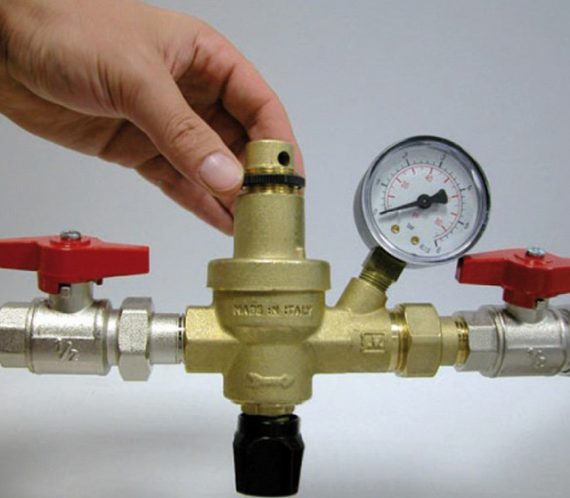
The reasons for the increase in pressure. Ways to solve the problem
To understand that there is too much pressure in the system, you can use the manometers. Normally, the readings are 1-2.5 bar. If the pressure gauge needle reaches 3 Bars, sound the alarm. If the increase is constant, it is urgent to find the cause and reduce the pressure.
Also pay attention to the safety valve: to relieve pressure, it will constantly exude water
The case in the expansion tank
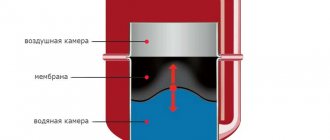
This tank can be located separately from the boiler or be part of the structure. Its function is to draw in excess water when heated. The hot liquid expands, it becomes 4% more. This surplus is sent to the expansion tank.
The size of the tank is influenced by the power of the boiler. For gas equipment, its volume is 10% of the total amount of the coolant. For solid fuel - 20%.
Diaphragm rupture. If the part is damaged, the coolant is not restrained by anything, therefore, it completely fills the expansion tank. Then the pressure starts to fall. If you decide to turn on the tap to add water to the system, the head will rise above normal. Leaks will appear in the connections.
Replacement of tank or diaphragm is required to relieve pressure.
Pressure below or above normal. A machine pump will help to achieve normal values (nominal) in a gas boiler.
- Drain all water from the system.
- Close the valves.
- Pump the circuit until you are sure there is no water.
- How to release the air? Through the nipple on the other side of the inlet.
- Download again until the indicators reach the norm specified in the instructions for "Ariston", "Beretta", "Navien" and other brands.
The location of the tank after the pump provokes water hammer. It's about how the pump works. When it starts, the head rises sharply, and then also drops. To avoid such problems, in a closed heating system, install the tank on the return pipe. The next pump cuts in front of the boiler.
Why the pressure rises in closed systems
Air accumulates in a double-circuit boiler. Why does this happen:
- Incorrect filling with water. The fence is drawn from above, too fast.
- After the repair work, the excess air was not deflated.
- Mayevsky's air release taps are broken.
The pump impeller is worn out. Adjust or replace part.
Fill fluid correctly to relieve or reduce pressure. The intake is carried out from below, slowly, while Mayevsky's taps are open to bleed off excess air.
Open system problems
The problems are the same as described above.
It is important to properly fill in water and bleed air. If after this the pressure has not returned to normal, it is necessary to drain the system.
Secondary heat exchanger
The unit is used to heat hot water. Its design consists of two insulated tubes. Cold water flows through one, hot water through the other. In case of damage to the walls, the appearance of a fistula, the liquids mix and enter the heating part. Then there is an increase in pressure.
If you do not want to repair and solder the heat exchanger, you can replace it. To do this, buy a repair kit and get to work:
- Close the supply valves.
- Drain the water.
- Open the case, find the radiator.
The assembly is secured with two bolts. Unscrew them.
- Dismantle the defective part.
- Install new gaskets in the mountings and connect the heat exchanger.
Other reasons
There are other reasons for these problems:
- Overlapped fittings. During the intake, the pressure rises, the safety sensors block the equipment. Inspect the taps and valves, unscrew them all the way. Make sure the valves are working.
- Clogged mesh filter.It gets clogged with debris, rust, dirt. Remove and clean the part. If you don't feel like cleaning regularly, install a magnetic filter or a flush filter.
- The make-up valve is out of order. Perhaps its gaskets have worn out, then you can get by with a replacement. Otherwise, you will have to change the tap.
- Problems with automation. Faulty thermostat or controller. The reason is wear, factory defect, incorrect connection. Diagnostics and repairs are carried out.
Check whether the boiler protection parts are in good working order: pressure gauge, valve, air vent. Clean radiators and other components from dust, soot, scale. Prevention helps prevent serious damage to gas equipment.
Other problems
In addition to the above reasons, there are other moments when the pressure in the heat generator rises above the norm:
- Shut-off valves closed or insufficiently open. The head on the supply stream increases, the unit is blocked. To release the pressure, open the valves all the way, check if the stopcocks are leaking.
- The dirt filter is dirty. Washing the filter will help to reduce the pressure, if it is completely in poor condition, replace it with a new one.
- Faulty make-up tap when water drips from it. The liquid from the water main, where the pressure is about 2.5-3.5 bar, flows into the heating circuit, where the pressure is less.

Make-up tap in the heating system
As a result, the pressure in the heating circuit increases. In order to reduce it, replace the tap, but most often the replacement of the gasket is required, it wears out quickly, especially if the water is very hard.
Pressure drop
An increase in pressure in closed heating systems is not the only problem, in some cases there is a sharp drop in operating pressure, while among the reasons why the pressure level drops, the following should be highlighted:
- hidden leaks of the system, the appearance of corrosion, loosening of connections, leaks of fittings;
- rupture of the tank membrane, which requires replacement or repair of equipment;
- pressure drops in the system are observed if the nipple is poisoned, such an air leakage leads to a deflation of the tank, and this causes damage to the membrane;
- there are cracks on the boiler heat exchanger, which leads to a coolant leak;
- pressure drops associated with the appearance of air bubbles lead to a decrease in the overall temperature in the system and its shutdown;
- one of the reasons for a decrease in pressure can be a sour or slightly open tap used to discharge water into the sewer system.
Other problems
In addition to the above reasons, there are other moments when the pressure in the heat generator rises above the norm:
- Closed or insufficiently open shut-off valves. The head on the supply stream increases, the unit is blocked. To release the pressure, open the valves all the way, check if the stopcocks are leaking.
- The dirt filter is dirty. Washing the filter will help to reduce the pressure, if it is completely in poor condition, replace it with a new one.
- Faulty make-up tap when water drips from it. The liquid from the water main, where the pressure is about 2.5-3.5 bar, flows into the heating circuit, where the pressure is less. Make-up tap in the heating system
As a result, the pressure in the heating circuit increases.In order to reduce it, replace the tap, but most often the replacement of the gasket is required, it wears out quickly, especially if the water is very hard.
How to increase the pressure in the boiler


If the pressure drops due to the expansion tank, then its volume is incorrectly calculated or the inner diaphragm is damaged. The situation is corrected by a more accurate calculation of the required volume or by replacing the tank.
If the pressure in the heating system drops immediately after its first start, then this is the norm. The freshly filled circuit, if filled with ordinary tap water, is full of air. As soon as it is converted to bubbles and removed from the pipes, the parameters of the contour are normalized. You can also try to remove the bubbles by hand using a manual air release.
Worst of all, if the pressure has dropped in the system laid inside the walls and floors - pipes are often masked and completely recessed in building structures. If something happens to them, you will have to thoroughly suffer in order to localize the malfunction. The situation can be prevented by a more careful choice of materials for building a heating circuit.
Before raising the pressure, it is necessary to check the tightness of the system. To do this, you need to inspect:
- All heating devices - often leaks form where they connect to pipes. Leaks between individual sections are also possible;
- Pipes - microcracks often lead to leakage of the coolant, due to which the pressure gradually drops;
- Fittings are another common place for coolant leaks;
- Boilers - double-circuit models have a complex internal structure; it is necessary to inspect the circulation pump, three-way valve and heat exchanger.
It is best if a specialist takes over the inspection of the double-circuit boiler.
Increased pressure in the heating system causes an imbalance in the operation of the equipment, frequent blockages of the boiler. As a result, individual elements are subjected to increased stress, which leads to circuit breakdowns and equipment failure. Why is the pressure in the heating system increasing? There are several reasons for this phenomenon, most often these are leaks, imbalance in the operation of individual elements, a malfunction in the automation or incorrect settings.
Air lock as a cause of pressure increase
Another possible reason why the pressure itself rises is the presence of air in the heating circuit.
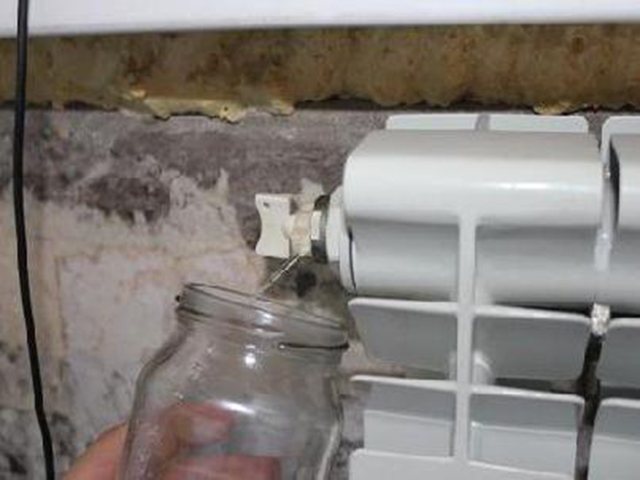


Airborne exposure can occur due to:
- when the heating circuit fills up too quickly with liquid - the system should be filled slowly, with the air release valves open. The valves are open until liquid flows from the highest point of the system;
- Mayevsky's taps are broken, change taps;
- the impeller of the circulation pump has become loose, because of this, air may enter, adjust the impeller.
Norm and control
We have already said that the pressure in a gas boiler should be in the range of 1.5-2 atmospheres - this is the norm for a system that is put into operation and is in a heated state. In multi-storey buildings heated by centralized boiler houses, this figure is higher. Here, pipes and batteries must withstand not only high pressure, but also water hammer - this is an abrupt increase in pressure.
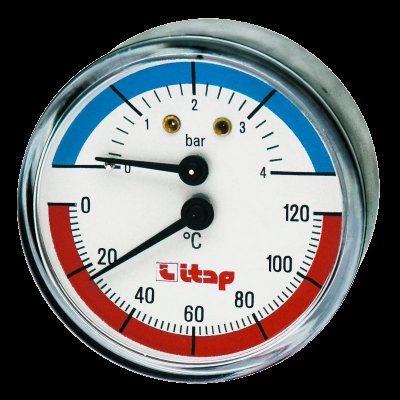


If drops are typical for centralized systems, then for autonomous heating they are rare - the volume of the coolant here is not so large that serious jumps are observed. In a cold state, the normal indicator is 1-1.2 atm., And in a heated state, a little higher.
In private households, autonomous heating systems are used, powered by single-circuit and double-circuit boilers. The latter are becoming more widespread. In addition to heating, they solve the problem of preparing hot water. One circuit in them heats the coolant circulating through the pipes, and the other ensures the operation of the hot water supply system.
If there is no expansion tank
The expansion tank for the domestic heating network is the second most important element (after the boiler). Water, with a change in temperature, changes in volume. The volume inside the circuit is always constant, therefore, an expansion tank is additionally connected to the circuit, where excess coolant can be diverted, i.e. performs the function of a compensator. Consequently, RB is a safety device that prevents emergency situations - an increase in pressure, depressurization of pipes, etc.
The use of boiler equipment without an expansion tank is highly discouraged.
For stable operation, the pressure of the RB must correspond to the volume of the system, since when replacing radiators with pipes, the volume of the coolant must be increased. At the same time, too large RB will not maintain the operating pressure in the circuit.
The standard is an expansion tank, designed for 120 liters of heating medium in the circuit (typical two-room apartment). If the tank is too small, then the water will be discharged during heating and expansion through the safety valve. When the boiler is turned off, when the liquid temperature decreases, the boiler will not start up, because its volume, and, therefore, the head will be insufficient. In such cases, additional power supply is required.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tgwLKEVRgYk%3F
Error codes and causes of malfunctions of wall-mounted gas boilers Baxi
Summary sheet of fault indication of wall-mounted gas boilers Baxi, equipped with a liquid crystal display (LCD), models Eco Compact, Four Tech, Eco Four, Main Four, Main 5.
E01 (01E) - flame control sensor. Boiler shutdown after three unsuccessful ignition attempts:
- No gas, gas valve closed, low pressure in the gas pipe.
- The phase and zero of the wires of the mains are reversed for phase-dependent models of boilers.
- Defective, dirty flame control ionisation electrode
- Defective ignition unit or electrodes.
- Gas valve defective or incorrectly adjusted.
- Lack of air for gas combustion in the boiler burner
E02 (02E) - heating circuit temperature sensor. Overheating of the heating agent in the heating circuit:
- Temperature sensor malfunction.
- Insufficient heat transfer to the sensor - it is recommended to apply thermal paste in the place where the sensor body is adjacent to the adjacent boiler part.
- Insufficient circulation of the coolant through the heat exchanger due to pump malfunction, air in the system
E03 (03E) - draft sensor (thermostat in boilers with open or pneumatic relays in boilers with a closed combustion chamber). Insufficient draft in the flue or chimney system:
- Draft sensor malfunction.
- Fan failure.
- Reducing the cross-section of the chimney or chimney.
For boilers with an open combustion chamber only. As a result of a draft violation, the flue gas thermostat overheated and, as a result, the boiler was shut down. Check the chimney for the required draft.
Troubleshooting tips:
Check the chimney for tightness of seams and connectors, for compliance with the manufacturer's recommendations for length and diameter, for the absence of obstructions in the chimney (clogging, icing), for blowing out and draft support by the wind (for the location of the chimney head relative to the roof)
Check the free flow of air into the room where the boiler is installed. There must be an inlet from the street or from an adjacent room with windows.
For a boiler with an open combustion chamber, if the air comes directly from the street, then a ventilation inlet with a size of 8 cm2 per 1 kW of boiler power is sufficient, but not less than 200 cm2. If the air supply comes from an adjacent room in the building, then the minimum size of the supply ventilation opening should be determined at the rate of 30 cm2 per 1 kW of boiler power. The supply valve in the room with the boiler is installed at a height of no more than 30 cm from the floor. It can be a ventilation grill in the wall or in the door, or just a gap under the door.
Note: electric hoods are prohibited in the boiler room.
Check the function of the flue gas thermostat.
E04 (04E) - flame control sensor. Frequent, more than six times, loss of flame on the burner:
- The reasons listed in E01 and E42 are
- Exhaust gases entering the boiler supply air duct.
E05 (05E) - heating circuit temperature sensor. No signal from the sensor:
- Malfunction of the temperature sensor of the heating circuit or open circuit with the electronic board.
E06 (06E) - DHW temperature sensor. No signal from the sensor:
- Malfunction of the DHW temperature sensor or open circuit with the electronic board.
E07 (07E) - NTC flue gas temperature sensor. No signal from the sensor:
- Malfunction of the flue gas temperature sensor or open circuit with the electronic board.
E08 (08E) - electronic board. Flame supervision circuit error:
- There is no grounding of the electronic board, there is no contact in the circuit between the board (connector X4) and the power supply box.
- Electronic control board defective.
E09 (09E) - electronic board. Gas valve safety loop error:
- Electronic control board defective.
E10 (10E) - minimum pressure switch of the heating circuit. Insufficient coolant pressure in the heating circuit:
- Check the pressure gauge and add water to the heating circuit if necessary.
- Minimum pressure switch defective.
E12 (12E) - differential hydraulic pressure switch. No signal from the pressure switch:
- The circulation pump does not work.
- The heating system is airborne.
- Insufficient circulation of the heating medium (filter clogged, high hydraulic resistance of the heating system).
- Faulty pressostat (membrane, microswitch, impulse tube)
E13 (13E) - differential hydraulic pressure switch. False signal from the pressure switch: stuck contacts of the pressure switch microswitch.
E22 (22E) - electronic board. Boiler shutdown due to low voltage in the mains, less than 162 V.:
- The voltage in the electrical network does not comply with the standard.
- Electronic board defective.
E25 (25E) - heating circuit temperature sensor. The rate of temperature rise in the heating circuit is more than 1 ° C / s:
- The circulation pump does not work.
- The heating system is airborne.
- Insufficient circulation of the heating medium (filter clogged, high hydraulic resistance of the heating system).
- The temperature sensor of the heating circuit is defective.
E26 (26E) - heating circuit temperature sensor. The excess of the coolant temperature by more than 20 ° C from the set one:
- The circulation pump does not work.
- The heating system is airborne.
- Insufficient circulation of the heating medium (filter clogged, high hydraulic resistance of the heating system).
- The temperature sensor of the heating circuit is defective.
E27 (27E) - DHW temperature sensor. Incorrect sensor position:
- The DHW temperature sensor is incorrectly installed.
- DHW temperature sensor defective.
E32 (32E) - temperature sensors of the DHW and heating circuit. Exceeding the heating temperature above 95 ° C twice in a row.Reduction of the water temperature in the DHW circuit by 3 ° C:
- Scale in the bithermic heat exchanger.
- Malfunction of the NTC temperature sensor of the DHW circuit.
E35 (35E) - flame control sensor. Flame signal after burner shutdown:
- The gas valve is defective, does not completely cut off the gas supply.
- Moisture ingress on the electronic board of the boiler.
- Interference from the electrical network. It is necessary to install a voltage stabilizer with galvanic isolation from the mains, check that the boiler is properly grounded.
E36 (36E) - flue gas temperature sensor. Flue gas NTC sensor defective.
E40 (40E) - flue gas temperature sensor. GDC does not pass flue gas temperature cyclic tests:
- Flue gas NTC sensor defective.
- Chimney or air flow obstruction.
E41 (41E) - gas valve. GDC does not pass cyclic tests for ionization current:
- No gas, gas valve closed.
- Defective, dirty flame control electrode.
- Gas valve defective.
- Gas valve not calibrated.
E42 (42E) - fan. GDC fails initial tests. Boiler shutdown after three unsuccessful attempts:
- Fan defective.
- Obstruction of the air supply channel.
E43 (43E) - electronic board. Blockage due to possible clogging of the air duct or too low gas pressure:
- The reasons described in E40 and E41.
- Inconsistency of the quality of the power supply to the requirements of the standard (low voltage, interference)
E50 (50E) - NTC flue gas temperature sensor. Blocking due to an increase in the flue gas temperature above 180 ° C:
- Insufficient coolant circulation.
- Flue gas NTC temperature sensor defective.
E55 (55E) - gas valve. Gas valve not calibrated. Calibration is required (parameters F45 and F48 of the service menu).
E62 (62E) - flame control electrode. Actuation of safety devices in the absence of stabilization of the flame signal or flue gas temperature:
- Defective or dirty flame control electrode.
- Flue gas temperature NTC sensor defective.
E65 (65E) - electronic board. Actuation of safety devices due to frequent, 10 times within 10 minutes, blockage of the air supply duct: causes described in E40 and E41.
E96 (96E) - electronic board. Undervoltage in the power supply network.
E97 (97E) - electronic board. The frequency of the mains voltage is different from 50 Hz.
E98 (98E) - electronic board. Internal error on the electronic board. Incorrect configuration of board parameters:
- The parameters have not been configured depending on the type of boiler.
- Parameters F03 and F12 of the service menu are set incorrectly.
- Defective electronic board.
E99 (99E) - electronic board. Internal error of the electronic board, which accumulates as a result of interference from the power supply network and leads to an automatic restart of the boiler.
On the display the exclamation mark in the triangle flashes... The boiler is operating at minimum power. Flue / air duct clogged or gas inlet pressure too low. To reset the fault, temporarily disconnect the heat demand from the heating or DHW system. If the problem persists, contact an Authorized Service Center.
On the display the "radiator" and "tap" icons flash alternately. Scale has formed or the DHW temperature sensor is incorrectly positioned. Fix the clamp of the DHW temperature sensor to the pipe and check the contact with the temperature sensor. Check the DHW temperature sensor (*). Check the primary heat exchanger for limescale deposits (when drawing water from the DHW circuit, the domestic water temperature at the boiler outlet does not rise, while the heating water supply temperature to the heating circuit rises rapidly; in addition, the water flow is too low due to partial clogging heat exchanger).
DHW temperature sensor and heating flow temperature sensor: resistance value is about 10 kΩ at 25 ° C (resistance decreases with increasing temperature). Flue gas temperature sensor: resistance value is about 49 kΩ at 25 ° C (resistance decreases with increasing temperature).
More articles on this topic:
⇒ How to reduce the high gas consumption of the boiler for heating the house ⇒ DHW boiler for a double-circuit boiler or column ⇒ Setting the pressure in the heating system with a membrane expansion tank
⇆
More articles on this topic
- How to properly insulate the attic
- Do-it-yourself soundproof drywall frame partitions
- Norms and rules for planning a private house, cottage
- Prefabricated - monolithic often ribbed ceilings from light stone blocks
- What area of premises to choose for building a house
- Broken roof of a house with an attic with your own hands
- Visor, outer door canopy
- How to make shelves in the house
Best Answers
amateur:
You must have a vent, an air vent. Put a hose on it so as not to get wet, and quietly opening the tap - try to relieve the pressure. (this is my opinion, but it is better to call a specialist.)
Boss Heat:
In any place of the heating system where there is a drain tap (Mayevsky tap, battery drain, etc.), open it and pour it into a jar or bucket. It is most convenient to turn the relief valve on a wall-mounted boiler.
Eliseikin:
Look for the drain valve .. must be!
alexm66:
The boiler has a drain valve (usually at the bottom). It usually opens with a key - there is no flywheel on it. The instructions for the boiler indicate its location. In this case, it is advisable to stop the boiler.
So I say:
Before releasing the pressure, check the opening of the valve on the expansion vessel. If closed, open, the pressure should drop. If it was opened, bleed off the battery in any convenient place. In no case do not relieve the pressure from the boiler safety group yourself - if a speck gets under the valve seat, it can be very difficult to wash it off, so the valve drips.
Victor:
Put on the expansion tank and forget about pressure surges.
L @ rchik:
Bleed air from the radiators, the pressure will immediately drop. Do not go into the well-oiled mechanism (boiler).
The movement of the coolant in the heating system
When organizing heating systems, various options can be used, but recently closed-type systems have been more popular, in which the movement of the coolant occurs due to the operation of the circulation pump. A gas burner heats water (or antifreeze) in the primary heat exchanger, and a pump pumps it through a radiator system, transferring heat to the premises.
At the same time, for normal circulation of the coolant, it is required that the system be completely filled with water, and since the liquid tends to expand when heated, it is necessary to somehow compensate for the increase in volume. For this, expansion tanks are provided in heating systems.
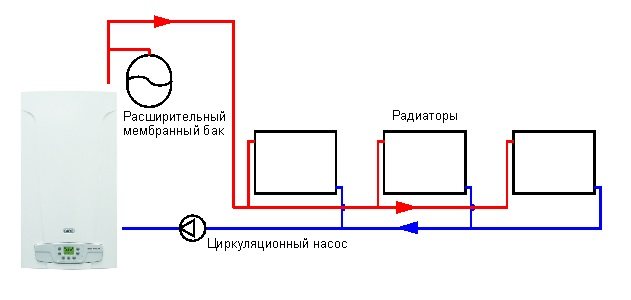

The diagram shows a system in which the boiler acts only as a heater. In household wall-mounted boilers ECOFOUR, an expansion tank and a circulation pump are already built-in, which is why such boilers are convenient to use in small apartments.
What can jams in the circuit lead to?
The importance of air ducts cannot be overstated. Traffic jams in the circuit can lead to different processes:
- violation of circulation;
- pressure surges;
- decrease in the efficiency of heating equipment;
- corrosion of metal.
Stand-alone air vent
Installing an air vent in the heating system prevents the formation of plugs and pockets. Bumping into them, the coolant stops. Sometimes plugs cut off whole sections with radiators from the circuit. At the same time, the pressure in the system increases. When it reaches a critical level, an emergency release of the coolant occurs. This, in turn, leads to a drop in pressure.At the same time, there are many cases when air was collected in the batteries, the circuit continued to work, only half of the radiator becomes cold. This significantly reduces the efficiency of heating and slightly increases the cost of its operation.
One of the greatest threats to open systems is rust. At the same time, the question of how to remove air from the heating system arises only at the design stage. Such circuits are assembled at an angle from pipes with a large diameter, respectively, there is a lot of water in the system. Considering the fact that the coolant is in contact with air and draws it into circulation, the oxygen level in the pipes is more than sufficient. Since it takes a long time to discharge air from the heating system, oxygen intensively reacts with the metal. The result of the interaction is the formation of corrosion on the inner walls of the pipes. Rust sometimes eats up the tank so much that you have to change it.
Direct consequences of traffic jams in the circuit entail indirect ones, which are no less dangerous:
Occurs when the valve for bleeding air from the heating system and all sensors are in good order and work correctly. Due to an increase in pressure, an emergency release of the coolant occurs, which leads to a decrease in its amount in the circuit. After cooling down, there will be not enough fluid in the system, the pressure will drop sharply. If it does not correspond to the minimum required to turn on the boiler, the heater will not turn on accordingly. And from this moment in winter, the countdown begins when the pipes will defrost. Depends on how insulated the house is. It happens that this happens in just three hours. In this case, unpleasant news awaits at home from work;
This happens if a malfunction occurs in the valve for bleeding air from the heating system, or temperature control equipment. Unlikely situation, although possible. The results are very disastrous. At best, boiler repair or replacement, at worst - injury;
rupture of the circuit and ejection of a hot water fountain.
A very likely situation, the joints may not be tight enough. With increasing pressure, they do not withstand and crack. At the same time, a hot coolant pours out of the pipe, like a fountain. Not only does the circuit need to be repaired, so also the neighbors do the ceiling, since you filled it in order. This is the chain that simple airing of the system can cause.
Settings and adjustments of boilers Vilant
The gas boiler vaillant atmotec pro vuw int 240 3-3 began to give error F28. Where he stands, I visit twice a week, upon arrival I find cold batteries, a red diode and an F28 error. I restart it by pressing the "troubleshoot" button - it helps for a while. It can even work for a day without failures. But then it's still F28. It was possible to detect the following symptoms: 1. The boiler can "fall into an error" right during the operation of the burner for heating. That is, the boiler is working for heating, the yellow indicator is on, suddenly red, error F28. 2. Ignition works "every other time". It happens like this: the crackling of the electrodes is twice as long as the "usual" one (by sensations) - the electrodes become silent - some mechanical sound inside the boiler (as if something is turning, opening, closing) - again the crackling of electrodes, now of the usual duration - starting the boiler in heating mode, normal operation. That is, starting from the second ignition attempt. 3. All of the above appears only in heating mode. When the boiler is running on hot water supply, everything is fine. Change the electrodes? Or is it a gas problem? The Vilant 240-3-5 Atmo tek plus double-circuit boiler was installed and put into operation. The launch was carried out independently with the inclusion of all the required programs. Worked without problems for 2 months. Yesterday I turned on the water draw at two points at the same time and heard a specific gurgle in the device. I turned off one point and after a short time everything calmed down. DHW is set to 39 ° C. After that, I turned on the water draw in one place and tried to add the DHW temperature to the maximum.Already after 45 gr. some vibration of the apparatus began to appear and a specific gurgle, as if the water was boiling. When the heating circuit is operating up to 80 gr. nothing of the kind is observed. What could it be? The wall-mounted boiler vaillant atmotec pro vuw int 240-3-3 r2 is gaining pressure in the heating system, how to fix it? Replace the make-up valve, my ball valves began to pass water after three years. It is also possible that the water passes through the secondary heat exchanger into the heating system. Wall-mounted gas boiler Vilant Turbo Tek 24 turned on and off often, after about 5-7 minutes. Since yesterday, work has become a little different. For example, tonight did not turn on for at least 2 hours, then turned on and worked for a long time. All that has changed since then is grounding, which had never existed before. Could this only affect the operation of the boiler? Or is it just a coincidence? The gas is started up by a metal pipe, but with a dielectric insert. Gas consumption per day remained the same, the temperature in the house did not change. And the hot water supply used to work with off / on every 10-15 seconds, while the yellow lamp was on and the green one was blinking. Today, for the first time, the hot water supply also started smoothly, without shutdown, only a green light was on. This year, my device also works with a burner lock. That is, it turned on, caught up to the set +5, drives the pump (I did not set it to continuous mode) for 5 minutes, and if the return temperature did not fall to the switch-on temperature, it stalls for 5 minutes (I did not exactly detect it). The difference from last year is that he reduced the power from 24 to 14, having estimated the power of his radiators. There is no grounding in the apartment (there is grounding). The DHW will be turned off during water sampling if there is a small water flow and the boiler cannot maintain the set temperature at minimum power (if the gas valve is configured). Adjust the DHW temperature so that the burner does not switch off. If you have it through the boiler, I don't see any problems. And if on a straight line - it is uncomfortable. We carried out the assembly, installation and connection of the Vaillant Turbotec pro VUW 242-3 boiler. It heats 200 m2 for the second year last year in frosts down to -15-20 and consumed 400 m3 of gas per month. In the summer, the company that sold it to me carried out MOT, nothing else changed in the heating system or in the modes of use. Now, in a month at a positive temperature outside, the device has consumed 600 m3. Tell me what could have happened and how to fix it? They could have changed the settings of the gas valve, maybe just because of the clock. Put on a room thermostat. In operation Vilant Turbo Tek 24, error f28 lights up what can it be? You restart the boiler and everything works, but after a day or two, this error pops up again. The same error popped up. I suffered with this problem for three weeks. The boiler was turned off every day or two. First, we changed the board, it didn’t help, we installed it. They sinned on the power supply, put a transformer with galvanic isolation, a dielectric spacer from the gas hose. Some other events. Then I was advised to wipe the contacts (electrodes) that light the burner with alcohol. After that, the problem didn't bother me anymore. The gas boiler Turbotec plus VUW INT 362-3-5 does not start, falls into error 37, the exhaust fan does not start. Tell me how you can check it? 220 is supplied to the three-pin connector. The control board came out of standing, the one on the fan. Is it possible to put an additional pump to raise the return temperature? Since the system is large and designed for central heating. The burner works strangely, back and forth, you can hear it by the sound, because of this, as I understand it, the temperature jumps. Previously, it did not work like that, the burner is modulating, has caught up with the temperature and maintains it. Try the following: 1. Return the bypass back. 2. turn down the heating power to such an extent that the error disappears. Once per 60 gr. works - it should work.Answer, who knows, in the Turbo Tek 24 kW boiler there should be a hot secondary heat exchanger and a return pipe from the pump (when operating with CO), although the return pipe itself at the inlet is not hot. The device heats up to 75 degrees (supply), but in fact does not heat up the last batteries. Probably the pump of the heating system does not press through, but through the built-in regulated bypass of the heating system and goes back to the heat exchanger. Therefore, the last radiators are also subcooled. Perhaps you need to look at the three-way. It drives water along the DHW circuit. Atmotec vuw int 240-3-3 gave error f28. After cleaning the gas valve, the indication of the flowing water temperature is incorrect, more by 15-20 degrees. The question is, what needs to be done so that the indication is correct, with the one that comes out of the tap? There is nothing you can do. It has been and always will be. This boiler does not have a DHW temperature sensor. When you turn on the program P.6, error f75 comes out, which indicates a malfunction of some valve. Do I understand correctly that the problem is that the scale has done its job? And you need to clean this valve between the circuits, if so, where is it located and how is it usually cleaned? Find the description of error F75 in the instructions. I don't think the three-way valve is the cause. And the noises can indeed be caused by scale in the heat exchangers. Service the boiler by flushing the heat exchangers. Installed turbotec pro vuw 242-3. Why does the handle set the hot water temperature to 55 degrees, does it heat up to 75, while it goes into overheating? Is the temperature set with a knob or do you need to lower it in the settings to less than 65C +10 (C)? Everything is fine, but at this temperature, scale will form. This boiler does not have an NTC sensor on the DHW circuit. The display shows the temperature in the primary circuit (as with heating). Those. to heat the DHW to 55, the boiler keeps about 75 in the primary circuit in your case. All TEC Pros have this situation. DHW knob - to set the DHW temperature. The heating circuit temperature will not be 75, but slightly higher (by 10-20 degrees) than the DHW temperature you ordered. The Vaillant VUW INT 242-3-5 Turbo Tek plus boiler is in operation. There is a problem. Heat carrier water is dripping from the lower drain hole of the circulation pump. Dripping at a rate of 1 drop every 10 seconds. The circulation pump itself does not emit extraneous sounds during operation. As a result, the pump head was removed and corrosion was found on the flask, which is located on the same side as the winding. As I suppose, water can get there only from the front of the pump through the air vent plug, through the rubber gasket (this option disappears, since I put the plug on flax and saw that there were no smudges). And the second option is through a crack in the flask, but there was no visible damage on the flask and after cleaning it was like new. Through the gasket between the snail and the head, water cannot enter the winding area, so this option is swept away. Correct me if there are any other paths for the coolant to enter this area. The rotor itself moves only forward and backward, there are no lateral backlashes. But I was a little puzzled by the fact that when the system was filled under pressure - when the front plug of the pump air vent was opened - the rotor itself was pulled back and water dripped from this hole, without being affected by a screwdriver. As I understand it, the rotor should have been pushed out under pressure and not let the water drip, and if you only press on it, the water would have to go, and when released, the rotor had to return to its original state and block the flow of water to the outside. We carried out the repair as follows: the gasket between the volute and the pump head was replaced. Only it is still not clear how the water could get inside the pump head through the drain hole. We installed and put into operation the Vilant Atmo Tek 24 boiler. When the burner is fired up, the piezo bursts for 5-8 seconds, the gas ignites, the piezo bursts again for 5-10 seconds, the gas goes out, the second ignition attempt begins. Firing up occurs in the same way as the first time, then the device works normally.I cleaned the piezo rods, the output sensors, no results whatsoever. It is necessary to measure the gas pressure. Yes, and maintenance is required. The boiler atmotec plus 24, 2008 is in operation. Worked properly until this season. At first, it began to drop out rarely, then more often error 75. The circulation pump was changed to the original one a year ago due to knocking and, consequently, backlash of the pump rotor. On the recommendation of the service technicians, I completely flushed the boiler (both heat exchangers, cleaned all tubes and sensors), it did not help, changed the pressure sensor, after replacing the pressure sensor, the device worked properly for 2 weeks, then again the F75 error error once a day, or even more often. Drip 3-way, carefully disassembled, replaced the oil seal (everything is clear, not a drop). Then I changed the expansion tank to an external 24 l. (The membrane broke, moreover, again), turned it on without a stabilizer (I did not notice the difference), took it from another pump and replaced the capacitor, measured the resistance of the pump windings (I got 240 and 320 ohms, but I don’t remember exactly) , there is no result, the same error 75. I found out that the rotor was jammed on the additional circulation pump (the pump is on the flow), I replaced it. There is no result, 75 error, and at 1 speed the pump starts 5 times and falls into error 75 (as I understand it, it cannot create the initial pressure in the system to start the boiler), starts at 2 speeds, but sometimes not the first time, periodically again error F75. From communication with service workers, they offer me to replace the pump again, because they do not see another malfunction. It seems to me myself that the problem is with the pump. The external tank was on the return line, when he found that the membrane on the standard tank (which is inside the boiler) had broken, he removed it and connected the external tank instead of the standard tank directly to the pump module (a copper tube comes out of it, through an adapter 3/8 - 1 / 2, then a reinforced hose and a tank are next to the boiler). The auxiliary pump Aquario AC 324-180, stands on the supply 50 centimeters from the boiler. Before that, Vester was standing, the pump did not work all this season, and maybe the last one (the rotor jammed), I discovered it recently when I wanted to revise it and changed it. Accordingly, for 1-2 seasons, the boiler worked with the external pump turned off, last season there was no such mistake, this season it all started. That is, the influence of the operation of the external pump on the frequency of occurrence of the error F75. Now, after connecting an external pump, the error falls out absolutely unpredictably, it may work for 1-2 days (which is extremely rare), it may not start for 4-5 restarts in a row, it may turn off after an hour, maybe after 2. 1. Try to turn off the “auxiliary »Pump (if everything works without it). 2. Disassemble the old pressure sensor (without a special tool, possibly with the destruction of the mount). Remove the rubber membrane - it may be covered with a hard "crust" (due to the operation of the boiler with diluted ethylene glycol and a dirty heat carrier). Remove the "crust" with alcohol - the elasticity of the membrane should be restored, that is, if a "crust" forms, then the ethylene glycol degradation products will follow you until the CO is completely flushed from antifreeze (this is not easy) and the pressure sensors will have to be changed regularly. 3. Try to "press down" a little the service valve of the boiler supply - perhaps the pressure surges when starting the pump will increase. You have a pump from the PRO boiler, but I don't see a big problem in this. Your boiler already has a built-in regulated bypass - the need for a jumper with a non-return valve is extremely doubtful. I suggest a 3-speed boiler pump, turn off the external one, watch the process. If possible, identify the time of occurrence of F75 - heating or DHW. Vailant boiler VUW INT 280-2-5 R3, in operation since December 2007. Two heating circuits. Symptoms: over the past couple of months, the efficiency of hot water supply has gradually decreased - both the temperature of the water and its consumption.This week the temperature of underfloor heating has dropped noticeably - the temperature does not rise above 30 degrees, while the boiler supply temperature is set to 70 degrees. The temperature in the radiator circuit is similar, but it is understandable there - it is warm outside now, and almost all radiators have thermostatic valves. Observation of the boiler operation showed: - no errors are generated; - when the hot water tap is opened, the boiler switches, as expected, to the DHW mode; - in heating mode, the burner turns on for a short time (from a few seconds to a minute), while the flow temperature rises to the set value (70 degrees) and the burner turns off, the pump runs, as expected. At the same time, the "return" temperature practically does not increase and is 25-30 degrees. One gets the impression that any of the sensors, in my opinion, prematurely "gives a command" to turn off the burner. Which sensor should you pay attention to? Over the entire period of operation (7 years), none of the heat exchangers and the boiler itself have been flushed. There is an idea to flush the heat exchangers, while, as I understand it, it will be necessary to replace the O-rings (O-rings) on the heat exchanger connection pipes. Your boiler model does not have a pressure sensor. The thought of flushing and maintenance is good, but it doesn't hurt to look into the return filter as well. I would start by flushing the heat exchangers. Fill the heat exchanger with acid (hodgepodge) for half a day, clean both heat exchangers, also remove all tubes, clean the seats for the rubber bands, clean the 3-way valve, the filter mesh, where the pressure sensor, the pressure sensor may be overgrown with deposits on the membrane, so you need to restore it elasticity. Do this procedure and see. Further it seems to me it is necessary to look at the pump. Malfunction of the gas boiler Vaillant Atmotec pro VUW INT 240-3-3. When the boiler is ignited with hot water, a few seconds after normal ignition, a spark jumps between the ignition electrodes, the height of the burner flame drops sharply. Then, if the spark jumps again, the burner goes out and error F28 pops up. If the burner is working for heating, and you open the water supply, everything works fine, the water heats up. We increased the gas supply to the gas valve, started the P1 diagnostic program, wiped the control electrode - nothing helps. If the control electrode is heated by the burner during operation for heating, then the burner also works for hot water. When starting the burner to hot water with the heating turned off, the situation described above occurs. It is very similar to a small current in the combustion detection chain. Was the ionization current measured by the specialist during his visit? 1. Poor or no grounding. 2. Presence of potential on the boiler drum. 3. Malfunction of the stabilizer or uninterruptible power supply, if any. Installed and connected gas boiler Vaillant Turbotec VUW INT 240-3-3 (2007 onwards). 3 days ago, he turned off the heating (reduced the temperature). Yesterday I left, and I was not at home for a day, I arrived - error F28 is on. Every day they turn off the lights for a couple of hours now, I don't know if this has any meaning or not. I took the instructions and studied them. I tried to do a reset - it does not help. When turned on, some kind of valve buzzes, like on the water supply. And even there is no attempt to ignite, it is immediately reset to error F28. If you turn off the gas main, everything is the same. Still such a moment, no one lives in the house and gas. tiles are rarely used. When the gas is turned on, it seems like air flows for a while, because sometimes the match blows out, and the burner does not ignite. Maybe there is a need to bleed the air in the boiler? Or the reason is the gas valve. What else to see at the F28? The presence of gas on the boiler. Achieve stable combustion of gas on a gas stove. Then try to start the boiler. It may not start right away until all the air from the line is bled.Vaillant VUW INT 240-2-3 R1 wall-mounted boiler malfunction. Yesterday suddenly a LED on the panel lit up - a crossed out wick. I understand that he says that he cannot light a flame, but why is this happening? It seems that no one touched him. Ignition does not go, there is no flame. Last year we did prophylaxis. Red button - does not respond. Once the error was not cleared - he cured it with a pencil, rubbed the key on the back, which is pressed against the board.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler works with certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of storeys in the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Typically, for a private house, the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a multi-apartment five-story house, this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story house - 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is reached in heating mains, here it is equal to 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at a fairly decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustments are required. At the same time, special regulators are used to reduce, and pumps are used to increase. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise in some areas there will be sharp fluctuations, a drop in the temperature of the coolant. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Control devices
To control the water pressure in the heating boiler and heating system, manometers and thermomanometers are used. The latter are combined devices for monitoring two parameters at once. After starting the circuit, it is necessary to control the indicators so that they do not go beyond the normal range.
In some double-circuit floor-standing and wall-mounted boilers, traditional dial gauges are absent. Instead of them, electronic sensors are installed here, information from which is transmitted to the electronic unit, after which it is processed and displayed. Another approach is also possible - if the heating unit is devoid of a pressure gauge, it is provided by the safety group.
The security group itself includes the following nodes:
- Manometer or thermomanometer - to control the temperature and pressure in the heating circuit;
- Automatic air vent - prevents contour airing;
- Safety valve - relieves the coolant pressure when it rises excessively.
Be sure to provide this unit in a closed heating system.
Air lock as a cause of pressure increase
Another possible reason why the pressure itself rises is the presence of air in the heating circuit.
Airborne exposure can occur due to:
- when the heating circuit fills up too quickly with liquid - the system should be filled slowly, with the air release valves open. The valves are open until liquid flows from the highest point of the system;
- Mayevsky's taps are broken, change taps;
- the impeller of the circulation pump loosened, because of this, air may enter, adjust the impeller.
How to bleed air from the boiler
Modern heat sources are equipped with automatic air vents or Mayevsky taps located in the upper part of the unit. Such a constructive solution allows air to be vented during operating mode, without stopping the heating process of the room, just like from any radiator on which a similar valve is installed.
To do this, periodically open and close Mayevsky's tap, at intervals of several minutes. The procedure is repeated until a hiss or whistle appears, indicating the release of an airlock. The appearance of sound requires holding the bleed device in the open position until the appearance of the coolant.
The lack of special devices for eliminating plugs on the boiler requires resorting to the help of the same devices on pipelines located above the heat source.
The ideal conditions for freeing from the air lock in the boiler is the possibility of a separate shut-off of the heat source circuit with a return pipe and a circulation pump. When turned on, the pumping of the coolant is ensured, and periodic opening of the Mayevsky valve or monitoring the operation of the automatic air vent, by pressing the spool, allows the closed circuit to be released from the plug.
If there is no circulation pump in a closed circuit that cuts off the boiler with a return pipeline, then the energy source is turned on: gas, electricity, and in solid fuel, the furnace is ignited. After heating the "supply" pipeline, the air release device is periodically opened. The heat carrier, when heated, will rise from the boiler along the main due to heating and return through the connecting pipeline - back to the heat exchanger. This technique requires careful temperature monitoring, especially when servicing a non-solid fuel heat source. The movement of the coolant along such a circuit will be very slow and this is taken into account when performing work.
If there is no possibility of shutting off the boiler water circuit and there are devices for venting air only in the upper part of the line, it is necessary to drain the coolant, and then fill in the entire required volume of water. Before embarking on such global events, it is recommended to cut off all devices (except for the boiler) and, by turning on the pump, release the pressure through the nearest air vent on the line until sound or bubbles appear. The lack of a result indicates the need for complete drainage of the coolant.