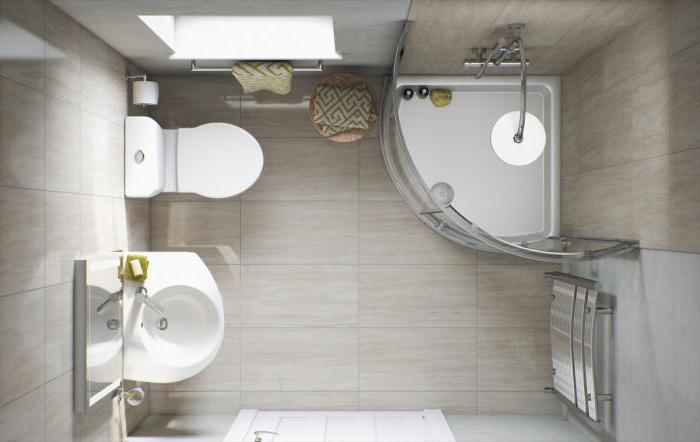
1. The heated area of a building should be defined as the area of the floors (including the mansard, heated basement and basement) of the building, measured within the internal surfaces of the external walls, including the area occupied by partitions and internal walls. In this case, the area of staircases and elevator shafts is included in the floor area.
The heated area of the building does not include the area of warm attics and basements, unheated technical floors, basement (underground), cold unheated verandas, unheated staircases, as well as the cold attic or part of it not occupied by the attic.
CALCULATION OF HEATED AREAS AND BUILDING VOLUMES
5.4 Thermal insulation of external walls should be designed to be continuous in the plane of the building facade. When using combustible heaters, it is necessary to provide for horizontal cuts made of non-combustible materials at a height of no more than a floor height and no more than 6 m. Fencing elements such as internal partitions, columns, beams, ventilation ducts and others should not violate the integrity of the thermal insulation layer. Air ducts, ventilation ducts and pipes, which partially pass through the thickness of the outer fences, should be buried to the surface of the thermal insulation from the warm side. It is necessary to ensure a tight adjoining of the thermal insulation to the through heat-conducting inclusions. In this case, the reduced resistance to heat transfer of a structure with heat-conducting inclusions must be at least the required values.
5.11 It is recommended to design the filling of gaps in the abutments of windows and balcony doors to external wall structures using expandable synthetic materials. All porches of windows and balcony doors must have sealing gaskets (at least two) made of silicone materials or frost-resistant rubber with a durability of at least 15 years (GOST 19177). It is recommended to install glass in windows and balcony doors using silicone mastics. Blind parts of balcony doors should be insulated with heat-insulating material.
Calculation of heating by the area of the room
Note: the external finishing layers of ventilated structures of the facade or roof (for example, siding or roofing material) are not taken into account, since their thermal resistance does not have a significant effect on the overall insulation.
Naturally, the amount of heat loss through all building structures of the building will very much depend on the level of winter temperatures. It is quite understandable that during the winter the thermometer readings "dance" in a certain range, but for each region there is an average indicator of the lowest temperatures characteristic of the coldest five-day period of the year (usually this is typical of January). For example, below is a schematic map of the territory of Russia, on which approximate values are shown in colors.
How to find out what is included in the living area of a private house, and how it can be calculated
If the management company incorrectly calculates the cost of heating due to the incorrectly indicated total area in the documents, it is necessary to reissue the technical passport, after which the corresponding changes are made to the cadastral passport and certificate of ownership. After that, the management company will have to recalculate.
- If there are niches in the building, the height of which is less than 2 m, they cannot be taken into account as part of the living space of the premises.
- If the area of space under the flight of stairs is no more than one and a half meters, it will also not be taken into account when assessing the size of the house.
Payment
The procedure for calculating the heating bill will completely depend on how the house is heated and what heating devices are installed in the room. There are several basic options for equipping a house with devices and appliances, on which how heating in an apartment is calculated largely depends:
- In a residential-type house, only one device is installed, which is common, and in apartments and non-residential premises, metering devices are completely absent.
- A common device is installed in the house, which is needed to account for heating, but also individual rooms in the house are equipped with individual devices.
- There is no general heating meter in the house.
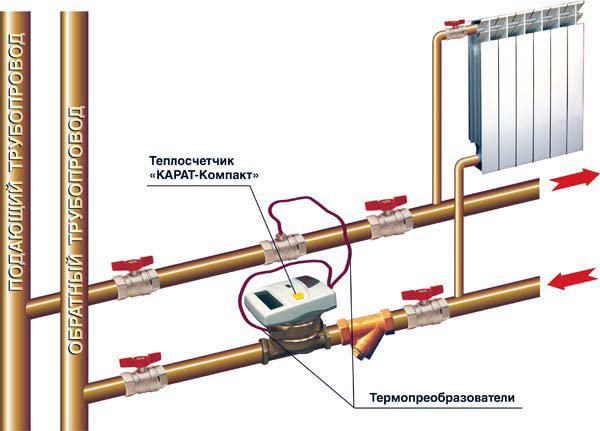
One of the options for installing the device for heat metering
First of all, you need to find out if one common household appliance is installed in the house, and also whether there are other individual heating meters in residential or non-residential premises.
Private house projects
The area of a residential building does not include the area of the underground for ventilation of a residential building, an unexploited attic, a technical underground, a technical attic, non-apartment utilities with vertical (in canals, mines) and horizontal (in the interfloor space) wiring, vestibules, porticos, porches, outdoor open stairs and ramps, as well as the area occupied by protruding structural elements and heating stoves, and the area within the door
А.2.1 The area of apartments is determined as the sum of the areas of all heated rooms (living rooms and auxiliary rooms intended to meet domestic and other needs), excluding unheated rooms (loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces, cold storage rooms and vestibules).
Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation of September 30, 2011
6. The total area of a dwelling, a dwelling house consists of the sum of the area of all parts of such a dwelling, a dwelling house, including the area of premises for auxiliary use, intended to satisfy citizens' household and other needs related to their living in a dwelling, with the exception of balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces.
3. For premises in buildings erected according to standard designs from prefabricated prefabricated structures with a standard layout on the floors, it is allowed to determine the areas for the basement, first and standard floors. For subsequent floors, the area can be taken as standard, with the exception of rooms in which there are changes in the layout.
Heated area of the apartment: did you calculate correctly?
Probably, in your case, the indicator "heated area" was calculated before the entry into force of the Rules for the provision of utilities (2006) by excluding the areas of unheated premises (loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, vestibules) from the total area of the apartment on the basis of the rules for calculating the area. This can be confirmed by those. passport for the apartment.
I pay for the central heating of the apartment according to the tariff (without meter). The registration certificate for the apartment says: Living area -55.8 sq.m, Auxiliary premises area - 18.4 sq.m, Total area - 74.2 sq.m. The personal account for the payment of heating of OOO LUKOIL-Teplotransportnaya Kompaniya states: Heated area 62.2 sq. M. m.
Heated area
was revised four times and decreased by almost 2.5 times: from 11 cubic meters to 4.5 cubic meters per square meter heated area
per month. In addition, the regional coefficients for individual regions and the number of storeys of buildings, the duration of the heating period and the social one were revised. 1news.info 05/30/2018 14:04
meters 1. The number of house meters in the last heating season __366__pcs, covered by meters _1196383.74_m 2, which is 78.7% of the total heated area
... 2. The number of house meters in the current heating season is _585_pcs, covered by meters __1486221.49__m 2, which is _97.9_% of.6264.com.ua - site of the city of Kramatorsk 05/22/2018 11:25
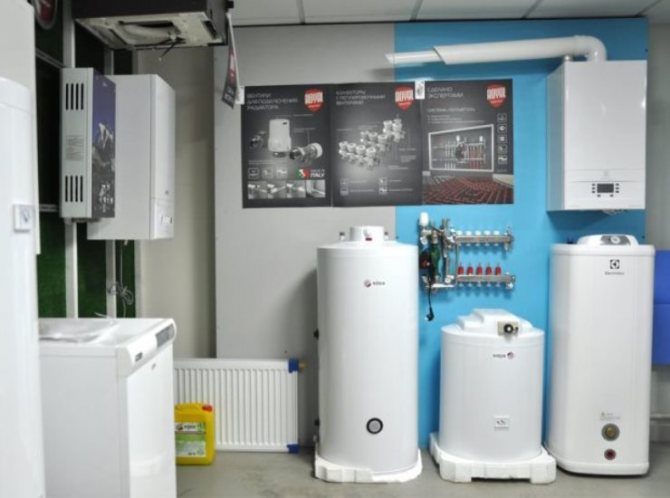
Selection of a heating boiler
Heating units, depending on the intended purpose, are single-circuit and double-circuit, can be installed wall-mounted and floor-standing. Boilers also differ in the type of fuel.
Gas modifications


Modifications of gas boilers depending on the area of the room
Manufacturers produce various devices, so when choosing, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- The purpose of the installation of heating communications. Single-circuit options are used for heating, double-circuit options with a built-in boiler for 150-180 liters can provide a house with hot water and heat it.
- The number of heat exchangers in a dual-circuit model. The only bithermal element heats water as a heat carrier and a hot water supply resource at the same time. In versions with two, the heating primary is used for heating, the secondary is used for heating the DHW system.
- Heat exchanger material. Cast iron accumulates heat for a long time and does not corrode, steel is practically insensitive to temperature fluctuations.
- Combustion chamber type. The open chamber works on natural draft, therefore the boiler needs a separate room with good ventilation. The closed unit removes the combustion products through a coaxial horizontal chimney.
- Features of ignition. In the electric ignition mode, the wick will burn constantly, but the equipment needs electricity to work. Models with piezo ignition are independent, but manually switched on.
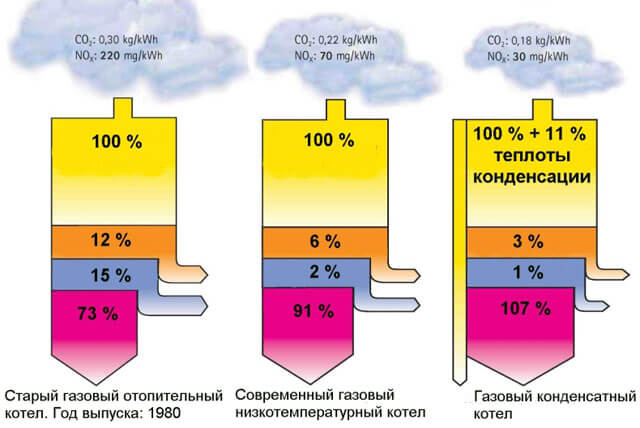
Condensing gas units with a water economizer differ in performance, but the fuel fee is almost doubled.
Electric models


Models of electrical equipment with the possibility of connecting a boiler
The devices are distinguished by almost silent operation, compactness and safe operation. Owners of houses and summer cottages can purchase modifications:
- On tubular heating elements. Devices with heating elements are suitable for wall mounting, automated, but often break down due to scale.
- On the electrodes. Small devices connected to a circuit of two or more batteries. The boiler is efficient, equipped with temperature settings, but is sensitive to the coolant.
- Induction. Equipped with an overheating protection system, they quickly heat up the coolant, have an efficiency of 97%.
Induction boilers are expensive equipment.
Combined units


Solid fuel gas boiler for heating and water heating
They heat any area, they can operate in a universal mode and on two or three types of fuel. The type of power supply is selected by the user:
- solid fuel + gas;
- solid fuel + electricity;
- gas + electricity;
- gas + diesel.
One type of fuel resources is the main one, the second is auxiliary, which does not heat the house, but only maintains a normal temperature regime.
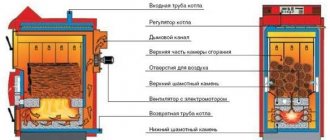
Solid fuel boilers
They work on wood, sawdust, coal, coke, special briquettes, are distinguished by safety and ease of use. For a private house, you can pick up units:
- Classic. They function according to the principle of direct combustion; the furnace must be filled every 5-6 hours.
- Pyrolysis. They work on the principle of afterburning residual gases in a special chamber. Fuel is loaded every 12-14 hours.
The devices require a chimney with good draft and are installed in a separate room. The user must periodically clean the combustion chamber from soot and tar.
Liquid fuel devices
They run on diesel fuel, therefore they are placed in a separate room. The boiler room is equipped with an exhaust hood and a high-quality ventilation system. Heavy oil is stored in sealed containers in a separate room. All liquid-fuel devices are automated, productive, and have great power.


Solid fuel


Diesel oil
Total area and living area of the house
Due to the fact that the size of utilities depends on the area
, it is necessary that the area in the documents correspond to reality. Sometimes this requires ordering a new technical passport for a dwelling. Based on the data contained in it, a cadastral passport is drawn up, and information from it is indicated in the certificate of ownership.
People often confuse concepts such as total area and living area, the main thing is to be guided by the documents when determining the area, however, if you need to know the size of the area for specific purposes, it would not be superfluous to consult a lawyer who, knowing the legal features of a particular issue, will help to you not only in word, but also in deed.
Calculation of heating by the area of the room
The calculator proposed below provides for a calculation for a multi-layer structure, including the main layer (pos. 1), already existing insulation (if any) (pos. 2), a layer of internal (pos. 3) and external (pos. 4) finishing. If there are no layers in reality, then this item in the calculator is simply not filled.
As shown above, the floor is one of the significant sources of heat loss. This means that it is necessary to make some adjustments in the calculation for this feature of a particular room. The correction factor "g" can be taken equal to:
Recommended reading: Traveling in the metro using a student's social card
How the area of the house is calculated
But the bodies of technical inventory to determine the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe premises use the Instruction on the accounting of the housing stock of the Russian Federation. And therefore, the BTI documents on determining the area of an apartment or an individual residential building contain general information, where the account includes a balcony, loggia, terrace, etc. Such premises are referred to the total area, but with a decreasing coefficient: 0.5 - loggias; 0.3 - terraces and balconies; 1.0 - also terraces and cold storage rooms.
In accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of total area includes the sum of the areas of all rooms and parts of a given premises, including the areas of rooms (premises) for additional or auxiliary purposes (use), which are intended for household and other needs of citizens. Such premises are: kitchens, corridors, bathrooms, etc.
Principles and calculation formula
The calculation of heating registers for the area of the room will be based on 100 W per 1 m2. However, the formula will be supplemented with several correction factors.
It will look like this: Q = (S × 100) × a × b × c × d × e × f × g × h × i × j × k × l × m.
The coefficients in the form of Latin letters are simply taken from the alphabet, and are not one of the physical quantities. Below we will describe each of them separately.
Coefficient "a"
Indicates the number of exterior walls in a particular room. It turns out that the more walls a room has, the more heat it carries.
For the coefficient "a" the following values are used:
- 0.8 - if there are no external walls;
- 1.0 - one wall;
- 1,2 - two walls;
- 1.4 - three walls.
Coefficient "b"
Contains data on the orientation of the walls of the building to the cardinal points. This is important because sunlight still penetrates the inside of the building even during the coldest season and affects the temperature in it. In addition, on the sunny side of the building, the level of heat loss is significantly lower.
The calculated values of the coefficient "b" depending on the cardinal direction are as follows:
- 1.1 - orientation to the east or north;
- 1.0 - The outer walls are facing south or west.

Coefficient "c"
This indicator indicates the dependence of the location of the building on the "wind rose" in winter.
For buildings that are located in closed areas, this indicator is not so important. However, in open areas, strong winds can significantly shift the thermal balance of a building. In addition, the leeward side will be more protected from heat loss than the windward side, where heat will leave the room faster.
So, when calculating cast-iron heating batteries for the area of an apartment, the values of the coefficient "c" can be taken equal to:
- 1.0 - for the leeward side;
- 1,1 - walls are placed parallel to the wind direction;
- 1,2 - windward walls.
Coefficient "d"
This coefficient allows you to take into account the climatic features of a particular region in which the building is being erected. The fact is that the level of external temperatures will have a significant effect on the amount of heat loss in a building. Therefore, to calculate the capacity of the heating system, it will be necessary to find out the average indicators of low winter temperatures, which are observed in the coldest time of the year (usually in January).
Based on the temperature indicators of the region, the value of the coefficient "d" will be as follows:
- 1.5 - -35 ℃ and below;
- 1.3 - from -30 ℃ to -34 ℃;
- 1.2 - from -25 ℃ to -29 ℃;
- 1.1 - from -20 ℃ to -24 ℃;
- 1.0 - from -15 ℃ to -19 ℃;
- 0.9 - from -10 ℃ to -14 ℃;
- 0.7 - not less than -10 ℃.
Heated building area
TSN 23-333-2002: Energy consumption and heat protection of residential and public buildings. Nenets Autonomous Okrug
- Terminology TSN 23 333 2002: Energy consumption and heat protection of residential and public buildings. Nenets Autonomous Okrug: 1.5 Degree day Dd ° С × day Definitions of the term from different documents: Degree day 1.6 Glazing coefficient of the building facade ... ... Dictionary-reference book of terms of normative and technical documentation
TSN 23-329-2002: Energy efficiency of residential and public buildings. Thermal protection standards. Oryol region - Terminology TSN 23 329 2002: Energy efficiency of residential and public buildings. Thermal protection standards. Oryol Region: 1.5 Degree day Dd ° C · day Definitions of the term from different documents: Degree day 1.6 Glazing coefficient ... Dictionary-reference book of terms of normative and technical documentation
What is included in the total living area of the apartment - controversial points
- General
- the sum of all areas of housing that must be accounted for in accordance with the RF Housing Code. - Residential
- the sum of the areas of living rooms, which are allocated as such in the design of the building. The semantic purpose of this room is the permanent residence of a person. - Useful
- in our country - this is the sum of the areas of all rooms, taking into account the balcony, mezzanine, except for staircases, an elevator shaft, a ramp and the like, abroad - the sum of only the areas used.
The buyer has signed an agreement with the developer on equity participation, with the expectation of buying an apartment of 77 sq. m. Including the area of the loggia. However, in the contract, there were no references to the coefficients used in the calculations and a copy of the floor plan of the building.
30 Jul 2020 1453
In accordance with part 10 of Article 41 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2007 No. 221-FZ "On the State Real Estate Cadastre" (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2007, No. 31, Art. 4017; 2008, No. 30, Art. 3597, 3616 ; 2009, No. 1, article 19; No. 19, article 2283; No. 29, article 3582; No. 52, article 6410, 6419; 2011, No. 1, article 47; No. 23, article 3269; No. 27, Art. 3880; No. 30, Art. 4563, 4594) I order:
Approve the Requirements for determining the area of a building, premises in accordance with the appendix.
Registration number 22231
Requirements for determining the area of a building, room
I. General requirements for the definition of areas
1. The area and total area of the building, premises are defined as the area of the simplest geometric figure (rectangle, trapezoid, right-angled triangle, etc.) or by dividing such an object into simple geometric figures and summing the areas of such figures.
2. The value of the area and the total area of the building, the room is determined in square meters rounded to 0.1 square meters, and the values of the measured distances used to determine the areas - meters rounded to 0.01 meters.
3. For premises in buildings erected according to standard designs from prefabricated prefabricated structures with a standard layout on the floors, it is allowed to determine the areas for the basement, first and standard floors. For subsequent floors, the area can be taken as standard, with the exception of rooms in which there are changes in the layout.
II. Determination of the area of the building, room
4. The area of a building is defined as the sum of the areas of all aboveground and underground floors (including technical, attic, basement).
The floor area should be measured within the inner surfaces of the outer walls at a height of 1.1 to 1.3 meters from the floor.
Floor area with sloped exterior walls is measured at floor level.
The area of the building includes the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums and other halls, verandas, outdoor glazed loggias and galleries.
The area of the building also separately includes the area of open unheated planning elements of the building (including the area of the exploited roof, open external galleries, open loggias, etc.).
The area of multi-height rooms, as well as the space between flights of stairs more than the width of the march and openings in the ceilings of more than 36 square meters, should be included in the building area within only one floor.
5. The area of a room is defined as the sum of the areas of all parts of such a room, calculated by their dimensions, measured between the finished surfaces of walls and partitions at a height of 1.1 - 1.3 meters from the floor.
III. Determination of the total area of a dwelling, a dwelling house
6. The total area of a dwelling, a dwelling house consists of the sum of the area of all parts of such a dwelling, a dwelling house, including the area of premises for auxiliary use, intended to satisfy citizens' household and other needs related to their living in a dwelling, with the exception of balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces.
The area of premises for auxiliary use includes the area of kitchens, corridors, baths, bathrooms, built-in wardrobes, storage rooms, as well as the area occupied by an intra-apartment staircase.
Measurement of the distances used to determine the total area of a dwelling, a residential building, is carried out along the entire perimeter of the walls at a height of 1.1 - 1.3 meters from the floor.
When determining the total area of a dwelling, a dwelling house, it is necessary:
The area of niches with a height of 2 meters or more should be included in the total area of the premises in which they are located. The area of arched openings should be included in the total area of the room, starting with a width of 2 meters;
The floor area under the march of the intra-apartment staircase, with a height from the floor to the bottom of the protruding structures of the march of 1.6 meters or more, should be included in the total area of the room in which the staircase is located;
The area occupied by protruding structural elements and heating stoves, as well as located within the doorway, should not be included in the total area of the premises.
When determining the total area of the attic floor, the area of this room is taken into account with a height from the floor to the inclined ceiling:
1.5 meters - with an inclination of 30 degrees to the horizon;
1.1 meters - at 45 degrees;
0.5 meters - at 60 degrees or more.
For intermediate values, the height is determined by interpolation.
Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation of September 30, 2011 No. 531 "On approval of the Requirements for determining the area of a building, room"
Registration number 22231
Features of calculating heat losses
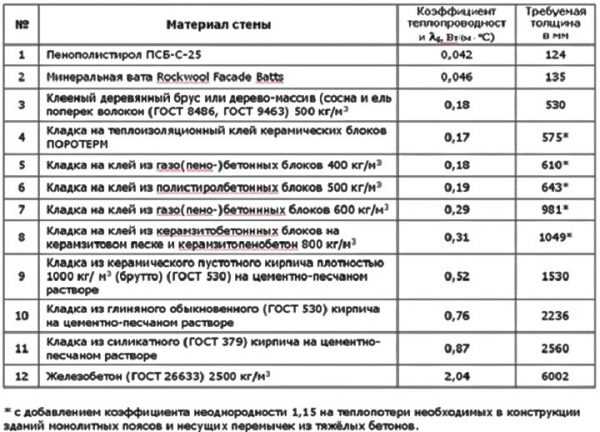

Heat loss depending on the type of material
Most often, the heat depends on the material of the floor, ceiling surface, walls, the number of openings, and the characteristics of insulation. It is possible to calculate autonomous heating taking into account heat loss in a private house using the example of a corner room with an area of 18 m2 and a volume of 24.3 m3. It is located on the 1st floor, has ceilings of 2.75 m, as well as 2 external walls made of 18 cm thick timber with plasterboard sheathing and wallpaper. The room has 2 windows with dimensions 1.6x1.1 m. The floor is made of wood, insulated, with an underground floor.
Calculation of surface area:
- External wall without windows - S1 = (6 + 3) x 2.7 - 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 = 20.78 m2.
- Windows - S2 = 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 = 3.52 m2.
- Floor - S3 = 6 × 3 = 18 m2.
- Ceiling - S4 = 6 × 3 = 18 m2.
Calculation of heat loss of surfaces, Q1:
- Outer wall - S1 x 62 = 20.78 x 62 = 1289 W.
- Windows - S2 x 135 = 3 × 135 = 405 W.
- Ceiling - Q4 = S4 x 27 = 18 × 27 = 486 W.
Calculation of the total heat loss by summing the data. Q5 = Q + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 = 2810 W.
The total heat loss of one room on a cold day is -2.81 kW, that is, the same amount of heat is supplied additionally.
Document overview
In cadastral activities, the area of the building and premises is important. The Ministry of Economic Development of Russia has established how to define it.
So, to establish the area and total area of a building (room), you need to refer to the area of the simplest geometric figure (rectangle, trapezoid, right-angled triangle, etc.).Or break such an object into the latter and summarize their areas.
The corresponding value is expressed in square meters, rounded to the nearest 0.1. The measured distances used for the specified purposes are meters rounded to the nearest 0.01.
The area of the building is calculated as the sum of the areas of all aboveground and underground floors (including technical, attic, basement). At the same time, do not forget about the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums and other halls, verandas, outdoor glazed loggias and galleries. Here, the area of open unheated planning elements of the building is also taken into account separately.
The area of the room is the sum of the areas of all its parts, calculated by their dimensions, measured between the finished surfaces of the walls and partitions at a height of 1.1-1.3 m.
The total area of a dwelling and a house consists of the sum of the area of all their parts. This also includes the area of auxiliary use premises that satisfy the needs associated with living in a residential area (except for balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces). We are talking about kitchens, corridors, baths, bathrooms, built-in wardrobes, storage rooms, as well as the area occupied by the staircase inside the apartment.
The distances used to determine the total area of housing are measured along the entire perimeter of the walls at a height of 1.1-1.3 m from the floor.
Heated area of apartments or useful area of premises, m2;
Heated building volume, m3;
D
- degree-day of the heating period, ° С day (1.1).
Specific consumption of heat energy for heating buildings >
must be less than or equal to the normalized value
≤
. (5.2)
5.1 Determination of heated areas and building volumes
This item is carried out in the section of the diploma project for residential and public buildings.
1. The heated area of a building should be defined as the area of the floors (including the mansard, heated basement and basement) of the building, measured within the internal surfaces of the external walls, including the area occupied by partitions and internal walls. In this case, the area of staircases and elevator shafts is included in the floor area.
The heated area of the building does not include the area of warm attics and basements, unheated technical floors, basement (underground), cold unheated verandas, unheated staircases, as well as the cold attic or part of it not occupied by the attic.
2. When determining the area of the attic floor, an area with a height of up to an inclined ceiling of 1.2 m with an inclination of 30 ° to the horizon is taken into account; 0.8 m - at 45 ° - 60 °; at 60 ° and more - the area is measured up to the plinth.
3. The area of living quarters of a building is calculated as the sum of the areas of all common rooms (living rooms) and bedrooms.
4. The heated volume of a building is defined as the product of the heated floor area by the internal height, measured from the floor surface of the first floor to the ceiling surface of the last floor.
In case of complex shapes of the internal volume of a building, the heated volume is defined as the volume of space bounded by the internal surfaces of external fences (walls, roof or attic floor, basement floor).
5. The area of external enclosing structures is determined by the internal dimensions of the building. The total area of the outer walls (taking into account window and door openings) is determined as the product of the perimeter of the outer walls along the inner surface by the inner height of the building, measured from the floor surface of the first floor to the ceiling surface of the last floor, taking into account the area of window and door slopes with a depth from the inner surface of the wall to the inner surface of a window or door block. The total area of the windows is determined by the dimensions of the openings in the light. The area of the outer walls (opaque part) is defined as the difference between the total area of the outer walls and the area of windows and outer doors.
6.The area of horizontal external fences (covering, attic and basement floors) is defined as the area of the floor of the building (within the inner surfaces of the external walls).
With inclined surfaces of the ceilings on the last floor, the coverage area of the attic floor is defined as the area of the inner surface of the ceiling.
The calculation of the areas and volumes of the space-planning solution of the building is carried out according to the working drawings of the architectural and construction part of the project. As a result, the following main volumes and areas are obtained:
Heated volume Vh
, m3;
Heated area (for residential buildings - the total area of apartments) Ah
, m2;
The total area of the outer envelope of the building, m2.
5.2 Determination of the standardized value of the specific consumption of heat energy for heating the building
The standardized value of the specific consumption of thermal energy for heating a residential or public building is determined according to table. 5.1 and 5.2.
Standardized specific consumption of heat energy for heating single-family detached and blocked residential buildings, kJ / (m2 ° С day)
Table 5.1
| Heated area of houses, m2 | With the number of floors | |||
| 60 and less | ||||
| 1000 and more | ||||
| Note - At intermediate values of the heated area of the house in the range of 60-1000 m2, the values should be determined by linear interpolation. | ||||
Standardized specific consumption of heat energy for heating buildings, kJ / (m2 · ° С · day) or [kJ / (m3 · ° С · day)]
Table 5.2
| Building types | Number of storeys of buildings | |||||
| 1. Residential, hotels, hostels | According to table 5.1 | for 4-storey single-family and block houses - according to table. 5.1 | ||||
| 2. Public, except for those listed in pos. 3, 4 and 5 tables | ||||||
| 3. Polyclinics and medical institutions, boarding houses | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
| 4. Preschool institutions | ||||||
| 5. After-sales service | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
| 6.Administrative purposes (offices) | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
Heated building area
the total area of the floors (including the attic, heated basement and basement) of the building, measured within the inner surfaces of the outer walls, including the area of staircases and lift shafts; for public buildings, the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums is included. (See: TSN 23-328-2001 of the Amur Region (TSN 23-301-2001 JSC). Standards for energy consumption and heat protection.)
Construction dictionary.