Water hammer compensator in internal water supply systems FAR
—>
| Name | The size | Retail price, rub. | Discount price, rub. |
| Water hammer compensator in internal water supply systems FAR FA 2895 12 | 1/2″ |
You can download the full price list for FAR valves in Excel format here.
The phenomenon of "water hammer" occurs in the event of a sudden opening or closing of equipment (drive of a mixing valve, pump, etc.), which leads to the appearance of excessive pressure in the system. The FAR water hammer compensator takes over the excess pressure, maintaining normal operating parameters for the system components. Also, its task is to significantly reduce the noise from vibration, which occurs as a result of the closure of the water consumer.
Characteristics
- Accession - НР 1/2 ″;
- Maximum pressure - 50 bar;
- Nominal pressure - 10 bar;
- The maximum operating temperature is 100 ° C.
Design
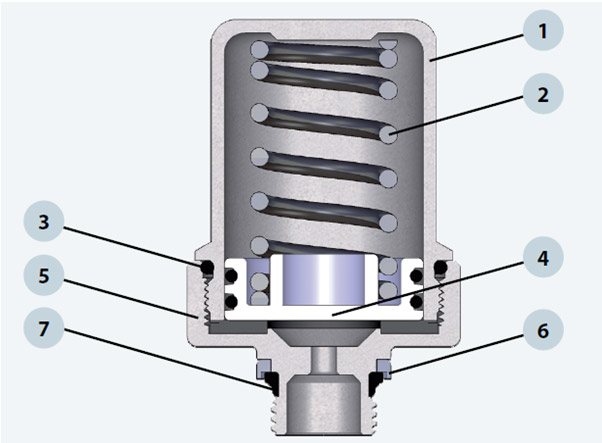
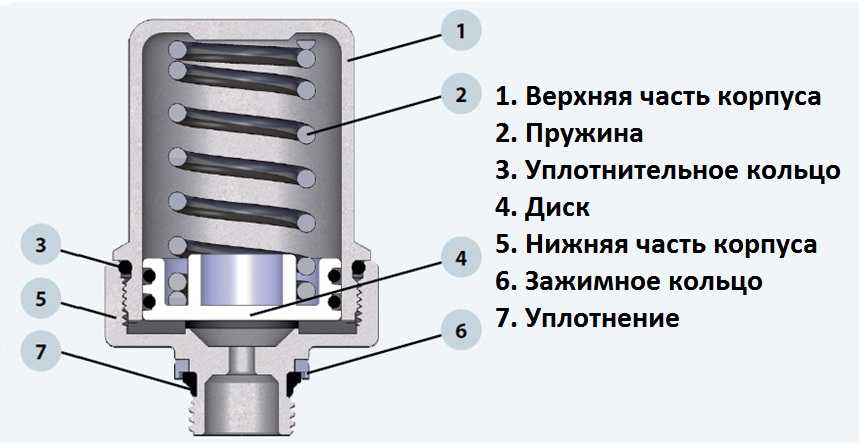
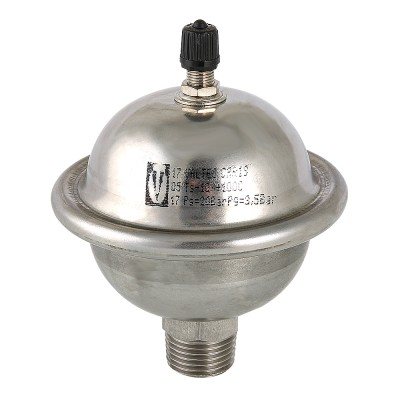
1. Upper body - CW617N brass; 2. Spring - AISI 302; 3. O-ring - EPDM; 4. Disc - plastic; 5. The lower part of the body - brass CW617N; 6. Clamping ring - brass CW614N; 7. Sealing - EPDM.
The overpressure is relieved by an air chamber and a steel spring connected to a double sealed plastic disc, which absorb most of the overpressure.
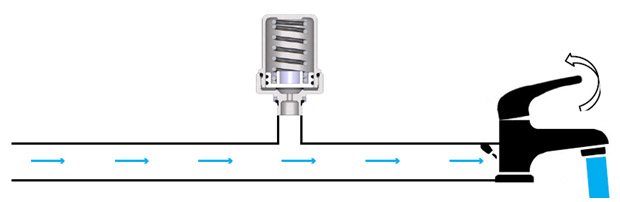

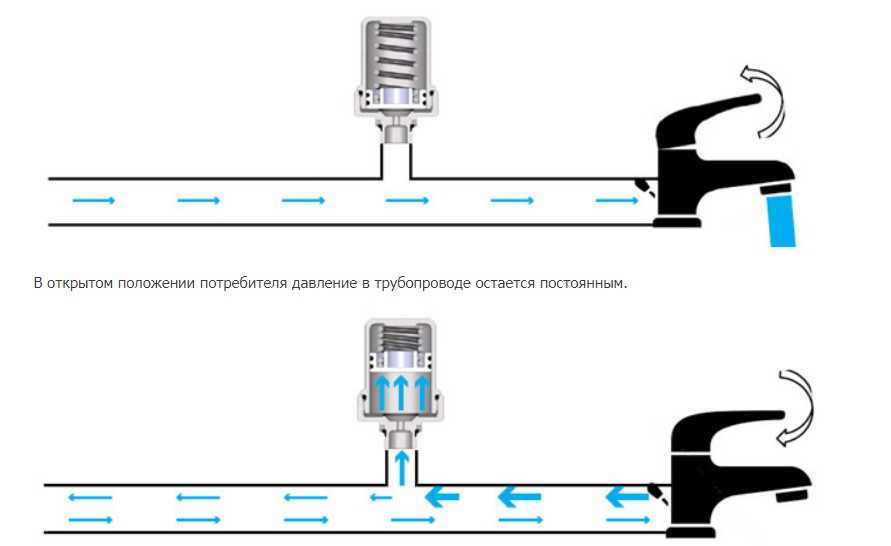
In the open position of the consumer, the pressure in the pipeline remains constant.
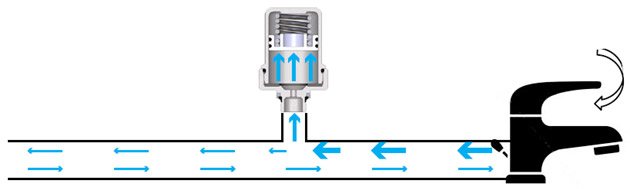

When the consumer is closed, the pressure in the pipeline increases and the FAR water hammer compensator absorbs the excess pressure, protecting the system components.
It is recommended to install a water hammer compensator at the end of the pipeline to consumers (ball valves, plumbing fixtures, motorized valves, etc.) or on manifolds.
An example of installing a water hammer compensator on Multifar manifolds.
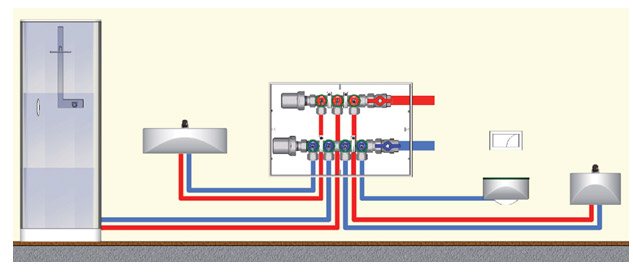

An example of installing a hydraulic shock compensator to the consumer.
The water hammer compensator can be installed vertically or horizontally.
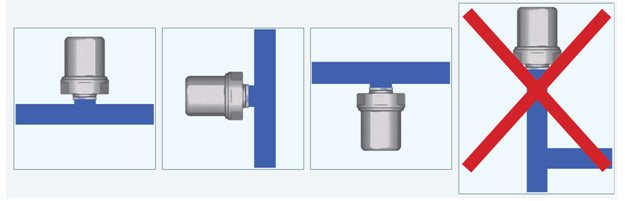

When installing a water hammer compensator, make sure that its location does not create areas where water stagnation can occur, which leads to the growth of bacteria. For example, installing the expansion joint at the top of the riser should be avoided.
Complex modernization of the system
Maximum system stabilization (for example, in houses with old and unreliable plumbing and heating systems) requires the installation of equipment that effectively neutralizes excess pressure in the pipes. This includes the following types of devices:
- Compensators and shock absorbers. Powerful accumulators act as shock absorbers, capable of collecting excess fluid, eliminating the negative consequences of its accumulation. The compensating device is a hydraulic accumulator installed in the direction of water movement in the sections of the heating circuit where the highest probability of pressure fluctuations in the system is observed. Externally, the accumulators look like steel flasks with a volume of up to 30 liters, consisting of two sections, which are separated by a rubber or rubber membrane.
- Safety diaphragm valve. This device is located on the branch of the pipeline for the release of liquid in case of excess pressure. Currently, most radiators of heating systems are equipped with this device. Typically, the valve is operated by a controller or some type of rapid response device.The latter is triggered when the safe pressure level is exceeded, protecting the system from water hammer. In the event of a dangerous surge in pressure, the valve opens completely, and when it drops to normal levels, the regulator closes slowly.
- Thermostat with maximum protection. This is a special safety device that monitors the pressure in the system and stops its operation until the critical point is reached. The device has a spring mechanism located between the valve and the thermal head. The system is triggered when overpressure is detected and prevents the valve from closing completely. These devices are installed strictly in the direction indicated on the body.
What is a water hammer in a pipeline, the causes of
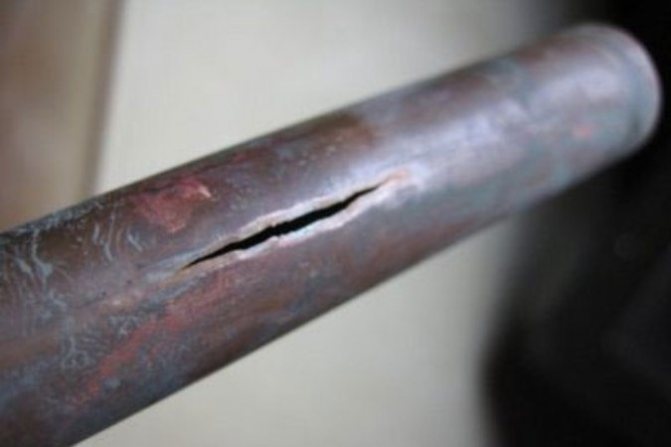
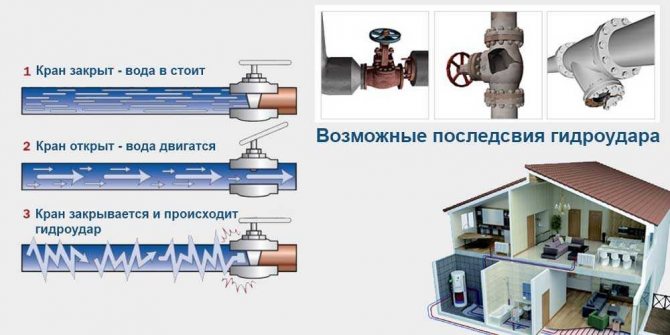
Water hammer - This is a sharp increase in pressure in systems transporting fluid, which occurs when a sharp change in the speed of fluid movement. A pressure surge can cause the destruction of some elements of the system. Failures occur if the tensile strength of the joint or material is exceeded.
If we talk about our houses and apartments, water hammer occurs in heating and water supply systems. In heating systems of private houses - at the start or stop of the circulation pump. Yes, by itself it does not create pressure. But the sharp acceleration or stop of the coolant is the load that acts on the pipe walls and nearby devices. In closed-type heating systems, there is an expansion tank. It compensates for water hammer if the pump is nearby. In this case, additional devices may not be needed. You can check the need to install a compensator on a pressure gauge. If the needle does not move or moves only slightly, everything is fine.
In centralized heating systems, water hammer occurs when the damper is suddenly closed, when the taps are quickly opened to fill the system after repair / maintenance. According to the rules, it is necessary to do it slowly and gradually, but in practice it happens differently ...
In the water supply, water hammer occurs even when the tap or other stop valves are suddenly closed. More pronounced "effects" are obtained in airborne systems. When driving, water hits the air locks, which creates additional shock loads. We may hear clicks or crackles while doing this. And if the water supply system is divorced with plastic pipes, during operation, you can see how these pipes are shaken. This is how they react to water hammer. You've probably noticed how the metal braided hose twitches. The reason is the same - pressure surges. Sooner or later, they will lead to the fact that either the pipe will burst at its weakest point, or the connection will leak (which is more likely and more common).
Why was this phenomenon not noted earlier? Because now most of the taps have a ball valve and the flow closes / opens very abruptly. Previously, the taps were of valve type and the damper was lowered slowly and gradually.
How to deal with water hammer in heating and water supply? You can, of course, teach the inhabitants of an apartment or house not to turn the taps abruptly. But a washing machine or a dishwasher cannot be taught to be careful about pipes. And the circulation pump cannot be slowed down during the start and stop process. Therefore, water hammer compensators are added to the heating or water supply system. They are also called absorbers, shock absorbers.
What can be done to “repay” water hammer in the water supply system?
Check valve can be supplied
Will this valve be another drastic cut-off valve with the same effect?
What can you say about this -
Author SergeyAM
To damp water hammer, it is proposed to use a pressure oscillation damper of an extremely simple design. The damper of pressure fluctuations is located inside the pipeline 2, through which the liquid is pumped.The damper is a metal strip 1, along the length of which windows 3 are cut out. The resulting visors 4 are bent alternately in opposite directions. The angle between the visor 4 and the plane of the tape 1 is 35-45 ° for water or 25-30 ° for oil. The width of the tape 1 is chosen so that it can freely enter the inside of the pipeline 2. The length of the tape 1 is equal to the length of the protected section of the pipe 2. One end of the tape is fixed inside the pipe by welding, and the other end of the tape is rotated around the longitudinal axis by 3 - 5 turns and also secured by welding.
Pipe 2 with a tape 1 placed inside it is a hydraulic shock absorber.
The damper of pressure fluctuations works as follows. The fluid flow when moving along the plane of the tape 1 enters the window 3 and deviates from the plane by the visor 4. The flow acquires an oscillatory (sinusoidal) motion with a certain frequency. Since there are many windows on the tape, the flow oscillation frequency will always exceed the natural oscillation frequency of the fluid flow, determined by the unevenness of the terrain. Thus, the most abrupt pressure fluctuations are smoothed out and the largest gas bubbles are crushed. Additional damping of pressure fluctuations is facilitated by the rotation of the belt around the longitudinal axis with a step of 1.5-2 m (5-7 m for large-diameter pipes), as a result of which the flow acquires an additional rotational motion, which also dampens part of the water hammer energy. This is how the energy of water hammer is extinguished by converting the energy of the accelerated translational motion of the fluid flow into oscillatory and rotational movements.
The essence of the proposal lies in the fact that the internal clearance of the pipeline at the location of the damper installation changes insignificantly (determined by the cross-section of the tape), therefore, the resistance of the damper to the liquid flow in the case of laminar and continuous flow is small. When a liquid flows through a pipe in a turbulent mode and with inclusions of gas plugs, the resistance increases sharply due to a change in flow directions. There is an equalization of the velocities of the gas and liquid flows during the passage of multidirectional visors, which leads to extinguishing of water hammer.
The optimal place for installing the damper is in lowlands, after gentle and especially steep slopes, where the fluid flow accelerates and acquires additional energy, which subsequently causes a destructive water hammer due to the collapse of bubbles (flow breaks) in the fluid.
What is a water hammer compensator: types, design, principle of operation
There are two types of water hammer compensator: diaphragm and spring-loaded valve. They perform the same function: they take in excess fluid, thereby reducing the load on other elements of the system. Since these devices are small, they protect those devices that are located in the immediate vicinity.
How the membrane expansion joint works and works
A membrane hydraulic shock absorber is a container that is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. One of the parts is filled with air, the other is normally empty. The air in the filled part is pumped under a certain pressure. For checking / pumping up pressure in this part of the body there is a spool (nipple). The products are supplied from the factory with an initial pressure of 3 bar. This is the "standard" value for most heating systems in single-storey private houses. If the pressure needs to be changed, a pump is connected to the nipple and brought to the required value. This value is 20-30% higher than the worker in a particular system. But it should be well below the performance limit of the compensator itself.
As long as the pressure in the system does not exceed the pressure in this part of the reservoir, nothing happens.When a water hammer occurs, under the influence of the increased pressure, the membrane stretches, part of the liquid enters the reservoir. As it normalizes, the elastic membrane tends to return to its normal state, pushing fluid back into the system. Thus, the jump is smoothed out.
Features of the spring water hammer damper
The second type of hydraulic shock compensators works according to the same principle: liquid is passed into the body when the pressure rises. But the access to the container is blocked by a plastic disc, which is supported by a spring. The pressure at which the liquid begins to flow inward depends on the spring force. There is no way to regulate it (in any case, so far no regulated models have come across), so you have to select a device with suitable parameters.
Related article: Do-it-yourself plumbing installation in an apartment
The principle of operation of this damper is similar to that described above. As long as the pressure in the system is normal, the spring presses the disc against the body. When a water hammer occurs, it is compressed, water enters the body. As the pressure decreases, it becomes less than the spring force. It gradually expands, returning fluid to the pipeline.
As you can see, both devices work in a similar way. Spring models are considered to be more reliable, since the working elements in them are less susceptible to wear (metal spring and durable plastic). But membranes are also made of materials that do not lose their elasticity for a long time. An additional plus is the ability to set the pressure at which the membrane will begin to stretch. But the disadvantage can be considered the need to regularly check the pressure and, if necessary, pumping.
Features of plastic pipelines
Among which:
- the working pressure for pipes made of this material is up to 10 atmospheres (it may be necessary to test pipelines for strength and tightness);
- the upper limit of the operating temperature range exceeds 90 degrees. This is enough for the distribution of hot water supply and heating systems;
- the material is absolutely non-corrosive, inert with respect to most household chemicals, not biodegradable;
- the quality of the surface of polypropylene pipes and the properties of the material prevent deposits on the walls of plaque, including lime;
- service life of polyethylene pipelines - at least 30-50 years;
- polypropylene is absolutely safe for human health, does not release toxic compounds into water and air;
- this polymer is fireproof.
The installation technology involves the use of welding (an iron for soldering polypropylene pipes) to obtain reliable connections.
With the availability of the appropriate equipment, it is possible for everyone to master the skills of installing systems from polypropylene pipes.
Among the disadvantages of polypropylene pipes, experts note the impossibility of giving them the required shape.
Due to this, the turns of the lines are performed exclusively with the use of fittings.
Another serious drawback of this polymer is its high coefficient of thermal expansion.
Thanks to him, polypropylene pipes are characterized by significant elongation and / or sagging when transporting hot media (hot water or heat carrier of heat supply systems), and at high outside temperatures.
Where and how to install: installation recommendations
The water hammer compensator is small in size, only a small amount of water can fit in the body (less than 200 ml usually). It is installed in the immediate vicinity of the source of the appearance of a water hammer: a ball valve, a water comb, on a hose to a washing machine or dishwasher, after a circulation pump, on a comb for underfloor heating.
You can mount it in any position: up, down, to the side.For membrane models, it is only important that there is free access to the nipple. Regardless of the design, it is not recommended to install the device on long branches from the mains. The supply pipe section should be as short as possible.
When choosing, pay attention to the maximum working and compensated pressure. The second point is the connection diameter. Usually it is 1/2 ", but there are also 3/4 and" inches.
When connecting a washing machine and / or dishwasher, a tee is installed on the hose. One free outlet of the tee goes to the machine, the second is equipped with a water hammer compensator.
How to choose a device correctly
To find out which compensating element is best installed on polypropylene, you need to understand in detail the device of these devices.
Polypropylene (PP) piping is installed very often. With its help, they equip the supply of hot water, where the temperature rises to almost a hundred degrees. During use, polypropylene has shown a number of characteristics, thanks to which it is ideal for plumbing systems and heating. It is not afraid of the influence of aggressive chemical environment, has a low weight and is quite durable.
For this reason, it is recommended to install flexible expansion joints in areas with a length of more than ten meters. They make it possible to reduce thermal expansion.
To select and install it correctly, you must take into account the diameter. It must match the diameter of the pipeline itself. Most often, the diameter that the expansion element has is from 20 to 40 mm. For a house and apartment, a 20 millimeter device will be enough.
As for the manufacturer, it is better to give preference to well-known world brands. They represent high quality goods for polypropylene nets, which are successfully used in many areas.
Other ways to deal with water hammer
One of the possible options for neutralizing a water hammer has already been announced - to close the taps smoothly. But this is not a panacea, and it is inconvenient in our fast-paced times. And there are also household appliances, you cannot teach them. Although, some manufacturers take this point into account, and the latest models do with a valve that smoothly shuts off the water. That is why expansion joints and neutralizers are becoming so popular.
You can also fight water hammer using other methods:
- When installing or reconstructing water supply or heating, insert a piece of elastic pipe in front of the source of the water hammer. It is reinforced with heat-resistant rubber or PPS plastic. The length of the elastic insert is 20-40 cm. The longer the tube, the longer the insert.
- Purchase of household appliances and valves with smooth valve travel. When it comes to heating, problems with a warm water floor are often observed. Not all servos run smoothly when closing the flow. The way out is to install thermostats / thermostats with a smooth piston stroke.
- Use pumps with soft start and stop.
Water hammer is a really dangerous thing for a closed system. He breaks radiators, breaks pipes. To avoid problems, it is better to think over the control measures in advance. If everything is already working, but problems have appeared, it is wiser and easiest to install expansion joints. Yes, they are not cheap, but repairs will cost more.
Manufacturers, characteristics, prices
It is best to buy a water hammer compensator from well-known companies. This is not the area where it is appropriate to save. The most popular are several companies:
- FAR. The compensator of this company is without a diaphragm, with a spring and a shut-off disc. Connecting thread 1/2 ", maximum pressure 50 bar, nominal - 10 bar. Temperature resistant up to 100 ° C. Price from $ 30.
- Uni Fitt. Same design with spring loaded disc. There are two body options: brass and brass with nickel plating.1/2 inch connection. Maximum temperature 90 ° C, nominal pressure 10 bar, peak pressure 20 bar. The length of the protected pipeline is 10 m. The price is from 15 $.
There are other firms, but they are not as popular. some were overpriced, others did not gain credibility. For now, anyway.
What is water hammer and why are they afraid of it
Water hammer is a sharp and very strong pressure surge in pipes. Able to break the joints and pipes themselves, rip valves and cause a flood. Small water hammers act gradually, over and over again squeezing out the gaskets, slowly but surely deforming and destroying the water supply and heating pipes with microtraumas.


Pressure, as one of the parameters of the heating and water supply system, plays a key role. It is due to the pressure difference that the fluid flow is formed. Modern heating systems use hydraulic pumps. The flow rate, head and volume depend on the pressure indicator. In open systems, which were commonly used in the past, the fluid pressure was equal to atmospheric pressure, so an increase in the temperature of the carrier was accompanied by a fluid overflow into the expansion tank.
The disadvantage of such a system was the gradual evaporation of the liquid, the impossibility of increasing the boiling point, and the lack of protection from hydraulic shocks.
The liquid is practically not compressed. When the layers are compressed, elastic forces of large magnitude arise, which can be transmitted at high speed in the medium. A sharp change in pressure in one part of the apartment line could lead to the destruction of pipeline elements in another part.


Opening the tap or any valve can provoke a water hammer. A striking example is the destruction of a newly laid line at its first start, when the water supply opens with the valves of the mixers closed.
What is water hammer?
In general terms, water hammer is any impact of the aquatic environment that leads to accidents in the service infrastructure. In plumbing systems, this phenomenon occurs most often, and there may be several reasons for it. For example, closing a valve or a mixer tap can sharply increase the pressure in the circuit, which will lead to a pipe rupture or breakdown of power pumping equipment - these will be the consequences of a water hammer. Less common are similar accidents with a sharp drop in pressure. This happens if, for example, the user of the water supply system completely turned off the pump or turned on the tap without holding the technological interval. For both situations, protection against water hammer is needed, which can be expressed both in the installation of a frequency converter and in the use of the pressure compensator in question.
Closed heating system
If the pipeline is made sealed, then when the liquid heats up, the pressure will begin to rise sharply, which can cause pipes or connections to begin to collapse. However, pressure exceeding atmospheric pressure offers many advantages.
- As you know, the boiling point rises, therefore, the support can be used more efficiently.
- Increased pressure increases the efficiency of the hydraulic pump.
- The sealed system does not need periodic recharge.
The pressure regulator in a closed system combines the functions of a diaphragm expansion joint and an expander. It is a container divided into two parts by an elastic partition.

In one part, there is air under pressure, and the other part is connected to the line. During thermal expansion, the liquid presses on the membrane, as a result of which it sags into the area filled with air. With a decrease in air volume, its pressure increases and begins to compensate for the excess fluid pressure.
When the apartment heating system is in working order, the membrane expansion joint is in dynamic equilibrium.Each increase in fluid side pressure is accompanied by an increase in air pressure. But it turns out that such a system is not only capable of damping thermal expansion, but also works as a water hammer damper.
Prevention of water supply and heating systems
Together with strict adherence to the rules for the operation of water supply systems, it is necessary to carry out special preventive measures 1-2 times a year. Maintenance of equipment helps to avoid not only water hammer, but also other destructive processes that lead the water supply system to an unsatisfactory technical condition.
The constant flow of water causes inevitable vibrations in the pipeline, slightly changing the pressure in the system. This does not necessarily lead to a water hammer, but it will promote the formation of microcracks in the structure of the metal shell of the pipes. If, however, a water hammer nevertheless occurs, the pipe may burst precisely in the places of microcracks. Particular attention should be paid to areas of increased internal stress, which include bends, mechanical joints and welds.
Prevention includes the following activities:
- checking the state of a group of protective devices (safety valve, pressure gauge and air vent);
- checking the pressure and adjusting it behind the expansion tank diaphragm;
- checking the degree of wear of components and testing the system for possible leaks;
- checking the position of shut-off and control valves for leaks;
- checking the appearance and functionality of filters that trap sand, scale and small particles of rust with cleaning and rinsing the elements if necessary.
All these precautions are quite feasible at home without the involvement of specialists. If, in the process of prevention, significant flaws of certain components were found, a leak is observed, or extraneous noises are heard, it is necessary to contact specialized services as soon as possible for a more thorough analysis of the entire system and its possible repair.
Diaphragm expansion joint device
In the market of building materials and parts for heating systems, the expansion tank is known as a membrane hydraulic shock absorber. It can be installed not only in the heating system, but also in the water supply system. The main purpose of the tank is to unload the system in the event of an increase in pressure.
The diaphragm, made of elastic material, is a pressure regulator. The shape of the tank is not subject to standardization. The choice of external form depends solely on the conditions of the surrounding space and aesthetics. The most common expansion joints are in the form of a cylindrical balloon.


The half of the reservoir where the air is located has an outlet with a spool. Through it, you can add or reduce the amount of air in the tank. When buying a membrane expansion joint, the air is under pressure equal to tenths of atmospheric pressure. During commissioning, this pressure increases according to the system's performance. The compensator has only one connecting pipe, because there is no through flow of liquid.
Possible consequences of a water hammer and its danger
The signs of the phenomenon can be recognized by extraneous sounds in the system: clicks, knocks, collapses. Visual signs will also help: leaking taps, mixers, compression fittings-connectors with rubber gaskets.
When the water supply system is exposed to frequent water hammer, even with a weak force, the gaskets, seals are squeezed out first. Violation of the tightness of the system can lead to the appearance of centers of deformation and rupture of pipes.
As a result of the pressure increase, the water supply is interrupted. But this is not the only nuisance. If a water hammer has led to a complete rupture of a pipe, for example, in an apartment building, the entire structure is left without water.The flow of liquid spoils the property of the apartment owners, the neighbors of the lower floors are flooded. As a result - work on the repair and restoration of several housing objects.
A water hammer in the hot water supply system, in addition to the final damage to property, threatens with burns. The danger threatens when the heating system is depressurized, where the carrier maintains a temperature of + 70C and is constantly under pressure. A break in a battery or pipeline during the winter heating season will damage the system. Frost will finish the destructive business - the pipeline will have to be changed.
Varieties
There are several types of device classifications in force. The most practical is the grouping according to the types of membranes used. Today, almost all devices are manufactured with a diaphragm membrane. Non-separable cylinder made of durable steel. Usually consists of two hemispheres, welded together. The membrane is mounted in such a way that the reservoir cavity is divided into two parts. The connecting pipe remains in one part and the spool in the other.
The balloon membrane must be replaced. But modern materials are able to withstand increased loads for quite a long time without loss of integrity and elasticity, so the need to replace the membrane has practically disappeared. The reservoir for the balloon membrane is collapsible. The water is in the rubber chamber and does not come into contact with the inner walls of the tank. The spherical membrane is practically not used today, it is considered a rarity.


The use of P, S and L -shaped systems allows you to create compensating devices directly at the installation site. Bent expansion joints are manufactured from bends and straight pipe sections by welding. The diameter, wall thickness and steel grade of pipes for bent expansion joints must be the same as for the main sections of the pipeline. The compensation capacity of such structures fluctuates depending on the diameter of the pipelines, the larger the diameter, the greater the compensation capacity. It is recommended to take the horizontal arrangement of bent expansion joints during installation. When placed vertically or inclined, the use of air or drainage devices is required. To create the maximum compensating ability, the bent expansion joints had to be stretched and secured with spacers in the cold state before installation. In this position, they were installed and mounted on the pipeline by welding. The spacers were removed only after the expansion joint was connected to the pipeline.
Stuffing box expansion joints are made of pipes, or sheet steel grade St.Z. They are installed strictly along the axis of the heat pipe, without distortions. They can be one-sided and two-sided with an increased compensating capacity twice as much as one-sided. The main disadvantage of such devices is the use in the construction of stuffing box-type packing made of asbestos printed cord and heat-resistant rubber. Such a system requires constant attention and maintenance. The installation of stuffing box expansion joints or additional bends in the pipeline entails the need to allocate significant areas for their installation and an increase in operating costs.The use of bent compensators requires the device of special compensatory niches, which were a no-passage channel, according to the configuration corresponding to the shape of the compensator (the design of such a channel is similar to the design of the channel used on the heating network route).
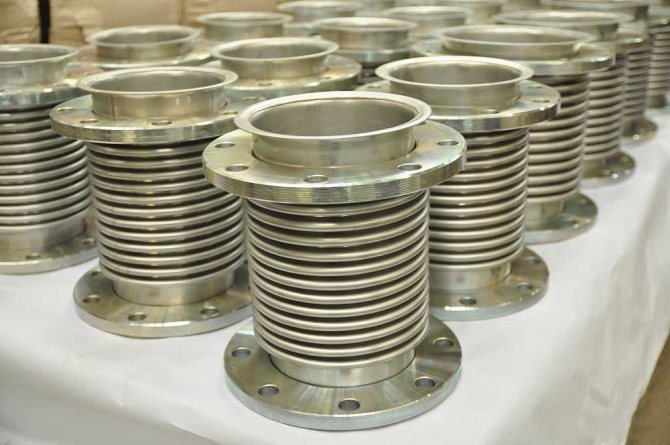
The use of compensators for water supply systems makes it possible to provide: 1) compensation for thermal expansion of pipelines; 2) compensation for misalignment in pipeline systems resulting from installation work; 3) isolation of vibration loads from operating equipment; 4) isolation of vibration loads from the flow of the transported medium; 5) reliable connection of pipes of various types; 6) prevents the destruction of pipes during deformation of pipelines; 7) seals pipelines;
Compensators for water supply systems allow to damp a number of vibrations arising during the operation of the pipeline and pumping equipment, to compensate for the movement of the pipeline when the temperature of the conduction or the environment changes, entailing thermal expansion due to heating by the working medium, and also absorbs the displacement of pipes when soil and supports settle, significantly extending the service life of the pipeline. The device consists of a corrugated shell (flexible bellows) made of multilayer stainless steel. The compensating capacity, axial travel, depends on the number of bellows and the number of flexible bellows in each bellows. Working medium: water, steam, air, natural gas, other gases, liquids, non-aggressive in relation to the materials used in the construction of the device. Not intended for work with working environments that are used in chemical, petrochemical, oil refining hazardous production facilities. The compensator can be manufactured with an external protective casing to protect the bellows from external influences, as well as an internal shield to protect the bellows from the influences of the working environment.
Expansion joints of various designs are traditionally used to protect the pipeline from thermal expansion and deformation arising during operation. The most widespread, due to the ease of installation, reliability of the design and durability, are compensators based on a metal bellows that ensures the safety of the heating system throughout the entire period of operation and does not require constant monitoring and maintenance. Such designs allow you to prevent various deformations that occur in the pipeline due to temperature and pressure differences. Due to the fact that the expansion joints are entrusted with the function of increasing the service life of the water supply system, their reliability must be ensured throughout the entire life of the pipeline. The absence of compensating devices in water supply systems leads to undesirable consequences, significant deformations or a breakthrough of the heating system, a significant part of such accidents often occur in winter at the height of the heating season. Until recently, outdated compensating systems, such as stuffing box, P, S, L -shaped expansion joints, were adopted in water supply systems. Such devices are simple and relatively inexpensive. At the same time, they have a number of significant drawbacks: P, S, L -shaped expansion joints require the allocation of a significant area for their installation, and stuffing boxes require periodic maintenance and constant monitoring, and when laying underground, the construction of special chambers. Thus, the initial savings on the cost of the expansion joints themselves entail a loss of usable area, a significant increase in the cost of installation and staff of maintenance personnel.
Considering the above disadvantages, the most optimal solution is the use of maintenance-free bellows expansion joints.The working part of such devices is a bellows made of an elastic corrugated metal shell, which has the ability to stretch, compress and bend under the influence of temperature differences, pressure, vibrations, soil movement and mechanical influences. The use of bellows expansion joints in the construction of pipelines and the reconstruction of heating systems in high-rise residential buildings reduces the risk of causes leading to the destruction of the pipeline. At the same time, bellows expansion joints are tight, compact, durable and do not require maintenance during the entire service life.
All expansion joints for water supply systems in the manufacturing process undergo strict technological control and a range of tests for strength and compliance with a number of parameters. For testing and testing, one sample comes from each batch, which must withstand loads exceeding the nominal several times. If the sample does not pass the test, the entire batch is checked.
The result of violation of manufacturing technology can be: loss of stability of expansion joints, loss of stability of folds of the corrugated part of the bellows, loss of lateral stability of the bellows during axial compression, etc.
The calculation of the elongation of a section of a steel pipeline is carried out according to the formula: L = 0.012 × N × (T1-T2), where: 0.012 mm / (m × C) is the coefficient of thermal elongation of carbon steel. N m - pipe height. Т1 ° С - maximum water temperature in the heating system. T2 ° C is the minimum temperature of the heating system installation. L = 0.012 * 30 * (90- (-10)) = 36 mm. When calculating expansion joints in high-rise buildings, similar calculations are used. For example, for a 20-storey building, you will need to install 3 bellows expansion joints for each pipe of the heating system.
When choosing a compensator for heating systems, it is very important to determine the operating parameters and the service life of the pipeline. To select the correct expansion joint and calculate the operating time, it is necessary to build on the number of cycles and the length of expansion joints for water supply systems. For standard heating systems (at 70-90 ° C), the compensating capacity is calculated as Δ = 1 mm / m. Each expansion joint must be installed between 2 fixed supports for a 30 m long vertical pipeline (10 storey building). It should be borne in mind that compensators for water supply systems for 50 cycles can be used from one to five years, compensators for water supply systems for 1000 cycles can be used from five to fifteen years, for 5000 cycles - at least 25 years, if the operating conditions do not create additional loads and the environment does not have a destructive effect on the materials of the compensator. The full working cycle is the compression-expansion of the expansion joint along the axis, for the entire value of the permissible stroke. For example, if the axial travel is 210mm for 5000 cycles, then the axial travel is considered +/- 105mm. Suppose, compensators are included in the calculation of heating networks: The first is an expansion joint with a bellows of 1080 mm (designed for at least 1000 working cycles); The second is an expansion joint with a 630 mm bellows (designed for 50 working cycles). But during the period of operation, the compensator will not work continuously for the entire length of the axial stroke, it will depend on the conditions: temperature of the working medium, pressure surges, etc. In the case when the expansion joints do not experience the maximum possible loads, their axial compression and expansion will be less than +/- 105 mm and, as a result, the period of operation will increase. The amount of axial expansion-contraction is directly related to the number of operating cycles: the more one, the less the second. For example, an expansion joint equipped with a 630 mm bellows with 210 mm compression-expansion stroke (+/- 105) will work 50 working cycles, but if it is used with +/- 95 compression-expansion, it will be able to perform 75 working cycles when it is have a stroke of +/- 31.5 mm, then its resource will increase to 5000 working cycles. An expansion joint with a bellows length of 1080 mm with a compression-expansion of 210 mm (+/- 105) will work 1000 working cycles, but if it is used with a compression-expansion +/- 95 mm, it will work 1100 working cycles, if the response value is +/- 31.5 mm, then its resource will increase to 140,000 working cycles.Therefore, before ordering expansion joints, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the conditions in which the expansion joint can be used, and also calculate the margin of the required axial travel of the bellows.
To increase the elasticity of the compensator, a multilayer version of the bellows can be used, such a technological method provides a multiple reduction of stresses in the metal of the bellows part. The bending moments of stress in the corrugations are reduced by a number of times equal to the number of layers in a square. The technology of corrugation formation allows maintaining the thickness of all layers with the same deformation along the entire length of the bellows. In addition, the reliability of the device during operation depends on the design and quality of the welded joint of the bellows with the connecting pipes, the main task of the design of such a joint is to ensure the unloading of the circular welded seam from bending stresses acting in the bellows corrugations during compression - tension.
Installation rules
If earlier certain installation requirements were imposed on the expansion tank, then in a closed system the compensator can be installed anywhere. However, this is only a theoretical assumption. The requirements for location at the highest point are no longer relevant, since, according to Pascal's law, the pressure is the same everywhere.
The compensator is mounted where there are plumbing units, inputs or interconnections.
- On the one hand, this is due to the fact that nodes are a frequent cause of water hammer, therefore, it is more expedient to install a device that extinguishes excess pressure in the immediate vicinity of taps and valves.
- On the other hand, aesthetics play a significant role here. Against the background of straight pipes, neatly laid around the perimeter of the room, the balloon will not look well.


An important condition for installation is the absence of a long or curved outlet to the cylinder. Since water does not circulate in the outlet, this can lead to stagnation and, as a result, to the multiplication of microbes. Bends should be short and straight.
From these considerations, it is worth choosing the place of localization of the compensator.
What it is?
When the temperature of the liquid in the plastic pipe changes, the process of linear deformation occurs. This can lead to sagging, which over time will lead to cracking. To compensate for the expansion of polypropylene that occurs during temperature or pressure surges, a special PP expansion joint must be installed.
The expansion joint is a simple part that has a high degree of flexibility. Visually, it resembles a loop, but there are products similar to a piece of corrugation. Often, these parts are supplied with fittings for their installation on the pipeline.