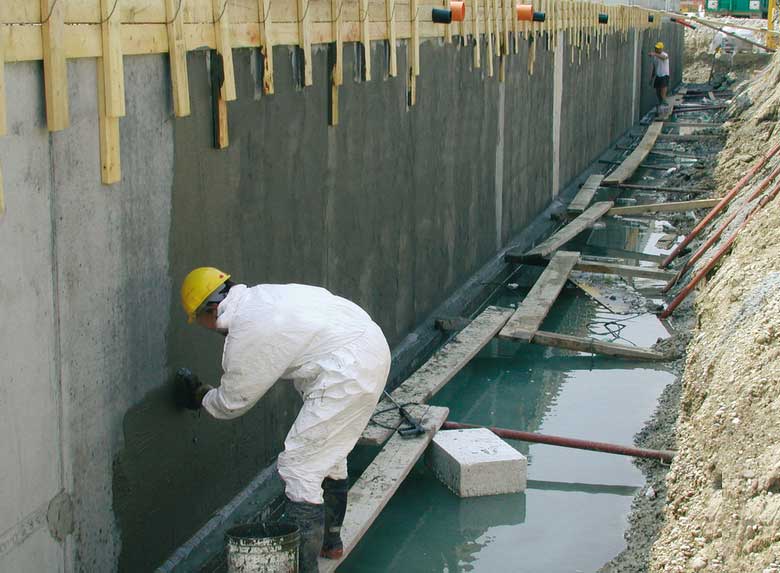
Building structures with high humidity experience numerous negative influences, due to which their external condition deteriorates, the structure is damaged and the strength of materials is lost. One of the most destructive factors is the penetration of moisture into walls, foundations and other structures of a building.
Penetrating into the interior, moisture leads to a deterioration of the microclimate. There is dampness in the air, mold and mildew appear in the cold corners of the room, furniture and finishing materials lose their former attractiveness, and homeowners themselves begin to experience health problems.
High humidity can spoil the life of the owners of a cottage or a country house for years. Even with forced ventilation, dampness does not disappear unless the cause of its formation is eliminated. It is necessary to find out in what ways moisture can penetrate into the house.
NO-TILL as a way to manage moisture accumulation in soils
Gary Peterson, Colorado State University
Professor Gary Peterson is not only a person of deep knowledge, but also an open conversationalist, capable of captivating practitioners with original ideas and the simplicity of clear thought. At a conference in Dnepropetrovsk, where Peterson read this report, he instantly grew friends and new acquaintances, he was invited to visit, to farms, and he responded sincerely, because a week of staying on this land was enough for him to fall in love with Ukraine.
Precipitation and atmospheric evaporation demand
In arid conditions, natural precipitation is the only available source of moisture. Semi-arid regions such as Eastern Europe and Western Asia receive variable and limited rainfall. Therefore, the successful cultivation of crops in non-irrigated soils depends on adequate water storage in the soil to maintain the crop until the next rainfall. Crops in rainfed areas rely solely on water in the soil accumulated between rainfall, and because of unreliable rainfall, water accumulation in the soil is extremely important for cropping crops in rainfed lands.
There are three principles of moisture accumulation:
1) water accumulation - the preservation of precipitation in the soil;
2) water retention - the retention of water in the soil for later use by crops;
3) efficient use of water - efficient use of water to obtain an optimal harvest. It is only recently that we have technology that has significantly changed the approach to rainfall management in rainfed areas. When mechanical tillage was the only way to control weeds and prepare the seedbed, managing sediment build-up and retention in the soil was very laborious. The cultivated fields were not covered at all and were significantly affected by wind and water erosion. Intensive tillage has many negative effects on the soil itself, including a decrease in organic matter and damage to the soil structure. Using reduced tillage and no-till allows us to efficiently collect and store water. In most cases, when reduced tillage and no-till systems are well established, they lead to more sustainable crop production in rainfed areas. This article will look at the principles of catching sediment and storing it in the soil.
Device selection criteria
To choose a high-quality desiccant designed for an apartment or house, you should pay attention to the main technical characteristics and operating parameters.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Material that does not burn or melt
The principle of operation of the apparatus is as follows:
- The condensing air dryer is an electrical appliance with an evaporator, a compressor and a hot heat exchanger. To remove excess moisture, a cold heat exchanger is used, which directs the condensate to the evaporator and removes it through the sump to the outside. Residual masses are blown in by a fan, sent to a hot heat exchanger, heated to room temperature and sent to the room;
- the moisture absorber eliminates the presence of electrical components. Mini dehumidifiers can be selected for each room, because a special tablet is placed in the container. The condensates are absorbed by the silica gel and become brine flowing into the sump. It is drained. Low-power devices remove moisture from 20 m3 of air in 2-3 months, then the silica gel tablet is changed;
- assimilation. These industrial dehumidifiers are used both in production and in a large house. The operating mode of the device is continuous, so the condensate is discharged, and dry air flows enter the room. The disadvantages of the models are minimal energy efficiency, simultaneous removal of moisture and heat, the impossibility of using in humid climates.
A household dehumidifier can process 10 to 100 liters of liquid in 24 hours. To find a moisture absorber, you need to multiply the area of the room by 0.7.
Installation method
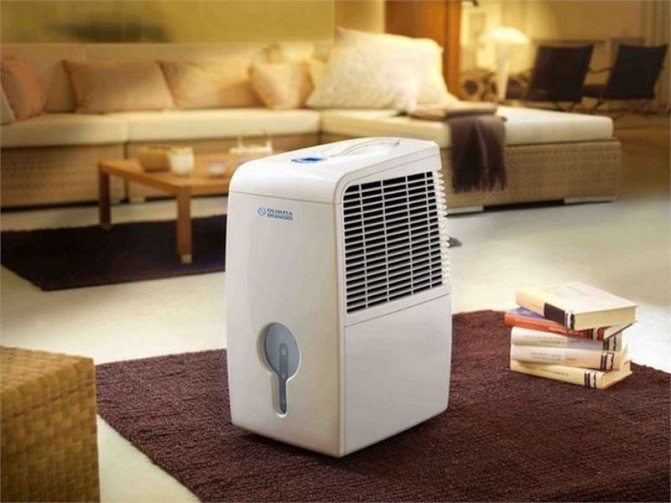

Manufacturers produce a dehumidifier for an apartment with mounting:
- desktop - mini-devices allow you to install an electrical unit at home with mains power;
- wall-mounted - fixed with complete anchors on a vertical surface;
- floor-standing - large units for processing large volumes of ambient air.
The optimal air flow is provided by the apparatus that passes the masses 3-4 times in 1 hour. The intensity of the device also depends on the size of the room. To dehumidify a room of 50 cubic meters, it is advisable to use a household electric dehumidifier for an apartment, with a capacity of 150-200 m3 per hour.
Noisiness
A household moisture absorber should not interfere with the comfort of the occupants. The normal noise level of the device is 30 to 35 dB.
If you need a condensation dehumidifier, it will be right to think about the type of tank. Some devices have a principle of operation similar to an air conditioner - moisture from the pallet is removed into the sewer. "Advanced" models have an auto-restart function when filling the tank.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with What walnuts affect
A home dehumidifier is equipped with:
- humidity control sensors for automatic start and shutdown if the set parameters are reached;
- touch screen for easy and comfortable control;
- aromatization and ionization to create a comfortable microclimate;
- timer - turns on at a specified time.
Water accumulation
Conservation of water begins with the accumulation of accidental precipitation (rain or snow). Water accumulation must be maximized within the economic constraints of a given situation. The principles governing soil properties that affect the ability to store moisture are as follows: soil structure, aggregate formation and pore size. We will also look at the interaction of water storage and retention versus evaporation. For example, shortening the time for water to stagnate on the soil surface and move moisture deeper into the soil reduces the potential for evaporation. This is especially important in regions where there is a great potential for evaporation following rainfall in summer.
Visualization of precipitation trapping
We must try to ensure that the water contained in the raindrop immediately falls into the gaps between the soil aggregates and is held there for further use by the crop. First, let's imagine capturing rainfall in terms of a raindrop that hits the surface of the soil and penetrates deep into the ground (Figure 1). Note that the longer the gaps between soil aggregates are open, the less water is obstructed and absorbed faster, thus the accumulation of precipitation will be excellent.
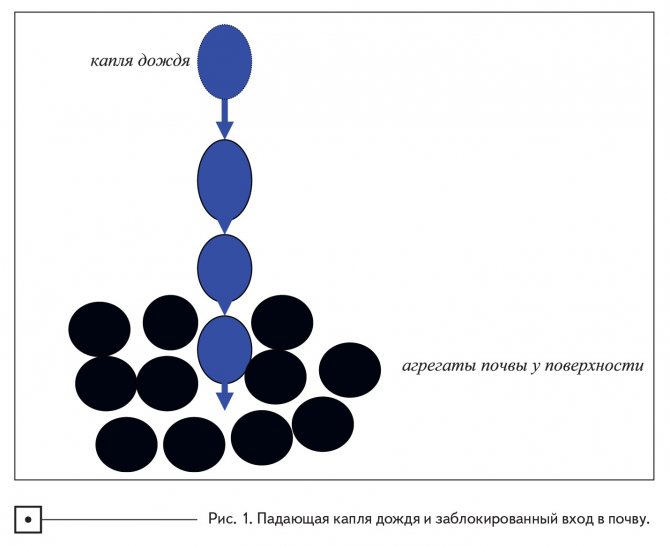

The entry of water into the soil, at first glance, looks like a very simple process, when the incoming water simply displaces the air present in the soil. However, in reality, this is a complex process, since The rate of water infiltration into soil is influenced by many factors, such as soil porosity, soil water content and soil profile permeability. Water retention is a complex phenomenon as the maximum infiltration rate is reached at the onset of precipitation and then rapidly declines as water begins to fill the pore space on the surface.
Soil texture strongly influences the infiltration rate, but soil texture cannot be changed with management. A large number of macropores on the surface (large pores), like those found in coarse soils (sandy loams, etc.), increase the rate of moisture infiltration. Soils with a fine structure (silty loams and heavy clay loams) usually have fewer macropores (small pores), and, therefore, the infiltration rate on such soils is lower compared to soils with a coarse structure.
Soil aggregation also controls the size of soil macropores. Thus, soils with the same structure, but with different degrees of aggregation, can differ significantly in terms of the size of macropores. Fortunately and unfortunately, the degree of soil aggregation can be changed through management methods such as no-till, crop residues, which help to restore aggregation. It is extremely important to remember that finely textured soils, such as silty loams or heavy clay loams, remain well structured so that there are open paths for water to move downward. Remember, any technology that reduces the structural size will reduce the pore size at the surface and therefore limit the penetration of water into the soil. The best thing about this is a structure that can resist change. Weakly structured soils quickly lose their ability to absorb water if the structural aggregates break down and the pores on the soil surface become smaller. This can happen either due to too intensive soil cultivation, or due to natural phenomena, such as rain.
The soil surface itself should be of interest for management, since the conditions at the soil surface determine the ability to trap moisture. When working in drought conditions, our goal is to use techniques that result in increased infiltration rates in a realistic and cost-effective manner within a defined cropping system.
How to choose a material?
In search of an answer to the question of what is the best way to insulate the floor, do not forget about the norms of building heating technology, which are different for each region of Russia. Thermal insulation will be more effective if you choose the best option for your particular flooring.
Payment
First of all, it is necessary to calculate the thickness of the material. For this, resistances are taken into account:
- air acceptance by the floor - R1;
- passing through the floor of heat - R2;
- heat transfer - R3.


All layers are taken into account, including the air gap. The density of the material is divided by the coefficient of its thermal conductivity. The result of the calculation is the value of the coefficient of heat transmission through the floor.
A product with a thickness equal to the sum of all resistances should be equal to the heat resistance rate for a specific region, determined according to SNiP II - 3 - 1979 "Construction thermal equipment".
The microclimate in your home, warmth and comfort in winter cold weather and autumn bad weather will depend on the accuracy of the calculation.
Concrete floor
For a concrete floor, wood chip insulation, which is mounted on a polyethylene film for waterproofing, is perfect. Mineral wool is also convenient for installation. Thermal insulating paint and foam work effectively.
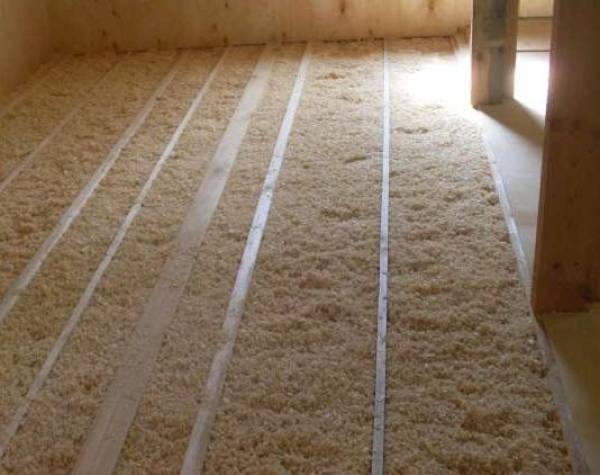


Inspect the concrete base before starting work. If you find cracks, then be sure to remove them with polyurethane foam.
Wooden floor
For the wooden floor of a private house, mineral wool is perfect, which is convenient to lay under the boards. If you plan to replace the floor after insulation, then use polystyrene or polystyrene foam. It is not always possible to put a dense insulation, in this case, use a cork or chipboard.
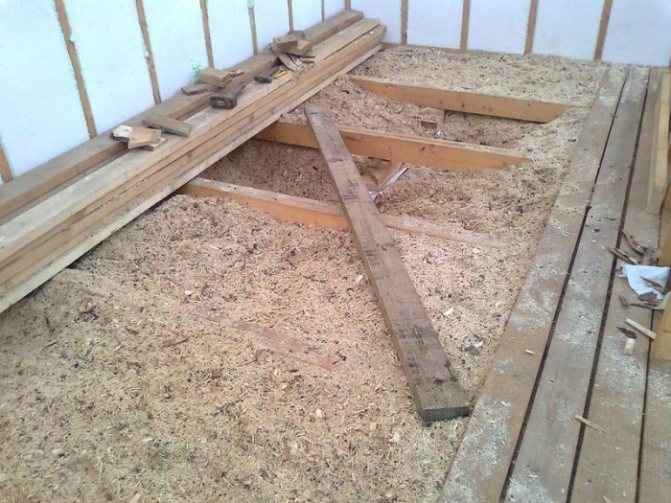


Floors play a huge role in keeping the room warm. Heat loss through cold floors reaches 20% of the total volume. By insulating floors in an apartment or a private house, you not only create an optimal microclimate for your family, but also save energy and money resources.
Visualizing the effect of a raindrop
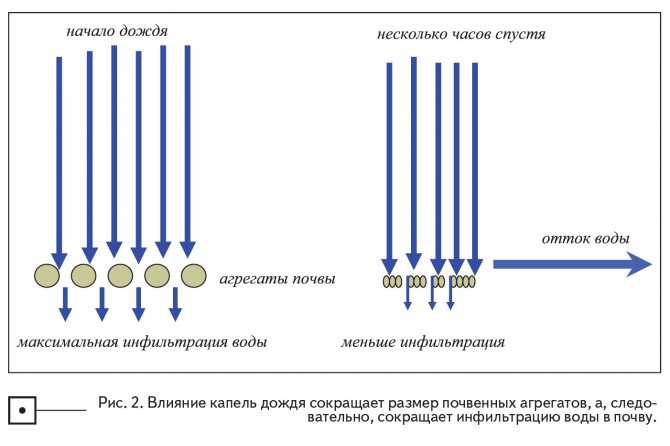
What really happens when a drop hits the soil surface? The size of the droplets depends on the strength of the thunderstorm, which, in turn, is predetermined by the climate of a particular geographic region. The diameter of the droplets varies from 0.25 to 6 mm (the average is about 3 mm), and now compare the diameter of the droplet with the diameter of the soil aggregates into which this drop falls, and the soil, in turn, is not covered with anything; the size of soil aggregates is usually less than 1 mm. When a droplet with a diameter of 3 mm, flying at a speed of 750 cm / s, hits an aggregate with a diameter of less than 1 mm, the damage is often very significant. If we put this in relative mass, then this phenomenon is similar to the fact that a car weighing 80 kg crashes into a person weighing 1600 kg, moving at a speed of 27 km / h. Wind-blown rain, which accelerates the droplet speed, leads to greater impact, because a drop accelerated by the wind carries a charge of energy 2.75 times more than rain in calm conditions. It is quite obvious that soil aggregates will be destroyed, especially if they are constantly hit by raindrops during thunderstorms of any duration. The energy of raindrops has a negative effect on the structure of the soil surface, literally "exploding" soil aggregates. When the aggregates explode, the remaining small particles clog the macropore space of the soil and the infiltration rate decreases (Fig. 2). Obviously, during a short or mild thunderstorm, the effect of rain drops will be less. No-till provides a solution to this dilemma, because With this technology, plant residues remain on the surface, protecting the soil surface from the effects of rain drops.

Rating of the best household moisture absorbers
If you are unsure of how to quickly and correctly select a high performance dehumidifier, check out our list of the best models.
In active operation, a household dehumidifier is capable of removing moisture from 135 m3 of air per hour, which is 20 liters per day. An electric outdoor moisture absorber for a home for 10 thousand rubles. equipped with ionization and cleaning functions, as well as a timer. Condensate is discharged through the drainage pipe. The device is electronically controlled, the parameters are displayed on the LCD display. The power is 480 W, the noise level is 44 dB.
Benefits:
- inexpensive cost;
- the choice of the duration of work at the discretion of the user;
- plastic elastic wear-resistant body.
Disadvantages:
- there are vibrations in the body;
- a little noisy.
Compact air humidity regulator for 12.8 thousand rubles. suitable for an apartment or house. The device can be installed in rooms with an area of 20 m3, used for drying laundry and preventing mold. The power of the floor device is 600 W, the noise level is 48 dB. The reservoir is 3 liters. The maximum air exchange rate is 20 cubic meters per hour or 20 l / day. Equipped with LCD display, humidity sensor, fragrance. There are wheels for moving.
Benefits:
- compact dimensions;
- high-quality assembly;
- suitable for basement floors;
- works quietly;
- convenient control.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Is the bear dangerous for humans
Disadvantages:
- no timer;
- low power;
- heavy - weighs 13.5 kg.
Ballu BDH-25L
The air consumption of the device per day is 25 liters, i.e. 210 cubic meters are processed in 1 hour. The compact model is suitable for rooms of 50 m2, changes the humidity parameters by 20%. A dehumidifier for an apartment is equipped with a 6.5 liter condensate tank. with fill indicator. Noise is equal to 45 dB. The cost of the model on the online home appliance market is 15.3 - 18.6 thousand rubles.
Benefits:
- large condensation tank;
- availability of a restart timer, humidity control functions.
Disadvantages:
- makes noise when working;
- the liquid from the tank must be poured out 3 times a day.
Neoclima ND-30AEB
The floor-standing machine is suitable for saunas, swimming pools, apartments or houses with an area of 35-40 square meters. On the manufacturer's website, the moisture absorber is offered for 15.9 thousand rubles, but the online store sells it for 15 thousand rubles. The power of the device is 500 W, the complete container is designed for 6 liters. Noise index - 48 dB. 24 liters of water are removed per day. The fan speed can be adjusted.
Benefits:
- beautiful appearance;
- several modes (basic, day, night, continuous);
- there is a heating function;
- adjustment of the noise level.
Disadvantages:
- no carry handle;
- instructions included for another model;
- is noisy and may malfunction.
Master DH 716


Universal apparatus for 17.5 thousand rubles. Suitable for bathroom, basement, laundry room, living room, pantry, bookstore or summer house. The device with an active carbon filter prevents the development of bacteria and mold, is equipped with a hygrometer. The compact device is equipped with a transparent container with a fullness controller.
Benefits:
- simple functionality;
- light weight;
- very quiet operation;
- ease of operation and maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- fragile plastic case.
DanVex DEH 300
A Finnish mobile moisture absorber costs 20.9 thousand rubles. It is suitable for rooms where the humidity is higher than normal (swimming pools, greenhouses, saunas), as well as for granaries and libraries. The power of the device is 500 kW, the air consumption is 250 m3 / h or 30 l / day. Available with mechanical panel, hygrometer, removable water filter. The indicators can be seen on the LCD. The noise level is 55 dB, there is an auto-restart of the fan upon reaching the preset settings.
Benefits:
- beautiful body;
- energy consumption class A;
- removes moisture vapor from windows, walls, lighting fixtures;
- automatic mode of operation.
Disadvantages:
- inconvenient to fill in liquid;
- in night mode it functions very loudly;
- no rubber pads on the legs.
Protection of soil aggregates from the influence of rain drops
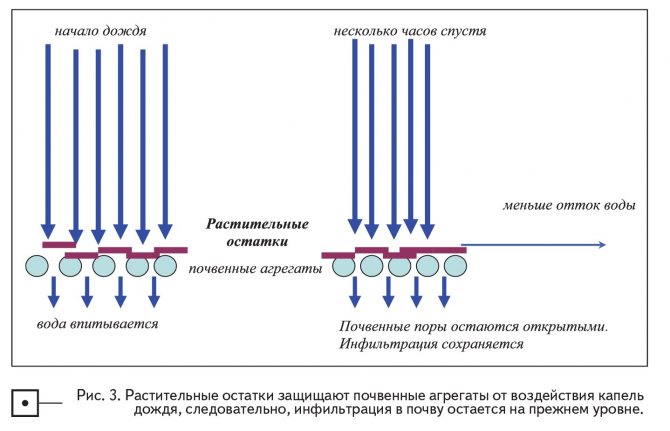
Water retention can be carried out at an adequate level if we can keep the pores on the soil surface open. Therefore, protecting soil aggregates from rain droplets is the key to maintaining maximum water capture for a given soil situation (Figure 3).
No-till, keeping plant residues on the surface, is a partial answer to how to protect soil aggregates.In Figure 3, you can see how the crop residues absorb the energy of the raindrops so that the soil aggregates remain intact. Thus, water infiltration takes place normally. By controlling weeds with herbicides, we can simply control weeds without mechanical treatment, leaving our soil as protected as possible from the effects of rain energy.

Under no-till, soil cover is maintained all year round because the total soil cover is the sum of the cover from the growing crop itself and the cover from the residues. Obviously, soil cover is very dynamic and can range from 0% to 100% within a single growing season, depending on which crop is currently growing and which tillage technology is being used. During sowing, for example, the soil cover consists only of plant residues. As the crop grows, coverage is already mainly done by the foliage of the crop itself. When the cover created by the crop itself takes on the impact of a drop of rain, just like plant debris, water smoothly rolls down to the soil surface with a much lower energy charge, therefore soil aggregates are less susceptible to destruction, the pores on the soil surface remain open, and infiltration is maintained at an appropriate level. As the crop grows, the amount of plant residues decreases, because natural decay occurs due to the activity of microorganisms. When the cover created by the growing crop begins to shrink, residues again become the main soil protection and the cycle ends. Remember that mechanical tillage, during and after crop growth, reduces the amount of plant residues on the surface, and, consequently, the protection of the soil surface.
The benefits of water accumulation due to the cover are most noticeable in regions with summer precipitation; for example, the growing cycles of maize (Zea mays L.) or grain sorghum in the Great Plains of North America occur when 75% of the annual rainfall falls. Conversely, rain-fed regions with little rainfall in winter (the Pacific Northwest in the United States) do not have a well-developed cover when most of the rain falls. However, early formation of crops planted in the fall to obtain at least partial soil cover is recognized as a good soil protection and a way to control water outflow during the winter months.
Protection of devices from dust and moisture. Understanding the notation of the IP standard


We have been dealing with a variety of devices for many years. During this time, thousands and thousands of gadgets have passed through our hands, and our customers have asked us a great many questions about them. Among all these questions, there are those that are constantly repeated. More often than others, there are questions about dust and water protection of gadgets. And we know why. The fact is that almost all manufacturers indicate the compliance of their device with the IP standard.
Also, gadget companies like to write that their device can withstand pressure of 3-5 atmospheres or even more. Buyers of such gadgets, trying to be guided by logic, believe that if 5 atmospheres is indicated, then the device can be immersed to a depth of 50 meters. And if so, that it is definitely possible to swim in it, and even more so, you can take a shower. But logic doesn't always work where marketers are. Let's try to figure out what it all means.
IPXX - what does it mean?
So, the IP standard is an international standard that classifies the degree of protection of devices against the penetration of solid particles of the smallest fraction (in fact, dust) and water. By the way, the degree of protection provided by the enclosures (IP code) is determined according to GOST 14254-96. The standard is developed on the basis of the IEC 60529 1989 standard.and entered into force on January 1, 1997, the International Protection Rating introduces the designation IPXX, where numbers are used instead of "XX". As an example, the two most common standards for consumer devices are IP67 and IP68.
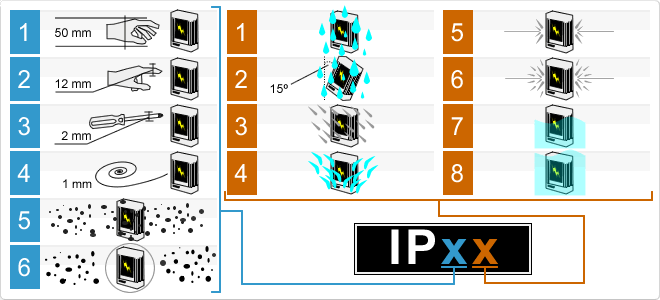

Here, the first digit indicates the degree of protection against foreign solids (dust, metal, human fingers, etc.). Minimum protection 0 (the device is suitable only when used in a housing), maximum - 6 (complete protection against dust).
The second number shows the degree of protection against moisture penetration. The minimum protection is 0 (any moisture can damage the device), the maximum is 8 (the device is not afraid of water, it can be immersed to a depth of more than 1 meter).


Water resistance tests are carried out in such boxes.
The numbers can sometimes be followed by letters, which provide additional information about the degree of protection of the device from external factors. But for consumer devices, this type of designation is rare, so we will not consider it now. According to Wikipedia, the maximum IP rating is IP69-K. This is how they mark the cases of devices that can withstand high-temperature high-pressure washing. In this case, it was even necessary to introduce additional marking (let me remind you that the generally accepted designation for maximum protection against water is 8, not 9).
| Level | Defence from | Description |
| 0 | — | No protection |
| 1 | Vertical drops | Vertically dripping water should not interfere with the operation of the device |
| 2 | Vertical drops at an angle of up to 15 ° | Vertically dripping water should not interfere with the operation of the device if it is tilted from the working position by an angle of up to 15 ° |
| 3 | Falling spray | Rain protection. The spray falls vertically or at an angle of up to 60 ° to the vertical. |
| 4 | Spray | Protection against splashes falling in any direction. |
| 5 | Jets | Protection against water jets from any direction |
| 6 | Sea waves | Protection against sea waves or strong water jets. Water entering the housing should not interfere with the operation of the device. |
| 7 | Short-term dive to a depth of 1 m | During short-term immersion, water does not enter in quantities that interfere with the operation of the device. Continuous immersion operation is not expected. |
| 8 | Diving to a depth of more than 1 m for more than 30 minutes. | The device can work in submerged mode |
Sometimes, instead of one of the numbers in the designation of the degree of protection of a particular gadget, you can see X. For example, IPX7. In this case, the designation says that the device has not been tested for protection against dust, but it is not afraid of water.
Meters and atmospheres - where is the dog buried here?
Manufacturers of electronic devices also work with the IP standard, but more often they also use an alternative rating indicating the atmospheres. Garmin, Pebble, Polar and other manufacturers of electronic devices often test their devices themselves to determine how well they are protected from the effects of water.
| Pressure / Depth | Protection |
| 3 atm (30 m) | The device is not afraid of splashing water, but you cannot take a shower in it, you cannot swim, swim, and even more so, dive. Better to keep your gadget away from water |
| 5 atm (50 m) | The device is well protected from water, you can leave it on in the pool, go fishing, swim and do some kind of water work that does not require immersion |
| 10 atm (100 m) | It can be used for almost any water work, swimming and submerging under water for a while. Diving enthusiasts can work with such devices without any problems. |
| 20 atm (200 m) | You can dive to a relatively large depth, that is, for example, scuba diving, use the device when working in sea water |
Inexperienced users, seeing the designation of 30-50 m, immediately decide that with such a gadget you can dive, swim, or even keep the device in an aquarium. In fact, as you can see, a device with a designation of 3 ATM or 30 meters is afraid of water, and very much.


It is also interesting that manufacturers understand the labeling in their own way. For example, the same Fitbit Surge has a 5 ATM mark. In an amicable way, this means that you don't have to take it off while swimming. But the manufacturers say that swimming in this gadget is not worth it, since the Surge may not withstand the blows during the swim. What's the matter? And the fact that the water resistance of devices is tested in still fresh water (in most cases). During swimming, the pressure can change abruptly, and the water will nevertheless find a loophole, ruining the gadget.
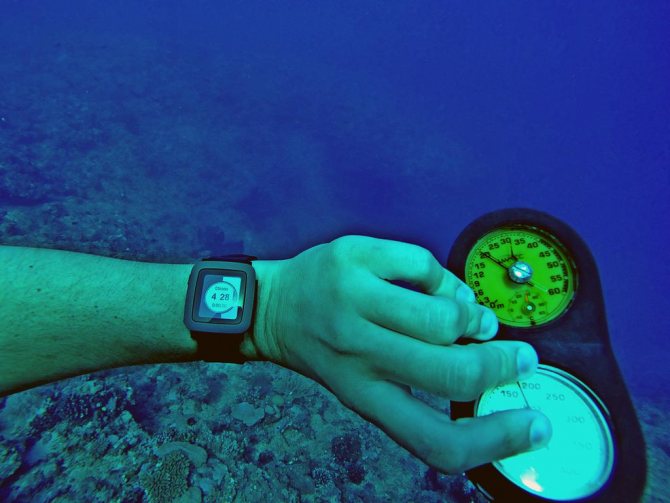


Diving enthusiasts sometimes put their devices at great risk
But with Pebble Time, things are different. Developers everywhere indicate the degree of protection in "30 m", but the description of the device says that you can swim with it in the pool. But this does not mean at all that, having put on this watch, you can dive in it in the sea. Sea water is not at all fresh, it contains much more salts, and this can lead to damage to the device. As mentioned above, most devices are tested in fresh rather than salt sea water.
It is worth knowing
- Most of the water resistance tests are carried out in fresh water. If the manufacturer has not indicated that the gadget is not afraid of salt water, then it means that testing in the sea or ocean has not been carried out;
- Tests are carried out at positive temperatures, usually 15-35 degrees Celsius. If you enter a sauna or bath in a watch that is not afraid of water at normal temperature, it may deteriorate;
- The leather strap is not waterproof;
- If the device is not afraid of water, when immersed in water, check that all openings of the gadget, which should be closed, are closed;
- A gadget with minimal protection from water does not necessarily break if you take a shower or swim in it. But there is no guarantee that if you took a shower twice and everything was fine, then nothing will happen the third time;
- It is best not to press the screen or physical buttons of the device underwater.
First of all - instructions
At Madrobots, we believe that it is best to read the instructions for your device carefully. Of course, not everyone does this, but if you are going to go to the sea or even just take a shower in a new device, it is better to read the instructions from the manufacturer.
And in any case, it is worth remembering that electronic devices are complex systems that consist of many parts. No matter how reliable the device is, it's better not to risk it again, so that later it will not be excruciatingly painful.
Other effects of crop residues on water retention
In addition to absorbing droplet energy and protecting soil aggregates from destruction, crop residues physically block the outflow of water, reduce evaporation levels during rain, allowing water to enter the soil profile before outflow begins. General water infiltration is a consequence of how long water will be in contact with the soil (a time of opportunity) before it starts flowing down a slope. Increasing this time component is a key management tool in water storage. The main principle of increasing the "time of opportunity" is to prevent the outflow of water, slow it down, and thus provide the opportunity to stay in contact with the soil for a longer time, and, therefore, to be absorbed. Crop residues on the soil surface increase the “time of opportunity” because physically block and slow down the outflow of water. Contour seeding also increases the benefit of crop residues in slowing down water outflow, as ridges play the role of mini-terraces.
Duley and Russel (1939) were among the first to recognize the importance of soil protection with crop residues. In one of their experiments, they compared the effect of 4.5 t / ha of stacked straw with an equal amount of embedded straw and uncovered soil on moisture accumulation.Moisture accumulation accounted for 54% of rainfall with stacked straw, compared with 34% when straw was covered and only 20% with uncovered soil. Their experiment did not separate the effects of crop residues into components such as soil protection, evaporation and water blocking, but comments suggest that maintaining porosity and physically blocking water significantly reduced moisture outflow during thunderstorms and were major contributors to increased water accumulation during thunderstorms. season.
Data from the study by Mannering and Mayer (1963) clearly show a protective mechanism of plant residues affecting the infiltration rate in silty loams with a slope of 5%. After four simulations of rain for 48 hours, the soil covered with 2.2 t / ha crop residues had a final infiltration rate that was not much different from the original. The researchers found that the straw absorbed the energy from the droplets and spread it out, preventing the soil surface from crusting and blocking.
Demonstration of the negative impact of machining
Soil aggregation decreases with an increase in the intensity of tillage and / the number of years of cultivation (Fig. 4). Mechanical tillage negatively affects soil aggregates for two main reasons: 1) physical crushing, which leads to a reduction in the size of the aggregates; 2) an increase in the levels of oxidation of organic matter, which occurs due to the destruction of macroaggregates and the subsequent discovery of organic compounds by soil organisms. The distribution of the sizes of aggregates also changes in such a way that microporosity increases due to macroporosity, which leads to a decrease in the rate of infiltration. The degree to which mechanical tillage affects infiltration is governed by a complex interaction of the type of tillage, climate (especially rainfall and temperature) and time, together with soil characteristics such as structure, organic structure and organic matter content. Therefore, long-term cultivation of any soil reduces the resistance of the aggregates to physical destruction, for example, exposure to raindrops and mechanical tillage of any kind. However, both clay minerals in the soil and organic matter stabilize soil aggregates and make them resistant to physical destruction. A decrease in the amount of organic matter reduces the stability of the aggregates, especially if it is already low.
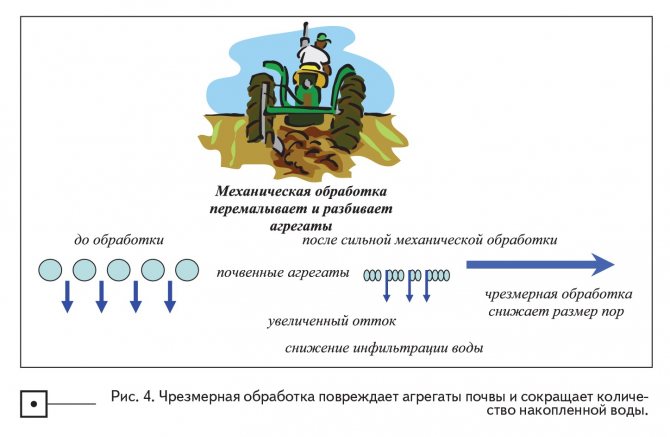

Of these two basic soil properties that regulate the formation of aggregates, mechanical tillage in any form affects the content of organic matter. The degree of practicality of altering the organic matter level will vary depending on the conditions. the level of organic matter is largely determined by two processes: accumulation and decomposition. The first is determined mainly by the amount of organic matter introduced, which is highly dependent on precipitation and irrigation. The second is mainly temperature. The goal of maintaining or increasing organic matter levels is easier to achieve in cool, humid conditions than in hot and dry conditions.
The "freshness" of organic compounds is necessary for the stability of the aggregates. In soil ecosystems, newly added or partially decomposed plant residues and their decay products, also known as “young humic substances”, create a more “mobile” array of organic matter. Older or more stable humic substances, which are more resistant to further decay, create a "stable" body of organic matter. It is generally accepted that a mobile body of organic matter regulates the supply of nutrients to the soil, especially nitrogen, while a mobile and stable body affects the physical properties of the soil, such as aggregate formation and structural stability.The formation of a mobile and stable array is a dynamic process that is regulated by several factors, including the type and amount of organic matter applied and its composition.
There has been a lot of interest in determining how soil cultivation affects the structural development and maintenance of soil in relation to organic matter content, especially with the advent of no-till technology. Increasing the intensity of soil cultivation increases the loss of organic matter from the soil and reduces the aggregation of the soil.
Snow accumulation and melt water retention
Many rain-fed lands receive significant annual precipitation in the form of snow. Effective accumulation of snow water has two characteristics: 1) trapping snow itself and 2) trapping melt water. Since snow is often accompanied by wind, the principles of trapping snow are the same as those used to protect soils from wind erosion. Crop debris, windbreaks, strip cultivation and artificial barriers were used to maximize snow trapping. The basic principle of these devices is to create areas where the wind speed from the leeward side and the barrier is reduced, thus trapping snow particles from the other side of the barrier. Repetitive barriers, such as standing stubble, keep the wind above the surface of the crop residues, and therefore the "trapped" snow remains unreachable for subsequent wind movements.
Research by scientists from the Great Plains of the United States showed that standing stubble retained 37% of winter precipitation, and fallow fields without plant residues retained only 9%. The proportion of the field covered with plant residues on the vine obviously influences the collection of snow. Scientists studying the effect of sunflower cut height on snow retention have found a strong correlation between stored moisture in the soil and cut height: the higher the cut, the more snow is captured.
The introduction of no-till technology has made it possible to significantly improve snow catching with the help of plant residues on the vine. Prior to the introduction of no-till, the mechanical treatment required to control weeds resulted in a decrease in the proportion of crop residues and the overall proportion of soil coverage in crop residues, and hence in a decrease in snow capture.
Capturing snowfall remains the simplest part of accumulating the snow moisture resource; the capture of melt water is much less predictable and manageable. For example, if the soil freezes before it snows, the water is less likely to be absorbed than when the soil is not frozen. In northern latitudes, soils usually freeze before snow falls. Moreover, the depth of soil freezing depends on the amount of water in the soil in autumn, as well as on the insulating effect of snow, which increases with increasing depth of snow cover. Dry soils freeze deeper and faster than wet soils, but frozen dry soils reduce water outflow compared to wet soils.
Maintaining infiltration when the soil freezes before snowfall and / or winter rains is difficult. The levels of infiltration of frozen soils are determined by two factors: 1) the structure of the frozen soil, i.e. small granules or large aggregates similar to concrete, 2) the water content of the soil during frost. Soils that are frozen with low moisture content do not interfere with water penetration because the aggregates leave enough room for infiltration. Conversely, soils frozen with a high water content freeze into massive, dense structures (like concrete) and practically do not allow water to penetrate inside. Sudden thaw and rain on such soils can lead to large outflow and erosion.The accumulation of winter precipitation can be maximized using the following principles: 1) trapping snow with plant residues on the vine; 2) maximization of macropores on the surface during those periods when the soil is frozen.
Polymer
All polymer heaters are produced using similar technologies, have a porous structure and low weight.
Styrofoam
It is one of the most popular polymers used to insulate walls (both inside and outside) and floors in private houses. He has undeniable advantages:
- very convenient to use, easy to cut, fit;
- does not absorb moisture, is resistant to decay;
- does not deform during the entire service life;
- keeps warm well;
- has a low cost.
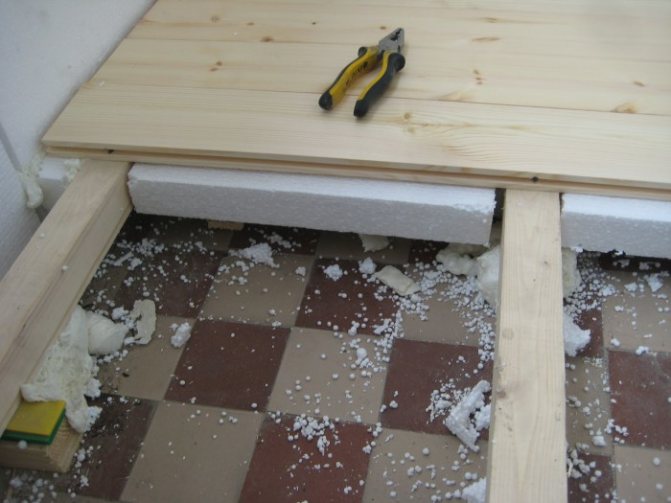


The disadvantages of foam include low fire resistance. In addition, an unpleasant odor may occur when heated.
Styrofoam is well mounted on any surface, but it is most effective for insulating a concrete floor.
Penoplex
The innovative building material penoplex has a cellular structure and good heat-saving qualities. Like polystyrene, it is simple and easy to install, does not deform, does not absorb moisture.
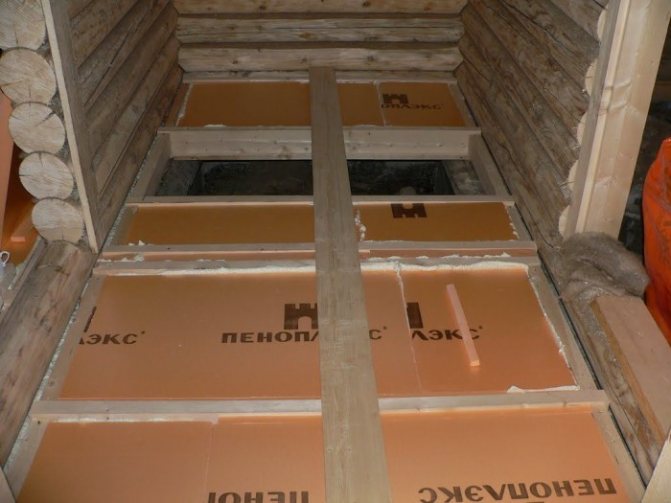


Penoplex has a long service life. Its disadvantages include rapid flammability and the release of hazardous substances during combustion. It can be easily mounted on concrete and wooden floors under the screed or laid on the joists after the frame has been installed.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene is gaining more and more popularity. It is one of the inexpensive polymers, lightweight, durable, solid. Resistant to high and low temperatures, wear-resistant. The material does not absorb moisture, it is not subject to damage by fungus and mold.
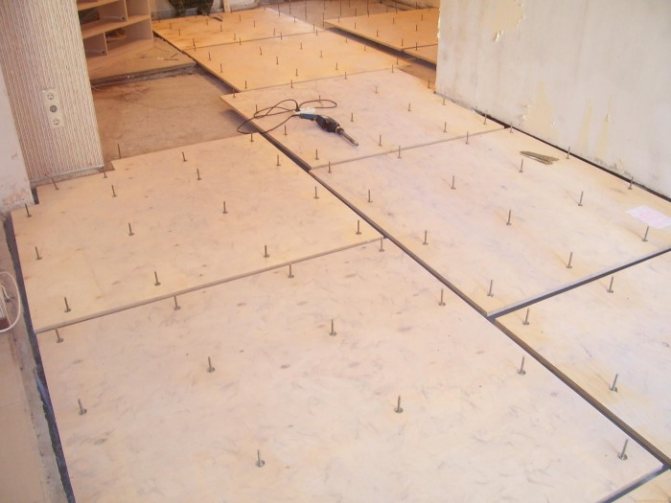


With long-term operation, the properties of expanded polystyrene are preserved, which is facilitated by its cellular structure. Like all polymers, it has little fire resistance. Easy to work with, easy to assemble.
Izolon
An excellent insulation is izolon - foamed polyethylene. Izolon has zero water absorption, which makes it impossible for mold or mildew to appear.
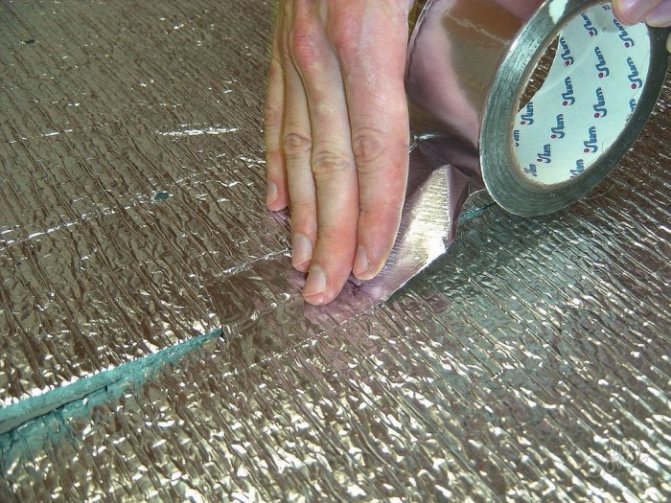


Keeps warm well, lightweight, elastic material. It is produced in rolls, which are easily laid on the surface and secured with adhesive tape. Self-adhesive isolon can be purchased.
Polyurethane foam
By spraying, polyurethane foam is applied to the floor, which creates an even layer of insulation. It is a lightweight and durable polymer that is resistant to decay and mildew.
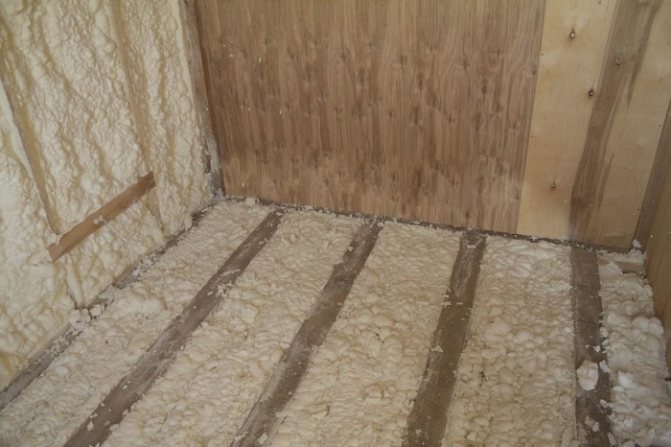


Has good fire retardant properties. It is absolutely safe for human health.
Paint
A special polymer paint, which is the thinnest insulation, copes very effectively with thermal insulation. This is a new development in the building materials market. Possesses water-repellent and fireproof qualities, the paint is easy to apply and dries quickly.
Synthesis of water storage principles
Favorable conditions for infiltration at the very surface of the soil and sufficient time for infiltration are keys to efficient water storage. However, the most important principle is to protect the soil surface from droplet energy. During the winter months in temperate zones, when large leaves have not yet appeared to absorb the energy of the drop and allow water to pass through, vegetation (plant residues) has the function of reducing outflow levels. The coating absorbs droplet energy, protects soil aggregates and increases the size of macropores, which in turn reduces outflow. Moreover, during the growing season of the crop, the water content of the soil in small amounts ensures a good infiltration rate.
Mineral
The use of such materials does not require special construction skills.
Mineral wool
One of the most popular floor insulation materials is mineral wool. It is a natural, eco-friendly product with fireproof properties.
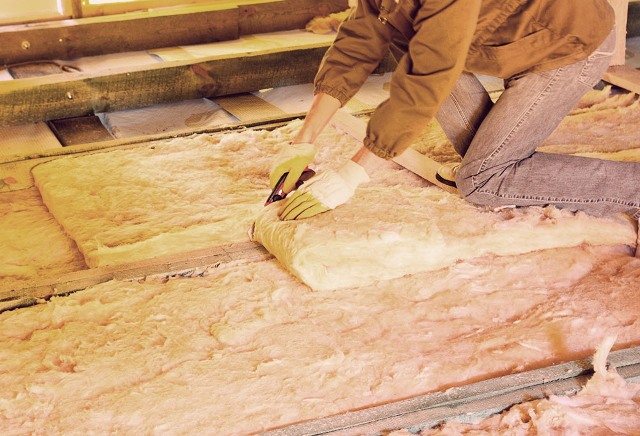


Mineral wool is durable, does not shrink, does not deform with temperature drops. Provides excellent sound and heat insulation. It is produced in different sizes of slabs, rolls and mats, which makes it easy to install on a concrete floor. The disadvantages include a rather large layer thickness.
Expanded clay
A type of heat-treated clay - expanded clay - is not bad for the floor. Durable, resistant to dynamic loads and temperature drops, provides good noise insulation, perfectly retains heat.
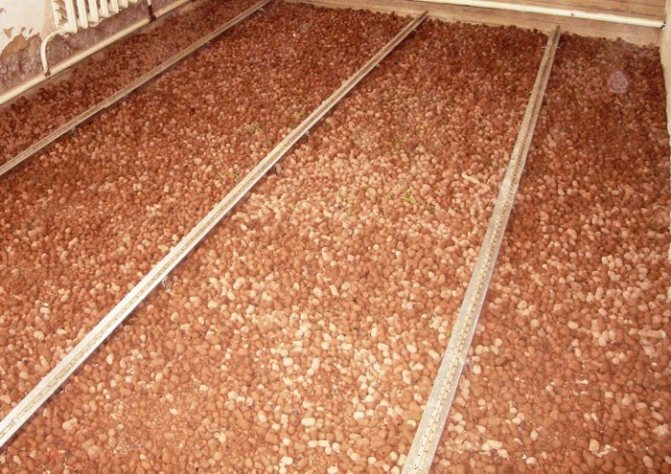


It is produced in the form of granules, which are simply distributed between the lags by hand. Expanded clay is relatively inexpensive. It is fragile, absorbs moisture well, which, of course, is a disadvantage.
Water retention in soil
After the water has been collected, the evaporative property of the air begins to "pull" it out. Therefore, even if no crops are present in the field, the soils lose moisture due to evaporation. In this section, we will demonstrate how no-till affects soil water retention after we have collected enough moisture during rainfall. The protective property of plant residues increases infiltration because they not only protect soil aggregates, but at the same time affect the rate of evaporation, especially during the initial stages of evaporation, after precipitation.
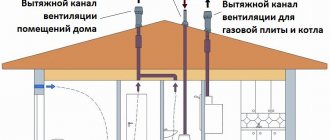
Fighting dampness in the apartment
If excess vapors appear during cooking, they can be reduced by installing an additional fan on the cooker hood. The air must be circulated so that moisture does not settle on walls and glass. Additional ventilation of the premises helps here. For the hood to work efficiently, air must flow through the vents.
To reduce evaporation, pans should be covered with lids during cooking. You can also turn on forced ventilation.
The poor condition of the ceiling also affects the indoor climate. It can be plastered again.
What are the reasons and how to get rid of excess moisture in the apartment? With the appearance of plastic windows, air circulation in the apartments deteriorated due to their tightness. Frames must be equipped with built-in ventilation. If you managed to get rid of excess moisture on the window, this is an indicator that a normal microclimate has been established in the apartment.
A cold wall can cause dampness. This is especially noticeable in panel houses. Usually the walls are insulated, then covered with plasterboard. In this case, the expansion joints between the panels are first sealed. This is done from the outside, since the walls are covered with plaster from the inside.
On the ground floors, you can often see salt deposits or mold at the bottom of the wall. This could be due to dampness coming from the basement or poor floor insulation. In this case, it is sealed and insulated. It is checked for leaks in heating pipes or water supply.
Demonstration of evaporation of water from soil
Evaporation occurs because the air demand for water is always high, even in winter, in relation to the soil's ability to retain water. In other words, the air potential is always negative in relation to the soil potential. Warm air has a greater ability to retain moisture than cold air. Thus, as the temperature rises, the evaporation potential increases. Evaporation is highest when the soil is moist (high water potential) and the air is dry (i.e. the relative humidity is low). When the soils dry out at the surface, water rises to the surface to replenish the evaporated water (Figure 5). With constant evaporation, the distance traveled by water increases, which reduces the rate of flow of water to the surface in the form of liquid or vapor, the rate of evaporation decreases, and the soil surface remains dry (Fig. 5). Finally, water only begins to move towards the soil surface in the form of vapor, which results in a very low evaporation rate.Each subsequent precipitation starts the evaporation cycle anew, because the soil surface becomes wet again.
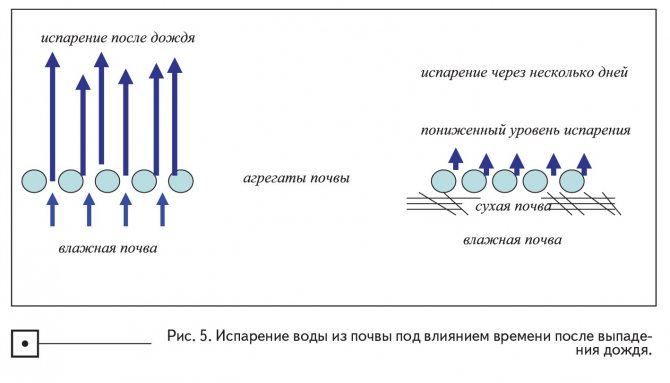

In addition to air temperature, other atmospheric influences such as solar radiation and wind affect evaporation. Solar radiation gives energy to evaporation, and wind speed affects the vapor pressure gradient on the soil-atmosphere horizon. High humidity and low wind speed result in a lower vapor pressure gradient on the soil-atmosphere horizon and thus lower the evaporation rate. As the relative humidity decreases and the wind speed increases, the evaporation potential gradually increases. On a windy day, moist air is constantly replaced by dry air on the soil surface, leading to faster evaporation.
The evaporation of water from the soil goes through three stages. Most of all water is lost at the first stage, and at subsequent stages the level of losses decreases. Evaporation in the first stage depends on environmental conditions (wind speed, temperature, relative humidity and solar energy) and the flow of water to the surface. Losses are significantly reduced during the second stage when the amount of water on the soil surface is reduced. During the third stage, when the water moves to the surface in the form of steam, the speed is very low. The greatest potential for reducing evaporation levels lies in the first two stages.
Let's demonstrate how plant residues left on the soil surface affect the evaporation of water from the soil. Obviously, they will reflect solar energy, cooling the soil surface, and also reflect the wind; both of these effects will reduce the initial rate of evaporation of water (Fig. 6).
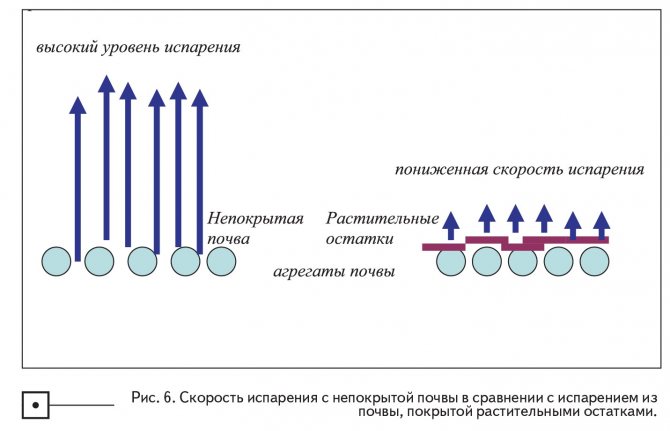

Plant residues on the soil surface, present in no-till technology, significantly reduce the level of evaporation in the first stage. Any material, such as straw or sawdust, or leaves or plastic sheeting spread over the surface of the soil, will protect the ground from rain energy or reduce evaporation. The orientation of plant residues (on the root, laid mechanically or in the form of a cover) also affects the evaporation rate, because orientation affects aerodynamics and reflectivity, which in turn affects the solar energy balance at the surface. An example of the efficiency of using plant residues is given in the scientific work of Smika (1983). He measured the loss of water from the soil that occurs over a 35-day rainless period. Losses were 23 mm from uncovered soil and 20 mm with plant residues laid, 19 mm with 75% laid residues and 25% standing residues and 15 mm with 50% laid residues and 50% standing residues on the surface.
The amount of residues was 4.6 t / ha and the standing residues were 0.46 m in height.
The reader should remember that plant residues do not stop evaporation, they delay it. If a lot of time passes without precipitation, the soil under plant debris will begin to lose as much water as uncovered soil. The only difference is that uncovered soil will lose water quickly, and plant residues will decrease the rate at which water will leave the soil (Figure 7).
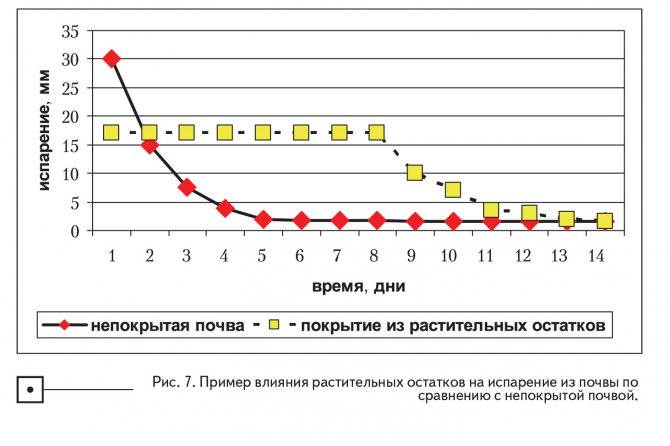

The benefits of slowing evaporation with crop residues in a no-till system can be demonstrated using the data in Figure 7. Suppose it rains on day 0, ie. and uncovered soil (line indicated by diamonds) and soil covered with plant residues (line indicated by squares) are in the same conditions in terms of moisture content. After 3-5 days, very rapid evaporation has occurred on uncovered soil and the surface will be almost air dry. In contrast, on soil covered with plant debris, the evaporation rate was much lower and it does not dry out until 12-14 days after the rain falls.Now, let's imagine another rain falls on the seventh day; since uncovered soil is already dry on the seventh day, rain must re-wet the dry soil before moisture retention begins. If it rains very briefly, only the amount of water that has evaporated will be replenished. In contrast, the soil that was covered with plant debris evaporated very slowly, so by the seventh day the soil under the plant debris is still moist (shown in Fig. 6). This means that if it rains on the seventh day, it does not need to wet the dry soil (it does not exist), so the water immediately begins to move deep into the soil, and its accumulation occurs.
Slowing down evaporation with crop residues in no-till systems helps to retain moisture because the soil surface dries more slowly. However, if it does not rain for an extended period, soil covered with plant debris will not retain more moisture than uncovered soil.
The reader should understand that even if there is a long time between rains and evaporation dries up the soil, plant residues are beneficial in any case. they will protect the soil from the energy of the raindrops when it rains again.
How to make new towels more absorbent?
By and large, you can independently make both a condensation and an absorption moisture absorber - if you have everything you need at hand, then there will be no problems with manufacturing. Let us consider in more detail the principles of manufacturing both types of moisture absorbers.
- Do-it-yourself condensation desiccant for an apartment. To make this device with your own hands, you will need an old, but working refrigerator or a small-sized freezer - it is in it that condensate from the air will settle and it is into it that you need to organize the air supply. That is, mount a fan in the freezer door and cut the outlet hole in it. You will get some mixture of a dehumidifier and an air conditioner - in order to prevent cooling of the air in the room, an additional fan heater must be installed at the outlet of the evaporator. Yes, the power consumption of such a desiccant will be rather big and the device will look at least ridiculous. It is for this reason that it is better to choose a dehumidifier of the absorption principle of operation for self-production.
Do-it-yourself desiccant for an apartment photo - Absorbent moisture absorber. For it to work, you need to buy the so-called selikogel - it is he who is the most important component of a homemade desiccant. If there is this substance, then there will be no problems with everything else - it is through it that an air stream will need to be passed. Therefore, you need some kind of container - plastic bottles are perfect here (a couple of the same size). In fact, they will have to make a container for silica gel with many holes through which air will pass, and also equip this container with a small fan - for example, a cooler from a computer. Alternatively, if we are talking about the simplest device for dehumidifying air in one room, this very silica gel can simply be poured into a plate and completely trust the laws of nature. Yes, it will be long, but cheap and, as they say, cheerful.
In principle, this is all that can be said about the independent manufacture of such a useful device as a moisture absorber for the home. The only thing that can still be added here is to say a few words about the appearance of a homemade air dryer - oddly enough, but this factor plays a huge role for a modern person.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
The author of the article is Alexander Kulikov
Does not allow moisture to pass through, while allowing the baby's skin to breathe.It is the most common fabric in waterproof reusable diapers.


There are two types of layer application: PUL (polyurethane lamination) and TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane). The polyurethane layer in TPU fabrics is heat-bonded. It is more expensive than PUL, in which various chemicals containing formaldehyde and phthalates, which are hazardous to human health, can be used at the final stage to obtain the waterproof properties of the fabric.
The fabric with a polyurethane layer is used for the manufacture of diapers, waterproof covers for cloth diapers, swimming panties, waterproof layer of absorbent pads, in bags for wet clothes.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with How to make a country house from a change house
Bamboo
Fast growing unpretentious plant. It is believed that bamboo tissue resists the growth of bacteria. However, in most cases, chemicals are used to transform the plant into soft tissue (bamboo rayon). Therefore, bamboo rayon can never be labeled as "organic". Another method of processing bamboo is costly, but environmentally friendly, when the plant is mechanically treated with enzymes and the so-called bamboo flax is obtained.
For diapers and absorbent liners, the most commonly used bamboo viscose with a heel or loops on one side.
When shopping for absorbent towels, you shouldn't always choose the most expensive items, thinking they will work best. Cotton and cotton blends are highly absorbent materials, as are bamboo, microfiber and terry towels. The absorbency of a towel is directly proportional to the length of the fiber.
Sometimes in the process of making the towel, a special wax is applied to the fabric, which makes it easier to weave or knit the fibers. Also, sometimes there may be dye residues on the coating, which may remain on the fabric during the production process. When a towel is purchased and used for the first time, it can repel water rather than absorb it.
This is because the production coating remained on the fabric. To rid the fabric of this layer, wash the towel in hot water before use. Some new towels may need to be washed twice before use. Make sure to wash the towel separately, especially during the first two washes, to prevent the color from dyeing.
To make the towel more absorbent, do not use fabric softeners when washing. Such products with a thin layer of chemicals can make the fabric water repellent.
Have you ever noticed that new towels seem to repel water rather than absorb it? It usually takes many machine cycles to make the towel more absorbent, but with our tips you can speed up the process.
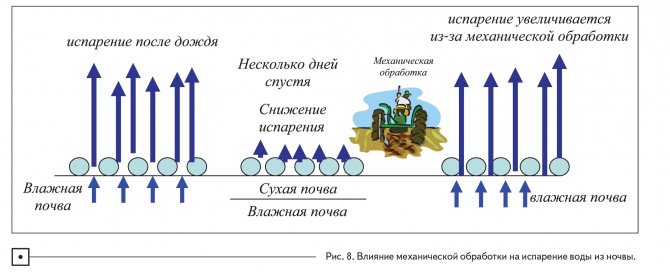
Demonstration of the effect of soil cultivation on moisture evaporation
When the soil is mechanically cultivated, the moist soil opens up to the surface. This means that rapid evaporation begins immediately after processing (Fig. 8). Obviously, if mechanical treatment is used to control weeds, it will waste moisture because constantly exposes wet soil to rapid evaporation on the surface. In contrast, no-till, which uses herbicide-based weed control, does not lead to evaporation because there is no impact on the soil. The soil remains wetter at the surface, and therefore the next rain will not rewet the dry soil, but will penetrate deeper into the soil and accumulate for future use.

Netcol fabric: properties.
In the household, nonwoven fabric is simply irreplaceable. It quickly absorbs moisture and squeezes well, has the following properties:
- It is a thread-stitched non-woven fabric with high strength.It is very difficult to break it, since the fibers are tightly connected to each other.
- Suitable for cleaning all surfaces and does not leave lint on them.
- Netcol is sold in lightweight rolls. They are easy to transport and fold.
- Absorbs any liquid well.
- Has a natural composition. The material is made from cotton.
- Optimum thread density: 100 to 130 g / m2 Thanks to this characteristic, non-woven fabric is ideal for wet or dry cleaning.
- Has a weave "chain" and "tights".
One roll can contain up to 50 meters of this technical material. Its standard width is 80 cm. Outwardly, the packaging seems to be bulky, but such rolls are lightweight, well compacted in the warehouse, taking up not much space.
The netkol fabric has significant differences from the cotton material, despite the similar composition. Non-woven fabric has the best hygienic properties. It has high levels of hygroscopicity and low thermal conductivity (retains heat), air permeability.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with What product can be poured into a washing vacuum cleaner
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Therefore, netkol is used not only for technical and household needs, but even in cosmetology and medicine. You can hardly find a softer material that absorbs water so well. It also does not allow air to pass through, has good thermal insulation properties. This is a hypoallergenic canvas with a completely natural composition.
If a wet or dry cleaning is carried out in the room, then a cloth is always required that would absorb water well and leave no marks on the surface.
The netcol fabric is just that: moisture-absorbent, hygroscopic and durable. One of its sections seems to be voluminous, thick, but, in fact, it has a small weight. The material is comfortable to use, soft to the touch and completely natural.
It can quickly absorb moisture, after which the material can be squeezed out again and wiped off the surfaces. It is also convenient to use for dry cleaning of residential, industrial and commercial premises.
Netcol fabric is also used in cosmetology. It is ideal as a base for fabric masks, used in the production of strips for hair removal.
Netcol does not cause allergies, as it is 100% cotton. In beauty salons, you can also see absorbent disposable wipes made of this material, which are used for cosmetic procedures or for removing makeup, masks.
Netcol fabric is used for medical purposes as non-sterile dressings, cut. It is also suitable for household needs, since medical institutions require high-quality and at the same time inexpensive cleaning material. It is also suitable for wiping surfaces not only in ordinary rooms, but also in dressing rooms, intensive care units and wherever it is necessary to achieve perfect cleanliness.
The netkol cut quickly absorbs water, captures all dirt and dust particles, is well wrung out and washable. It can be used many times in a row and practically does not wear out. It is extremely difficult to break a piece of netcol, since the fabric has a high density and strength.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with How to clean a yellow metal watch bracelet. How to clean silver at home - chains, bracelets, rings? Cleaning a bracelet made of precious materials
If you cut a piece from a roll of netcoll, then the cut will not peel, stretch or deform. The material has low elongation, so it does not thin or tear. Netkol retains its original shape for a long time and can last for a year.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
Netcol fabric is also used for other purposes:
- For wrapping goods. This fabric can be used to cover the load to protect it from wind, moisture or cold.
- As a base for various fabric products.
- It is used in production not only for cleaning, but also for wiping parts from fuel oil paint, oils.
- It is used in emergency situations when you need to quickly collect any liquid or mixture from the surface. For example, netkol has been used many times in different countries to purify water from oil spills.
- It can replace geo-dense, as it has similar properties. Non-woven fabric can be used to wrap the roots of shrubs and trees.
The main advantage of netkol is its natural composition, hygroscopicity, strength and fast moisture absorption. It is ideal for cleaning, as non-sterile dressings and even as a geotextile. The fabric has a low price and is actively used in various fields.
conclusions
The key to effectively capturing water is to have favorable conditions at the surface of the soil so that water can enter the soil immediately, as well as those (conditions) that allow sufficient time for infiltration. The most important principle for achieving the penetration of water into the soil is to protect the surface from the energy of rain drops. The no-till system provides coverage with growing crops and crop residues. The coating absorbs droplet energy, protects soil aggregates and increases the size of macropores. At the same time, this coating slows down drainage, thereby increasing the accumulation of water in the soil for use by subsequent crops. To maintain the maximum amount of accumulated moisture, evaporation must be minimized. No-till reduces evaporation because With this technology, plant residues remain on the surface, which reduce the temperature of the soil and raise the wind above the soil. The use of water by weeds is a waste of moisture that could be available to cultivated plants. Mechanical tillage usually stops weeds immediately, but exposes moist soil to the atmosphere, resulting in increased evaporation losses. When using a no-till system, weed control is carried out using herbicides, which prevents harmful effects on the soil compared to mechanical tillage, while water accumulates in the soil. This is especially important in countries like Ukraine, where most of the precipitation falls in summer.


The reasons for the appearance of dampness in the apartment
- poor ventilation;
- poor waterproofing of the foundation;
- the heating system does not work;
- washing and drying linen indoors;
- the hood works poorly or is missing in the bathroom and in the kitchen;
- the presence of a large number of plants;
- fumes from cooking;
- external conditions.
The reasons for dampness and how to get rid of moisture in a private house are presented in the table.
| Cause | Remedy |
| Poor foundation protection | Drainage creation; sealing joints with waterproofing materials with polymer additives. |
| Ceiling leaks | Sealing floor slab joints with expanding cement, sealant or waterproof filler. |
| Wet the walls | Insulation and waterproofing outside; sealing joints with mortar. |
| Roof leaks | Roof and drainage system repair; insulation of the attic. |
| Ventilation fails | Restoration of working capacity and installation of additional ventilation. |
Before eliminating the problem, you must first of all establish the reasons for its appearance by examining the premises. Moisture protection is done first in the most vulnerable places.