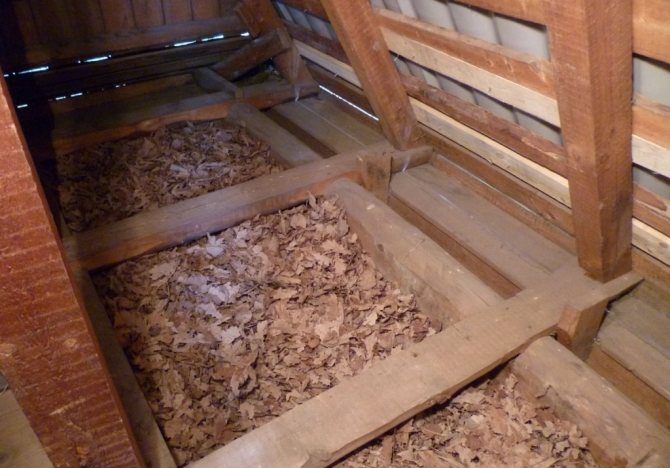
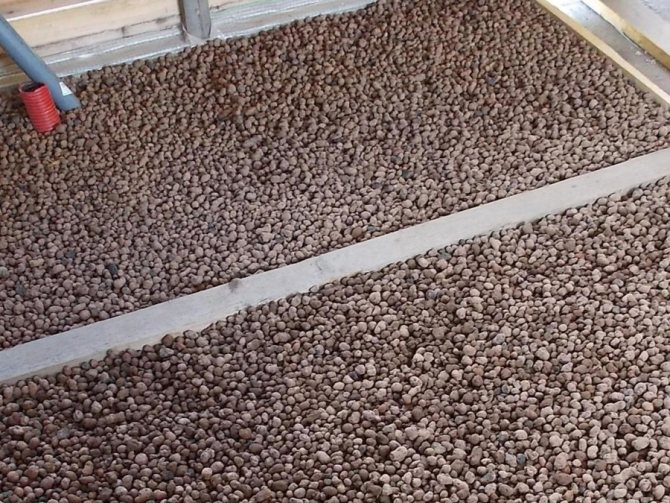
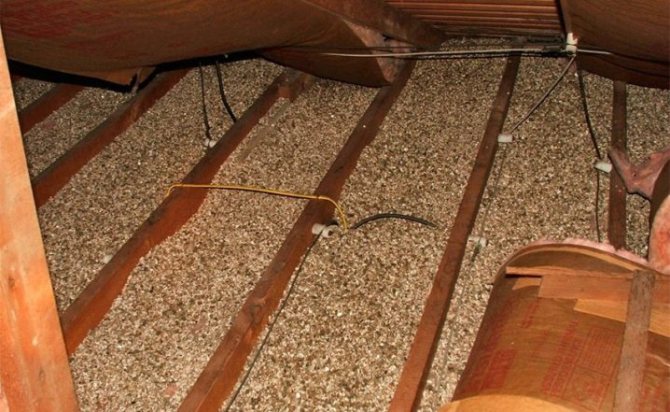
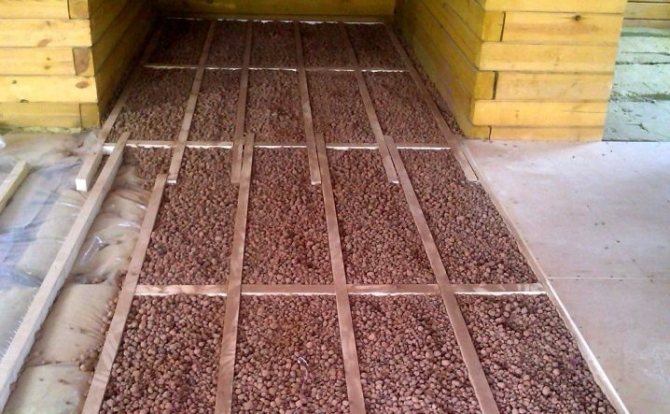
Method of preparation of moistened backfills
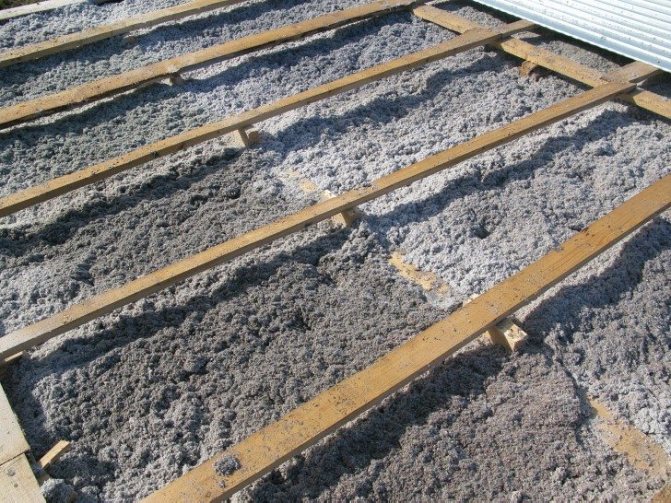
In the interval, binder and organic fillers are covered with layers. Then everything is mixed well and water is added. After 3-5 weeks, the backfill in the structures dries up with light compaction and sediment. Drying time varies with air temperature. Such backfills should not be used in timber frame buildings together with vapor barrier materials (roofing felt, roofing felt, glassine, etc.). They dry out for a long time, and sometimes they cause the formation of fungus. As you know, the fungus is very harmful to wood.
Plates made from organic materials are considered to be of higher quality insulation. Their size should be 50 × 50 or 70 × 70 cm, and the thickness should be from 5 to 10 cm.The ratio of the components for their preparation:
- 1.5 parts of quicklime + 0.3 parts of cement + 2-2.5 parts of water;
- or for 1 weight part of organic aggregate, take 4 parts of clay dough + 0.3 parts of cement + 2-2.5 parts of water;
- or 1-2 parts of trefoil clay + at least 0.7 parts of quicklime (you can have fluff) + 2-3 parts of water;
- or 1.5-2 parts of gypsum + 2-2.5 parts of water.
If lime dough is used, then the amount is doubled, and the amount of water is reduced.
First, dry materials are mixed, then moistened with water and mixed again until smooth. After that, the mixture is put into molds, leveled, the molds are removed and dried under a canopy or indoors. The drying time will depend on the temperature conditions and the binder used. Plates of plaster, lime, tripoli dry 2-3 weeks, clay products - on average about 4-5 weeks.
Frame, frame-panel board, panel board and those walls that are assembled from elements manufactured at the factory are considered more economical.
A wooden frame is a kind of structure consisting of lower straps that are laid along the foundation. Elements of such a frame are connected with nails, bolts. If the frame is cobbled, then staples are used. The frame racks are sheathed with boards. The distance between the outer and inner lining is filled with a special insulating backfill, straw or reed mats, or other slab insulation. In factory-made frame buildings, the outside of the boarding is often covered with asbestos-cement sheathing.
The popularity of insulation in the form of mats or slabs is understandable - they are easy to transport, convenient to work with, while saving time. But often builders use another type of insulation - backfill. It differs from foam or mineral wool boards in its structure. Perhaps, for some jobs, backfill insulation will be preferable.
Insulation is a low-density porous material, the granules of which are produced by firing foamed raw materials at a high temperature. The ease of manufacture is reflected in the low cost of thermal insulation, and the structure also saves on labor costs.
The disadvantages of backfill insulation are:
- their shrinkage by 10-15% of the initial volume;
- loss of thermal insulation properties when wet.
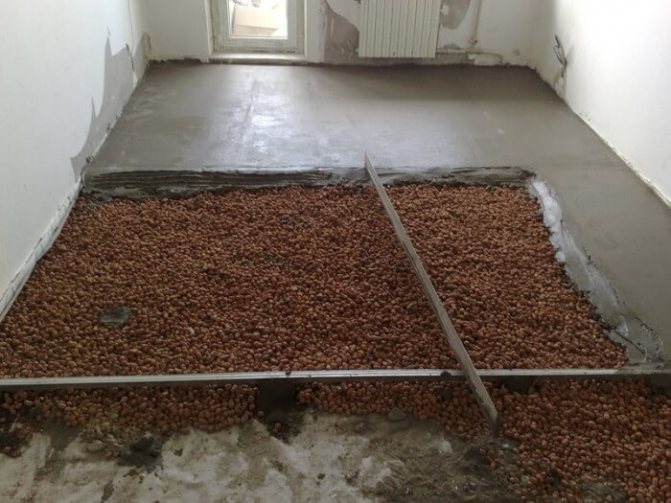
Backfill insulation is used, usually for horizontal surfaces. The job seems simple, but requires careful preparation. For example, when insulating the floor in buildings without basements, the soil is previously compacted and covered with a screed. Next, a waterproofing material is laid on the latter, and insulation is poured onto it. It looks like the situation with the insulation of the roof, only the screed is not required.Instead, a vapor barrier is laid on top of the backfill material.
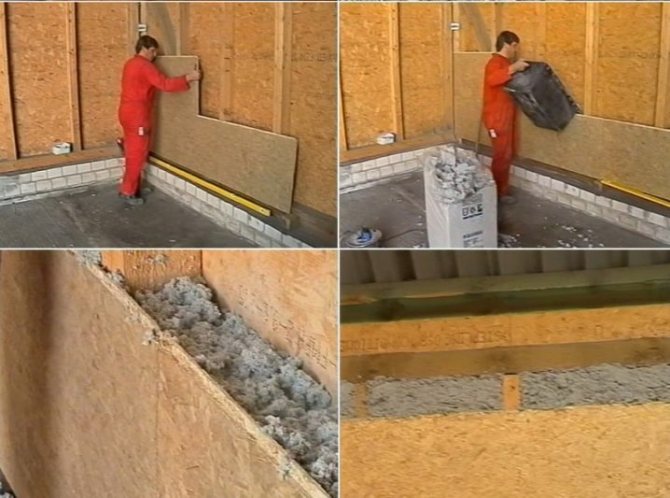
When cladding walls, a frame is pre-built, consisting of durable sheet elements. After that, a heater is poured into the resulting structure.
Backfill methods
The process of filling any insulation is the same: the material is poured into the cavity and rammed. It is recommended that the issue of insulation be resolved immediately when designing a house. If there are no internal cavities for filling insulation, interlayers are made using PVC panels or drywall.
A good option when the insulation is poured between facing and ordinary bricks, between the internal and external masonry. There may be ribs inside so that it is well distributed. Thanks to free-flowing thermal insulation, the walls can not be made thick, which saves costs. There are ready-made concrete products on sale - slabs, inside which there are already cavities filled with expanded clay, they retain heat 50% better than ordinary ones.
Variants
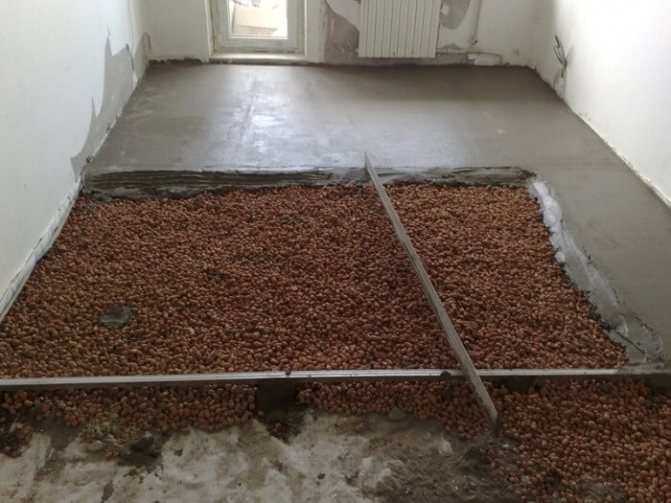
For the floor, such methods of insulation with bulk components are used. The first option is filling (or loose) insulation on the logs. On the floor, logs are made on posts, cranial bars are nailed, then the flooring is made of boards. A vapor barrier is placed on the flooring, expanded clay is poured. Further, if necessary, the next layer of thermal insulation, on it - a screed, a rough wood floor covering.

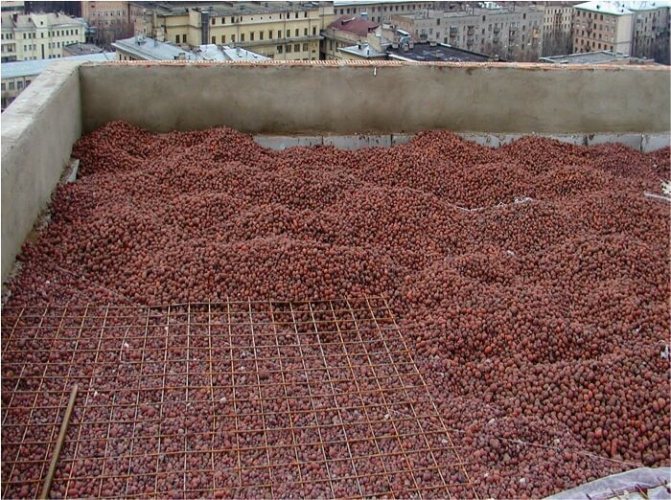
The second option is an embankment on top of a concrete slab. An option for low-quality housing - Khrushchev, for example - when it is possible to raise the floor level. The floor covering is removed, waterproofing is laid, expanded clay is poured on it in a layer of 5 - 10 cm. Then you can put a mesh for reinforcement, and a rough screed is made on it - the basis of the finishing floor covering. A vapor barrier is laid on top of the expanded clay pillow, and another layer of insulation is placed on it.


Finally, the third option is a dry expanded clay screed. A layer of expanded clay is poured, on it - a layer of gravel, then - another layer of expanded clay. The surface is leveled, gypsum-fibrous slabs are laid on it, and any finishing coating on them. published
If you have any questions on this topic, ask the specialists and readers of our project here.
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consumption - together we are changing the world! © econet
Draft dry backfill
The main disadvantage of dry backfills is that they settle and form voids. Therefore, if they are used, then the walls are erected 20-30 cm above the level of the ceiling beams, completely filling with backfill. As it settles, the backfill will fill the empty space. It is better to replace the backfill under the windows with fibrous or tiled materials. If there are none, retractable window sills are mounted in order to fill up the backfill through them.
In order for the insulating backfill to become less free-flowing, materials should be mixed into it, which will turn it into a solid filler. For example, take 85% sawdust and mix it with 10% fluff lime and 5% gypsum. In this case, the sawdust will harden and turn into the so-called thermolite. For such a mixture, wet, not specially dried, organic materials or sawdust are used. Sawdust is mixed with fluff, then this mixture is added to gypsum and immediately laid out in place, leveling and compacting well. The moisture present in the filler will slightly moisten the gypsum and it will set. The aggregate will turn into a loose mass, thicken, and due to this it will not settle.
For ceilings
Just like floors and walls, ceilings require insulation. The insulation materials discussed above may well be used in this case.
A more specific insulation is penoizol. In appearance, it somewhat resembles foam crumbs. This is where the similarity ends, if we do not take into account the characteristics of thermal conductivity.
Penoizol is absolutely non-flammable. Possesses high chemical and biological resistance. Rodents bypass him. For insulation of ceilings, it is good because it has a very low weight. Its density is from 5 to 75 kg / m³. Due to the low thermal conductivity, the thickness of the insulation layer is sufficient from 5 cm. During work, bulk material is used, in sheets and in liquid form.
Note: penoizol gives a slight shrinkage (0.1 - 5%). It is compensated when the work is performed by professional craftsmen using modern equipment. Otherwise, cracking of the insulation is inevitable. (this applies to the use of a liquid fraction).
Considering bulk insulation for the ceiling, one cannot ignore such a widely used material as sawdust. Sawdust is used for insulation as the cheapest material. As an independent insulation, their use is highly undesirable. The fact is that they are prone to decay due to moisture absorption.
They are also an excellent breeding ground for mice. Even if we do not take into account the fact that they are a fire hazardous material, it is not difficult to conclude that they are unsuitable. "Craftsmen" go to all sorts of tricks in order to somehow reduce these negative factors. For this, sawdust is mixed with expanded clay, lime, even broken glass and other building materials. Such measures somewhat improve the properties of the insulation, but not much.
As a conclusion, it should be noted that when insulating ceilings, the advantage is on the side filling heat-insulating materials.
Types of backfill insulation
Hundreds of years ago, in the construction of wooden houses from timber or logs, the very first backfill insulation was used - sawdust. Like modern counterparts, they were quite good in terms of thermal conductivity, but shrank or lost their properties when wet. Today's materials are more advanced in many ways. The most popular of them are discussed in detail below.
Insulation based on clay. It is used as an independent heat insulator for residential or industrial buildings, and in combination with concrete (expanded clay concrete is obtained). Today it is obtained by firing clay shale.
The production technology varies depending on the required size of the final granules.
After examining the marking of the backfill insulation, you can understand what size of granules of the material and for which parts of the house it is suitable. For example, expanded clay sand is used as a heat insulator for the floor or acts as a component of concrete sheathing. Granules with a diameter of 5-10 mm are suitable for pitched and flat roofs, floors, attic; larger than 15 mm - for warming a basement or foundation.


Expanded clay inevitably settles during operation, therefore, during the initial installation, it must be strongly tamped in order to minimize shrinkage. It is recommended to insulate the walls with the material only in regions where the temperature in winter does not drop below -20 degrees.
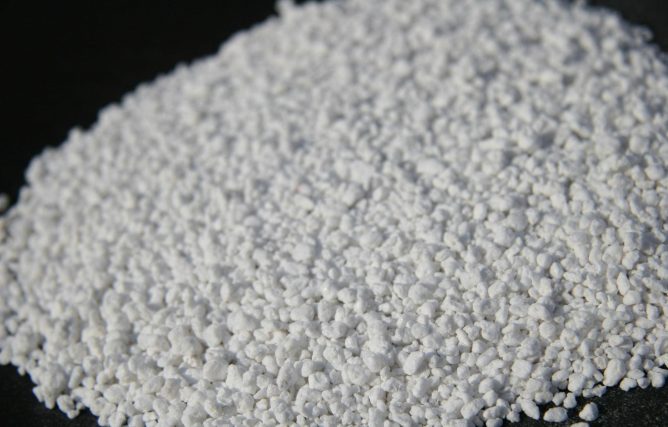
Insulation is made from silicate volcanic rocks using the same technology as expanded clay. When heated to 1000-1200 degrees, moisture evaporates from the surface of the stones, leaving air inside them. The result is white or gray granules with a diameter of 1 to 10 mm. The density of perlite ranges from 75 to 150 kg / m3, and for its color it is also called "glass insulation".
The smallest granules (1-2 mm) form perlite sand used in the following areas:
- insulation of residential buildings;
- production of acoustic materials;
- production of insulating plaster;
- creation of fire-resistant concrete.
Air-filled granules weigh less than expanded clay, therefore they are suitable for thermal insulation of walls.In addition, the material resembles mineral wool, since, in addition to retaining heat, it will prevent the penetration of extraneous noise into the room.


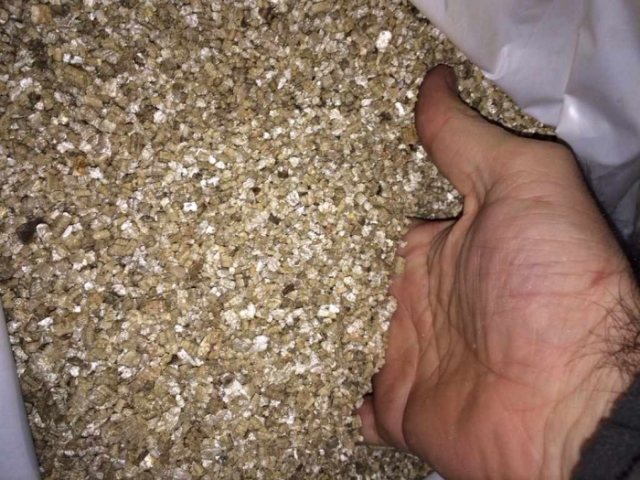
Expanded material from hydrated mica, through heat treatment, increased in volume 15-20 times. Has increased fire-resistant properties, due to which it is used when installing chimneys. Ideal for floors and walls.
A thin layer of vermiculite 5 cm thick will retain up to 70% of the heat of the room. This is enough for roof insulation. For walls, floors and foundations, it is recommended to make a double layer of material.
The density of vermiculite is lower than that of expanded clay or perlite - the largest bulk density is 100 kg / m3. This backfill insulation is supplied in bags of a certain volume, and is used in almost all premises of a residential building.


The advantages of vermiculite include:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity (0.04-0.06), comparable to foam and mineral wool;
- lack of the likelihood of voids and seams;
- high melting point (1400 degrees);
- absence of toxic materials in the composition;
- biological resistance (prevents mold, fungus, is not of interest to rodents);
- good sound insulation;
- the lightness of the material, allowing it to be used in frame houses, on load-bearing systems or foundations;
- ease of insulation work and time saving.
Ecowool.
A relatively new material that appeared on the market only 10 years ago. It is made from recycled paper raw materials, fire retardants (substances that prevent fire), antiseptics. It is safe for humans, resistant to decay, does not spread fire. It is more often used for thermal insulation of walls, mansards or roofs of complex structures.


Varieties of loose insulation
Materials from the group of loose insulation materials are used when repair work has already been completed and it is necessary to fill the voids in the built structures. There are different types of heaters, which are characterized by the following parameters:
- the degree of vapor permeability;
- material;
- weight;
- quality and durability;
- flammability;
- thermal insulation;
- price.
The place where the insulation will be installed also has an impact.
The most important parameter of bulk heat insulators is the material from which they are created. These can be polymers, clay, resin, stone chips and other natural and artificial materials.
Expanded clay
It is one of the oldest and most popular raw materials. It is actively used in modern construction as an insulator. It has an important advantage that simplifies installation - light weight and porosity. Loose expanded clay insulation is made from light-alloy clay. It is an environmentally friendly and safe raw material. Resistant to combustion, does not enter into chemical reactions, does not absorb water. Also, in the expanded clay heat insulator, rodents, mold and fungi do not start. The disadvantages include the accumulation of moisture, which can lead to the destruction of the structure.
It is produced in three types - loose (sand), gravel and expanded crushed stone.
Insulation made from expanded clay is cheaper than analogues. Can be used in conjunction with sawdust.
Granular polystyrene foam
Such insulation is also called polystyrene foam. It consists of a large number of balls, which, when loosened, lose their density and increase their volume. It is used for insulation of ceilings, roofs, floors and cellular installation.
Warming the floor of the house with expanded clay
Expanded clay is one of the most suitable materials for, especially if the budget is limited. Insulation can be carried out in one of several existing ways.
Classic version
provides for the following sequence of actions:


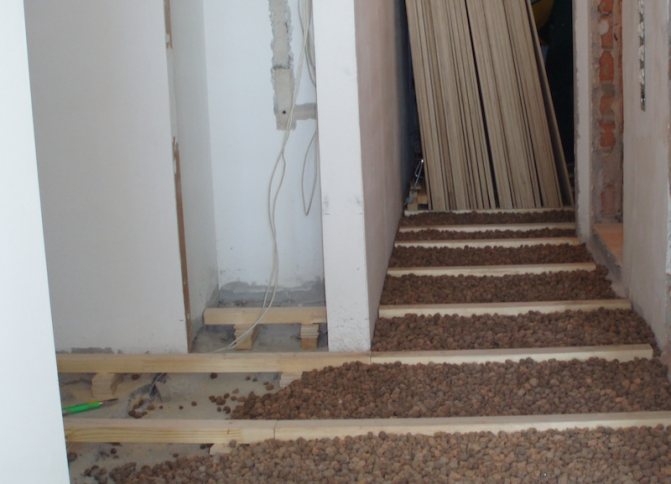
You can do without the time-consuming process of preparing the mortar and pouring the screed using simplified dry technology
:
- a vapor barrier is laid on the surface of the main floor;
- expanded clay is poured over the lighthouses, for reliability it can, of course, be fixed with cement milk;
- dense gypsum-fiber sheets are laid on expanded clay, which are held together with glue.
It is similar to the dry method and insulation option for lags:


Advantages and disadvantages
Loose types of insulation in the majority refer to environmentally friendly insulation (if natural materials were used in the production process). For example, perlite or perlite crushed stone is cast from glass of volcanic origin. Vermiculite is also of mineral origin - granules are formed during the heat treatment of certain rocks. Polystyrene (polymer insulation) does not possess such characteristics - its granules during long-term operation begin to emit styrene into the environment.
The operational advantages of mineral insulation:
- perfectly let steam through, not allowing the walls to get damp;
- serve for a long time without loss of technical characteristics;
- resistant to open fire - withstand temperatures from 1,000 degrees;
- not interested in rodents and insects;
- do not collapse under the influence of high humidity;
- do not lose their shape - granules or crushed stone do not split over time.
The disadvantages include the need to build an additional partition (insulation is filled up between the facing material and the wall). As a result, it requires an expansion of the foundation.
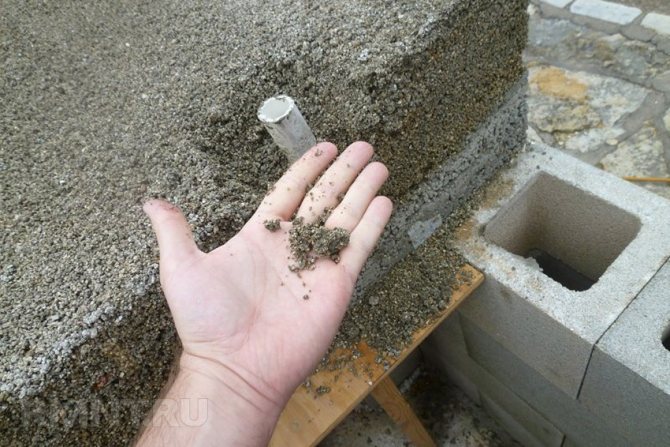


Vermiculite
It is also a natural floor insulation. The material is very hard, non-flammable. The water absorption of vermiculite is over 500%! The insulating properties of vermiculite are simply amazing. With a vermiculite layer only five centimeters thick, heat losses are reduced by almost 80%. The material is protected from mold and mildew. Vermiculite is also sold in bags or in bulk. Under certain conditions, such material can serve almost forever.


Basic elements of frame walls
The frame includes:
- top harness;
- bottom harness;
- walls;
- braces (struts) stiffness;
- additional components such as intermediate ledgers and struts.
Door and window openings are constructed between the racks.
When building two-story houses, two main types of frames can be used:
- With floor counters (when one house seems to be standing on top of another). This type of frame is easier to build as it allows the use of small material.
- With end-to-end racks on two floors. This type of framework is more stable. Long material is used for it.
The supporting pillars of the frame are mounted in the interval of 0.5-1.5 m, focusing on the desired size of doors and windows. Ordinary frame racks are made from boards measuring 5 × 10 cm or 6 × 12 cm. Corner frame racks are made from composite boards or from beams.
The bottom rail serves as the base of the frame. It is made up of logs, planks or beams. The corners of the lower harness are made using the "half-wood straight lock" technique. If floor beams are cut into the harness, then it is made of two crowns. If the floor beams simply rest on the pillars, then the strapping is made from one crown. Usually, the frame elements are fixed with nails, sometimes spikes are used.
To make the frame more stable, plank struts are attached on both sides between the posts. They are cut flush using a frying pan or semi-frying pan strapping. On top of the racks, the upper strapping is fixed and the ceiling beams are cut into it. The top harness is best attached to straight studs. Next, rafters are placed on the beams. Sometimes log (cobbled) beams are replaced with boards (planks) with a section of 5 × 18 cm or 5 × 20 cm and put them on the edge. Outside, the assembled frame is sealed with wooden planks and nailed to the racks with nails measuring 7-7.5 cm.The thickness of the boards is 2-2.5 cm.They can be replaced with asbestos-cement slabs or any other durable and resistant to atmospheric precipitation materials.
Features of the best insulation for walls and houses
One of the most pressing issues in the construction and renovation of a house is high-quality and reliable insulation of walls and floors. This question is relevant for houses that are just being built, and for those that have already been put into operation. When using expanded vermiculite, insulation can be performed in the shortest possible time, and the issue is resolved with great economic benefits.
Vermiculite promotes high-quality heat retention, which, in turn, leads to significant savings in space heating costs.
The porous structure of expanded vermiculite is represented by scaly pieces with a silvery or yellowish tint. Insulation is made using a special technology of accelerated firing. The material is non-toxic, not subject to decay processes, odorless and resistant to the appearance and reproduction of fungi and mold.


Features of vermiculite:
- Provides a high degree of fire protection.
- Has sound-reflecting and sound-absorbing properties.
- Reduces the thermal conductivity of floors and walls.
- Improves the moisture resistance of the entire building.
- Chemically inert.
If a fire starts in the room, then when exposed to high temperatures, vermiculite does not emit toxic gases harmful to health. This insulation is used in almost all branches of construction, as it is not exposed to fire. When warming the surface, vermiculite penetrates deep into voids due to a sufficient degree of fluidity.
Features of internal thermal insulation
When the placement of insulation from the inside is the only solution, the installation process and the choice of material must be approached responsibly, taking into account all the recommendations of specialists.
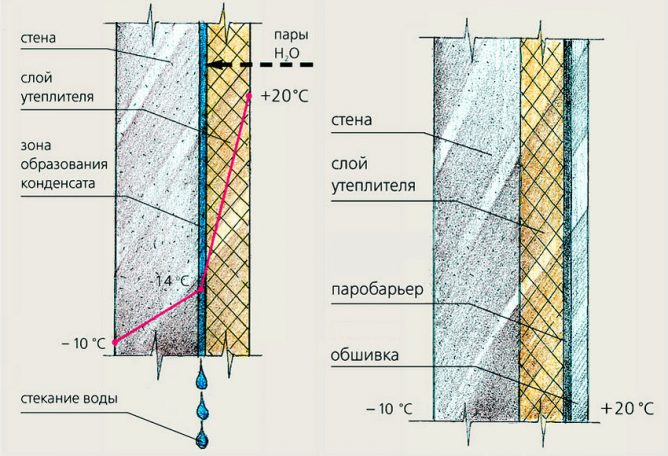
What is dew point and why should it be considered? This is the place where room steam converts to condensation at a certain temperature. With external insulation, the wall is heated by heating devices, and is protected from external influences by heat-insulating material.
In this case, the dew point is in the thickness of the wall, and its surface remains dry. If the insulation is placed inside, the structure freezes and moisture appears when it comes into contact with steam. The only way to prevent dampness and fungus growth is to use a vapor barrier. The dew point will remain inside, but moisture will not flow to it and the wall will remain dry.

Expanded clay production and fractions
For the production of expanded clay used low-melting clay grades
with a quartz content of 30%. They are processed in special chambers, where they are heated to a temperature of 1050-1300 0 С for 30-40 minutes, as a result of which swelling and formation of porous granules with a melted hermetic shell, which gives the material the necessary strength, occurs. The more pores in expanded clay, the better.
In the production process, as a rule, granules of different fractions:
- expanded clay sand
with a granule size up to 5 mm; - expanded clay crushed stone
- granules resembling cubes; - expanded clay gravel
- elongated granules.
By the size of granules, expanded clay of such fractions is distinguished: 5-10 mm, 10-20 mm and 20-40 mm.


Material features
There are several types of bulk material for insulation. Each of them has its own properties. List of loose heaters:


- expanded clay;
- expanded polystyrene granules;
- foam concrete crumb;
- ecowool;
- sawdust and sand;
- boiler slag;
- vermiculite.
Expanded clay
The usual appearance of this material is round or oval granules. Granules or other form of material is porous and very light (some species can stick to the surface of the water). Expanded clay is formed as a result of firing light-alloy clay.It is absolutely non-flammable, safe, environmentally friendly in its composition.


The material can be in three forms:
- sand with a grain size of 0.14 to 5 mm. It is used as a filler for lightweight concrete and for floor insulation;
- expanded crushed stone from expanded clay are granules with a fraction of 5–40 mm. The best option for thermal insulation of foundations and floors of residential premises;
- expanded clay gravel. Rounded granules 5–40 mm with a melted surface, absolutely fire resistant. Inside, they have closed pores, which gives them excellent frost resistance. Such gravel is recommended for insulating attic floors: the material is lightweight, has low thermal conductivity.


The size of its fraction must be present in the marking of the material:
- 5–10 mm - floors and roofs;
- 10–20 mm - baths and saunas, able to keep the temperature and humidity in the room for some time;
- more than 20 mm - for foundations and basements.
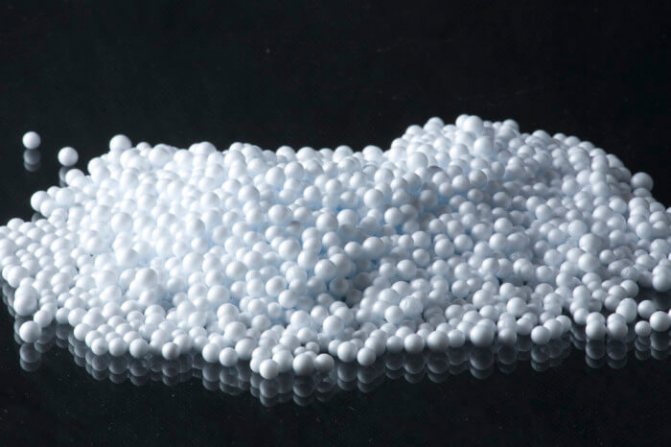
Styrofoam granules
This is the most controversial bulk material. It is a very light, airy white granules. It is used as a backfill when insulating roofs and walls, it is also used as an additive in a mixture for insulating concrete.


The disadvantages are toxicity and flammability, but its properties are not yet fully understood. Instead, it is recommended to use granulated foam glass. Expanded polystyrene is cheap, convenient for insulation by means of well masonry.
Vermiculite
It is a mica-based laminate. In the process of its manufacture, no chemical additives or impurities are used. It is an excellent option for insulating loggias, rooms. It is used as an energy-efficient interior and exterior cladding for housing. For the floor and walls, a layer of at least 10 cm is recommended, for the roof - at least 5 cm. Backfilling with this material 5 cm thick reduces heat loss by 75%, 10 cm - 92%.


- high air permeability of the insulation - the material is porous - which allows the walls to "breathe", ideal for natural circulation, air renewal and providing a microclimate in the room;
- environmentally friendly, without toxic substances;
- non-combustible, fireproof, belongs to the flammability group G1;
- fungi, mold, rodents, insects are not afraid of such isolation;
- special skills or experience, no special tools are needed to fill it. The layer of material is simply filled up and compacted. Additional fasteners are not needed;
- service life - more than 50 years.


For walls, a vermiculite backfill thickness of 10 cm is sufficient, for attics, roofs, interfloor floors - 5 cm. When laying, it is advisable to use a vapor barrier film - this will additionally protect the insulation from moisture.
Sawdust and sand
These are traditional heat-retaining materials used in attics and basements for centuries. Disadvantages: poorly insulated from moisture, pests can start in them. Sawdust - combustible, susceptible to mold, mildew. It is still recommended to use more modern materials.


For insulation, not ordinary sand is used, but perlite. It is lightweight, less hygroscopic, and resembles mineral wool in its characteristics. Due to its low bulk density, it does not create a load on the walls, does not expand them.
Ecowool or cellulose
The components of this insulation are ecowool (7%), shredded paper (81%), antiseptics (12%) and antipyrine (7%). The material is non-flammable and does not rot due to special impregnations. It has been used in the world for more than 80 years, in the CIS, it has been known over the past decade.


Boric acid is used as an antiseptic in this material, and borax is used as a fire retardant. These substances are environmentally friendly.
Non-absorbent insulation: use cases
Thermal insulation is an important stage in the construction of a house.Vermiculite is especially often used for insulating wooden buildings, as it has moisture-resistant properties. Vermiculite is made from mica. There is a liquid in the material, which evaporates when heated strongly, then leads to the expansion of the material.
Loose dry material is not afraid of rodents, insects and birds. In dry material, pathogens cannot start.
The material has unique properties: it picks up excess moisture, while remaining completely dry in the depths. Sometimes houses are fortified with a mixture of vermiculite and sawdust. Sawdust has good thermal insulation properties, but fungi and mold can grow in them.
What vermiculite can be used with:
- Styrofoam;
- Sawdust;
- Drywall;
- Warm plaster.


Vermiculite is often used for wall insulation when constructing a new building. This type of thermal insulation material is sometimes used as a filler in the production of heat-resistant concrete. The material is also used for plastering walls and ceilings. Granular vermiculite perfectly fills voids of different depths. The type of vermiculite does not affect its functionality.
Vermiculite properties:
- Reliability;
- Strength;
- Durability.
When using the material, it is important to remember that thermal insulation must be performed in accordance with all the rules, otherwise even the most reliable material can deteriorate. When performing thermal insulation with this type of material, one should not forget about the mandatory waterproofing and vapor barrier. Layer placement is a very important step - it must be done correctly. It is worth noting that when insulating the roof, vermiculite in granules is placed on a vapor barrier film. Vermiculite is widely used in construction, during its existence due to its unique properties, it has gained wide popularity and popularity.
For walls
To preserve heat in the house, you need to insulate not only the floor, but also the walls. And not only from the inside, but also from the outside. The choice of heaters is large, but I want to choose the best of them. To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of insulation and choose the one that suits the most.
The following materials are widely used for wall insulation:
The list of heaters is represented by a very wide range. Bulk insulation is still in great demand. The same old proven heaters that are used for the floor have proven themselves excellently. More modern ones also appeared. For example, foam glass is very popular among builders.
This environmentally friendly material is chemically resistant and does not lend itself to biological degradation. Granulated foam glass is used not only as an independent backfill, but also as a base for heat-insulating plaster. It is obtained from foamed raw granules. It is produced in the form of slabs, crushed stone and in granular form of various fractions.
It is worth noting: granulated foam glass is absolutely not afraid of groundwater. Therefore, in addition to walls, it can be safely used for insulating foundations and basements.
Penoplex - granules made of foamed polymers. It is realized in the form of slabs or chips. Absolutely non-absorbent. Very lightweight material. Requires protection from sunlight and chemical attack.
Please note: Penoplex can only be used in the operating temperature range (from -50ᵒC to + 75ᵒC).
For work on wall insulation, loose foam is very convenient. Especially when making the walls of the frame structure. Having in its composition very small granules (from 0.1 mm), it is able to penetrate into the smallest voids.
Expert advice: it is not recommended to use penoplex for insulating the walls of baths and saunas.
Mineral wool is widely used for insulating not only walls. Granule size from 10 mm. Has good vapor permeability. Fireproof. Does not change its properties up to 1000ᵒ С.Good sound insulator. Recommended for internal insulation. Sold in bags, in bulk, in rolls. When working with mineral wool, it is necessary to take measures to protect the respiratory tract and skin.
Please note: wet mineral wool significantly reduces its thermal insulation parameters. It is very difficult to dry .. Summing up, it can be noted with confidence that as a heater for walls, the leading place is taken by bulk heaters
Summing up, it can be noted with confidence that bulk insulation takes the leading place as a heater for walls.
Insulation of walls and ceilings
To keep the house warm and comfortable, it is necessary to insulate the outer walls. For this purpose, foam glass can be used, a granular eco-friendly material obtained from raw fractions by foaming. Such insulation for walls is chemically resistant and can be the basis of heat-insulating plaster. Foam glass is ideal for warming basement walls and foundations, since it is not afraid of groundwater.
Foamed polymer granule is the basis of polystyrene foam, lightweight and moisture-resistant heat-insulating material. Such a heat insulator does not have a very wide range of operating temperatures, therefore it is not recommended to use it for thermal insulation of baths. Frame walls can be easily filled with Penoplex. In this case, the granules fill the smallest voids.
Mineral wool for wall insulation can be used not only in the form of usual slabs or rolls, but also in the form of granules larger than 10 mm. Such bulk insulation is vapor-permeable and fire-resistant, not afraid of high temperatures. In addition to thermal insulation properties, granular mineral wool has good sound insulation properties. When laying mineral wool, it is necessary to provide protection for the skin and respiratory tract.
Mineral wool for wall insulation can be used not only in the form of usual slabs or rolls, but also in the form of granules larger than 10 mm.
To preserve heat in the premises, thermal insulation of the ceiling is often performed. Recently, penoizol, which outwardly resembles foam crumbs, has gained popularity. This lightweight, low-density material is highly bio-resistant. In such an insulating layer, rodents and mold will not start.
When choosing heat-insulating bulk materials, one should pay attention to such characteristics as thermal conductivity, density, moisture absorption, weight and size of the fraction. Most of the bulk insulation can be delivered and installed independently, which will significantly reduce the cost of insulation work, which is especially important for owners of summer cottages and small country houses.
An interesting argument comparing two types of insulation:
For floor
In any construction, the utmost attention is paid to thermal insulation. Floor insulation has not been ignored either.
Bulk insulation is best suited for this.
The most common among them are:
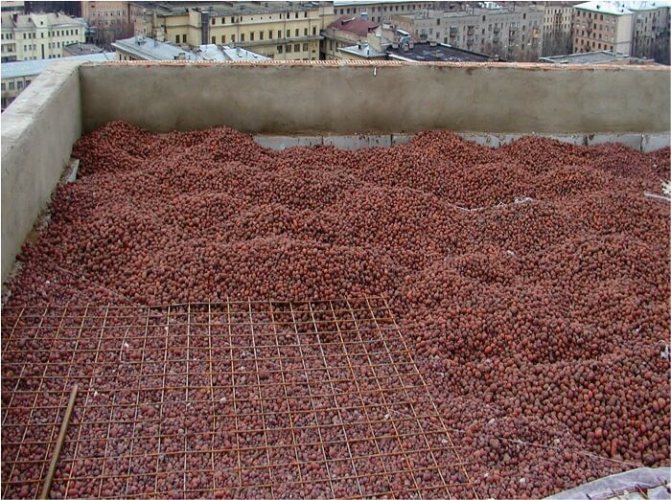
Expanded clay in floor insulation is the most massive insulation material. Low price, mass production and high thermal insulation properties played an important role in this. And, although it is made from clay, the result is a fairly light product. Weight of 1 m³ on average 350 kg.
It is appropriate to mention that expanded clay is the most environmentally friendly material. Not susceptible to moisture and at the same time frost-resistant. Sold in bags or in bulk. Expanded clay can be used as an independent insulation, and in combination with concrete. Expanded clay concrete not only retains heat, but in addition is also a very strong substrate, base.
The next representative of bulk insulation will be perlite. Its origin is volcanic rocks.
A distinctive, only inherent feature, a high percentage of moisture absorption.Studies have shown that it is able to absorb four times its own weight in moisture. It is because of this that it is recommended for warming rooms with high humidity.
Environmentally friendly natural material that does not enter into any chemical reactions. Possesses high fire resistance.
Withstands temperatures up to 900ᵒ С. Having porosity up to 40% it is an excellent insulation. For insulation, it is used in the form of perlite sand. You can buy it in the same way as expanded clay, in bags or in bulk.
This is interesting: Perlite is not only used in construction, it is also used to filter vegetable oil, fruit juices and beer.
Vermiculite is also an excellent natural insulation. Differs in its hardness. Along with high fire resistance (up to 1200ᵒC), it has an impressive moisture absorption coefficient - more than 530%. Possesses amazing thermal insulation properties.
With a layer thickness of only 5 cm, heat loss is reduced by 75%. It is an environmentally friendly material. Possesses high chemical and biological resistance. Prevents mold and mildew growth. Having a small volumetric weight, it does not create a load on the foundation. It is sold, like all bulk insulation - in bags and in bulk.
For floor insulation, not only bulk insulation is used. Polyfoam, mineral wool, liquid insulation, cork and a number of others are also often used. Each of them has both positive and negative sides. Some are very good, but expensive. For example, cork insulation. Others, like Styrofoam, are not fire resistant.
A good floor insulation is obtained from ordinary sawdust, but it requires special antiseptic treatment. In addition, it shrinks very quickly and cakes. The most optimal parameters for floor insulation are bulk insulation.
Please note: loose insulation tends to shrink. Dense compaction reduces its size.
Expanded clay
This is a bulk insulation. The most popular in its class for today in the issue of floors. Expanded clay is quite inexpensive, and the material also has excellent thermal insulation properties. The insulation is made of clay, but at the exit the expanded clay is very light, a cube of such material weighs no more than 350 kilos.
Do not forget that expanded clay is one hundred percent environmentally friendly and non-combustible material, it is not afraid of water and is frost-resistant. Usually such material can be bought either in bags or in bulk. It is noteworthy that expanded clay is both a heater and an excellent substrate or base. The service life of such a material is calculated practically for centuries!
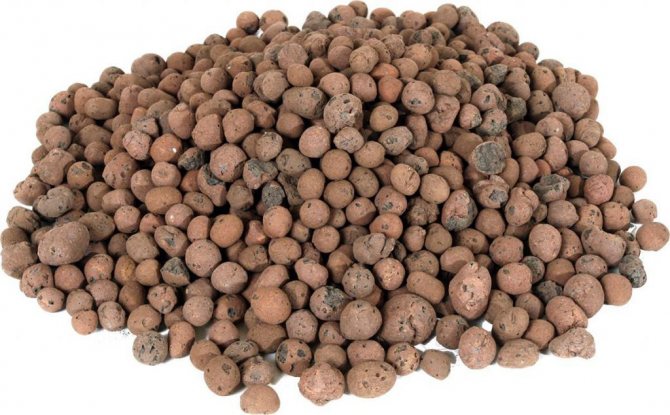


View gallery
Warming the walls of the house with expanded clay
For wall insulation with expanded clay, use three-layer masonry method
, which is applicable only for newly erected houses: the first layer is the load-bearing wall, the second layer is expanded clay with cement milk, the third layer is the external finish. There are three technologies:
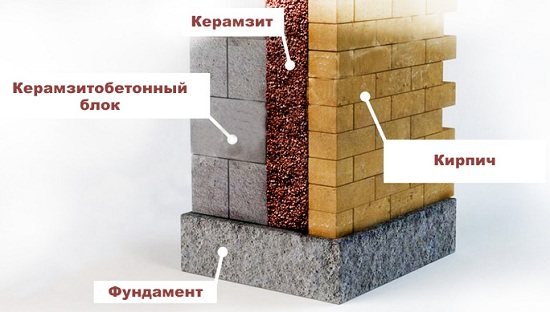

If they are insulated walls
, then expanded clay insulation must be tamped very carefully.
Walls
the most difficult thing to insulate with expanded clay. Since its thermal insulation properties are somewhat worse than that of its closest competitor, it is necessary to leave cavities 20-40 cm thick, and this is a significant load on the load-bearing walls, so an additional foundation will have to be made outside. The complexity of the technology and the cost of all additional manipulations practically negates the efficiency of expanded clay insulation, so for wooden houses it is better to consider another option for wall insulation.


The main advantage of timber frame walls over log walls is that they require less wood to produce. Frame houses are always warm, with good sound insulation, and most importantly, they are easy to build.
The best insulation: 4 characteristics
Usually vermiculite is used to insulate the walls and floors of a wooden house. The material is distinguished by its chemical neutrality and safety. Insulation is produced in various states: plates, powder, thick paste.
The thickness of the insulation in the form of slabs can vary from 20 mm to 60 mm. Pits can be safely cut into the required pieces using an ordinary construction knife.
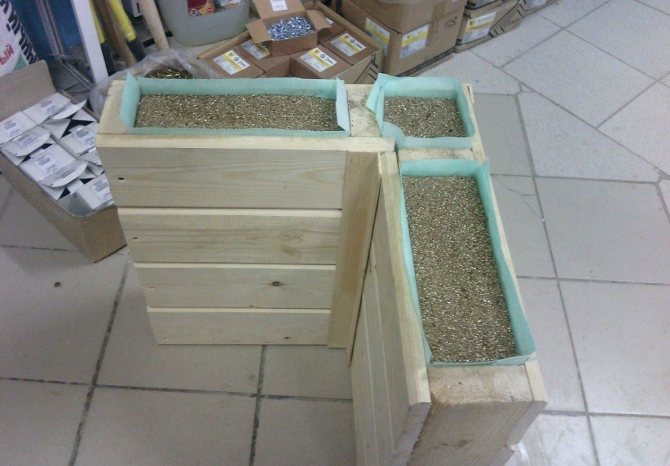


One person can insulate a house with vermiculite. The thermal conductivity of vermiculite significantly exceeds the thermal conductivity of heat-concrete. The material has thermal insulation properties due to its high density.
Vermiculite characteristics:
- High degree of strength;
- High density of the internal structure;
- Ease of installation;
- High moisture resistance.
In the production of heat-insulating material, a special technology is used, which assumes the presence of cavities with closed circuits. This structure makes the material very moisture resistant during the entire operational period. Vermiculite, intended for insulation of floors, walls and ceilings, has a rather high cost.
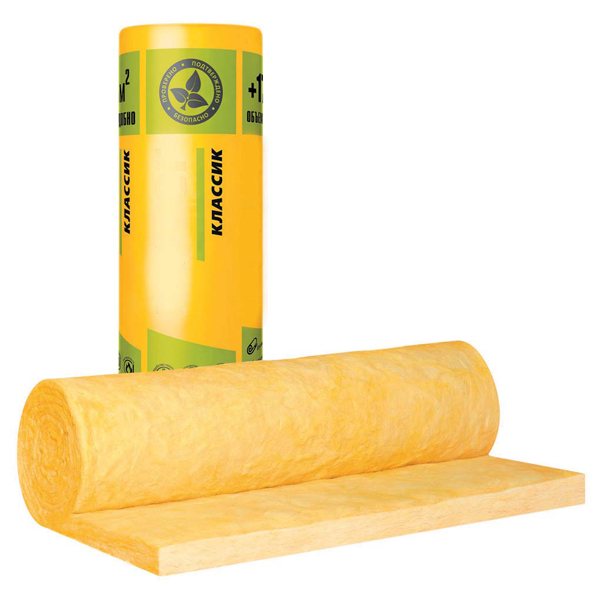
Features of insulation with mineral wool
Although the material is not vapor-tight, it is often used for DIY interior insulation. Among the advantages of mineral wool:
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity - 0.04-0.45;
- does not support combustion;
- basalt wool slabs are easy to install;
- affordable cost;
- excellent sound insulation.
Insulation can be installed in residential and non-residential premises, for which cheaper glass wool is suitable. It is fireproof, frost, rodent and mildew resistant. The disadvantages of the heat-insulating material are high hygroscopicity and vapor permeability. Mineral wool is used for DIY insulation of brick and concrete walls, but it is not recommended for wooden houses.


Installation of thermal insulation is carried out using the following technology:
- The surface of the wall is covered with a layer of anti-fungal impregnation.
- With the help of a laser level, a line for attaching the starting profile is outlined along the entire perimeter of the future structure.
- A waterproofing sheet is laid on the wall and attached to the floor and ceiling.
- The guide profile is fixed according to the markings made. After its attachment, the locations of the vertical posts and hangers are marked. The step of the CD wall profile is 60 cm, which allows one 120 cm drywall sheet to overlap two cells and reduce the number of joints.
- To insulate the vertical surface, mineral wool is used in slabs. Such material facilitates installation and does not shrink over time. Plates should fit snugly into the designated sections, but not crumple, otherwise their characteristics will deteriorate.
- A vapor barrier film is mounted on top of the insulation. It is recommended to use penofol - foamed polyethylene foam. The reflective layer will protect the room from heat loss and prevent steam from penetrating into the mineral wool. A layer of foil is directed towards the room, the joints of the canvases are glued with special tape.
- The installation of drywall sheets completes the thermal insulation. They are attached to the galvanized profile with self-tapping screws.
The service life of the insulation is up to 10 years. When installing mineral wool, it is imperative to protect the skin, eyes and respiratory system from small fibers.
Insulation of walls from the inside is carried out in exceptional cases
It is important to use a material with suitable characteristics and carefully seal the wall with a vapor barrier film. In order not to violate the integrity of the finish, it is not recommended to install sockets and switches on it.
Backfilling process and its features
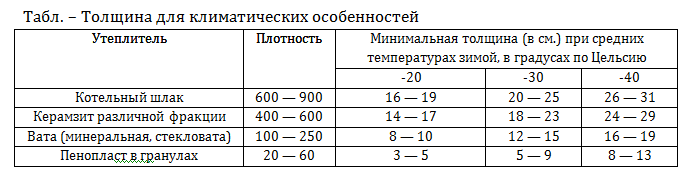
Thickness table for temperature conditions:

Recommendations
For backfill, there are the following recommendations.Firstly, bulk material settles over time, so it needs to be tamped well. It is advisable to use boiler slag and expanded clay in regions where temperatures do not drop below -20 ° C in winter. Insulation of pitched roofs with expanded clay and similar compounds is carried out outside, after laying the vapor barrier. Along the slope between the rafters, transverse stops are installed - they evenly distribute the insulation.
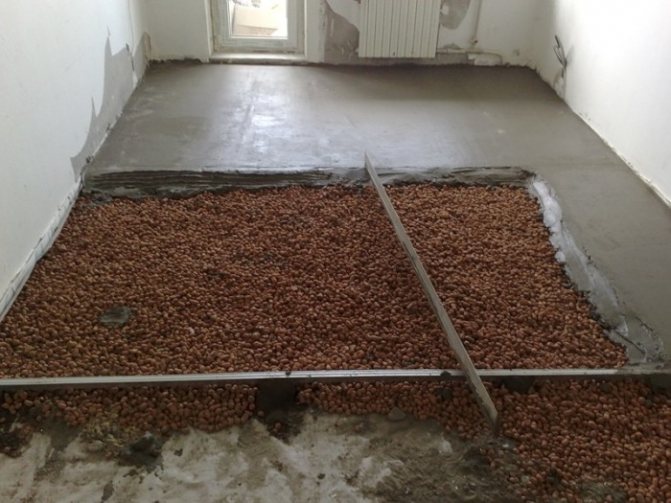


After laying on the floor or in the basement, it is well rammed to prevent shrinkage and deformation of the finish. The only problem is moisture ingress, loose insulation is quite hygroscopic. In baths and saunas, and, incidentally, everywhere, the insulation layer should have high-quality hydro and vapor barrier. It is necessary to ensure that there are no cracks in the decoration, and bulk material does not wake up through them. It is also worth remembering that expanded clay is quite heavy. It is necessary to ensure that with its mass it does not burst too weak partitions or walls.
Scope of backfill insulation
Since the material in question is light and almost does not make the structure heavier, it is usually used when sheathing a sloped roof. It also finds application in the insulation of such areas of houses:
- attic floors;
- attic;
- frame structures (walls);
- floor, foundation;
- horizontal partitions between floors;
- brick walls.
The optimal combination, price, quality, as well as the combination of lightness with reliable thermal insulation contributed to the growth in demand for the considered backfill insulation. If the house needs good protection from the cold, and there is little time for work, expanded clay, perlite, vermiculite and ecowool will act as excellent assistants in the implementation of the plans.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YmB-_dss9ow