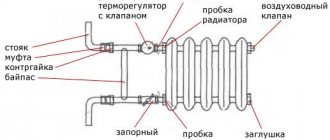
Heating is the most important engineering section, without which comfortable living in a cottage is impossible. Heating a private house must be done correctly, and this is a great art. It is necessary to have knowledge of many subtleties and nuances in order not to make mistakes. Such knowledge can only be provided by a complex of theory and practical experience.
If you have questions about the organization of the correct heating of a private house and you need an engineer's consultation, then call or write to us. Specialists will be happy to answer questions and clarify the nuances that interest you.
Heating system selection
Choosing a heating system for a cottage is not an easy task. There are many pros and cons to be foreseen. In this case, it is necessary to consider and analyze the following parameters:
- Fuel availability
- Reliability - the technologies used must be time-tested
- The cost of both the heating system itself and its operation and maintenance
- The prevalence of technologies on which the heating of the house is built, and the availability of specialists for regular maintenance
- Maintainability
- Appearance and compatibility with design
- Individual wishes and their feasibility without sacrificing the overall quality of the heating system
Further, we tried to reveal the main nuances, the knowledge of which will help you make an informed choice. If you have any questions, you can always contact us for advice.
Features of polyethylene pipes
Conventional polyethylene pipes, with the designation PE, are used for the installation of heating, sewerage and water supply systems, including drinking water supply. Pipes made of such material have some features, among which the following can be distinguished:
- Resistance to subzero temperatures. Operation and maintenance of polyethylene systems is allowed at -20 degrees. This is important when carrying out any production work in the winter, including the installation of new equipment and the repair of damaged areas.
- Flexibility and ductility. These properties make it possible to avoid deformation of pipes, not only during bending. Flexible pipes for heating made of cross-linked polyethylene are capable of expanding when the working medium freezes and shrinking when it thaws. In this case, the product takes on the previous shape.
- The use of polyethylene pipes at a temperature of the working environment no more than 400C.


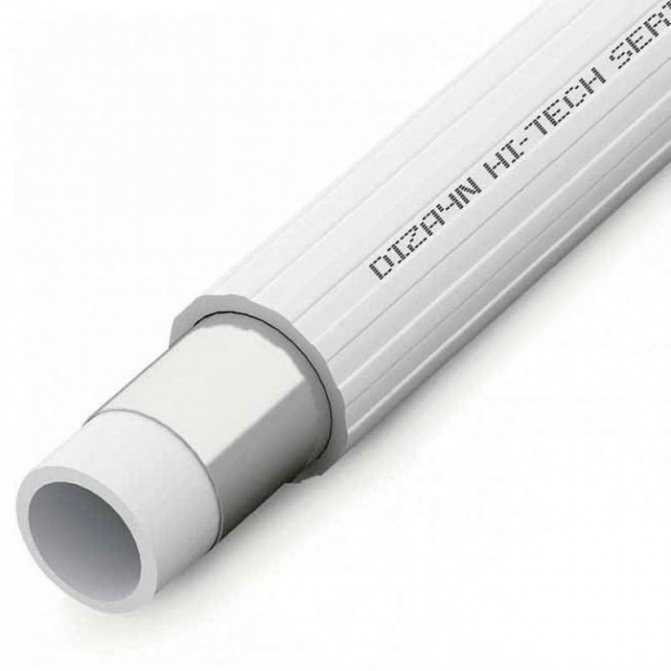
The last feature can be called a disadvantage, but progress in the scientific and technical direction helps to solve the problem. Thanks to this, special pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene were designed, which can be used in water supply and heating systems with a coolant temperature of up to 900C. The new material is designated PEX.
Types of heating in a private house
All heating systems can be classified according to the following parameters:
By type of fuel
Depending on the fuel consumed, heating systems installed in private country houses can be of the following types:
- Gas (main or liquefied gas)
- Electrical
- Solid fuel (firewood, sawdust, pellets, coal, etc.)
- Liquid fuel (diesel fuel, waste oil, etc.)
- Geothermal - systems based on renewable (alternative) energy sources
They all have their own advantages and disadvantages. Natural gas is the optimal fuel for Moscow and the Moscow Region.If a country house has the ability to connect to a gas main, then you can choose this option without hesitation.
By type of coolant
Based on the type used in the heating circuit of the coolant, the heating of the house can be of the following classes:
- Water
- Air
- Steam
- Combined - combining several types of coolant
In Moscow and the Moscow Region, the most common type of heating is the use of water heating systems. We will dwell on them in more detail.
Calculation of the home heating system


In order to be exactly sure that the heating system of your cottage will function correctly, it is necessary to carry out the design. But if the cottage is small, then the design can be omitted. In this case, it is necessary to conduct an engineering calculation of heat losses.
The essence of the calculation is reduced to determining the required thermal power. It characterizes the amount of heat that must be transferred to each heated room in the cottage. The required heat output corresponds to the heat loss. Heat losses - the amount of heat that leaves a country house through its enclosing structures (thermal circuit).
Calculation of heat losses is carried out for each individual room and cottage as a whole. On its basis, a heating boiler is selected, and radiators or other heating devices are selected.
There is a simplified methodology that allows you to calculate the approximate thermal power required for each room in a suburban private house. To do this, the area of the room is multiplied by 100-130 W (depending on how many external walls there are). However, this method gives approximate results that do not take into account a number of factors.
There are special formulas for precise calculation. First, the thermal resistance R is determined (in m2 * C / W). It is equal to the ratio of the thickness of the protective structures (in meters) to their thermal conductivity. This is a tabular value.
| Material | Thickness | R |
| Brick | 0.8 m | 0,6 |
| 0.7 m | 0,5 | |
| 0.6 m | 0,4 | |
| 0.3 m | 0,2 | |
| Log | 0.3 m | 0,6 |
| 0.2 m | 0,5 | |
| Beams | 0.2 m | 0,8 |
| 0.1 m | 0,4 | |
| Insulated frame | 0.2 m | 0,7 |
| Foam concrete | 0.3 m | 0,7 |
| 0.2 m | 0,5 | |
| Plaster | 0,03 | 0,04 |
| Ceiling or attic floor | 1,4 | |
| Wooden floor | 1,9 | |
| Wooden double door | 0,2 | |
After that, the formula is applied to calculate the amount of heat loss (in watts) that occur through the heat circuit:
Q = S * (Tvn-Tnar) / R
S - area of the heated room,
Tvn - required room temperature,
Tnar is the minimum outdoor temperature during the coldest period of the year.
Heat energy is also consumed through ventilation (both natural and forced). Its amount is calculated using the following formula:
Q = c * m * (Tvn-Tnar)
m is the mass of air in rooms (the product of the total volume of rooms and the density of air, c is its heat capacity, which is 0.28 W / kg * C).
To calculate the required total heat output, it is necessary to add the amount of heat loss through the walls, floor, roof and through the ventilation. The resulting amount is multiplied by a factor of 1.3.
In addition to the thermal calculation, a hydraulic calculation can also be performed. It serves as the basis for the selection of pipeline diameters and parameters of pumping groups. This calculation is part of the heating project.
Heating medium circulation
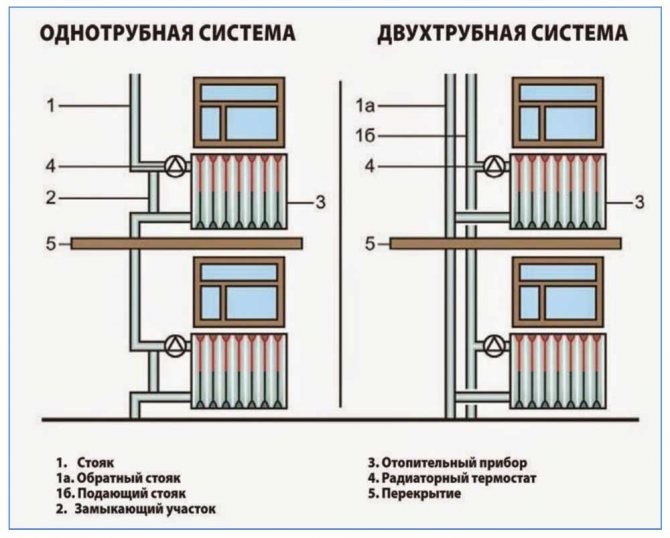
Depending on the method of moving the coolant through the pipes, the heating of the house can be designed in two ways:
Option with forced circulation of the coolant
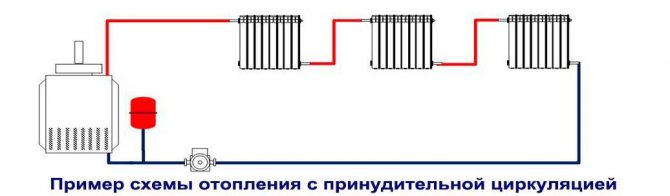

For a heating scheme of a private house with forced circulation, a circulation pump must be installed in the heating system. It provides the movement of the heated liquid through the pipes to the radiators. In this case, no slope of the lines is required.When radiators are installed in the system, it is necessary to install Mayevsky taps on them to displace air locks. The cooled heat carrier is fed back to the boiler room through the return loop.
The advantages of the option with forced movement of the coolant are:
- High speed of movement of the coolant. As a result, the liquid in the return loop practically does not cool down. This allows you to optimize the use of fuel or electricity (depending on the type of boiler)
- The ability to adjust the temperature regime of each of the heating devices
- Minimization of the internal cross-section of pipes without reducing the resistance of the medium in the lines
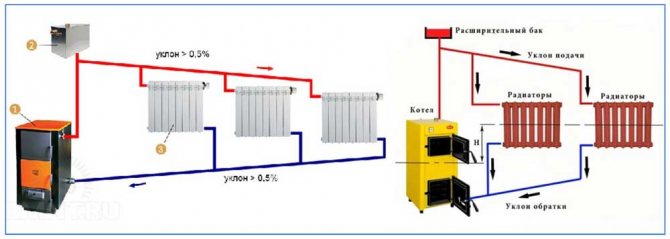
Version with natural circulation of the heating medium
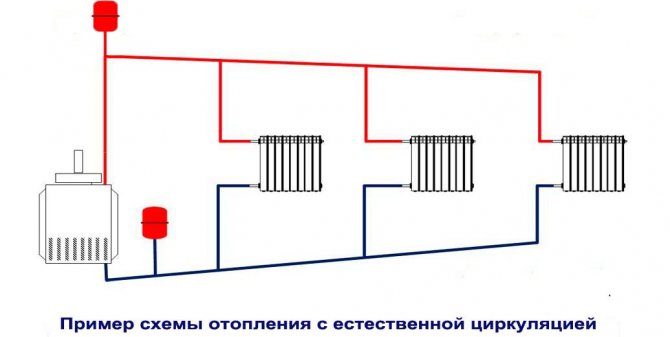

Other used names for this system, built on the basis of this option, are gravitational, convective. Heating a private house with natural circulation of the coolant - an economical option
The principle of operation is as follows. When heated, the density of the water decreases. Therefore, the hot water in the supply circuit is forced upward by the heavier chilled water in the return circuit.
To prevent water hammer due to an increase in volume (and, as a result, the pressure of the coolant in the system), an expansion tank is installed in the upper part of the system. As a result, more heated layers enter the radiators, and the cooled coolant enters the boiler along the return circuit.
In addition to the convection principle, the gravitational principle also works in this heating scheme for a private cottage. To do this, a slight slope is made in the incoming circuit from the riser to the heating devices, enhancing the movement of the coolant by gravity. Accordingly, the return circuit provides for a slope in the direction of the boiler.
This method has few advantages:
- Low price
- No circulation pump needed, which needs power supply. This allows a heating system independent of electricity (provided that a suitable boiler is used)
The main disadvantages of such a heating system are that the circuit with natural circulation of the coolant has a low level of comfort and reliability.
Reasons for filling and resetting the system
First of all, you need to figure out in what situations it becomes necessary to drain the coolant from the heating circuit. The first case is obvious - the system must be emptied before carrying out repair work. Heating is completely reset when it is necessary to repair and replace shut-off valves, as well as planned and emergency replacement of sections of the main pipeline.
The second case is the reset of the system for the whole summer and the subsequent replacement of the coolant. The whole problem is that the gaskets located between the sections of cast-iron radiators at some point completely lose their elasticity. In the presence of hot water in the radiator, the sections increase in size and press on the gaskets, but when the temperature drops, due to the decrease in pressure, leakage begins.


Of course, this phenomenon does not occur immediately - the leak occurs several years after the batteries are put into operation. In most cases, it is impossible to deal with this, since not one radiator begins to leak, but almost all the heating devices connected to the system. To get rid of this problem, the water from the system is drained immediately after the end of the heating season.
This solution has several disadvantages:
- When the coolant is poured into the heating system, you will have to get rid of the air that has got into the circuit. Usually, this operation is performed by residents of the upper floors, but if they are absent, it will be impossible to eliminate air jams. In the presence of a bottom filling, this problem is solved by switching the riser to the discharge mode, but in other cases it will be difficult to solve the problem.
- It is impossible to remove all moisture from the heating circuit, and in combination with air, it greatly accelerates the corrosion process of batteries. Obviously, all this leads to a decrease in the service life of the heating devices and the entire system.


To understand why it is necessary to constantly fill the closed heating system of private houses with a coolant, it is worth starting from two factors:
- Material for making pipes and batteries. If the system uses elements of ferrous metal, then it is highly undesirable to drain the circuit for a long time. It's another matter if aluminum radiators and polymer pipes are installed in the house - these materials are completely resistant to corrosion, so the absence of a coolant in the system will not harm them in any way.
- The total volume of the coolant in the system. It is simply unprofitable to drain water from a system with a large volume - in private houses you have to pay for water according to the meter. However, this factor is rarely decisive, since in most cases the volume of the coolant required for heating is not so large that its effect on costs becomes noticeable.
Methods for laying heating pipelines
In the heating system of a cottage, pipes can be laid in two ways:
Open way of laying
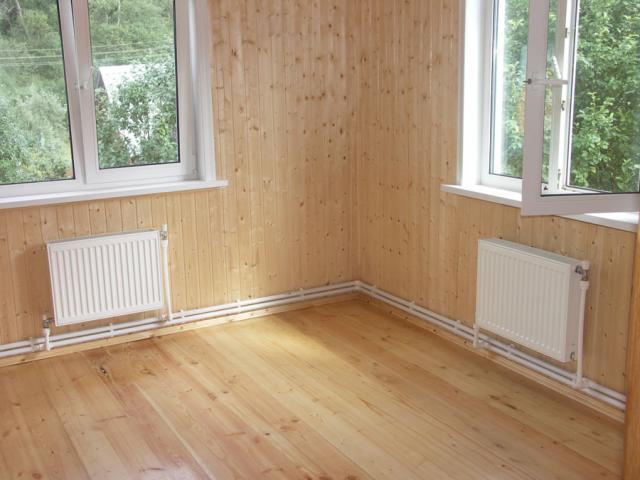


In this case, they are laid along the walls, parallel to the skirting boards. Throughout their entire length, they are in sight.
The advantages of this method:
- Access to pipes without dismantling structures
- Low heat loss
- Simple heating installation
Main disadvantages:
- The pipeline often spoils the appearance of the premises, does not fit into the design
- In order to avoid sagging and deformation, not all types of pipes can be used.
Hidden way of laying
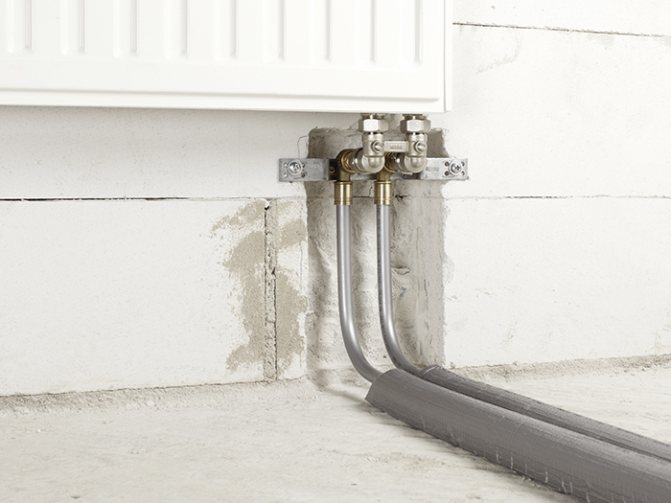


The pipe is walled up in the wall, in the floor or decorated with external material.
The main advantages of hidden pipelines:
- The ability to hide the highways so that they do not spoil the interior
- The ability to use pipes made of modern materials
Among the disadvantages are:
- Access to pipes is difficult if necessary for their possible repair, replacement of individual sections, elimination of emergency situations
- Due to the high heat losses of the line, it is necessary to insulate
When routing in a covert manner, only reliable and proven pipes should be used. The best option is cross-linked polyethylene pipes.
Filling the coolant with this method must be performed only after a hydraulic test of the heating system.
Basic rules for the installation of heating pipelines
It must be remembered that the routing of pipelines is carried out after all the heating devices are installed in the selected places. The optimal assembly sequence is as follows:
Marking the passage of heating pipes
It is better to do this in advance, before installation. In the process of marking, as a rule, installation difficulties are revealed, which are caused by the architectural and construction features of the cottage. Knowing them, you can prepare in advance for their solution or change the paths of the routes.
Most often, the marks of the passage of highways are applied to the walls. In some cases, they can be performed on the floor, but in this case they can be overwritten by people passing through the premises.
Making the necessary technological holes and strobes
It is also better to complete this stage in advance on the entire front of the work. The locations of the necessary holes and the passage of the strobes are determined during the marking.
The grooves can be cut with a chasing cutter. If this tool is not there, then they are first marked with a grinder, and then hollowed out with a perforator.
Thermal insulation of pipes
This must be done if you are routing hidden. The main purpose of insulation is to prevent heat losses and increase the efficiency of the system as a whole.
Insulation is carried out with a special heat insulator, which is made for the diameter of the pipes. It is put on pipes by hand at the installation site. The most effective and durable is a rubber-based heat insulator. But its price is also higher in comparison with analogues.
Laying and fixing pipes on building structures
Pipes must be secured not only with open, but also with hidden wiring of the heating system of a private cottage.
With open wiring, the pipes are attached to the walls with special clips. Self-tapping screws or nails are used as fasteners (depending on the material of the walls).
If hidden wiring is performed, then the pipes are fixed to the wall in grooves or to the floor with special clamps or punched tape. If the line consists of several pipes, for example, coming from the collector, then they must be fastened into loops. The fasteners that are used in this case are the same.
Connection to heating devices
Depending on the design of the radiator, pipes can be connected to it either directly or by means of a multiflex. In any case, for connection, the connecting fittings are used, which are supplied in the kit.
With collector wiring in the heating system of a private house, the connection is made not only to heating devices, but also to floor collectors. As in the previous case, the connection is carried out with complete connecting fittings.
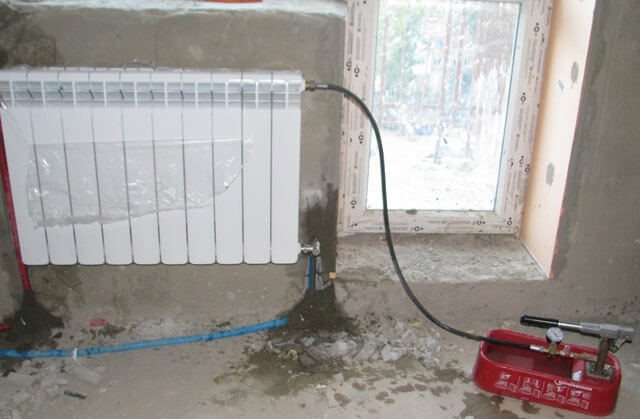
Hydraulic and pneumatic tests
This is a necessary component of installation work. During their implementation, the system is filled with water or air. Then, with the help of a special pump or compressor, an excess pressure is created in it (~ 1.5 workers when tested with water). An hour later, the results are taken - there should be no pressure drop.
If during the test there is a drop in pressure in the system, then leaks are identified. Then work is done to eliminate the causes of the leak. After that, the hydraulic tests of the system are carried out again.
Sealing holes
Pouring the floor screed and sealing the grooves with hidden pipe laying should be performed only after successful hydraulic tests. These are general construction works. The sealing of the chase is usually done by hand, most often with plaster.
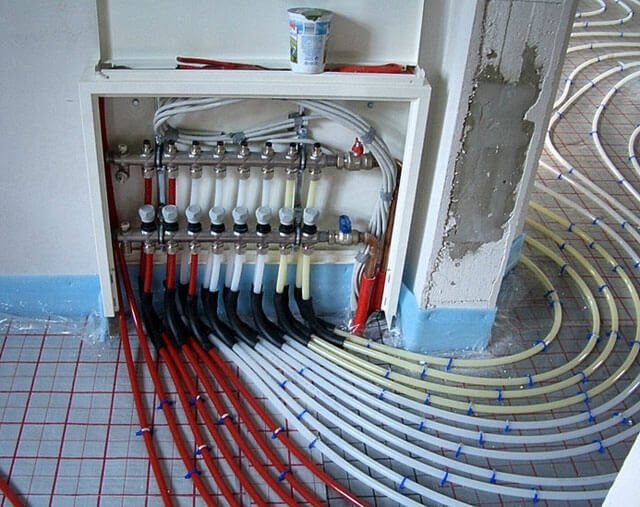
Collector (beam, fan) heating circuit
With collector wiring, each heater is connected to the manifold with two lines - supply and return.
The main advantage of collector heating is that the circuit allows you to regulate the temperature of the coolant on each specific heating device or in each of the circuits in the water underfloor heating system.
When using heating pipelines made of modern materials (for example, cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic), there are no pipe joints between the collectors and the heating devices. This increases the reliability of the system. In this case, do not worry about the formation of leaks in the cavities. The collector circuit for heating a private house is carried out only in a hidden way. In cottages, this type of wiring is in demand more than others.
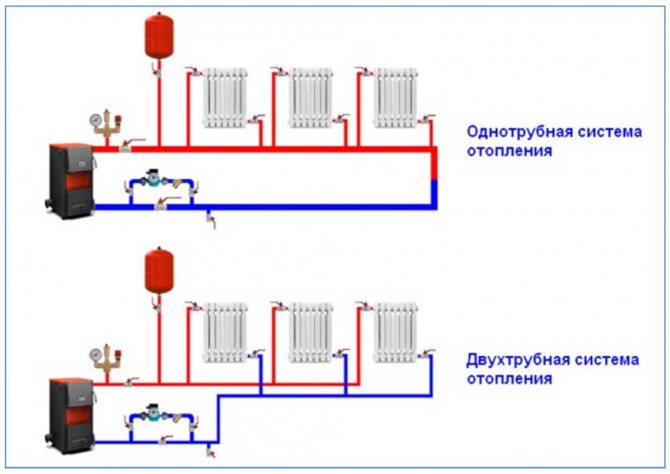
Two-pipe scheme
Heating a house with a two-pipe scheme involves connecting radiators in series. At the same time, the lines are common for all heating devices.
There are two options for implementing a two-pipe system:
Twin-pipe passing (Tichelman loop)
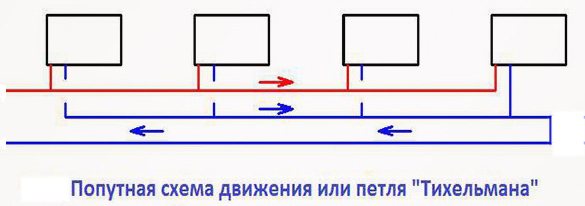

The movement of the coolant in the forward and reverse circuits occurs in the same direction. The return loop starts with the first radiator and the feed ends with the last one. The correct movement of the coolant is organized by selecting the diameter of the pipelines. Using the Tichelman loop, you can achieve uniform heating of the premises.
Double-pipe dead-end
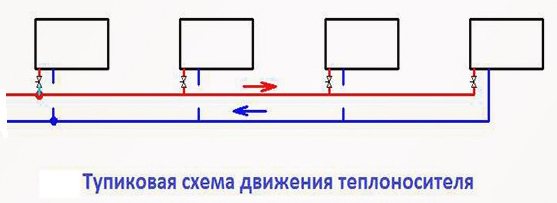

It differs from the previous type in the multidirectional movement of the coolant in the forward and reverse circuits and consists of several branches (arms). The last heatsink in each branch is a dead end. The return circuit begins from this radiator.
A two-pipe dead-end heating system is more difficult to implement than a passing one. Careful calculation of the hydraulic component of the system is necessary. In addition, the load on each shoulder must be equal. It is recommended to equip each arm with no more than five heating devices.
The advantages of two-pipe systems are low selling price and reliability of operation (in comparison with one-pipe systems).
Among the shortcomings, one can single out - the need for a large number of heating pipe connections. This significantly reduces the reliability of the system, and is especially critical with hidden laying.
In addition, there is no possibility of individual adjustment of each heater separately, which often does not allow setting the required temperature in a particular room.
With two-pipe wiring, the lines can be laid, both open and hidden. In the first case, copper or polypropylene pipes are usually used, in the second - from cross-linked polyethylene. Cross-linked polyethylene is used due to the increased reliability of the pipe-to-fitting connection.
Fitting installation: a delicate matter
It may seem that the fittings for the heating system will not be difficult to install. In fact, difficulties may arise due to the wide variety of pipe models and fittings themselves, often their threads may not match. Therefore, it is very important to know how to connect threaded connections so that everything is tight.
The first option is to use a thread-sealing fluoroplastic film (FUM). It must be tightly wound with a thick layer on the thread. Here you need to have experience in order to tighten everything until it stops. It often happens that the film can slide off and not go under the thread.
Therefore, there is a second option - the use of a special thread, which is wound so that it does not look out from under the thread, and the threaded connection is tightened. After that, it is recommended to leave the structure for about 12 hours.
Before winding the thread, you need to screw the thread of the part into the pipeline to check that the threads do not have any malfunctions. Fittings for connecting heating radiators must be screwed in freely.
After that, the thread is wound and the fitting is finally twisted. The thread is wound obliquely so that it constantly crosses the thread. The required number of turns is usually indicated on the package, but it is recommended to increase this number several times.
Next, you need to cut off the pipe of the desired size, leaving a little for the stock.
Now, using a fitting, a part of the pipeline is connected.
One-pipe scheme ("Leningrad")
One-pipe heating distribution is an outdated scheme, but sometimes it is still used. It uses one pipe, forming an annular contour. Radiators are connected in series to this pipe. Through this pipe, the coolant is supplied to the radiators and through it it goes back to the boiler.
The only plus of "Leningrad" is its low price. A significant drawback is the different temperature of the coolant in the radiators. The radiators farthest from the boiler do not heat up sufficiently. For heating in private houses in today's realities, the Leningrad scheme is practically not used precisely because of this.
Heating pipe materials
When developing a system, depending on the method of laying the pipes, their material is selected. This is due to its thermal expansion and flexibility.
For example, steel pipes can be installed both inside and outside. It is recommended to lay cross-linked polyethylene and metal-plastic in a hidden way.An open way of laying them is undesirable, since the aesthetics of the interior is disturbed due to significant sagging. It is advisable to lay polypropylene lines openly. Otherwise, possible leaks at the joints may not be detected in time.
Next, we will take a closer look at the main types of heating pipelines and list their main advantages and disadvantages.
Crosslinked polyethylene
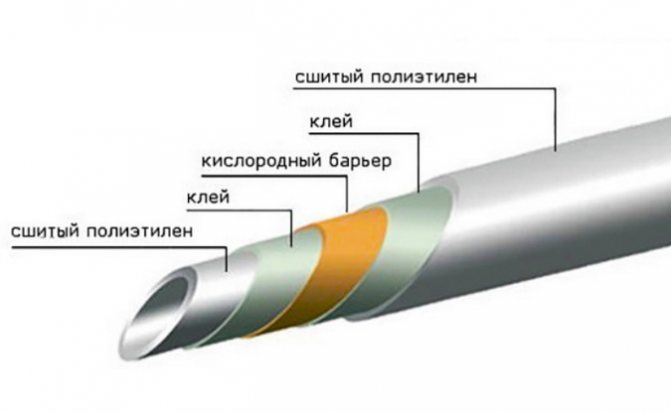

Modern technologies for the manufacture of pipes from this material allow achieving high consumer properties. The pipes produced by cross-linking methods are marked with PEX.
Leading manufacturers of XLPE pipes produce press fittings for them. They are crimped using a special tool. The resulting compounds are highly durable.
Benefits:
- Flexibility, tensile strength, the ability to return to its original state even with severe deformation
- Ability to withstand high pressure - up to 10-12 atmospheres
- Simple installation of heating, when using these pipes
- Resistant to high temperatures and aggressive environments
Disadvantages:
- UV Vulnerability
- The softness of the coating (this can lead to the fact that the walls of the pipes will be eaten by mice and rats). This is also why such pipes are used mainly in internal communications. It is recommended to lay them in the ground in metal shells.
- XLPE pipes and fittings are relatively expensive
- The high cost of a tool for joining a pipe to a fitting
Polypropylene


It is a lightweight material derived from petroleum products. Both the pipes themselves and the fittings are made from it. Pipes are connected to each other by soldering fittings.
Benefits:
- Low price
- Resistant to aggressive chemicals
- Ease of assembly
- Low price of tool for soldering connections
Disadvantages:
- Deterioration of properties due to exposure to sunlight
- Flammability
- Criticality to high (above 70 degrees C) coolant temperature
- Low durability
Installation of heating in a private house, using polypropylene pipes, is used for open laying of an internal heating system.
Modern polypropylene pipes, in order to improve their consumer qualities and reliability, are reinforced. Reinforcement materials - fiberglass or aluminum. The best option for heating is fiberglass-reinforced polypropylene.
Metalloplast
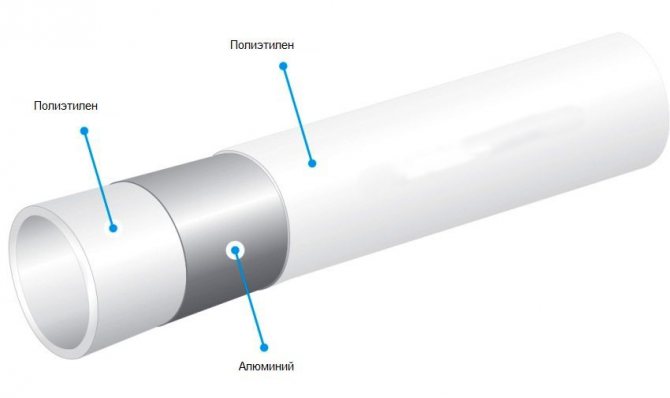

The name of the material reflects its structure. It consists of layers of polyethylene, aluminum and an adhesive layer. Pipes made from this material are used with brass fittings.
Benefits:
- High strength
- Durability
- Resistant to high temperatures, sunlight and aggressive environments
- Flexibility
- Ease of mounting metal-plastic pipes
Disadvantages:
- Poor resistance to system pressure
- Relatively high cost
- Thermal deformation tendency
- Delamination when exceeding the maximum allowable pressure
- High cost and non-versatility of the tool for working with material
Heating in a private house with metal-plastic pipes is used mainly for internal laying.
Steel


This material is traditionally used for the manufacture of heating pipes. Until recently, almost all pipes for space heating were made only from this material. The mains are connected by a welded method or by means of threaded fittings.
Benefits:
- High strength, resistance to mechanical stress
- Ability to withstand any temperature and pressure of the coolant
- Low price
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming and complex installation of heating in a private house on these pipes
- Lack of flexibility
- Corrosion susceptibility
- Internal "overgrowth"
- The service life (in comparison with modern materials) is relatively low - up to 15-20 years, depending on the operating conditions.
Copper


Heating systems built on copper pipes are rare. The reason is the high price of such pipelines.
Benefits:
- High strength, resistance to mechanical stress, high temperature and pressure
- Long service life
- No corrosion
- Aesthetics (with open padding)
Disadvantages:
- High material price
- Criticality to the presence of impurities in the coolant and to its composition
- Time-consuming heating installation in the house
- Negative galvanic processes when docking with some materials
It should be remembered that it is not permissible to install copper pipes in front of steel pipes and radiators. This leads to negative galvanic processes. To avoid this, it is necessary to lay copper pipes after the steel sections along the flow of the coolant or to make a galvanic gasket from a neutral material (for example, bronze, brass).
Stainless steel
Heating a house from stainless steel pipes is significantly more expensive, but they are devoid of one of the main drawbacks - susceptibility to corrosion. As a result, stainless steel pipes last much longer and can be used in almost any heating system. But their cost is very high and they are used in very rare cases.
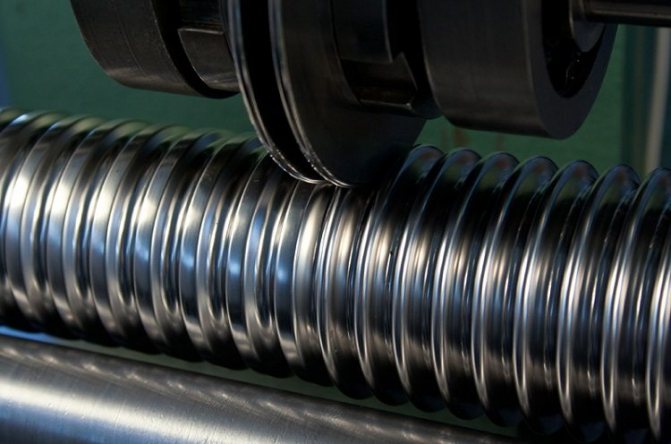
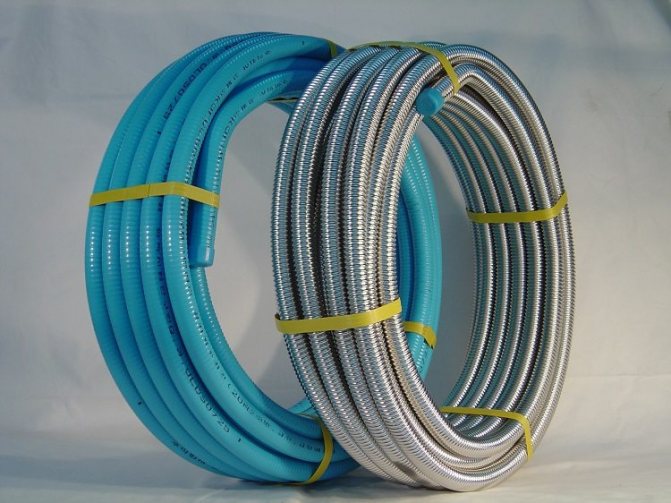
Bellows pipes
They are corrugated stainless steel flexible hoses. They are not often used in heating systems. Sometimes they act as inlets to radiators or convectors, if the use of ordinary pipes for this purpose is difficult for some reason.
Flexible stainless steel pipes for heating: price
Warmth and comfort are the main criteria for a comfortable home. Heating systems play the main role in the arrangement of housing, providing heating of the room and a suitable temperature regime. The choice of pipes for heating must be approached with all care, the efficiency of the entire system and the service life of the structure depend on them. First of all, heating pipes must ensure the tightness of the system, its strength and durability. High-quality steel, from which corrugated pipes for heating are made, provides anti-corrosion protection, as well as the reliability of both autonomous and centralized water supply systems.
Corrugated stainless pipes for heating
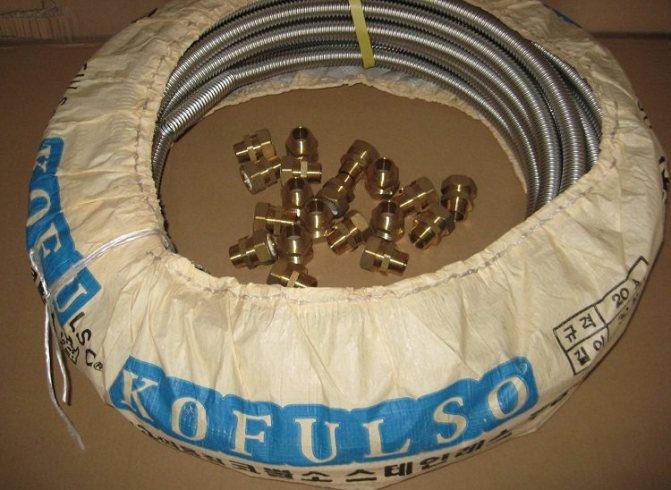
GC "Flexor" offers a reliable solution to the issues of organizing pipelines for water heating systems in any premises - these are flexible corrugated pipes made of stainless steel SUS304 and brass fittings for them.
With the help of corrugated stainless pipes and fittings, you can carry out:
- connection of heating radiators
- replacement of heating risers in the premises
- installation of pipelines from main and local (heating boilers) heat carrier sources directly to residential and non-residential heated premises.
- as an additional active element of the heating system (heat exchanger or analogue of a heating radiator)
Advantages of using flexible corrugated pipes in heating systems:
1. Resistance to corrosion and silting:
the material from which the pipes are made (stainless steel SUS304) and the nature of its processing (polished steel tape) allows the use of flexible corrugated pipes in heating systems where both industrial water and other combined heat carriers are used as a heat carrier.
2. Resistance to high temperatures:
The operating temperature of pipelines made of flexible corrugated stainless steel pipes (with connecting elements - fittings for corrugated stainless pipes) is up to + 150 ° C, which makes it possible not only to use them as the main pipelines of the heating system, but also at the points of connection to main sources or distribution nodes of access to the coolant with an increased temperature regime.
3. Resistance to defrosting:
Perhaps the most important advantage of flexible corrugated stainless steel pipes, which are used as piping for heating systems, is the unique resistance to "defrosting" of the heating system.
Unlike all other types of pipes used in the installation of heating systems (copper, steel, metal-plastic, polypropylene) flexible corrugated stainless pipes during "defrosting" (freezing of the coolant in the heating system) do not collapse or fail, but completely retain their operational quality, and after warming up or replacing the coolant in the system, they are ready for further full use.
This phenomenal quality is achieved through the corrugated structure of the pipe. In the event of freezing and as a result of expansion of the coolant, the pipe immediately compensates for the linear expansion of the pipeline, preventing excessive pressure on the pipe walls and at the pipe-fitting-heater connections, thereby preserving the integrity and functionality of the entire defrosted pipeline system.
4. Resistance to water hammer:
All the same corrugated structure of pipes for heating from Flexor Group of Companies guarantees the integrity of pipelines in heating systems of residential apartments, administrative, retail and technical premises during periods of routine maintenance on pre-season preparation for pressure testing of heating systems or at the time of the occurrence of destructive hydraulic shocks.
Pipelines made of corrugated stainless steel pipes and brass fittings to them withstand excess pressure in the system up to 60 Atm., At a working pressure of 15 Atm. for pipes with a diameter of 12 mm, 15 mm, 18 mm, 12 atm. for a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm and 10 atm. for pipes with a diameter of 25 mm and 32 mm.
5. Does not require subsequent preventive maintenance:
Pipelines for heating systems made using corrugated stainless pipes do not require any pre-seasonal or off-season preventive maintenance in the form of tightening union nuts of fittings or flushing the pipeline system.
The service life of the stainless steel pipeline is not limited.
The service life of silicone gaskets in fittings is up to 30 years.
6. Ease of installation:
For the production of all types of work on the installation of pipelines of heating systems and connection of heating devices, special skills and the use of costly installation methods (welding, the use of hydraulic or electrical tools) are not required. All work is carried out only with the use of two open-ended or adjustable wrenches. The lightness of the material and convenient packaging allow the manufacture of individual sections of the pipeline directly at the installation site, while ensuring 100% accuracy of the required dimensions and, accordingly, 100% material savings.
7. Cost savings:
The unique properties of corrugated pipes - flexibility, low weight, convenient packaging, ease of installation - together, they allow to comprehensively save up to 30% of logistics and labor costs for organizing pipelines for heating systems compared to organizing such pipelines from other types of pipes (polypropylene, metal-plastic, copper, etc.) etc.).
However, the main source of savings when using corrugated stainless steel pipes in heating systems is the most favorable price in comparison with analogues offered by Flexor Group of Companies. The price of a pipe for heating is indicated on the website for 1 meter.
fleksor.ru
Heating devices
Various types of heating devices can be used for water heating in a house - radiators, convectors, registers, underfloor heating. We will describe in more detail about each of these devices below.
Radiators
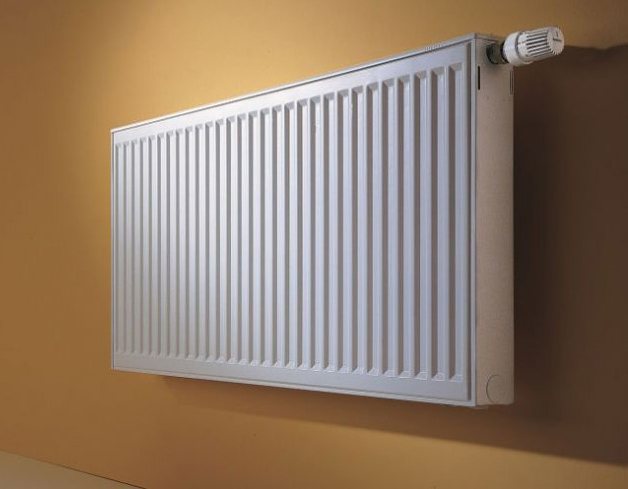


The most common heating devices are radiators.They may differ in the number of sections (in addition, there are non-sectional radiators) and material. The larger the frontal surface area, the more heat the device generates.
Radiators are divided into the following types:
- Steel
- Panel
- Tubular
- Bimetallic sectional
- Aluminum sectional
- Cast iron
They can have the following connection type:
- Lower
- Lateral
- Diagonal
Convectors
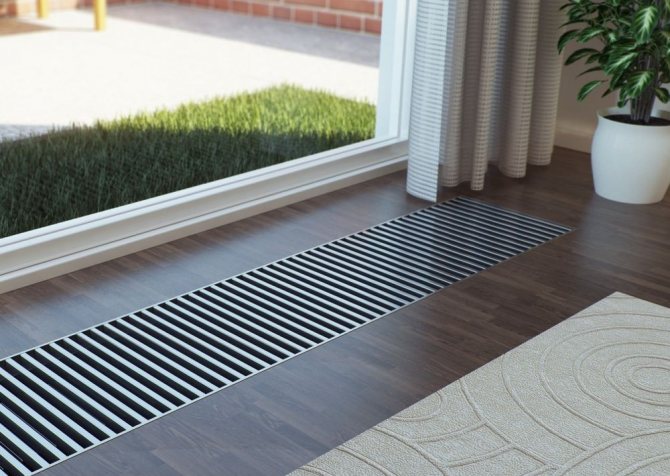


In addition to radiators, home heating can be done with water convectors. Their principle of operation is based on the fact that heated air rises upward, displacing cold air. This phenomenon is called convection, hence the name of this device. As a rule, convectors are installed under windows. The warm air coming up from them creates a "curtain" that blocks the flow of cold air from outside.
By their location, convectors can be:
- Wall mounted
- Floor standing
- Embedded
Wall-mounted appliances are attached to the wall using special brackets. They have a small mass, therefore, unlike radiators, they can be installed even on plasterboard partitions.
Floor convectors are mounted on the floor using the legs supplied. They are small in size, but have high heat dissipation.
Built-in convectors are installed in a niche under the floor. The grill at the top of the appliance is flush with the floor. In some cases, this lattice is decorated to match the style of the interior.
By the type of convection, convectors can be divided into devices:
- Natural convection
- Forced convection
In the first case, streams of warm air flow upward, cold air flows downward due to the difference in density, where, in turn, they are heated by the converter. Further, this process occurs cyclically, in a natural way.
In models with forced convection, electric fans are built into the devices. Due to the operation of the fans, the convection process is accelerated, the heat transfer is increased.
Convectors, as a rule, look more aesthetically pleasing than radiators, and built-in ones are not visible at all (except for the grille). Therefore, they are often installed when design is of great importance. They are also used where traditional radiators cannot be used, for example:
- In front of the glass doors of the balconies
- With "low windows"
Convectors are often used not only for heating living quarters, but also in swimming pools and winter gardens.
Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) for a private house.


Cross-linked polyethylene itself has sufficient mechanical strength and temperature resistance, which allows it to be used not only as an insulating layer in reinforced-plastic pipes, but also as the main material for the production of pipes. Today there are three technologies for sewing polyethylene, denoted by indices in the form of lowercase letters of the Latin alphabet - a, b and c. The material obtained by any of the three technologies is indexed by the corresponding letter in the pipe marking, for example, PEXc. Indexes for designation were assigned in chronological order as technologies developed, i.e. PEXa is no better or worse than PEXb, these are materials with identical characteristics obtained using different technologies.
The assortment of manufacturers producing XLPE pipes includes both pure polymer pipes and pipes reinforced with a layer of aluminum foil. Pipes can also differ in their field of application - for heating systems, sanitary water supply systems, or universal.
No rubber seals are used in XLPE pipe joints - the pipe material itself serves as a seal. The diameter of the outer part of the fitting, which is inserted into the pipe, is slightly larger than the inner diameter of the pipe.During installation, the end of the pipe is expanded with a special tool, then a fitting is inserted into the pipe, after which a bushing is pushed onto the fitting with a press tool, which squeezes the pipe around the fitting from the outside, pressing the plastic material of the pipe into the relief of the fitting. The movement of the jaws of the press tool during crimping occurs along the axis of the pipe, therefore this type of pressing is called axial.
Separately, it should be noted that, unlike polypropylene pipelines, where the outer diameters of pipes are standard, and metal-plastic systems, in which, in addition to unified outer diameters, pipes are most often produced with a standard wall thickness, manufacturers of cross-linked polyethylene piping systems use slightly different outer and inner diameters of pipes, therefore, fittings from one manufacturer may not be suitable for use with pipes of another and vice versa (an exception to this rule is some exotic solutions of domestic manufacturers, which are not considered in this article).
Advantages:
- ease of installation;
- heating pipes and connections can be walled up in a screed or walls of a country house (manufacturer's warranty);
- reliability of connections (over the more than 10-year history of the presence of such systems on the Russian market, there have been no cases of leakage of connections installed in compliance with the technology);
- installation of connections does not require serious qualifications and experience;
- the use of non-freezing liquids does not affect the service life of the connections;
- in the event of dismantling or changing the pipeline scheme, it is possible to reuse the fittings;
- due to the design features of the system, the fittings create almost no additional hydraulic resistance.
Disadvantages:
- installation requires a special expensive tool;
- the cost of pipes and fittings is higher than that of widespread metal-plastic systems and polypropylene pipelines.
Registers
Another type of heating devices are registers. They are welded or assembled structures made of metal (usually steel) pipes. The pipes are connected to each other by jumpers through which the coolant circulates. Cottages are rarely heated by registers due to their unattractive appearance. Registers are used most often at industrial facilities.
Heating the house with underfloor heating
In recent years, water-heated floors have been gaining popularity. If the room is large, radiators do not always effectively heat the entire space, especially in the center of the room. In this case, in addition to radiators, it is advisable to install underfloor heating. The heated air rising from them fills the entire space evenly.
Other components of the heating system
Heating a house, in addition to pipelines and heating devices, may include the following elements.
Circulation pump
The circulation pump is used in schemes with forced movement of the coolant. A circulation pump is installed on the return pipe between the boiler and the nearest radiator located along this pipe.
Its principle of operation is as follows. The pump motor is driven by a rotating rotor. The pump begins to take the coolant from the circuit on one side, and on the other to push it through the pipes.
Expansion tank
It is a steel tank with two chambers inside. These chambers are separated by a membrane. One of them is intended for filling with water, the second is an air expansion joint.
Expansion tanks are installed in closed-type heating systems to compensate for possible water shocks.
Buffer capacity
Its purpose is a supply of heated coolant and ensuring the operation of the heating system for a certain time with the heat source turned off.
Heating in a house with solid fuel functions optimally when using this container. During the day, when a solid fuel boiler is operating, the coolant is heated in a buffer tank. And at night, the cottage can be heated from this container with an inoperative boiler, while the coolant has not cooled down.
How to start an open gravity heating system
There are no particular difficulties with open systems. Filling the heating system with a coolant in this case is very simple: just pour a certain amount of water directly into the expansion tank. When water appears at the bottom of the tank, you need to stop pouring it. You should not be overzealous with the amount of water - with thermal expansion, its excess will pour out through the tank.
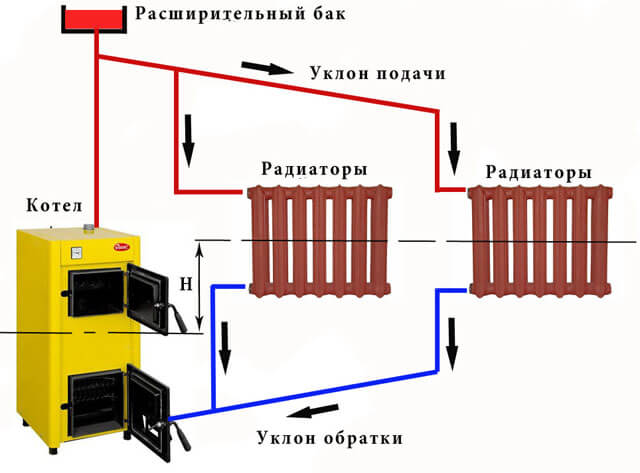

In the event that the system was assembled only recently, and the heating system is filled with a coolant for the first time, then it is also worthwhile to conduct a tightness test. To do this, it is enough to inspect all connections of pipelines and radiators.
Heat carrier
The main types of heat carriers in heating systems are water, various antifreezes and their mixtures in certain proportions.
Antifreeze is a liquid that is an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or potassium acetate with the addition of modifying additives. They lower its freezing point.
Heating a house using a coolant, to which special inhibitors are added, prevents oxidation, corrosion, and scale formation. Their content can be from fractions of a percent to 3-4% by weight.
Which coolant to choose is decided individually, depending on the situation. If the probability of failure of the boiler is small, there are no problems with fuel, it is better to use water. Many boiler manufacturers prohibit the use of antifreeze agents; there are frequent cases of refusal of guarantees on this basis.
Features of flexible chimneys
The flexible chimney is a round, hollow profile. For the manufacture of such a pipe, sheet metal rolled into a spiral is connected using a lock seam.
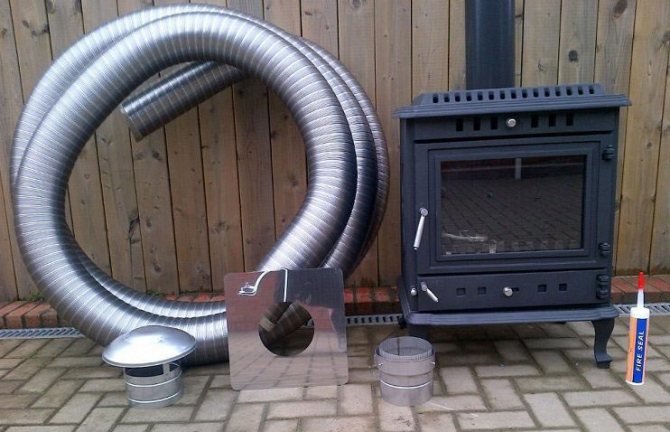


The structure of the product differs in that a steel wire is inserted between the metal layers, thanks to which the pipes acquire such properties as flexibility and strength. They have different cross-sectional sizes, but the most common are pipes with a diameter of 110 - 300 mm.
Each part of the pipe is 65 centimeters long, but it can be easily extended up to 3 meters. The flexibility allows the chimney to be installed with different bends and many bends. The wall thickness varies from 0.25 to 1 mm.
The corrugated pipe can be used to equip a part of the chimney (passage through a wall or ceiling, as well as when reconstructing an indirect brick chimney) or for installing the entire chimney duct.
Note! It is recommended to install the corrugated chimney to a heating system operating on different fuels with high or low temperature flue gases.
Reliability is ensured due to the following properties:
- cylindrical spiral shape with a locking connecting seam;
- a reinforcing layer in the form of a wire, which makes the body more resistant to mechanical damage, but retains the flexibility and elasticity of the product.
By the type of strength, light, heavy and superheavy pipes are distinguished.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: PVC-U casing pipes for well arrangement
Preparatory work
Before starting work on the installation of heating a private house, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work. Their goal is to reduce the possibility of downtime for the assembly team to a minimum during the production process. Preparatory work includes:
- Ensuring construction readiness - the heating circuit must be closed, the premises must be cleared of construction debris, there must be interfloor floors or logs
- Arrangement of niches for the installation of radiators and manifold cabinets - if necessary
- Preparation of the wall surface for the installation of radiators - preferably a fine finish
- Complete finishing of the boiler room
- Making all the necessary holes in the floors, making grooves and niches
Read other articles on this topic
| Heating a private house with electricity | Water heating in a private house |
| How to save on heating a country house | About heating schemes for a private house with a gas boiler |
| Features of heating a country house with electricity | Installation of a heating system in a private house |
| Gas consumption for heating a private house - consumption calculation | Heating a house with liquefied gas |
| Heating a private house made of polypropylene with your own hands | Heating and water supply of a country house: a description of the installation technology |
| Heating wiring for a two-story house | How to heat your home without gas |
| Heating system of a private house with natural circulation | Heating options for a frame house |
| Collector heating system of a private house | Autonomous heating of a private house |
| The best heating for a private house | Heating scheme for a two-story house |
| Heating wiring diagrams from a boiler in a private house | Heating a private house from metal-plastic pipes |
| Private house heating project | Heating system installation: rules and description |
Services on this subject
| Heating design | Turnkey solid fuel heating |
| Turnkey gas heating | Turnkey heating |
| Heating in a turnkey wooden house | Turnkey water heat-insulated floor |
| Installation of a water heated floor | Heating a two-story house |
| Heating installation in a cottage | Heating a country house: options and prices |
| Heating installation | Heating installation in a private house |
| Installation of engineering systems for water supply and heating | Diesel heating of a country house |
| Turnkey autonomous heating | Air heating of a country house |
| Prices for installation of heating in a private house | Design and installation of heating systems |
| Water heating in a private house | Electric heating of a country house: options and prices |
| Heating in a townhouse | Gas heating design |
| Heating design cost | Private house heating calculator |
| Installation of a water-heated floor in a private house | Price for installation of a water-heated floor |
| Installation of a water-heated floor on a wooden floor |
Schematic diagram of the heating system
The individual heating system of a country house consists of a boiler, a circulation pump, an expansion tank, heating radiators and pipes connecting all these elements. Water is used as a heat carrier if the heating system works for the entire heating season (country house of permanent residence), or antifreeze if the heating system is turned off for long periods during the heating season (country house or summer cottage of periodic residence).
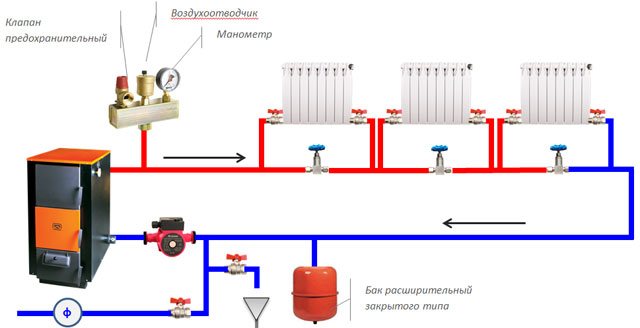

Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of an individual heating system of a country house.
The principle of operation of an individual heating system is as follows. The boiler heats up the coolant and, under the action of the circulation pump, the coolant moves through the pipes and heating devices. When heated, the coolant increases in volume, the expansion tank compensates for this, protecting the heating system from overpressure and possible pipe ruptures.