Indoor cooling is the main function of the air conditioner, therefore the choice of air conditioner is primarily determined by the cooling capacity. In turn, the necessary air conditioner capacity directly depends on the size of the room that needs to be cooled.
FROM cooling capacity power consumption should not be mixed as these are completely different parameters. The cooling power is several times higher than the power consumed by the air conditioner. For example, an air conditioner that consumes 700 W has a cooling power of 2 kW, and this should not be surprising, since the air conditioner works just like a refrigerator, a refrigerant (freon) takes heat from the air in the room and transfers it to the outside through a heat exchanger (outdoor unit of the air conditioner) ... The power ratio is called energy efficiency of the air conditioner (EER). For domestic air conditioners, this parameter will have values in the range of 2.5 - 4.
Below is the distribution table capacities air conditioners. Using it, you can select the types of air conditioners that are most optimal in certain conditions. For example, in small rooms or offices where low-power air conditioners are required, it is more rational to install mobile, window or wall models. Air conditioners other models have more power and, accordingly, higher prices, so it is better to purchase them for cooling large premises (sales areas, warehouses, etc.)
| Refrigerating capacity, kW | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 14 | 17 |
| Standard model sizes | 05 | 07 | 09 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 48 | 60 |
| Mobile air conditioners (mobile monoblocks and split systems) | ||||||||||
| Window air conditioners | ||||||||||
| Wall-mounted air conditioners | ||||||||||
| Cassette air conditioners | ||||||||||
| Duct air conditioners | ||||||||||
| Column conditioners | ||||||||||
| Floor and ceiling air conditioners |
Power units
Quite often, in addition to the usual power measurement units for us, others are also used. For example, British thermal unit, which is measured in BTU / hr. It is determined by the amount of heat that needs to be heated for one pound of water per degree Fahrenheit.
With the SI system, it has the following relationship:
- 1W = 3.4 BTU / h or
- 1000 BTU / h = 293 W
Quite often, the models are called "nines" or "twelve", since they are marked with the mention of these and other numbers, and the performance is measured in BTU / h.
Indoor unit type
The second important characteristic when choosing an air conditioner is the type of indoor unit. Monoblocks are divided into window and mobile air conditioners.
Window air conditioners - built into the window opening. They have more disadvantages than advantages, and therefore are almost out of use.
Advantages: low cost and relatively easy installation.
Disadvantages: very noisy; during installation in a window opening, the thermal insulation of the window is violated, because of this, in winter, cold air freely penetrates into the room; the window space is obstructed.
Mobile air conditioners - can be either monoblock or split-system. Thanks to the castors, they move freely around the room. A flexible hose is connected to the unit, with the help of which hot air is released outside.
The advantage is that they do not need installation, and the disadvantage is that they make a lot of noise during operation.
Wall mounted split systems and multisplit systems are the most optimal option in terms of efficiency and price for both home and office. Advantages - comparative ease of installation and use.
Floor and ceiling air conditioners are used mainly in rooms with complex structures. For example, when it is impossible to attach the air conditioner to a wall that is too thin.They distribute cold air very well around the entire perimeter of the room, even if it is irregular in shape. More expensive models can simultaneously direct air in four directions at once. Among the disadvantages are the high cost and not very beautiful appearance.
Cassette air conditioners - designed mainly for rooms with high ceilings. Built into false ceilings.
Advantages: even distribution of air in four directions, as well as the invisibility of such a model. Disadvantages: installation is possible only with the help of specialists at the stage of construction or overhaul of the house.
Column air conditioners - used in very large rooms where there are no special design requirements. They are large in size. Usually quite expensive. The main advantage is that these models cool the air quite strongly, and the temperature range can drop to minus 35 ° С.
Duct air conditioners - similar to cassette air conditioners, differ only in that they take up much less space under the ceiling. The main disadvantages are the high price and complexity of installation, which is carried out at the stage of building a house. The advantage is that one such air conditioner replaces about four wall split systems.
An example of calculating the power of an air conditioner
Let's calculate the capacity of the air conditioner for a living room with an area of 26 sq. m with a ceiling height of 2.75 m in which one person lives, and also has a computer, TV and a small refrigerator with a maximum power consumption of 165 watts. The room is located on the sunny side. The computer and the TV do not work at the same time, as they are used by the same person.
- First, we determine the heat gains from the window, walls, floor and ceiling. Coefficient q
choose equal
40
, since the room is located on the sunny side:Q1 = S * h * q / 1000 = 26 sq. m * 2.75 m * 40/1000 = 2.86 kW
.
- Heat gains from one person in a calm state will be 0.1 kW
.Q2 = 0.1 kW
- Next, we will find heat gains from household appliances. Since the computer and the TV do not work at the same time, only one of these devices must be taken into account in the calculations, namely the one that generates more heat. This is a computer, the heat dissipation from which is 0.3 kW
... The refrigerator generates about 30% of the maximum power consumption in the form of heat, that is
0.165 kW * 30% / 100% ≈ 0.05 kW
.Q3 = 0.3 kW + 0.05 kW = 0.35 kW
- Now we can determine the estimated capacity of the air conditioner:
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 = 2.86 kW + 0.1 kW + 0.35 kW = 3.31 kW - Recommended power range Qrange
(from
-5%
before
+15%
design capacity
Q
):3.14 kW < Qrange < 3.80 kW
It remains for us to choose a model of suitable power. Most manufacturers produce split systems with capacities close to the standard range: 2,0
kW;
2,6
kW;
3,5
kW;
5,3
kW;
7,0
kW. From this range we choose a model with a capacity
3,5
kW.
Interestingly, models from this series are often called "7" (seven), "9" (nine), "12", "18" "24" and even air conditioners are labeled using these numbers, which reflect the power of the air conditioner not in the usual kilowatts, and in BTU / hour
... This is due to the fact that the first air conditioners appeared in the United States, where the British system of units (inches, pounds) is still used. For the convenience of buyers, the capacity of the air conditioner was expressed in round numbers: 7000 BTU / h, 9000 BTU / h, etc. The same numbers were used when marking the air conditioner so that its power can be easily identified by the name. However, some manufacturers, such as Daikin, tie model names to wattage, as the Daikin FTY35 air conditioner has a power of 3.5 kW.
Calculation of performance by squaring the room
The second available method is to calculate the power of the air conditioner by the area of the room.This is a favorite technique of sales representatives, reminiscent of the selection of heating equipment according to the specific amount of heat per unit area. The bottom line is this: with a ceiling height of up to 3 m, 100 W of cold energy should be released per 1 m2 of the room. That is, for a room of 20 m2, an air conditioner with a capacity of 2 kW is required. If the ceilings are higher than 3 m, then the specific refrigerating capacity is taken not 100 W / m2, but more, in accordance with the table:
In addition to the consumed amount of cold for the entire area of the room, power is added to it to compensate for heat inputs from people and household appliances who are constantly in the room. In this case, it is proposed to take the following values of the released heat: from 1 person - 300 W, from a unit of household equipment - also 300 W. This means that if in the aforementioned room of 20 m2 there is always 1 person working on a computer, then another 600 W must be added to the 2 kW obtained, for a total of 2.6 kW. Details can be viewed in the video:
In fact, in accordance with the regulatory documentation, the amount of total heat emitted by a person at rest is 100 W, with little movement - 130 W, with physical work - 200 W. It turns out that in this method of calculation, the heat input from people is somewhat overestimated.
Additional parameters to consider when choosing an air conditioner
There are many factors that have a significant impact when choosing an air conditioner. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the role of the fresh air flow when opening the window. The simplified method for calculating the power of the air conditioner does not take into account the opening of windows for ventilation. This is due to the fact that even in the operating instructions for the system it is indicated that the air conditioner should only operate with the windows closed. In turn, this creates certain inconveniences, since the windows can be ventilated only when the device is turned off.
It is not difficult to solve this problem. You can ventilate the room with the air conditioner on at any time, but do not forget to close the front door to the room (so as not to create drafts). It is also necessary to take this nuance into account when calculating the power of the system. To this end Q1
increase by 20% to compensate for the heat load from the supply air. It is necessary to understand that with an increase in capacity, electricity costs will also increase. For this reason, air conditioners are not recommended for use when airing rooms. At the highest possible temperature (summer heat), the air conditioner may not maintain the set temperature, since the heat inflows may be too strong.
If the refrigerated room is located on the upper floor, where there is no attic, then the heat from the heated roof will be transferred to the room. The heat gain of the ceiling will be much higher than that of the walls, so we increase the power Q1
by 15%.
The large area of glazing of windows also plays a significant role. It is quite easy to track this. It is enough to measure the temperature in a sunny room and compare it with the rest. During the usual calculation, it is provided for the presence of this window in the room, up to 2 m2. If the glazing area exceeds the permissible value. Then, for each square meter of glazing, an average of 100-200 watts is added.
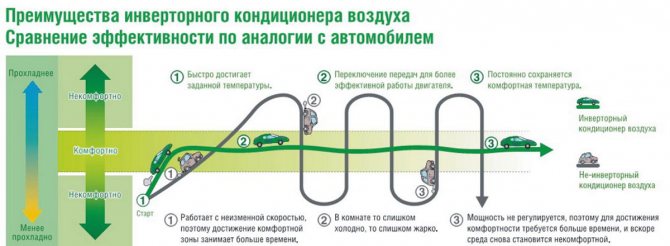
An inverter air conditioner is well suited for operation over a wide range of heat loads. It has a variable cooling capacity, so it is able to create comfortable conditions in a given room.
Online calculator for calculating cooling capacity
To independently select the power of a home air conditioner, use the simplified method for calculating the area of the refrigerated room, implemented in the calculator. The nuances of the online program and the entered parameters are described below in the instructions.
Note.The program is suitable for calculating the performance of household chillers and split systems installed in small offices. Air conditioning of premises in industrial buildings is a more complex task, solved with the help of specialized software systems or the calculation method of SNiP.
Correspondence of model series and power of the air conditioner in BTU and kW
| The lineup | BTU | kw |
| 7 | 7000 BTU | 2.1kw |
| 9 | 9000 BTU | 2.6kw |
| 12 | 12000 BTU | 3.5kw |
| 18 | 18000 BTU | 5.3kw |
| 24 | 24000 BTU | 7.0kw |
| 28 | 28000 BTU | 8.2kw |
| 36 | 36,000 BTU | 10.6kw |
| 42 | 42,000 BTU | 12.3kw |
| 48 | 48000 BTU | 14.0kw |
| 54 | 54,000 BTU | 15.8kw |
| 56 | 56,000 BTU | 16.4kw |
| 60 | 60,000 BTU | 17.6kw |
How it works?
The name of the device "air conditioner" comes from the English word "condition" - condition, condition. That is, it is an apparatus designed to maintain the interior air of the room within the specified conditions, creating a controlled microclimate. These devices work in such a way that they continuously transfer heat from the room to the surrounding space, or, if necessary, vice versa.
Heat is transferred with the help of a heat carrier, the role of which was played at different times by various substances; the first air conditioners used ammonia as a heat carrier. In our time, freon plays the role of a coolant. "Capture" and release of heat works according to the phase transition method, this is a method of transition of a substance from one state of aggregation to another.
Everyone could personally observe this property of the phase transition of a substance while swimming in summer. When a person comes out of the water he feels cold, even though the ambient temperature is above 30 ° C. This is due to the fact that during evaporation, water takes heat from the surface of the body and from the surrounding space.
Motorists know that when exposed parts of the body come into contact with volatile substances such as gasoline, it will feel cold. And at freezing temperatures, contact with a volatile substance can even cause frostbite.
In the same way, climatic technology works approximately, only with the amendment that freon does not evaporate into the surrounding space, since it is rather wasteful. Evaporation itself takes place inside a special tubular circuit called an evaporator. Freon remains inside the circuit, and heat goes into the surrounding space.
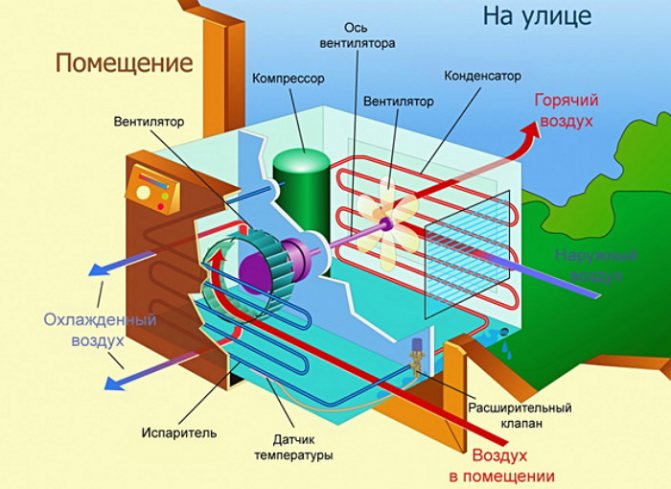
The air conditioner works as follows:
- Freon is compressed in the compressor to 15-20 atmospheres and released into the condenser.
- At the moment when freon comes out and the compressor pressure drops sharply and freon turns into hot steam.
- The condenser serves to transfer freon from a gaseous to a liquid state, this process is accompanied by a large release of heat. It is during this process that heat is released, and therefore the condenser must be in contact with the outside air.
- Liquid freon enters the evaporator, where, when the pressure drops, the refrigerant turns into a gaseous state, which is accompanied by active heat absorption, therefore the evaporator must be in direct contact with the air of the room to be cooled.
- Freon in a gaseous state enters the compressor, and the process starts over.
In the event that it is required that the air conditioner works for heating, then with the help of a four-way valve, the air flow is redirected so that warm air enters the room, and heat is taken outside. Accordingly, it is necessary that the outside air itself be warm enough to heat the refrigerant.
If the outside temperature drops to zero, that is, exactly when heating of the room is required, it is impossible to use the air conditioner for heating. Therefore, air conditioners cannot be used as the main means of heating a room.