Heating design prices
| № | Job title | Description | unit of measurement | Price in rubles |
| 1 | Heating system design | Project composition:
| m2 | 80 |
| 2 | Underfloor heating system design | Project composition:
| m2 | 80 |
| 3 | Design work on the water supply system | Project composition:
| m2 | 50 |
| 4 | Design work on the sewerage system | Project composition:
| m2 | 50 |
| 5 | Ventilation system design work | Project composition:
| m2 | 60-120 |
| 6 | Design work on the air conditioning system | Project composition:
| m2 | 70 |
| 7 | Boiler room project | Project composition:
| set | from 7000 |
| 8 | Low-current systems project. | Project composition:
| m2 | 70 |
| 9 | Visualization of the boiler room project in 3D | Project composition:
| set | from 9600 |
| 10 | Departure of the designer to the object | At the conclusion of the contract, the amount is counted towards the payment for design work. | 2100 | |
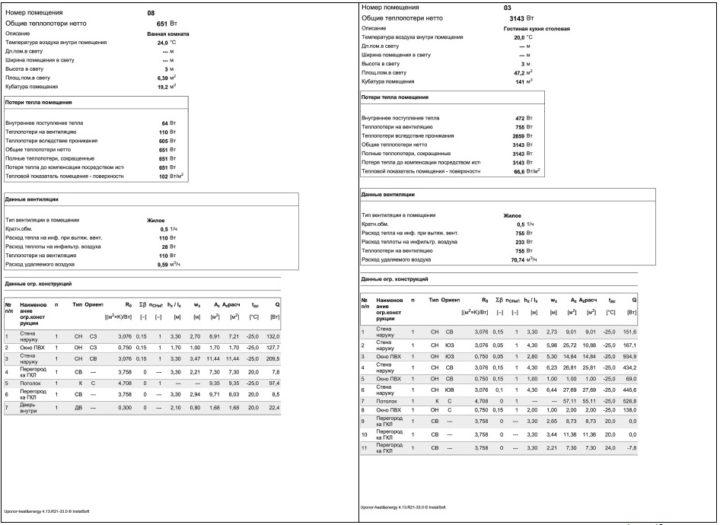
| 11 | Heat engineering calculation | Calculation of the heat loss of the building. | m2 | 25 |
| 12 | Transfer of drawings from paper to electronic form | m2 | 25 |
Design at EuroHolod is:
- Cost optimization
- Energy efficiency
- Qualification
- A complex approach
- Equipment selection: optimally selected characteristics of ventilation units and not the most expensive brand of the manufacturer in the price-quality ratio, significantly reduce the cost of equipment and do not affect the required parameters.
- Duct optimization: correctly calculated and optimally located air duct routes reduce the required volume of metal products, therefore, costs are reduced.
- Preventing rework: you will not need to change architectural and engineering solutions for related communications that do not require ventilation systems at the design stage, which will save you from unnecessary expenses for alterations, modifications and replacement of equipment.
- Possibly significant reduce operating costs electricity and hot water, taking this into account in the design of ventilation and air conditioning systems.
- For this, systems with heat recovery, recirculation of supply air and equipment with optimal energy consumption are used.
- Practical experience: our designers have not only theoretical knowledge, but also experience in the management of objects and delivery to public services.
- Ready-made solutions from 2 days: plans for premises within 2000 m2 will be ready within 2 - 5 days, depending on the complexity of the object.
- Finalization of the project for free: in most cases, the project needs to be finalized due to changes in architectural, design and technological solutions.
- All the necessary documents are available: certificates of the project SRO and ISO-9001, the license of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, etc.
- We have a lot of completed projects and real customer reviews.
- We design a complex solution in which all sections of engineering systems agreed between themselves.
- EuroCold also organizes selection of equipment, installation and further service.
- We guarantee quality of our services and carry them out in a short time.
- All are counted wishes the customer and the necessary edits are made.
The heating system is the most expensive engineering system of any building. Its device requires about 5% of the total cost of construction. Each building has architectural and design features, so the use of averaged calculations is impossible. You have to take into account a lot: the area of the building, climate features, orientation to the cardinal points, places of heat loss, and much more, which plays an important role.
The design department of our Company professionally performs the design of heating systems for objects of any complexity and purpose, allowing the Customer to save money, getting a high level of operation during the heating season.
- Air conditioning installation cost
- Ventilation installation cost
Preliminary design
The draft design (ED) of the heating system is intended to determine the requirements for the solutions of the object and to confirm the possibility of its creation. Sometimes the draft design stage is skipped, and all the work envisaged at this stage is performed at the feasibility study stage. We do not take this approach.
Our company is ready to offer several options already at the ES stage. The draft design is carried out with the preparation of an explication of the main equipment, equipment brand and manufacturer. That allows you to choose the optimal and less costly way to solve the problem at the earliest stage.
Terms of reference and commercial proposal
At the second stage, on the basis of the approved draft design and preliminary calculations, the following are developed:
- a document containing a textual description of the heating system being created - terms of reference (TOR);
- and possible investment costs for its creation - commercial proposal (KP).
Customers often turn to us with the question: "How much does the services of your specialists cost and how much will the heating system of my house (workshop, enterprise, etc.) cost me?" At the same time, the person who asked this question does not have any project for the desired heating system, and sometimes there is no answer to the question to himself: "What do I want myself?" Naturally, we cannot give an answer to such a question “in flight”, and we have to explain for a very long time why we cannot do this. Therefore, below we give a standard form of technical specifications for the design of a heating system, from which it is clearly seen how many questions the designer needs to answer in order to complete the design work. And this is far from a complete range of all questions. And only on the basis of the finished project, the estimator already has the opportunity to issue an estimate for the object. And for us, as specialists, one thing is unambiguously clear that if someone "in flight" says the price, then this is just a shameless deception of the customer and nothing more. Miracles don't happen.
Heating project - a complete package of project documentation
The fourth stage is the execution of work on the preparation of complete specifications for heating equipment and materials, as well as the design of project documentation in a form that meets the established norms and rules.
Carrying out work on all four stages allows you to create a complete package of project documentation, which is called a heating project. The proposed projects of heating systems allow us to perform all further installation work on the installation of equipment with high quality.
Design stages
Stage "P"
Stage "P" is intended for the examination of the project and obtaining a building permit, for agreement with the customer, specialized structures.
At the project stage ("P"), project documentation is developed, which includes:
- Explanatory note with a general description of the concept adopted for the object by sections
- General data sheet and characteristics of engineering systems
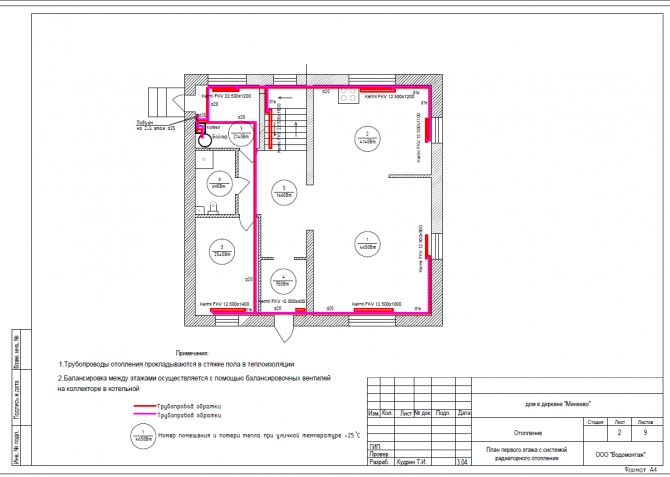
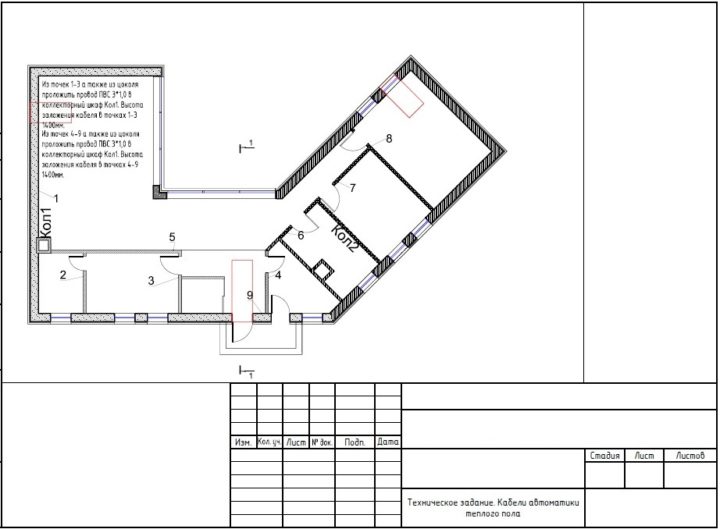
- Floor plans of engineering systems in one line
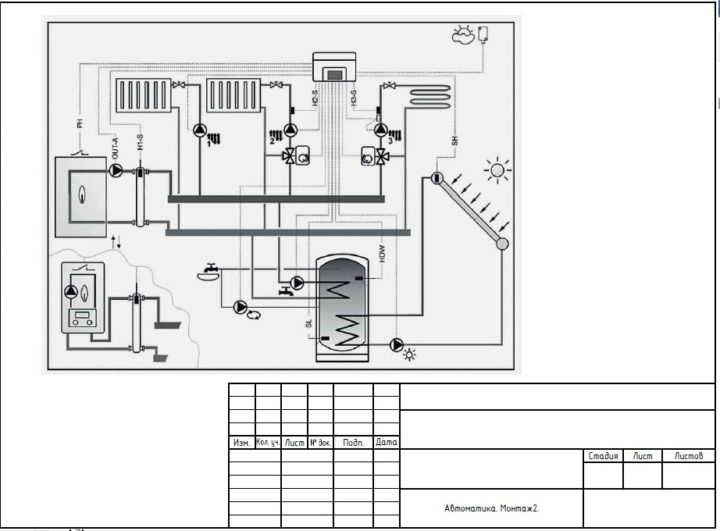
- Schematic diagrams of systems
- Main equipment specification
Stage "R"
At the "P" stage, after the design and architecture have been agreed upon, working documentation is provided for the construction and installation work.
Development of a working project ("R") includes the entire range of design and settlement works, which include:
- Calculation of air exchange, aerodynamic calculation, calculation of heat inflows and heat losses, hydraulic calculation
- General data sheet and characteristics of accepted engineering systems
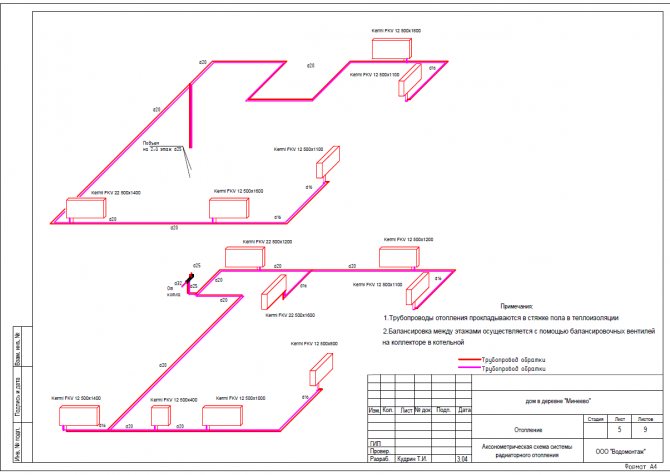
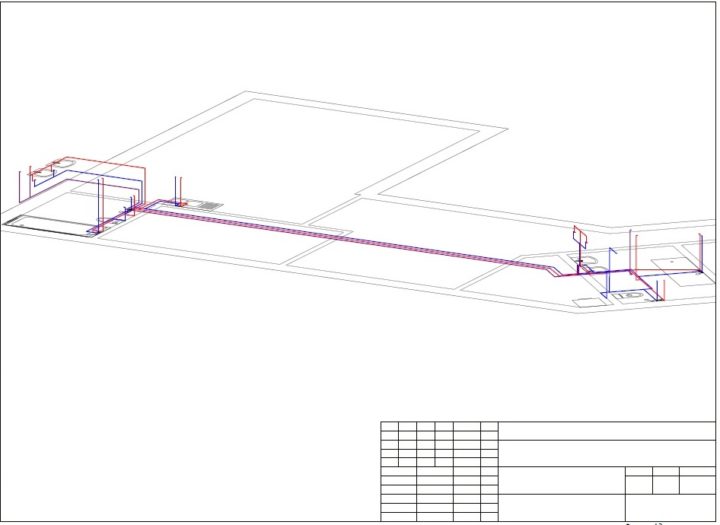
- Plans of all floors with the layout of engineering systems, indicating all sections (diameters), estimated costs, types and number of air distribution devices, equipment bindings, electrical loads and other necessary information for the installation of engineering systems
- Axonometric diagrams of engineering systems
- Specification of equipment and materials
- Estimate with the scope of work
When determining the heat load of heating systems, the features of the thermal regime of the premises are taken into account. In premises with a constant thermal regime, which include industrial buildings, agricultural buildings, residential and public buildings, the heat load is determined from the heat balance. In rooms with a variable mode, when determining the heat load, two periods are distinguished - working and non-working. There may be no need for heating outside office hours. In all cases, when calculating the power of heating systems, it is necessary to take into account the minimum hourly heat release. In addition, heating systems must provide normalized air parameters by the beginning of the working period. Heating calculated only for the period of non-working hours is called standby heating.
The type of heating directly depends on the area of the house.Due to its low inertia, the system with natural circulation can be used for structures with an area of no more than 100 m2. The calculation and design of heating systems is carried out taking into account a number of features. For example, for buildings with a larger area, forced circulation of the coolant is required by the inclusion of circulation pumps in the system.
Heating scheme of a private house
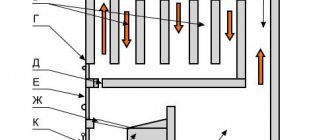
To understand the heating scheme of a private house erected with your own hands, you need to know some rules. They relate to the installation work, as well as the competent selection of heating equipment, piping and the type of heating system. In this article, we will analyze all the schemes and find out what nuances must be taken into account in order for the system to work efficiently.
Immediately, we will decide that we will consider only water heating using boilers and pipes. Firstly, this system is considered to be the simplest and most reliable. And, secondly, you can choose such a scheme and build such a system that its work will be effective, and the practical side of the matter will be observed.
The principle of operation of such a heating system is as follows. The coolant in the heating boiler heats up and flows through the pipeline to heating devices - radiators. Here it gives off heat and returns along the return circuit to the boiler. And the whole process is repeated anew. It turns out that water heating is a kind of cyclical technological process.
Which system should you choose?
The design of heating a private house is carried out taking into account the energy carrier that will heat the room. There are several of the most common systems by which heat is supplied to all internal rooms of the building:

- water;
- air;
- electric;
- open fire.
By "open fire" is meant a fireplace or stove. Both of these heat sources are ineffective in terms of full-fledged home heating, since they distribute hot air unevenly. They are most often included in a heating project as decorative elements. Let's dwell on other systems in more detail.
Types of heating schemes
So, what is the best heating scheme for a private house? There are two of them:
- One-pipe.
- Two-pipe.
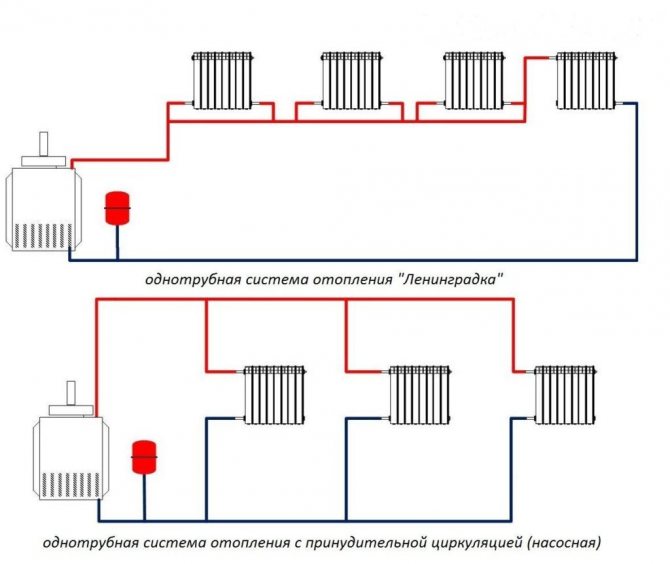
One pipe system
Of the two above, this is the cheapest and simplest system. It is a ring in which heating radiators are installed in sequential order. The coolant moves from the radiator to the radiator until everything passes and returns to the boiler. Very simple.
It would seem that such a scheme should be optimal, because it is simplicity and economy that are often the fundamental factors influencing the choice.
But not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. Judge for yourself. The heat carrier, heated to a certain temperature (usually +75 C), moves to the first heating device. He gives him a certain amount of heat, while cooling down by several degrees.
One-pipe heating scheme
In the second radiator, it is not yet clear that the coolant has cooled down. But already in the fourth or fifth it will be noticeable.
Having reached the last radiator, the coolant will have a temperature of approximately +45 C. And the room cannot be heated at such a temperature.
What to do? There are two ways out:
- Increase the number of sections of the last radiators, thereby increasing the heat transfer area.
- Increase the temperature of the heating medium leaving the heating boiler. And this will require more fuel consumption.
Both options have an economic component, which, unfortunately, is not distributed in the direction of reducing costs, but, on the contrary, in the direction of increasing. And here you have to choose what is best for you.
There is another option. This is a scheme with forced circulation of the coolant. What it is?
This is when there is a unit in the heating system, usually a circulation pump, which creates a small pressure inside it. It ensures an even distribution of the coolant over all radiators. In addition, hot water moves through the system at a low speed, and this affects the inertness of the system, so that rapid heating occurs.
This option is more effective than the first two, but the circulating pump installed in the system operates from the electric current network. What is the inconvenience?
- Firstly, it consumes a little electrical energy, but this is an additional cost.
- Secondly, if there is no electricity, then there is no pressure inside the heating. And in winter, turning off the power supply in suburban villages is not uncommon.
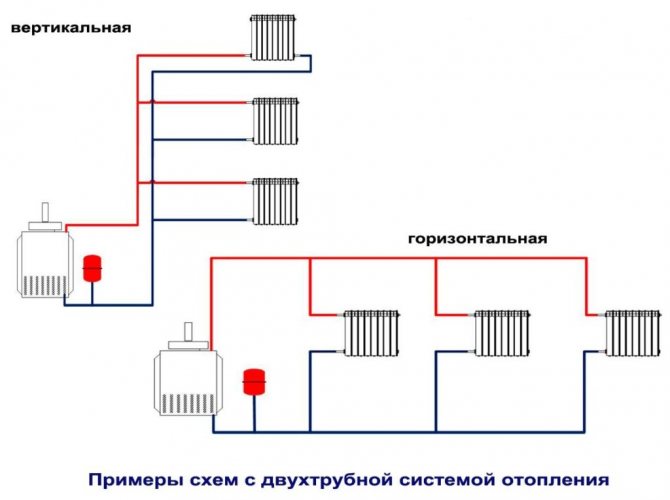
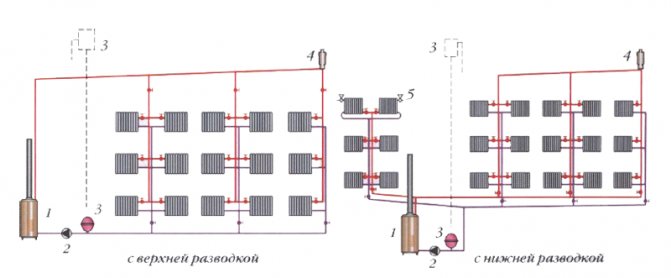
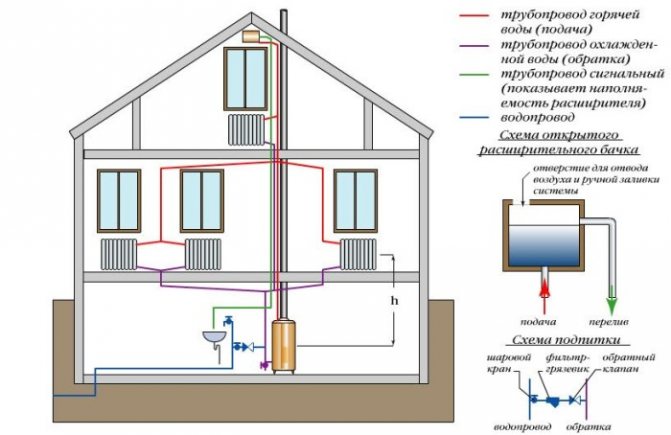
Two-pipe system

Two-pipe heating system of a residential building
To say that she is better than the first is to say nothing. This scheme works much more efficiently, because each radiator has its own separate pipe with a coolant. But they have only one reverse circuit. And from each radiator a separate pipe goes down to the return, through which the coolant is removed.
In general, this system is not complicated. It is only necessary to choose how the coolant will be supplied to the radiators - according to the beam or collector scheme.
In the first case, the supply pipe rises up to the ceiling into the attic, where its own individual pipe is diverted from it to each pipe. It turns out a kind of contour, similar to the sun, where in the center there is a pipe from the boiler, and the rays of the pipes diverge to the radiators to the sides. Hence its name - ray.
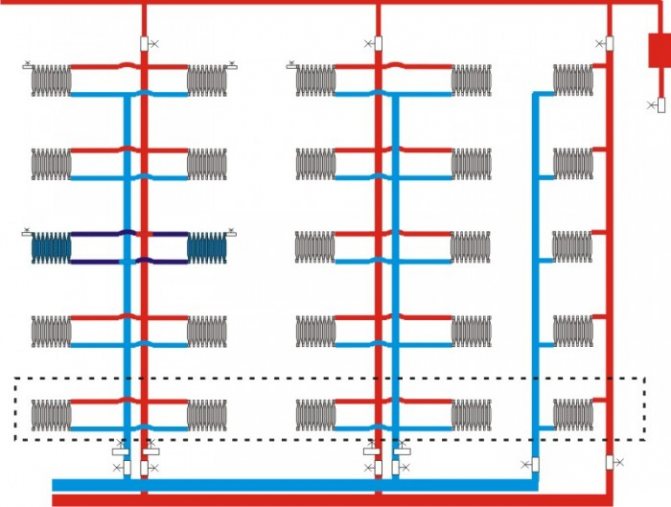
The collector circuit is considered more modern. A special device is installed in the attic, which is called a collector. It consists of a pipe structure through which the coolant is distributed throughout the system. Shut-off valves are also installed here, cutting off each circuit.
This makes the system convenient to operate, and also simplifies the repair process, if necessary. So, you can repair not only a separate supply circuit to the room, but even a free-standing radiator.
In all respects, the collector circuit is superior to the others. But a two-pipe system, and even more so a collector system, has one significant drawback. This is a large amount of material used to build this circuit. This includes pipe, shut-off valves, monitoring and control devices and sensors. Therefore, you will have to fork out here. But if you want your home to always be warm in all rooms, then just such a scheme will help you do this.
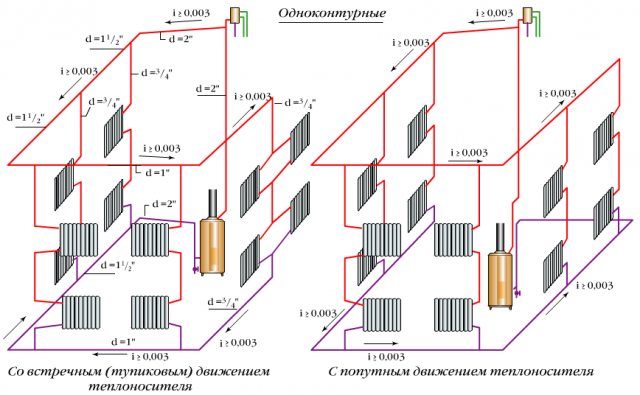

Single-circuit systems with natural circulation
Can a circulation pump be installed in a two-pipe heating system? How relevant is it? There is no great need for this, because the two-pipe system with natural circulation works efficiently. So there is no need for extra expenses.
Now he returns to the question of whether it is possible to build a heating system in a private house with your own hands. Here, as elsewhere, a lot will depend on the skills of using various tools and experience in carrying out installation work. If you do not have either one or the other, the consequences may not be very rosy.
First of all, the boiler will boil, and the batteries will be cold. If the slope of the upper piping is incorrectly made, it will be cool in the rooms, even with a hot boiler. The same applies to the return loop.
If you install a circulation pump in the wrong place, it will work for one season and stop, start leaking, that is, problems will appear. Well, if you put the expansion tank incorrectly, you will get a shortage of coolant in the system.
And there are many more such nuances. So, ideally, the installation of a heating system is the work of craftsmen.But if you want to save money and your budget is tight, then you have to learn.
Heating system classification
Distinguish between local and central heating systems:
- Local systems are systems in which all elements are combined in one device and the system is designed to heat one room. Local systems include - stove heating, gas (when burning fuel in a local device - gas convector, infrared emitter) and electric
- Central systems heat a number of rooms from the center (heat generator, boiler room, CHP), in which heat is generated, which is transferred by the coolant to the heating devices of the heated rooms
The heating system is a set of elements required to heat a room. The main elements are heat sources, heat pipes, heating devices. Heat transfer is carried out using heat carriers. Despite the presence of disadvantages for all types of heat carriers, they are all widely used in heating and heat supply systems, they can perfectly get along in one room, providing a solution to the problems of heating and heat supply, protecting structures from ice and providing a room with hot water.
The main ways of transferring heat from the heater to the room:
- Convective heating. It includes all types of heating in which heat energy is transferred due to the movement of volumes of hot and cold air. Warm air flow rushes up, cold / cooled air goes down. Hence, the main disadvantage of convective heating is the large temperature difference in the room, i.e. high air temperature near the ceiling and low air temperature near the floor. The most striking example is heating with heat guns and fan heaters.
- Infrared (radiant) heating is a type of heating in which heat is transferred by radiation. The heaters are placed directly above or below the heated area. The main disadvantage is that with incorrect calculation (installation) and operation (long-term use), overheating of objects and the human body
- Convective - radiant. Most heating devices (radiators, convectors, warm floors and walls) are convectively radiant, but the ratio of convection and radiation is different for everyone. When choosing a heating method, it is important to take into account that the optimal and most comfortable ratio of radiant and convective heat is 50/50.
Almost all heating devices use the indicated heat transfer paths, but all in different proportions.
Predominantly convective heating devices include convectors with mechanical and natural impulses. They are built-in, wall-mounted, floor-mounted, disguised as interior items, etc. Also, convective appliances include heating units, fan coil units, air heating systems.
The design of air heating is highly interdependent on ventilation and air conditioning systems and will be justified in cases of heating large premises - warehouses, sales areas, as well as in conjunction with standby water heating systems with periodic use of premises.
In stamped panel radiators, the radiating component begins to prevail over the convective one.
All kinds of radiant panels belong to the devices, which almost completely use the radiating component.
New design and installation technologies, as well as new materials (polypropylene, metal-plastic pipes, cross-linked polyethylene pipes, modular installation systems) reduce the cost of design and installation work, and reduce the heating installation time, and all this together only makes this technology popular.
The main types of heat carriers for the heating system:
- Steam - when condensing in heating devices, it gives off a significant amount of heat due to the latent heat of vaporization. Therefore, the mass of steam at a given heat load is reduced in comparison with other heat transfer fluids. But steam as a coolant in heating systems is inferior to water, since the temperature of the devices will be above 100 ° C, which leads to the sublimation of organic dust deposited on the devices, and to the release of harmful substances and unpleasant odors into the room. Also note that steam systems can be sources of noise. At low pressures (used in heating systems), steam has a significant specific volume, which leads to an increase in pipe cross-sections
- Air - an easily mobile heat carrier - is fire safe; in air systems, simple regulation of the constancy of the room temperature is possible. But due to the low heat capacity of the air to meet the given heat load, the air mass must be significant, which leads to the presence of channels with a large cross section for its movement and additional energy consumption. Air heating in some cases can provoke the development of harmful bacteria, legionella. Therefore, air heating is used only at industrial enterprises, combining it with forced ventilation systems or by installing heating units in workshops
- Water - has a high heat capacity and density, which allows you to transfer large amounts of heat with a small volume of coolant. This ensures small pipelines and relatively low heat losses. The sanitary-hygienic temperature of the heaters is easily reached, but the movement of water requires a lot of energy. Water circulates through closed pipes, and then the heat is transferred to various heating components, and from them the entire room is already heated
Water heating is currently the most widespread due to its advantages over other heating systems:
- low surface temperature of various devices and pipes
- ensuring the same temperature in rooms
- silent work
- long operational periods
- fuel economy
- ease of maintenance and operation
The experience of operating water systems has shown their best hygienic and operational performance. Hot water heating systems are the most reliable, quiet, simple and convenient to operate, and can have a significant horizontal radius of action. The vertical range of the system is determined by the hydrostatic pressure.
In water and steam systems, the heat carrier - water or steam - is heated in a heat generator and transferred through pipelines to heating devices. In air systems, heated air enters the room directly from the ventilation system.
According to the method of moving the coolant, central heating systems are divided into systems with natural circulation and systems with mechanical induction (forced circulation). For such a circulation, water heating options must be equipped with one or more pumps. After the coolant passes through the entire heating circuit, it is completely cooled and returned back to the boiler. Here it heats up again and thus allows the heating devices to generate heat again. Heating with circulation of natural water has recently been used extremely rarely.
Of course, the question of which heating system is better is impractical, since this or that system is effective in certain conditions. Comparison of heating systems should be made, taking into account all their pros and cons, focusing on the installation conditions and their own capabilities.
Which heating boiler to choose?


It is no secret that there is a fairly large selection of modern heating boilers. They are divided into types according to the fuel on which they work. Which one to choose depends on the circumstances. It is based on the fuel that is easiest to find in your area, and which is cheaper than everyone else.
Manufacturers are now offering dual-fuel combination models. For example, gas and firewood, gas and electricity, coal and electricity, firewood and diesel fuel. When one fuel runs out, it can be replaced with another. Therefore, the advice is to choose the boiler that is convenient for you both in terms of fuel supply, and in terms of operation and maintenance.
Heating pipes


REHAU metal-plastic pipe
Which pipes are best? For hot water heating, the best option are metal-plastic pipes that can withstand high temperatures. But if a solid fuel boiler is installed in the heating system of a private house, then it is better to use metal pipes. Indeed, sometimes the temperature of the coolant leaving the boiler can be more than + 100C, and the plastic cannot withstand it.
When choosing schemes for installing heating in a private house, you need to think carefully about everything, weigh and approve the budget exclusively for heating at the family council. It is from the money that you will have to dance. If the budget is large, then you can install a two-pipe scheme, and even with a collector and a pump. If it is small, then you can do with a one-pipe scheme. But if you add a little money and buy a circulation pump, then even this system will work well.
- Example 1. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a two-pipe scheme
- Example 2. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a one-pipe scheme
- Example 3. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a collector circuit
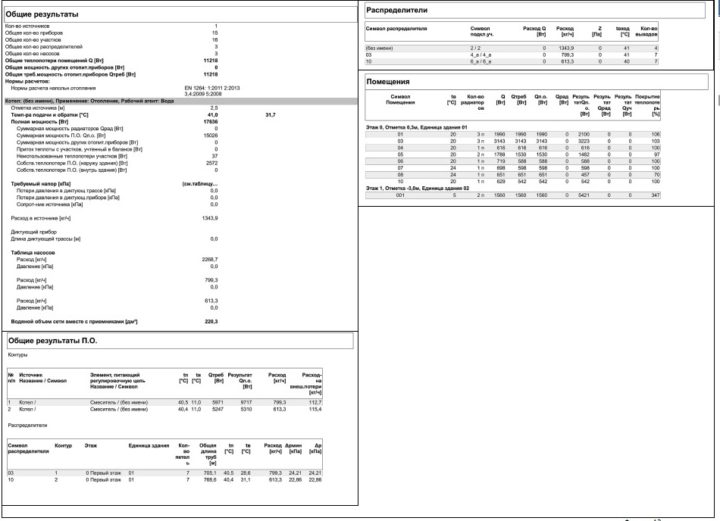
After a hydraulic calculation, it may turn out that the resistance of the heating system is too high. You can, of course, purchase a more powerful circulation pump. It is possible, as already suggested in the previous article, to increase the diameters of the pipes. But there is another option: change the way the radiators are connected. Therefore, I decided to add this article, which considers examples of heating systems projects for the same house.
In the previous materials, I performed calculations for a two-pipe heating system. You can replace it with a one-pipe one and perform all calculations on a new one ...
Well, not all, of course: the heat loss does not need to be re-counted. And also there is no need to re-count the sections of the radiators. It's only about the hydraulic calculation.
So, as I said, below are three examples of the project of the same house, but in each example the radiators are connected in a different way. All these schemes have already been sorted out, but I think it will be useful to refresh your memory.
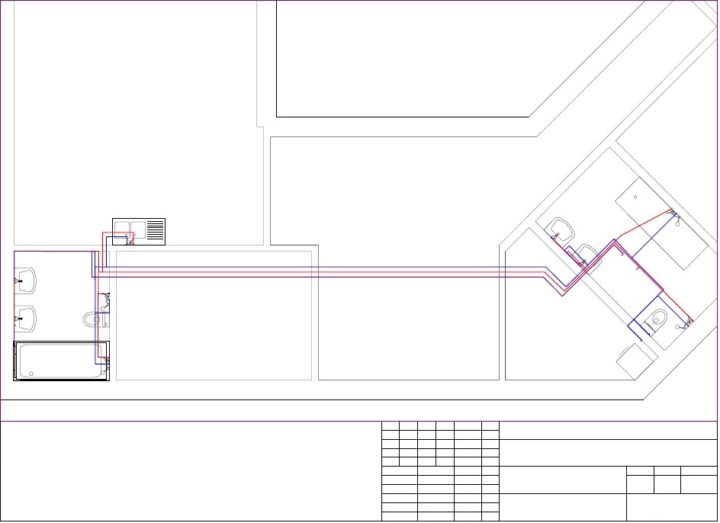
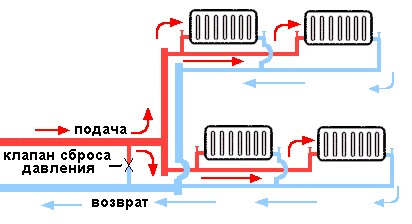
Example 1. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a two-pipe scheme
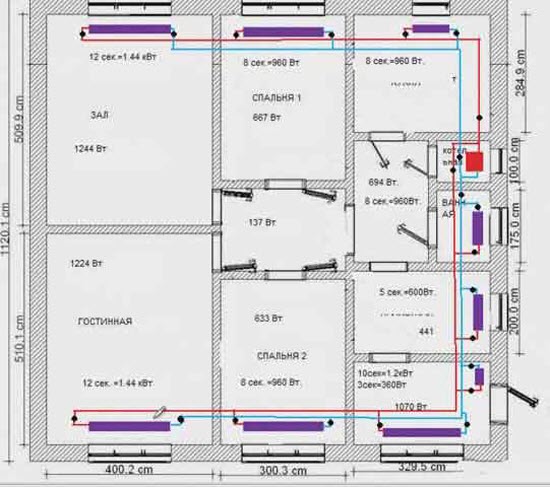

There is a boiler in the boiler room (red rectangle). Moreover, it is immediately worth making a reservation: if the boiler is wall-mounted, then it is not necessary to install it in the boiler room, it is allowed to install it both in the kitchen and in the hallway. But when designing, you need to remember about the chimney.
So, back to the heating system.
Radiators, as expected, under the windows; on the diagram radiators in purple.
In order not to pull pipes around the perimeter of the entire house, the pipeline is designed with two loops.
The supply pipe is marked in red, the return pipe is blue. Black dots on the supply and return are shut-off valves (radiator taps, thermal heads, etc.). Shut-off valves must be installed - in case the radiator for any reason fails, and it will need to be disconnected from the system for replacement or repair without stopping the entire system.
In addition to shut-off valves on each radiator, the same valves are on the supply for each wing, immediately after the boiler.
Why are shut-off valves installed here? As you can see from the diagram, the length of the system loops is not the same: the “wing” going up from the boiler (if you look at the diagram) is shorter than the one that goes down. This means that the resistance of a shorter pipeline will be less. Therefore, the coolant can go more along the shorter wing, then the longer "wing" will be colder. Due to the taps on the supply pipe, we will be able to adjust the uniformity of the coolant supply.
The same taps are installed on the return flow of both loops - in front of the boiler.
Regulatory framework for the design of heating systems
The heating system (CO) is a complex of engineering equipment. In order for all CO components to work with the expected efficiency, a preliminary development of a building heating project is required.
Such work has the right to be performed by a specialized company that has the appropriate permits and qualified personnel. For example, our company.
The fundamental document is SP 60.13330.2012 (approved by order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation No. 279 of 06/30/12). This joint venture is a revised version of SNiP 41-01-2003.
The JI project is created with the obligatory consideration of the requirements of the current regulatory and legislative acts, which regulate the issues of explosion and fire safety of the facility, energy efficiency, environmental friendliness, sanitary norms and rules, etc. The list of these standards is very extensive. For example, the following standards can be cited:
• SP 14.13330.2014 (SNiP II-7-81 *), the Ministry of Construction of the Russian Federation approved the aforementioned set of rules on 02/18/14 by its order No. 60 / pr. The current version of the document is dated 11/23/15; • SP 131.13330.2012 (SNiP 23-01-99 *). The Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation approved the aforementioned set of rules by order No. 275, issued on 30.06.12. The document is valid with changes made as of 11/17/15; • SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10. Approved by Resolution No. 64, adopted by the State State Civil Service of the Russian Federation on June 10, 2010 (as amended as of December 27, 2010); • Interstate standard 30494-2011. This GOST as a Russian standard was introduced on 12.07.12 by order No. 191-st. published by Rosstandart of the Russian Federation.
To the table of contents
Example 2. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a one-pipe scheme
The diagram below shows the same house design, but the heating system is one-pipe.
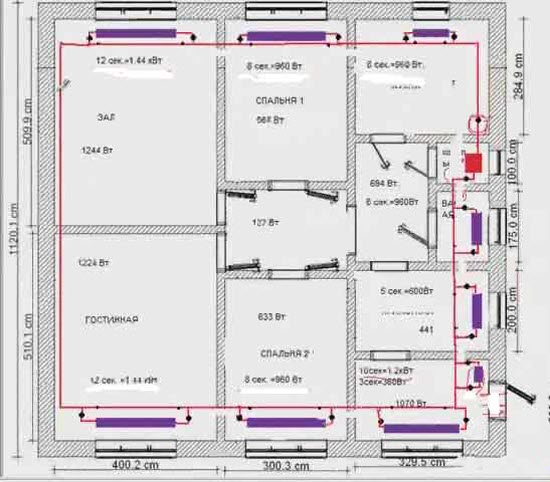

In principle, the requirements are the same here (shut-off valves on each radiator, on the supply and on the return).
The only difference is that the pipe runs along the entire perimeter of the house, and not in separate circuits, as in the example with a two-pipe system. In addition, it must be remembered that with a one-pipe system, a pipe of a smaller diameter should be placed under the radiators (in the diagram, such areas under the radiators are marked with dots). This is necessary for uniform heating of the radiators. You can read more about the nuances of a one-pipe heating system from a separate article.