forecast
The weather in the house is formed due to temperature, humidity and, in part, its pressure. To maintain these parameters at a comfortable level, a whole complex of devices is usually used, with a standard approach including ventilation and air conditioning equipment, as an option - endowed with some additional functions ... - Heating equipment and engineering systems | No.2 (52) '2011 Gas flowing water heaters
Gas instantaneous water heaters, otherwise called gas water heaters, are one of the oldest types of household equipment that runs on natural gas. The principle of their operation has not changed at all since 1894-95, when Robert Weillant and Hugo Junkers invented and began to produce these very useful and still quite widespread devices ...