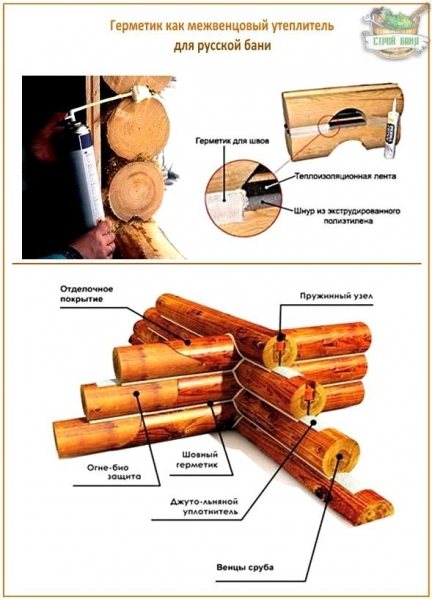
Various materials can be used to insulate a house from a bar or log. Each insulation has its own technical characteristics, its own level of thermal insulation and its supporters. Laying mezhventsovy insulation is the most important condition for warmth in a house made of timber. Various insulation materials are in demand because they have good thermal insulation properties. Mezhventsovy insulation is considered to be just the material that can keep heat in a wooden house as reliably as possible. It is presented in several versions - non-woven fabric, flax-jute, linen, ribbon tow. Jute is made from jute linen that comes to us from India and Bangladesh.
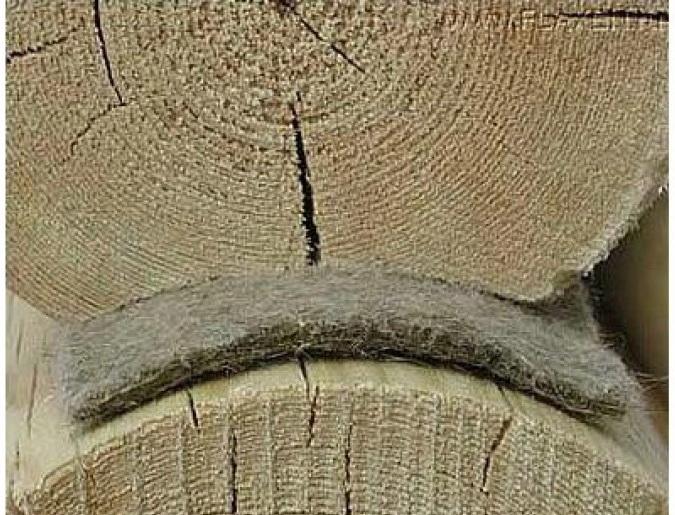

Fig 1. Mezhventsovy insulation made of flax and jute is widely used in the insulation of seams in houses from a bar
His majesty is jute
What is jute? Initially, jute is a plant of the linden family, namely spinning (bast), which grows from the subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, South America and Australia. Most of the products sold on the domestic market are made from raw materials imported from Bangladesh.


Someone will ask, but after all, we have quite a good insulation growing here - flax, why do we need to export raw materials thousands of kilometers away? Yes, it can grow. However, in the Russian climate, it is not so easy to grow and preserve flax. Therefore, the factories for the procurement of raw materials almost all closed as one. The current situation has led to a shortage of raw materials for the production of linen insulation. A foreign solution came to the rescue - jute fiber.


The plant has a structure similar to flax. Flax is used for the production of textiles, while jute is used for the manufacture of technical equipment - bags, ropes and insulation. This application is due to the greater rigidity of the jute fibers in front of flax.
Plants gain their strength due to the high content of lignin, a resin that is a natural polymer. This substance promotes the hardening of other substances that make up the fibers and greatly increases their strength. Below in the table you can see a comparison of the characteristics of the lignin content in jute and other plants.
| Material | Lignin content% |
| Jute | 20 |
| Linen | 2 |
| Hemp | 4 |
It is not difficult to determine which material will be more durable and durable. But, here is the other side of the coin. Jute fiber is stiffer, making it more difficult to lay. The pluses include the absence of problems when drilling. Jute insulation does not wrap around the drill as it does with softer materials such as linen.
How to choose the right insulation
Many builders use jute and flax-jute as insulation in the joints between the beams of a wooden house. Linovatin is also a fairly popular material for wall insulation in individual construction.
If this is your first time building a house from a bar, the question may arise: what kind of insulation is best to use? What is the difference between jute, tow and linen? Which one is better to insulate the house?


Rice 3. Linen batting is a 100% linen nonwoven fabric.
There are no simple and unambiguous answers to these questions. You can consider all the characteristics of materials and factors that affect the choice of insulation.


Fig 4. If you install the insulation correctly and carefully, it will last a very long time
Tape insulation is appreciated by builders. It is easy to mount it, just rolled it out in a row and nailed it here and there with a stapler. It is uniform across the entire width and fills the entire space between the beams.
Distinctive properties
There are no special differences between linen and jute insulation. Therefore, both the one and the other material can be used both in the work of insulating the seams of houses from a bar, and in the process of assembling a house. But there is one caveat: the most important thing in insulation materials is their density. Sometimes the density of the insulation is more important than its thickness. Dense material is of better quality than thick, but loose material.
Today, experienced builders highly value tape heaters, which, firstly, speed up the installation process, and secondly, they are very evenly distributed between the crowns and perform their function perfectly.
Is there an alternative?
Do you need it? We have already seen enough of the advantages of this material, although we have considered its disadvantages. Let's highlight the most significant ones:
- The cost is higher than that of flax;
- Rigidity - difficulty in laying;
- With low-quality raw materials, it is not environmentally friendly. For example, this will never happen with moss - no chemicals are added to it.
By the way, in order not to be distracted from the topic, in a separate article we talked in detail about mezhventsovy heaters, namely the 3 most popular, except for jute.
Comparative analysis of jute heaters
We offer you to review and compare different tape seals. For this we will choose two jute materials - "thin" and "thick".
The so-called "thick" jute insulation for timber is a relatively new material on the construction market. This material looks lush and is relatively inexpensive. But an attractive appearance does not indicate a high density of the material. Why lush insulation, if it will still be flattened under the weight of the crowns of the house?
The production technology for such inexpensive jute is chemical thermal bonding. Synthetic fibers (lavsan), which are present in this stapler, stick to each other under the influence of high temperatures.
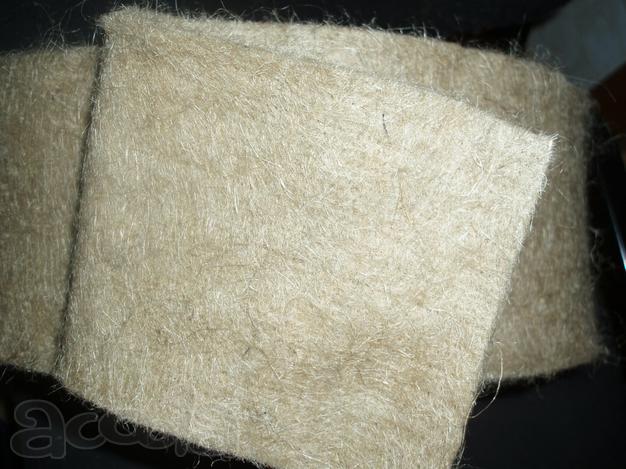


Fig 5. Dense jute
Using this method, you can achieve the following advantages:
- consumption of raw materials decreases several times, and this makes the process more economically profitable;
- production speed is much higher.
But do you need this reduction in price?
Technology for the production of "thin" jute: the fibers are attached with long jute fibers, and they attract short ones. This needle-punching technique is very difficult and expensive, but the result is a very uniform heat-insulating layer of high quality, which has the following characteristics:
- the insulation will not exfoliate;
- moisture does not accumulate in it, the material "breathes";
- no substances hazardous to health and wood are released;
- not screwed on when drilling holes for pins.
The best option
The experience of professional builders shows that the optimal solution in terms of price / quality is a combined option - it is flax-jute or jute felt with flax impurities (sometimes other components). Jute gives the structure the required rigidity, and linen gives elasticity and elasticity. The ratio can be 10/90 or 50/50.
There are standards for the use of flax jute for different types of timber:
- For example, for a 150 x 150 mm beam, the width of the jute insulation should be 152 mm with a thickness of 5-8 mm;
- For a chopped block, a wider felt with a width of 100-150 mm is used. In the case of a rare log house with a thickness of 250 mm and more, you can find ribbons of a similar width. For example, the website of one jute manufacturer states that, if necessary, you can cut ribbons up to 1600 mm wide.
Materials unsuitable for insulation
Option # 1 - mineral wool
Ordinary mineral wool also cannot serve as a heat insulator for a timber in any way - its threads have moisture absorption close to zero. All moisture in this material is held by the tension of the fibers and does not disappear anywhere. In addition, this material allows heat to pass through and even creates a dew point when firing up the sauna.And yet unscrupulous builders sometimes manage to use it.
Option # 2 - isover
As for Izover, which has recently become incredibly popular, in those places between the crowns where there is no gap, it is compressed by almost 100%, and here its heat transfer is somewhat less than that of other material under the same conditions. But in the places of gaps, Isover is a little fluffed up and quite normally copes with its functions of a heat insulator. On the other hand, the ability to accept and remove moisture from Izover is almost the same as that of many other mezhventsovy heaters, but this material does not burn, does not rot, it does not need to be caulked, and over time it does not crumble like dust. Unpleasant dusting can be eliminated with an airtight finish.
So, let's summarize. This is what Isover is preferred by many as a mezhventsovy heater:
- Does not burn, does not rot;
- Convenient to work;
- Squeezes well and leaves no gaps;
- Doesn't like birds;
- Doesn't need additional caulking.
But this fashionable material also has a significant drawback: it is not too environmentally friendly, and with a slight break it emits prickly and allergic dust. And it also quickly accumulates moisture ... And many lazy builders convince future owners of baths to use this particular insulating material - after all, it is much easier for them to work this way: it is cut easily, downright rolling on a log, construction is quick and costs less. That is why, despite advertisements from neighbors, not many people want to put Izover inside the walls of the bathhouse - especially those who saw it in the process of use: even with a dry timber, the insulation turned out to be 2/3 wet.

Also synthetic materials like them are often a dangerous source of phenol. So, let's conclude: mineral wool in a compressed state does not remove moisture at all, and Izover, if not closed with a vapor barrier, turns into a sponge altogether. The decision is yours.
Option # 3 - polyurethane foam
Used as a mezhventsovy insulation and polyurethane foam. It is appreciated for such properties:
- Fast technological installation.
- Good adhesion, due to which the timber is glued tightly. When drying, it will not twist, and the steam room will not warp.
- The foam seals the corners of the frame much better than moss or tow.
- The hardened one-component foam is not flammable and does not emit toxins, which, however, the multicomponent foam cannot boast of.
- The caulking process after the foam is quite simple.
But for all its advantages, foam as a mezhventsovy insulation does not please with such qualities:
- It is not elastic, due to which microcracks may appear over time (and wood, like any living material, can slightly change its volume).
- In winter it does not tolerate cold - it crumbles.
- Low resistance to ultraviolet best. Over time, the sun turns to stone and crumbles.
- Not environmentally friendly enough.
And, note, polyurethane foam is used as a mezhventsovy insulation today relatively little, and therefore many other negative consequences of such insulation are not yet known. But the foam itself is also used as a mezhventsovy heater in such an alternative:
- Option number 1. The timber is put in half a meter, and after the construction is completed, they are penalized. So it supposedly dries faster, and then the remaining wide gap can be foamed. Fast, airtight and no caulking required. From inside the bath, the cracks are caulked with a linen rope.
- Option number 2. Before applying the foam, let the bath sit completely on the tow. After all, the settlement of the building occurs due to the shrinkage of the timber itself - and this is at least a year and a half. After that, a 5 cm gap is punched in the tow and the groove is foamed, and, finally, they are protected with a sealant at the seams.
As for the choice of the brand of foam, so far Macroflex Pro is most suitable for this purpose. In a word, there are a lot of materials, and, as they say, how many people - so many opinions.There are also those bathhouse owners who built their steam rooms ten years ago and are quite satisfied with Izover as a sealant. They argue that the timber after the rains will be wet in place of the insulation, regardless of the type of the latter: it is moss, or a modern material. And the main advantages become a decisive factor: these are the cheapness and ease of construction of the installation. It is only important not to take the cheapest Izover (it is also called Chinese) - you can really get poisoned from it.
How much will jute cost
The price of jute flax depends mainly on the density. The density is selected according to the project and largely depends on the weight of the structure lying on the insulation.
For example, a well-known Russian jute felt is sold with a density of 250 g per m / p, thickness 2-4 mm (thin), 100 mm wide at a price of 4.5 rubles per meter, 150 mm wide at 6.5 rubles per running meter. With a thickness of 4-6 mm, prices will increase to 5.7 and 8.55 rubles, respectively.


If the width of the strip for the log house is insufficient, the material can be laid in 2 layers. Material consumption increases and the cost, of course, also increases.
Characteristics and properties of insulation
Insulation types
- Flax is a material, the composition of which is one hundred percent flax.
- Linen-jute is a material that contains flax and jute in a proportion of 15-20% / 85-80%, respectively. But this ratio can vary.
- Flax ribbon tow, like the first described type, is one hundred percent flax. This material is used as a heater for the seams between the joints, between the beams. In addition, it has proven itself well in caulking wooden structures, as well as in sealing joints between logs, in window and door openings. Typically, tape tow is 15 cm wide and 0.8-1 cm thick.


Fig 2. It looks like a tape jute tow
Neglected case
If, all the same, grinding did not help and the frame is in a deplorable state (blackening has penetrated deep into the structure of the tree), you will have to resort to using chemical compounds - bleaches. If everything is simple with an antiseptic, then you need to be more careful when choosing a bleach. Initially, it is recommended to buy several chlorine-containing compounds for a sample in a minimum volume and try to bleach several different sections of the bar. It is best to carry out the procedure in dry and clear weather.
After finding the best result, you can safely buy more bleach. The durability of bleaches lasts an average of 24 hours. During this time, the chemical composition will work, after which you can look at the results. If the desired effect is not achieved, it is necessary to repeat the procedure by reapplying the bleach over the entire area of the log house. Next, we turn to the already familiar antiseptic procedure.
Homemade bleach recipes:
- For 10 liters of ordinary water, 2 kg of lime and 500 grams of baking soda are dissolved. The composition is mixed and settled. After that, it is applied with a brush to the surface of the tree;
- 1 liter of water and 500 grams of caustic are mixed and applied to the frame;
- A solution of hydrogen peroxide in water in a ratio of 1 to 3.
All these solutions cannot be stored for a long time, as they quickly disappear.












