Flushing the system before starting
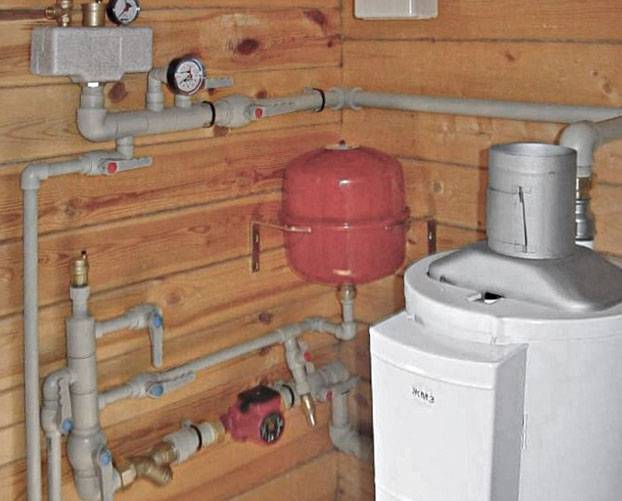
Water heating circuit.
If there is water in the heating system, it must be drained. Next, you should dismantle the heating radiators. Then connect the pipes for supplying water from the water supply system to the outlet of the system, and the drain pipe to the inlet to the system. All formed connections must be well secured with pre-prepared clamps. It should be remembered that the higher the pressure water is supplied, the better the cleaning will be (but not more than two atmospheres). A pump is usually used to generate pressure. You can sprinkle bleach on the water to achieve a disinfecting effect. On average, this procedure can take about two hours. At the end of the drain, pure water will flow without additional impurities.
Cleaning the heating system can be carried out using special chemicals: additives or anti-corrosion fluids
They should be treated with caution, since they are not suitable for all materials and can damage some elements of the system.
After cleaning, the radiators are mounted in the opposite direction of their dismantling. You should additionally check the tightness of the system by visual inspection and detection of leaks.
Filling the heating system with water
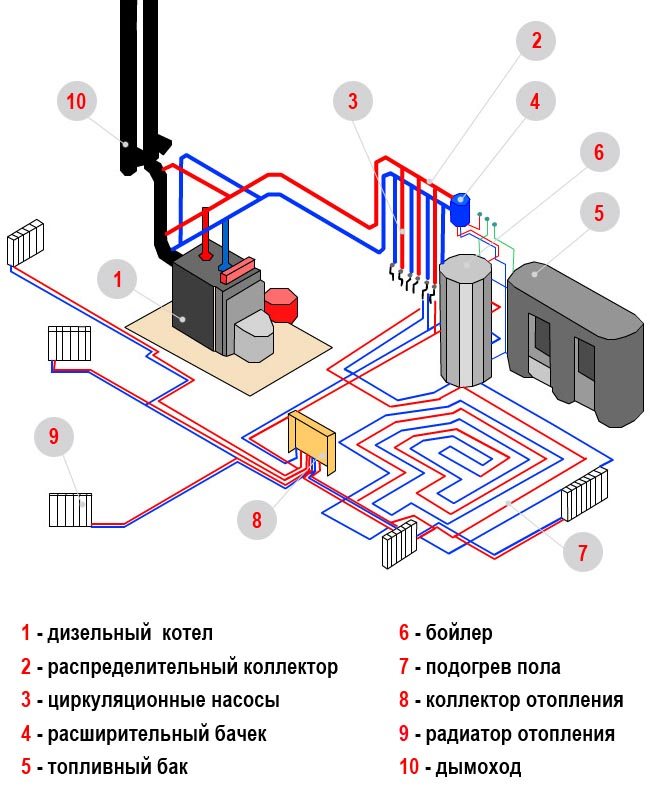

Diagram of a water heating device.
The reasons for filling the heating system can be: possible emergency situations due to which the water had to be drained, seasonal water discharge, release of air locks.
Before filling the heating system with water, especially if it is being started for the first time, it must be flushed. Remains of factory production - shavings, preservatives - can be found inside the structural elements of the system.
If the system is not filled for the first time, then during the service, substances hazardous to proper operation have accumulated in the heating registers and pipes, such as scale, lime stones. All of these products can cause serious damage to the boiler and the entire system.
The main types of heat transfer fluids

Heating system.


The principle of operation of the heating system is that the coolant moves from the heat source to the end point through the pipes, heating them. The type of heat carrier used depends on the type and design of the heating equipment, which can be liquids and gases.
The most popular are liquid coolants:
- Water is the most readily available and cheapest resource. According to statistics, about 70% of heating systems use water, which has a high density and heat capacity. In addition, this type of coolant has gained such popularity due to its properties such as low viscosity, high heat transfer coefficient, and simple temperature control. The main disadvantage is the ability to freeze at zero temperature. If water freezes in the heating system, this will lead to rupture of pipes and failure of all equipment.
- Antifreeze - this type of coolant is not as widespread as water, and its use is 5%. It is used for heating office buildings and residential buildings, where the heating system does not allow the use of water due to the increased risk of corrosion. The main advantage of antifreeze is freezing in frosts of 60 - 70 degrees.
The following gases are used as a heat carrier:
- Water vapor - mainly used in industrial buildings, as its use is prohibited in residential and public buildings.Water vapor maintains the temperature of heating devices at 100 degrees, according to sanitary standards, this figure should not exceed 80 degrees.
- Flue gases are toxic, therefore, recently they are used only for heating water and in order to save electricity to obtain a heat source.
- Air is characterized by a low heat capacity, therefore, to move it through the heating system, high energy costs are required. It is most cost-effective to use air as a heat carrier, provided that it performs two functions simultaneously: heating and ventilation.
At present, organic fluids are being introduced as a heat carrier, which have excellent freezing rates and have a low viscosity. However, they have not yet received wide distribution, due to their high cost and scarcity.
Energy Blog
The water heating system (Fig.5.17) includes a boiler 1, an expander-air heater 10, heating pipes 2, a feed pump 8, tanks 6 and 7 for water and fuel, valves 5, 9, a sump 5 and a tap 4 for draining water from boiler.
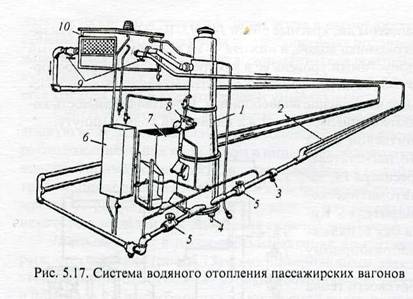

The circulation of water in the heating system (shown by arrows) occurs continuously due to the temperature difference in its various parts. Artificial circulation of water is also provided with the help of a circulation pump installed on the pipeline supplying water to the boiler, the supply of which is turned on in cases where the outside air temperature is lower than the design one or when accelerated heating of the car after settling is required.
With a combined (electric-coal) heating system (Fig. 5.18), the water in the boiler is heated by high-voltage heating elements located in the water jacket, and in the absence of electricity, due to the heat of the combusted solid fuel - coal).
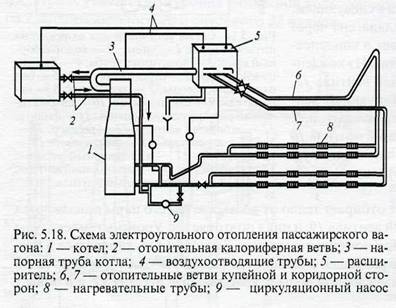

The heating elements are powered by a single-wire train line with a nominal voltage of 3000 V DC or single-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz on the way from locomotives, and at dumping points - from stationary devices. Various types of wagons are equipped with a hot water heating system with a combined boiler. This system consists of a boiler with an expander and heating devices. The boiler (Fig. 5.19) with electric coal heating has a conventional coal furnace 4 and a water jacket 2, in which 24 high-voltage heating elements 3 are located on the support flange 11.
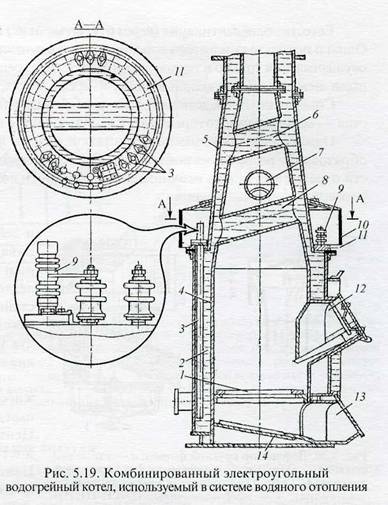

To increase the surface of the heated water, circulation pipes 6, 7, and 8 are installed in the conical part of the furnace. In the lower part of the furnace there are grate 1 and an inclined ash pan 14. Coal is loaded into the boiler through the furnace hole 12, through which slag is extracted. Ash and fine slag are removed through the opening of the ash pan 13. Three insulators 9 are placed on the support flange in the furnace zone, through which high-voltage wires are fed to the heating elements of the boiler. In order to ensure electrical safety, the boiler casing 5 is grounded. For this, a special bolt is provided in its lower part, to which the ground wire is connected. The heating elements are covered with a protective casing 10, on which an interlock is installed that breaks the circuit of the coils of high-voltage contactors when the casing is lifted and high voltage is present. In the raised position for inspecting the heating elements, the casing is suspended from chains. The volume of water in the system is 855 liters, of which 370 liters are in the boiler and expander. The heating circuit, heating elements and other high-voltage equipment are the same for different types of cars. The high-voltage heating elements have a total power of 48 kW and are divided into two parallel groups, each of which consists of two parallel legs, including six heating elements connected in series.To protect the boiler, a thermal relay is provided that turns off the electric heating elements when the water temperature in the boiler rises above 90 ° C, and a minimum level relay that turns them off when the water level in the expander drops more than 200 mm. In air-conditioned cars, additional low-voltage electric ovens and an air heater are used, which are powered by an autonomous power supply system with a DC voltage of 110V. In passenger cars of interregional and suburban communications, heating with the help of electric furnaces and air heaters is most common. In the systems of water supply and water heating of modern passenger cars, plastics are widely used for the manufacture of many parts and assemblies. Water tanks, washbasins and toilets are made of fiberglass based on polyester resin, pipes, fittings, valves, bushings, tees, as well as other connecting and regulating parts are made of low density polyethylene. In the toilets, the floor is made of fiberglass instead of cement, covered with metlakh tiles. The use of plastics ensures a decrease in the empty weight of a carriage, an extension of the service life, a decrease in labor intensity and costs in the manufacture and repair of water supply systems, heating and internal equipment.
Share with your friends
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Skype (Opens in new window)
- Yet
- Send this to a friend (Opens in a new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Similar
Open gravity heating system start-up process
In modern houses, open heating systems are rarely satisfied; such technologies have long been considered a relic of the past. But they still exist, so you should consider how to fill them with water. In any such heating system, there is an expansion tank at its highest point; it is designed to accumulate water after an increase in its volumes in the system with increased pressure during a rise in temperature. The tank is an open tank with or without a lid. Through the tank, the system is filled with water. Large volumes of liquid, of course, will be quite problematic to fill in small containers, moreover, to the highest point.
The most rational would be to use a conventional vibration pump for household use. To do this, prepare a capacious container, fill it with water. The previously prepared hoses are attached to the pump with clamps. Such a pump has a submersible type of structure. The hose through which water will be taken must be lowered into a prepared water tank. The hose from which the water will be discharged is immersed in an expansion tank. The pump is turned on, the pressure in the system should be from one and a half to two atmospheres. When lowering, add water to the prepared tank and lower the hose into it below. When the heating complex is full, water will be visible at the bottom of the expansion tank, the system can be considered filled.

Installation diagram of the hot water heating system.
Excess air will come out of the pipes at the first fire through the expander. It should be noted that during the heating season, when the system maintains a constantly high temperature, the water will gradually evaporate from the expander. It is necessary to make up by adding water to the expander to the required level. You should also monitor the temperature on the thermometer attached to the heating boiler. Upon reaching its level above 80 ° C, the water will soon begin to boil and splash out.In this case, it is necessary to block the access of oxygen to the furnace to reduce the intensity of combustion.
WATER SUPPLY AND AIR CONDITIONING DEVICES IN PASSENGER CARS
1. Purpose and arrangement of the passenger car water supply system. ERW is a water supply device in passenger cars designed to provide passengers with drinking water and satisfy domestic needs, as well as to replenish the heating system with water on the way of the train. Such systems provide devices for boiling and cooling drinking water, for supplying hot water in washbasins, toilets and sinks for washing dishes in the service compartment of the conductor. All passenger cars have a gravity water supply system. The volume of the spare water tank is calculated based on the Average consumption rate for 1 passenger per day 20 liters. To pass. wagons are considered optimal water supply for 12 hours. The total volume of water in the system is about 1000 liters.
The water supply system consists of: 1. Large and small cold water supply tanks. 2. Boiler installations are designed for heating water in the hot water supply system. 3. Loading pipes with connection heads located on the side walls. 4. 2 washstands in the toilets and a sink for washing dishes in the attendant's service compartment. 5. Boiler KMB water cooler from drinking water. All elements are interconnected by pipelines and have negative water valves.
2. Filling the passenger carriage water supply system with water and draining water from it. It is carried out outside the car through filling pipes with connecting heads. The conductor is obliged to determine the amount of water in the system 5-10 minutes before arriving at the water filling station, to turn on the water filling alarm on the remote control. When the train stops at the station, warn the outfitter of the need to refuel. Check the refueling process. When draining water from the system, open all valves and taps and drain the water from the boiler.
Check the presence of water in the system in our carriage in the toilet from the working side view the Gauge glass of the small tank. In German from the non-working side
3. The principle of operation and the device of the hot water supply system of the passenger car. see question 1 and 2.
4. Design and principle of operation of a combined continuous boiler. KND Marita to heat and water by burning solid fuel on, electric heating or both heated together. The volume of the capital space of the CPV is. 9l. Fully boiled water 15 liters. The heating time of water from + 17 ‘С to +100’ ’‘ C is 10 minutes on solid fuel, due to electric heating - 20 minutes. Boiler productivity from 12-18 l / hour. TEN - thermo electric heater
KND consists of: Body, ash pan with a box, Furnace, cavity of not boiled water, cavity of boiled water, main valve, strainer, float chamber, three-way valve. There is a water tap, thermometers and water gauge glass on the KND body.
Possible boiler malfunctions, their causes and remedies. - Too little water in the boiler, As a result of lack of water in the system or clogged strainer. - The float valve does not close. Float leakage or seizure 8.5 Yanik does not heat water due to electric heating. - Boiler fuse blown. - Burned out heating element. Tell pam.
5. Basic rules for the operation of the water supply system of the passenger car. When preparing the car for the trip, the conductor must check the technical condition of the water supply system. In this case, special attention should be paid to the absence of water leakage from: From taps, threaded connections, bends, pipelines, in the places where the pipeline is connected to the tanks.
On the way, it is necessary to periodically monitor the amount of water in the system.Check the condition of the control valve, check t in the heating devices. In winter, do not allow the "cold" car to be refueled with water. Refueling of such cars is carried out only after starting the heating system and bringing t inside the car to +10. + 12'C. If a water leak is detected from the system, the conductor is obliged to take action and call a pem.
2. ADDITION. Water from the water supply system is drained: 1. At the command of the head of the train If the train is being serviced. 2. Without waiting for the command of the chief If the heating system does not work in winter, the conductor must drain the water from the system. The water from the car system must not be drained near the installed electrical equipment, in parks.
6. Purpose and principle of operation of the heating system pass. carriage. The heating system is used to maintain normal temperature conditions inside the car, regardless of changes in the outside air t. t inside the car should be + 20, + -2'С, at t outside air up to -40's and speed up to 160 km / h. To maintain the temperature, all passenger carriages of long-distance trains are equipped with a combined heating system.
The water heating system can operate in the following modes: - heating the carriage room with heating pipes and heated air from the ventilation system; - heating by branches of heating pipes with enhanced water circulation.
The heating system consists of: Combined continuous boiler, the water in which is heated by burning solid fuel, due to the operation of high-voltage heaters of the heating boiler, or both at the same time.
7. The main units of the car water heating system. The hot water heating system with top piping is the most common, because it can only work by natural circulation. Such a system has a boiler for heating water with an expansion volume. Expand is designed to receive excess water resulting from an increase in volume when heated to release water from air. The circulation of water occurs due to the change in specific gravity during heating. As long as the boiler is cold, all the water in the system is at the same temperature. As soon as the boiler firebox is lit, the water temperature in it begins to rise, at the bottom of the firebox the water will be hotter, the balance in the system will be disturbed and the lighter hot water begins to move upward and further along the vertical pipes. Cool, the water returns to the goat through the lower pipes creating circulation in the system.
The boiler consists of: A furnace and a blower with an ash pan, a water jacket, a heating boiler in which high-voltage heaters are immersed, there is a thermometer and a hygrometer on the boiler body. From the hot water boiler, water enters the expander, then through 2 branches located at the side walls, the water along the upper wiring reaches the risers located in the toilet and the corridor of the non-working side. At the junctions of the upper wiring and risers there are valves, nozzles for air release and steam plugs, a point in the lower part to the old people on each side, the connection of heating pipes, which are then connected into one common pipe passing through a mud collector and circulation pumps (electric manual), then water enters the lower part of the boiler. If the ambient temperature is below -30'C, the conductor is obliged to apply forced circulation of water in the system.
8. Technical service. water heating of the passenger car during preparation for the trip, on the way, and on arrival at the point of forms. When preparing the car for the trip, the conductor is obliged to check the condition of the heating boiler. Check the serviceability of circulation pumps, measuring instruments, the presence of water in the system, the absence of leaks in the system, the availability of technical documentation, the heating system, the manufacturer's instructions. Check the availability of inventory (bucket, ax, duck, scraper, kapik-cut). It is forbidden for the conductor to: 1. Store flammable objects in the boiler room 2.Throw out the burning coal from the car 3. Extinguish the firebox with water or snow 4. Start the heating system, start the boiler and the boiler installation in the absence of water
Upon the arrival of the wagons, the formation and turnover point of the conductor is obliged to clean the furnace and ash pan from the hall and slags, transfer the entire inventory to the receiving conductor, create a system in a corrected state. It is necessary to service the heating system with a dressing gown, a hat, and if there are loins.
9. Typical malfunctions in the water heating system of pass.v-on and ways to eliminate them. 1. Fault Formation of air locks in the heating pipes (the water circulation in the system has stopped, the pipes are cold, at low outside temperatures the pipes may freeze, especially under the floor) Cause of occurrence. Filling the system with water with closed taps. Boiling water in the boiler (and steam and air get into the pipes). Remedy. Open the air outlet screens. Turn off the circulation pump or artificially circulate with a hand pump.
2. Malfunction. Insufficient heating of the carriage with incomplete opening of the shut-off valves on the heating pipes. And. emerged. Inattentive maintenance of the heating system. Remedy. Fully open the shut-off valves.
3. Malfunction. Clogged heating pipes (when opening the drain cock, dirt comes out of the pipes). And. emerged. Poor pipe flushing during periodic car repairs. Remedy. At the turnover station, partially drain the contaminated water by opening the sludge traps with the simultaneous replenishment of the system with clean water. Routes to increase circulation with a pump. Flush the heating system at the forming station.
4. Malfunction. Partial freezing of heating pipes. And. fuss Inattentive maintenance of the heating system. Remedy. Frozen place Wash a rag with a soft material and heat the field with hot water. Simultaneously strengthen the boiler furnace and turn on the circulation pump.
5. Malfunction. Boiling of water in the boiler (circulation in the pipes worsens, the water level in the boiler expander of the boiler decreases.
6. Malfunctions. There is little water in the expander. (Water does not come from the water taps) Inattentive maintenance of the system or water leaks through the pipe branch going to the toilet. Remedy. Immediately refill expander for maximum level.
10 .. the main components of the ventilation system pass. carriage. Ventilation is the process of air exchange in a room. There are 2 types of ventilation. Natural and mechanical. Natural, which does not require any energy costs. Mechanical ventilation requires mechanical costs.
There is a ventilation system in two ways: 1. Due to the non-density of doors and windows (infiltration) 2. Due to the action of deflectors. When the deflector operates, a pressure difference is generated. The pressure on a convex surface is lower than the pressure on a non-convex surface. In summer, the valves are open. In winter, when open at 25%.
Mechanical ventilation inlet consists of: 1. Air intake grille 2. Air passes through mesh filters 3. Ventilation unit 4. Chamber for air treatment (heating, cooling) Air cooler located in air-conditioned cars. Air enters the air duct, which is located between the ceiling and the roof of the car, above each compartment from the air duct through an air-folding grille - "multivent", the air enters the passenger area. Removal of air from the passenger compartment is carried out through the leakage vents of windows and doors, tk. the air pressure inside the carriage is slightly higher than atmospheric
More than 20 temperature sensors are installed in the carriage, which automatically regulate the rotational speed of the fan electric motor.
11 .. ventilation operation mode in winter, summer and transitional periods of the year. In winter operation, the valve for supplying water to the liquid heater from the heating system must be open. The transitional period of the year in the air is heated by an electric heater. During the summer period of the year, the cold water supply valve of the heater must be closed. The signs of unsatisfactory ventilation are fogging of windows in hot weather in summer.
12. Purpose of the passenger car air conditioning system. Air conditioning is the artificial treatment of air with changes in temperature, humidity, physical and dry cleaning, supplied to the carriage of air in accordance with the standards for passenger cars with air conditioning. t in the summer must be inside the car from 21-25 ° C. Relative air humidity from 30-60%. Unevenness t in height and length of the carriage is allowed no more than 3'С. The speed of air movement in the area where passengers are staying should be no more than 0.25 m / s. The amount of dust should not exceed 1 ml per 1 m3. The content of carbon dioxide should not exceed 0.1%
13. What units does the air conditioning unit consist of? Today, air-conditioned cars of Domestic construction, Tver Carriage Works and German-built cars are in operation. In domestic cars, the air conditioning installation is made in the form of a monoblock structure located between the roof and the ceiling above the working vestibule. Installation type UKV-PV. "+" Domestic VHF Football is hermetically sealed compared to German ones. "-" The upper position at the VHF reduces the stability of the car. Unrepairable.
14. Location of the main units of air conditioning units on wagons built in Russia built in Germany. A German-built wagon uses a MAB refrigeration unit - // compressor, condenser, receiver. this unit is located under the cars, and the evaporator (air cooler) is located in the chamber with a ventilation unit that processes the air. "+" MAB - // 1. The lower location of the system increased the stability of the car 2. Better cooling of the compressor and condenser "-" 1. Freon losses in the compressor due to the fact that the compressor shaft goes out and is connected to the engine shaft.
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
How to pour water into an open heating system
In order to fill the open heating system of a private house with a coolant, a slightly different procedure is used. The main difference from closed networks lies in the internal pressure of the circuit: here it corresponds to atmospheric pressure, which makes it possible to use an expansion tank as the main control device. In open heating systems, it is mounted above all other elements.
- Draining the old fluid and cleaning the circuit. This is done in the same way as in the case of a closed system.
- To pour water into an open system, an expansion tank is used, which looks like an open tank. After removing the lid, they begin to pour water: filling a small circuit is usually carried out with a bucket. Filling large systems in this way is quite tedious, so it is best to use a domestic vibration pump. This will require a capacious tank with pre-prepared water. The pump is equipped with flexible hoses with clamps: one end is immersed in a container with water, and the other in an expansion tank.


Extended tank
- It is recommended to supply water slowly so that the air has enough time to escape.When using a vibration pump, it is necessary to ensure that the pressure in the circuit during its filling is within 1.5-2 atm. When it is lowered, more water is added to the preparatory container so that it is possible to immerse the suction hose deeper. The water supply is shut off after it starts pouring out into the expansion tank.
- At the end of the procedure, it is necessary to free the circuit from air plugs. To do this, in turn, they open Mayevsky's taps on all available radiators, closing them only after the appearance of water. In order not to wet the floor, it is recommended to place a portable container under the taps. Having released the gas from all the batteries, they are topping up the water in the tank. As practice shows, the final release of the open system from air occurs through the expander after the first firebox.
During intensive use of open heating (most often in winter), the coolant will gradually evaporate through the expansion tank. This is explained by the high temperature of the coolant. To maintain the performance of the system, it must be periodically refilled, making sure that its temperature does not rise above +80 degrees.
Filling underfloor heating
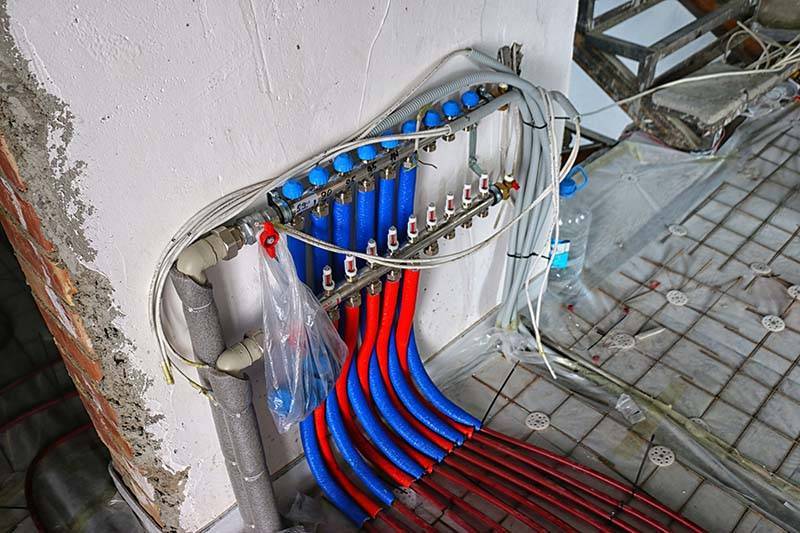


Warm floors have their own characteristics. They are not filled all at once, but one by one. If you fill everything at once (and they have different lengths), then air will definitely remain in the long circuits, which is almost impossible to remove from there. Therefore, we proceed as follows.
The collector is fully assembled. All circuits overlap on the return, except for one. The pump turns on, and through the supply of this circuit, the heating system is filled until a clean coolant without a sign of air flows from the drain hole. After this has happened, the circuit is closed. All others are filled in the same way.
Here, it is advisable to have another hose in order to direct it into a bucket with a coolant in order to avoid spills.
After that, the drainage hole is closed, all circuits are opened and the operation of the warm floor is checked.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that the radiator network system can be filled with coolant against its movement. You cannot do this with warm floors, you only need to fill it from the straight side, because otherwise the coolant will not move through the rotameters
Selection of pressure values in the system and expansion tank
The higher the working pressure of the coolant, the less likely it is for air to enter the system. It must be remembered that the working pressure is limited to the maximum permissible for the heating boiler. If, when filling the system, a static pressure of 1.5 atm (15 m of water column) was reached, then a circulation pump with a pressure of 6 m of water. Art. will create a pressure of 15 + 6 = 21 m water column at the boiler inlet.
Some types of boilers have a working pressure of about 2 atm = 20 mWC. Be careful not to overload the boiler heat exchanger with an impermissibly high pressure of the heating medium!
The diaphragm expansion vessel is supplied with the factory set pressure of an inert gas (nitrogen) in the gas cavity. Its common value is 1.5 atm (or bar, which is almost the same). This level can be raised by pumping air into the gas cavity with a hand pump.
Initially, the internal volume of the tank is completely filled with nitrogen, the membrane is pressed against the body by the gas. That is why closed systems are usually filled up to a pressure level not exceeding 1.5 atm (maximum 1.6 atm). Then, having installed the expansion tank on the "return" in front of the circulation pump, we will not get a change in its internal volume - the membrane will remain motionless. Heating the coolant will lead to an increase in its pressure, the membrane will move away from the tank body and compress the nitrogen. The gas pressure will rise, balancing the coolant pressure at a new static level.
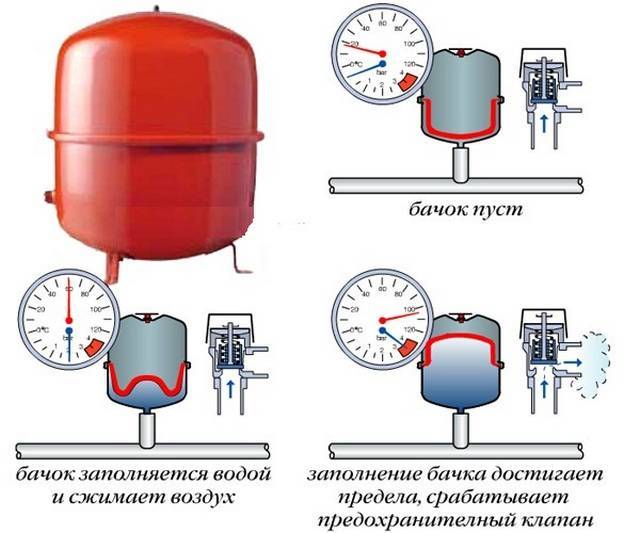

Expansion tank pressure levels.
Filling the system to a pressure of 2 atm will allow the cold coolant to immediately tighten the membrane, which will compress nitrogen also to a pressure of 2 atm. Heating water from 0 ° C to 100 ° C increases its volume by 4.33%. The additional volume of liquid must enter the expansion tank. A large volume of coolant in the system gives a large increase in it when heated. Too large initial pressure of the cold coolant will immediately use up the capacity of the expansion tank, it will not be enough to receive excess heated water (antifreeze)
Therefore, it is important to fill the system up to the correct defined pressure level of the heating medium. When filling the system with antifreeze, you need to remember that its coefficient of thermal expansion is greater than that of water, which requires the installation of an expansion tank of a larger capacity.
Conclusion
Filling closed heating systems is not just a standard final step before commissioning. Correctly or incorrectly performing this step can seriously affect the performance of the system, in the worst case even damage it. Compliance with the filling technology is the key to obtaining a stable heating system.
How to implement alternative heating of a private house
Two-pipe heating system of a private house - classification, varieties and practical design skills
One-pipe and two-pipe heating distribution in a private house
Collector heating system of a private house - advantages and disadvantages
Heating system classification
To fill it out correctly, you need to know what type it belongs to. There is a classification of systems according to the method of pipe routing: from the top, from the bottom, horizontal, vertical or combined. According to the method of connecting devices using pipes, the systems are: one-pipe and two-pipe.
Also, in the system, water can circulate naturally or forcibly (if a pump is used). In terms of the scale of action, local and central heating systems are distinguished. In the direction of the movement of water in the pipes - dead-end and associated. All these types are used in everyday life in a mixed manner.
Railway passenger car heating system and heat generator
The invention relates to the field of mechanical engineering, more specifically to devices for heating vehicles, including railway cars. The heating system includes a heat generator, the inlet of which is connected to the outlet of the electric water pump, a bypass line connecting the outlet of the heat generator to the inlet of the pump, water heating radiators and the power supply system. A throttle and a low pressure ejector are installed on the bypass line in the direction of the water flow. The heat generator contains a water movement accelerator made in the form of a high pressure ejector, at the outlet of which a diffuser is installed with a gap. The outlet of the high-pressure ejector and the inlet of the diffuser are located in a sealed chamber, and the chamber is in communication with the environment through an air leak. The outlet of the diffuser is connected to the inlet of the braking device, the outlet of which is connected to the water supply line. The technical result is to increase the efficiency of the heating system, reduce energy consumption and improve the safety of service. 2 sec. and 1 wp f-ly, 2 dwg.
The invention relates to the equipment of railway cars, namely to heating systems for passenger cars. An electric heating system of a railway car is known, consisting of electric heating devices (electric ovens, air heaters) that directly heat the inside and outside air entering the car [1]. However, such a heating system has a power of about 40 kW and it can only be equipped with cars, the electric power supply of which is carried out centrally from the power station car or from the contact network through an electric locomotive.Such a car cannot be used as part of trains with other sources of electricity, which limits the use of cars with electric heating. It is known a system of combined (electric coal) heating of cars, taken as a prototype, containing a hot water boiler with high-voltage heating elements installed inside it, an expander made in the form of a separate tank, water plate heater, upper and lower piping and high-voltage generator [2]. The upper distribution and lower heating pipes form a closed heating network. The basic principle of operation is the natural circulation of water when it is heated in a hot water boiler. Hot water from the expander enters the upper distribution pipes and vertical risers, then into the lower heating pipes, where, giving off heat to the ambient air, it cools down and, due to the temperature difference in the boiler and risers, returns back to the boiler. To enhance the circulation of water at low outside air temperatures, a circulation pump is installed at the inlet to the boiler. However, this heating system has, on the one hand, low efficiency in the case of using coal for heating the car, and on the other hand, it requires special safety measures using automatic devices during operation of high-voltage heating elements potentially hazardous to human life. Known heat generator, taken as a prototype, containing a housing with a fluid accelerator placed inside it, made in the form of a cyclone, a brake device connected to the outlet pipe, and the latter is connected to the cyclone by means of a bypass pipe , and a torsion device installed between the fluid motion accelerator and the braking device [3]. The torsion device is made in the form of sequentially placed nodes, each of which is a combination of two or more helicoids. This heat generator works on the principle of direct conversion of the kinetic energy of the flow of the liquid circulating through it into the thermal energy of the liquid. The main disadvantage of the described heat generator is the insufficiently high intensity of energy conversion processes, which reduces the efficiency of the heat generator and increases its overall dimensions. When creating the invention, the problem of increasing the efficiency of the heating system was solved. of a passenger railway car and, as a consequence, a decrease in energy consumption for heating a car with a simultaneous increase in the safety of service due to the exclusion of high-voltage electric heating elements, potentially dangerous for human life, from the heating system. a closed heating circuit, consisting of hot water radiators, a water heating device and a water pump, and a power supply system, according to the invention As a device for heating water, a heat generator was used, operating on the principle of direct conversion of the kinetic energy of the liquid flow into the thermal energy of the liquid, and the outlet of the heat generator is connected by a bypass line to the inlet of the water pump, and a low pressure ejector is installed on the bypass line along the direction of water movement. The problem can be solved due to the fact that in the known heat generator containing a fluid accelerator and a braking device connected to the outlet pipe, according to the invention, a diffuser is installed between the fluid accelerator and the braking device, and the fluid accelerator is made in the form of a high pressure ejector, and the outlet of the high-pressure ejector and the inlet of the diffuser are placed with a gap relative to each other and placed in a sealed chamber,which is connected with the environment with the help of an air inlet. The use of a heat generator as a device for heating a liquid, the outlet of which is connected by a bypass line with a low-pressure ejector installed on it with the pump inlet, makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the heating system by increasing the speed of water movement in the heating circuit of a passenger carriage by creating an additional pressure drop between the inlet and outlet of heat consumers by the low pressure ejector. An additional installation on the bypass line in front of the low pressure ejector of the throttle allows you to adjust the ratio of water flow through the bypass line and through the heat consumers and thereby control the water flow rate in the heating circuit. communicated with the environment, allows in general to intensify the processes of energy conversion in the heat generator and thereby increase the efficiency of its operation. The invention is illustrated by drawings, where figure 1 schematically shows the heating system of a passenger car; 2 schematically shows the design of a heat generator. The heating system includes a heat generator 1, the input of which is connected to the output of the water electric pump 2, a bypass line 3 connecting the output of the heat generator 1 to the input of the pump 2, water heating radiators 4 connected in parallel-series in the direction circulation of water flow, and a power supply system (not shown in the drawing). On the bypass line 3 in the direction of the water flow, a throttle 5 is installed, made in the form of at least one washer with an opening, the diameter of which is much smaller than the flow area of the water supply line 6, and a low pressure ejector 7. The heat generator 1 contains a water accelerator made in the form high pressure ejector 8, at the outlet of which a diffuser 9 is installed with a gap, and the outlet of the ejector 8 and the inlet of the diffuser 9 are located in a sealed chamber 10, and the chamber 10 is in communication with the environment through an air leak 11. The outlet of the diffuser 9 is connected to the inlet of the brake device 12, the outlet of which is connected to the water supply line 6. The heating system works as follows: When the electric water pump 2 is turned on, water is supplied under pressure to the inlet to the heat generator 1. In the high-pressure ejector 8, the speed of water movement increases, which creates a reduced pressure (relative to the ambient pressure) in the sealed chamber 10. When air is supplied inside the chamber 10 through the leak 11, the accelerated water flow is mixed with a metered portion of air, which intensifies the process of turbulization of the flow water. Further, the turbulized water flow enters the diffuser 9, where there is a sharp increase in pressure in the water flow to a value at which the saturation temperature of water vapor reaches the ambient temperature. In this case, vapor bubbles are formed inside the water flow, which, when the water flow enters the braking device 12, begin to condense (collapse) with the release of energy for heating the water entering the supply line 6. The main part of the heated water goes to the water heating radiators 4, and part of the flow water is directed through the bypass line 3 and enters the pump 2. At the same time, the speed of water movement in the heating circuit increases due to the creation of an additional pressure drop between the inlet and outlet of water heating radiators by the low pressure ejector 7. through the bypass line and water heating radiators 4 and, accordingly, the change in the speed of the water flow in the heating circuit. Sources of information 1. Ed. L.D. Kuzmich. Cars: design, device and test methods.- M .: Mechanical Engineering, 1978, p. 267, 268.2. Bolotin Z.M. and other Electric and combined heating of passenger cars. - M .: Transport, 1989, p. 92 - (prototype). 3. RF patent No. 2125215, IPC F 25 B 29/00 (prototype).
Claim
1. Heating system of a passenger railway car, containing a closed heating circuit, consisting of water heating radiators, a device for heating water and a water pump, and a power supply system, characterized in that a heat generator is used as a device for heating water, operating on the principle of direct transformation of kinetic energy flow of liquid into heat, and the outlet of the heat generator is connected by a bypass line to the inlet of the water pump, and a low pressure ejector is installed on the bypass line in the direction of water movement. 2. The heating system of a passenger railway car according to claim 1, characterized in that a throttle is installed on the bypass line along the water flow in front of the low pressure ejector. A heat generator containing a fluid accelerator and a braking device connected to the outlet pipe, characterized in that a diffuser is installed between the fluid accelerator and the braking device, and the fluid accelerator is made in the form of a high pressure ejector, and the high pressure ejector outlet and the diffuser inlet are located with with a gap relative to each other and placed in a sealed chamber, which is in communication with the environment by means of an air leak.
FIGURES
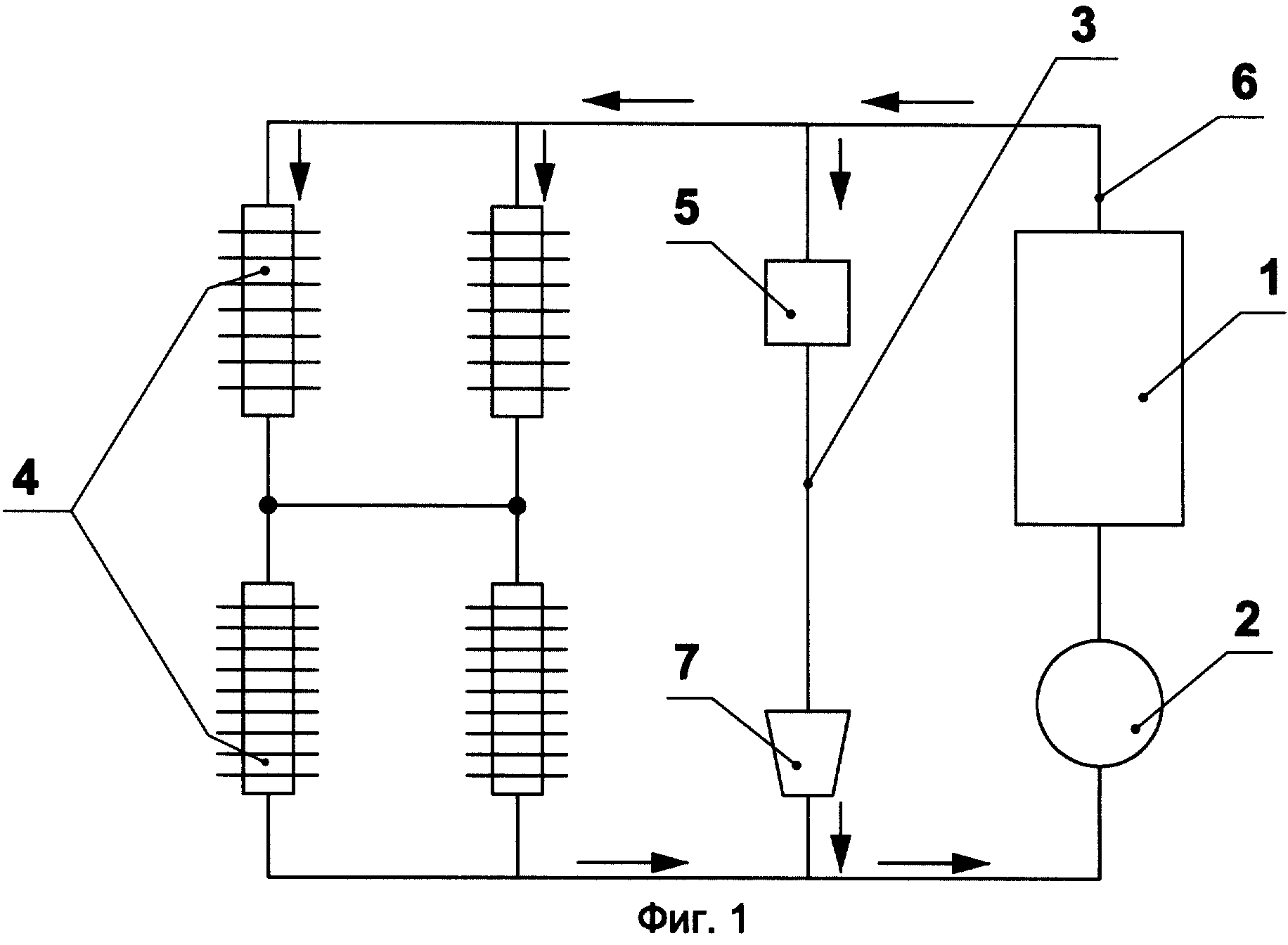

,
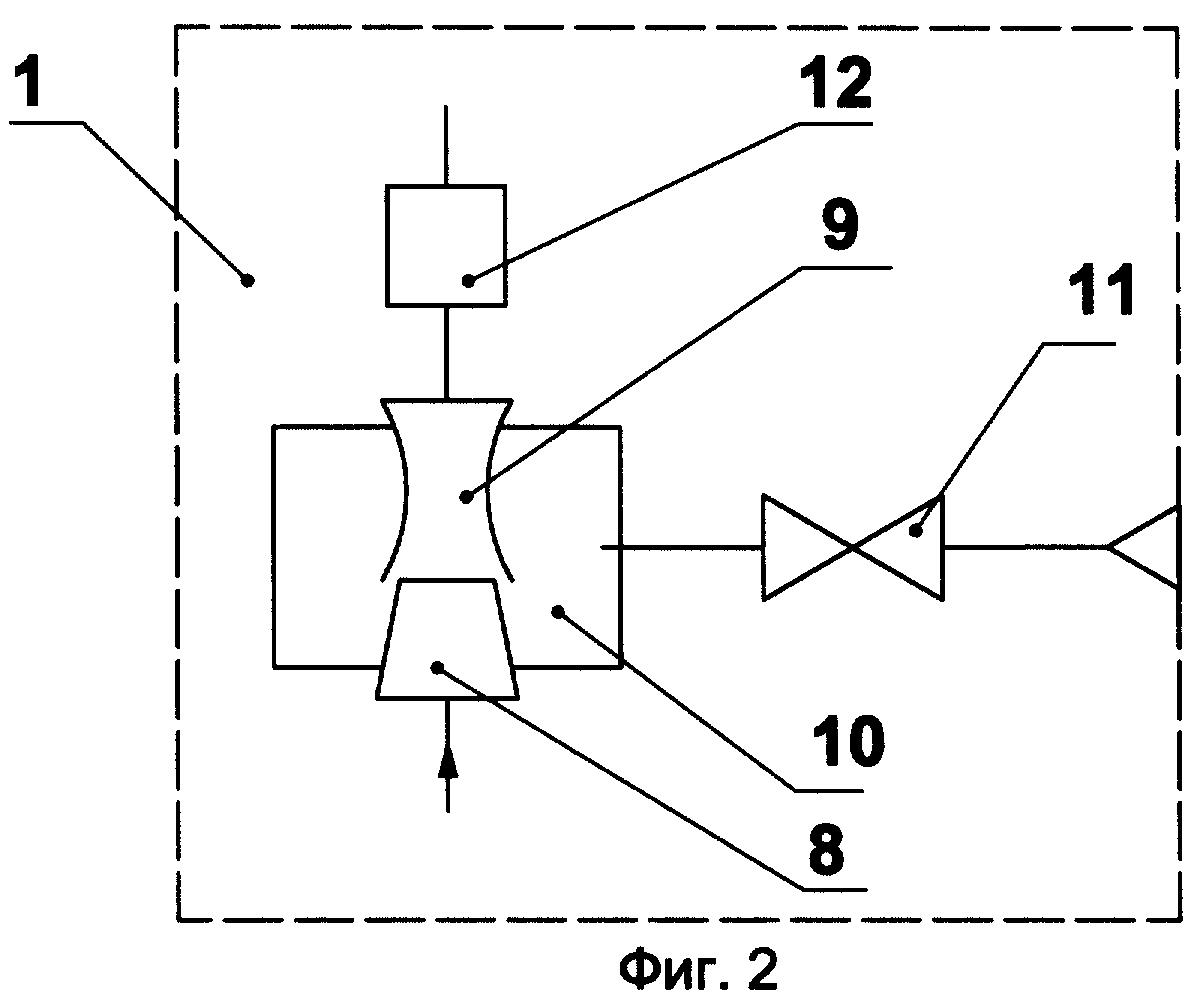

When filling with heating medium
There are only two known situations that require the performance of this technological operation:
- commissioning of heating (at the beginning of the heating season);
- restarting after repair work.
Usually, the heating water is drained in late spring for two reasons:
- Water is inevitably contaminated with corrosion products (inside radiators, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes are not subject to it). Leaving the old water for the new season, you risk breaking the circulation pump with solid impurities.
- Non-running flooded systems of country houses can "unfreeze" in the event of a sudden cold snap - such cases are not uncommon. In this sense, antifreeze coolant is preferable. The high-quality composition has high anti-corrosion properties, increasing the "inlet" interval up to 5-6 years. There are known cases of uninterrupted operation of heating on the same volume of antifreeze for 15-17 years. It is recommended to drain low-quality antifreeze after 2-3 years.
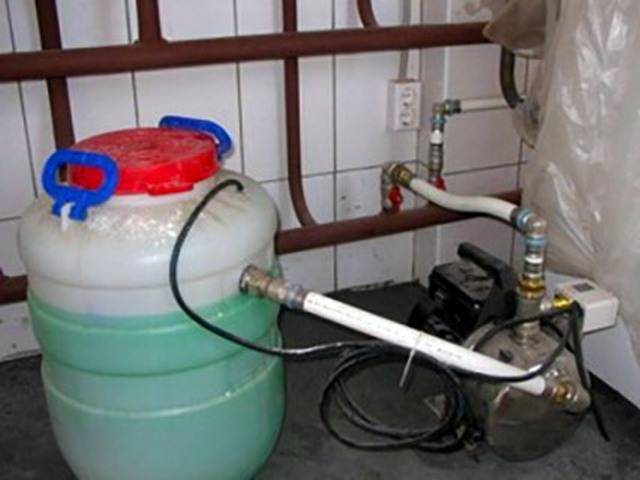


Antifreeze injection into the heating system.
8.2. Heating and water supply for passenger cars
Heating
The heating system is used to maintain normal temperature conditions inside the car, regardless of changes in the outside air temperature. According to the technical specifications of the Ministry of Railways for the design and construction of passenger cars, the air temperature in the carriage must be at least 18 ° C at an outside temperature of -40 ° C, and in the pre-embankment corridors and toilet corridors - at least 16 ° C; in cars with electric heating, automatic control must ensure a temperature within 20 ± 2 ° С, and at a speed of 160 km / h, the temperature deviation from the indicated one in height and along the length of the carriage should not exceed 3 ° С. In addition, the heating system must heat the air supplied by the ventilation unit, provide heating of water in the hot water supply system, and in the cars of the last years of construction, also heating the heads of the water-filling and drain pipes. Heating devices of any system must be fire safe, easy to maintain, reliable in operation and economical to operate. The surface temperature of heating devices should not exceed 70 ° C, so that a moderate radiant heat is generated and dust is not burnt.The air heats up in the car when the heating system is operating in the event that there is a temperature difference between the heating devices and the air. Then heat is transferred from heating devices with a higher temperature to the air of the car, i.e. heat exchange occurs.
Depending on the method of generating heat, three heating systems are used to heat passenger cars: coal-water, combined (electric-coal) and electric. In the first two, the heat carrier is water, which is heated in the boiler by coal (coal-water system), coal or electric heating elements lowered into the boiler (combined system). With electric heating, the air in the car is heated directly by electric furnaces.
In all wagons with water heating, the rooms are heated by heating pipes in which hot water circulates. The device and operation of water heating are based on the physical law, according to which, when heated in a boiler, the volume of water particles increases and the density decreases, so they, as lighter ones, rush upward. At the same time, the water particles in the pipes are cooled, their volume decreases, and their density increases, as a result of which they, as heavier, sink down. Thus, due to the difference in the density of water in the boiler and heating pipes, there is a continuous circulation of water in the heating system in a closed loop: boiler - heating pipes - boiler. In addition to natural circulation, artificial circulation is used using hand, piston and centrifugal pumps driven by an electric motor.
Electric heating
as the main one used in interregional, open cars and restaurant cars built in Poland and Germany. With an electric heating system, the car is heated using electric ovens located on the floor in passenger rooms, corridors, service
compartment and toilets, as well as with the help of an electric heater. Heating using ovens is called convection, and using a heater - air
.
Depending on the type of carriage, from 30 to 52 furnaces with a total capacity of up to 26 kW, divided into three groups or more, are installed in the car. To facilitate the conditions for regulating the temperature of the air entering the car, the electric heater is a two-section with a total power of 22 kW. Thus, the total power consumption for heating the car is 48 kW. Air heating is carried out by electric furnaces. Such cars can only be operated on electrified sections. Electric heating elements in the cars are powered by DC or AC electric locomotives. Heating devices for electric heating are powered from a high-voltage undercarriage, connected through an electric locomotive to a DC contact network with a voltage of 3000 V or an alternating single-phase current with a voltage of 25000 V. In the second case, a transformer is installed on the electric locomotive, which reduces the voltage from 25 to 3 kV.
The DC power supply circuit for heating devices is shown in Fig. 8.2. Electric energy from the contact network 4 through the current collector 5 of the electric locomotive 3, the high-speed switch 2, the heating contactor 1, blocked by the train heating key, and the intercar high-voltage connections 6 are supplied through the undercar heating line 8 through the outlet 7 to the electric heaters of the passenger car 9. A similar heating system has interregional cars built by the Kalinin Freight Car Building Plant (KVZ).
Fig. 8.2. DC power supply circuit for heaters
table of contents .. 51 52 57 ..
Preparatory work
They are performed regardless of the state of the equipment.
Hydraulic test


Both old and new pipes must be flushed and tested:
- With the help of water, the strapping is cleaned of technological debris, scale.With the addition of chemicals it is possible to remove scale and rust. If the operating rules are followed (the coolant is not drained in the summer), this procedure is carried out with a break of two years.
- Testing is performed with air at high pressure. For crimping, the working indicator is multiplied by 1.25 (the value varies depending on the material and the volume of water). The pressure for the entire time of operation can drop by no more than 1%.
Overlapping reinforcement
After completing the inspection, it is necessary to tighten all the valves leading to the drain of liquid from the radiators, and also close the air valves.
Checking for problems
During hydraulic tests, the system is inspected for cracks and cracks, leaks. After that, you need to check the performance of the equipment: pump, expansion tank, boiler and others.
System pressure and make-up
Stable working pressure is the key to efficient operation of the heating system. Let's figure out why the pressure in the heating system drops. This is due to a decrease in the volume of the coolant, which is caused by inevitable leaks in the nodes and joints, the release of liquid from the air vents during the manual air release of radiators, etc.
An automatic make-up valve connected to the water supply will protect from a pressure drop below the required values. In small systems, a mechanical valve is installed, but in this case, the consumer needs to regularly check the pressure gauge readings and add the required volume of coolant manually.
Conclusion. The ability to correctly fill a closed-type heating system will allow you to properly prepare it for the heating season and launch it after repair or maintenance work.
Related videos:
Closed heating system. How to fill with water correctly
Nowadays, many owners of apartments and private houses choose closed heating systems. A closed system is a scheme within which the movement of the coolant is carried out by means of the movement of the coolant - a pump, that is, forcibly. A special feature is a membrane-type expansion tank. Main elements. boiler, tank - membrane, radiators, pump, pipes, also fittings, fasteners and filtering equipment. But very often buyers of such a "closed heating" soon wonder how they can fill it and how to close the heating pipes. Below we will tell you how to properly fill a closed heating system with water.
The heating system is filled through the power supply to the boiler. This is done using an electric pump as well as a manual crimper. The system is filled with prepared network water or antifreeze, made according to a special method - it is an anti-freeze coolant. At this time, air is deflated in the entire inner part of the system (taps, radiators, air vents, and so on). When the required pressure is reached, you can already start up the system. Sometimes it is difficult to create the ideal pressure. Closing the heating pipes will largely depend on individual wishes, the design solution of the room and the location of the pipes themselves in the apartment, their number and size.
Difficulties often arise when filling with water. If the system is closed, then the expansion membrane tank must also be closed (up to 6 bar pressure inside the tank), the safety valve up to 3 bar. Special valves should also be installed to release air in places of accumulation, as well as a valve for replenishing and filling pipes and heating equipment. The sequence of actions when filling a closed system is as follows:
Unscrew the screw on the pump. Unscrew the shaft of the pumping system with a screwdriver. Tighten the screw tightly. Open the charge screw. Fill the system so that the pressure is equal to approximately 0.5 bar. (you can start from 0.3 bar).It is imperative to check for leaks during this procedure! Raise the operating pressure in the system to 2 bar. Make sure that there is no leakage anywhere. Bleed the air in absolutely all internal places of the system. The next step is to pressurize the system about one and a half bar. This will be the most optimal pressure for a closed heating system. If the system is going to be cooled or heated, then the fluctuations should not be significant (from 0.1 bar to 0.5 bar). Watch out for the vibration range! Sudden changes threaten to break down all equipment, pipes and fittings!
There is no water level in such closed systems. The presence or absence of water is controlled by pressure. At a normal amount, it should be between one and two bar.
A closed heating system is easy to operate, less susceptible to corrosion and destruction, it is easy to replenish and, if necessary, drain. If you have any questions, or found faults in the heating system (freezing, leaking, etc.), then immediately contact the support service!
Heating boilers are one of the main types of heating equipment and are devices for heating up to a certain temperature of the heating medium entering the heating system. The heat carrier passes through a closed circle of the heating system.
Before you start looking for contractors to improve your own balcony, answer yourself one question: what do I want as a result of glazing Perhaps you just want to use this room for drying.
Such cast-iron batteries, familiar to the majority of the population, installed many years ago, can no longer fully cope with the functions assigned to them for heating premises and have a rather unattractive appearance.
Solid fuel heating boilers are devices that heat a room using solid fuels (for example, wood, coke, briquettes or coal). Usually, such boilers are universal, as they can work on anyone.
Filling the water supply system with water.
Introduction
The birthday of electric traction is considered to be May 31, 1879, when the first electric railway, 300 m long, built by Werner Siemens, was demonstrated at an industrial exhibition in Berlin. The electric locomotive, reminiscent of a modern electric car, was driven by a 9.6 kW (13 hp) electric motor. An electric current with a voltage of 160 V was transmitted to the engine via a separate contact rail, the rails along which the train moved - three miniature trailers at a speed of 7 km / h, benches accommodated 18 passengers - served as a return wire.
In the same 1879, an in-plant electric railway line, about 2 km long, was launched at the Duchenne-Fourier textile factory in Breuil, France. In 1880, in Russia, F.A.Pirotsky succeeded in setting in motion a large heavy carriage with an electric current, which could accommodate 40 passengers. On May 16, 1881, passenger traffic was opened on the first city electric railway Berlin - Lichterfeld.
The rails of this road were laid on an overpass. Somewhat later, the Elberfeld - Bremen electric railway connected a number of industrial points in Germany.
Initially, electric traction was used in urban tram lines and industrial plants, especially in mines and coal mines. But very soon it turned out that it is profitable on the pass and tunnel sections of the railways, as well as in suburban traffic. In 1895, the USA electrified the Baltimore tunnel and the tunnel approaches to New York. Electric locomotives with a capacity of 185 kW (50 km / h) have been built for these lines.
At present, the total length of electric railways around the world has reached 200 thousand km, which is approximately 20% of their total length.These are, as a rule, the most heavily loaded lines, mountainous sections with steep climbs and numerous curved sections of the track, suburban junctions of large cities with heavy electric train traffic.
For new lines, electrified on alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz, voltage of 25 kV, six-axle electric locomotives VL60 with mercury rectifiers and collector motors were created, and then eight-axle with semiconductor rectifiers VL80 and VL80s. Electric locomotives EPM-512 (Figure 1) were also converted to semiconductor converters.


Figure 1 - Electric locomotive EPM-512.
Technological section.
1.1 General information.
All passenger cars are equipped with a gravity-fed cold and hot water supply system. The volume of the system is about 1200 liters, based on approximately 20 liters per person per day and the interval between refueling and replenishing the system up to 12 hours.
The service timetables of each train contain a list of stations where water refueling is carried out.
The design of the water supply system should ensure the prevention of water pollution in it, the possibility of effective cleaning, rinsing and disinfection, as well as complete drainage from the reserve tanks and distribution pipelines.
The entire water supply system is made of materials that do not adversely affect water quality.
1.2 Water supply system.
The water supply system (Figure 2) includes:
1) water storage tanks located on both sides in the upper part of the car;
2) distribution pipelines;
3) isolation drain valves and taps.
Filling with water is carried out from the bottom of the car through the filling nozzles (heads).
At low outside temperatures, in the event of freezing of the water inlet pipes, the system can be filled with water through the reserve head, which is located in the boiler room.
In winter, it is necessary to monitor the serviceability of the heaters of the filling pipes and
constant circulation of hot water in them.
Water filler pipes are located:
- in compartment cars (GDR) - on both non-working sides of the car body;
- in second-class and compartment cars built by TVZ - under 7 compartments (compartment

side) and under the dustbin (corridor side) on the non-working side of the car.
Figure 2- Water supply system for a non-compartment sleeping car.
1.3 Hot water supply.
The hot water supply system includes a hot water boiler in the boiler room, an expander, a tank above the ceiling of the boiler room and the corresponding pipelines. In winter, hot water enters the boiler from the heating system, in summer from a hot water boiler fired with solid fuel. All tanks are equipped with water taps and gauge glasses.
Despite some structural differences between cold and hot water supply systems, the rules for their operation for all types of cars are the same. Control over the good condition of the water supply systems is entirely entrusted to the conductor. In winter, it is necessary to carefully monitor the serviceability of the heating filling pipes and the constant circulation of hot water in them. When filling the system with water from a stationary source, control the filling of the tanks. In the oblique corridor of each car, a diagram of the position of taps and valves is posted for each operation of the water supply system. In the books of the service timetables of each train, there is a list of stations at which water refueling is carried out.
Filling the water supply system with water. When the outside air temperature is below 0 ° C, the system should be filled after keeping the carriage in a heated room for at least a day or after filling the heating system and heating the air in the car to a temperature of at least 12 ° C.
Water is poured into the tanks from under the wagon, through the filling heads. When filling the system with water, valves and taps must be open, the rest, as well as the mixer tap, must be closed.
The filling of water into the system must be stopped when the warning lamp, located at the filling head on the wagons equipped with the water filling alarm, comes on, or when water appears from the front pipe and the opposite filling pipe. The taps should be opened when measuring the water level in the system. To prevent overflow of water onto the railroad track when filling the system, there is a locking device installed in the ceiling space in front of the end wall of the tank, and check valves and on the filling pipes in the toilet and the corridor of the non-boiler end.
Draining water from the water supply system. When the water is completely drained from the system, all valves and taps must be opened, while the water from the boiler is drained in accordance with the instructions in the technical description and the operating instructions for the continuous boiler. When draining water from the tanks, it is necessary to connect hoses to the taps and drain into the toilet bowls.
Partial drainage of water from the system is carried out through taps, mixer and toilet bowls.
If the boiler stops firing at negative outside temperatures, the water from the water supply system must be completely drained before draining the water from the heating system.
The work of the water supply system. Valves must be open to ensure that water is drawn from the cold water supply system.
Cold water supply has a constant mode regardless of the season.
Filling the water supply system with water.
The hot water supply system operates in two modes - winter and summer. In winter mode, when the heating system boiler is operating, the water in the boiler is heated by hot water from the heating system, which flows into the coil directly from the boiler. In this case, the valve and the tap must be open.
In summer mode, when the boiler of the heating system is not working, the water in the boiler is heated by the heat obtained by burning fuel in the stove's furnace. In this case, the valve and the tap must be closed. The stove is powered by wood or charcoal.
Before filling the system, the conductors should check for the presence of the filling (filling) head o-rings. When filling with water, valves and taps must be open, and the rest must be closed. Water is supplied from under the car through the filling heads. The filling of the system should be stopped when water appears from the vest pipe. As with non-compartment wagons, the system can be refueled through a reserve filling head.
When filling the car with water, the water supply system must not be overfilled. It is necessary to constantly monitor the serviceability of the vestibule pipe of the tank, not to allow it to clog or freeze. Blockage of the vestibule pipe, including the riser of the wash basin, to which this pipe is connected, will immediately cause the tank to swell or overfill the tank pan with excess water, rupture of the rubber gasket of the tank lid and, as a result, flood the ceiling of the toilet and the corridor of the non-boiler end of the car.
If water leaks through the rubber gasket (when the rubber shrinks and the bolt fastening of the tank cover is loosened), it is necessary to tighten the bolts in a timely manner.
Draining water from the water supply system. When draining water from the system, open all valves and taps and drain the water from the boiler.
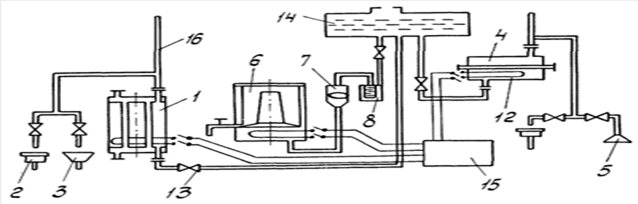

Figure 3 - Diagram of the hot water supply system.
Economic section
2.1
The calculation methodology given below will make it possible to determine the base cost of a railway ticket for any train formed by Russian Railways. The calculated base cost does not take into account the additional services of branded trains (meals, etc.), service charges and VIP classes. Calculation accuracy ± 5%
The principle of forming the base (tariff) cost of a Russian Railways ticket is zonal, the length of one zone increases depending on the total distance and can be determined from Table 2. Each zone has a length I-
and borders - lower
(but)
and the top
(B).
The values
ai1ᶻ
are used further in the formulas.
The calculation will require the following input data: distance (L),
date of travel (to determine the seasonal coefficient according to Table 3 "Seasonal coefficients"). It is also important to know the type of carriage and the category of the train to determine additional parameters of the formulas.
The basic ticket price can be calculated using the formula:
Рbase = (Ln
+
La) xPxMxKs,
(1)
Where:
Estimated distance:
Lp
=
(Vlz-a / lz) хlz / 2 + L,
(2)
Additional distance Lа
determined according to table 4 based on
car categories.
Cost per kilometer R
determined according to table 5 based on the type, category of train and car
Interstate coefficient M.
Seasonal factor Ks
depends on the year and for 2020
determined according to table 3 based on the expected
travel dates.
Additional data but
and
1z
are determined according to table 1.
Calculation of the cost of travel in a reserved seat carriage.
A reserved seat ticket for a fast non-branded train 85/86 Moscow-Makhachkala to Makhachkala, travel date 09/07/16, distance 3025 km:
Estimated distance: Ln =
(3025/200 - 1700/200) x 200/2 + 3025 =
= (10.13-8.5) x100 + 3025 = 4188.
Base cost: Рbase =
(4188 + 200) x 0.37 x 2.0 x 1.0 = 11767.12 rubles.
Where Lа = 200, P =
0,37,
M =
2,0,
Ks =
1,0.
Calculating the cost of travel in a compartment carriage.
Compartment ticket for fast non-branded train 85/86 Moscow-Makhachkala to Makhachkala, travel date 09/07/16, distance 3025 km:
Estimated distance: Lp
= (3025/200 - 1700/200) x 200/2 + 3025 =
= (10.13-8.5) x100 + 4025 = 4188.
Base cost: Pbase
= (4188 + 220) x 0.84 x 2.0 x 1.0 = 4045.44 rubles.
Where Lа
=220,
R
= 0,84,
M =
2,0,
Ks
= 1,0.
Calculating the cost of travel in a SV carriage.
SV ticket for a fast non-branded train 85/86 Moscow-Makhachkala to Makhachkala, travel date 09/07/16, distance 3025 km:
Estimated distance: Lp
= (3025/200 - 1700/200) x 200/2 + 3025 =
= (10.13-8.5) x100 + 3025 = 4188.
Base cost: Pbase
= (3188 + 225) x 1.68 x 2.0 x 1.0 = 12107.68 rubles.
Where Lа
=225,
R
= 1,68,
M =
2,0,
Ks
= 1,0.
Table 1- Zones (for calculated distances).
| Distance (a-b). Km | Zone length (la), km |
| 0-200 | |
| 200-700 | |
| 700-1700 | |
| 1700-3700 | |
| 3700-6700 | |
| More than 6700 |
Table 2- Seasonal coefficients of Russian Railways (TO,)
for 2020.
| Period | Number of days | Coefficient K5 |
| 1st of January | 0,50 | |
| January 2 - January 10 | 1,00 | |
| January 11-February 18 | 0,85 | |
| February 19 - February 23 | 1,00 | |
| February 24 - March 4 | 0,85 | |
| March 5-March 8 | 1,10 | |
| March 9-April 28 | 0,90 | |
| May 1-May 7 | 1,20 | |
| May 8-May 10 | 1,10 | |
| May 11-June 9 | 0,50 | |
| June 10-June 14 | 1,00 | |
| June 15-June 30 | 1,10 | |
| July 1-July 15 | 1,05 | |
| July 16-August 30 | 1,10 | |
| August 31-September 30 | 1,20 | |
| October 1-December 24 | 1,00 | |
| December 25 - December 26 | 0,90 | |
| December 27-December 28 | 1,00 | |
| December 29 - December 30 | 1,20 | |
| Dec. 31 | 1,00 |
Table 3-Additional distances (La).
| Car category | Additional distance La |
| LED | |
| PL | |
| TO | |
| SV |
Table 4- Cost per kilometer (P).
| Train category | Train type (P) | Car category | Price rub / km |
| Fast | Branded | LED | 0,39 |
| Fast | Branded | PL | 0,56 |
| Fast | Branded | TO | 1,26 |
| Fast | Branded | SV | 2,52 |
| Fast | Unbranded | LED | 0,35 |
| Fast | Unbranded | PL | 0,50 |
| Fast | Unbranded | TO | 1,13 |
| Fast | Unbranded | SV | 2,27 |
| Passenger | Branded | LED | 0,35 |
| Passenger | Branded | PL | 0,50 |
| Passenger | Branded | TO | 1,13 |
| Passenger | Branded | SV | 2,27 |
| Passenger | Unbranded | LED | 0,23 |
| Passenger | Unbranded | PL | 0,33 |
| Passenger | Unbranded | TO | 0,76 |
| Passenger | Unbranded | SV | 1,51 |
Occupational Safety and Health
3.1 Labor protection requirements during operation of the heating system
The boiler room must be kept clean and tidy, not cluttered with foreign objects. The doors of the boiler room on the route must be locked with a key. They should only be opened when necessary. In a carriage with combined heating, the heating elements should be turned on with the help of packet switches.
Before turning on the heating elements of the boiler or firing it up with solid fuel, make sure that there is water in the boiler and in the heating system. In the absence of water in the boiler and in the heating system, turning on the heating elements or heating the boiler furnace is not allowed. The contacts of the boiler heating elements together with the installation wires must be covered with special protective covers. Regardless of the presence or absence of high voltage on the heating elements of the boiler, it is prohibited to lift the protective cover.
When the heating system is operating on solid fuel, before lighting the boiler, it is necessary:
- close the side vestibule doors and coal pockets;
- make sure that the flue cleaning flap door is tightly closed;
- check the serviceability and correct installation of the grate and the flame arrester, opening the valves and dampers that ensure the circulation of water in the heating system.
- check the serviceability of the manual and circulating water pump.
The boiler must be fired up with paper and finely chopped wood. As the wood burns up, the firebox is loaded with solid fuel evenly along the grate. In this case, the firebox door must be closed and the ash-pan door open. It is not allowed to use firewood, the length of which exceeds the dimensions of the furnace, as well as fuel that does not correspond to the operating documents of the car.
In order to avoid the emission of flame by flue gases and burns to the face and hands, open the boiler furnace door smoothly, being at arm's length from the door. The ash pan should be closed at this time.
During the operation of the boiler, it is necessary to constantly monitor:
- behind the process of heating water in the boiler;
- behind the water level in the system using a water sampling tap. If there is no water in the tap, it is necessary to replenish the system from the water supply system using a hand pump. It is not allowed to pump water with a manual pump into the heating system when the high-voltage combined heating is switched on.
If the water level in the system drops below the permissible level and it is impossible to replenish it, it is necessary to stop heating the boiler, and at negative outside temperatures, completely drain the water from the heating and water supply and water supply systems in order to avoid its freezing.
Individual section
4.1 Indicators of the presence of faulty wagons on trains
| On railway sections where devices for detecting faulty cars in passing trains (DISK, PONAB) are installed, signal light indicators placed on the supports of the contact network or individual masts can be used (Figure 4). Figure 4 - Signal light indicator. When glowing stripes of transparent white color appear on the signal indicator, signaling the presence of faulty cars in the train, and receiving instructions by radio communication from the station attendant (train dispatcher) about the possibility of the train following to the station or the need for its immediate stop on the stretch, the driver must accordingly : |
take measures to smoothly reduce the speed to 20 km / h and follow with special vigilance, observing the train, on the path of receiving the station with a stop, regardless of the readings of the output signal;
stop the train by service braking on the stretch, inform the train drivers on the stretch, inspect the faulty wagons and report to the station duty officer (train dispatcher) about the possibility of following the train to the station or requesting the train inspectors of the wagons.
At the same time, the station attendant (train dispatcher) takes additional measures to ensure the safe passage of trains: informs the train drivers on adjacent tracks and, if necessary, delays the departure of trains from the station.
Visible signals
Visible signals are expressed by color, shape, position and number of signal readings. Signaling devices are used to provide visible signals - traffic lights, discs, boards, lanterns, flags, signal indicators and signal signs.
According to the time of their application, visible signals are subdivided into:
daytime, served during daylight hours; to provide such signals, discs, shields, flags and signal indicators (switches, track barriers, dropping devices and hydraulic columns) are used;
night, served in the dark; such signals are lights of prescribed colors in hand and train lanterns, pole lamps and signal indicators.
Night signals should also be used in the daytime with fog, blizzards and other unfavorable conditions, when the visibility of daytime stop signals is less than 1000 m, speed reduction signals - less than 400 m, shunting signals - less than 200 m;
round-the-clock, served equally in the daytime and in the dark; such signals are traffic lights of established colors, route and other light indicators, permanent speed reduction discs, yellow square boards (green back), red discs with a reflector to indicate the tail of a freight train, signal indicators and signs.

Figure 5.
Figure 6.
4.3 Actions of the train crew in the event of a failure in the schedule.
LNP having received information from the person on duty at the station or at the station about a new route, is obliged to inform the head of the structural unit and the senior dispatcher (dispatcher) of the Situational, establish points through which the train will not follow, inform passengers leaving at these stations, the order of transfer, make this is the necessary marks in travel documents. LNP provides control over the disembarkation of passengers at stations, issuance of travel documents to them from about.
When a passenger train turns on its way or leaves transit points, a point of formation and turnover with a change in the order of the arrangement of wagons in the train, notify by telegram to the address of all ticket offices along the train and large stations. When the train stops for a long time at a station or a stretch, the LPP must, by all available means, find out the reason for the train stop, make an announcement on the train radio network about the estimated time of departure of the train. If necessary, conductors should calmly explain to passengers the reason for the delay, avoiding panic. If necessary, be guided by paragraph 40 of these Regulations. In the event of a failure in the schedule of passenger trains, LNP is obliged to inform the operational duty officer (dispatcher) of the corresponding structural unit or branch, as well as the head of the structural unit and the senior dispatcher (dispatcher) of the Situation. At the nearest station, LNP confirms the transmitted information with a telegram.
List of sources used
1. Apatseva V.I. Passenger Stations - M .: RGOTUPS, 2013. - 162 s;
2. Uniform norms of production and time for carriage, road transport and warehouse loading and unloading operations. M: Transport; 2013. - 280 s;
3. Kulibanova V.V. Marketing: service activities. Textbook SPb: Peter, 2013. -240 s;
4. Kiselev A.N. Service on transport (railway) / A.N. Kiselev, N. D. Ilovaisky. M .: Route; 2013.-585s;
5. Klochkova E.A. Labor protection in railway transport. M .: Route; 2014.-412s;
6. Savin V.I. Transportation of goods by rail. Reference manual. Moscow: Delo and Service Publishing House; 2013.-528s;
7. Semenova V.M. Organization of cargo transportation. M .: Publishing; 2013.-304s;
8. Standard instruction on labor protection for the conductor of the TOI R-32-TsL-733-2013 passenger carriage;
9. Charter of the railway transport of the Russian Federation. - M .: Book Service, 2013 .-- 96 p.
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Filling a closed heating system
A closed heating system is used most often. Its difference from the open one lies in the structure of the expansion tank. In a closed heating complex, the expander is hermetically sealed, and the filling of the system is carried out in a different way.
To begin with, prepare all the necessary materials and tools. Including: a volumetric tank, hoses for pumping water from the tank to the system, clamps for firmly fixing the hoses, pliers for installing clamps, a vibrating household pump to forcibly fill the system with water.
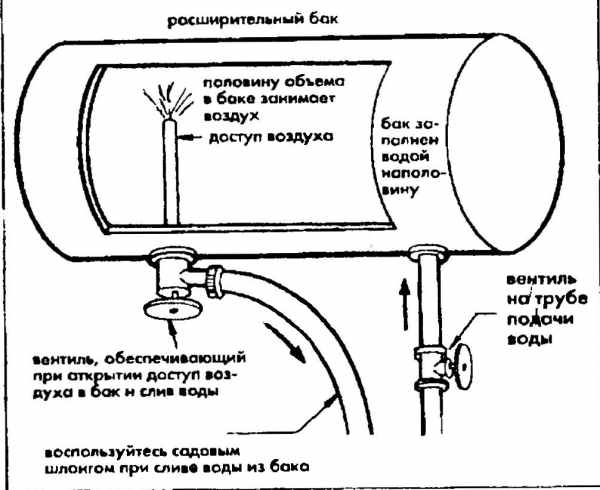

Diagram of air removal from the heating system.
Before pumping, it is necessary to tightly fasten the pump to the prepared hoses using clamps. Fill the prepared tank with water and place it near the system filling valve. The pump should also be located nearby.The hose that takes the water should be lowered into the tank, and the hose supplying the pumped-over water is fixed with a clamp on the filling valve. Taps and dampers for air release of the heating complex must be open. Turn on the pump and start supplying water to the pipes. The pressure on the pressure gauge should rise gradually. When the entire circuit is full, the pressure gauge should reach two atmospheres. Then the pump should be turned off. Disconnect hoses and turn off filler cock.
If it is not possible to use the pump to fill the heating complex, then you can use the water supply. The circuit is quite similar to the one described above. It is enough to attach one end of the water intake hose to the water tap, and the other end to the filling one into the system and gradually open the filling hose first and then the tap. In this case, the pressure will have to be monitored additionally using a separate pressure gauge.
The final operation of filling the system with water will be to remove excess air from its circuit. In modern installations, special devices are provided for this purpose. The system can be vented using this bypass device.
Filling the heating system will be most convenient when two people work, since it is necessary to simultaneously control the pressure level in the system and the operation of the pump, being near the injection valve, and monitor the tightness and the process of airing the heating radiators during the entire filling process.
What water is better to pour into the heating system
There are several types of water poured into the heating circuit:
Plumbing. This also includes liquid taken from a well, well, or the nearest body of water. The main advantage of this option is its cheapness. However, the quality of such a coolant is rather low: it rather aggressively affects the inner walls of the circuit due to salts and oxygen dissolved in it.
Boiled. Boiling allows you to remove from the water some of the oxygen and salts that precipitate. However, it is rather difficult to prepare water for the volumetric contour in this way.
Purified with reagents. To neutralize harmful impurities, instead of boiling, it is convenient to use special chemicals - reagents. Water prepared in this way needs to be thoroughly filtered before pouring into the system.
Distilled. It is sold in plumbing stores in containers of various sizes. Rainwater also has similar properties, which some owners of private houses specially collect for subsequent use in heating networks.
Antifreeze. They are used instead of water in cases where the heating system is prone to freezing (the crystallization temperature of antifreezes is much lower than that of water). Due to its high cost, this method of filling the heating circuit is rarely used.


Antifreeze for heating
Conclusion
Filling the heating circuit with water is a rather complicated and time-consuming procedure, which is recommended to be performed at least by two people.
During its implementation, it is important not to rush, carefully following all the recommendations
Particular attention should be paid to the preparation of water for pouring into the circuit: in cases where, for financial or other reasons, liquid from the water supply is used, it must at least be boiled. To remove sediment and rust particles that gradually accumulate in the coolant, it is recommended to equip the system with special mud filters
5.4.3 Heating system
The heating system in passenger cars is of two types: water and electric. The water system is used on all types of locomotive-hauled passenger cars equipped with an autonomous power supply system from undercar generators and storage batteries.The locomotive-hauled carriages are equipped with an electrical system and are supplied centrally from a power station car or from an overhead line through an electric locomotive.
The water heating system (Fig.5.17) includes a boiler 1, an expander-air heater 10, heating pipes 2, a feed pump 8, tanks 6 and 7 for water and fuel, valves 5, 9, a sump 5 and a tap 4 for draining water from boiler.
The circulation of water in the heating system (shown by arrows) occurs continuously due to the temperature difference in its various parts. Artificial circulation of water is also provided with the help of a circulation pump installed on the pipeline supplying water to the boiler, the supply of which is turned on in cases where the outside air temperature is lower than the design one or when accelerated heating of the car after settling is required.
With a combined (electric-coal) heating system (Fig. 5.18), the water in the boiler is heated by high-voltage heating elements located in the water jacket, and in the absence of electricity, due to the heat of the combusted solid fuel - coal).
The heating elements are powered by a single-wire train line with a nominal voltage of 3000 V DC or single-phase alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz on the way from locomotives, and at dumping points - from stationary devices.
Various types of wagons are equipped with a hot water heating system with a combined boiler. This system consists of a boiler with an expander and heating devices. The boiler (Fig. 5.19) with electric coal heating has a conventional coal furnace 4 and a water jacket 2, in which 24 high-voltage heating elements 3 are located on the support flange 11.
To increase the surface of the heated water, circulation pipes 6, 7, and 8 are installed in the conical part of the furnace. In the lower part of the furnace there are grate 1 and an inclined ash pan 14. Coal is loaded into the boiler through the furnace hole 12, through which slag is extracted. Ash and fine slag are removed through the opening of the ash pan 13. Three insulators 9 are placed on the support flange in the furnace zone, through which high-voltage wires are fed to the heating elements of the boiler. In order to ensure electrical safety, the boiler casing 5 is grounded. For this, a special bolt is provided in its lower part, to which the ground wire is connected.
The heating elements are covered with a protective casing 10, on which an interlock is installed that breaks the circuit of the coils of high-voltage contactors when the casing is lifted and high voltage is present. In the raised position for inspecting the heating elements, the casing is suspended from chains. The volume of water in the system is 855 liters, of which 370 liters are in the boiler and expander.
The heating circuit, heating elements and other high-voltage equipment are the same for different types of cars. The high-voltage heating elements have a total power of 48 kW and are divided into two parallel groups, each of which consists of two parallel legs, including six heating elements connected in series. To protect the boiler, a thermal relay is provided that turns off the electric heating elements when the water temperature in the boiler rises above 90 ° C, and a minimum level relay that turns them off when the water level in the expander drops more than 200 mm. In air-conditioned cars, additional low-voltage electric ovens and an air heater are used, which are powered by an autonomous power supply system with a DC voltage of 110V. In passenger cars of interregional and suburban communications, heating with the help of electric furnaces and air heaters is most common.
In the systems of water supply and water heating of modern passenger cars, plastics are widely used for the manufacture of many parts and assemblies.Water tanks, washbasins and toilets are made of fiberglass based on polyester resin, pipes, fittings, valves, bushings, tees, as well as other connecting and regulating parts are made of low density polyethylene. In the toilets, the floor is made of fiberglass instead of cement, covered with metlakh tiles. The use of plastics ensures a decrease in the empty weight of a carriage, an extension of the service life, a decrease in labor intensity and costs in the manufacture and repair of water supply systems, heating and internal equipment.
Why does the pressure drop in a closed heating system
There is only one reason why the pressure drops - the lack of tightness, that is, a leak. The question is to find her. A characteristic sign of a leak is a puddle in a certain place or a brown spot when the water has time to dry. During the search, you should inspect the following nodes and elements:
- pipe connections and fittings: it happens that cracks appear in the latter;
- automatic air vents: a faulty element with a stuck float will leak water;
- shut-off and control valves, safety valve;
- expansion tank: a crack in the membrane will cause a drop in pressure, air in the system and frequent shutdowns of the boiler.
To eliminate the leak, you cannot do without partial or complete emptying of the pipelines. At the end of the work, you will have to pour water into the system again, create the necessary pressure and monitor the pressure gauge for several days.