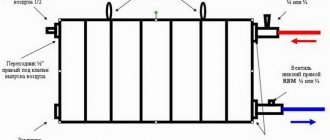
How sections are added
After you have empirically determined that the reason for the cool temperature in the house is not a clogged radiator at all, you should find a store that sells heating equipment not far from your house (so that you do not have to travel far away and thereby waste your time). You need to buy the same sections that your radiator is equipped with - made of cast iron, aluminum, or bimetallic.
It shouldn't turn out that you choose unsuitable sections - because of such an error, you simply won't be able to add them, that is, the money spent will be thrown into the wind, so be careful. The procedure for building up sections is carried out in the same sequence of actions for all types of heating radiators.

To join the sections, you need a connecting nut - nipple
We proceed directly to increasing the number of sections. The first step is to unscrew the footboard using the radiator wrench from the side to which you plan to add one or more elements. After you have unscrewed the futorka, a nipple (connecting nut) is applied to the section where the sections are joined. It is necessary to take into account the following important feature: the threads at different ends of the nipple are different, and in order to correctly install new sections, you must follow the following rules:
- The right side of the nipple should be directed towards the side where the connection with the new element will be made;
- Accordingly, the left one is towards the already present sections of the heating radiator.
In order to prevent further battery leakage, you should put on the nipple intersectional gaskets (they can be rubber, parasite, or gel)
At the same time, you need to put them on carefully and carefully - this will serve as a guarantee that the gasket will be located as evenly as possible, without unwanted distortions. Next, you need to tighten the thread
This action should also be carried out without sudden movements, in a leisurely rhythm, and carefully. If you want to build a high-quality heating radiator, then there can be no question of any rush.


To prevent leakage, an intersection gasket is required.
It is highly undesirable to damage the metal thread - because of this, not the most harmless problems may appear, the solution of which will have to spend additional time and financial resources.
The enlarged radiator must be placed back on the bracket and re-connected to the central heating pipe. To do this, you must arm yourself with a wrench of the appropriate diameter and tow, which is necessary for wrapping pipe threads when screwing on the radiator.
It is not difficult to add sections to a heating radiator, for this you do not need to work in a team of heating installers for 10 years. But you cannot do without a serious approach, the availability of elementary tools and the removal of your personal time by this process. However, you can also resort to the second option for solving the problem of insufficient heating of the room - to become a client of a company providing such services, whose employees will do everything themselves, quickly and efficiently.
Calculation of the number of radiators
How much do I need to add? Here you need to move your brains a little and try to calculate the required number of sections, based on the type of radiators, the volume of the heated room, the number of windows, their condition, the material of the walls, the location of the room and other factors.Consider the option with cast iron batteries, the power of one section of which is on average 100 -150 watts.
The power of other types of radiators is usually indicated in the technical data sheet for the product.
We make a calculation for a one-room apartment with an area of 18 sq. m, where the ceiling height is standard and equal to 2.5 m. Windows - plastic double-glazed windows, corner apartment, located in the average climate of our country. The radiators in the apartment are connected through the top wiring.
18 (area) x 100 = 1800 W.
The correction factor for the ceiling height in our case is 0.8, since 3 m is taken as a basis. 1800 x 0.8 = 1440 W. Taking into account the angular placement of the apartment, the correction factor will be 1.8. We multiply the received power of 1440 by 1.8 and get the power = 2592 kW. This value should be multiplied again by the factor for the presence of windows. In our case, there are 2 windows and K = 1.8. 2592 x1.8, we get the next power value equal to 4565 kW. Plastic double-glazed windows give K = 0.8, the final power is 4565x0.8 = 3732 Kw. Now you can determine how many cast-iron sections to keep warm in the apartment. 3732: 150 = 24.8 i.e. 25 sections.


Naturally, this calculation is very approximate. The number of sections may vary depending on the temperature of the coolant supplied to the centralized heating network, on how insulated the doors, ceiling and walls and their material, on the area of the windows, on the presence of fencing screens on batteries, curtains and others. But if a significantly smaller number of sections are installed in your apartment, then they should be added in any case.
Installing new radiator sections
You should immediately make a reservation that you need to add sections of exactly the same type and brands that are already in your apartment. Otherwise, the whole venture may fail due to a discrepancy between the dimensions of the cross-section of the inlet and outlet, dimensions in height, and the material of manufacture.
First of all, you need to turn off the water and drain the one that flows out when you unscrew the footwear. After that, connecting elements (nipples) in the form of a nut are applied to the docking place and on top of the intersectional gaskets made of rubber, paronite or special gel.
The nipple is threaded on both sides, and on each side it is cut in different directions. The right side of the nipple is inserted when adding new sections is done from the left side. This means that the left side of the nipple must be inserted into the hole of the existing battery. The gaskets must be applied very carefully and, one might say, gently.
Installation of aluminum radiators
Assembling and setting up a heating system is a responsible business, professionals will cope with it best of all. But if you wish, you can do the installation of aluminum radiators with your own hands.
First you need to assemble the device:
- Screw in the supplied plugs and plugs.
- Assemble the thermostats and connect the shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet of the device.
- Check the nipples and secure the air valves.
The assembly-disassembly diagram of the device is attached to the kit. It is better if the assembly is carried out by a specialist, then there will be a guarantee that all the taps are installed correctly. It is not allowed to clean aluminum with abrasives when installing adapters or building up sections - a coolant leak may begin.
Attention! It is necessary to screw the air valves so that at the end of the process their outlet heads point up. Having marked the installation location of the battery under the window in accordance with the indicated indents, brackets are attached to the wall
To do this, you need to drill holes with a puncher and insert plastic dowels, and screw the brackets into them. While screwing in the fasteners, from time to time it is necessary to hang a radiator on them in order to maintain a distance of 5 cm from the wall
Having marked the location of the battery installation under the window in accordance with the indicated indents, the brackets are attached to the wall. To do this, you need to drill holes with a puncher and insert plastic dowels, and screw the brackets into them. While screwing in the fasteners, from time to time it is necessary to hang a radiator on them in order to maintain a distance of 5 cm from the wall.
Battery Connection Diagrams
The device can be connected in several ways:
Diagonal. Experts consider it to be the most energy efficient. The supply pipe is connected to the upper pipe, and the outlet pipe is connected to the lower pipe, but on the opposite side of the radiator. With this scheme, the battery gives off the maximum thermal energy received from hot water into the space. The disadvantage of this method is that the pipes running on top do not fit well into the design of the room.
Side. The pipe supplying the coolant is connected to the side fitting (right or left), the return pipe is connected to the parallel lower one. If the pipes are brought in in the reverse order, the heat transfer of the device will drop by 50%. Such a scheme for connecting aluminum heating radiators works ineffectively if the sections are of a non-standard size, or their number exceeds 15.
From a design point of view, aluminum radiators with bottom connections win. With such a layout, pipes are not visible, they are hidden in the floor or in the wall. The batteries are connected to the system through the pipes located at the bottom of the instruments. Typically, bottom-connected radiators are mounted on floor brackets. The battery is attached to the wall with one hook, just to maintain balance.
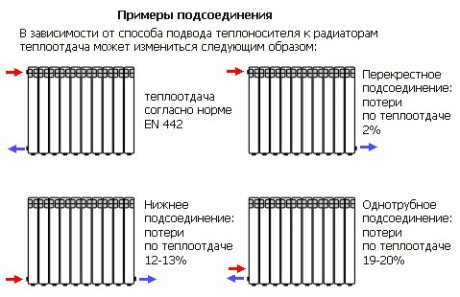

Wiring diagrams for heating radiators made of aluminum
Important! Aluminum batteries have standard pipe parameters, so you don't need to buy any additional adapters from the radiator to the pipes. The device also comes with a Mayevsky cock, designed to bleed air.
Connection and commissioning
Before installing aluminum devices, the autonomous system is flushed with water. Alkaline solutions cannot be used.
Important! Aluminum is easy to wrinkle and scratch with tools, so it is better to mount the battery in the original plastic packaging. Once connected, the polyethylene can be removed
In an effort to connect aluminum heating radiators at no great cost, some homeowners are using blind, non-separable pipe and radiator fittings. But heating a house in the northern hemisphere is not a point to save money on. It would be wiser to install "American" - quick-disconnect threaded assemblies, when the pipes are joined and disconnected by means of one union nut.
The procedure for connecting radiators to the heating system:
- Make sure that there is no water in the system or it is shut off at the installation points.
- Hang up the radiator and connect to the pipeline using squeegees.
- Seal all threaded connections using sanitary flax. Enough 4-5 turns in the direction of the thread.
- Pressurize the system.


Aluminum battery connected to the heating system
The installation of an aluminum heating radiator can be done independently, but it would be wiser to entrust the matter to specialists who have all the necessary permits to perform such work. The slightest inaccuracy in the installation can lead to leaks and ineffective functioning of the heating system.
Aluminum battery


Before installing heating devices, it is necessary to correctly make all the calculations and calculate the required number of nodes, because the temperature in the room during the heating season will depend on this. If this work is not carried out correctly, then you will have to build up the heating batteries, and for this you need to read the instructions:
- Calculations are made based on the following data: with a ceiling height of 260 cm, 2 sections are needed for heating 1 m2.
- Before assembly, make sure that all components and parts are selected correctly. To build up the compartments, the supply pipes are disconnected and the plugs are turned out either from the top or from the bottom;
- An additional section is combined with a heating battery, an O-ring is installed, which is made of rubber (heat-resistant) and, using a special key, the nipple is screwed into the aluminum manifold. The gripping depth is 4 threads;
- After they are convinced that the structure is strong, they proceed to docking the next section;
- At the end of the assembly, the plugs are put in place and the connections are made, but already with the displacement of the supply pipe.
It is important! Experts advise installing heating devices with a supply of sections, since it is easier to reduce their number than to add. It should also be noted that not all types of aluminum radiators are equipped with additional compartments. Such models include extruded, which are a one-piece, molded structure produced by pressing and therefore cannot be increased. If this type of radiator is installed and the room is poorly heated, then you need to purchase and install an additional battery.
Technique for performing work on connecting radiator sections


Extending radiators is a useful skill for a home craftsman. Knowing how to join the sections, it will not be difficult to provide your own microclimate in each room.
Before connecting two radiators, the power is calculated. The formula is simple - 1 kW of thermal power is required per 10 m2. The section performance is indicated in the data sheet. This data will be useful for calculations. After that, you need to buy the required number of elements, find tools and assemble a heating device.
Tools and accessories for work
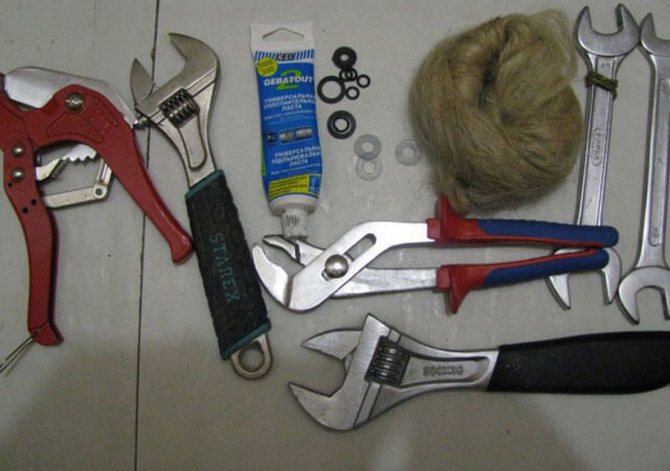


To assemble a heating radiator with your own hands will come in handy:
- wrench or adjustable wrench;
- radiator key;
- plugs with right and left threads - 1 pc .;
- nipples;
- paronite gaskets;
- cross-section spacers made of durable, flexible material;
- battery sections;
- sandpaper of fraction No. 120.
Cotton gloves are useful for protection. It is more convenient to install batteries together, an assistant will not interfere.
Step-by-step battery build-up process
Do-it-yourself heating radiator assembly is performed at any time. If the heating season has already begun, the network must be shut off, the coolant must be drained from the circuit and the heater must be dismantled.
How to connect the battery:
- Lay the dismantled radiator on a horizontal surface. To avoid scratching the surface of the battery and the table (floor), lay down a cloth. Remove all additional elements - taps, temperature sensors. For flushing, take the battery into a bathtub, open the plugs and rinse with a stream of water.
Check the integrity of the threaded connections, the ends of the heater. If there are build-ups of deposits, sand the joints. Place the battery again on a flat, horizontal surface. The area is selected flat to ensure the tightness of the joint. The slightest curvature of the position will lead to an uneven joint. For seals, choose only paronite gaskets. It is a durable, flexible material that can withstand heat without loss of quality. Check the quality of the nipple thread
Smooth and even cutting without chipping is the key to a strong docking. Move the sections by inserting spacers between them. Carefully start tightening the nipple. The part has a left-hand thread on one side and a right-hand thread on the other.
This means that when rotating, both sections are attracted. It is more convenient to carry out work with a special radiator key. The tool may come with a battery, but is also sold separately.


- Grab the sections a little, check the evenness of the joints and tighten until tight. The number of turns of the nipple turns on each section must be equal.
Knowing how to increase the heating battery, it is easy to assemble a system with the required power indicators.After building up the sections, the radiator is checked for tightness.
For a household check you will need:
- a piece of pipe with a cross section of 15 mm;
- automobile pump with a pressure gauge;
- nipple from the tire.
Now solder the nipple to the pipe, and insert it into the radiator. This design is needed for air pressure testing. Install a plug on one of the radiator inlet openings. Connect a car pump with a pressure gauge to the nipple. Pump in air at a pressure of 1 bar. If the tightness of the joints is broken, a whistling of air will appear. You need to find a leak, tighten the nipple or change the gasket. Pressurize again. If there are no leaks, install the radiator into the network.
Water pressure testing is carried out in the same manner. Instead of air, colored water is pumped in. Let the device stand for 5 hours, inspect for leaks. If there is a leaky joint, water will leak out. Tighten the joints, check again, install the battery in the system.
The extended battery increases in weight. Before installing the radiator, it is advisable to strengthen the fasteners, screw in additional brackets. This will save the device from collapse, because the battery will be even heavier with the coolant. The device is built into the network in the selected place, taking into account the increase in the length of the battery.
Assembling the radiator
To obtain a positive result, you should take care of the quality of the radiator gaskets. As a rule, paronite options are used that have sufficient strength and durability. You also need to check the condition of the nipples, especially the quality of the thread and the integrity of the sockets. There should be no chips on them, and the cutting should be complete and even.
Observing the sequence of actions, with due attention, you can do the assembly yourself. This will require:
- Place the radiator and prepared sections on a flat surface.
- Slide the sections and put nipples with gaskets between them.
- Gently start tightening the nipple. Since it has a left-hand thread on one side and a right-hand thread on the other, when twisting, the sections are simultaneously attracted to each other. Knowing this feature of the nipple, even a beginner will understand how to remove a section from a bimetallic radiator. It is enough to twist it in the opposite direction, and the sections will move away from each other. The work is carried out with a special radiator key.
- After all the nipples are inserted and lightly tacked, they must be screwed on tightly, making the same number of turns. This is important to avoid distortions. If 3 turns were made on one nipple, then the same amount of movement is performed on all the others.
To understand that the assembly of the bimetallic radiator sections was carried out correctly, you can only carry out the appropriate test.
Connection diagrams
The most fail-safe circuit for connecting heating radiators in a private house with a bottling and a boiler is a single-pipe Leningrad. Heating devices are connected in parallel with the filling, which is laid along the perimeter of the room.
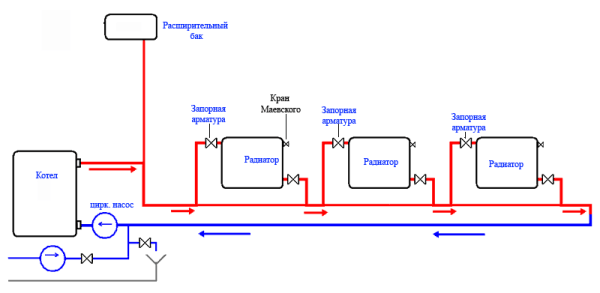

Somewhat cheaper in installation, but much more problematic in operation is a circuit using a series connection of batteries. Suffice it to say that their independent adjustment is impossible in this case.
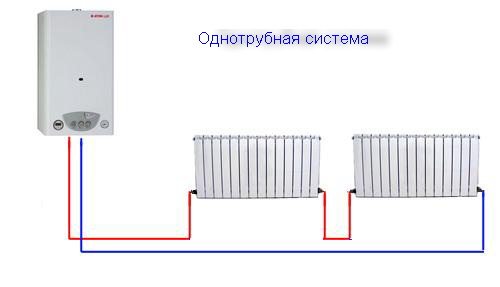

Single-pipe version with series connection.
Finally, a two-pipe system involves connecting each radiator as a jumper between the supply and return lines. It is inconvenient in that it requires the already mentioned balancing - limiting the passage of heating devices closest to the boiler.
What can be the diagrams for connecting heating radiators to the supply line?
- One-sided. connections are connected to the upper and lower radiator plugs on the right or left. It is compact, but makes the heating of the device uneven: the last sections will always be colder than the first.
- From bottom to bottom.In this case, the battery must be equipped with an air vent. The advantages of the solution are that the radiator, with such a connection, does not require flushing and always heats up along its entire length.
- Diagonal. Heating of the sections is even more uniform; however, the bottom corner of an instrument with a blind plug will gradually silt up.
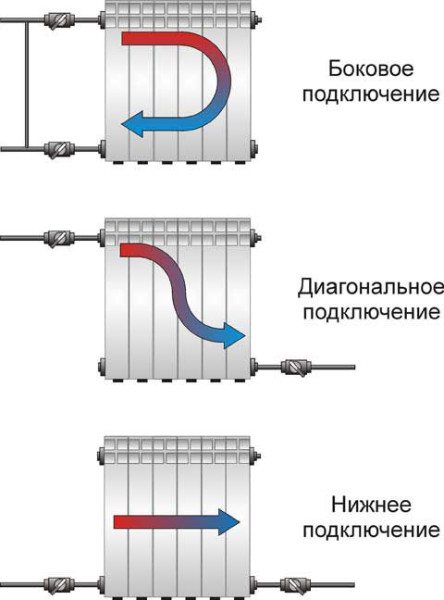

Connection options for connections.
Connection diagrams
The batteries must be connected to the heating circuit according to the selected scheme. Violation of the sequence and building rules will provoke leakage of almost 50% of the heat.
Violation of the connection technique will cause uneven heating, lead to a breakthrough, leakage. It is important to choose the right system, to correctly connect it to the radiators. Installation will require concentration and accuracy of calculation.
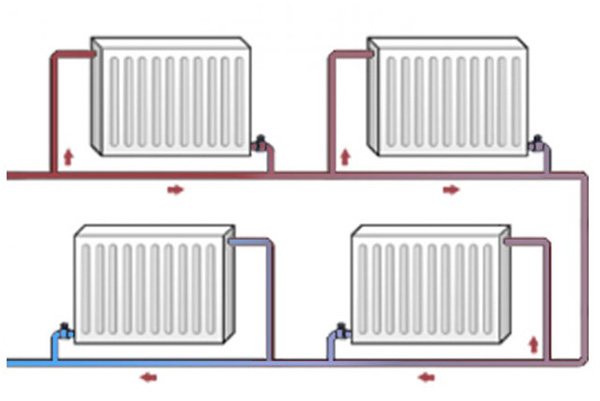

Connection methods
Radiators are connected in several ways:
- Consecutively - you need one pipe of the heating circuit.
- Parallel - Requires 2 pipes connected with an upper, lower bend.
- Through and through - the water in the system flows through the heating device.
Bimetallic heating radiators
Comparative characteristics with other types of batteries


The photo shows a tall, narrow device.
First you need to understand what heating radiators are, and how they differ from each other.
Let's list the main types:
- Cast iron batteries are one of the most common types found in most Soviet-style apartments. It is a system of connected cast iron sections with fairly thick walls and a large mass. It is distinguished by high strength and durability, however, it has low efficiency and heat transfer, and a large thermal inertia can also be noted;
- Steel tubular registers are a system of pipes of a sufficiently large diameter, or one pipe in the form of an S-shaped bend (for example, a heated towel rail). This type of device is usually installed in large rooms - concert halls, cinemas, sports complexes, supermarkets. They are distinguished by high power and large volume of the coolant;
- Steel heating panels. They are welded profiled steel plates, inside of which there are channels for the circulation of the coolant. They have a rather low resistance to water hammer and low strength, are prone to corrosion and are not very reliable;
- Aluminum radiators are a more modern type of batteries, which are distinguished by increased heat transfer and efficiency, a low volume of coolant and a low weight of the device. Due to their low thermal inertia, they lend themselves well to automatic and manual temperature control. They are demanding on the quality of the coolant and its acidity, have an average strength and service life;
- Copper batteries are a tube system with plate finning. They are distinguished by the highest heat transfer and efficiency, high strength and resistance to water hammer, absence of corrosion and long service life. The only drawback of copper units is the high price;
- Bimetallic radiators, externally and in design, resemble aluminum devices with the difference that the inner walls of the channels are made of steel or copper. Thus, it is possible to increase the efficiency and heat transfer of the battery, but maintain its strength and durability.


The cast-iron battery familiar to many.
To understand the main distinguishing feature of a bimetallic device, one should better understand its design. The main task of any battery on a liquid coolant is to ensure maximum heat transfer from the coolant to the environment, while having a sufficient margin of mechanical and corrosion resistance for long-term efficient operation.
The degree of heat transfer directly depends on the thermal conductivity of the metal and the thickness of the walls. The most thermally conductive materials are aluminum and copper, so the most efficient appliances are made from non-ferrous metals.


The most efficient heat sinks are made of copper.
On the other hand, steel and ferrous metals show the highest strength. But they are prone to corrosion and have low thermal conductivity. At the same time, steel is much cheaper than copper and aluminum, which is also an advantage.
The design of the bimetallic radiator is distinguished by the fact that the inner walls of the channels are made of durable anti-corrosion steel or pure copper, and the outer walls and fins are made of lightweight and heat-conducting aluminum. This solution made it possible to combine the advantages of steel and non-ferrous metals in one device.


The inner surface of the channels and the collector is made of steel.
Important! Bimetallic radiators have combined the advantages of products made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, becoming the most progressive and modern type of heating devices.
Advantages and disadvantages


The convector fits perfectly into a modern interior.
Consider the positive and negative aspects of using aggregates with combined metals in the composition. Let's start with the benefits:
Heating system options
The most common and demanded are one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems. Let's take a closer look at each of them and the correct connection of the heating batteries in each case.
A single-pipe heating system is used today mainly for multi-storey buildings.
The hot coolant spreads through the pipes from top to bottom, evenly distributed over all heating devices. Such a system is installed quite easily and requires a relatively small amount of materials. But at the same time, it also has a number of disadvantages:
- there is no possibility of adjusting the degree of heating of individual radiators;
- on the lower floors, the temperature of the batteries can be significantly lower than on the upper ones, since the coolant reaches them already cooled;
- in the event of a breakdown on any floor, the entire riser is turned off;
- it is quite difficult to disconnect from the system for the installation of autonomous heating.
One-pipe heating system
A two-pipe heating system is most often used to create heating in private houses, cottages. It involves connecting two pipes to the radiator at once: one to the battery is supplied with hot coolant, and the other is the outflow of already cooled water
It is important to take into account that all radiators in a two-pipe system are connected only in parallel.
A two-pipe heating system has several significant advantages. First of all, the temperature of all radiators will always be the same, no matter how far from the boiler they are installed.
In addition, with this type of system, it is possible to adjust the degree of heating of each individual radiator - this allows you to create the most comfortable temperature in each room.
Two-pipe heating system
A heating system of this type includes the following elements:
- a radiator with a valve at the top and a plug at the bottom;
- radiator plugs;
- valve with thermostat;
- bypass;
- shank;
- stopcock;
- couplings and locknuts;
- heating pipes (metal, polypropylene).
Heating system composition
It should be noted that the same set of accessories, with the exception of a valve with a thermostat and a bypass, is suitable for the installation of a one-pipe heating system.
Radiator selection
You should start with the choice of a radiator, and the main criterion for choosing will be the working pressure for which the radiator is designed. For a private house with its own heating system, a radiator with a working pressure of 6-7 atmospheres will be enough, but if you need to connect a radiator to the central heating system of an apartment building, it must withstand a pressure of at least 10 atmospheres.
Currently, the consumer is offered two options for aluminum radiators - standard or European and reinforced. The latter can work under pressure up to 12 atmospheres. When connecting to a central heating system, you must choose exactly among the reinforced radiators.


The number of sections plays a big role
Next, you need to decide on the required number of sections. To do this, we determine the amount of heat. Necessary for heating the room and divide by the heat transfer of one section of the selected radiator.
The amount of required heat for a standard room can be taken equal to 1 kW per 10 m2 of the area of the room. For non-standard premises and more accurate calculations, we will use a ready-made table:
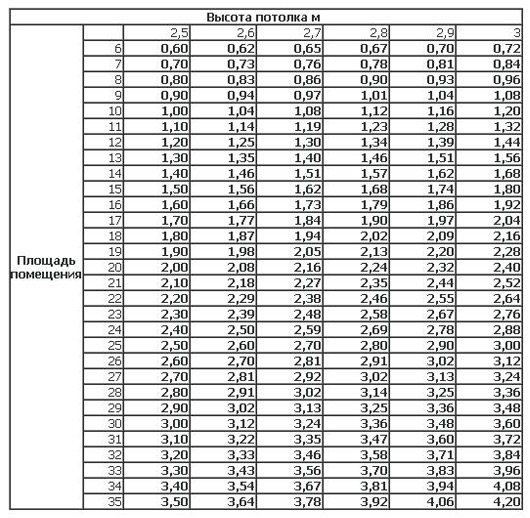

Radiator power table
It should be remembered that the battery connection diagram of more than 12 sections must be double-sided, diagonal or saddle. With a one-sided connection diagram of the battery from a large number of sections, a "pocket" of cold water will form on the side of the radiator opposite to the pipes. "Extra" sections simply will not work, we get harmful ballast.
Using forced discharge, the battery can be expanded to 24 sections even with one-way supply, but in this case the radiator must be reinforced.
It should be remembered that it is necessary to supply the coolant to reinforced radiators under high pressure only through metal pipes. Metal-plastic may not withstand such pressure, and the consequences will be the most dire.
It should also be taken into account that the heat transfer of the radiator indicated in the documentation is relevant only for one-sided or diagonal supply of the coolant to the radiator. When using the bottom feed, feel free to subtract 10-15 percent.
If the heating system is installed in a private house, then it is possible to choose the general scheme of heating organization yourself - one- or two-pipe.
Features of mounting radiators
When installing heating radiators and when connecting a heating radiator, the requirements specified in SNiP should be strictly observed. In particular, this applies to maintaining the required distance between the radiator and the wall, floor and window sill:
- the distance from the upper part of the radiator to the window sill should be at least 10 cm. If the specified gap is lower, this may impede the movement of the heat flow - thus, the room will warm up worse;
- the distance from the bottom of the radiator to the floor should be at least 12 cm. If it is less, there is a risk of a significant increase in the temperature difference at different heights of the room;
- the distance from the rear wall of the radiator to the wall must be at least 2 cm. Otherwise, the heat transfer of the radiator will be disturbed.
Heating battery installation requirements
It is also important to take into account the fact that the installation method and how to correctly connect the heating radiators. also affects the quality of space heating
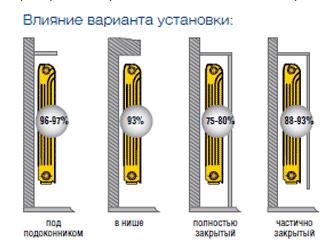
So, options for installing radiators are possible:
- open under the windowsill - the maximum efficiency of the heating system - 96% -97%;
- open in a niche - the efficiency is slightly lower - 93%;
- in a partially closed form - there is a decrease in efficiency up to 88%;
- fully closed - heating efficiency is only 75% -80%.
Heating radiator installation examples
The piping of the radiator and how to properly connect the radiator can be done using various types of pipes. The main thing is strict adherence to all the specified requirements and rules. If the radiator is connected without errors, the heating system will not need to be repaired for many years. Now we know how best to connect heating radiators - but it's even better to ask professionals about it.
Many homeowners are not happy with the heating efficiency of their apartment.This issue is especially acute during severe cold weather. Sometimes poor heating is associated with a worn out radiator. In this case, the heating structure is replaced with more efficient and powerful equipment. Today, ceramic radiators, bimetallic and aluminum radiators are on sale. But the most reliable and durable are cast-iron models. If the battery is in excellent condition, it is impractical to change it. In this case, you can add sections to the radiator. This article is devoted to how to build up a heating battery.
Placement of heating devices
It is of great importance not only how to connect heating radiators to each other, but also their correct location in relation to building structures. Traditionally, heaters are installed along the walls of rooms and locally under windows to reduce the penetration of cold air currents in the most vulnerable place.
There are clear instructions for this in the SNiP for the installation of thermal equipment:
- The gap between the floor and the bottom of the battery must not be less than 120 mm. With a decrease in the distance from the device to the floor, the distribution of the heat flow will be uneven;
- The distance from the back surface to the wall on which the radiator is mounted must be from 30 to 50 mm, otherwise its heat transfer will be disturbed;
- The gap from the upper edge of the heater to the window sill is maintained within 100-120 mm (not less). Otherwise, the movement of thermal masses may be difficult, which will weaken the heating of the room.
Bimetallic heating devices
To understand how to connect bimetallic radiators to each other, you need to know that almost all of them are suitable for any type of connection:
- They have four points of possible connection - two upper and two lower;
- Equipped with plugs and a Mayevsky tap, through which you can bleed the air collected in the heating system;
Diagonal connection is considered the most effective for bimetallic batteries, especially when it comes to a large number of sections in the device. Although very wide batteries, equipped with ten or more sections, are undesirable to use.
Advice! It is better to ponder the question of how to properly connect two heating radiators 7-8 sectional instead of one device of 14 or 16 sections. It will be much easier to install and easier to maintain.
Another question - how to connect sections of a bimetallic radiator may arise when rearranging sections of a heater in various situations:

The place where you plan to install the heater is also important.
- In the process of creating new heating networks;
- If it is necessary to replace a failed radiator with a new one - bimetallic;
- In case of underheating, you can build up the battery by connecting additional sections.
Aluminum batteries
Interesting! By and large, it should be noted that diagonal connection is an excellent option for any type of battery. Not sure how to connect aluminum radiators to each other. connect diagonally, you won't go wrong!
For closed-type heating networks in private houses, it is advisable to install aluminum batteries, since it is easier here to ensure proper water treatment before filling the system. And their cost is much lower than that of bimetallic devices.


Of course, over time, moving along the radiators, the coolant cools
Of course, you will have to try before you connect the sections of the aluminum radiator for regrouping.
Advice! Do not rush to remove the factory packaging (film) from the installed heating devices before finishing the finishing work in the room. This will protect the radiator coating from damage and contamination.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=y9a35JHa0TM
The work process itself does not take much time, you do not need any special skill or expensive equipment, you can purchase all the necessary tools at any hardware store. And do not forget, the connection will serve you for a long time and without hassle only if you used high-quality materials in your work and followed all the rules for installing the heating system.
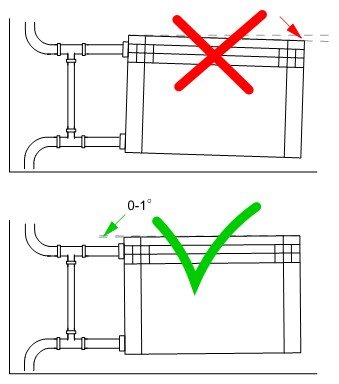

We are talking about exactly what is indicated in this figure.
In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic.
How to install correctly
Now how to hang a radiator. It is highly desirable that the wall behind the radiator is level - it is easier to work this way. The middle of the opening is marked on the wall, a horizontal line is drawn 10-12 cm below the window sill line. This is the line along which the upper edge of the heater is aligned. The brackets must be installed so that the top edge coincides with the drawn line, that is, it is horizontal. This arrangement is suitable for forced circulation heating systems (with a pump) or for apartments. For systems with natural circulation, a slight slope is made - 1-1.5% - along the flow of the coolant. You can't do more - there will be stagnation.
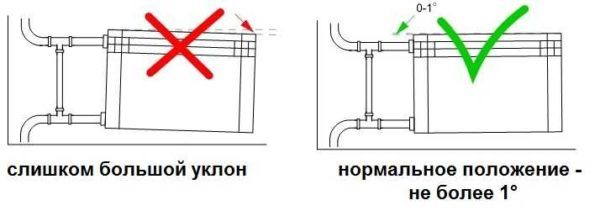

Correct installation of heating radiators
Wall mount
This must be taken into account when installing hooks or brackets for heating radiators. Hooks are installed like dowels - a hole of a suitable diameter is drilled in the wall, a plastic dowel is installed in it, and the hook is screwed into it. The distance from the wall to the heater can be easily adjusted by twisting and unscrewing the hook body.


Cast iron battery hooks are thicker. This is a fastener for aluminum and bimetallic
When installing hooks under heating radiators, keep in mind that the main load falls on the upper fasteners. The lower one serves only for fixing in a given position relative to the wall and is installed 1-1.5 cm lower than the lower collector. Otherwise, you simply cannot hang the radiator.


One of the types of brackets
When installing the brackets, they are applied to the wall in the place where they will be mounted. To do this, first attach the battery to the installation site, look where the bracket will "fit", mark the place on the wall. With the battery down, you can attach the bracket to the wall and mark the location of the fasteners on it. In these places, holes are drilled, dowels are inserted, the bracket is screwed onto the screws. Having installed all the fasteners, the heater is hung on them.
Fixing to the floor
Not all walls can support even lightweight aluminum batteries. If the walls are made of lightweight concrete or covered with plasterboard, floor installation is required. Some types of cast iron and steel radiators come immediately on legs, but they do not suit everyone in appearance or characteristics.


Feet for installing aluminum and bimetallic radiators on the floor
Possible floor installation of aluminum and bimetallic radiators. There are special brackets for them. They are attached to the floor, then the heating device is installed, the lower collector is fixed with an arc on the installed legs. There are similar legs with adjustable height, there are fixed ones. The method of fastening to the floor is standard - on nails or dowels, depending on the material.
Types of systems
- One-pipe system - one pipeline is mounted, through which the heat source is supplied and the waste fluid is outflowed. Best used when installing a small number of batteries. This is usually done when arranging heating of apartments, where the riser runs in all rooms. With this scheme, each subsequent radiator will be colder than the previous one, but the number of pipes that are routed through the room decreases.
- The two-pipe system is the best method of the device, it makes it possible to maintain a uniform temperature of the heating fluid throughout the entire circuit. When installing such systems, the supply line is usually located under the level of the window sill, and the return line above the baseboard.
How best to connect heating radiators in one case or another, we will consider below, after we analyze each connection method separately.
- Lateral - with this method, the supply and return flow are supplied from one side. Works well with heating structures with up to 15 sections;
- Diagonal - it is better to use it on long heating elements. The communications are connected to the upper hole on one side and the diagonally opposite outlet.
- The lower one is the least effective option, it requires a high pressure in the coolant along the entire length of the heating structures. To preserve heat transfer, heaters with an increased number of sections are used. To ensure the normal temperature of private houses, it is used only if there is a pump of sufficient power in the heating system.
Checking radiators
To make sure your batteries are clean and free of air, the first step is to open the taps on the radiators and drain off some water. In this case, you will see whether there is air in the system or not by the characteristic intermittent flow of the water jet. After that, you can start flushing the radiators.
But first you need to shut off the water supply to the heating system of your apartment. It is good if you have the necessary taps installed that disconnect each radiator from the line. Otherwise, you will have to contact the service organization for the help of a plumber.
Let's say you were able to detach your radiators yourself. Now they need to be checked for dirt. To do this, they need to be rinsed and it is better to do it in the bath. Direct a stream of water from the tap into the hole and see what kind of water pours out of the second hole. It is necessary to rinse until the water comes out clean.
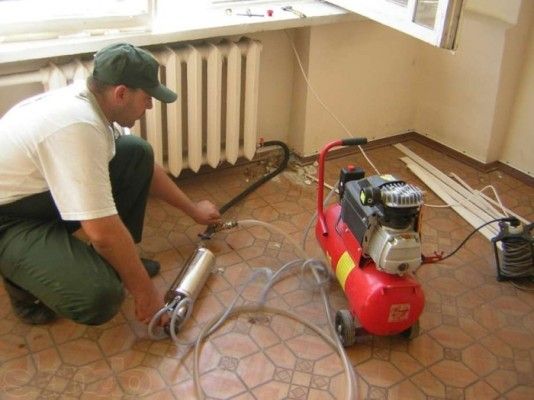


If initially it was unclouded, then you still have to solve the question of how to build up the radiator sections.
Choice of coolant
How to fill bimetallic radiators in those rare cases when they are used in an autonomous heating circuit?
In the vast majority of cases, ordinary water is used as a heat carrier. In addition to the fact that the cores of the bimetallic sections have sufficient corrosion resistance, when the circuit is filled with water, their contact with atmospheric oxygen is completely excluded. Meanwhile, rust is not possible in an oxygen-free environment.
In cases where it is possible to stop the heating circuit at negative temperatures, it is practiced to refuel bimetallic radiators with non-freezing coolants:
- An aqueous solution of propylene glycol;


Propylene glycol based heat carrier.
- Antifreeze;
- Transformer oil.
What tool to cook?
Tools and elements of the heating battery required to add sections:
- new sections;
- radiator and gas (aka pipe) adjustable wrench;
- nipples - two for each new section;
- intersectional gaskets - one per nipple;
- side plugs (left and right threaded);
- gaskets (rubber, paronite or gel) for plugs;
- linseed tow and thick oil paint (preferably the color of batteries) or sealing tape for threads such as "Fum";
- sharp large knife.
Note: 3 options for free heating of a private house
What it is
So, a bimetallic radiator: what is it? The main characteristic of any heating device is its heat transfer, the amount of heat that it is able to transfer from the coolant to the air in the room.
Heat transfer is determined by two factors:
- Heat sink surface temperature;
- Its area.
Increasing the heat exchange surface area is possible in two ways:
- By increasing the internal volume of the section. There are a number of limiting factors here - the weight of the section (and, accordingly, the load on the mounts) and the dimensions of the radiator;
- Due to the formation of developed ribbing.
However: the main condition for high heat transfer of a device with a large fin area is the high thermal conductivity of the metal from which it is made. Otherwise, the cold ribs simply will not remove heat from the inner channels of the sections.
Three relatively inexpensive metals have been widely used in the mass production of heating devices for a long time - steel, cast iron and aluminum. The thermal conductivity of aluminum is four times that of the first two metals:
| Metal | Thermal conductivity, W * m / K |
| Steel | 47 |
| Cast iron | 50 |
| Aluminum | 200 |
It would seem that the choice is obvious: the high thermal conductivity of aluminum makes it possible to create a compact and lightweight device with the highest heat transfer. And this is really so, but the trouble is - the low mechanical strength of the metal limits its use in the kennels of central heating.


In some cases, the strength of aluminum is insufficient.
The reason is the high probability of water hammering. It is necessary to abruptly close the valve or gate valve - and the inertia of practically incompressible water will create a shock wave, the pressure at the front of which will reach 20-25 kgf / cm with the ultimate strength of aluminum batteries not exceeding 16.
So what is a bimetallic radiator that has the heat dissipation of an aluminum and the strength of a steel pipe? It is just a core made of corrosion-resistant steel, on the surface of which aluminum fins are molded by casting. The use of two metals with different properties allows you to get rid of the weak points of each of them, creating an ideal design for central heating systems.
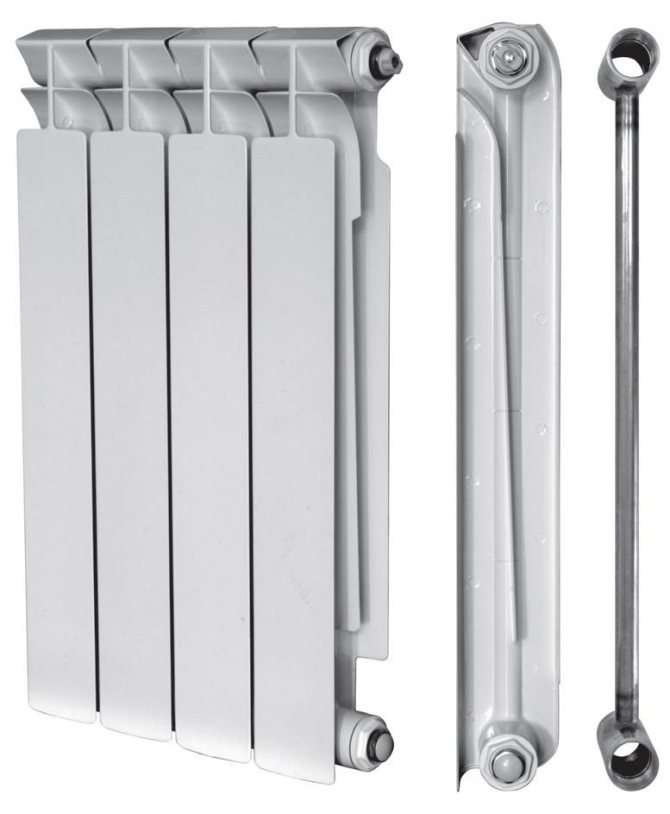


The steel core provides strength, the aluminum fins provide high heat dissipation.