In terms of electrical conductivity, the metal takes the second place after silver, the thermal conductivity is high, and the metal does not react with water. Therefore, copper pipes, GOST 617-90, are used in our country for the transportation of liquids and gases. They do not crack or deform at very high and very low temperatures, do not transmit oxygen and ultraviolet light.
Their main advantage is their versatility, they are suitable for all utilities, do not deteriorate from chlorinated water, and inhibit the growth of bacteria. They are not subject to corrosion, the service life of copper pipes reaches 100 years. There are few disadvantages, but they are. Pipes are damaged in hard or soft, alkaline and acidic environments; corrosive liquids cannot be transported in them. Large impurities leave deep scratches.
Copper cannot be combined with other metals; this will be followed by electrochemical corrosion. Therefore, mainly, the use occurs for civilian purposes, and not for the transportation of active substances, even in factories it will be more of a heating system, rather than the transportation of chemicals. The heat transfer of a copper pipe allows it to be successfully used in heat exchangers, cooling radiators, in air conditioning and heating, in computer coolers and heat pipes.
For which systems do you need a calculation?
The heat transfer coefficient is calculated for a warm floor. More and more rarely, this system is made of steel pipes, but if products from this material are selected as heat carriers, then it is necessary to make a calculation. The coil is another system, during the installation of which it is necessary to take into account the heat transfer coefficient.

Steel pipe radiator
Registers - presented in the form of thick pipes connected by jumpers. The heat transfer of 1 meter of such a design is on average 550 watts. The diameter ranges from 32 to 219 mm. The structure is welded so that there is no mutual heating of the elements. Then the heat transfer increases. If you correctly collect the registers, you can get a good room heating device - reliable and durable.
Types of pipes for heating
Let's take a look at the most popular options.
Steel
This material has been forgotten for a while, but thanks to modern joining systems, without welding, steel pipes are gaining popularity again.
Main characteristics:
- resistance to high temperatures (the pipe is able to withstand heating up to 1500 degrees without deformation);
- high thermal conductivity;
- low coefficient of linear expansion;
- large margin of safety.
Material advantages:
- The only way to ensure the natural circulation of the coolant is due to the ability to select a pipe of any diameter. This is especially true now, when solid fuel boilers are increasingly appearing in people's homes. Often the circulation pump is not used in this configuration;
- High resistance to water hammer allows you to feel calm with centralized communicationswhen it is impossible to control the fluid supply process;
- Affordable cost;
- Good thermal conductivity allows the use of the pipes themselves as a heating device.
Disadvantages:
- Corrosion susceptibility. Therefore, zinc or insulation is often used. Indoors, regular painting is required;
- Complexity of installation. Even without welding, certain skills are required for high-quality wiring;
- Large mass. Long spans need high-quality wall mountings;
- Rough inner surface. This fact leads to a narrowing of the internal space, especially due to the low quality of the coolant, which is ubiquitous in our country;
- Obligatory thermal insulation in an unheated room. High thermal conductivity is not only a plus, but also a minus.


Steel pipes are the only way to ensure natural circulation of the coolant due to the ability to select a pipe of any diameter
Copper
A relatively new material for heating, but perfectly suitable for these purposes. Main characteristics:
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- high pressure resistance;
- heating without consequences up to 300 degrees;
- plastic. This pipe is not afraid of negative temperatures, the frozen water inside will not bring harm.
Benefits:
- Durability. The minimum service life is from 50 years;
- Ease of installation;
- Do not develop on the walls microorganisms;
- Attractive appearance;
- Almost ideal for use in harsh climates. All the dangers of operating the pipe are not terrible due to their properties.
Disadvantages:
- High price;
- Susceptibility to electrochemical corrosion. Therefore, the presence of electrical wiring nearby requires insulation of the pipe with polymers;
- Lack of ability to combine with other metals (except for bronze). In the places of their contact, copper will collapse.


Copper pipes are almost ideal for use in harsh climates
Metal-plastic
Popular material consisting of 5 layers, including polyethylene, glue, aluminum foil. Combines the positive characteristics of plastic and metal.
Characterized by:
- good temperature indicators (acceptable for systems with a coolant up to 110 degrees);
- flexibility - bends easily even by hand;
- durability;
- resistance to temperature and pressure changes;
- lack of corrosion.
Positive sides:
- Ease of installation. To distribute pipes to rooms, it is not at all necessary to invite a specialist; a person with minimal construction skills will cope with the work;
- Acceptable service life (up to 25 years old);
- Small linear expansion (slightly more than copper) in the presence of thermal conductivity;
- Chemical neutrality allows lay a network inside walls, floors;
- Smooth inner surface.
Negative sides:
- Expensive fittings;
- Destruction during defrosting, in connection with which the outer gasket is excluded;
- Small gap inside. You can't get away from this, fittings are made the only way.


It is not at all necessary to invite a specialist to distribute the pipes to the rooms; a person with minimal construction skills will cope with the work.
Polypropylene
A completely new material that has rapidly conquered a large niche in the heating pipe market. For the passage of the coolant, a reinforced version is used, which excludes thermal expansion, and therefore sagging.
Main characteristics:
- mechanical resistance;
- lack of corrosion;
- durability;
- resistance to water hammer, temperature drop;
- low thermal conductivity.
Benefits:
- Ease of installation. This will require a special soldering iron and little skills in working with it. At the same time, it is not necessary to buy a device, many hardware stores lease it for little money;
- Affordable price;
- Huge service life (up to 100 years old);
- Neat appearance;
- Light weight;
- No corrosion allows you to safely use the material when laying inside walls and floors;
- Low thermal conductivity does not require thermal insulation when passing in basements and attics;
- Not afraid of negative temperatures, a defrosted system will not lead to the destruction of the structure.
Disadvantages:
- Media temperature limits. In most cases, this is 80 degrees.So in northern latitudes or in the immediate vicinity of a boiler room with central heating, it can be dangerous to use this type of pipes;
- Can't be repaired. If a certain area is damaged, you need to either cut out a piece and weld a new one with the fittings, or change the span completely from fitting to fitting;
- Even a small deviation from the horizontal during installation requires the use of a special fitting. Operation, even when slightly bent, is prohibited.


For the passage of the coolant, a reinforced version is used, which excludes thermal expansion, and therefore sagging
How to optimize the heat dissipation of a steel pipe?
During the design process, the specialists are faced with the question of how to reduce or increase the heat transfer of 1 m. Of the steel pipe. To increase, it is required to change the infrared radiation upward. This is done by means of paint. Red color enhances heat dissipation. It is better if the paint is matte.

Payment
Another approach is to install ribbing. It is mounted externally. This will increase the heat transfer area.
In what cases is it necessary to decrease the parameter? The need arises when optimizing a section of the pipeline located outside the residential area. Then experts recommend insulating the site - isolating it from the external environment. This is done by means of polystyrene, special casings, which are made from special foamed polyethylene. Mineral wool is also often used.
Copper pipe parameters
A copper pipe is best suited for individual heating, the characteristics of which prevent rupture during a pressure surge inside the system and its freezing. Plastic metal can withstand the expansion of water during freezing, a country house with a copper heating system is not afraid of any frost and utility accidents.


The metal is used for the manufacture of products of the highest quality, sometimes products are covered with a layer of polyvinyl chloride to reduce heat loss. The dimensions of copper pipes depend on whether they are hard or soft. Rigid ones are produced in lengths from 3 to 5 meters, soft ones are rolled into coils with a length of 25 to 50 m. The weight of a copper pipe depends on the diameter and wall thickness, the theoretical weight of 1 mm is calculated according to special tables. These calculations are especially important when laying gas pipelines.
We make a calculation
The formula by which heat transfer is calculated is as follows:
Q = K * F * dT, where
- K is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of steel;
- Q is the heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is made, m2 dT is the value of the temperature head (the sum of the primary and final temperatures, taking into account the room temperature), ° C.
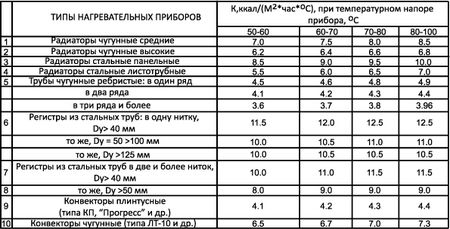
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its value also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the value of the coefficient is in the range of 8-12.5.


dT is also called temperature head. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the exit from the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the entrance to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2). The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
dT = (0.5 * (T1 + T2)) - Tк
If the steel pipe is insulated, the resulting value is multiplied by the efficiency of the insulating material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given off during the passage of the coolant.


Scopes of copper pipes
Copper communications are most popular in Europe, where they have been recognized for over 60 years. For a while, they were replaced by cheap steel, then plastic, but now everything is returning to normal. New technologies make it possible to install from them pipelines for drinking and technical water supply, heating, systems for liquid and gaseous fuels, waste water.


The use of copper pipes for plumbing is classic. The bactericidal properties improve the quality of the supplied water, and the matt sheen of the visible areas gives the interior a sophisticated look. Not only freezing, but also boiling are not terrible for such a water supply, the elasticity of copper dampens all shocks. Brazing is required in this case.
It is ideal to use copper pipes in surface heating systems, the coefficients of thermal expansion of them and of the screed are equal. Liquid fuel in such communications is safe, it cannot ignite due to its complete tightness.
It is also safe to carry out gas distribution with these pipes in an apartment building, it is the tightness that saves lives here. Having spent money once, you can get a reliable and durable pipeline that can serve for more than a century - this is the best quality characteristic.
Polypropylene pipe PN25 in accordance with GOST
Modern polypropylene pipes are highly reliable, durable and have an affordable price. The polypropylene pipe with a nominal pressure PN25 is not subject to corrosion, is resistant to temperature drops, is easy to install and is made of environmentally friendly materials. The main properties in accordance with GOST are shown in the table.
| GOST | Parameter | Indicator |
| DIN52612 | Thermal conductivity, at +20 ° С | 0.24 W / cm |
| 15139 | Density | 0.9 g / cm3 |
| 23630 | Heat capacity at +20 ° С (specific) | 2 kJ / kgf |
| 21553 | Melting | +149 ° C |
| 11262 | Tensile strength (at break) | 34 ÷ 35 N / mm2 |
| 18599 | Elongation of the yield point | 50 % |
| 11262 | Yield strength (tensile) | 24 ÷ 25 N / mm2 |
| 15173 | Expansion ratio | 0.15 mm |
Read the material on the topic: Types of polypropylene pipes
















