Thermal insulation of pipelines is a set of measures aimed at preventing heat exchange of the carrier transported along them with the environment. Thermal insulation of pipelines is used not only in heating systems and hot water supply, but also where technology requires the transportation of substances with a certain temperature, for example, refrigerants.
The meaning of thermal insulation is the use of means that provide thermal resistance to heat exchange of any kind: contact and carried out by means of infrared radiation.

The greatest application, expressed in numbers, is the thermal insulation of pipelines of heating networks. Unlike Europe, the centralized heating system dominates the entire post-Soviet space. In Russia alone, the total length of heating networks is more than 260 thousand kilometers.
Much less often, insulation for heating pipes is used by private households with an autonomous heating system. Only in a few northern regions are private houses connected to the central heating main with heating pipes located outside.
For some types of boilers, for example, powerful gas or diesel boilers, the requirements of the code of rules SP 61.13330.2012 "Thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines" are prescribed separate from the placement building - in the boiler room, which is several meters away from the heated object. In their case, a piece of harness passing through the street must be insulated.
Pipe laying methods
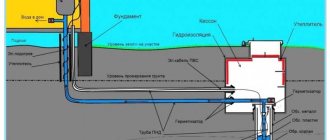
On the street, insulation of heating pipelines is required both for open ground placement, and for hidden laying - underground. The last method is channel - a reinforced concrete gutter is first laid in the trench, and pipes are already placed in it. Channelless placement - directly in the ground. The used insulating materials differ not only in thermal conductivity, but also in steam and water resistance, durability and installation methods.


The need to insulate cold water pipes is not so obvious. However, one cannot do without it in the case when the water supply system is laid by an open ground method - the pipes must be protected from freezing and subsequent damage. But inside buildings it is also necessary to insulate water pipes - to prevent moisture condensation on them.
Insulation types
Today, when laying pipelines, the following types of insulating materials are much more often used:
- Bitumen;
- Folgoizol;
- Polyurethane foam shell;
- PU foam sheath;
- Glass wool;
- Mineral wool;
- Rubber casing;
- Polyethylene anticorrosive insulation.
Now let's take a closer look at any of them.
Bitumen
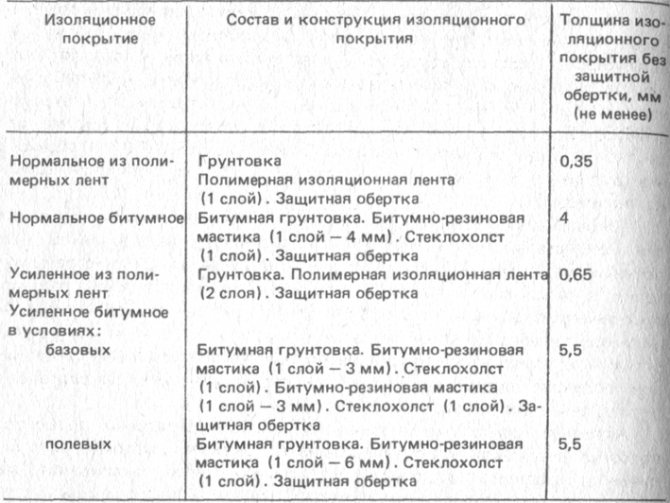
Until recently, bitumen insulation of steel pipes was the most common. It is a narrow layer of polyethylene, which is protected by a bituminous coating. In addition, fiberglass is usually used over this coating.
Bitumen waterproofing of pipes is designed to protect the steel surface from corrosion, which is possibly caused by its contact with the ground and various chemical elements in the ground. Much more often this method is used to cover highways, which are laid in sandy, rocky or clayey soil.
Note! The average operating temperature of a system covered with bitumen must be in the range of -40 - +65 degrees Celsius.


Folgoizol
Folgoizol, in addition, can be attributed to bituminous coatings, since it consists of narrow aluminum foil and bitumen-rubber binder.
Among the advantages of this material, it is possible to highlight the following points:
- Low price, which ensures cost-effectiveness.
- Reliability;
- Ease and speed of application - pipes with a sheet of foil insulation.
Much more often, foil pipe insulation is used for channel and channelless laying of water pipelines and heating mains.
Glass wool, mineral wool
Insulating materials, proven by practice. They meet the requirements of SP 61.13330.2012, SNiP 41-03-2003 and fire safety standards for any method of installation. They are fibers with a diameter of 3-15 microns, in structure close to crystals.
Glass wool is made from glass production waste, mineral wool from silicon-containing slag and silicate waste from metallurgy. The differences in their properties are insignificant. They are produced in the form of rolls, stitching mats, plates and pressed cylinders.
It is important to be careful with materials and be able to handle them correctly. Any manipulation should be carried out in protective overalls, gloves and a respirator.


Installation
The pipe is wrapped or covered with cotton wool, ensuring uniform filling density over the entire surface. Then the insulation, without too much crushing, is fixed with a knitting wire. The material is hygroscopic and easily gets wet, therefore, the insulation of external pipelines made of mineral or glass wool requires the installation of a vapor barrier made of a material with low vapor permeability: roofing material or polyethylene film.
A cover layer is placed on top of it, which prevents the penetration of precipitation - a casing made of roofing sheet, galvanized iron or sheet aluminum.
Basalt (stone) wool
More dense than glass wool. Fibers are made from melt of gabbro-basalt rocks. It is absolutely nonflammable, withstands temperatures up to 900 ° C for a short time. Not any insulating materials, like basalt wool, can contact surfaces heated to 700 ° C for a long time.
Thermal conductivity is comparable to polymers, ranging from 0.032 to 0.048 W / (m · K). High performance indicators allow using its thermal insulation properties not only for pipelines, but also for arranging hot chimneys.
Available in several versions:
- like glass wool, in rolls;
- in the form of mats (stitched rolls);
- in the form of cylindrical elements with one longitudinal slot;
- in the form of pressed cylinder fragments, the so-called shells.
The last two versions have different modifications, differing in density and the presence of a heat-reflecting film. The slot of the cylinder and the edges of the shells can be made in the form of a spike connection.


SP 61.13330.2012 contains an indication that the thermal insulation of pipelines must comply with safety and environmental protection requirements. By itself, basalt wool fully complies with this instruction.
Manufacturers often use a trick: to improve consumer performance - to give it hydrophobicity, greater density, vapor permeability, they use impregnations based on phenol-formaldehyde resins. Therefore, it cannot be called 100% safe for humans. Before using basalt wool in a residential area, it is advisable to study its hygiene certificate.
Installation
The fibers of the insulation are stronger than those of glass wool, so the ingress of its particles into the body through the lungs or skin is almost impossible. However, when working, it is still recommended to use gloves and a respirator.
The installation of the roll cloth does not differ from the way in which the insulation of heating pipes with glass wool is carried out. Heat protection in the form of shells and cylinders is attached to the pipes using mounting tape or a wide bandage. Despite some hydrophobicity of basalt wool, pipes insulated with it also require a waterproof vapor-permeable shell made of polyethylene or roofing material, and an additional one made of tin or dense aluminum foil.
Insulation of gas pipelines
To insulate pipes transporting gas, various insulator options are used. For example, you can insulate a gas pipeline with a special paint or varnish, but in most cases, modern protective materials are used.
What requirements an insulator for gas pipes must meet:
- first of all, an insulator for a gas pipeline must be able to uniform, monolithic installation on a pipe;
- and it is also very important that the insulating material for the pipeline has a low water absorption coefficient and, in general, high waterproofing properties;
Important! The insulating material must protect the pipe from exposure to ultraviolet radiation, since ultraviolet rays are a destructive factor.
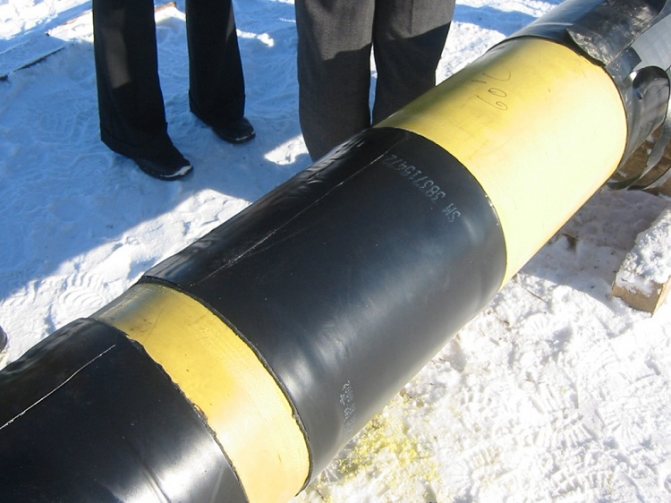


The material for insulating gas pipes must have high moisture resistance
- also a high-quality protective material must be highly resistant to corrosive effects and the effects of any other aggressive chemical compounds;
- the insulator must be strong enough to protect the gas pipeline from mechanical stress;
- the coating must not have any damage (cracks, chips, etc.).
Consider the main types and types of pipeline insulation:
- bituminous mastics. Such heat insulators are produced with different additives that are mixed with the main material - bitumen. Supplements can be of three types:
- Polymeric.
- Mineral.
- Rubber.
Such additives provide protection against cracking and, in addition, improve adhesion to the surface of the gas pipe. It is also worth noting that bituminous mastics have proven themselves well at low temperatures.
- tape materials. Insulating tapes are usually made of polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). At the production stage, an adhesive material is applied to one of the sides of such a tape, by means of which the tape is mounted on a gas pipeline.
Depending on the design features of the pipeline and the region in which it is being laid, the following types of tape insulation are used:
- Regular.
- Reinforced (DC).
- Highly reinforced (VUS).
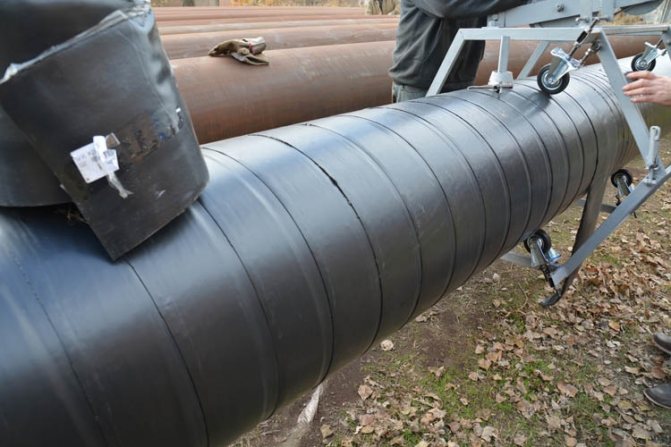


To protect gas pipelines, tape insulation is often used today, which is wound around the pipes using a special device.
The latter type of insulation is the most reliable and effective and is most often used to protect pipelines in settlements. VUS is resistant to aggressive corrosive effects and active chemicals.
The VUS is produced using the extrusion method. Insulation of the pipe with extruded polyethylene is carried out to increase the protective functions of the pipeline. Insulating pipes with extruded polyethylene is a very reliable option for protection. Extruded tapes have excellent waterproofing properties and are installed on pipes that are laid even in unfavorable climatic conditions.
Foamed polyurethane (polyurethane foam, polyurethane foam)
Reduces heat loss by more than half compared to glass wool and mineral wool. Its advantages include: low thermal conductivity, excellent waterproofing properties. The service life declared by the manufacturers is 30 years; The operating temperature range is from -40 to +140 ° С, the maximum maintained for a short time is 150 ° С.
The main brands of PPU belong to the G4 flammability group (highly flammable).When changing the composition with the addition of fire retardants, they are assigned G3 (normally combustible).
Although polyurethane foam is excellent as an insulating material for heating pipes, keep in mind that SP 61.13330.2012 allows the use of such thermal insulation only in single-family residential buildings, and SP 2.13130.2012 limits their height to two floors.


It might be interesting
Thermal insulation
Distinctive features and variety of ceiling tiles ...
Thermal insulation
How to insulate the ceiling in a wooden house?
Thermal insulation
What is a heating cable?
Thermal insulation
Warm "pie" for a metal chimney
The thermal insulation coating is produced in the form of shells - semicircular segments with tongue-and-groove locks at the ends. Ready-made steel pipes are also commercially available, insulated from polyurethane foam with a protective sheath made of polyethylene.
Installation
The shells are fixed to the heating pipe with ties, clamps, plastic or metal band. Like many polymers, the material does not tolerate prolonged exposure to sunlight, therefore, an open ground pipeline when using PU foam shells requires a cover layer, for example, of galvanized steel.
For underground channelless placement, heat-insulating products are laid on waterproof and temperature-resistant mastics or adhesives, and outside they are insulated with a waterproof coating. It is also necessary to take care of anti-corrosion treatment of the surface of metal pipes - even the glued snap joint of the shells is not tight enough to prevent condensation of water vapor from the air.
Materials for insulation of hot water pipelines
Communications transporting hot water require the organization of insulation, which has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity. This is necessary in order to reduce the heat loss rates of the pipes. Without proper insulation, the pipeline will dissipate heat to the environment, showing low efficiency.
Consider what types of insulation materials can be used to protect a pipeline transporting hot water:
- Foam Polymer Mineral Pipe Insulation (PPM) is an insulating material obtained by mixing foamed polyurethane foam and mineral filler.
PPM insulation is used, as a rule, only for hot water pipelines. PPM insulation consists of three main layers with different densities. PPM insulation is a multifunctional protective structure, since each of its layers performs its own function: protection against corrosion, thermal insulation and waterproofing. Such a monolithic structure is resistant to temperature extremes, and also has good strength, which makes it possible to protect the pipeline structure from mechanical stress.
Helpful information! Insulation of pipelines can be both external and internal. Internal pipe insulation has two main functions: protecting the pipe from corrosive effects and increasing the throughput of the pipeline.
- polyurethane foam (PPU). This material is used primarily to enhance the waterproofing performance of communication. Differs in good thermal stability and is able to withstand temperature jumps. In addition, it should be noted that heat loss during the organization of insulation from polyurethane foam is no more than 5%.
- highly reinforced insulation (VUS). This is a special type of insulation that consists of two or three layers and is used to protect pipelines from the damaging effects of corrosion. It should also be said that VEG is resistant to low temperatures and can be used in unfavorable climatic conditions.


Highly reinforced insulation is used to protect highways operating in harsh climatic conditions
Expanded polystyrene (polystyrene, PPS)
It is produced in the form of shells, which outwardly practically do not differ from polyurethane foam - the same dimensions, the same tongue-and-groove joint. But the application temperature range, from -100 to +80 ° C, with all this external similarity makes it impossible or limited to use it for thermal insulation of the heating pipeline.
SNiP 41-01-2003 "Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning" states that in the case of a two-pipe heat supply system, the maximum supply temperature can reach 95 ° C. As for the return heating pipes, everything is not so simple here: it is believed that the temperature in them does not exceed 50 ° C.
Foam insulation is more often used for cold water pipes and sewers. However, it can be used over other insulation materials with a higher permissible application temperature.
The material has a number of some disadvantages: it is highly flammable (even with the addition of fire retardants), it does not tolerate chemical influences (it dissolves in acetone), and falls into balls upon prolonged exposure to solar radiation.
There are other non-polystyrene foams - formaldehyde, or, in short, phenolic. In fact, this is a completely different material. It is devoid of these disadvantages, it is successfully used as thermal insulation for pipelines, but it is not so widespread.


Installation
The shells are fixed to the pipe using a bandage or foil tape, it is allowed to stick them to the pipe and to each other.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam as a pipeline insulation is an environmentally friendly and efficient insulation. It is characterized by a neutral odor, is not susceptible to fungus, endowed with increased resistance to harmful environments, does not degrade, is completely harmless to humans and the environment.


Directly for large-diameter pipes, a spraying method is applied, as a result of which a seamless continuous insulation is formed, a peak reduction in heat loss is guaranteed. Spraying is carried out at the place of work, using special equipment for thermal insulation of pipelines, the simplicity and speed of the procedure is a clear advantage. For work on pipes of small diameter, shells based on polyurethane foam are considered, which provide a high level of thermal insulation, this method is affordable at its cost.
Foamed polyethylene
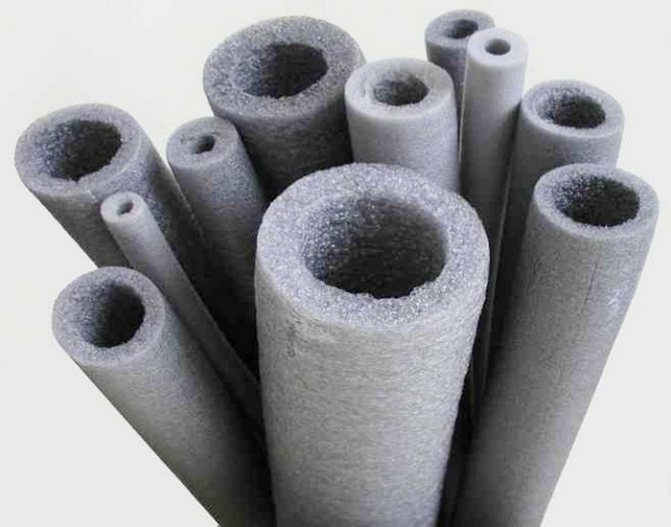
The temperature range at which the use of high pressure foamed polyethylene is allowed is from -70 to +70 ° С. The upper limit is not compatible with the maximum temperature of the heating pipe, usually taken in calculations. This means that the material is of little use as thermal insulation for pipelines, but it can be used as an insulating layer on top of a heat-resistant one.
Polyethylene foam insulation has found almost no alternative application as protection against freezing of water pipes. It is very often used as a vapor barrier and waterproofing.
The material is produced in the form of sheets or in the form of a flexible thick-walled pipe. The latter form is more often used, since it is more convenient for insulating a water supply system. The standard length is 2 meters. The color ranges from white to dark gray. It is possible to have a coating of aluminum foil that reflects infrared radiation. Differences concern internal diameters (from 15 to 114 mm), wall thickness (from 6 to 30 mm).


The application ensures that the temperature on the pipe is above the dew point, and therefore prevents the appearance of condensation.
Installation
An easy way with the worst vapor control results is to cut the foam material in a small indentation along the side surface, open the edges and put it on the pipe. Then wrap the entire length with mounting tape.
A more difficult solution (and far from always feasible) is to shut off the water, completely disassemble the insulated sections of the water supply and put on solid sections. Then put everything back together.Secure the polyethylene with ties. In this case, only the junction of the segments will become a vulnerable spot. It can be glued or also wrapped with tape.
Insulation purpose


To begin with, many insulation methods are applicable to different systems: water supply, sewerage, heating and ventilation. But in our article we will consider only those methods that are applicable to hot and cold water pipes.
Pipeline insulation is divided into two types:
- thermal insulation measures;
- waterproofing.
The purpose of each type of isolation measures is as follows:
Fastening materials for pipes
- Thermal insulation of the external cold water supply pipeline is needed to protect the system from freezing in the cold season. If the water in the pipe freezes in frost, then it will not be able to enter the house, and it will be rather difficult to find the ice plug and eliminate it.
- Thermal insulation of the outer pipes of hot water supply is needed so that hot water does not cool down during transportation to the consumer. In addition, this protection helps to increase the service life of the system.
- Thermal insulation of hot water pipelines is also carried out, which will be located in grooves - channels cut in the wall. In this case, these methods of protecting pipes are needed for the reason that the temperature of the water in the pipes in contact with cold brick or concrete walls may drop.
- Waterproofing of external pipes for hot and cold water supply is needed to protect them from corrosion. The fact is that the moisture present in the soil can cause rusting of steel pipes. However, this does not apply to plastic products.
- Various types of waterproofing are used to protect pipeline joints from leaking.
- As for the cold water supply systems inside the house, their waterproofing is carried out in order to protect against condensation, which, collecting on the pipes, can cause them to corrode. Again, this does not apply to non-corrosive plastic piping.
There are different types and methods of waterproofing and thermal insulation of pipelines and their joints. Let's consider them in more detail.
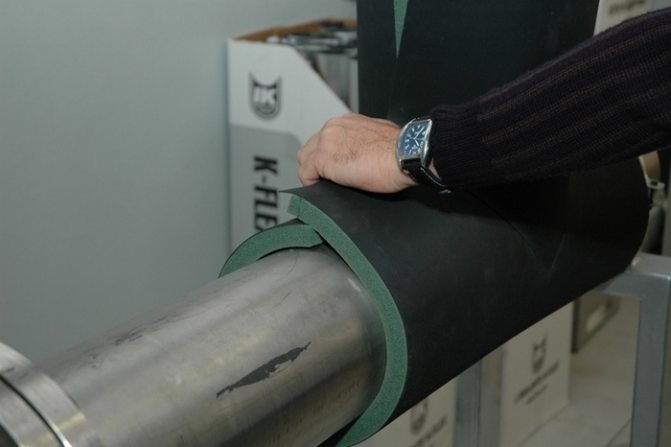
Foamed rubber
Closed-cell foam synthetic rubber is the most versatile material for keeping warm and cold. Designed for a temperature range from -200 to +150 ° C. Complies with all environmental safety requirements.
It is used as insulation of cold water pipelines, insulation of heating pipes, often found in refrigeration and ventilation systems. Heating pipes installed inside buildings and insulated with rubber do not require a vapor barrier.
Externally similar to expanded polyethylene, it is also produced in the form of sheets and flexible thick-walled pipes. Installation is also practically the same, except that such thermal insulation of pipes can be attached with glue.


Features of the insulation of the steam pipeline and gas pipeline
Besides transporting water, there are pipes for steam and gas transmission, but they also need thermal insulation. Therefore, there are other insulation materials with good properties intended for insulation of heat supply pipelines. For example, for those transporting steam. The main criterion for choosing an insulating material is considered to be a low coefficient of heat loss. Satisfy this requirement: mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, polyurethane foam and special paint.
And for the insulation of gas pipelines, you should choose a material with high waterproofing properties and a low water absorption coefficient. In addition, one should not forget that the gas pipeline needs protection from the effects of damaging ultraviolet rays. And also the insulator must have increased strength in order to protect the pipes from mechanical damage. To such insulating heaters bituminous mastics and tape insulation can be attributed based on polyethylene or PVC.