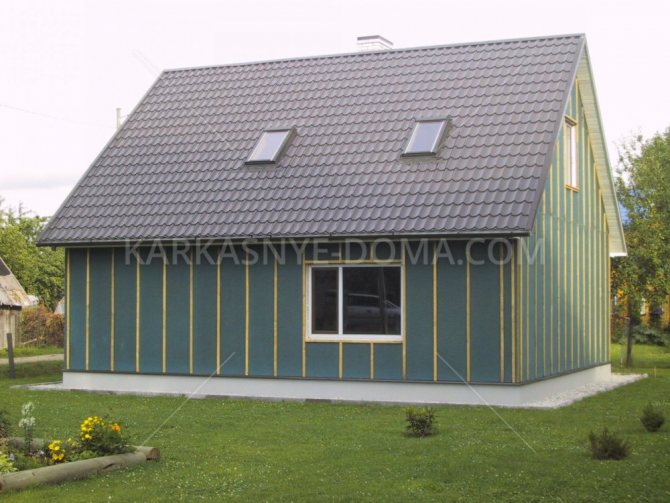
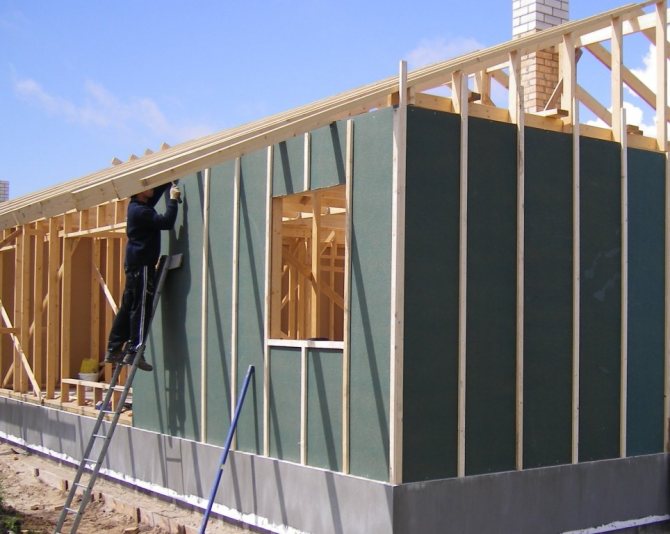
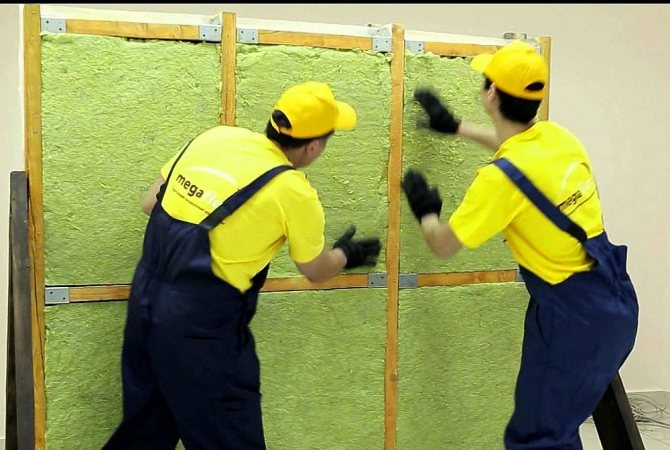
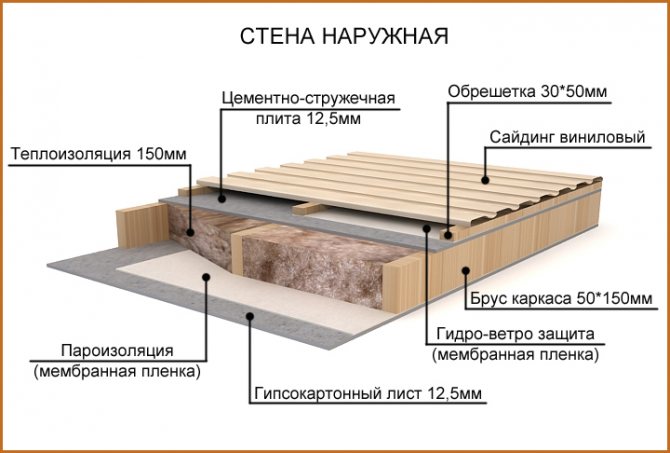
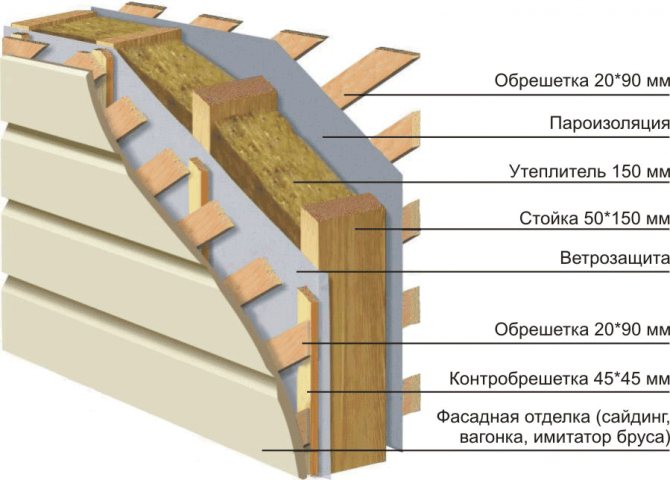
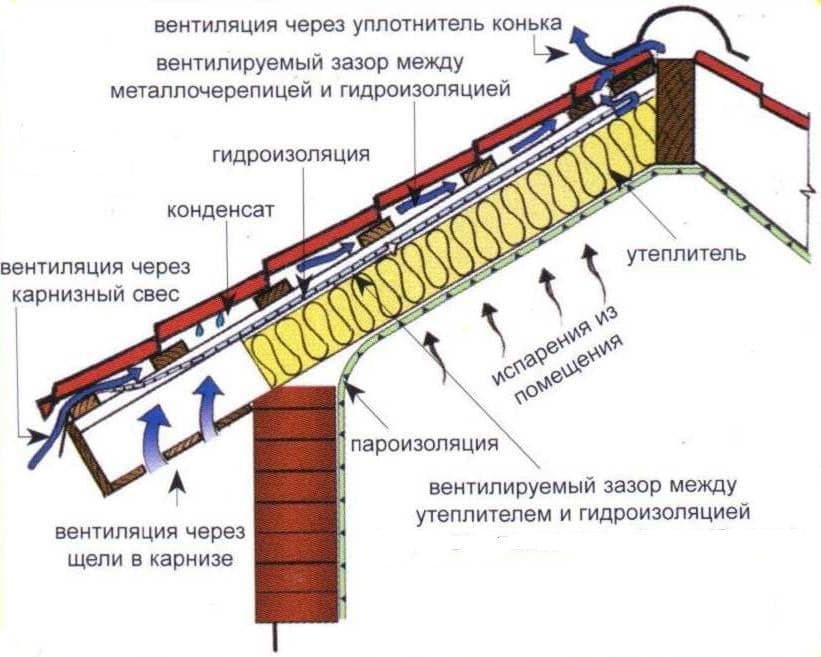
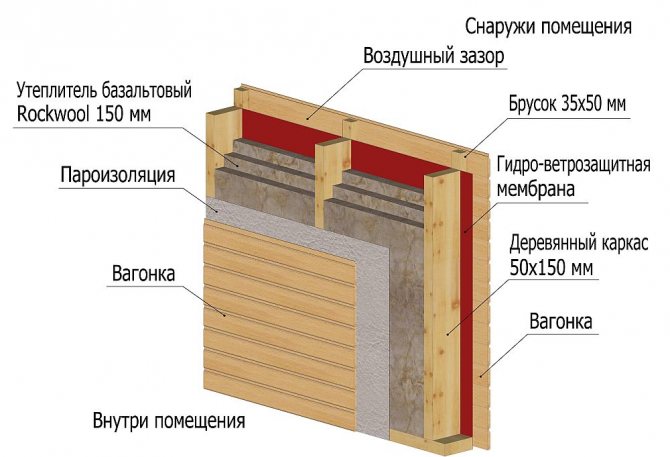
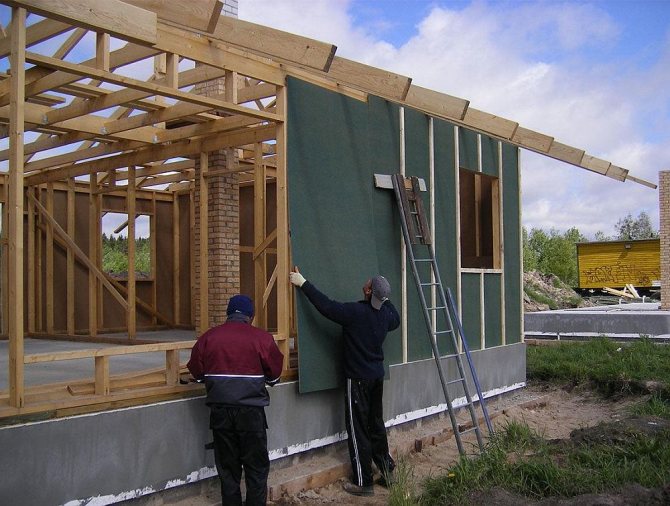
In modern construction, special attention is paid to the thermal characteristics of buildings and structures. As a rule, with a high-quality arrangement, you can protect the building from the cold in winter, and in the off-season from the heat, as a result of which you can significantly save on heating and air conditioning. When carrying out construction work, it is recommended to correctly carry out not only the installation of thermal insulation, but also wind protection. Wind protection for the roof is an excellent barrier to prevent cold air currents from entering the insulation, as a result of which the thermal insulation of the entire room is significantly increased.
About us
My first interview appeared on the Internet, I gave it to one very talented teacher Sergei Bondarenko, who, in addition to teaching students, also runs a good website dedicated to teaching computer literacy.
In it you can learn a little about me, about my life, and about how I myself came to IT technologies. Read, judging by the comments, the interview was successful.
How wind protection works
The windscreen actually does two things. Not only does it prevent air masses from penetrating into the insulation in the wind, but also acts as a moisture insulation.
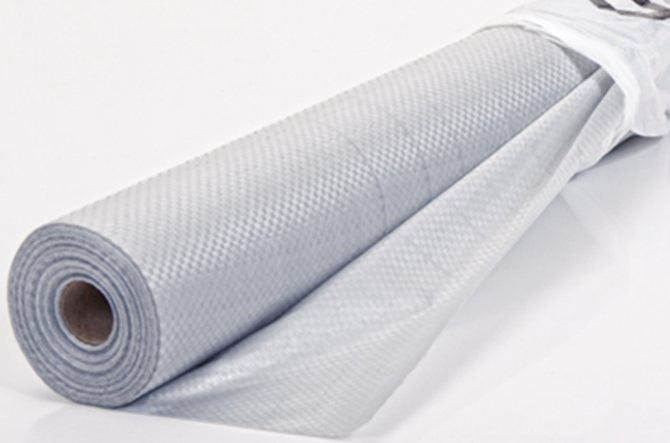
A separate type of films is used for arranging an insulated roof. Such films are often called a subroofing membrane, by the way, for some reason, many builders neglect it, as it turns out in vain ...
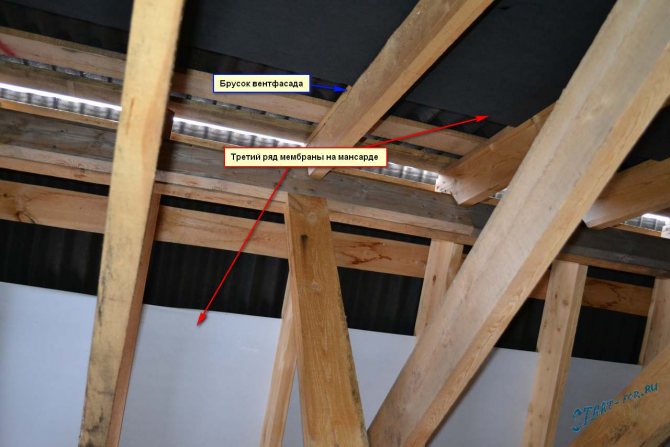


Roof membrane
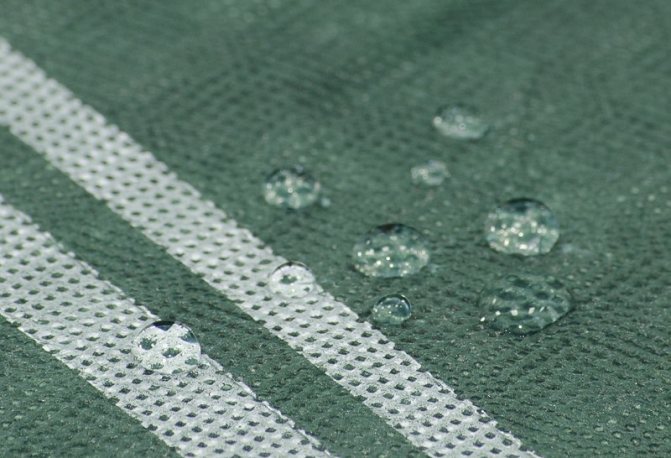
The windproof membrane consists of specially sintered polymer fibers. The film itself is arranged in such a way that on the one hand it is smooth and does not allow moisture to penetrate from the street into the house, on the other it has a rough surface.
How to choose a windscreen for the roof
In the process of choosing a windproof film for the roof, it is recommended to take into account a number of nuances. These include the following points:
- toxicity - as practice shows, a windproof film for a roof should be made of environmentally friendly materials, while toxic substances should not be released during operation;
- technical characteristics - in this case, the level of strength, resistance to ultraviolet rays, the permissible range of exposure to temperature conditions are of particular importance;
- operational period.
In addition, many consumers take into account the cost of the product. The most expensive option is superdiffusion membranes, but at the same time they have high technical characteristics.
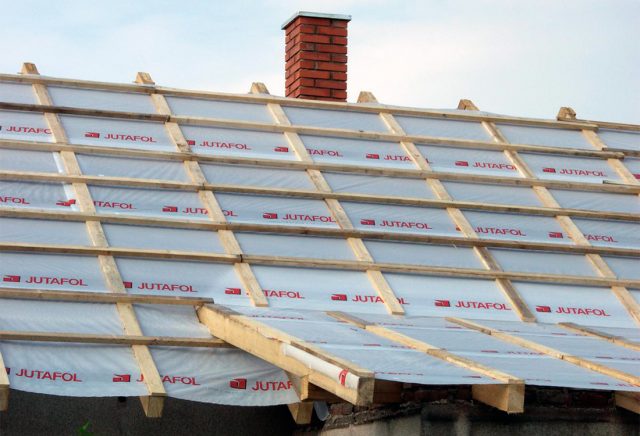


Role in a frame house
For a frame house, a windproof membrane is of great importance. Since heaters are used in such a house, it becomes necessary to protect them from moisture and blowing. Probably, many have seen what happens to the insulation when it lies under the open sky.
The fibers fluff up, the trapped moisture does not want to leave it at all, and freezes by winter, which leads to the loss of the thermal insulation properties of any mineral wool insulation.
This has little to do with foam, it is not afraid of moisture, and is not subject to moisture accumulation. Therefore, the use of a membrane in a house with foam insulation may be considered optional by many.
But this is a misconception, the film also protects the building frame from atmospheric influences, and fulfills its function of protecting it from the wind. In any house, this is very important, even a log house, especially a lumber one.
Features of the use of different types of wind protection
In addition to diffuse membranes, in practice, they often use rigid insulation options, for example: OSB, fiberboard plates and Isoplan panels. Let's consider the pros and cons of each type of wind protection, and note the specifics of their application.
Using OSD: the pros and cons
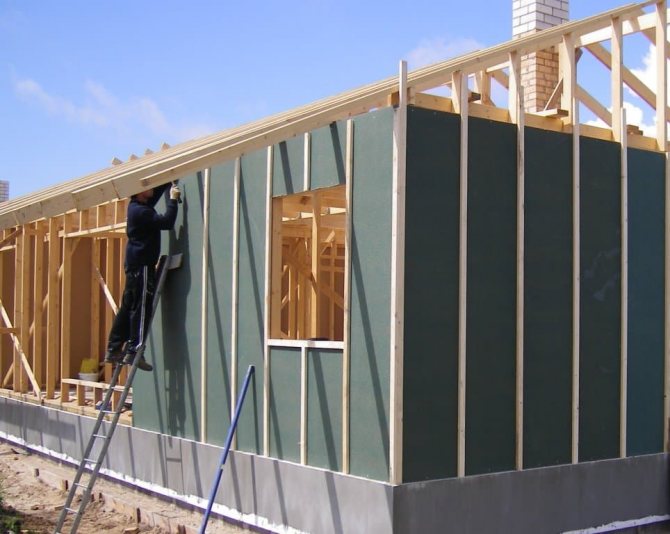
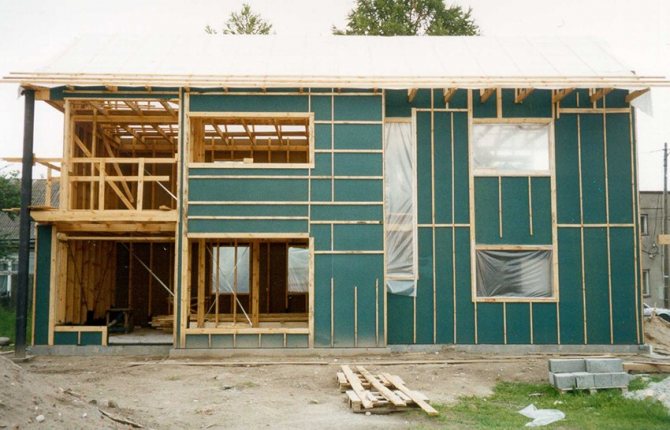
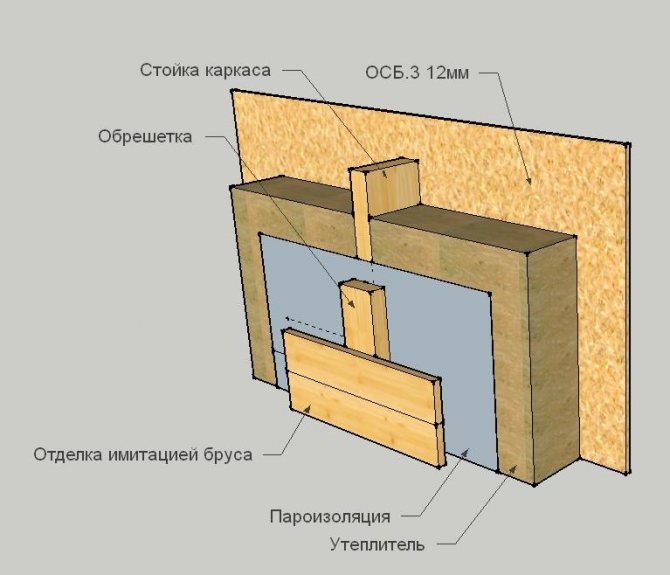
Sheathing the outer walls of a frame house with OSB slabs solves several problems. Rigid slabs are the basis for subsequent cladding and effective wind protection.
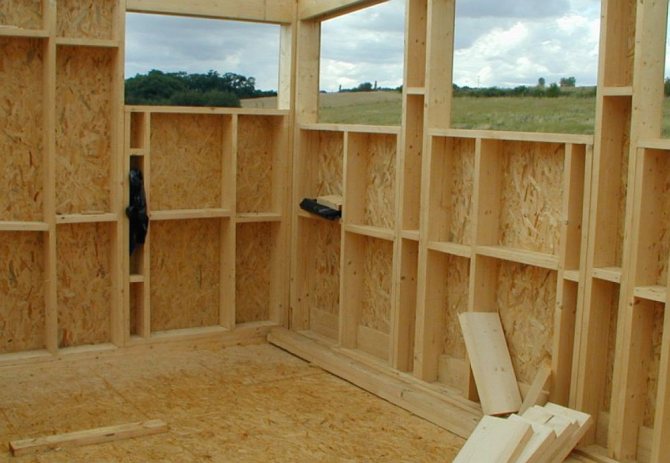


Material advantages:
- providing additional heat and sound insulation;
- strength - OSB perfectly restrains wind gusts;
- sufficient vapor barrier;
- environmental friendliness.
However, OSB does not tolerate a humid environment well and needs additional waterproofing... In addition, rigid, oriented strand boards tend to change their linear dimensions with temperature changes. As a result, the formation of gaps between the sheathing sheets and the blowing of the walls.
Some for OSB waterproofing suggest covering the slabs with plastic wrap. But such a solution negates the vapor permeability of the substrate, and is fraught with undesirable consequences: wetting of the insulation, deterioration of the microclimate in the house - an increase in humidity, the appearance of dampness.
Useful: How to build a garden house with your own hands
Izoplat - insulation and wind protection
Isoplat is a sheet material made from softwood. No glue is used for pressing the fibers - forming into plates occurs due to the softening of a natural polymer.


Izoplat characteristics:
- high thermal conductivity - 0.045 W / (m * k);
- moisture resistance due to the treatment of the outside with paraffin;
- fibrous structure provides good vapor permeability;
- sound insulating ability - reducing the noise effect by 23-26 dB;
- high density - 230-270 kg / m3;
- environmental friendliness, biostability and relative fire safety - when ignited, the material is charred, and the resulting ash blocks the access of air to the wooden frame;
- simplicity of installation and tightness of the docking of the windproof plates due to the “thorn-groove” fixation.


Main disadvantage of Izoplat - significant financial costs for arranging the wind protection of a frame house. Despite the declared moisture resistance, manufacturers do not recommend leaving the sheets open for a long time. Excessive wetting can lead to a change in the geometry of Isoplat - the material is taken in "waves".
Windproof properties of fiberboard slabs
The material consists of 50-60% wood fibers, the rest is made up of Portland cement and various additives. This structure has endowed the slabs with a number of positive characteristics:
- high water resistance along with vapor permeability - fiberboard plates "breathe", maintaining a favorable microclimate, and are not afraid of moisture;
- fire safety - the material tolerates high temperatures, and does not emit toxic substances during combustion;
- low thermal conductivity - wood-cement sheets reduce heat losses in the room.
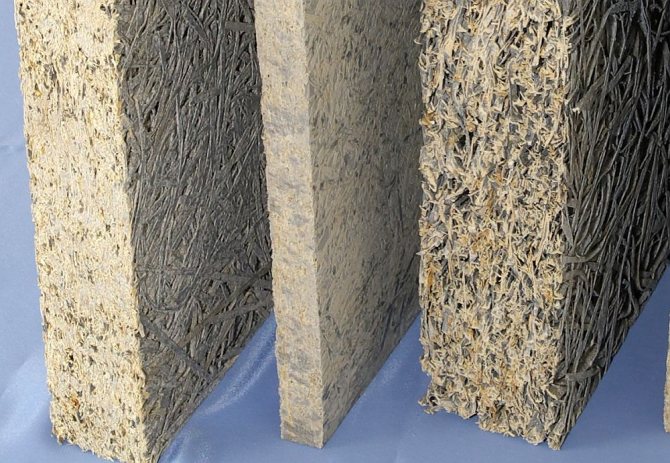


An additional plus is strength, the density of fiberboard is 250-1050 kg / m3. Plates provide reliable protection of the frame from adverse external factors, including gusts of wind. In addition, the material is easy to process, it can be milled and cut. Fiberboard is a good base for finishing: facade plastering or siding fastening.
Many experts consider fiberboard sheets to be the optimal solution in frame construction - the material meets all the requirements of wind insulation.
Facade plasterboard - rough cladding
Drywall for outdoor use, thanks to the hydrophobic impregnation, becomes a good protective screen against climatic influences. Facade gypsum plasterboard prevents the fibers of insulating materials from blowing out and moisture penetration into the insulating layer.
The main advantages of drywall, like rough cladding:
- leveling the surface of the walls;
- wind insulation for any wind rose - the erected barrier adjusts the air pressure, while maintaining the vapor-permeable properties of the insulation;
- protection against precipitation and condensation;
- resistance to temperature fluctuations - the material does not change shape and size;
- environmental friendliness and frost resistance.
Compared to fiberboard and isoplate, plasterboard finishing is cheaper. However, the material will not provide additional thermal insulation like its competitors.
The disadvantage of facade gypsum board is possible deformation and destruction of the structure during prolonged contact with liquid or regular exposure to high temperatures. Drywall should not be left open for a long time and used for windproofing the roof.
Diffuse membranes for special applications
The windproof diffuse membrane is actively used in both frame and capital construction. Its main purpose is to protect the insulation from moisture while maintaining the vapor permeability of the heat-insulating material.
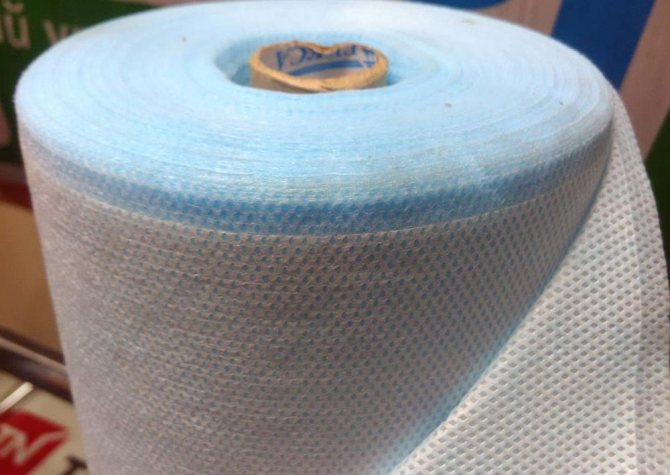


Diffuse membranes have a number of advantages:
- strength and elasticity;
- ease of installation - installation can be performed at any outdoor temperature;
- compliance with the main requirements of wind protection: vapor permeable in one direction and resistant to moisture;
- fire resistance and environmental safety;
- immunity to UV rays and different temperatures;
- durability of operation.
The membrane maintains normal ventilation of the insulation, helps to remove wet vapors from the room, providing the most comfortable microclimate.
The main competitive advantage is the opportunity temporarily do without finishing material... The diffuse sheet will protect the structural elements for several weeks. A more durable superdiffuse membrane will perfectly cope with the role of a temporary roof.
Useful: Block house and imitation of a bar in the exterior decoration of the house
Spunbond - expediency of use
Spunbond is a covering material characterized by high permeability. Geotextiles are used mainly in horticulture and horticulture, but some craftsmen have learned to use it in frame house-building.
Strengths of spunbond as wind protection:
- good breathability;
- high strength, elasticity and ease of installation;
- resistance to adverse factors: operating temperature range - from -50 ° С to +100 ° С, biological and chemical inertness.
A controversial point in the advisability of using geotextiles is water permeability. To minimize the likelihood of water penetration to the insulation, you should adhere to the nuances of installation:
- fasten the canvas vertically to protect the walls;
- do not use for insulation of roofs if the slope angle is less than 35 °;
- to equip the ventilation gap under the layer of wind protection for better "ventilation" of the spunbond and insulation.
Errors in the use of films
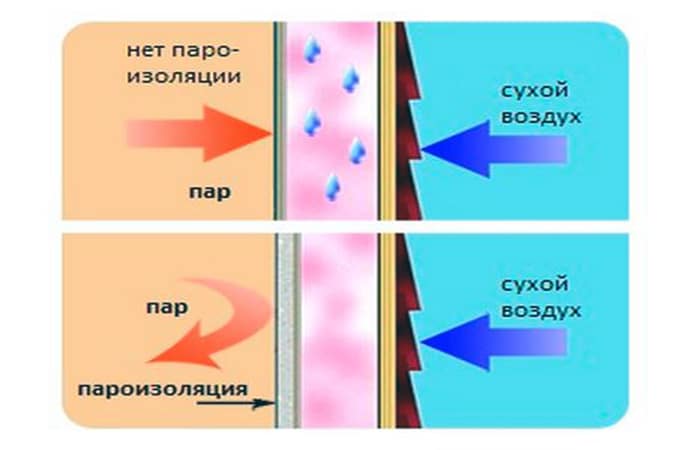
Very often inexperienced builders make mistakes when choosing and installing a windscreen for a home. A common phenomenon is the use of vapor barrier outside the house. People simply do not understand the principle of the film, and they think that the house can be wrapped in any kind of film.
When buying, carefully look at what kind of film you are offered! There are not always smart sellers, and you can easily buy a membrane designed for vapor barrier.
I myself saw such houses, a pitiful sight, but they are already sewn up with siding or even better metal profiles. When applying vapor barrier instead of wind protection, moisture is not removed from the structure of the walls, and falls into condensation.
As a result, the walls get wet, and if this is a frame house, then the damage to the insulation is one hundred percent, and if the blockhouse, then hello fungus, mold and rot.
Another mistake is the use of a profiled sheet as a facade of a house with its laying directly on the wind and moisture protection membrane, and, accordingly, on the insulation.The film simply ceases to perform its functions and condensation reappears.
Make a vertical ventilated gap between the facade and the membrane. This will allow the vapor and moisture that appears on the membrane to evaporate freely, and you will protect yourself from the problems described above.
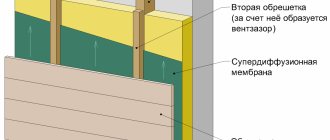
Ventilation and maintenance of the normal moisture level of the wooden frame and insulation
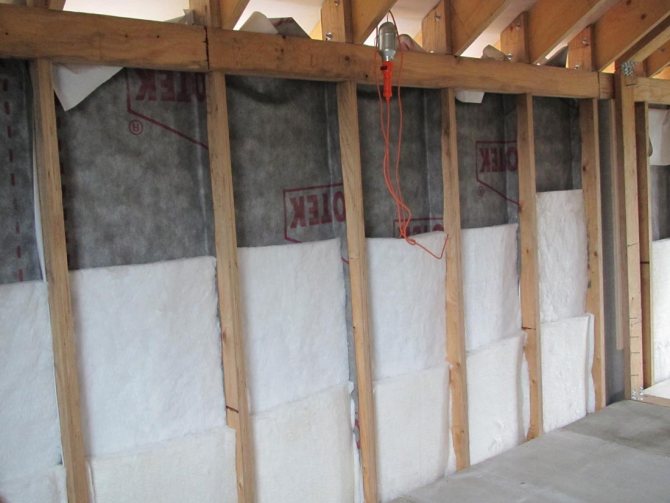
Fiber insulation and wooden frame elements need constant ventilation. This is necessary to remove excess moisture that penetrates into hygroscopic building materials from the air in the form of water vapor.
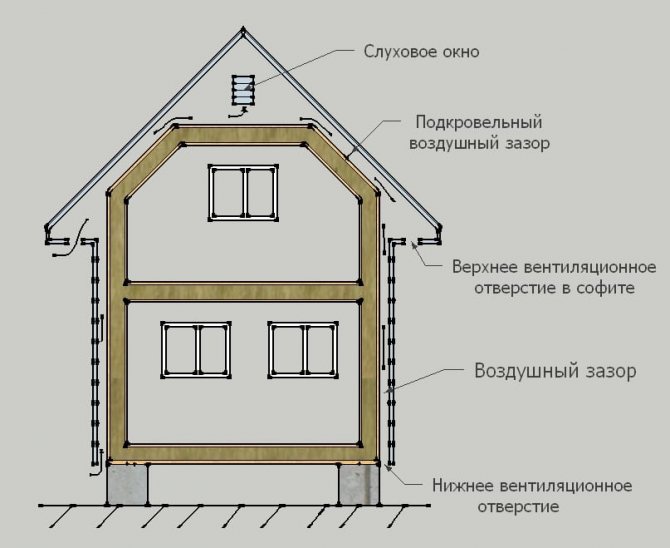

So that moisture does not accumulate in the insulation and wooden elements of the frame house, the internal structure of the walls and roof needs constant ventilation. Provide its ventilation gaps, along which a weak air flow moves from bottom to top
In the off-season, during the period of rains and fogs, the humidity of the outside air is high, water vapor penetrates into fibrous wood and insulation, settles in their structure. In significant quantities, water vapor in winter condenses in liquid form inside the enclosing structures at the “dew point”. If the tree gets wet, it will be attacked by fungi and the process of destruction will begin. Wet mineral fiber insulation loses its heat-saving properties, and thermal insulation made of organic materials (for example, ecowool) will also begin to rot.
It is extremely important to keep the wooden frame and thermal insulation dry, otherwise it will be cold in the frame house, and it will not last long. To prevent waterlogging of wood and insulation, it is necessary to ensure the constant removal of excess moisture. This is achieved by a ventilation device inside the enclosing structures. There are two possible options for the ventilation of frame walls and rafter roof:
Location of the ventilation gap under the windscreen
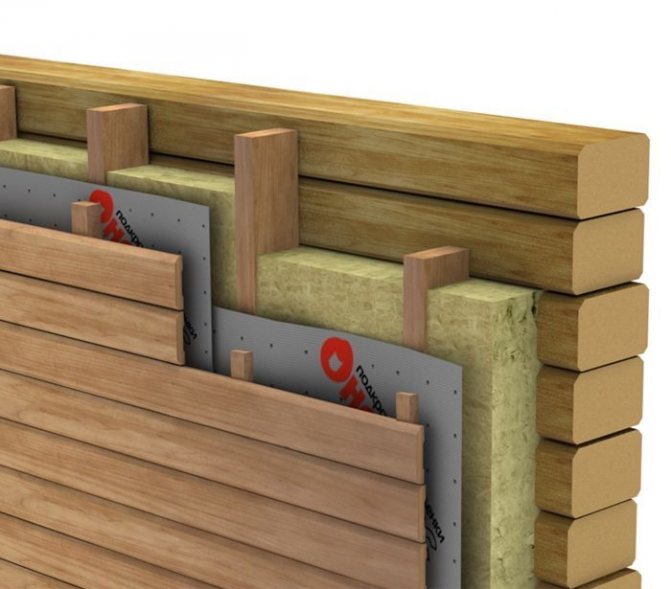
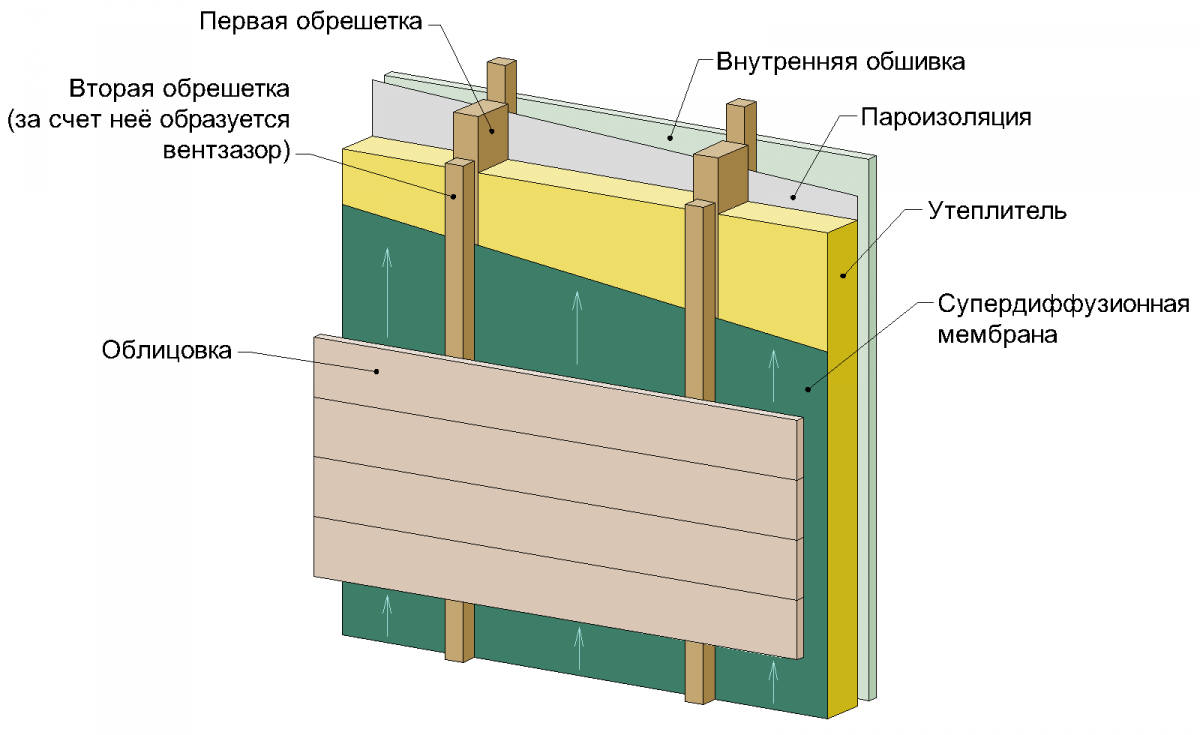
The ventilated air gap is placed between the wind insulation and the insulated frame. Under the windscreen when viewed from the outside. Air from the street enters the ventilation gap through the slots.
The advantage of this solution is good ventilation of the insulation. Another advantage: if the wall cladding is not blown through, it can also serve as wind insulation at the same time. For example, sheathing of a frame house with OSB, DSP or plywood on the outside replaces wind insulation. Oriented strand boards do not form condensation, are not blown by the wind, and ventilation of the wall structure is carried out through the ventilation gap located under the OSB. With blown-off sheathing (for example, siding) or roofing (for example, euro slate), a vapor barrier film or any other non-blown material (for example, roofing felt) can serve as wind insulation.
Disadvantage: when the ventilation layer is located under the windscreen, the insulation will be blown out to some extent in a strong wind. Another disadvantage, albeit insignificant, is the relative complexity and increased thickness of the structure. Condensation-forming coverings (roofing and wall cladding) must also be ventilated from the inside. Accordingly, a ventilation gap must also be located between the outer skin and the wind insulation. That is, there are two ventilation gaps with this solution, on both sides of the wind insulation.
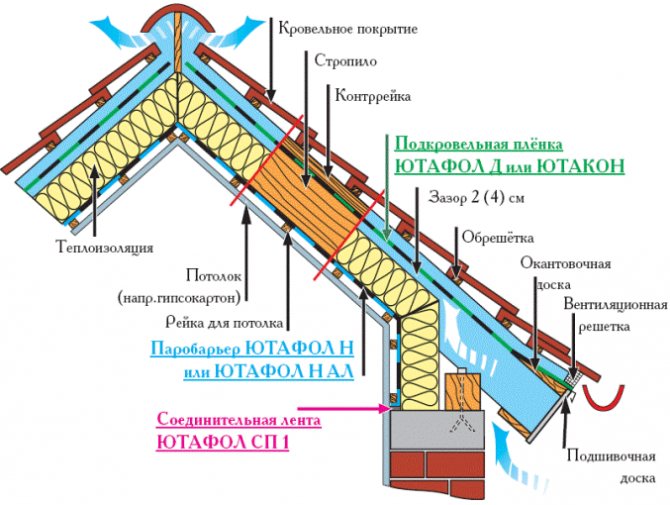

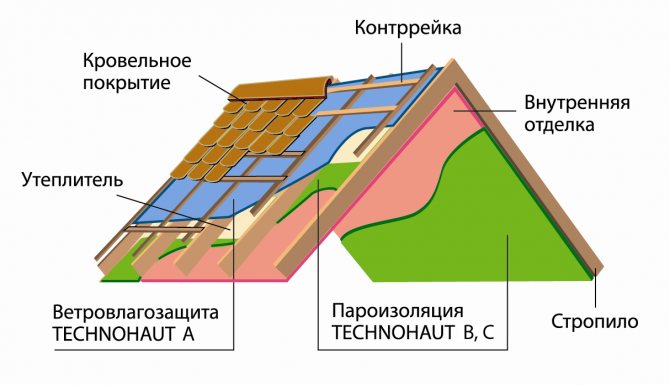
There are two ventilation gaps in the rafter roof structure. The lower one is located under the wind insulation, it is into it that air comes directly from the street and the ventilation of the insulation is carried out.
The upper ventilation gap serves only to remove condensation from the roofing
Location of the ventilation gap in front of the windscreen
The ventilation gap can be located between the outer cladding (for walls), roofing (for roofs) and wind insulation. At the same time, the gap between the wind insulation and the insulation is absent or it exists, but air from the street does not enter directly into the gap, the air flows do not carry away heat.
The release of excess moisture from the insulation and wood to the outside occurs through the windproof material. With such a solution, additional requirements are imposed on the wind insulation: while maintaining the windproof properties, it must be gas permeable and allow water vapor to pass through sufficiently. This type of wind insulation is called vapor permeable membranes or diffusion membranes.
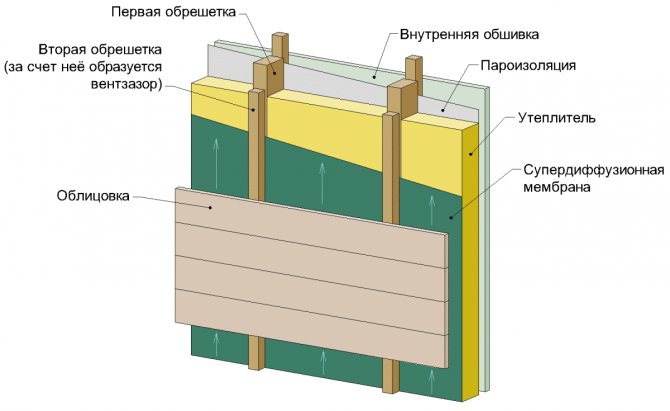

Frame wall construction with a ventilation gap located between the cladding and the windproof membrane. The insulation is completely protected from blowing, the gap is provided by a counter-rail, stuffed over the membrane
Plus the use of membranes and the location of the ventilation gap in front of the wind protection - in the complete absence of blowing and maximum safety of the structure of the frame wall and roof. In the presence of one gap, the structure of the frame is simplified and its thickness is reduced.
Cons: diffusion membranes are more expensive than conventional vapor barrier films. However, the difference in cost is relatively small.
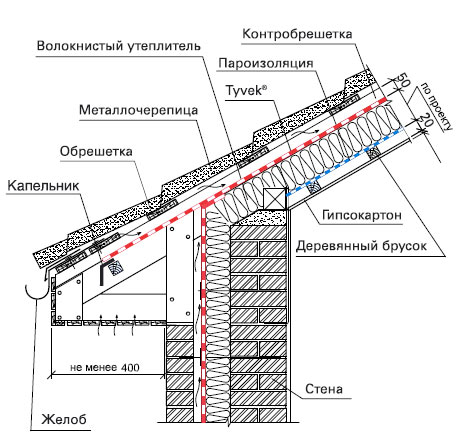

The ventilation gap in the rafter roof structure, into which openings from the street are open and through which the insulation and the wooden frame are ventilated, is located above the wind insulation. With this solution, the windproof film must be vapor-permeable and waterproof. Condensate slides down the membrane
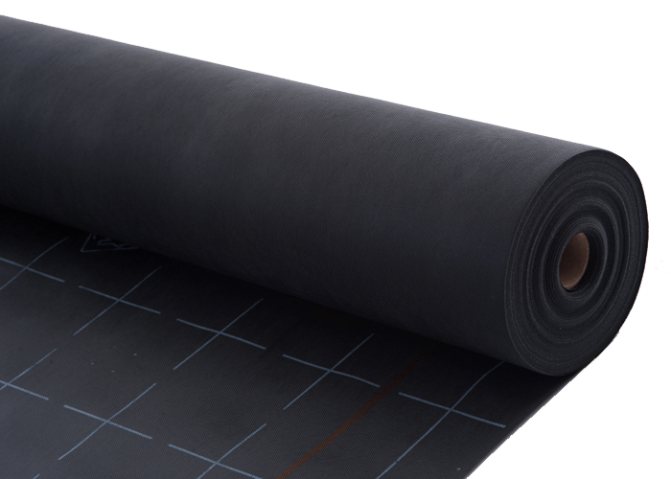
What are the membranes
There are a huge number of wind protection films on sale. They all differ both in price and quality. If you do not want to take risks on your home, then do not skimp. A quality membrane cannot be cheap.
On my own I can divide films into three types:
- Cheap membranes, outwardly very similar to a covering material, I would not use them for home. Sew up a shed, there is a garage, well, or use it as a flooring for loose insulation on horizontal surfaces.
- More expensive and high quality windproof films with different surface structures and high density. This was used for the walls of the house, brand Ondutis A120.


I bought such a membrane
This is the best thing that I had in my hands from the commercially available in our city. Certainly not Tyvek, but still a pretty dense film. (If Tyvek would have taken it) - Superdiffusion membranes. These films are used for insulated pitched roofs. They absolutely do not allow water to pass through themselves from outside to inside, and easily release steam outside. Often they are made in multi-layer, in order to obtain the corresponding properties. Well, of course, you can also use them on the walls. They are absolutely not blown by the wind.
Windscreen laying technology
Before starting the installation of the windshield, prepare:
- The required amount of film, counting the squares of the walls.
- A stapler and staples, staples still in your pocket, when you hold a four-meter-long canvas, you really don't want to run after the staples that run out.
- Scotch tape for gluing canvases. Look for the best one recommended for these purposes.
- Assistant, preferably more than one, especially on the roof.
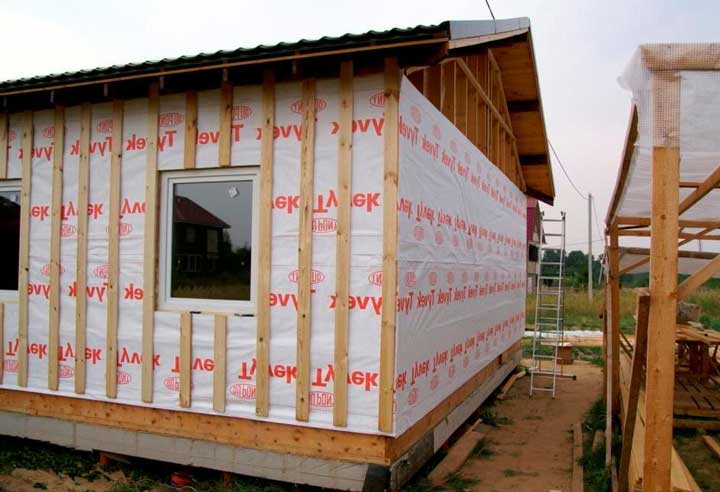
The principle of laying the film both on walls and on a pitched roof is practically the same.
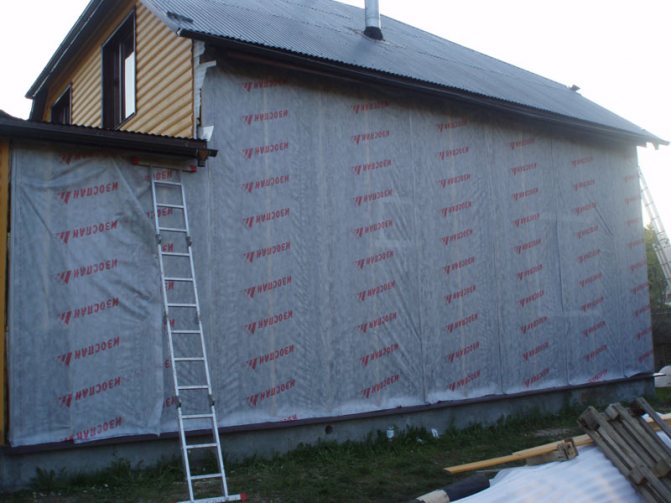
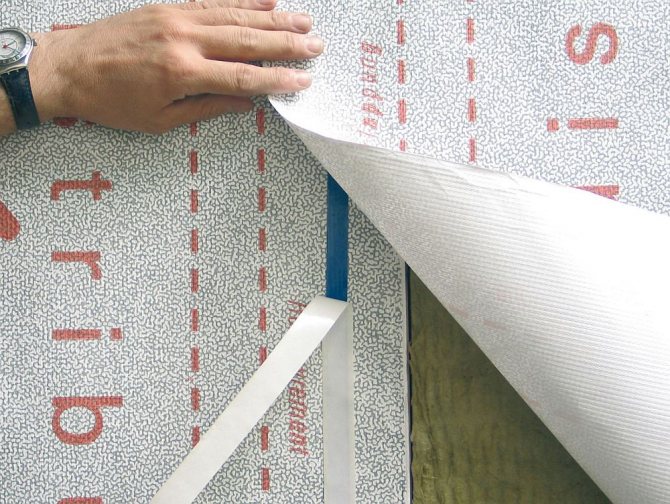
- We roll out a strip of the required length along the wall of the house, check for the correct position with the smooth side outward (in general, it should be written on the film which side is outward, so if this is not the case, then read the documentation for the membrane)
- We pull the windshield along the wall of the house without fanaticism, then punch it with a stapler to the racks or slab sheathing, depending on the structure of the building.
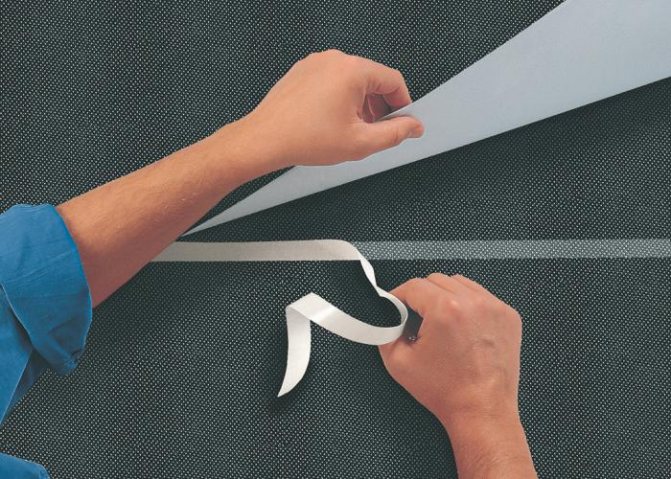
- We glue a special double-sided tape to the upper edge of the film, do not remove the paper from the tape. We will later pull it out from under the upper film
- We roll out the next row of film and also shoot it. We continue until the wall is completely filled from bottom to top.
- We pull out the paper from the tape and carefully glue the membranes together.
- We nail in vertical bars to organize the ventilation gap, with the frequency necessary for a particular type of facade. It is on these slats that we fasten the facade of the building.

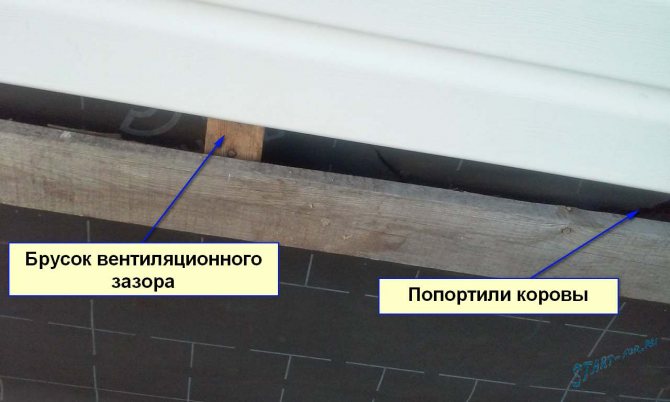
Ventilation gap bar
It is important to close the windscreen as soon as possible, over time the film loses its properties as a result of exposure to sunlight. Each film has its own timing, but I would close in the first month after installing the membrane.
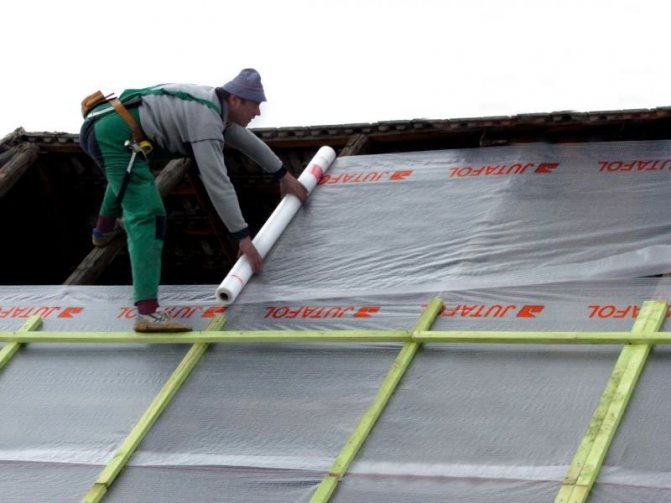
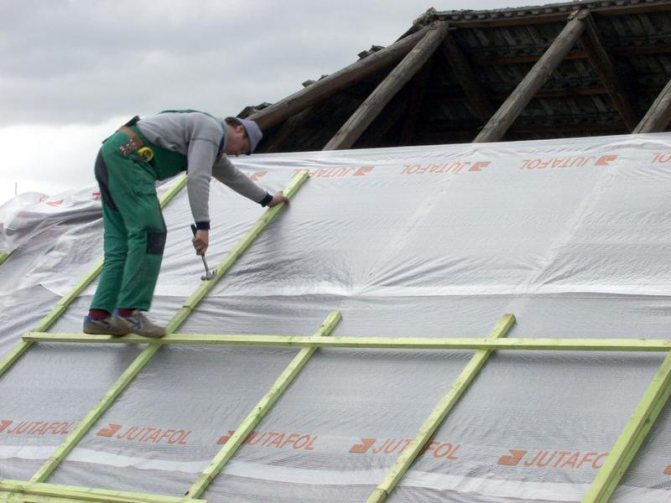
For the roof, everything is done in the same way, from bottom to top, and with gluing. Just be careful, it is very inconvenient to climb the rafters, and click the stapler. Long arms or a helicopter)))
What is a roof windscreen for?
The wind protection of the roof is used during construction works for the following purposes:
- to keep the insulation lightweight;
- for dividing into several zones - cold (outside) and warm (inside);
- thanks to the wind protection, the fiber of the heat-insulating material is under reliable protection;
- wind protection of the roof is a barrier that prevents the influence of climatic precipitation on the building material;
- wind protection helps to reduce heat losses, as a result of which you can significantly save on heating.
In addition, wind protection is actively used for the following purposes:
- as an insulating material for roofs, attics, attic floors;
- in the process of arranging the walls and facades of buildings and structures, wind protection contributes to the creation of ventilation, as a result of which the surface begins to breathe;
- as an overlap for floors on logs - in this case, you can also use a film that prevents water penetration, but at the same time perfectly passes steam;
- the waterproof film is excellent for framed partitions - it prevents particles from spraying from the mineral wool used.
As you can see, roof windscreens are widely used in all construction industries and are very popular.
How did I do
In my house, I used two types of membranes, for the walls I took an ordinary windproof film, and for the inclined parts of the attic, a super diffusion.
When insulating the attic, the use of a superdiffusion membrane is more relevant. When laying the insulation, you can not steam with a gap between the film and the insulation, but lay the mineral water tightly. This gap is required when using conventional windscreens.
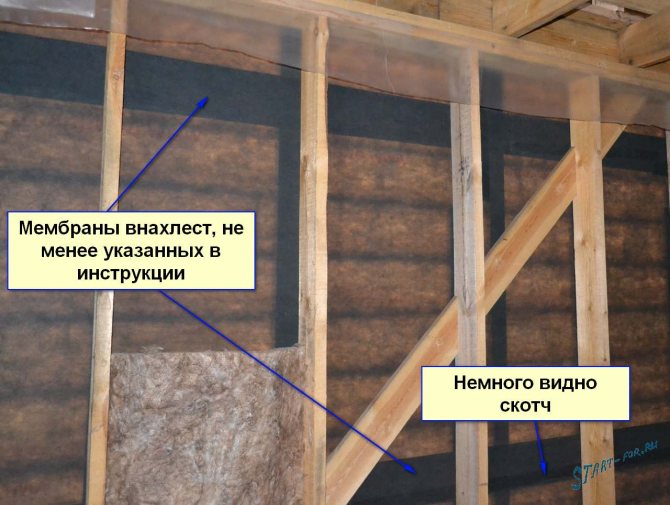


House wall
He stretched the canvas as he described, started from one corner and walked around the whole house with a roll, at the same time fastening the film to the racks. When I finished the first row, I started the second, and so on to the very top.
It was interesting to attach the membrane to the rafters, the roll is wide, the rafters are high, just as we were not perverted, but we did it! Two rows of membrane on each ramp of the superdiffusion, and one row of conventional windscreen. I put the usual one where the non-insulated part of the slope is.
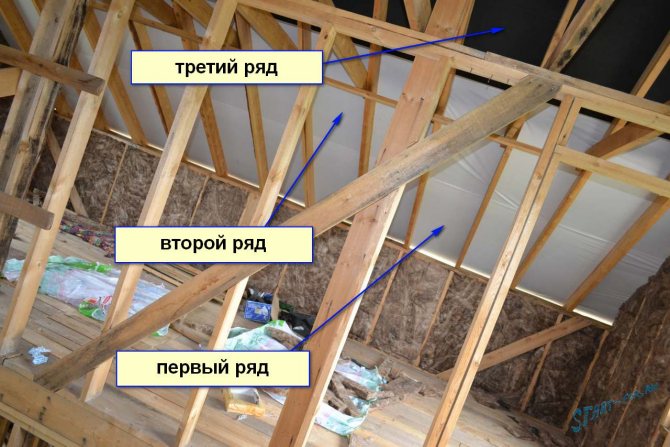


Three rows of windscreen
For gluing I took scotch tape, the same company Ondutis, I want to say right away, it dries up in the sun in a moment, and everything comes off. Where I closed it with siding did not come off, and everything sticks. In theory, the adhesive of these tapes should not dry out under any circumstances ... I glued it again after installing the siding, it seems to hold on.
Installation of roof windscreens
If it is planned to build a house with a pitched insulated roof, then the windproof membrane for the roof must be laid on the outside of the heat-insulating material. If necessary, the windscreen can be mounted directly on the insulation layer, while leaving a gap for the ventilation system. Installation work, as a rule, depends entirely on the chosen wind and moisture protection film.
Installation work is required to be carried out according to the following step-by-step algorithm:
- The first step is to roll out the roll material.In this case, the canvas used must be laid from bottom to top in the direction towards the ridge perpendicularly, or lay the film parallel to the ridge. Each subsequent layer of the used waterproofing film for the roof is recommended to be laid with an overlap of 10-15 cm.
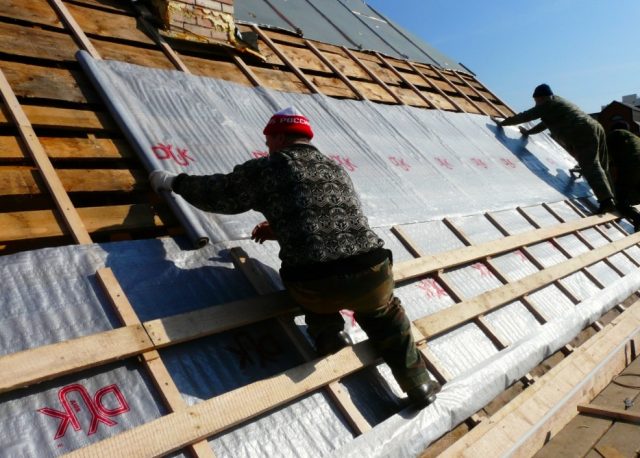


- All existing joints must be glued with a special tape, the outer rows should be fixed to the roof sheathing. After the membrane is completely mounted on the roof frame, it is necessary to mount counter battens made of wood. Fastening should be done with self-tapping screws or nails.
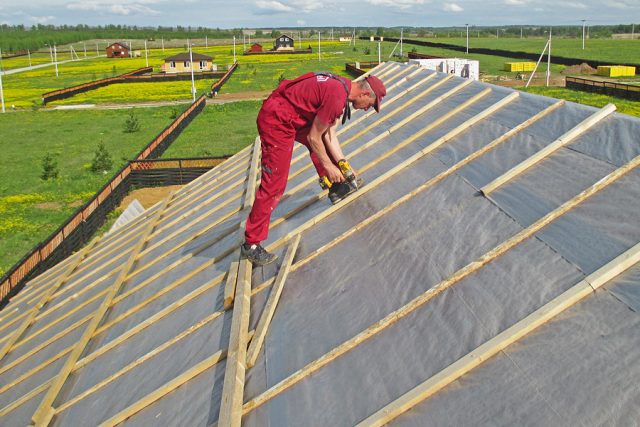


- When the counterrails are fully installed, they move on to arranging the lathing or make a continuous flooring. These works completely depend on what kind of material was used. It is not recommended to use nails and staples on top of the windshield for fastening in places where there are no joins from wooden battens.

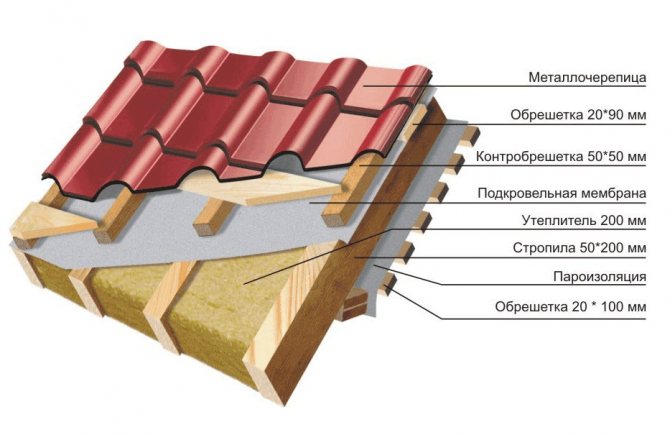
In this case, it is recommended in advance to ensure that there is a gap for the ventilation system between the windproof and roofing material.