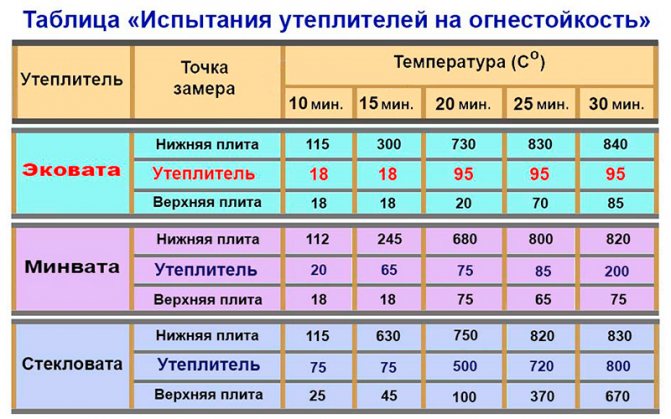
Flammability properties are of decisive importance for the fire safety of substances and materials. In this respect, all known compositions are divided into flammable and non-flammable. These terms define their flammability. Based on this quality of materials, it is possible to calculate in advance the optimal option for fire protection of a structure even at the design stage. Which materials are non-combustible, and which are prone to rapid ignition, can be calculated with great accuracy at the preliminary stage of construction.
What materials are non-flammable?
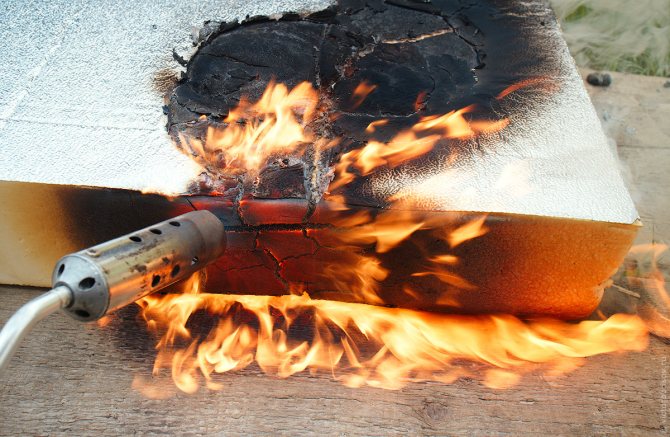
The group of non-combustible materials includes those that, in the process of exposure to an open flame, retain their original state. At the same time, they do not ignite, do not char, do not smolder and do not contribute to the spread of fire.
As a regulatory source, classifying substances according to the degree of fire hazard, the Technical Regulations on Industrial Safety Requirements of 2008 are used. The main material on this issue is contained in article 12 of this document. Additional information on fire and explosion hazard is contained in GOST 12.1.044-89.
In accordance with these regulations, the flammability group refers to the parameters that determine the combustion of materials under different conditions. It should be noted that:
1.
The category of non-combustible substances includes compounds that are incapable of burning in a normal environment.
2.
There is a group of non-flammable substances that, when in contact with air or water, become explosive and fire hazardous. This group also includes compounds with the chemical properties of powerful oxidizing agents. To accurately determine the properties of materials and assess their fire resistance, it is necessary to find out their composition, what characteristics the substances of which they are composed have.
In the course of certification activities and expertise, the working and chemical properties of the test substances are precisely established. The results obtained are taken as a basis for the development of GOSTs, technical conditions for the operation of enterprises, the issuance of a certificate, and the development of fire-prevention measures at the facility.
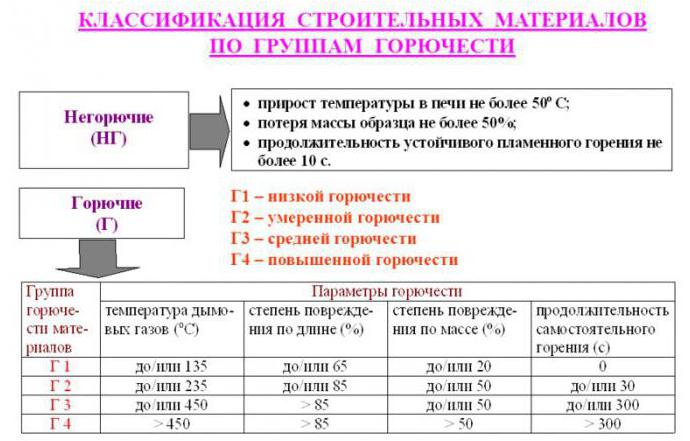
Highly flammable

The group, which includes materials, during the combustion of which the temperature of the flue gases begins to exceed the threshold of 450 ° C. The G4 flammability class has a degree of material damage along the entire length of the sample of more than 85%, a degree of destruction of more than 50%, and self-combustion exceeds 300 seconds.
Additional requirements are imposed on the flammability materials G1, G2. When burning, they should not form melt droplets. An example is linoleum. The flammability class of this floor covering cannot be 1 or 2 due to the fact that it melts strongly during combustion.
Scope of application
The main purpose of determining the degree of flammability of substances lies in the practical field. The results of these activities are usually used in the construction and landscaping industry. The combined use of flammable and non-flammable substances will ensure high fire safety in combination with a moderate amount of production costs.
The materials used in the construction industry make it possible to make the safe operation of buildings after completion of construction. Non-combustible materials for the bath can reduce the risk of fire to acceptable values. An example is the active use of hollow materials in construction.
Especially often a brick with voids inside the structure is used in this capacity.In addition, it is used as a non-combustible material for stoves in low-rise structures. It should be remembered that the contact points of chimneys and stoves docked with combustible structures must be insulated with fire retardants: mastic, plaster, sealant.
Non-combustible material for the chimney must be insulated at the junction with flammable elements. In the construction industry, hazardous materials are actively changing to formulations that are stable and resistant to fire. The traditional wooden floor structure is almost completely replaced by a conventional screed combined with floor ceramics or non-combustible linoleum. Non-combustible materials for walls and ceilings are widely used both in low-rise construction and in apartment buildings.
Materials based on wood and wood shavings are consistently being replaced from the construction industry. Usually, these materials are changed to block elements, for example, tuff blocks or foam concrete products. As finishing panels, both internal and external, non-combustible sheet material is used.


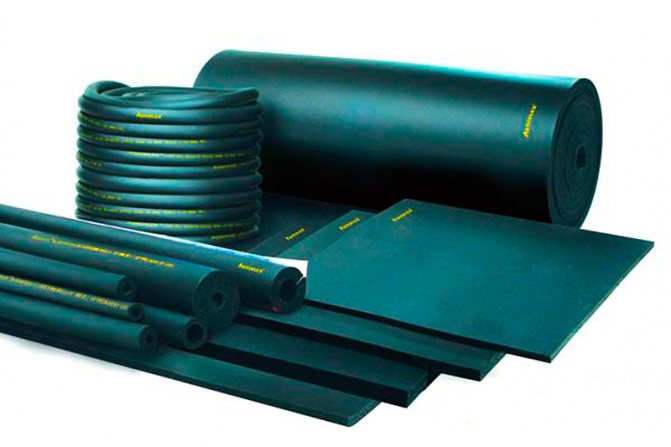
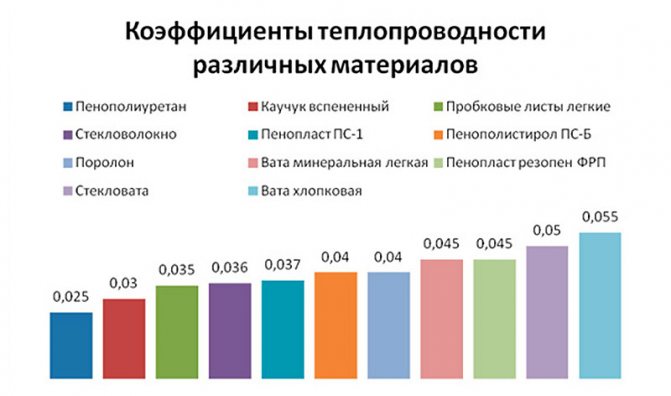
For insulation of walls, ceilings, floors, roll and sheet material based on basalt and other mineral fibrous compositions is used. These products are characterized by high fire safety and are used:
- for thermal insulation of technical openings for windows and doors;
- to ensure thermal insulation of the outer floors, roof structures, floor of the room;
- for insulation of upper superstructures and attic floors;
- in order to ensure thermal insulation of pipelines for various purposes, including water pipelines, gas pipes, wastewater discharge system, cylindrical structures or roll samples are used as heat-saving elements;
- fibrous mineral compounds are also used for sound insulation in premises for various purposes.
Various metal structures also have a high degree of fire safety. This number includes:
1.
Cast iron and steel used to create pipe products, industrial and construction equipment, fittings for pipelines. From these metals casings are cast for machine tools and equipment for various purposes, they are used for the production of engineering equipment.
2.
Conventional steel is actively used for the production of fittings for structural fittings. Elements of supporting structures for structures of various purposes are created from steel.
3.
Copper, aluminum and various alloys based on them are used as conductive materials in the energy sector.
Drywall


View gallery
Another kind of non-combustible panels, quite well-known both in professional circles and among ordinary homeowners. True, in this case it is the fire-resistant modification of drywall that is meant, since in standard versions it refers to a combustible finish. Refractory boards of this type can withstand up to 20 minutes of direct contact with the flame. This indicator is far from the record values and it is difficult to attribute it even to the average, but this disadvantage is offset by the low price. The fact is that non-combustible materials based on the same calcium silicate base are calculated to meet high fire safety requirements, and therefore are more expensive. In the case of drywall, you can expect to get an inexpensive but visually attractive coating that has basic fire protection.
Classification of materials
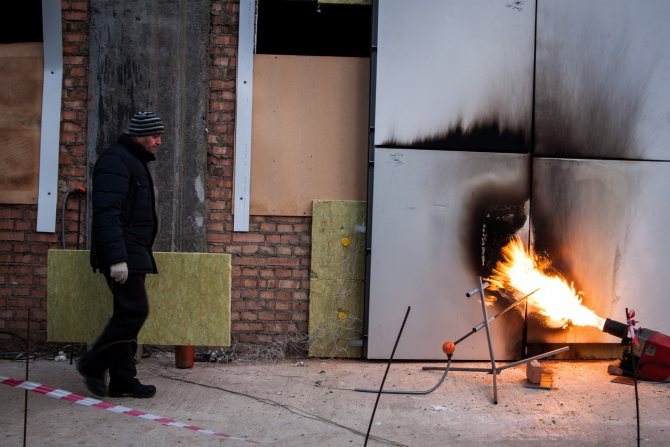
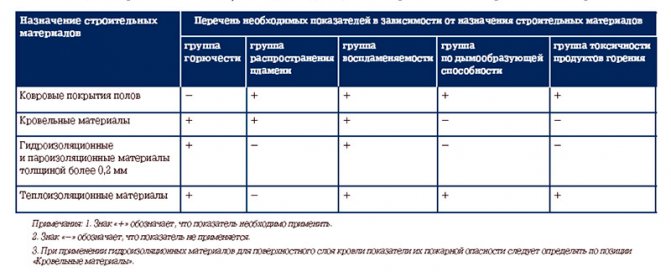
GOST 30244-94 is the main document defining methods for classifying materials by flammability classes. This normative act sets out the methods for testing materials and identifies two groups:
- non-combustible "NG";
- combustible "G".
The group of non-combustible includes compounds that withstand tests, which are as follows:
- reduction in the mass of the tested substance - no more than 50%;
- the temperature should rise by no more than 50%;
- time of stable burning with open fire - up to 10 seconds.


All types of materials that participated in the tests and did not pass even one of the criteria are classified as combustible. Differ in fire resistance and construction objects. Among this category, two types of buildings can be distinguished:
1.
All construction details are made of non-combustible compounds. The main load-bearing elements have an extreme degree of fire resistance, which allows them to withstand up to 2 hours of exposure to an open flame.
2.
The difference in the second category is the use of metal structures that have not been treated with fire protection. Metal elements should be used when creating openwork elements of trusses, beams and other patterns in the area of the roof of the building. In this case, the fire resistance limit will be 1.5 hours.
Objects that meet the above fire resistance requirements to the greatest extent meet fire safety standards. As an additional classification of non-combustible compounds used in the construction, reconstruction and repair of structures, several types of division are used.
Depending on the type of products manufactured, substances are divided into:
- produced in the form of a roll, tile, technological sheet;
- in the form of a free-flowing substance;
- in the form of rigid elements such as metal trusses or reinforced concrete slabs.
Depending on the purpose of the product:
- decorative finishing materials, such as tiles for various purposes or wall panels;
- finished building structures, for example, slabs, bricks, floors;
- bulk materials for various purposes, heat-insulating and sound-insulating molded products.
Fabric NG
Non-combustible fabrics are widely used in construction, they are made from the following types of raw materials:
- Polyesters. Filaments are synthesized from various polyesters and phosphorus compounds. Weaving - any: from jockard to velvet. Fabrics are characterized by non-flammability, durability, resistance to ultraviolet and infrared radiation, safety for human health. When exposed to direct fire, it decreases in size, but does not emit toxins.
- Carbon. These are materials obtained by synthesis. They are composed only of carbon and are highly flame retardant. For example, filaments of electric lamps are made from such materials. In addition, these NGs are resistant to chemicals, stretching, deformation and temperatures above +300 degrees C.
- Silica. Similar to quartz fabrics. Resistant to temperatures, temporarily able to withstand up to + 2000 degrees C. Environmentally friendly fabric, even filters are made from it.
- Quartz. Fiber is pulled from the mineral at high temperatures. Outwardly, the material resembles fiberglass, but withstands heating of more than +1300 degrees C, while the properties do not change. The fabrics were used to make space suits for Soviet cosmonauts.
- Aramid. It is a polymer product. The plastic has transverse and longitudinal stitching. It is produced using different technologies, depending on the specific method, it has different characteristics. The weave of the fabric may vary. The products can withstand temperatures up to +370 degrees C, and are very durable. The list of aramid materials is constantly expanding.
- Asbestos. This group is made from fine natural silicate fibers. It can withstand heating up to +500 degrees C and has good insulating parameters. But asbestos is not safe for human health, so it should not be used as a non-combustible material for wall decoration in a residential building or office, and other interior work. It is good for external cladding and for cladding special rooms, for example, boiler rooms, garages, hangars, gazebos, switchboards and other objects.
It should be understood! On sale are fabrics that do not burn due to treatment with special flame retardant compounds. These impregnations suppress combustion and are widely used for fire fighting purposes. The price of such NG-fabrics is low, so they are widely used. But they retain their properties for a certain time, mainly - this is 1 year. After expiration, it will be necessary to re-process.
Types of substances
It is customary to distinguish between three main types of non-combustible substances of various origins. The first type includes solid materials presented in various structural and aggregate states. It can be free-flowing substances, and structures, and individual piece products.
This number includes:


- various samples of rocks, both rocky and softer, including limestone, dolomite, marble;
- concrete and reinforced concrete products;
- loose rocks, including gravel, sand, crushed stone;
- binders - chalk, clay, cement, gypsum, lime, plasters, mortars;
- cast iron and steel products of various types and designs - corners, channels, beams;
- non-ferrous metals, including bronze, copper, brass, aluminum alloys;
- mineral fibers such as basalt;
- various types of textile materials, including asbestos fabric, basalt fiber;
- ordinary and fire resistant glass.
Liquid substances:
- foaming agents and detergents;
- all types and conditions of water, from the source of drinking and ending with the use as a heat carrier;
- synthetic fluids that are incapable of burning;
- acids, alkalis, salts in the form of an aqueous solution.
Gaseous substances:
- carbon dioxide;
- nitrogen;
- freon;
- argon.
Requirements for fire safety of materials
The modern regulatory framework is not limited to one document regulating the fire safety of substances and materials. The list of basic documents includes: 1.
GOST 30244-94 contains information on the procedure for testing building materials subject to fire. The norms of the document do not apply to paints and varnishes, granules, bulk substances, solutions used in construction.
2.
GOST 4640-2011 regulates the conditions for the production of mineral wool from rocks of various origins, slag waste from metallurgy, silicate materials. The main area of application of fibers is construction.
3.
NPB 244-97 contains standards for finishing and facing materials, waterproofing, roofing samples, floor coverings.
4.
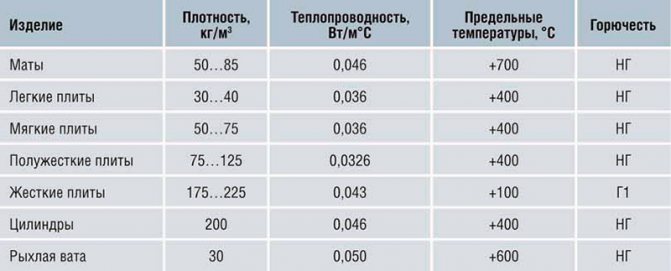
GOST 32313-2011 regulates the quality condition of products of various shapes made of mineral wool, made in the form of plates, mats, cylinders with and without metal. Used in industry and construction to provide thermal insulation properties.
5.
GOST 21880-2011 defines the technical conditions for the production of mats used for thermal insulation of housing and communal services and industry. The products are manufactured using stitching technology.
6.
GOST 32603-2012 regulates the production of metal panels using mineral wool-based insulation.
7.
GOST 32314-2012 contains information on products made on the basis of mineral wool. The scope of application of the products is the construction industry.
The norms contained in these regulations do not limit the requirements for materials to a single fire resistance. The documents also contain other characteristics of the compositions used in the production area:
- resistance to various deformations after heating or exposure to water;
- moisture resistance and hygroscopicity;
- heat-conducting qualities;
- the ability to withstand mechanical stress, including breaking and bending;
- specific viscosity of the substance.
Non-combustible substances and materials in a cold state demonstrate completely different qualities than under the influence of an open flame.It is important to establish the suitability of a particular structure for use as a reliable link capable of withstanding design loads, including exposure to open flames.
Posted: 19/05/2020
Technical and operational characteristics
The main property of such materials is fire resistance, which expresses the temperature at which the deformation process begins. With regard to this value, the effectiveness of their use for various purposes is considered. In addition to this parameter, others are considered. Namely, how the refractory behaves under the influence of strong heating:
- change in shape and violation of the integrity of the product under load at elevated temperatures;
- the parameters of the compressive force when heated, they reflect the stability of the structure;
- neutrality to chemical influences.
On a note! Fire-resistant materials withstand significant temperatures, minimum values - +1580 degrees C, maximum - 3 thousand degrees C. Products capable of retaining properties at the highest temperature parameters are called super-refractory.
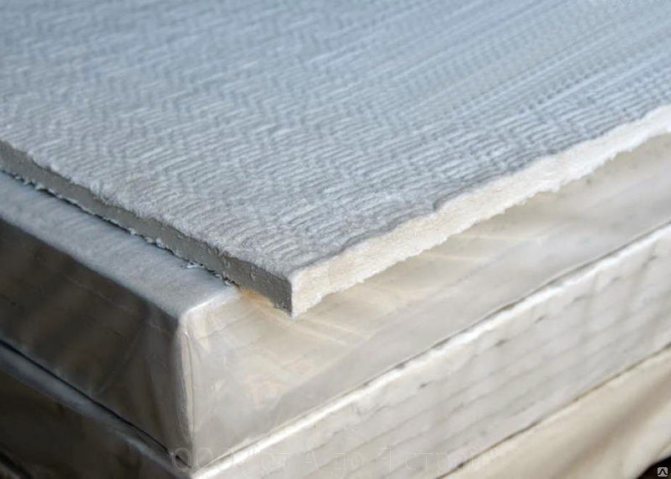


Refractory cardboard MKRKL