Narrowing the diameter of the heating pipe consequences
The right choice: calculating the diameter of the pipe for heating
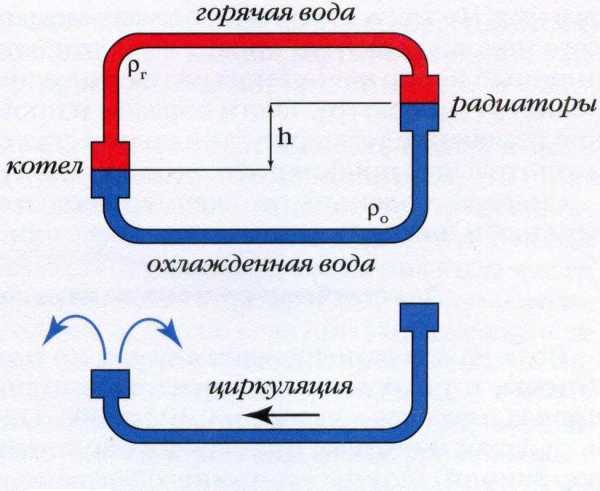
Before installing heating in a house, you must first correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes. The calculation will be considered on systems with forced ventilation. In such systems, the movement of the coolant is provided by a constantly running circulation pump. When choosing the diameter of the pipes, it is taken into account that their main task is to ensure the delivery of the required amount of heat to the heating devices.
Data: how to calculate the diameter of a pipe for heating
To calculate the diameter of the pipeline, you will need the following data: this is the total heat loss of the dwelling, and the length of the pipeline, and the calculation of the power of the radiators of each room, as well as the wiring method. The divider can be one-pipe, two-pipe, forced or natural ventilation.
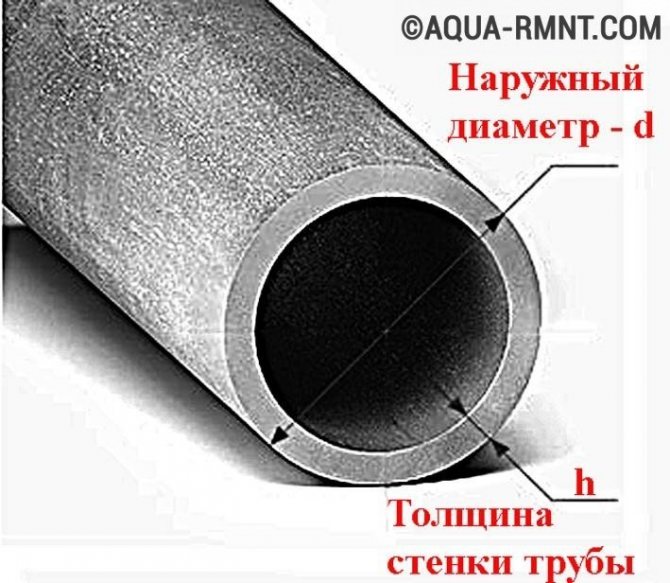
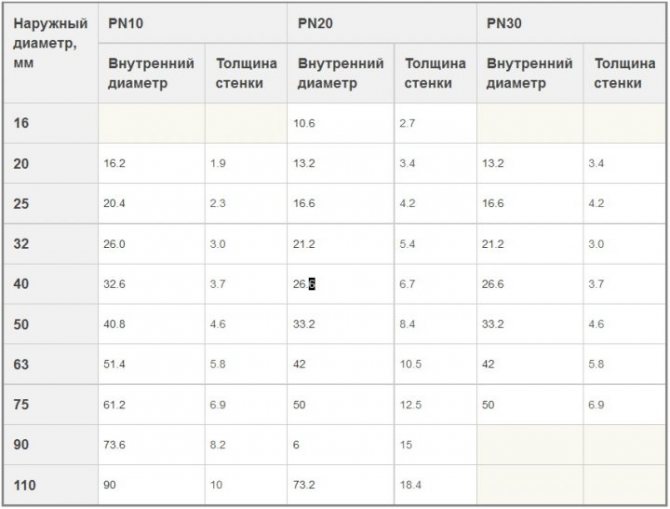
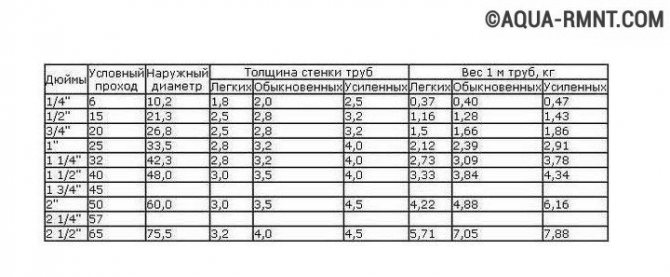
Also pay attention to the markings on the outer diameter copper and polypropylene pipes. The internal one can be calculated by subtracting the wall thickness. For metal-plastic and steel pipes, the inner dimension is affixed when marking.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to calculate the exact cross-section of the pipes. One way or another, you will have to choose from a couple of options. This point is worth explaining: a certain amount of heat must be delivered to the radiators, while achieving uniform heating of the batteries. If we are talking about systems with forced ventilation, then this is done using pipes, a pump and the heat carrier itself. All that is needed is to drive out the required amount of coolant for a certain period of time.
It turns out that it is possible to choose pipes of a smaller diameter, and supply the coolant at a higher speed. You can also make a choice in favor of pipes of a larger cross-section, but reduce the flow rate of the coolant. The first option is preferred.
Selecting the water speed in the heating system
Higher water velocities and smaller pipes are the most common choices. If you increase the diameter of the pipe, then the speed of movement will decrease. But the latter option is not so frequent, reducing the movement is not very beneficial.


When choosing pipes, you should also take into account the possible speed of water in the heating system.
Why high speed and smaller pipe diameter are more beneficial:
- Products with a smaller diameter cost less;
- It is easier to work with pipes of a smaller diameter at home;
- If the gasket is open, they do not attract attention so much, and if the installation goes into the walls or floor, then smaller strobes will be required;
- The small diameter provides a smaller amount of coolant in the pipe, and this, in turn, reduces the inertia of the system, which saves fuel.
Special tables have been developed, according to which the size of pipes for the house is determined. Such a table takes into account the required amount of heat, as well as the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as the temperature indicators of the system. It turns out, in order to carry out the selection of pipes of the desired section, the necessary table is found, and the diameter is selected from it. Today, there may be a suitable online program that replaces the table.
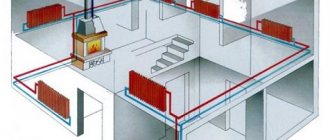
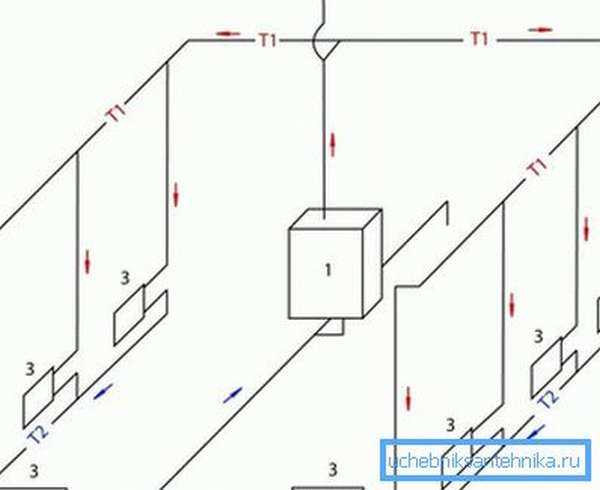
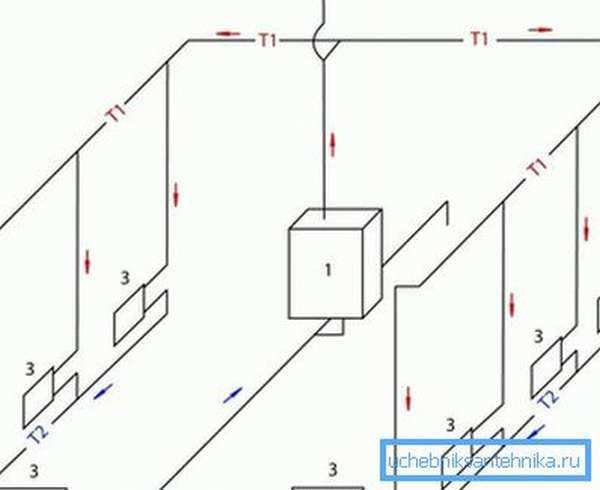
Heating system wiring diagram and diameter of pipes for heating
The heating wiring diagram is always taken into account. It can be two-pipe vertical, two-pipe horizontal and one-pipe. The two-pipe system assumes both upper and lower placement of the lines. But the one-pipe system takes into account the economical use of the length of the lines, which is suitable for heating with natural circulation. Then the two-pipe system will require the mandatory inclusion of the pump in the circuit.
There are three types of horizontal routing:
- Dead end;
- Beam or collector;
- With parallel movement of water.
By the way, in the scheme of a one-pipe system, there may also be a so-called bypass pipe. It will become an additional line for fluid circulation if one or more radiators are turned off. Usually, shut-off valves are installed on any radiator, which allow you to shut off the water supply if necessary.
What can be the consequences: narrowing the diameter of the heating pipe
Narrowing the pipe diameter is highly undesirable. When wiring around the house, it is recommended to use the same standard size - you should not increase or decrease it. The only possible exception is the long length of the circulation circuit. But even in this case, you need to be careful.


Many experts do not recommend narrowing the diameter of the pipes, as this can adversely affect the entire heating system.
But why is the size narrowing when replacing a steel pipe with a plastic one? Everything is simple here: with the same inner diameter, the outer diameter of the plastic pipes themselves is larger. This means that the holes in the walls and ceilings will have to be expanded, moreover, seriously - from 25 to 32 mm. But for this you will need a special tool. Therefore, it is easier to pass thinner pipes into these holes.
But in the same situation, it turns out that the tenants who made such a replacement of pipes, automatically "stole" from their neighbors on this riser about 40% of the heat and water passing through the pipes. Therefore, it should be understood that the thickness of the pipes, which is arbitrarily replaced in a thermal system, is not a matter of a private decision, this cannot be done. If steel pipes are replaced with plastic ones, you will have to expand the holes in the ceilings, whatever one may say.
There is also such an option in this situation. It is possible, when replacing risers in old holes, to skip new sections of steel pipes of the same diameter, their length will be 50-60 cm (this depends on such a parameter as the thickness of the overlap). And then they are connected by couplings with plastic pipes. This option is perfectly acceptable.
Calculation of the diameter of a pipe for heating: how to calculate, the speed of water in the system, the consequences of narrowing, the coolant
Calculation of the pipe diameter for heating precedes the calculation of the total heat loss, boiler power and radiator power for each room. Also, a wiring method is chosen, a diagram and calculations are drawn up.
trubyisantehnika.ru
Calculation of heating pipes - heat supply in an apartment in a city and a privatized house
Whether we change worn out sections of risers and connections in an apartment, whether we design the heating system of a country house from scratch - over time we will need to buy materials. Heating devices, valves, fittings and ... pipes. How not to miss with their diameter?
This is what our publication is about.
The work of the heat supply is determined no less from the diameter of the pipes than from the type of batteries
What are the calculations for?
Why not take the diameter by eye? Or, to be on the safe side, with a deliberate margin?
Here it is worth dividing two quite different cases.
- In an apartment in the city, if the diameter of the riser is underestimated, we get slow circulation in it. All your neighbors above and below will get colder. But with an excessive cross-section of the pipe, we do not get any bad consequences, apart from dubious aesthetics.
However: with an increase in the pipe diameter, its cost increases non-linearly. A pipe diameter of 32 millimeters is almost four times more expensive than a pipe with a diameter of 16 millimeters. This is clear: its mass grows in proportion to the square of the diameter, and simultaneously with the mass, the cost of producing a running meter also grows.
The cost of the pipe grows in proportion to the square of the diameter
- But in a private house, if the diameter is overestimated, we will suffer not only financially. The volume of the heat carrier becomes larger, and significantly. Hence - the large inertia of the system: after the boiler is fired up, the heating devices will heat up very slowly.
If the piping is done in the basement or in the attic, heat loss will also increase: a thick pipe has a decent surface area.
To underestimate the cross-section of the heating system is also the worst option: to maintain the proper temperature, the design of the radiators will have to make the circulation in the system faster. This leads to noises at bends and valves, not to mention throttling points.
Where to get the diameter values
Let's stipulate right away: the hydraulic calculation of pipelines is a rather complex engineering task that takes into account quite a few factors.
This includes:
- The material of the pipe and the index of its roughness, on which the hydraulic resistance depends.
- The degree of its wear.
- Heat carrier head.
- Number of turns and their angle.
- Number and type of valves.
- Planned operational period.
Clarification: the degree of wear affects the hydraulic resistance of the profile pipes. The roughness of the surface inside polymer and metal-polymer pipes remains almost unchanged for some time. Which, however, does not make the calculation not heavy.
For the correct calculation of heating systems of high-rise buildings and highways, engineers use, in other words, Shevelev's tables and complex formulas; we need the most common solution.
In the case of standard projects of high-rise buildings, the usual reduction of the pipe diameter by a step will provide an opportunity to save very large sums
Let's divide the problem into its components.
Apartment in the city
Here it is enough to learn a few of the simplest rules:
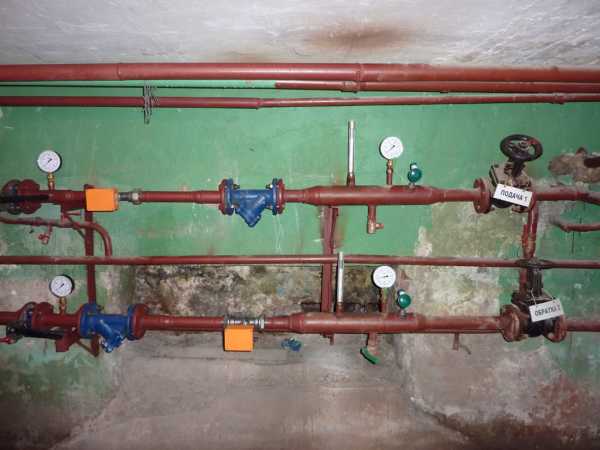
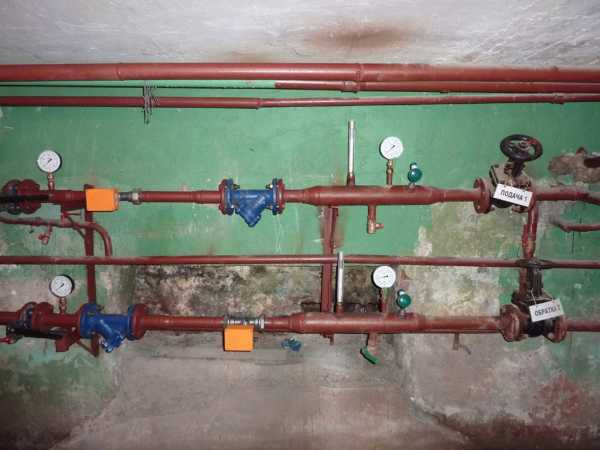
- When replacing a heat supply riser, a pipe of the same diameter is taken as used by the builders. It is not necessary to either overestimate or underestimate the diameter. An exception is the notable case of previous repair work done by unqualified professionals. If the cross-section of the riser in a short section changes from DU25 to DU15, it is better to cut it out by removing the diameter transition.
- For connection to a heat exchanger of different types, a DU20 pipe is sufficient. Narrowing of the pipe is allowed only after a bridge, which can be made with a DN15 pipe.
- If a choke, a thermostatic head, or even just a valve is placed in front of the radiator, the jumper is strictly required and has the same diameter as the riser.
If you do not want a part of the heat to pass by the heating batteries during the peak of cold weather, put the valve on the jumper. Of course, if the throttling valve is not fully open, the valve on the jumper must be in the "open" position.
Only and exclusively modern ball valves are used. They are much more reliable when compared with the morally old screw and in the "open" position have a small hydraulic resistance.
In the photo, all the needs are met. New riser of the same diameter as the outdated one; the jumper is made with the same diameter. The heater is cut off by ball valves
Gravity heating system
regardless of the number of storeys in the house, the length of such a system is limited by the largest difference that can create a thermal expansion of the heat carrier. The outline cannot be long; the area of the room that is heated and the heating capacity of the boiler are also limited.
If so, the task can be facilitated by giving the exact values of the diameters.
- For a house with an area of up to 70-80 square meters, the filling is performed with a DN 32 pipe. For a larger area - DN 40 or even DN 50.
Important: do not confuse the symbolic diameter with the outside. DU is a parameter approximately equal to the inner section of the pipe and introduced to unify fittings and connectors. The outer one can significantly stand out from it due to the decent wall thickness.
It is best to install shut-off valves on it; chokes or thermostats for balancing the system will not be superfluous.A common problem with convective circulation systems is that the heating devices closest to the boiler are much hotter than the distant ones.
The diameter of the filling is 40 millimeters, the liners are 20. If necessary, the design of the radiator is changed by valves. Strictly speaking, this is not true; but the scheme is quite workable
Forced type circulation system
In order to calculate the required pipe diameter with our own hands in an arbitrary case, we still have to get into the jungle. However, not very far: instead of a complex calculation, we will use a table.
The table makes it possible to choose the size of the pipe without too complicated calculations.
How do I use this table?
The instruction is not very complicated.
However, we need additional information about where to get the necessary speed of movement of the heat carrier and the heat flux in watts.
- The boundaries of the speed of water in pipes are 0.6 - 1.5 meters per second. At a lower speed, distant heaters will noticeably cool down; if it is higher, the noise background of the water at the fittings will become audible.
- The approximate amount of heat required for a privatized house can be calculated based on a rate of 60 watts per cubic meter of volume. For a warm region, the resulting amount is multiplied by 0.7 - 0.9, for the severe cold of Chukotka or Yakutia - by 1.5-2.0.
Let's take as an example a pipe for a heating circuit of a house with an area of 75 square meters somewhere in Krasnodar.
The ceiling height is 3 meters; we will not divide the heating system into several independent circuits; the speed of water in the pipes is limited to 1 meter per second.
- We calculate the need for heat. The volume of the room is 75 * 3 = 225 m3. For its heat supply at the peak of cold weather, you will need 225 * 60 = 13500 watts. The warm climate of Krasnodar will force us to reduce the need for heat to 13500 * 0.7 = 9450 watts.
- Now we are looking for the required speed of water movement in the contour in the upper horizontal line. Let's remind - it is equal to 1 meter per second.
- Found it? We move vertically down the table until in the top line of the square we see a value greater than the required 9.5 kilowatts. Rounding here should be done only upwards.
- In the fourth square from the top, we find a value of 14370 watts, at which we can complete the search. As you can easily see, it corresponds to the inner diameter of the pipe of 15 millimeters. This means that we can stop our own choice on a half-inch pipe made of steel or polypropylene with an outer diameter of 20 millimeters.
With the same permeability, the outer diameter of the profile pipe is smaller due to thinner walls
Using the table, you need to take into account that it gives values for the mouth of the temperatures between the supply and return of 20 degrees. Which, nevertheless, is considered quite common for local heating systems.
Useful little things
In conclusion - a certain amount of unsystematic information, which may be useful to the reader during the design of his own heating system.
- The advantage of a small cross-section of pipes - low thermal inertia of the system - negates the use of cast iron radiators. Their parts have a large internal volume, and the heating devices themselves heat up due to their large mass and relatively low thermal conductivity for a long time. A good choice for local heating is aluminum radiators.
- But still, sometimes thermal inertia is considered a plus. If you live in the house regularly and use a solid fuel boiler, which needs to be loaded with firewood or coal a couple of times a day, the fact that the batteries will cool down for a long time will only please.
- In addition, a heat accumulator will help to expand the inertia of the system - an insulated tank with a volume of 300-2000 liters. Among other things, it will help to heat the house with electric current, using it at an inexpensive night rate. The tank is mounted at the most different point of the contour and accumulates heat at night; during the day, the hot heat carrier in it gives off heat energy to the batteries.
- With collector wiring from the collector, metal-plastic or polyethylene (of course, cross-linked polyethylene) pipes of a very small diameter are used. An external section of 16 millimeters in this case is fully sufficient.
With a collector scheme, a large diameter of the connection is not required. Each insert supplies only one heater
- Pipes of various types fit into the screed only in one piece, without any connections - welded or fitting. The exception is polypropylene: its welded joints do not stand out from a solid pipe for durability and strength; however, the material is not very flexible like metal plastic or pex pipe.
Conclusion
We hope that the proposed pipe selection methods seem good to you. As in most cases, the video at the end of the post will offer additional information on this curious topic. Mild winters!
how to calculate, the speed of water in the system, the consequences of constriction, the coolant
Before installing heating in a house, you must first correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes. The calculation will be considered on systems with forced ventilation. In such systems, the movement of the coolant is provided by a constantly running circulation pump. When choosing the diameter of the pipes, it is taken into account that their main task is to ensure the delivery of the required amount of heat to the heating devices.
Data: how to calculate the diameter of a pipe for heating
To calculate the diameter of the pipeline, you will need the following data: this is the total heat loss of the dwelling, and the length of the pipeline, and the calculation of the power of the radiators of each room, as well as the wiring method. The divider can be one-pipe, two-pipe, forced or natural ventilation.
Also pay attention to the markings on the outer diameter copper and polypropylene pipes. The internal one can be calculated by subtracting the wall thickness. For metal-plastic and steel pipes, the inner dimension is affixed when marking.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to calculate the exact cross-section of the pipes. One way or another, you will have to choose from a couple of options. This point is worth explaining: a certain amount of heat must be delivered to the radiators, while achieving uniform heating of the batteries. If we are talking about systems with forced ventilation, then this is done using pipes, a pump and the heat carrier itself. All that is needed is to drive out the required amount of coolant for a certain period of time.
It turns out that it is possible to choose pipes of a smaller diameter, and supply the coolant at a higher speed. You can also make a choice in favor of pipes of a larger cross-section, but reduce the flow rate of the coolant. The first option is preferred.
Selecting the water speed in the heating system
Higher water velocities and smaller pipes are the most common choices. If you increase the diameter of the pipe, then the speed of movement will decrease. But the latter option is not so frequent, reducing the movement is not very beneficial.


When choosing pipes, you should also take into account the possible speed of water in the heating system.
Why high speed and smaller pipe diameter are more beneficial:
- Products with a smaller diameter cost less;
- It is easier to work with pipes of a smaller diameter at home;
- If the gasket is open, they do not attract attention so much, and if the installation goes into the walls or floor, then smaller strobes will be required;
- The small diameter provides a smaller amount of coolant in the pipe, and this, in turn, reduces the inertia of the system, which saves fuel.
Special tables have been developed, according to which the size of pipes for the house is determined. Such a table takes into account the required amount of heat, as well as the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as the temperature indicators of the system. It turns out, in order to carry out the selection of pipes of the desired section, the necessary table is found, and the diameter is selected from it. Today, there may be a suitable online program that replaces the table.
Heating system wiring diagram and diameter of pipes for heating
The heating wiring diagram is always taken into account. It can be two-pipe vertical, two-pipe horizontal and one-pipe. The two-pipe system assumes both upper and lower placement of the lines. But the one-pipe system takes into account the economical use of the length of the lines, which is suitable for heating with natural circulation. Then the two-pipe system will require the mandatory inclusion of the pump in the circuit.
There are three types of horizontal routing:
- Dead end;
- Beam or collector;
- With parallel movement of water.
By the way, in the scheme of a one-pipe system, there may also be a so-called bypass pipe. It will become an additional line for fluid circulation if one or more radiators are turned off. Usually, shut-off valves are installed on any radiator, which allow you to shut off the water supply if necessary.
What can be the consequences: narrowing the diameter of the heating pipe
Narrowing the pipe diameter is highly undesirable. When wiring around the house, it is recommended to use the same standard size - you should not increase or decrease it. The only possible exception is the long length of the circulation circuit. But even in this case, you need to be careful.

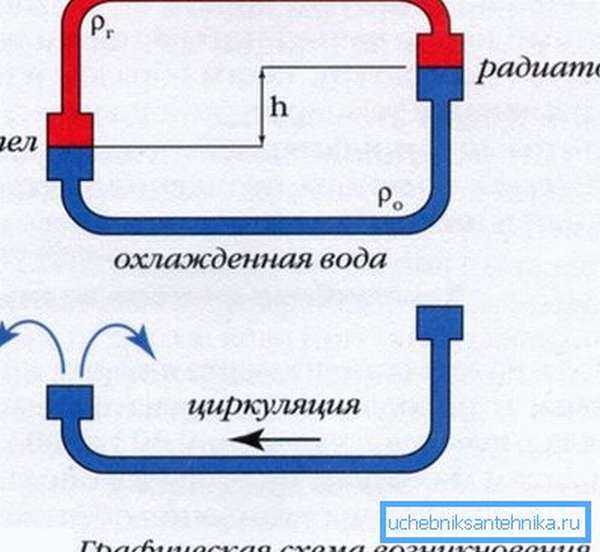
Many experts do not recommend narrowing the diameter of the pipes, as this can adversely affect the entire heating system.
But why is the size narrowing when replacing a steel pipe with a plastic one? Everything is simple here: with the same inner diameter, the outer diameter of the plastic pipes themselves is larger. This means that the holes in the walls and ceilings will have to be expanded, moreover, seriously - from 25 to 32 mm. But for this you will need a special tool. Therefore, it is easier to pass thinner pipes into these holes.
But in the same situation, it turns out that the tenants who made such a replacement of pipes, automatically "stole" from their neighbors on this riser about 40% of the heat and water passing through the pipes. Therefore, it should be understood that the thickness of the pipes, which is arbitrarily replaced in a thermal system, is not a matter of a private decision, this cannot be done. If steel pipes are replaced with plastic ones, you will have to expand the holes in the ceilings, whatever one may say.
There is also such an option in this situation. It is possible, when replacing risers in old holes, to skip new sections of steel pipes of the same diameter, their length will be 50-60 cm (this depends on such a parameter as the thickness of the overlap). And then they are connected by couplings with plastic pipes. This option is perfectly acceptable.
Correct calculation of the pipe diameter for heating (video)
If you are incompetent in calculating the diameter of pipes, return lines, schemes and the choice of a coolant, it is better to call specialists and ask them to comment on their work.
Happy projects!
Add a comment
teploclass.ru
What is it for
But in reality - why do you need to calculate the diameters of heating pipes? Why not simply take pipes that are obviously oversized? Since in this way we will protect ourselves from excessively slow circulation in the circuit.
Alas, there are a couple of big flaws in this approach.
- Material consumption and the price of a running meter grows in proportion to the square of the diameter. The costs will be far from cheap.
See: in order to maintain the same operating pressure with increasing pipe diameter, it is necessary to increase the wall thickness, which further increases the material consumption.
- Equally important, the increased diameter of the pipeline indicates an increase in the amount of coolant and the increased thermal inertia of the system. It will warm up longer and cool down longer, which is not always necessary.
- Finally, with an open laying of thick heating pipes, they will not really decorate the room, and with a hidden one, they will increase the depth of the strobes. in the walls or the thickness of the screed on the floor.
which one to choose, the consequences of narrowing to the apartment, selection according to the table

Heating a house or apartment is not such a simple engineering system as it might seem at first glance. When drawing up a project, it is required make a lot of calculations, in particular, the required pipeline diameter.
Choosing the right diameter is a guarantee of a reliable, comfortable and efficient system heating of premises.
For example, heating without a pump, where the coolant circulates by gravity, may not work at all with too narrow pipes, and a scheme with forced circulation when the diameter is too low will make noise or not warm up the premises to the desired temperature. Therefore, you should use the calculation rules that will allow you to reduce heat loss to a minimum.
Odnoklassniki
Effect of pipe diameter on efficiency for a heating system in a private house
It is a mistake to rely on the "bigger is better" principle when choosing a pipeline cross-section. Too large pipe cross-section leads to lower pressure in it, and hence the speed of the coolant and heat flow.
Moreover, if the diameter is too large, the pump simply may not have enough performance to move such a large volume of coolant.
Important! A larger volume of the coolant in the system implies a high total heat capacity, which means that more time and energy will be spent on heating it, which also affects the efficiency not for the better.
Selection of pipe cross-section: table
The optimal pipe cross-section should be as small as possible for a given configuration (see table) for the following reasons:
- a small volume of coolant heats up faster;
- less clearance creates more resistance
ogon.guru
Calculation of the diameter of the pipe for heating - a crucial stage - Plumber's Tutorial
At a time when it comes to installing a heating system, it is often easy to choose a pipe based on the advice of the usual or the recommendations of the sellers in the store. Calculation of the diameter of a pipe for heating is not always performed.
Choosing a standard size at random, there is a risk that the heating system will not work efficiently.

Influence of diameter on heating operation
The installation instructions for the heating system hardly touch upon the issues of calculating the pipeline (besides, determine how to calculate the diameter of the pipe for heating).
At the same time, when moving through the pipe, the coolant encounters several types of resistances and this must be taken into account when selecting a standard size:
- rubbing against walls... Due to this, some of the speed is lost,
- loss of speed when cornering... It is unrealistic to lay out the wiring around the apartment without turns (in addition, there are turns at an angle of 90?),
- change in diameters... If, when wiring around the apartment, try to use different standard sizes, then resistance to flow movement will also be observed at the interface of various standard sizes.
Note! Narrowing the diameter of the heating pipe is undesirable. When wiring around the house, you must use the same size. An exception is allowed when the length of the circulation circuit is enormous; under such conditions, it is possible to expand the speed of movement of the coolant by reducing D.
As for the pipeline itself, its main feature affecting the movement of the coolant can be called the inner diameter (Dvn). The smaller it is, the greater the pressure, and vice versa - with an increase in DP, the pressure in the system decreases. This must be taken into account at the time when the selection of the diameter of the pipe for heating is performed.
A common mistake of amateur plumbers is connected with this phenomenon. They are sure that if you take a larger size, then a room will pass through the radiators and a larger amount of coolant will warm up faster.
In fact, the effect will be the opposite - due to the drop in pressure, the batteries will remain cool. Under such conditions, the installation of a more wonderful circulation pump can help out, but the price for a solution is high, it is much easier to choose the right diameter correctly.

Heating system calculation example
In most cases, a simplified calculation is performed based on such parameters as the amount of the room, the level of its insulation, the difference in temperature flow and the speed of the coolant in the supply and discharge pipelines.
The diameter of the pipe for heating with forced circulation is determined in the following sequence:
- the total amount of heat that needs to be supplied to the room is determined (thermal power, kW), it is possible to be guided by the tabular data,


- setting the speed of water movement, determine the optimal D.
Calculation of heat output
An example will be a standard room with dimensions of 4.8x5.0x3.0 m. Heating circuit with forced circulation, you need to calculate the diameters of heating pipes for wiring around the apartment. The main calculation formula looks like this:
the formula uses the following designations:
- V is the number of rooms. In the example, it is equal to 3.8 * 4.0 * 3.0 = 45.6m3,
- ? t is the difference between outdoor and indoor temperatures. In the example, 53 ° C is taken,
- K is a special coefficient that determines the degree of insulation of the building. In general, its value ranges from 0.6-0.9 (effective thermal insulation is used, the roof and floor are insulated, at least double-glazed windows are installed) to 3-4 (buildings without thermal insulation, for example, change houses). In the example, an intermediate option is used - the apartment has standard thermal insulation (K = 1.0 - 1.9), K = 1.1 is taken.
Total thermal power should be equal to 45.6 • 53 • 1.1 / 860 = 3.09 kW.
It is possible to use tabular data.

Determination of the diameter
The diameter of the heating pipes is determined by the formula
Where the notation is used:
- ? t - the difference between the temperatures of the coolant in the supply and outlet pipelines... Considering that water is supplied at a temperature of about 90-95? C, and it has time to cool down to 65-70? C, the temperature difference can be taken equal to 20? C,
- v is the speed of movement of water... It is undesirable for it to exceed the value of 1.5 m / s, and the minimum permissible threshold is 0.25 m / s. It is recommended to stop at an intermediate speed of 0.8 - 1.3 m / s.
Note! The wrong choice of the diameter of the heating pipe can lead to a drop in speed below the minimum threshold, which, in turn, will lead to the formation of air jams. As a result, the work efficiency will become zero.
The value of Dвн in the example will be v354 • (0.86 • 3.09 / 20) / 1.3 = 36.18 mm. If you pay attention to the standard sizes, for example, the PP pipeline, you can see that there is no Dvn. Under such conditions, the closest diameter of the propylene pipes for heating is easily selected.
In this example, it is possible to select PN25 with a double diameter of 33.2 mm, this will lead to a small increase in the speed of movement of the coolant, but it will still remain within acceptable limits.
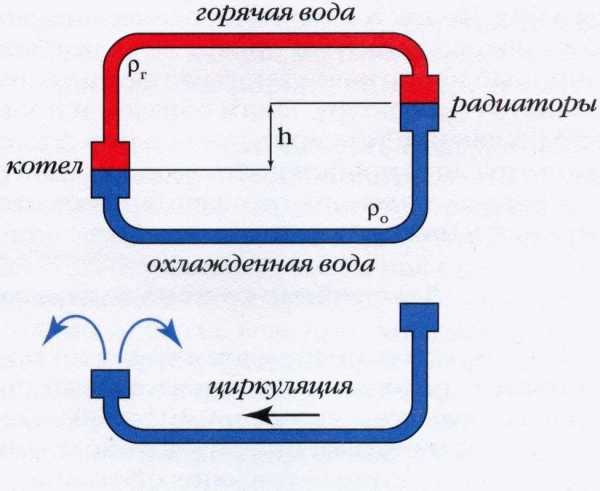
Features of heating systems with natural circulation
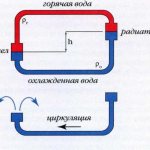
Their main difference is that they do not use a circulation pump for pressure. The liquid moves by gravity, at the end of heating it is forced upward, after that it passes through the radiators, cools down and returns to the boiler.


Compared to systems with forced circulation, the diameter of pipes for natural circulation heating must be larger. The basis of the calculation in this case is that the circulating pressure exceeds the loss for local resistance and friction.

In order not to calculate the value of the circulating pressure any time, there are special tables compiled for various temperature differences. For example, if the length of the pipeline from the boiler to the radiator is 4.0 m, and the temperature difference is 20 ° C (70 ° C in the outlet and 90 ° C in the supply), then the circulation pressure will be 488 Pa. Based on this, the speed of the coolant is selected using the transformation method D.
When performing calculations with your own hands, a verification calculation is also necessary.In other words, the calculations are carried out in the reverse order, the purpose of the check is to establish whether the losses in local resistance and friction do not exceed the circulating pressure.
Summarizing
The calculation of the heating pipeline is a very important task at the design stage. The information in the article will allow you to independently calculate the heating system, so that a comfortable microclimate in the house is guaranteed (see also the article ‘Which particular pipes for heating are better: analysis of the 4 most common options’).
In the video in this article, the calculation of the pipeline is carried out at the permissible speed.
Loading…
partner-tomsk.ru
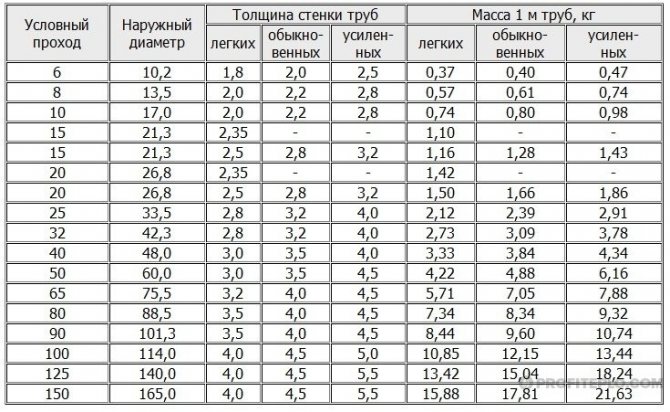
Features of calculating the cross-section of metal pipes
For large heating systems with metal pipes, heat losses through the walls must be taken into account. The losses are not so great, but with a large length, they can lead to the fact that the temperature on the last radiators will be very low due to the wrong choice of diameter.
Let's calculate the loss for a 40 mm steel pipe with a wall thickness of 1.4 mm. Losses are calculated using the formula:
q = k * 3.14 * (tv-tp)
Where:
q - heat loss per meter of pipe,
k is the linear heat transfer coefficient (for a given pipe it is 0.272 W * m / s);
tv - water temperature in the pipe - 80 ° С;
tp - air temperature in the room - 22 ° С.
Substituting the values, we get:
q = 0.272 * 3.15 * (80-22) = 49 W / s
It turns out that almost 50 W of heat is lost per meter. If the length is significant, it can become critical. It is clear that the larger the cross section, the greater the losses.
If you need to take these losses into account, then when calculating the losses, the losses on the pipeline are added to the decrease in the heat load on the radiator, and then, according to the total value, the required diameter is found.
But for individual heating systems, these values are usually not critical. Moreover, when calculating heat loss and equipment power, most often the calculated values are rounded up. This gives a certain margin, which allows you not to make such complex calculations.
An important question: where to get the tables? Almost all manufacturers' websites have such tables. You can read it directly from the site, or you can download it yourself. But what to do if you still haven't found the tables you need for the calculation.
You can use the diameter selection system described below, or you can do it differently.
Despite the fact that when marking different pipes, different values are indicated (internal or external), with a certain error they can be equated.
From the table below you can find the type and designation for a known inner diameter. You can immediately find the corresponding pipe size from a different material. For example, you need to calculate the diameter of metal-plastic heating pipes. You did not find the table for MT. But there is for polypropylene.
Select the dimensions for the PPR, and then use this table to find analogs in the MP. Naturally, there will be an error, but for systems with forced circulation, it is permissible.
Selection of the diameter of heating pipes - Teplopraktik
The diameter of the heating pipes depends on how much of the coolant will pass through them. Obviously, the diameter will be larger on the main supply pipe from the heating boiler, on a branch with three radiators it will be even smaller, and on the final radiator it will be the smallest. Accordingly, the diameter of the pipe will depend on the total heat output of the radiators that feed this pipeline.
In addition, the diameter of the pipeline depends on the speed of movement of the coolant in the system and on the supply / return temperature difference. The higher this difference, the smaller the required pipe diameter. The standard temperature difference is 20 ° C. In more comfortable systems, this difference is less - 10 ° С.
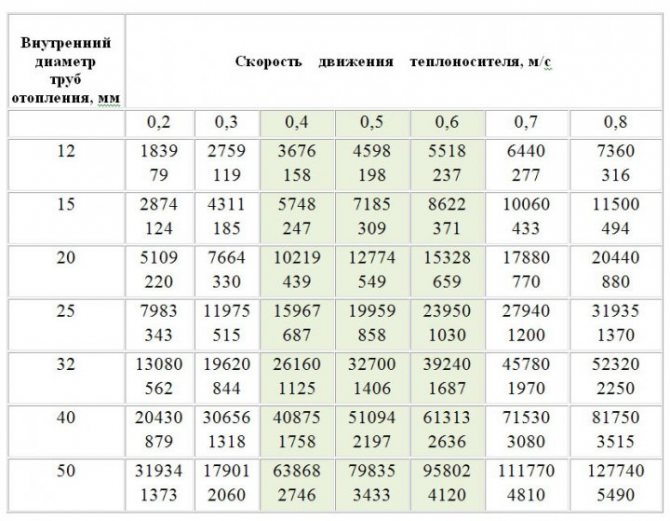
A heating system with a circulation pump is characterized by a high speed of the coolant, while a system with natural circulation has a low speed, so this must be taken into account when selecting heating pipes. It is not necessary to include in the calculation of pipelines too high speed of movement of water in the pipes, becausethis will create various unpleasant noises and murmurs in the pipes. If the speed is too low, there is a risk of air congestion in the system. The speed of movement in the pipes should be in the range of 0.4 - 0.6 m / s. The gravity system is characterized by a significantly lower speed of the coolant, therefore, the diameter of the pipes must be chosen larger.
Therefore, below we will indicate tables for the selection of pipe diameters for various systems with the specified parameters. The table uses the selection of the diameter of pipes from various materials. Steel pipes VGP are designated by the inner diameter, while polypropylene, metal-plastic and cross-linked polyethylene pipes are designated by the outer diameter. This is taken into account in the table for the selection of pipe diameters.
Supply / return temperature difference - 20 ° С, water speed 0.5 m / s - STANDARD HEATING SYSTEM | ||||
| Heat load, kW | Required inner pipe diameter, mm | Selection of a pipe for the required inner diameter: | ||
| VGP steel | Polypropylene | XLPE | ||
| 50 | 39 | 1.5 inches (40mm) | 50 | 50 |
| 40 | 35 | 1.5 inches (40mm) | 50 | 50 |
| 30 | 30 | 1.25 inches (32mm), quarter inch) | 40 | 40 |
| 20 | 25 | 1 inch (25mm) | 32 | 32 |
| 15 | 21 | 1 inch (25mm) | 32 | 32 |
| 12 | 19 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 10 | 17 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 8 | 16 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 6 | 14 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 5 | 12 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 4 | 11 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | 10 | 3/8 '' (10mm) | 16 | 16 |
| 2 | 8 | 3/8 '' (10mm) | 16 | 16 |
| 1 | 6 | 3/8 '' (10mm) | 16 | 16 |
Supply / return temperature difference - 10 ° С, water speed 0.5 m / s - LOW TEMPERATURE HEATING SYSTEM | ||||
| Heat load, kW | Required inner pipe diameter, mm | Selection of a pipe for the required inner diameter: | ||
| VGP steel | Polypropylene | XLPE | ||
| 50 | 55 | 2 inches (50mm) | 63 | 63 |
| 40 | 48 | 2 inches (50mm) | 63 | 63 |
| 30 | 43 | 2 inches (50mm) or 1.5 inches (40mm) | 63 | 63 |
| 20 | 35 | 1.5 inches (40mm) | 50 | 50 |
| 15 | 30 | 1.25 inches (32mm) | 40 | 40 |
| 12 | 27 | 1.25 inches (32mm) | 40 | 40 |
| 10 | 25 | 1 inch (25mm) | 32 | 32 |
| 8 | 22 | 1 inch (25mm) | 32 | 32 |
| 6 | 19 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 5 | 17 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 4 | 16 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | 13 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 11 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 16 | 16 |
| 1 | 8 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 16 | 16 |
Supply / return temperature difference - 20 ° С, water speed 0.2 m / s - SELF-DRAIN HEATING SYSTEM | ||||
| Heat load, kW | Required inner pipe diameter, mm | Selection of a pipe for the required inner diameter: | ||
| VGP steel | Polypropylene | XLPE | ||
| 30 | 48 | 2 inches (50mm) | 63 | 63 |
| 20 | 39 | 1.5 inches (40mm) | 50 | 50 |
| 15 | 34 | 1.5 inches (40mm) | 50 | 50 |
| 12 | 30 | 1.25 inches (32mm), (quarter inch) | 40 | 40 |
| 10 | 28 | 1.25 inches (32mm), (quarter inch) | 40 | 40 |
| 8 | 25 | 1 inch (25mm) | 32 | 32 |
| 6 | 21 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 5 | 19 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 4 | 17 | 3/4 inch (20mm) | 25 | 25 |
| 3 | 15 | 3/4 inch (20mm)) | 25 | 25 |
| 2 | 12 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
| 1 | 10 | 1/2 inch (15mm) | 20 | 20 |
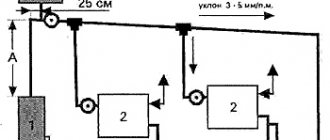
Application example: two-pipe system with circulation pump, total power 18 kW.
The wiring is made with a polypropylene pipe, the symbol is PP.
As you can see from the diagram, first a polypropylene pipe with a diameter of 40mm comes out of the boiler, its internal clearance is 25mm, which corresponds to a metal VGP pipe of 1 inch (25mm). Then there is an outlet to the boiler (4 kW) and underfloor heating (2 kW) of two PP pipes with a diameter of 16 mm. After that, part of the coolant separated, so there is no need for such a thick pipe. A thinner pipe - 32mm will already go for heating the 1st and 2nd floors, it will go to the first tee. On the tee, a branch is separated to the 1st floor, with a diameter of 25mm, and to the 2nd floor, also with a diameter of 25mm. A polypropylene pipe with a diameter of 16 mm is already suitable for the final radiators. And on the last 3 radiators, the supply pipe is also narrowed to 16mm.
In a one-pipe system, in contrast to a two-pipe system, the entire coolant of the system is supplied through one pipeline. Therefore, in such a system, the entire pipeline (after branching the pipe to the boiler and underfloor heating) will be 32mm in diameter, and 16mm pipes will be suitable for separate radiators from the main pipeline.
teplopraktik.ru
Calculation for a two-pipe system
There is a two-storey house with a two-pipe heating system, two wings on each floor. Polypropylene products will be used, operating mode 80/60 with a temperature delta of 20 ° C.
The heat loss of the house is 38 kW of thermal energy. The first floor has 20 kW, the second 18 kW. The diagram is shown below.
There is a table on the right, according to which we will determine the diameter. The pinkish area is the zone of optimal speed of movement of the coolant.
We begin the calculation.
We determine which pipe should be used in the section from the boiler to the first branch. The entire coolant passes through this section, therefore the entire volume of 38 kW of heat passes.
In the table we find the corresponding line, along it we reach the zone tinted in pink and go up. We see that two diameters are suitable: 40 mm, 50 mm. For obvious reasons, we choose the smaller one - 40 mm.
Let's look at the diagram again. Where the flow is split 20 kW goes to the 1st floor, 18 kW goes to the 2nd floor. In the table we find the corresponding lines, we determine the cross-section of the pipes. It turns out that we breed both branches with a diameter of 32 mm.
Each of the contours is divided into two branches with equal load. On the first floor, 10 kW (20 kW / 2 = 10 kW) go to the right and left, on the second, 9 kW (18 kW / 2) = 9 kW). According to the table, we find the corresponding values for these sections: 25 mm.
This size is used further until the heat load drops to 5 kW (see the table). Next comes the section of 20 mm.
On the first floor, we go 20 mm after the second radiator (see the load), on the second - after the third. At this point, there is one amendment made by accumulated experience - it is better to switch to 20 mm at a load of 3 kW.
Everything. The diameters of polypropylene pipes for a two-pipe system are calculated. For the return, the cross-section is not calculated, and the wiring is done with the same pipes as the supply. The technique, we hope, is clear.
It will not be difficult to carry out a similar calculation in the presence of all the initial data. If you decide to use other pipes, you will need other tables calculated for the material you need. You can practice on this system, but for a mode of average temperatures of 75/60 and a delta of 15 ° C (table below).