HWhen designing a private house, you always have to solve a dilemma, whether you need a boiler room in the house or not. If the house is large and there is a lot of space in it, the issue of organizing additional premises is not worth it. If the house is small in area and you have to save every square meter, then finding a location for the heating equipment is not always easy, especially since you still need to observe fire-prevention measures if you use natural gas for heating. This article is about whether it is possible to do without a boiler room in a private house.
Any technical room in the house is a waste of usable space, which is already small in a small house. It is often possible to do without such a room, while placing all the necessary engineering equipment in the house, but this requires the fulfillment of several conditions.
Requirements for the pipes used
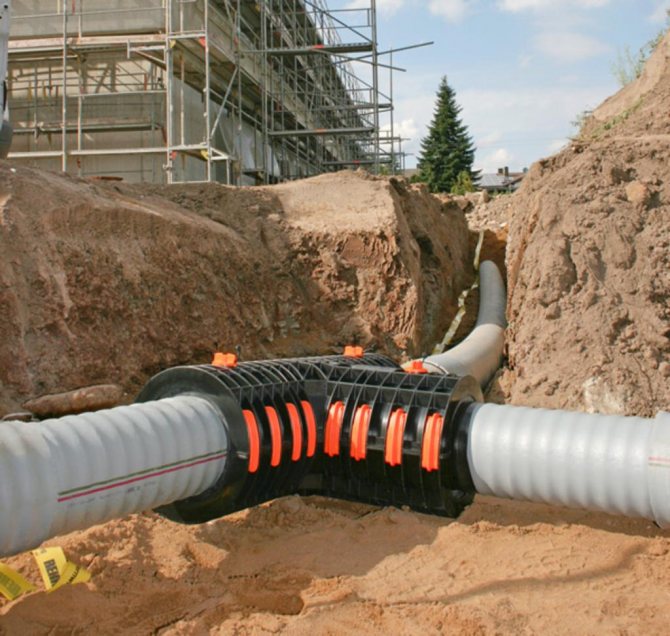


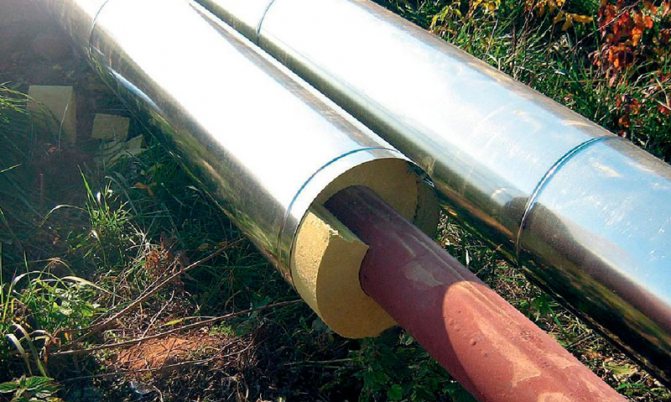
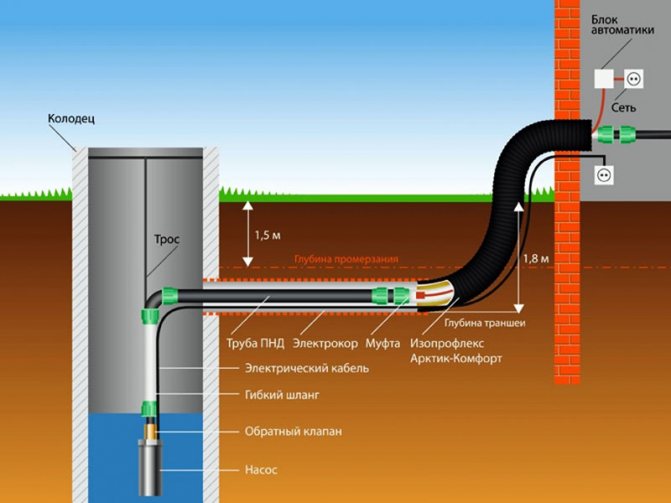
The material of the pipeline must be suitable for the temperature loads and the pressure in the pipeline. At a minimum, it must maintain performance at 95 ° C. With regard to pressure, for autonomous heating, a standard level of 1.5 atmospheres is considered. In the installation of heating mains for heating with such requirements, the following pipes are usually used:
- Galvanized steel. There are practically no temperature restrictions, and the pressure limits are about 12 atmospheres. Mechanical strength and resistance to deforming loads can also be emphasized. However, steel can cause a lot of problems due to threaded connections, not to mention the fact that metal is, in principle, a rather laborious material from the point of view of physical handling during installation.
- Polypropylene pipes. There are temperature restrictions (up to 95 ° C), and the maximum pressure is 9 atmospheres. However, the combination of mechanical strength, joint tightness and modest weight compensates for these disadvantages.
- Reinforced-plastic pipes. The optimal solution that is durable, flexible and practical. Such pipes for heating mains are used both in industry and in private households.
Benefits
- Shorter "path" from the generator to the consumer. Heat is less wasted along the way, because the very distance from the mini-boiler room to the apartment building decreases.
- The distance is less, which means that the consumer receives heat faster.
- Mini-boilers are a relatively new thing: they are not as worn out as centralized heating mains, they require less resources for maintenance and repair.
- The prime cost of such a boiler house is much lower just because of the previous three points.
- We can say that the main and main advantage of a mini-boiler room in an apartment building is its proximity to the heated object.
In addition, heating on / off can be adjusted to the actual air temperature outside the window, and not to the accepted standards. - Another "plus" is the absence of the need to obtain numerous permits for tapping into centralized heating networks. Often, the process is delayed, and residents do not have the opportunity to timely move into the purchased housing.
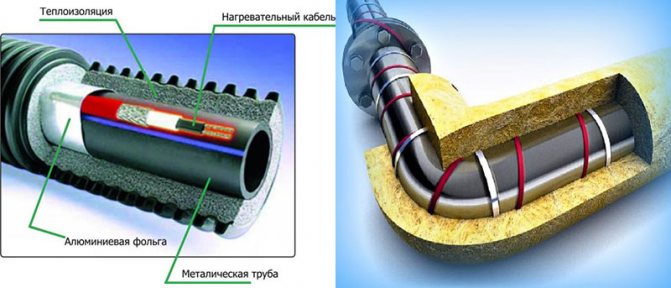
Insulation for heating mains


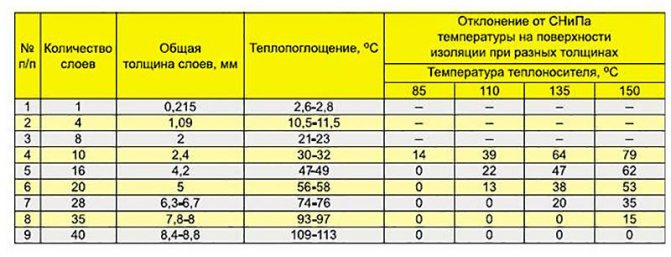
Even correctly selected pipes do not guarantee heat savings during transportation. This property depends on the coverage of the circuit - a heat insulator. Today, the following materials are used for such purposes:
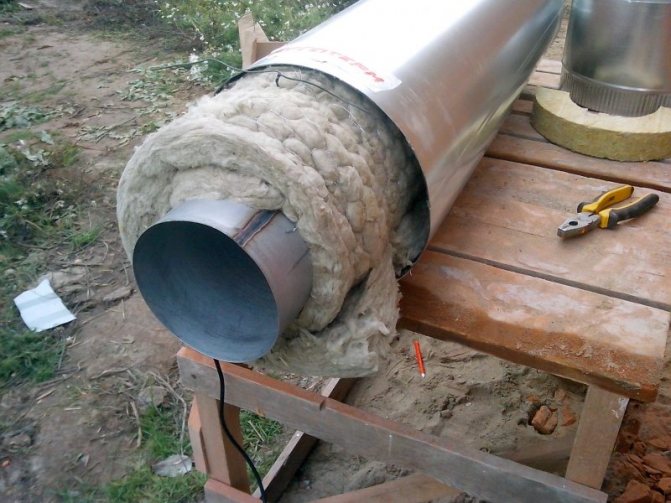
- Glass wool. It goes well with metal-plastic, has a low density and is cheap.But effective heat saving of glass wool can be provided only in combination with roofing felt or fiberglass. Accordingly, both costs and time for installation work increase.
- Basalt insulator. It has a cylindrical shape, is characterized by ease of installation and high thermal insulation performance. The only negative is that it is expensive in itself.
- Polyurethane foam (PPU). A type of plastic that demonstrates resistance to temperature extremes. But the main advantage of this material is different. There are practically no restrictions for the installation of PPU heating mains in terms of the complexity of the pipeline. The isolator can even be used in liquid form, which allows them to spot treatment of hard-to-reach local areas.
- Crosslinked polyethylene. Polymer-based structural insulator, among the main advantages of which are strength, resistance to thermophysical stress, chemical and mechanical stress.


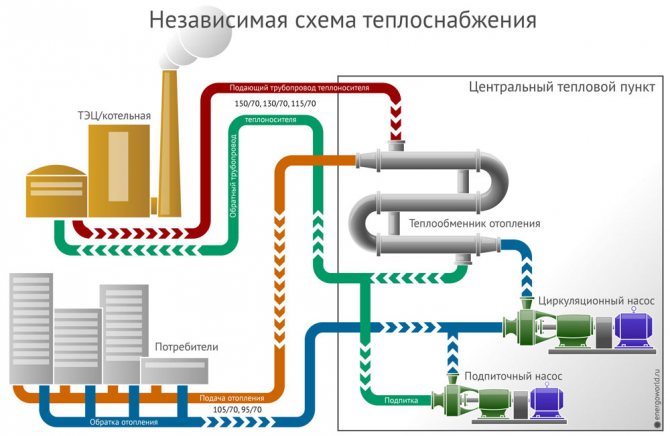
Own boiler room: good or evil
Currently, there are two main reasons for the construction of autonomous gas boiler houses in new residential complexes. Firstly, builders have actively begun to develop territories on the border with the Leningrad Region and regional lands that are not yet provided with an engineering infrastructure. Sometimes laying kilometers of heating networks from the boiler house to the new house significantly increases the developer's costs, and, accordingly, makes the price per square meter of housing more expensive. Today, builders are striving to optimize the cost of construction, taking into account the orientation of the demand of potential buyers for affordable housing. Secondly, it is no secret that connecting a house to engineering is a long and costly process, so builders are trying to reduce the dependence of construction on third-party organizations, which are difficult to influence. In addition, the release of the courtyard space from heating mains contributes to a more rational use of the building area, the arrangement of recreation areas, the construction of additional infrastructure facilities, etc.
Today, the share of projects under construction, where heat supply is provided from individual boiler houses, is small. This share can be estimated at about 10-15%. The most popular is the individual heating system on the suburban construction market - the main gas is supplied to the vast majority of cottage settlements, with the help of which heating and food preparation in the house takes place.
The most obvious advantage of heating from a gas boiler house in comparison with heating from urban networks is cost-effectiveness: due to the fact that the source of heat supply is not far away, heat losses are reduced, the time for supplying heat to residential buildings is reduced, and, accordingly, the costs of maintenance, service and maintenance are reduced. repair of heating systems. According to statistics, autonomous boiler houses reduce resource costs by 45% compared to centralized open systems. In addition, in the presence of an autonomous source of heat supply, residents do not depend on the citywide heating season and can independently quickly determine the temperature regime in their apartments by adjusting the heat supplied to the house. The disadvantages of an autonomous gas boiler house are the high cost of equipment - while this source of heat supply is still a rarity in the housing construction market, so the production of parts and components is not cheap. It is also worth pointing out a certain load of the ecological system, which makes it necessary to additionally provide for an exhaust gas removal system. Some inconvenience may be the need for additional space, which is allocated for the placement of an autonomous boiler room, but the second and third problems are removed by modern capabilities - for example, by installing a roof or block boiler room.
According to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, residents bear the burden of expenses for the maintenance of common property, including internal engineering systems.If an autonomous boiler room is the common property of residents, then they must repair and maintain boiler equipment independently at their own expense, while taking advantage of all the benefits of owning this property. In practice, this is achieved by including in the cost of monthly payments a certain percentage for unforeseen repairs or installation of a new boiler house. But note that the planned replacement of equipment is required in 25 years.
Heating main installation technology
The organization of the main heat supply system is carried out in several stages:
- Design. Based on the results of a comprehensive survey of the direction of the line laying, taking into account the requirements for the transportation of the coolant, a list of materials, their performance characteristics, and the installation configuration are determined.
- Preparation for laying. Technical conditions are being created for the future installation of pipes. The area of the gasket is cleared and, if necessary, trays (channels) are installed for the rear protection of the circuit.
- Installation of pipes. The direct installation of the heating main is carried out, in which the substrate and the insulation material are attached to the prepared trays. For this, clamps, anodized protection means and fixing hardware can be used.
- Testing and commissioning are in progress.
When a boiler room is needed
A boiler room is necessary when a powerful floor-standing boiler is used for heating. In this case, it will be necessary to build a capital chimney to remove combustion products and provide an air flow for the operation of the boiler. For equipment operating on natural gas in a boiler room, it is advisable to have a gas analyzer in case of a gas leak. A floor-standing boiler is used for houses with an area of 200 square meters or more. meters. In addition, a separate technical room may be needed to accommodate a floor-standing boiler for 150 liters or more. Such a need arises in large country houses with three or more bathrooms.
The question of whether it is possible to do without a boiler room in a private house is decided individually for each house, at the design stage. The decision depends on the required power of the heating boiler, the expected consumption of hot water, as well as on the availability and composition of the supply and exhaust ventilation and water treatment systems. In the next article I will tell you whether it is necessary to insulate a wooden house.
RECOMMEND TO READ MORE:
Heating line laying configurations
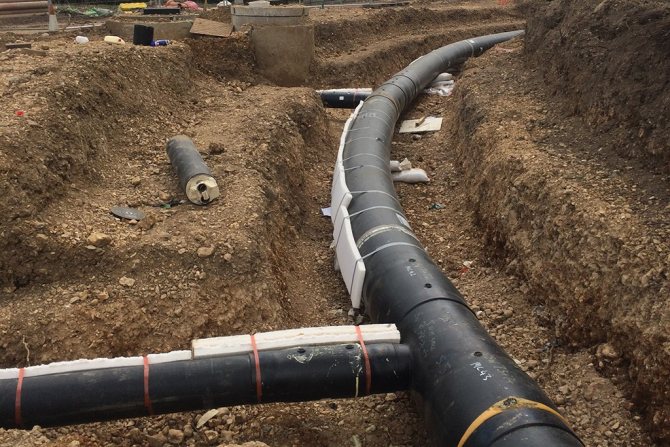


Several pipelines can be laid in one line. In this regard, a distinction is made between one- and two-pipe, as well as a beam method of laying. In the first case, only one circuit is used, in the second, respectively, two channels. With radial installation of a heating main, several circuits are connected to a collector, from which flows are directed to separate points of consumption. This system is beneficial in that it allows you to regulate the work of streams, alternately loading and distributing them depending on the current needs.
Criteria for choosing heaters for heating pipes
Looking at a hardware store, and even more so in a hypermarket, you can get confused by the abundance of thermal insulation materials. Moreover, this diversity is manifested both in the assortment of goods and in its value. When choosing, first of all, you need to focus on the technical characteristics of the material. A good insulation must meet the following requirements:
- low thermal conductivity;
- low water absorption;
- resistance to high temperatures;
- durability;
- ease of installation.
The times when multilayer insulation of pipes was widely used have long sunk into oblivion, leaving behind pictures with disheveled heating mains that are well known to all of us. Today, the priority is simple-to-install, practical and neat thermal insulation solutions.
The following materials are mainly used:
- mineral wool;
- stone wool;
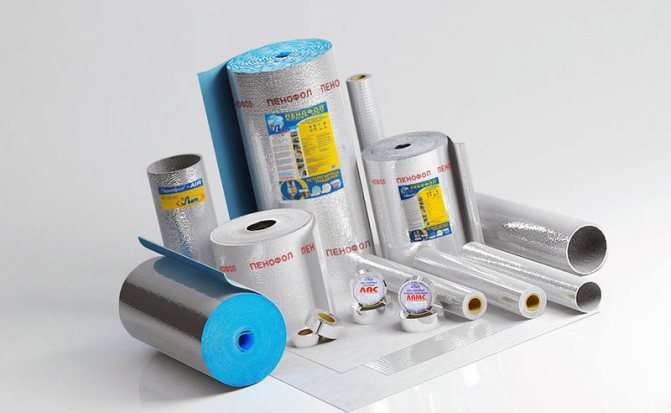
- polystyrene (penoizol, expanded polystyrene);
- polyethylene (penofol, polyethylene foam);
- artificial rubber;
- thermal insulation paint;
According to the method of installation, the following types of heaters for pipes are distinguished:
- Roll
- Shroud
- Sectional
- Sprayed
The choice of a specific type of thermal insulation depends on the financial capabilities of the developer, the method of laying pipes and their availability, the temperature of the coolant, and the availability of tools for installation.
Features of channelless laying
The main difference between this method of organizing heating networks is the rejection of load-bearing gaskets. That is, the installation of trays for a heating main of this type is not necessary - the installation is carried out directly on the ground. The lack of additional protection and support of the pipeline is compensated by the use of special fittings in polyurethane foam insulation with a polyethylene sheath. Also, for such networks, an on-line remote monitoring system is provided, which continuously monitors the state of insulation.
Trenchless pipeline laying methods
There are technologies for laying a pipeline in the ground without trenching.
Such methods are aimed at:
- reduce the volume of earthworks - gain in time and costs;
- to minimize damage to infrastructure - less costs for the restoration of decorative and road surfaces, unforeseen damage to highways;
- lay pipes in a straight line, without bending around obstacles of low difficulty;
- to minimize damage from earthworks to the environment.
Today, the industry uses the following trenchless methods:
- reorganization;
- piercing.
Sanitation - this is the replacement of old pipes with new ones, which, in turn, is done in two ways: by relining and by renovation.
Relining It is based on broaching a new polymer pipe of a smaller diameter inside the working pipeline while preserving the old one as a protective shell.
Renovation - installation of a new pipe to replace the worn-out with the destruction of the old one, the fragments of which will also protect the new line from external damage.
Piercing (punching) - this is a connection of two pits dug to the required depth with a puncture made at a certain wall height.
Of the listed methods, we will execute only the relining method in everyday life. A cable is inserted into one end of the old pipe and pushed until it exits the other end. Then a new whip is attached to the cable and pulled back. The applicability of this method depends on a number of factors:
- the state of the lumen of the old pipeline;
- diameter of the new pipe;
- the flexibility of the new lash;
- the length of the section being repaired;
- the ratio of the diameters of the old and new pipeline.
With a favorable combination of the above factors, the technical execution of the installation of a new pipe is not difficult. However, all this is applicable to broaching a new line without thermal insulation, and the condition of the insulation of the old pipe is unlikely to be satisfactory. Since it is not possible to insulate the heating pipes inside the old line, the method loses its attractiveness when applied to heating.
Therefore, when installing heating pipelines with burial in the ground in private housing conditions, it is impossible to do without digging a trench or, at least, alternatively laying the pipe on the ground with backfill.
znatoktepla.ru
Heating mains repair


Maintenance with diagnostics and repair procedures can be carried out both in a planned manner according to the schedule, and on a signal from the monitoring equipment. Repair and restoration operations are performed in the following order:
- Localization of damage using special equipment.
- Dismantling of tray ceilings.
- Dismantling the faulty section.
- Replacing, fixing or supplementing the problem area with a necessary element. Often, an electric welding installation of a heating main is performed at a point with damage to a pipe in a gas environment.
- Cleaning the circuit from dirt and foreign objects.
- Pressing works aimed at checking the tightness after repair.
- Assembling the structure.
Backfilling the trench
Backfilling of the trench begins after checking the heating system in operation - if the pressure test of the circuit reveals defects in its tightness, it will be necessary to eliminate them.
Backfilling of the trench is a crucial stage of work, on the correctness of which the uniformity of the distribution of loads and the durability of the pipeline section in the ground depend.
Backfilling of the trench begins with the laying of soft plastic soil on the sides of the pipe (in the sinuses). This is done evenly along the entire length of the pipeline, preventing it from shifting to the sides. The soil laid on the sides is carefully compacted, after which the pipeline is backfilled with a protective layer of at least 15 cm from the same material along the entire width and length of the trench in accordance with SNiP requirements. Compaction of this layer is performed to a lesser extent - this is a necessary condition for the formation of a strong protective vault from the soil above the pipe, which rests more on the sinuses on the sides of the pipe.
After the end of the compaction of the protective layer, the trench is completely covered with soil removed during digging, removing large stones from it. Backfilling must be carried out evenly along the entire length of the trench, avoiding the formation of pipe sections with a large difference in the vertical load from the soil.
The uniformly growing load from the backfill will be accepted to a greater extent by the protective soil vault above the pipe, and the residual value of the compressive force for the pipe is not terrible - it is designed for it.
If the trench is filled with separate sections, then the difference in the vertical load on the backfilled and open segments of the pipeline will lead to the emergence of tensile forces, which the pipe resists worse.
Why heating mains for a private house Flexalen?
Pre-insulated pipelines flexalen are a relatively new product in the field of thermal insulation. They are ready-made heating main, and combine high technical characteristics of polymer piping systems and high quality thermal insulation.
Due to the reliable and quick installation, durability of Flexalen pipes, pre-insulated pipelines are especially interesting when laying intra-quarter and external networks of any water supply on the territories of private houses and cottage settlements - hot and cold. Heating mains can be laid between buildings, in order to restore and equip city heating networks, as well as transport industrial and food liquids, not only water. But also other liquid substances.
Flexalen are flexible, pre-insulated, which makes it possible to lay them in a track, the length of which is up to 300 meters and of any configuration. To make installation, you do not need to use a special channel device, compensators and connections.