General concept of a conditioning device

This is an electrical device, the list of the main tasks of which includes maintaining comfortable climatic conditions in rooms for various purposes. In addition, there are small-sized air conditioners for vehicles and production equipment. The bulk of these devices is a class of household and industrial models. In the second case, the intended use has a slightly different nature than in the household segment. But in both categories, the basic concept of an air conditioner can be represented as follows: an electrical appliance whose work is aimed at regulating the temperature regime in a certain range. According to the standards, climatic equipment must provide the ability to regulate temperature in the range of 17-25 ° C. At the same time, modern devices are capable of maintaining modes in the range from -5 to 40 ° C. In addition, multifunctional devices also regulate humidity (coefficient - 50-60%), air mass mobility (up to 0.15 m / s) and even the content of some gases (for example, oxygen).
Features, advantages and disadvantages
Considering the purchase and installation of a split system or a conventional air conditioner, it is necessary to study their main differences.
Both devices are a kind of climatic technology. Their main differences are:
- Design. Split devices are manufactured in different variations. You can choose any model that fits perfectly into the interior. Whereas air conditioners are usually produced only in the form of a monotonous white block.
- Manufacturability. Modern split systems are equipped with many basic and additional functions, including the ability to remotely control. Experts regard the manufacturability of a conventional air conditioner as low.
- Noisiness. Conventional air conditioners generate a high level of noise during their operation. The split system creates a minimum noise level.
In comparison with conventional climatic technology, the split system has a list of undeniable advantages:
- the ability to maintain the temperature in the specified range;
- organization and maintenance of a comfortable microclimate;
- reduced noise level;
- reduction of the level of consumed electricity up to 30%;
- the ability to operate at temperatures below zero;
- ease of management;
- ease of maintenance.
Among the disadvantages, it is worth mentioning the high cost in comparison with a conventional air conditioner. The price can be 1.5-2 times higher. In addition, split devices are characterized by sensitivity to power surges. If you connect equipment without a voltage stabilizer, then the likelihood of breakdown increases significantly.
Purpose of the air conditioner
Most often, the equipment is designed for the task of lowering the temperature with the function of humidifying the air. In the summer, the cooling mode is especially in demand, but recently there have been models that provide heating due to a heat pump. Although there is no question of a full-fledged heating function even at the level of a household heater. In the definition of industrial air conditioners, it is fundamentally important to note their multifunctionality - these are devices that, in addition to temperature control tasks, also purify the air. This function is required in enterprises whose activities are related to the processing of materials and various kinds of raw materials, during which fine dust particles are emitted.To maintain sanitary standards at production sites and the comfort of workers, for example, in wood processing factories, an industrial air conditioner is used. In addition to extended functionality, it is also distinguished by its high power, which allows it to constantly serve premises with an area of up to 250-300 m2.
How to choose a split system?
There are a number of significant factors to consider when choosing the right model. First you need to decide on the type of indoor unit, depending on the stylistic design of the room and free space. Be sure to take into account the square of the room.
A split-air conditioning system for an apartment should, on average, have a capacity that is an order of magnitude smaller than its area. If the windows of the room face the sunny side, the resulting value must be multiplied by 1.1-1.3. If the HVAC equipment consists of several indoor units, make sure that the outdoor unit will be able to support it.
The manufacturing company deserves special attention. Preference should be given to a proven trademark, under which high quality products are traditionally made.
Attention! It is imperative to make sure that the permissible length of the route indicated in the passport and the height difference will allow the installation of the structure correctly.
It is worth checking the maximum and minimum noise levels declared by the manufacturers during operation, as well as the temperature range at which the equipment will function properly.
If the cost of a split system is of fundamental importance, then you can reduce costs by choosing a device with an optimal set of functions. The less additional functionality, the cheaper the climate technology will cost.
Compressor models device


It is this type of air conditioners that can work both for cooling and for heating the air, which largely determines its widespread use. The basic set of components in the internal structure of a compressor-type air conditioner can be represented as follows:
- Condenser is a compact radiator module in a block designed for outdoor installation (from the street side). This unit ensures the process of condensation, that is, the transition of gas into a liquid state. Usually radiators are made of aluminum or copper.
- The compressor performs the function of compressing the refrigerant (a working medium like freon) and maintains its circulation in the refrigeration circuit.
- The evaporative radiator is located in the indoor unit (indoors). Provides a process opposite to condensation, that is, with a sharp drop in pressure, the refrigerant already passes from a liquid state to a gaseous state.
- Regulatory fittings - a throttle that lowers the pressure in the area in front of the evaporator.
- The fans circulate the air flow, thereby blowing the condenser with the evaporator block.
Why does an air conditioner need freon
Everyone has heard that factory freon is dangerous for the environment, it makes it necessary to dispose of air conditioners (refrigerators) in a special way. We can add, the first refrigerators, air conditioners are life-threatening. Leakage of tetravalent sulfur oxide threatened the inhabitants of the house. Although freons were dangerous, air conditioners owe their widespread use in everyday life to the discovery of the 1920s: a new class of substances. The new ones are not so deadly, giving 100 points of head start to the previously used refrigerators. The class of substances is called freons.


Today, compounds whose names begin with the letter R and end with a three-digit number contain the proud term ozone-friendly in the technical description. They do not harm the fickle layer of the atmosphere, which, ignoring the ridiculous thickness of 2-3 millimeters, absorbs the lion's share of ultraviolet radiation, making the existence of life on the planet possible. Depletion of the ozone layer causes skin cancer and other pathologies.Public international organizations, advocating for the preservation of the environment, pounced on the manufacturers of air conditioners and refrigerators.
Not for nothing. Rare freon is safe, new environment does little harm. In addition, some refrigerants are non-flammable. Air conditioners are considered safe enough. Why is important. The first window air conditioners were produced in a single building. Monoblocks exist today, are becoming a thing of the past, giving way to split systems. One feature of newcomers with an unaccustomed name has ensured popularity. Air conditioners are formed by two blocks:
- Outer.
- Interior.
Actually, new air conditioners got the name by differentiation of units. A freon line is laid between the blocks. Traditionally insulated, protected hose. Regardless of the degree of sealing of the air conditioner components, freon slowly leaks into the environment. A break in the line is possible, the process will be faster. The air conditioner will fail, the city will receive another dose of harmful freon.


Split comes from the English split. In cooling mode, the outdoor unit contains the condenser and the indoor unit contains the evaporator. Are there other modes? Sure! A typical air conditioner (split system) operates on heating. It is achieved by the presence of a four-valve switch, thanks to the condenser unit, the evaporator are swapped. Freon starts flowing in the opposite direction.
Probably wondering why bother with freon, if the material is so dangerous. Why not build air conditioners. Freon has one irreplaceable property - it easily changes the state of aggregation. It turns from liquid to gas, taking up a huge amount of heat. The reverse process is accompanied by the absorption of a fair amount. And it happens at good temperatures: 2 degrees on the evaporator, 65 degrees on the condenser. The combination is phenomenal, otherwise freons would not have been used for the production of air conditioners.
Evaporative models device
A simpler design device that performs the tasks of cooling and ventilation. Its advantages include the absence of technological processes associated with the processing of harmful substances like freon in the course of work. This type of air conditioner device is formed by the following elements:
- Electric motor - controls the operation of the fan, which, in turn, provides the supply of air masses.
- Pipeline infrastructure. Formed by a pump with valves to control the processes of supply and discharge of the aqueous medium.
- Evaporative Filters - Purify water by preventing harmful particles from entering the air. They are usually made of cellulose and have a honeycomb structure.
- The water pan is made of high-strength plastic or metal, resistant to temperature extremes and water environment.
Modern models of evaporative air conditioners with the possibility of indirect evaporation have the advantage of eliminating the penetration of moisture into the room.
What is air conditioner
The modern concept of "air conditioner" (from the English air - air and condition - state) as a designation of a device for maintaining a given temperature in a room, has existed for a long time. Interestingly, the word air conditioning was first spoken aloud back in 1815. It was then that the Frenchman Jeanne Chabannes received a British patent for a method of "air conditioning and temperature control in homes and other buildings."However, the practical implementation of the idea had to wait a long time. Only in 1902 did the American engineer-inventor Willis Carrier assemble an industrial refrigeration machine for the Brooklyn printing house in New York. The most curious thing is that the first air conditioner was not intended to create pleasant coolness for workers, but to combat humidity, which greatly deteriorated print quality. The "fossil" ancestor of all modern split systems and windows can be considered the first room air conditioner, released by General Electric back in 1929. Since ammonia was used as a refrigerant in this device, the vapors of which are unsafe for human health, the compressor and condenser of the air conditioner were taken outside. That is, in essence, this device was a real split system. However, since 1931, when freon, safe for the human body, was synthesized, the designers considered it good to collect all the components and assemblies of the air conditioner in one case. This is how the first window air conditioners appeared, the distant descendants of which work successfully today. For a long time, the leadership in the field of the latest developments in ventilation and air conditioning belonged to American companies, however, in the late 50s and early 60s, the initiative firmly passed to the Japanese. In the future, it was they who determined the face of the modern climate industry. So in 1958, the Japanese company Daikin proposed the first heat pump, thereby teaching air conditioners to supply not only cold, but also heat to the room. And three years later, an event occurred that largely predetermined the further development of domestic and semi-industrial air conditioning systems. This is the beginning of the mass production of split systems. Since 1961, when the Japanese company Toshiba first launched mass production of an air conditioner divided into two units, the popularity of this type of HVAC equipment has grown steadily. Due to the fact that the noisiest part of the air conditioner - the compressor - is now taken out into the street, in rooms equipped with split systems, it is much quieter than in rooms with windows. The noise level is reduced by an order of magnitude. The second huge plus is the ability to place the internal block of the split system in any convenient place. Today, many different types of internal devices are produced: wall-mounted, sub-ceiling, floor-mounted and recessed into the false ceiling - cassette and duct. This is important not only in terms of design - different types of indoor units of air conditioners allow you to create optimal distribution of cooled air in rooms of a certain shape and purpose. And in 1968, an air conditioner appeared on the market, in which several internal ones worked with one external unit. This is how multisplit systems appeared. Today they can include from two to nine indoor units of various types. A significant innovation was the appearance of an inverter-type air conditioner. In 1981, Toshiba offered the first split-system capable of smoothly regulating its power, and already in 1998, inverters occupied 95% of the Japanese market. And finally, the last of the most popular types of air conditioners in the world - VRV - systems were offered in 1982 by Daikin.
Central air conditioners are industrial units that are used to treat air in large commercial and administrative buildings, swimming pools, industrial plants and others. The central air conditioner is non-autonomous, that is, for operation, it needs an external source of cold: water from a chiller, freon from an external condensing unit or hot water from a central heating system, a boiler. The main target functions of these systems are: comfort ventilation with heat recovery, heating and cooling; ventilation and dehumidification in the premises of swimming pools; industrial ventilation with and without heat recovery. The air processed by the central air conditioners is distributed through the air duct network throughout the room.
Precision air conditioners - This air conditioner is mainly used in rooms that require maintaining the specified parameters with high reliability and accuracy, such as medical institutions, industrial premises, laboratories, control posts, communication centers, halls of electronic computers, control rooms and other rooms. It is a monoblock that contains an air handling unit, a filter, a refrigerating machine with a freon air cooler, a water air heater and an electric air heater. The air conditioner is used both in systems with recirculated air and in systems with 100% supply air.
Autonomous air conditioning systems are supplied from the outside with only electrical energy, for example, cabinet air conditioners and the like. Such air conditioners have built-in compression refrigeration machines operating on freon-R22, R134A, R407C. Autonomous systems cool and dry the air, for which the fan blows the recirculated air through surface air coolers, which are the evaporators of refrigeration machines, and in the transitional or winter time they can heat the air using electric heaters or by reversing the operation of the refrigeration machine, according to the so-called “ heat pump ".
Most domestic air conditioners cannot operate at negative outside temperatures, especially in heating mode, therefore, in mid-latitudes, they can be used instead of conventional heating systems only during the transition period. Air conditioners adapted to work at low temperatures are called all-season (or - air conditioners with an all-season unit).
For cooling small volumes (for example, internal cavities of any equipment, PC processors), air conditioners based on Peltier elements are sometimes used. These air conditioners are quiet, lightweight, have no moving parts, are reliable and compact. But they have very limited refrigeration capacity, are expensive and less economical.
An air conditioner operating outdoors is called a supply air conditioner; indoor air - recirculation; on a mixture of outdoor and indoor air - air conditioning with recirculation.
Varieties of performance
1.Mobile - air conditioners that do not require installation; for use, it is enough to remove a flexible hose or a special block from the room to remove warm air. Condensation usually accumulates in a sump at the bottom of the mobile air conditioner
2. Window - consisting of one block; mounted in a window, wall, etc. Disadvantages - a high level of noise, a decrease in the illumination of the room due to a reduction in the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe window opening. Advantages - low cost, ease of installation and subsequent maintenance, no detachable connections in the freon line and, as a result, no freon leakage, maximum possible efficiency, long service life.
3. Split systems (English split - splitting) - consist of two blocks, indoor and outdoor, connected by a freon line route (usually copper pipes are used). The outdoor unit contains (like a refrigerator) a compressor, a condenser, a choke and a fan; indoor unit - evaporator and fan. They differ in the type of execution of the indoor unit: wall, duct, cassette, floor-sub-ceiling (universal type), column and others.
4. Multi-split systems - consist of an outdoor unit and several, more often two, indoor units, interconnected by a freon line route. Like conventional splits, they differ in the type of execution of indoor units.
5. Systems with variable refrigerant flow (VRF, VRV, etc.) consist of one outdoor unit (if the total capacity needs to be increased, combinations of outdoor units can be used) and a number of indoor units. The peculiarity of the systems is that the outdoor unit changes its cooling capacity (power) depending on the needs of the indoor units for a given power.
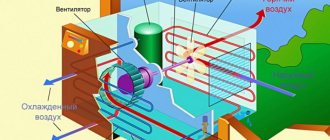
Air conditioner device
Compressor - compresses the working medium - refrigerant (usually freon) and maintains its movement along the refrigeration circuit.
Condenser - a radiator located in the outdoor unit. The name reflects the process that occurs during the operation of the air conditioner - the transition of freon from the gaseous phase to the liquid (condensation). For high efficiency and long-term operation, it is predominantly made of copper and aluminum.
Evaporator - a radiator located in the indoor unit. In the evaporator, freon passes from the liquid phase to the gaseous phase (evaporation). Also mainly made of copper and aluminum.
(Thermostatic expansion valve) - a pipeline choke that lowers the freon pressure in front of the evaporator.
Fans - create a stream of air that blows around the evaporator and condenser. They are used for more intense heat exchange with the ambient air.
[edit] Principle of operation The compressor, condenser, choke (capillary tube, thermostatic device) and the evaporator are connected by thin-walled copper (recently sometimes aluminum) tubes and form a refrigeration circuit inside which the refrigerant circulates. (Traditionally, air conditioners use a mixture of freon with a small amount of compressor oil, however, in accordance with international agreements, the production and use of old varieties that deplete the ozone layer are gradually being phased out.)
During the operation of the air conditioner, the following occurs. A gaseous refrigerant is supplied to the compressor inlet from the evaporator at a low pressure of 3 - 5 atmospheres and a temperature of 10 - 20 ° C. The air conditioner compressor compresses the refrigerant to a pressure of 15 - 25 atmospheres, as a result of which the refrigerant heats up to 70 - 90 ° C, after which it enters the condenser.
Due to the intensive blowing of the condenser, the refrigerant cools down and passes from the gaseous phase to the liquid phase with the release of additional heat. Accordingly, the air passing through the condenser heats up.
At the outlet of the condenser, the refrigerant is in a liquid state, under high pressure and with a temperature 10 - 20 ° C higher than the ambient (outdoor) air temperature. From the condenser, the warm refrigerant enters the thermostatic expansion valve, which in the simplest case is a capillary (a long thin copper tube twisted into a spiral). At the outlet of the thermo-regulating valve, the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant are significantly reduced, while part of the refrigerant can evaporate.
Downstream of the expansion valve, a low pressure liquid / gaseous refrigerant mixture enters the evaporator. In the evaporator, the liquid refrigerant passes into the gaseous phase with the absorption of heat, respectively, the air passing through the evaporator cools down. Then gaseous refrigerant with low pressure enters the compressor inlet and the whole cycle is repeated. This process underlies the operation of any air conditioner and does not depend on its type, model or manufacturer.
The operation of an air conditioner (refrigerator) without heat removal from the condenser (or hot junction of the Peltier element) is fundamentally impossible. This is a fundamental limitation arising from the second law of thermodynamics. In ordinary household installations, this heat is waste heat and is removed to the environment, and its amount significantly exceeds the amount absorbed when the room (chamber) is cooled.In more complex devices, this heat is utilized for domestic purposes: hot water supply, and more.
Malfunctions
One of the most serious malfunctions is associated with the air conditioner device and arises if the freon in the evaporator does not have time to completely go into a gaseous state. In this case, liquid enters the compressor inlet, as a result of which the compressor fails due to water hammer. There may be several reasons why freon does not have time to evaporate, but the most common are caused by improper operation of a poorly designed air conditioner. Firstly, dirty filters can become the cause of the malfunction (this worsens the airflow of the evaporator and heat exchange), and secondly, the inclusion of the air conditioner at negative outside temperatures. At negative temperatures (below -10 ° C) there is a real threat of liquid freon getting into the compressor cavity, which leads to its breakdown. [1] In more expensive, properly designed systems, there are additional sensors, containers that exclude the ingress of liquid freon to the compressor inlet. In such systems, the most likely failure is the failure of one of the sensors, which, however, leaves the refrigeration system viable. In household window air conditioners BK-1500, BK-2500 produced in the USSR (Baku plant), to eliminate this phenomenon, a boiling point was used (it is used in many models of the middle and upper price range of air conditioners).
Leaking refrigerant can also cause the air conditioner to malfunction / ineffectively. The main cause of the leak is the incorrect installation of the freon line, for example, poor-quality tube expansion. Over time, the most noticeable external manifestation of a leak, in addition to a decrease in performance, is the freezing of the liquid valve (high pressure side) on the external block of the split system, which is caused by a decrease in the refrigerant pressure, which is 4.5 - 5.5 bar in the norm for air conditioners with R22 refrigerant, due to whereby the liquid refrigerant begins to evaporate in the discharge tube itself, not reaching the evaporator (indoor unit radiator). However, freezing can also occur for other reasons.
The presence of air and moisture in the circuit over time can lead to failure of the compressor, clogging of the capillary with ice plugs. The reason for air entering the circuit is also the poor-quality installation of the split system. With proper installation, after the circuit is assembled, it is evacuated for a certain time (depending on the volume of the circuit, and for domestic systems it usually takes from 20 minutes to an hour) with a special vacuum pump in order to remove air and evaporate moisture present in the circuit.
The principle of operation of a compressor air conditioner


The operation of the device is based on the circulation of refrigerant (freon) along the circuit of pipelines with technological points of its processing. Refrigerant is supplied to the inlet of the compressor unit under low pressure, followed by the process of its compression and heating. Further, freon is sent to the condenser, where, due to intensive blowing, its temperature decreases, and the medium itself turns into a liquid state, while releasing heat. As a result, the air heats up. At the next stage, the principle of operation and the device of the compressor-type air conditioner will have several similarities with the models of the evaporative type, which is expressed by the function of the thermostatic expansion valve. The fact is that after leaving the compressor, freon enters this valve and some of it evaporates under conditions of decreasing temperature and pressure. In the evaporator, the refrigerant takes on a gaseous form, absorbs warm air and cools. This cycle is repeated several times until the set microclimatic indicators are reached.
What is an outdoor air conditioner unit for?


An external air conditioner unit is one of the constituent parts of a modern split system. It houses the condensing unit of the air conditioning system. This element of climatic equipment is designed to cool or heat a room using a refrigerant.
Inside the block there are:
- compressor;
- four-way valve;
- heat exchanger;
- capillary tubes;
- expansion coils;
- receiver;
- fan.
To maintain the unit's performance in winter, a special "winter kit" is sometimes installed.
Outdoor unit device
This is a rectangular box, inside which the following elements are installed:
- A fan is needed to blow off the condenser. Thanks to this, the air masses are actively moving in the outdoor unit.
- A condenser is a special device designed to cool freon for the purpose of its subsequent condensation.
- The compressor compresses the refrigerant to circulate it through the freon line to the indoor unit.
- The four-way valve is installed in air conditioners, which can work not only to heat the room, but also to cool it. It is needed to change the direction of movement of the refrigerant in different operating modes of the climatic equipment.
- The control board is located in the external modules of inverter-type units. Such devices have a stepless speed control of the fan blades and are more resistant to temperature extremes and atmospheric influences.
- Fitting fittings are needed to connect copper pipelines that connect two blocks and are designed to circulate the coolant.
- The protective grill protects the outdoor unit from the ingress of various insects, all kinds of polluting particles and objects that can block the fan blades.
- A drainage tube is installed to drain off condensed moisture.
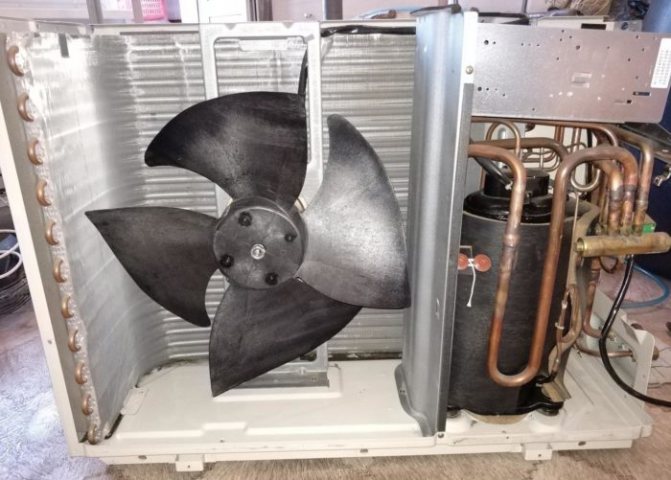


The unit contains a voltage stabilizer that protects against peak loads and normalizes the current parameters. Some models are equipped with special covers that protect the unit from the negative effects of snow, wind and freezing. To protect against falling ice, icicles and parts of the facade finish, a visor is installed above the outdoor module.
Air conditioner modes and why it does not turn on from the control panel
Parameters and principle of operation of the outdoor unit
The principle of operation of any climatic equipment is based on the transfer of thermal energy from one environment to another. If the unit works for cooling, then it transfers heat from the room to the outside. When heating the air in a house or apartment, the device performs the opposite action, that is, it takes heat from the external environment and transfers it to the room air.
When freon evaporates in the indoor unit, it absorbs the heat from the air in the room. And after getting into the outdoor unit, it condenses there. In the opposite direction, liquid freon goes from the external unit to the internal module, which is cooled again due to the fact that it has given thermal energy to the external environment. The room air passes through the air conditioner again and cools, giving off heat.
The principle of operation of the outdoor module is as follows:
- gaseous freon enters the compressor from a special container;
- here, under high pressure, it enters the condenser, where it turns into a liquid state and gives off heat;
- after the loss of part of the thermal energy, the refrigerant goes to the freon line;
- from it, freon passes into a throttling device (here the pressure drops and the substance cools down);
- the cooled liquid medium enters the evaporator tubes, where it begins to actively circulate;
- streams of warm air from the room also pass through the evaporator, they give off heat to freon and cool;
- the air conditioner supplies the cooled air masses to the room;
- during the receipt of heat from the room air, the refrigerant in the heat exchanger of the indoor unit goes into a gaseous state;
- From the heat exchanger, the refrigerant in the gaseous state goes back to the compressor, the process is repeated again.

Important parameters of outdoor units that must be taken into account when choosing climate control equipment are the power of the unit, the noise level emitted by the equipment during operation, the length of the line and the dimensions. The dimensions of the outdoor unit are directly related to its capacity. Average parameters are within 80x80x30 cm.
The capacity of a standard domestic air conditioner is sufficient to cool an area of 100 m². The permissible noise level should not exceed 32 dB, so as not to cause discomfort for apartment residents and neighbors.
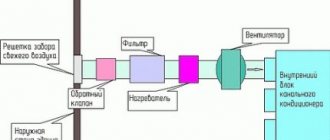
The principle of operation of the evaporative air conditioner
The cooling process as a result of the evaporation of the aqueous medium can be implemented in different ways, which is why direct and indirect regulation of the microclimate is distinguished. In the first case, cooling is based on an isenthalpic process and is recommended for cold weather applications. In summer, air conditioners with direct evaporation can be effective only with an insignificant humidity coefficient. The principle of an air conditioner with indirect cooling involves the use of a surface heat exchanger with an air cooler. Cooled air circulates through the channels connecting them, the temperature regulation of which will depend on external irrigation with water flowing into the sump. Indirect evaporation reduces the performance of the air conditioner, but expands the functionality of regulation due to the reduced moisture content of the supply air.
Split system operating modes
Most often, the split system allows the owner to use four modes:
- Heating
- Ventilation
- Cooling
- Dehumidification
The ventilation mode assumes that the air from the room is driven through the filters of the indoor unit, after which it becomes cleaner.
In such heat, which we face every summer, it is simply necessary to maintain the microclimate in the house at the proper level. So hurry up to buy a split system before the summer season comes into its own!
Varieties of air conditioners in terms of installation


- Mobile air conditioners. The smallest models that can be carried from place to place by plugging into a power outlet in any accessible place.
- Wall appliances. This is the classic and most common form factor, which is divided into two units - indoor and outdoor.
- Channel models. They are integrated into the main air duct system - as a rule, they are placed in an overhead recess with an outlet of the working part to the room.
- Cassette models. Also a kind of ceiling air conditioner, but which is not built into the ventilation channel, but communicates with it through the pipes.
- Floor and ceiling devices. Placed on the principle of conventional heaters - convectors or radiators. They have low performance, but due to their compact size and stylish design they are in high demand.
- Column models. The form factor, as the name implies, is presented in the form of a column. That is, the installation is carried out on the floor, however, unlike mobile air conditioners, such devices are mainly stationary and provide for communication with an external unit that works for cooling.
How the air conditioning system works
The principle of operation of the air conditioner is based on the ability of substances to change their state of aggregation depending on pressure. All liquids during evaporation (transition from liquid to gaseous state) absorb heat from the surrounding space. During condensation (transition from a gaseous state to a liquid), heat, on the contrary, is released. The functioning of the air conditioning system is impossible without gaseous hydrocarbons that contain fluorine, they are called freons.... In general, substances that efficiently remove heat during boiling and give off during condensation are called refrigerants. Thanks to them, not only air conditioners work, but also any other refrigeration equipment.


On a note! Freons R-22 and R-410A are most often used in air conditioners. However, the first type is gradually falling out of use, as it has been established that it depletes the ozone layer. The second freon does not contain chlorine, it is not dangerous for the earth's atmosphere, so manufacturers prefer it.
The boiling point of freon R-22 is -40.9 degrees Celsius, for R-410A it is -51.5. It is not easy to achieve such values in practice; additional cooling will be required. But this indicator is directly affected by pressure: the higher it is, the higher the temperature at which the liquid begins to boil. Therefore, for the transition of freons from one state to another, their pressure is changed to the required level with the help of special devices.
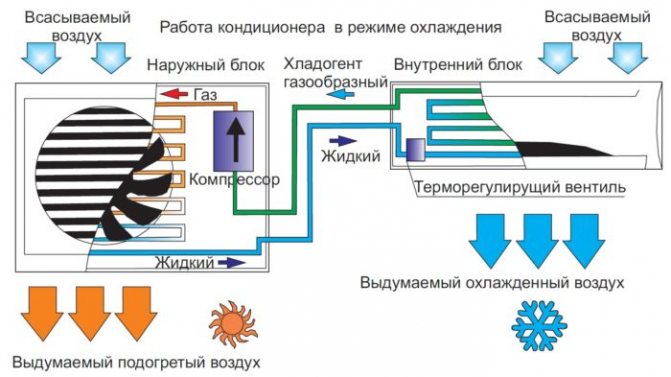
Description of the air conditioner operation for cooling
The main components of the apparatus are a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator and a thermostatic expansion valve (TRV) or an electronic expansion valve. These components are connected in a closed circuit through which the refrigerant circulates.
Freon gas enters the compressor from the evaporator. Freon is under low pressure, only a few atmospheres, its inlet temperature is + 10-20 degrees. The compressor device can be different, depending on the type of unit (screw, piston, rotary or scroll), but its purpose is always the same: to draw in gas, compress it and pump it into the next element of the circuit - the condenser. Freon pressure in this case reaches one and a half to two dozen atmospheres and more (for a car air conditioner - about 12 atm.), And the temperature rises to several tens of degrees above zero (+ 70-900).
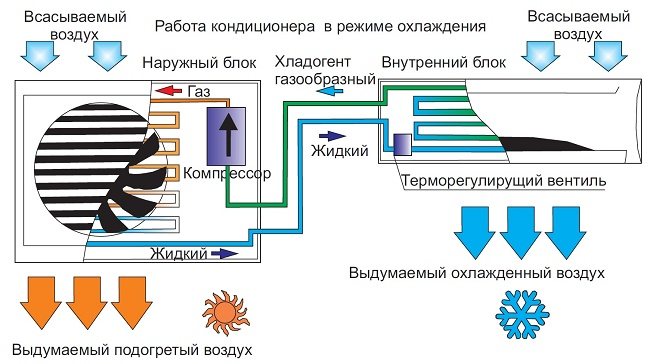

On a note! A condenser is a radiator or heat exchanger made of finned tubes that are blown by a fan.
In the condenser, the heated gas passes through the tubes and cools, since its temperature is much higher than that of the air, which washes the numerous elements of the heat exchanger. As a result, freon condenses and releases heat. So liquid freon comes out of the radiator, the pressure of which remains high, and the temperature drops and becomes only a dozen or two degrees higher than that of the outside air.
Then the substance passes through the expansion valve / expansion valve, which is also called a throttling device. It regulates the amount of freon that is needed to maintain a certain level of evaporation to cool the room to a specific temperature. In this unit, the pressure and temperature of freon decrease, as a result of which it turns into a mixture of liquid and gas.
Then the refrigerant enters the evaporator, the heat exchanger of which can consist of tubes under the casing or plates with channels where freon moves. Here the liquid turns into a gaseous state and absorbs heat from the surrounding space. There is also a fan opposite this heat exchanger, so the air flow that passes through the evaporator is cooled. The gas is then sent back to the compressor.
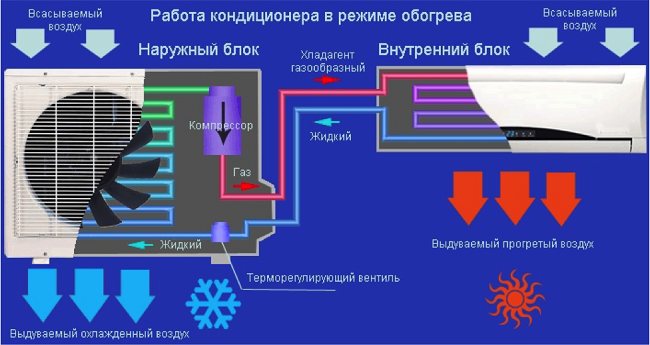
Description of the operation of the air conditioner for heating
Air conditioners that operate according to the cycle described above cool the air. But there are also models that support heating - they have a four-way valve that redirects the movement of freon in the system... At the same time, the evaporator and condenser are interchanged, so that warm air enters the room, and cold air, on the contrary, is discharged outside.
On a note! Climatic units that work for heating are more expensive than cooling ones.

Where does the air conditioner take air from?
To answer the question of where the air conditioner comes from, you need to consider the following types of devices:
- supply air - take air from the street;
- recirculating - use internal air;
- recuperative air conditioners - use a mixture of indoor and outdoor air.
Before buying climatic equipment, you should clarify exactly how the selected model takes in air. In the first and third cases, the room does not need to be regularly ventilated; in the second, on the contrary, it will be necessary to periodically open windows or doors in order to maintain the amount of oxygen in the room at a comfortable level.
Features of split systems
This group includes all models of air conditioners that are divided into two units, one of which is taken out into the street, and the other is mounted indoors. A typical split air conditioner device provides for the presence of a compressor, condenser, filters, fans and a connecting line. Actually, the main working processes take place in the external unit, and the internal module only provides communication with it, being also responsible for regulating the microclimate parameters. This separation reduces the harmful effects of the refrigerant and completely eliminates room noise from the working compressor.


As a result of the technological improvement of the two-block design, the concept of a multi-split system has appeared and is being successfully applied. The air conditioning device of this type differs in that several compressors with condensers and multi-way valves can be involved in one working infrastructure. Multi-component systems allow control from one indoor unit, while controlling the operation of several outdoor modules.
How are the air conditioner units
In its simplest form, all parts of the device are in one housing. The part of the apparatus, in which the compressor and condenser are located, is exposed to the outside, and the evaporator is placed inside the room. This is typical for window air conditioners. But the most popular are split systems, which consist of two blocks (indoor and outdoor) with different functions. In order to better understand how such a climatic device works, you need to consider its design in blocks.
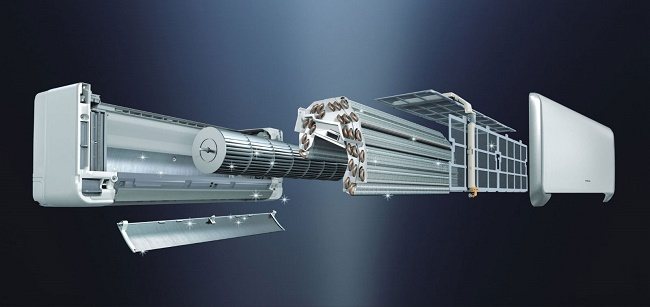

Indoor unit device
This part is installed directly in the room where you need to create a suitable atmosphere: in an apartment, office, sales area. The device of the indoor unit consists of components such as:
- fan - directs air inward;
- evaporator;
- coarse and fine filter system - trap dirt, dust, sand from the street;
- electronic control board;
- choke connections - connect the indoor and outdoor units;
- horizontal and vertical blinds - direct the air flow vertically and horizontally;
- indicator panel - displays the status and operating mode of the device using LEDs and / or LCD display;
- the front panel is a plastic grill through which air enters the unit.
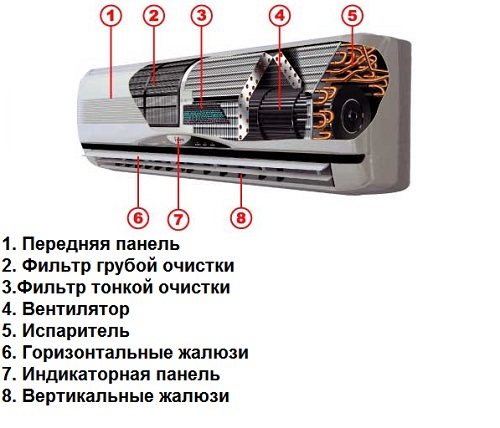

On a note! Manufacturers produce indoor units of various shapes and colors.
Outdoor unit device
The structure of the block, which is mounted outside, includes:
- compressor;
- capacitor;
- fan - blows on the previous component;
- freon filter - prevents foreign particles from entering the compressor;
- choke connections;
- cover for protecting pipe connections and electrical connectors.
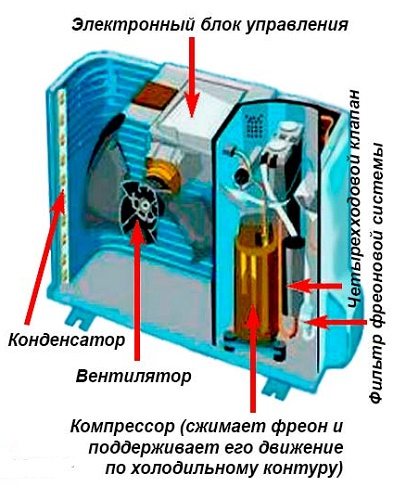

The structure of climatic devices of different types may differ.
On a note! The device of the outdoor unit of the air conditioner, also designed for heating, implies the placement of a four-way valve in this part. And in inverter models, the control board is located in the external unit, and not in the internal one.
Possibilities of modern air conditioners
Regardless of the form factor and principle of operation, most of the new generation models provide enhanced control over the processes of microclimate regulation. What is a modern air conditioner in terms of user control? It is an ergonomic device that, through remote control, provides information on temperature, humidity and even the composition of the air environment. The remote control usually has a digital display with control elements (sometimes touch-sensitive). Also, some devices integrate a Wi-Fi module to implement remote control at a remote distance via mobile devices.
Air conditioner operation
After installation, in addition to using the device for its intended purpose, the owner is required to perform a number of preventive maintenance operations. For example, the device of an air conditioning system with a compressor block provides for the presence of a special infrastructure for convenient measurement of performance indicators, by which it is possible to monitor the state of the refrigerant that periodically requires replacement. As for the evaporative systems, they need constant renewal of the aquatic environment with topping up. Also, to maintain the operating condition, it is recommended to regularly purge the communication channels, clean the blocks and the drainage system.


Pros of the air conditioner
Each type of this device has its own advantages and weaknesses, but, in principle, they are the optimal solution for fulfilling the tasks of regulating microclimatic parameters. For example, compressor models benefit from power and versatility of application, while evaporative models are distinguished by energy efficiency and ventilation capabilities. For industrial applications, a split air conditioner with a multi-component connection of operating modules is optimally suited. In this case, with a small amount of installation activities, it is possible to provide many rooms with effective high-power microclimate controllers.
Cons of the air conditioner
The main complaints about this equipment, in addition to the need for maintenance and their structural complexity, relate to harm to health. Moreover, this also applies to devices that do not provide for the use of refrigerants. After all, what is an air conditioner as a regulator of microclimatic parameters? This is a tool that theoretically allows you to change the temperature, humidity and air flow rates in an accelerated mode. If, however, the wrong approach to the process of changing these indicators, sharply adjusting their values, then the risk of diseases and, above all, colds increases.
The main functions of the air conditioner


An air conditioner is a device that is designed to maintain the required temperature in a room. It is mainly used for cooling, but in addition to its main function, it can perform a number of other tasks, let's look at them.
Heating
Heating mode is activated when the room temperature drops below the set temperature. Heating with an air conditioner is very effective, since the heat is not trapped at the ceiling, but is evenly distributed throughout the room. It is very convenient to use this mode in the off-season - in autumn or spring, when the central heating is not working and the temperature outside has dropped.
Ventilation
The air conditioner in this mode distributes the air evenly throughout the room. It is convenient to use, for example, in winter, when warm air from the central heating batteries accumulates at the top, and remains cold at the feet.
Dehumidification
To reduce air humidity in split systems, a special dehumidification function is provided without lowering or raising the temperature. Working in this mode prevents dampness of the walls and the appearance of mold in rooms with high humidity.The dehumidification mode is also convenient for eliminating discomfort during wet weather.
Filtration
All split systems are equipped with a coarse filter that traps dust, protecting the heat exchanger. Also, many modern air conditioners have additional filters: electrostatically charged, carbon fiber, disinfectant, etc. They clean the air from the smallest particles, tobacco smoke, pollen, mold spores, dust mite excrement, bacteria and some viruses.
Air conditioner operation functions
Setting the temperature
For cooling and heating modes, you can set the temperature with an accuracy of 1 ° С and can vary from +16 to + 30 ° С.
Auto mode
Sometimes it is not required to set the exact conditions in the room, and the very procedure for turning on the air conditioner may seem rather complicated. In this case, Full auto mode can be used. In which the air conditioner, after switching on, measures the temperature of the air in the room, determines in which mode it is necessary to work (cooling or heating), and then maintains the temperature set for this mode.
Night mode
This operating mode is set for a certain time, as a rule, for several hours, after which the air conditioner is turned off. The indoor fan turns on to silent mode. If the air conditioner was operating in cooling mode, then after 30 minutes. the set temperature is automatically increased by 1 ° C, and after another hour by 2 ° C. This change in temperature allows you to create a comfortable environment during sleep.
Hot start
This function is only available for heating mode. It allows the indoor fan to operate only when the temperature of the indoor heat exchanger is already high enough. This eliminates the possibility of cold air flow into the room.
Timer
The timer can be used to program the air conditioner to turn on and off automatically. For example, it can be programmed to turn on half an hour before your usual arrival from work, etc.
Self-diagnosis
During the operation of the air conditioner, the microprocessor controls the mode of its operation, as well as the state of the outdoor and indoor units. Each mode and possible malfunction has its own combination of LED operation on the front panel of the indoor unit, which can be used to determine the condition of the air conditioner.
Additional features
Additional air purification
Modern models of air conditioners have a coarse filter and several fine filters. For added protection against microorganisms, many manufacturers go beyond antibacterial and antifungal coatings for air conditioners. Progress does not stand still in terms of improving air filtration, in addition to the main fine filters, manufacturers equip additional air conditioners. Here we can distinguish anti-allergic, kakhetian and deodorizing filters, titanium-apatite photocatalytic filter, revolutionary Plasmacluster ion cleaning technology, etc.
Air mix
Among household air conditioners, only window and duct air conditioners can mix air from the street, conventional split systems are not capable of this. They process the indoor air in the room. However, to reduce the content of carbon dioxide in the air and create a comfortable indoor climate, some manufacturers offer split systems that mix a certain percentage of air from the street. Air is mixed using an external unit connected to the indoor unit by a flexible duct.
Inverter
The inverter air conditioner differs in that the compressor power smoothly changes depending on the room temperature. Those. after reaching the set temperature, the compressor does not turn off, as in a conventional split, but switches to work at a lower power.Such a system allows you to more accurately maintain the set temperature in the room and avoid sudden temperature changes. Due to the absence of frequent starts and the even operation of the compressor, the inverter air conditioner lasts longer, while consuming less energy. Another plus is that the difference between the set and the current temperature is always minimal and the fan runs at low speed, providing a low noise level. However, when buying an inverter air conditioner, you need to take into account that it is extremely sensitive to voltage surges.
Reduced noise level
To reduce the noise level, some manufacturers increase the diameter of the fans of the indoor units, lower the aerodynamic resistance of the heat exchanger, and install mufflers for the refrigerant. At the same time, the internal blocks of some wall-mounted split systems have become a little larger, but the noise level has decreased to 22-26 dB (A). For comparison, a whisper has a noise level of 25-30dB (A). And as mentioned above, inverter air conditioners have a lower noise level.
Ionizer
Air ionization is the saturation of air with negatively charged air ions. With a lack of aeroins in the air, health and ability to work deteriorate, lethargy and drowsiness appear. Special devices called ionizers are called upon to solve this problem. Nevertheless, if you do not want to clutter up your apartment or office with additional devices, an air conditioner can come to the rescue. Several manufacturers add ionization function to conventional split systems, most notably Panasonic and Mitsubishi.
Low temperature operation
Some air conditioners are additionally equipped with an all-season unit or a winter kit, which allows them to operate at very low temperatures (down to -20 ° C). However, it should be noted that when working in very low temperatures, the performance of adapted air conditioners significantly decreases. An air conditioner with an all-season unit is usually used where it is necessary to cool the air at any time of the year, for example, in the northern latitudes. It is not recommended to use it for heating, since it will not be able to sufficiently heat the air in case of extreme cold outside, and besides, the cost of such an air conditioner is several times higher than the cost of any heater.
Presence sensor
This is another convenient feature found in some Daikin air conditioners. In order to create the most comfortable conditions in the room, the motion sensor detects the location of the person and directs the air flow away from him. If the sensor does not detect movement for some time (usually 20 minutes), which indicates that there are no people in the room, the air conditioner automatically switches to economical operation. When a person appears, he enters the normal mode and maintains the set temperature more accurately. This feature provides comfort and saves up to 30% energy.