How does soot appear?
When fuel burns in a stove or in a fireplace, along with the release of heat, the process of release of volatile substances occurs, deposited inside the chimney - on its walls.
Soot and resinous deposits take a fancy to horizontal sections, various protrusions and irregularities, corners.
Gradually, the layer thickness increases, and the chimney channel narrows.
If, instead of transparent or white, dark smoke appears from the chimney, and the fire in the firebox acquires a dark orange hue, this is a signal that it is time to clean the chimney.
Why is the chimney dirty?
The clogging of the smoke channel occurs during the combustion of fuel, when vaporous and solid products are released from it, carried out by the flow of furnace gases. But under certain conditions, they fly out into the pipe not completely. This happens under the following circumstances:
- Burning raw wood. Fuel with humidity above 24% contains an increased amount of intracellular moisture, which actively evaporates as it burns. These vapors rise together with the furnace gases into the chimney. In a cold or insufficiently heated channel, they mix with cooled air, as a result of which condensate settles on its walls. And this is not just water, because the vapors contain oxidation products, so the precipitate is acids. They do not just flow down the walls of the pipe, a significant part of them lingers on the walls, precipitating solid combustion products from the smoke, while carbon deposits form on the walls, reducing the cross-section of the smoke channel.

When raw firewood is burned, excess moisture is released from them, which ultimately settles on the walls of the chimney and becomes a source of carbon deposits - Use of prohibited fuels. Of course, there are no direct contraindications, but woodworking waste, consisting of wood with fillers in the form of binders, cannot be used to fire the furnace. Such materials include plywood, chipboard and fiberboard waste. Such fuel emits a large amount of tar in the smoke, which intensively settles on the walls of the chimney. Resinous wood - pine or spruce - has a similar effect.
- Cold chimney. Condensation of moisture on the walls occurs at a certain temperature in the channel. This state of gases is called the "dew point". If such conditions are created inside the smoke channel, condensate settling on its walls occurs in an active mode, provoking the accumulation of soot. To get rid of this phenomenon, you need to reliably insulate the pipe, reducing its heat transfer to the surrounding space. After that, the chimney will warm up, and the dew point will rise higher, leaving the space inside the chimney.
- The presence of horizontal pipe sections. The greatest amount of soot is formed on the bends of the chimney, therefore, it is better not to use this method of laying without special need. If no other solution is possible, cleaners must be installed on the swivel elbows, which can be opened and free the elbow from soot build-up.
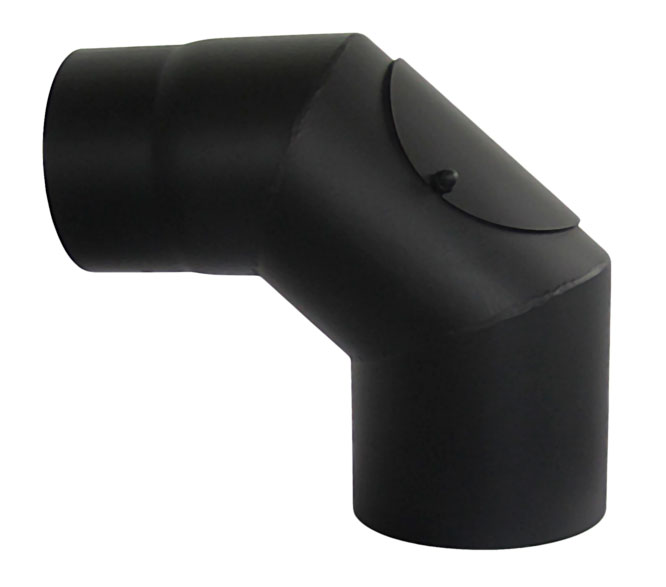


If you need to make a horizontal section on the chimney, the transition to it must be performed using a bend with a special hole for cleaning (revision) - Rough walls of the smoke channel. When constructing a chimney, it is necessary to mop the channel to improve the quality of its surface. Soot is deposited primarily on irregularities in the chimney.
- The furnace is heated with household waste. Such fuel is even more detrimental to the chimney than the use of plywood and other scraps.It always contains the remnants of plastic or plastic packaging, which release a lot of chemicals during combustion. In this case, the chimney is guaranteed to overgrow with soot faster than the end of the heating season.
What is the risk of plaque accumulation:
- the thrust and efficiency of the stove (fireplace) decreases;
- the inner walls of the chimney collapse;
- a malfunction in the chimney can cause fire and carbon monoxide poisoning.
The last circumstance is extremely important. Due to the high combustion temperature of soot, the chimney can collapse, any spark from the same fireplace can ignite deposits on the walls of the chimney and lead to a fire.
Soot can be of different fractions, oily, loose or resinous - the last variety is the most dangerous in terms of fire.
The temperature when burning soot reaches 1200 degrees, and although the fire does not last long, this phenomenon often has the most sad consequences.
In addition, when heated, the chimney can destroy the adjoining elements of the roof.
Plaque will form in any case, but its amount can be minimized by following simple rules.
SOUGH IN THE CHIMNEY! WHAT IS DANGEROUS AND HOW TO FIGHT WITH IT?
What is Soot?
This is a product of incomplete combustion of carbohydrates in furnaces, heat generating devices, formed at insufficient combustion temperature and (or) with insufficient amount of air.
Soot is a finely dispersed, almost pure (technical) carbon, the crystal lattice of which consists of hexagons with carbon atoms at their vertices. Crystals make up curved layers, which determines the almost spherical surface of its particles. The density of the soot particles is 2 g / cm3. The average number of crystals in one soot particle varies from 1.6 to 5.4 thousand pieces.
Bulk density, depending on compaction and moisture content, 0.05-0.5 g / cm3. The surface can be either rough or smooth.
The chemical composition of soot contains up to 98% carbon, small admixtures of minerals and sulfur. Also, the composition of soot deposits can include oxygen, up to 10% of the mass, aromatic resins and compounds of various substances.
Most often, the soot formed on the walls of heat-generating devices and chimneys does not have chemical and laboratory purity, due to its mixing with resinous deposits, contamination with dust and fly ash.
The production and use of carbon black will not be considered in this article.
So what is the danger of accumulating soot deposits in the chimney?
1. Dangerous! Combustion!
In the presence of atmospheric oxygen, under the influence of high temperatures and from a source of open combustion, soot can burn intensely, with the release of a large amount of heat. Combustion temperature from 800 to 11000C.
If soot ignites in the chimney, it is possible to ignite building structures, if the nearby combustible materials are not properly protected. Also, a potential fire hazard is represented by the spread of sparks from the pipe mouth or through the resulting leaks in the channel walls.
With prolonged and intense burning of soot, the materials of the chimney are subject to increased wear and tear and may become completely unusable.
2. Dangerous! Narrowing the pipe section!
Soot deposits on the walls of the channels can significantly reduce the cross-section of the pipe, which leads to a decrease in the throughput of the chimney, incomplete removal of combustion products through the chimney into the atmosphere, and provokes smoke emissions into the room.
As a result of incomplete removal of flue gases from the furnace, incomplete combustion of fuel, which not only aggravates the formation of soot, but also creates conditions for the release of carbon monoxide.
The ingress of a mixture of flue gases containing carbon monoxide into living quarters poses a deadly threat of poisoning! Dangerous!!!
3.Dangerous! Chimney blockages!
The soot deposited on the surfaces of the chimneys, supplemented by dust, ash and debris, gradually wakes up and can completely block the pipe section, forming a blockage - a dense plug.
When the device is running, this will lead to inevitable smoke pollution of the premises and can cause poisoning by combustion products, up to and including death.
4. Soot destroys chimney walls! Dangerous!
The soot adhering to the walls of the smoke channels, mixing with condensate, under the influence of high temperatures creates all the conditions for the formation of an aggressive environment that destroys the materials of the chimney.
There is a risk of losing the chimney's functionality and the inability to use the stove (fireplace or boiler), which threatens not only with the costs of its alteration, but also creates the risk of loss of all property from a fire caused by untimely replacement or repair of a destroyed chimney.
5. Soot will cause ovens to overheat! Dangerous!
The soot that falls out on the walls of chimneys and chimneys of furnaces acts as thermal insulation, preventing the furnace from warming up.
Because of this, the consumer begins to consume more fuel, receiving increased amounts of soot and additional economic costs. At the same time, it begins to heat in an even more intense mode, leading to the ignition of soot in the channels and to overheating of the stove and chimney. Which creates a danger of both fire and poisoning.
6. Soot in the air, it's dangerous!
The soot particles, due to their fine surface structure, pose a hazard to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and eyes.
Soot is classified as hazard class 3.
Maximum concentration limit of the substance, mg / m3.
Maximum one-time - 0.150
Average daily - 0.05
This should be taken into account both during operation and when organizing cleaning work for Fireplaces, Stoves and Chimneys.
It is necessary to use protective curtains on the combustion space, (especially open fireplaces), or around the stove to be cleaned. The chimney sweep performing the work must be provided with personal protective equipment for the eyes and respiratory organs.
What circumstances affect the amount of soot in the stove and chimney?
1. The amount of soot formed depends on the completeness of fuel combustion.
This is influenced by the following factors:
- Type of fuel;
(different types of fuel, depending on their chemical composition and the amount of impurities, have the ability to burn or not burn completely. When burning one unit of fuel, they can emit different amounts of soot and soot.);
- Fuel quality
;
(Fuel with a high moisture content or contaminated combustion emits more soot than clean and dry fuel.
This can be attributed to fuel contamination by ash that is not removed in a timely manner)
- Incomplete and not timely removal of flue gases from the furnace;
(Prevents the flow of fresh air into the combustion chamber, due to which the fuel is not burned with the release of soot and soot)
- Combustion air volume
;
(It is important to ensure that there is enough of it for complete combustion of the fuel. However, remember that there should not be too much of it. This can lower the combustion temperature, subcool the flue gases and reduce the efficiency of the entire apparatus. The amount of supply air must be precisely balanced.)
- Combustion temperature
;
(Subcooling by excessive air flow into the firebox is given above. The design of the firebox and the presence of cold parts in it, for example, a low roof, or a water heat exchanger, leads to a decrease in the combustion temperature and "smoking flame")
- Fuel combustion rate;
(Combustible gases released during fuel combustion do not burn completely, but are transferred to the chimney, under the influence of excessive (excessive) draft)
2. The amount of soot settling depends on:
- Subcooling of the removed flue gases;
(The low temperature of the flue gases leads to the formation of condensate on the walls of the channels and the participation of soot particles as a "dropping spot" on which moisture condenses. Moistened soot is more prone to adhesion and formation of deposits);
- Humidity of the walls of the chimney channel
;
(Any substances, including ash, dust and soot, adhere more to a moistened surface. And after sticking, moistened, they take on the following particles, intensively increasing their volume)
- Roughness of surfaces;
(There is probably no need to tell a lot here, and everyone will agree that smoother surfaces retain soot less)
- Chimney configuration
;
(It is important, even during the design and installation of chimneys (as well as fireplaces, boilers and stoves), to prevent the creation of narrowings, protrusions and difficult-to-maintain "nooks" on the paths of movement of flue gases. Being places of potential accumulation of soot, they will also act as a source problems.)
- Timely removal of soot and debris deposits;
(This affects both the amount of soot formed in the combustion chamber and the resulting build-up of soot deposits)
What to do to reduce the formation of soot as little as possible? According to the above, to reduce the amount of soot generated, you should:
- Use fuel that does not emit soot, low (15%) humidity, without contamination;
You can't burn everything in a stove and make a "waste incineration plant" out of it!
- To achieve complete combustion by using or altering the firebox, while adjusting the combustion air supply;
- Ensure complete removal of combustion products from the furnace into the atmosphere by installing a proper chimney that provides sufficient draft;
- Make chimneys smooth, dense, heat-insulated and protect them from precipitation;
- Service in a timely manner! It is necessary to inspect, clean and repair all stoves, fireplaces, boilers and chimneys from them.
How often should stoves, boilers, fireplaces and chimneys be serviced and cleaned?
The correct answer would be:
Chimney cleaning should be carried out as needed, but not less often than with the frequency determined by the current operating standards, as well as the manufacturer's documents for the installed equipment.
For solid fuel heat-generating devices, regardless of the materials of the smoke channels:
Once every 3 months - for heating stoves;
1 time in 2 months - for continuous stoves and hotbeds;
1 time per month - for stoves and other continuous (long-term) furnaces.
For gasified heat generating devices;
Once every 3 months - for brick canals;
1 time in 3 months, with the exception of the summer period - for brick channels of heating and cooking stoves;
Once a year - for channels made of steel, asbestos-cement and ceramic (pottery) pipes;
Once a year for rooftop gas-fired boiler houses.
When should the flue ducts be cleaned?
As mentioned above, the channels should be cleaned as needed, and the following external signs tell us about this:
- Weakening of traction;
- Smoke emissions into the premises;
- Lack of lumen in the canal;
- A large amount of soot waking up in your pocket;
- Local overheating of chimney and (or) furnace sections;
- Burning with soot;
- Soot over the firebox door;
- Scattering of soot from the mouth of the pipe observed on the roof and snow;
- The examination result shows the presence of deposits.
It is worth mentioning here that this applies to ovens that were in good condition and had no problem before.
How and with what to clean the chimney?
You can hear a lot of experienced stories, about the power of a handful of rock salt sprinkled on coals, about starch or dried potato peels added during combustion ...
The effectiveness of these funds for soot is substantiated by its "decoking", the deposition of substances on the surface of soot deposits and its shedding downward, rushing other particles along with it.
Modern manufacturers, based on the same principle, offer many different products both in bags and in briquettes, in powders or logs ...
I find it difficult to talk about the chemical compounds formed from the combustion of these agents in chimneys and their effect on the durability of materials, because I have not studied this issue, but I suppose - they definitely do not add life to the chimney.
Answering the question about the use of all these means and the effectiveness of the chemical cleaning method, I think that they are good only for prevention. It is naive to believe that some kind of magic means can clear a clogged chimney!
And an incompletely clogged chimney is not capable of self-cleaning. It should be rubbed with a brush, i.e. mechanical action is necessary!
First of all, chimney cleaning consists in removing blockages from construction debris and crumbling parts of soot and dust. It is produced by striking a steel ball on a cable from above along the debris or lifting it from below with rods (pipes). At the same time, the passage of the channel is checked.
After that, the debris is removed through hatches and cleaning pockets, and in their absence, by opening the walls of channels and furnaces, followed by sealing the technological holes.
To remove soot deposits from the channel walls, the following are used:
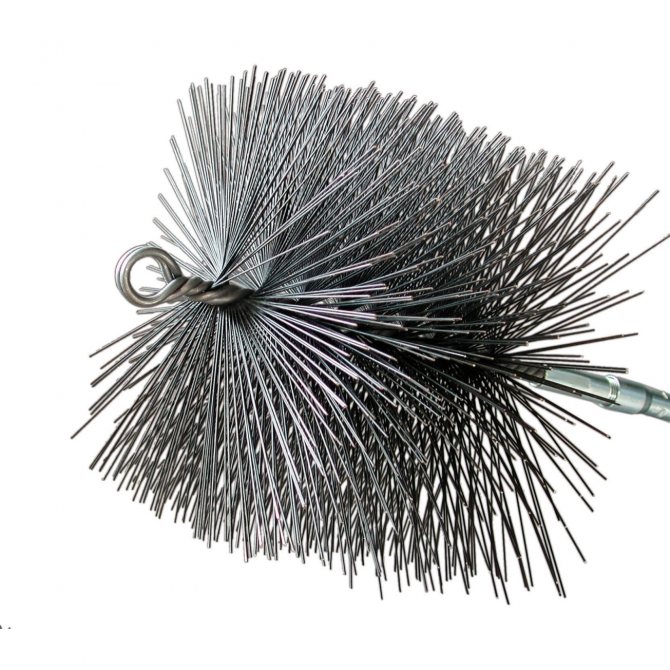
- Chimney sweep three. (cable, ruff, load) lowered from above, through the mouth of the pipe, shaking off soot deposits downward;
- Ruff on a carbon fiber rod. (According to his model, there are many home-made options from fiberglass reinforcement, or metal-plastic pipes) It is possible to use it for cleaning both from top to bottom and from bottom to top.
- Manual and improvised means: bottle brush, broom brush, plastic scraper is used for areas not very far from the cleaning hole;
- A flexible shaft with a ruff or "sun" connected to a drill cleans soot by rotating;
- Alkaline chimney cleaning machine with and without a feeder, also by rotating and pushing, removes soot deposits.
Chipping off of deposits from the walls of the channels and the pipe mouth is not permissible!
After all the soot has been cleaned off the walls, it is necessary to free the channels from its residues. To do this, apply:
- Chimney bucket with bucket. The bucket has a flat edge to fit snugly against the oven surface, and the bucket has a fold-out handle. Serves to remove crumbling debris from pockets and from the bottom of the chimney;
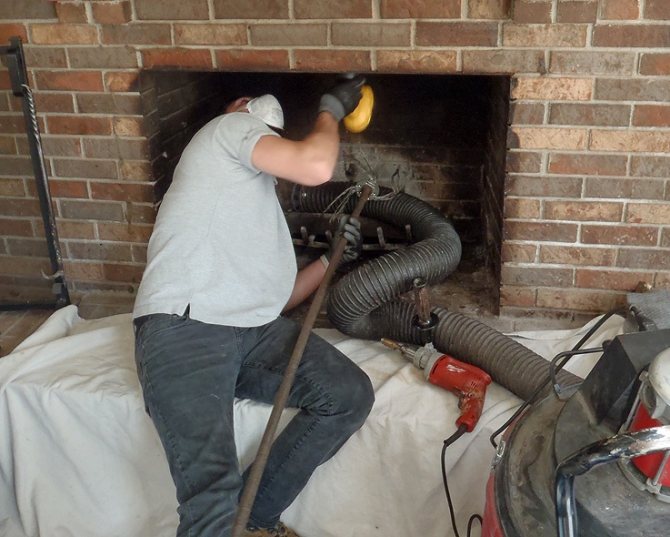
- Cyclone nozzle for soot. Connects to a household vacuum cleaner;
- Special or construction vacuum cleaner.
The use of nozzles that suck out soot and spray them in the surrounding air is prohibited!
It was proposed to wash away soot deposits in the canal with a soda solution, cleaning agents and detergents with disassembling the canal and in assembled form. However, it is necessary to evaluate both the convenience and cost-effectiveness of this process, and the structure with the state of the chimney.
Is it possible to burn soot in a chimney?
One of the most frequently mentioned folk remedies for cleaning chimneys is called aspen firewood.
It is difficult to attribute it to chemical methods, but it acts precisely as burning off soot in the chimney due to the high combustion temperature.
It is extremely dangerous to use it! since the spread of sparks from the mouth of the pipe, depressurization of the channel, and the presence of combustible structures of the building and other objects in the immediate vicinity of the chimney can lead to a fire.
Also, burning off soot, with a large amount of it in the channel, leads to a furnace fire.
What are the actions in case of a stove fire - ignition of soot in a chimney?
A stove fire is detected when the pipe becomes very hot, tongues of flame are visible from the mouth and sparks fly out, and a rumble is heard.
So the soot has ignited and you need to extinguish it.
To do this, close the air flow, all cleaning holes, and the mouth of the pipe, if possible.
Most often it is difficult to assess the degree of danger yourself, therefore, if there is no 100% certainty in the fire-fighting device of the chimney, call the firefighters! It's not worth the risk. They will back you up!
If the burning has not stopped, then it is necessary to fill the fire from the roof with water, from a bucket or hose. The fire brigade that has arrived in time will be very useful to you.
What to do with the chimney after soot has burned in it?
If a fire has been flooded, the chimney must be replaced!
If it has not been poured, then the channel must be inspected without fail.
Based on the results of the survey, a decision will be made on the suitability, full or partial replacement, or the need to repair the chimney.
Remember!
It is always easier to prevent a fire than to extinguish it!
And most importantly, it is also less expensive.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
0
Author of the publication
offline 18 hours
hotimsk
899999K
Belarus. City: Khotimsk
Comments: 0Public: 5295Registration: 10-01-2018
We take measures:
- first of all, the chimney must be built in compliance with all norms and rules, including height requirements;
- the fireplace structure must be properly arranged;
- the chimney must have good thermal insulation properties;
- when heating, it is better not to use resinous pine, spruce logs, wet firewood, freshly cut, with bark, and also not to burn various garbage in the oven;
- the device of the revision window is mandatory - for cleaning;
- it is desirable to arrange constructive bends as little as possible;
- it is necessary to regularly clean the firebox and ash pan;
- it is necessary to periodically inspect and check the condition of the chimney, as well as clean the channel - at least once a year.
It is worth noting that the cause of blockage in the pipe can be not only combustion products - birds' nests and cobwebs often complicate the functioning of the heating system.
For preventive purposes and in case of congestion, large accumulations of soot on the walls of the chimney, it is necessary to clean it.
Mechanical cleaning
The most effective method, as practice shows, is mechanical cleaning.
You can tidy up the chimney yourself or with the assistance of a specialist in this area - a chimney sweep.
To remove contamination you will need:
- hard brush made of flexible rods. Its length can be increased using separate parts - type-setting meter sticks;
- for round sections of the pipe, a ruff is suitable, for square and rectangular - a brush;
- at the first stage of cleaning, a scraper is used to remove dense plaque;
- a ball-shaped heavy metal core is used to eliminate congestion. It is forbidden to use eccentric dumbbells instead: a stuck object with a displaced center of gravity can lead to a blockage, which is extremely difficult to get rid of, and sometimes even dismantling of the chimney is required.
Sequence of work:
- chimney flues are cleaned from below, using a special brush, stove chimneys - from the roof;
- do not forget about precautions: the roof can be slippery in winter. Of course, you should not carry out work at a height in strong winds;
- cleaning holes, the firebox must be closed to prevent soot from entering the interior;
- we inspect the channel: a layer of soot with a thickness of more than 2 mm requires mechanical cleaning;
- we check the sixth for the presence of blockages - if there are any, we push them with the help of a heavy core fixed on the cable;
- remove dense plaque with a scraper, after which we continue cleaning with a brush, the diameter of which is larger than the section of the pipe;
- the final step is to open the cleaning holes in order to remove dirt, debris and combustion products from them. The firebox and blower are the last to be cleaned.
Use of chemicals
This method is great for independent use, it allows you to easily and with minimal effort to clean hard-to-reach bends.
The industry produces liquid, solid and bulk chemical chimney cleaners - for every taste.
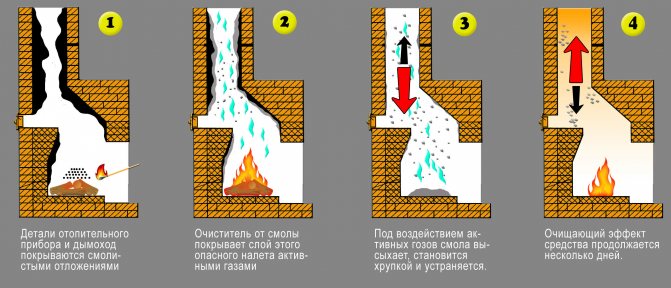
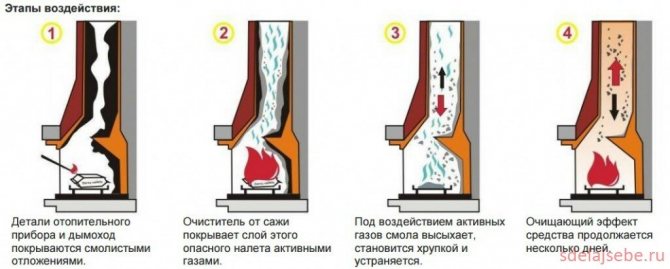
The principle of operation of such funds is as follows. During combustion, substances are released that destroy soot or lead to a catalytic reaction - and the deposits are burned at low temperatures.
One of the most common chemical cleaners is a chimney-log sweep: it is placed in the firebox with or without firewood.
The use of chemicals is excellent as a preventive measure, preventing plaque formation.
However, after using them, an unpleasant specific smell remains, and the premises must be well ventilated.
In some cases, mixtures may contain chlorine, which is harmful to human health.
Most of the tools are not universal - before purchasing, you need to read the instructions, which indicate which heater they are intended for.
It is undesirable to use such chemical methods for removing contaminants when there are furnace elbows - so that the fallen off soot does not completely fill up the channel.
Soot control chemicals
To reduce the need for chimney sweep services, you can use chemicals to prevent the formation of carbon deposits - liquids, powders or briquettes that must be added to burning wood. All of these tools help break down the soot layer and shed it down the walls of the chimney.
Most popular remedies:
- PKhK anti-fire powder - is burned simultaneously with firewood, 150-120 g is enough for one ton of fuel;
- Kominichek cleaner - a product made in the Czech Republic and sold in a package with five sachets weighing 14 g;
- log Chimney sweep - in the form of a bar, when burned, substances are released that clean out carbon deposits along with the flow of combustion products coming out through the chimney;
- powder Cheerful chimney sweep - contains resins that lower the temperature and help burn out carbon deposits, is not a toxic agent, which makes it stand out from competitors.
You can buy all of the above chemicals at any household supermarket.
According to the instructions, one sachet is enough to clean the stove or fireplace; two are required for a wood-fired heating boiler. The bag should be thrown on the burning wood without opening and the door of the firebox should be closed. The dose cannot be increased.
If the soot is very thick, it is best to repeat the procedure. For prevention purposes, it is advisable to burn one packet every two weeks. In addition to removing soot, this product increases the efficiency of wood-burning heaters and saves money when purchasing fuel.
The second most popular tool is the "Chimney sweep" log - a bar (briquette), during the combustion of which substances are released that affect soot deposits and contribute to their shedding down. The main purpose of this chemical cleaner is to prevent narrowing of the chimney section due to soot and carbon deposits.
Stove-maker's note: in large Russian stoves it is necessary to burn two "Chimney-sweep" briquettes at a time.
"Chimney sweep" consists of sawdust, coal wax with coal dust, ammonium sulfate, urea, zinc chloride, sodium sulfate, silica and phosphorus oxide. This product is especially effective for brick chimneys.
Before using the Chimney Sweep for the first time, you must make sure that there are no loose bricks, debris, bottles or bird nests in the chimney. The most efficient burning of a briquette on hot coals. Additives entering the pipe affect its inner surface for up to two weeks. All this time, soot falls into the furnace from above. After two weeks, it is advisable to clean the knee and the smoke damper.
The use of folk methods
There are several traditional tools that are analogous to special chemical "chimney sweeps".
Rock salt
During the heating, ordinary salt is poured onto the wood. This method will not help in the event of severe congestion, but as periodic prophylaxis it will do.
Potatoes
Chopped potatoes or peels are scattered over the burning logs. How much cleaning is required depends on the size of the oven - usually no less than half a bucket.
The steam, saturated with starch, softens the deposits in the chimney, and some of the soot simply comes out of the chimney.
This method is used as an independent method, as well as with the subsequent mechanical removal of contaminants. After this procedure, cleaning the canal with a brush is much easier and faster.
Aspen firewood
The use of aspen logs is considered to be quite effective. However, you should be very careful when heating the stove.
The flame reaches a great height, tongues of fire can appear even above the chimney.
Dry strong heat burns out soot, however, this increases the likelihood of a fire many times over: especially if there are cracks in the walls of the chimney, a spark can get into both the interior and the roofing.
Therefore, before using this method, you should make sure that the chimney, especially a modern one, will withstand and will not crack, otherwise a fire will not be avoided.