A car engine, like any internal combustion engine, heats up during operation, so it needs to be constantly cooled. Cooling systems are designed for this purpose. According to the principle of operation, they are of two types: liquid and air. The most widespread are the first ones, although they are more complex constructively. Air vents, with their simplicity, are much more prone to overheating.
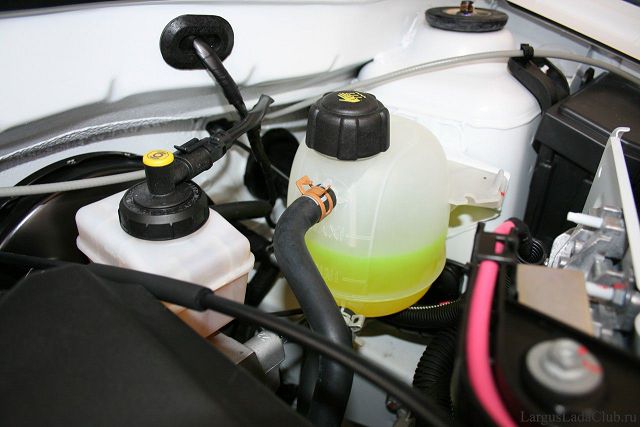

Since all engines today work with liquid cooling, in the engine compartment of any car there is a small container made of translucent plastic with a lid, designed for pouring antifreeze. This is the expansion tank of the engine cooling system. For different engines, the volume of the expansion tank ranges from 1.5 to 8 liters.
Its purpose
What is the expansion node for? The fact is that any liquid increases in volume when heated. So, the volume of water when heated to 100 ° C increases by 4.5%, antifreeze and antifreeze - up to 6%. So that when the coolant (coolant) heats up, it does not pour out of the system, an expansion tank is needed, which is a kind of buffer or compensator.
Until the middle of the last century, there were no expansion tanks under the hood, since ordinary water was used as a coolant, and the upper radiator tank played the role of a compensator, which was not topped up. With the advent of coolant based on ethylene glycol (antifreeze), the coefficient of volumetric expansion of which is greater than that of water, additional expansion tanks appear so as not to increase the radiator.
Thus, the expansion tank (RB) is designed to compensate for the volumetric expansion of the coolant when its temperature rises. The RB is located in the engine compartment so that the liquid level is approximately in the middle of the tank height.
In this case, the liquid in the radiator and the tank is located at the same level according to the principle of communicating vessels. Since the RB is located above the radiator, the expansion tank cap is used as the filler neck, which will be discussed below.

Tank filling fluids
Today's cars, built with the widespread use of new technologies, are very demanding on all process fluids, including cooling. The list of requirements is as follows:
- the liquid should boil at a temperature not lower than 110 ° С;
- freezing threshold - from minus 20 to -60 ° C, depending on environmental conditions;
- no foaming on contact with the pump impeller, minimum viscosity;
- the composition of the liquid should contain non-aggressive additives that prevent the appearance of scale on metal parts;
- the chemical composition should not change within 3 years or 60 thousand kilometers.
Related article: How to increase engine power - truly effective ways


Antifreeze is a purely domestic product, synthesized during the Soviet era
All these requirements are met by antifreeze or antifreeze, which is the same thing. The name antifreeze comes from the English word antifreeze, which means “non-freezing”. Antifreeze is a substance created on the same basis from ethylene glycol in the former USSR. The word consists of the abbreviation TOS (technology of organic synthesis) and the ending "ol", inherent in the names of chemical preparations.
The basis of antifreeze and antifreeze is the same - water + ethylene glycol in different ratios. Differences between products from different manufacturers may consist in a package of inhibiting additives, so it is undesirable to confuse fluids.Fatal consequences will not occur, but some substances can neutralize the action of others and the properties of "non-freezing" will deteriorate. In this case, the color of the liquid does not matter - it is just a dye.
Distilled water can be used to fill the tank in the following situations:
- for diluting the antifreeze concentrate to the required freezing point;
- in case of an emergency - complete or partial loss of coolant along the way;
- for the purpose of flushing.


The color of the antifreeze does not affect its properties, the additive package is important
Distilled (demineralized) water does not meet the above requirements: it freezes at zero temperature and boils at 100 ° C. Therefore, it is poured temporarily or as a solvent for antifreeze.
Tap water saturated with salts must not be poured into the expansion tank. An exception is a breakdown and loss of antifreeze on the way and the absence of a nearby auto shop. Repair the leak, fill the cooling system with tap water and get to the garage or service station, then drain it immediately. Otherwise, deposits will form on the inner walls of the water jacket of the engine and other units, impairing heat transfer.
Video: liquids for filling into the car cooling circuit
Design and operation
The expansion tank consists of a polypropylene body, a lid and two nozzles for connecting hoses of the liquid system. With the help of the lower hose, the device is connected to the cooling line, the upper one is used to remove vapors and air bubbles from the system. On modern models, float coolant level sensors are often installed.
For this option, the expansion tank is equipped at the top with another neck for installing the sensor. On the side surface of the container, there are several control marks, from the bottom - min to the top - max. In this interval, the coolant level should be located.
How does the device work? First, a little theory. The table shows the temperature modes of operation of modern motors. As you can see, the engines operate in critical temperature conditions.
| Engine temperature, ° C | Working | For a short time |
| 80 — 100 | 120 — 125 | |
| Boiling point of liquids, ° C (at atmospheric pressure) | water | 100 |
| antifreeze | 105 — 110 | |
| antifreeze | 120 |
To raise the bar of permissible temperature, designers increase the pressure in the coolant (more than atmospheric), due to which the temperature of its boiling rises. For this, the system is hermetically closed and overpressure is maintained. For different engines, this value ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 bar (kg / cm²).
At the same time, a significant vacuum (more than 0.03 - 0.1 kg / cm²) in the free space of the expander is also unacceptable, since air will be sucked into the system, which will lead to the appearance of air locks that impede the circulation of coolant and, consequently, to overheating of the engine ... Maintaining the coolant pressure at the required level is assigned to a special regulator located in the filler cap.
Tank lid - two in one
So, the RB cap, in addition to the protective function, also performs the task of a pressure regulator. As stated above, the pressure inside the tank should be up to 1.1 - 1.5 kg / cm². How is this achieved?
For this purpose, two valves are mounted in the cover: a safety valve and a vacuum valve. The first is a spring-loaded rubber diaphragm that is pressed from the outside and triggered when the pressure exceeds the force of the spring. The second consists of a rubber washer with a small spring installed inside a large one.
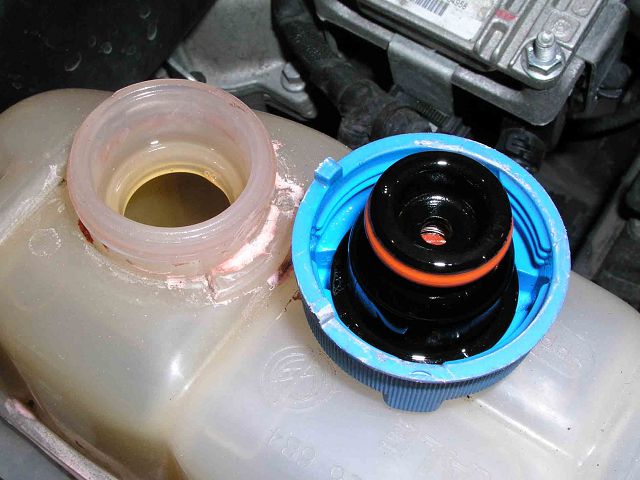


At the operating temperature of the coolant, both valves are closed, the pressure in the reservoir does not exceed the calculated one. Since the expansion tank is tightly closed, the pressure increases with increasing temperature, as a result of which the safety valve opens and bleeds off part of the air vapor, returning the valve to its previous position.
The absence of a safety mechanism would lead to coolant leaks, damage to connections and even rupture of cooling radiators and stove.
After stopping the engine, the fluid in the system cools down and decreases in volume, which leads to a vacuum inside the tank.The result can be air leaks through the connections, which on subsequent start-up will lead to the formation of air bubbles. This can lead to overheating and engine failure.
Here another small valve comes to the rescue - a vacuum one. Under the action of a vacuum, it opens and equalizes the pressure in the tank with atmospheric.
What to fill in the coolant tank
Purpose of the expansion tank
Coolants based on an aqueous solution of propylene or ethylene glycol have a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than distilled water. If the radiator is filled to capacity with such a coolant, then when the engine is started, the liquid will expand significantly under the influence of high temperatures, forming an excess. Further, it will begin to squeeze out of the radiator through the safety valve and fall into that very simple expansion tank, which serves as a reservoir for the accumulation of excess antifreeze.
When the engine is turned off and it has cooled down, the volume of coolant in the radiator will return to normal and a vacuum will develop in the cooling system.
The valve of the radiator cap will work and suck in air, thus, there is a high probability of air clots in the "cooling" jackets. This will entail more global disturbances in the heat transfer process and overheating of the power unit. That is why there was a need to install an additional container for excess liquid, which would not allow air to flow into the radiator, filling the free space with antifreeze. The expansion tank became such an element.
Today, there are such systems for the existence in which a valve, similar to the bypass valve on the radiator cap, is present on the expansion tank cap. Its purpose is to release excess steam and even overheated antifreeze. In this case, the function of a kind of upper part of the radiator is assigned to the expansion tank, which gives it every right to be considered an important element of the cooling system.
Expansion tank location
This device is located close to the radiator and is attached directly to the car body. The expansion tank protrudes half of its size above the radiator. This is necessary in order for the effect of communicating vessels to take place. They are connected to each other using a hose. On the one hand, it is attached to the bottom of the expansion tank, on the other, to the filler neck of the radiator.
Thanks to this constructive solution, the surplus of the heated coolant enters the expansion tank, and when the engine cools down, the volume of coolant in the system is compensated from the contents of the expansion tank. With this process, air cannot enter and accumulate in the radiator.
Expansion tank design
By its design, this element is extremely simple. It looks like a plastic container in which a special sensor is mounted, which reacts to changes in the normal level of the coolant. The tank is hermetically sealed with a lid with a pressure regulating valve, which is triggered when an excessive pressure in the system is higher than the nominal one.
Housing
Expansion tanks are mostly made of translucent plastic. There is a special scale on the side wall with which you can monitor the coolant level in the system. The bottom mark shows how much coolant you need to have at a minimum. The maximum coolant level when the engine is cold should not exceed three centimeters above the upper scale mark on the side of the expansion tank.
Expansion tank cap
The expansion tank cap of the power unit cooling system contains only three elements: a rubber mount, a snap ring and a top. The last element is the only block of air inlet and steam outlet valves.
When the engine starts to heat up, the coolant pressure in the cooling system, as well as in the expansion tank, accordingly, gradually begins to rise. When the pressure reaches a maximum of 120 kPa, the outlet valve opens. If the pressure drops below 83.4 kPa, it closes. If the pressure in the system rises excessively, it can damage the hoses and even the radiator itself. The expansion tank plug outlet valve prevents the pressure in the cooling system from rising to a critical level.
When the ignition is turned off and the engine cools down, the pressure in the system begins to decrease, and its vacuum occurs. When the pressure in the system drops below 3 kPa, the expansion tank inlet valve opens and air enters it. The pressure begins to gradually normalize due to the compensation of the coolant volume from the contents of the reservoir.
Possible malfunctions
Given the simple design of the expansion tank, it cannot even occur to the mind that there is something in it that can break. It's just a container with a rubber lid, but it is just that it is not a simple element. This is a pressure bypass valve, as we said earlier. It is on its correct operation that the normal functioning of the engine cooling system depends. Also the most common breakdowns can fairly be considered the leakage and rupture of the RB.
Expansion tank rupture
When the expansion tank ruptures, the coolant volume, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the engine cooling system, is significantly reduced, and this leads to its inevitable failure. If the RB has burst, it is strictly forbidden to continue driving. A burst expansion tank must be replaced immediately and refilled with the nominal coolant volume. It is strictly forbidden to add coolant, as this can damage the cylinder head. This is a significant breakdown and will seriously affect the operation of your vehicle.
Expansion tank leaking
It begins to leak due to a violation of the integrity of the body as a result of any mechanical damage, a defect in the connecting hose, or a broken or simply loose cover.
Broken expansion tank cap valves
If the expansion tank cap is worn out, corroded or the valves have disintegrated, the engine cooling system is depressurized. As a result, it is filled with excess air, which increases the pressure and disables the elements of the system. This, of course, leads to inevitable overheating of the power unit. Also, excess air provokes "clot formation" of the cooling system, as a result of which the stove stops working.
If the cover valves become clogged, then their function is also impaired. Again, excess air does not leave the system, it will depressurize, the pipes are damaged, and the engine is damaged. If the cover is slightly clogged, but the valves do not have time to draw in air and release it in a timely manner, then this has a detrimental effect on the radiator, it starts to flow. The thermostat and pump also break down.
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Pinterest, Yandex Zen, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting car events collected in one place.
RB malfunctions and causes
Lowering the coolant level:
- leakage of the plastic casing of the tank due to aging of the material, in particular, it was a chronic disease of the tanks of VAZ cars;
- the safety valve does not work, as a result of which the increased pressure squeezes the antifreeze through the joints.
- due to a reduced volume of fluid due to leaks;
- the vacuum valve does not work, as a result of which air appears in the liquid ("airing").


Visible drips of liquid:
- the expansion tank is leaking;
- safety valve malfunction.
Checking the performance of the cover
Simplified check: are the valves working?
We start the engine and, being careful, unscrew the lid: if a hissing sound of a deflated chamber is heard, the bypass valve works (however, it is not known whether it is correct or not).
After removing the cover, squeeze any hose of the cooling system with your hand. Continuing to hold it in this way, replace the cover. If it then regains its shape, most likely, the vacuum is filled. But if, even before starting the engine, the hoses look as if flattened, the vacuum valve is definitely not working.
More precisely, the safety valve can be checked with a pump and a pressure gauge. We attach the pump to the lower supply pipe of the tank, and plug the upper one with the help of improvised means: a bolt or a cylindrical drill that fits tightly into the supply hose.
We create pressure with the pump and control the moment when the safety valve is triggered (hissing sound). The pressure value recorded on the scale of the device indicates the actual response pressure.


If the relief valve is too tight, it can be repaired. Why spend extra money when it is enough to shorten the pressure spring by one or two turns, and the spring will become softer. The assembly is easy to disassemble, the main thing is not to lose small parts. And don't overdo it by biting off the loops. Do this little by little, checking the result.
Adding coolant
The liquid level in the tank is controlled by two extreme risks: min and max. How to properly add coolant to the expansion tank:
- Check the fluid level on a cold or cold engine (let it cool well).
- Open the RB cover (if the engine is not cool enough, grab the cover with a rag) and slowly turn it until the steam comes out.
- Add liquid without reaching the max.
- Close the cover and start the engine with the heating off. Warm up the engine for about 3 minutes at 2000 rpm and wait until the forced cooling fan turns on.
- Check the coolant level and top up to the max mark.
A little tip: keep an eye on the external condition of the tank and all elements of the cooling system. Fluid leaks in the engine compartment often indicate a malfunction of the expansion tank, primarily the cover.
As follows from what has been written, from such, at first glance, a secondary unit, like the expansion tank of the cooling system, it actually depends on how stable the engine of your car will work.
To understand what an expansion tank is for, you should familiarize yourself with the principle of operation and the main functions of such a tank. Without possessing this information, one might mistakenly think that the element is not of particular value and simply takes up space in the room. However, in practice, it performs a lot of important tasks and is an irreplaceable component of the heating system.
Design and principle of operation
Modern expansion tanks for cars are a reservoir made of durable thick-walled plastic with a filler neck and fittings for connecting to the elements of the cooling system. The shape of the tank is not functionally important, so manufacturers adapt it to the location of the tank.
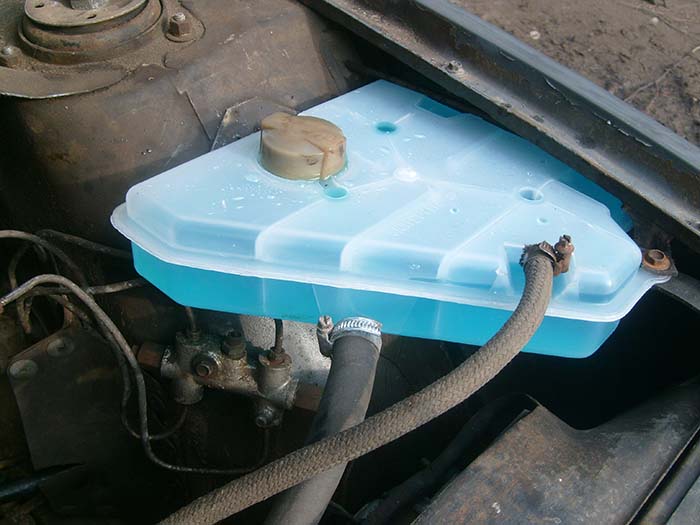


The shape of the tank depends on the place of its installation and can be different - round, rectangular or flat
The capacity of the vessel for expanding antifreeze is calculated for each car model and depends on the total volume of liquid in the pipes and units. Moreover, in a cold state, the tank is only half filled with antifreeze, the rest of the space is occupied by air that can be compressed under pressure. The tank neck is closed with a plug with a built-in air valve. The principle of operation of the tank is as follows:
- With a "cold" engine, the tank is half empty - the level of antifreeze is between the minimum and maximum marks on the body.
- After starting the engine, the antifreeze begins to expand and its level in the vessel rises, and the air gap contracts. The cover valve remains sealed.
- When the liquid reaches the operating temperature of 90-95 ° C and the maximum increase in volume, the pressure in the tank reaches the threshold for the air valve (1-1.2 bar or 120 kPa). It opens and releases air into the atmosphere.
- In the process of cooling the motor, the opposite picture is observed - the valve passes air in the opposite direction until the amount of antifreeze stops decreasing. This prevents air pockets in hoses and radiators.
Related article: What is MSC in OSAGO
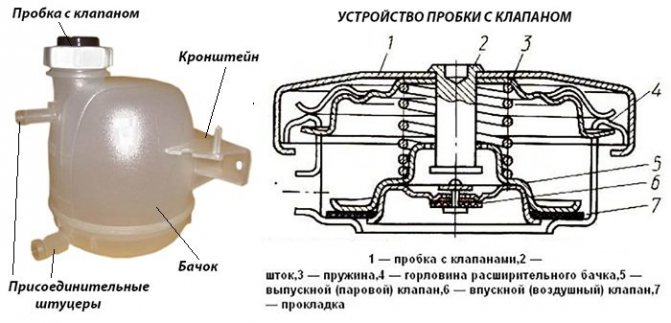

The device of the tank is quite simple - the tank body is closed with a plug with a built-in valve.
In an emergency, when antifreeze or water begins to boil for various reasons, the safety valve releases not only air, but also steam.
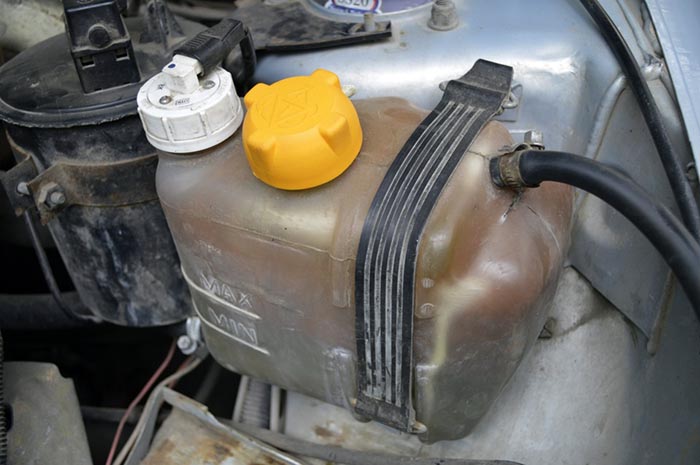


The built-in sensor signals an insufficient liquid level to the instrument panel
In some car models, for example, VAZ 2110-2115, the container is equipped with a second neck, into which the coolant level sensor is screwed. If, due to a breakdown or leakage of some unit, antifreeze begins to flow out and its level in the tank drops to a minimum, the sensor will work and warn the driver with a signal of the corresponding light on the instrument panel.
There are cars (both domestic and imported) in which the expansion tank is closed with a simple plug, not equipped with a valve and communicating with the atmosphere. In such systems, the function of pressure relief and return air intake is performed by the cap of the main radiator, and the reservoir only compensates for the expansion of the liquid.


The radiator cap is equipped with a bypass valve that directs the excess antifreeze to the expansion tank
Expansion tank in an open system


Due to the ease of installation, affordable cost and high efficiency rates, the expansion tank in an open-type heating system is very popular.
The benefits of open source options are as follows:
- Simplicity of design. In some cases, it is not necessary to purchase additional materials for arranging heating, and the working tank can be stored in the garage.
- Open systems are devoid of the problem of overpressure, since they are associated with the atmosphere. This eliminates the need to purchase a safety valve.
- Other advantages include the ability to use a tank for air extraction.
In addition to pluses, an open system also has minuses. First of all, it is the need to install the tank at the highest point. For this, it is important to take care of good insulation of the attic floor, otherwise the liquid in the tank will freeze at low temperatures.
Principle of operation
To understand why an expansion tank is needed, one should evaluate its operational characteristics, the specifics of work and the subtleties of self-installation. In liquid heating systems, water plays the role of a heat carrier.
With the help of special equipment, it travels over long distances and provides full heating of buildings with different storeys and areas. This contributes to the growing demand for the installation of water systems.

The key advantage of open systems is the ability to function without pumping devices.The movement of the coolant is carried out according to thermodynamic principles, since hot and cold water have different densities, and the pipes are inclined.
The task of the expansion tank for heating is to automatically stabilize the liquid pressure and store the remaining heated water.
The tank is mounted above the rest of the nodes, and the principle of its operation consists of the following stages:
- innings. The heated coolant moves from an electric, solid fuel or gas boiler to the radiators;
- return. The remains of warm water enter the tank, begin to cool down and return back to the boiler unit. As a result, the cycle repeats.
If the system is equipped with a one-pipe line, both procedures take place in one pipe. In two-pipe types, they are independent.
Where to locate
Since the circuit of an open heating system is closed, but not isolated from the outside air and leaks, the occurrence of an overpressure problem is excluded. In this case, the expansion tank must be installed in the correct place - above all other components. If you do not take this rule into account, the coolant will simply spill out.
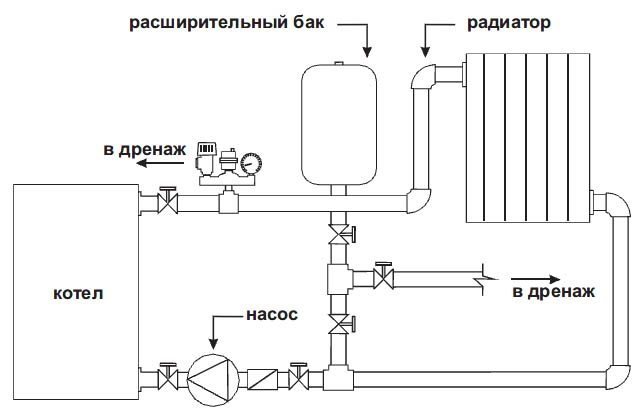

The high positioning also contributes to efficient air evacuation. Dissolved air is always present in the composition of the liquid, which can turn into a gas state and enter into a chemical reaction with metal surfaces in pipes and a heat exchanger.
In some cases, open tanks are combined with the return line, which is associated with design features or other layout considerations.
However, they remain at the highest point in the circuit to which the pipe is fed. With this installation, you will need to install special valves for the removal of gases.
How much tank volume is required
Having figured out why you need an expansion tank in an open heating system, you can move on to the next question - the choice of the volume of the tank. There are no strict restrictions or standardized rules in this regard.
The main thing is to evaluate the indicators of the coefficient of expansion of the liquid during heating, the capacity of the entire system and the optimal mode of operation in order to determine what the final volume of the liquid will be.
It is also necessary to take into account the "variable volume" compensating for the expansion. An overflow pipe is fixed at the upper border, and free space is left above the water level. Therefore, the indicator of 5% is conditional, and experienced specialists recommend adhering to the following ratio - tank volume + 10% of the system volume.
To determine the second indicator, you need to be guided by the following principles:
- If the installation of the system is completed, it is enough to take several measurements using a special device - a water meter. It will allow you to determine how much liquid will fit in an expansion tank for water supply or for heating a private house by heating radiators. The method demonstrates high accuracy, but is ineffective, since it is important to obtain a result for the installation of a water supply system, heating pipes and other units.
- Some craftsmen use a ratio of 15 liters per 1 kW of boiler plant power. The technique is unpopular due to its large margin of error.
- The volume of the heating system can be determined using simple calculations. If the project provides for the installation of a tank with contours of pipes of different diameters, a boiler and radiators, it is necessary to combine the volumes of all nodes and obtain the desired value. Initially, this method may seem rather complicated, but in practice everything is much simpler. In addition, on the network you can find special online calculators that allow you to get accurate values in a couple of minutes.
If the calculations are carried out to obtain the optimal tank volume, then the tank itself does not need to be taken into account.
Where is the expansion tank
In different models, the car tanks are located in places most convenient for the functioning of the cooling system.It is necessary to look for a tank near the radiator.
The vessel is made of durable and translucent plastic. On one part of the product, there are always scale divisions that allow you to monitor the level of antifreeze in the system. The last risk from the bottom indicates the minimum liquid level.
The maximum amount of antifreeze with a cold engine should be at a level slightly more than 30 mm above the upper line on the tank scale.
The main problems and breakdowns of the expansion tank
Most often, car owners complain about such a problem as the leakage of the expansion tank. It can be associated with a violation of the integrity of the tank (for example, after an unsuccessful parking or other collision), as well as with defects in the hose connecting the expansion tank and the radiator.
The strong pressure inside the tank is relieved by means of a special vent valve located on the tank lid. It is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the cover, clean it from scale and traces of corrosion, otherwise the valve and the entire system will quickly fail. A defective expansion tank causes a sharp drop in fluid in the engine cooling system, which has an extremely negative effect on its operation.
Heating is a key life support system for a private house and its stable operation is very important. One of the parameters that need to be monitored is pressure. If it is too low, the boiler will not work; if it is too low, the equipment will wear out too quickly. An expansion tank for heating is required to stabilize the pressure in the system. The device is simple, but without it the heating will not work for a long time.
When the heating system is operating, the coolant often changes its temperature - it heats up, then it cools down. Understandably, this changes the volume of the liquid. It increases and decreases. Excess coolant is just displaced into the expansion tank. So the purpose of this device is to compensate for changes in the volume of the coolant.
The principle of operation of the expansion tank for heating
Types and device
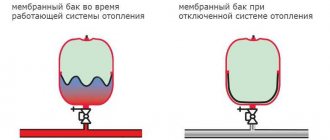
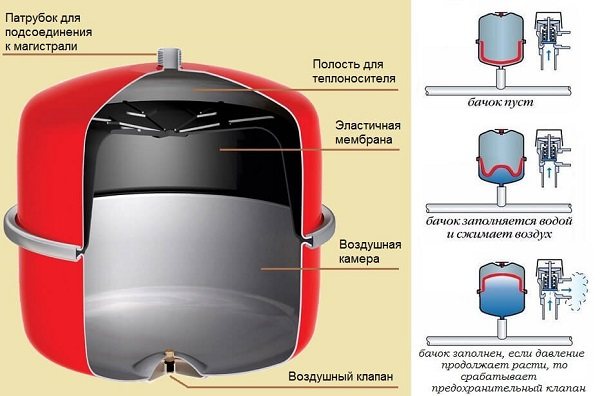
There are two hot water heating systems - open and closed. In a closed system, the circulation of the coolant is provided by a circulation pump. It does not create additional pressure, it simply pushes water at a given speed through the pipes. In such a heating system, there is an expansion tank for closed-type heating. It is called closed because it is a sealed container, which is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. In one part there is air, in the other excess coolant is displaced. Due to the presence of a membrane, the tank is also called a membrane one.
An open heating system does not provide for a circulation pump. In this case, an expansion tank for heating is just any container - even a bucket - to which the heating pipes are connected. It does not even require a cover, although it may be.
In the simplest version, this is a container welded from metal, which is installed in the attic. This option has a significant drawback. Since the tank is leaking, the coolant evaporates and it is necessary to monitor its amount - to top up all the time. You can do this manually - from a bucket. This is not very convenient - there is a risk of forgetting to replenish water supplies. This threatens the system with airing, which can lead to its breakdown.
Automated control of the water level is more convenient. True, then in the attic, in addition to heating pipes, you will also have to pull the water supply and also take out the overflow hose (pipe) somewhere in case the tank is overfilled. But there is no need to regularly check the amount of coolant.
There is a very simple method for determining the volume of the expansion tank for heating: 10% of the volume of the coolant in the system is calculated.You had to calculate it when developing the project. If these data are not available, you can determine the volume empirically - drain the coolant, and then fill in a new one, while measuring it (put it through the meter). The second way is to calculate. Determine the volume of pipes in the system, add the volume of radiators. This will be the volume of the heating system. Here we find 10% of this figure.
The shape can be different
Formula
The second way to determine the volume of the expansion tank for heating is to calculate it using the formula. Here, too, the volume of the system will be required (indicated by the letter C), but other data will also be needed:
- maximum pressure Pmax at which the system can operate (usually the maximum boiler pressure is taken);
- initial pressure Pmin - from which the system begins to work (this is the pressure in the expansion tank, indicated in the passport);
- coefficient of expansion of the heat carrier E (for water 0.04 or 0.05, for antifreeze it is indicated on the label, but usually in the range of 0.1-0.13);
Having all these values, we calculate the exact volume of the expansion tank for the heating system using the formula:
The formula for calculating the volume of the expansion tank for heating
The calculations are not very complicated, but is it worth messing around with them? If the system is open, the answer is unambiguous - no. The cost of the container does not depend on the volume very much, plus everything you can do it yourself.
Expansion tanks for closed-type heating are worth counting. Their price depends strongly on the volume. But, in this case, it is still better to take with a margin, since insufficient volume leads to rapid wear of the system or even to its failure.
If the boiler has an expansion tank, but its capacity is not enough for your system, put a second one. In total, they should give the required volume (the installation is no different).
What will the insufficient volume of the expansion tank lead to?
When heated, the coolant expands, its surplus ends up in the expansion tank for heating. If all the excess does not fit, it is vented through the emergency pressure relief valve. That is, the coolant goes down the drain.
Principle of work in a graphic image
Then, when the temperature drops, the volume of the coolant decreases. But since there is already less of it in the system than it was, the pressure in the system drops. If the lack of volume is insignificant, such a decrease may not be critical, but if it is too small, the boiler may not work. This equipment has a lower pressure limit at which it will operate. When the lower limit is reached, the equipment is blocked. If you are at home at this time, you can remedy the situation by adding a coolant. If you are not there, the system may unfreeze. By the way, working at the limit does not lead to anything good either - the equipment quickly breaks down. Therefore, it is better to play it safe a little and take a slightly larger volume.
Expansion tank for closed-type heating
The main advantage of a tank for a closed heating system is its compact size and the ability to be installed in any section of the circuit.
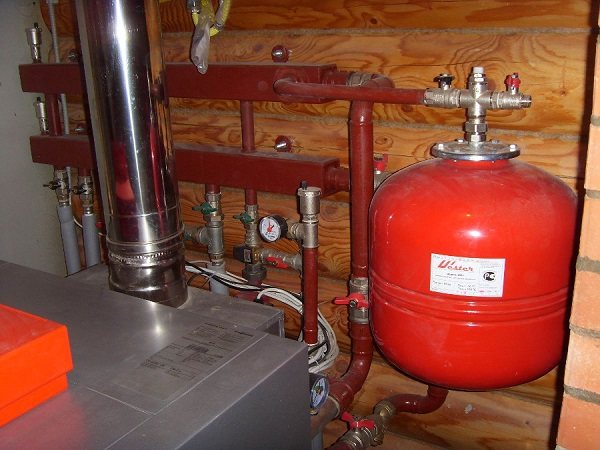


When installed in accordance with approved standards, there are no clear restrictions on the choice of the installation site. However, in many layouts, the reservoir is located near the pump.
What is an expansion tank?
Expansion tank - unit of the liquid cooling system of internal combustion engines; a specially designed tank designed to compensate for leaks and thermal expansion of the coolant circulating in the system.
Expansion tanks are also used in other systems of vehicles, tractors and special equipment: in the power steering (GUR) and in various hydraulic systems. In general, in terms of purpose and design, these tanks are similar to those of the cooling system, and their distinctive features are described below.
The expansion tank has several functions:
- Compensation of the thermal expansion of the coolant when the engine heats up - excess fluid flows from the system to the tank, preventing pressure growth;
- Compensation of coolant leaks - a certain amount of liquid is always stored in the tank, which, if necessary, enters the system (after the liquid is ejected, the atmosphere is overheated, if minor leaks occur, etc.);
- Control of the coolant level in the system (using the corresponding marks on the tank body and the built-in sensor).
The presence of a tank in the liquid cooling system is due to the characteristics and physical properties of the coolant - water or antifreeze. As the temperature rises, the liquid, in accordance with its coefficient of thermal expansion, increases in volume, which also leads to an increase in the pressure in the system. If the temperature rises excessively, the liquid (especially water) can boil - in this case, the excess pressure is released into the atmosphere through the steam valve built into the radiator plug. However, upon subsequent cooling of the engine, the liquid acquires a normal volume, and since some of it was lost during the release of steam, the pressure in the system drops - with an excessive decrease in pressure, the air valve built into the radiator plug opens, the pressure in the system is equalized to atmospheric. In this case, air enters the system, which can have a negative effect - air locks form in the radiator tubes, which impede the normal circulation of the liquid. So, after bleeding off the steam, it is necessary to replenish the water or antifreeze level.
Why do you need an expansion tank and how does it work
The urgent need for such a tank arose when, instead of water, special liquids were used for cooling, capable of retaining their physical properties even at extremely low temperatures.
The basis of these solutions is alcohol and ethylene glycol (less often propylene glycol). When heated, the alcohol expands and, under pressure, begins to look for a way out through the radiator fuse valve. In the process of cooling the internal combustion engine, the temperature of antifreeze or antifreeze decreases with the formation of a discharged void. The free areas are filled with air, which, upon subsequent activation of the motor, creates plugs that violate the free passage of liquid in the cooling system. This can lead to general overheating in the motor section.
The expansion tank, which was connected to the radiator with a hose, helped to avoid problems with overheating. The middle of the reservoir is at the level of the upper part of the radiator, so the heated liquid rises up, freely penetrating from the radiator compartment into the reservoir. The hose itself is attached to the bottom of the product, which allows excess antifreeze or antifreeze to return to the radiator when it cools down without air entrapment.
The design and features of expansion tanks
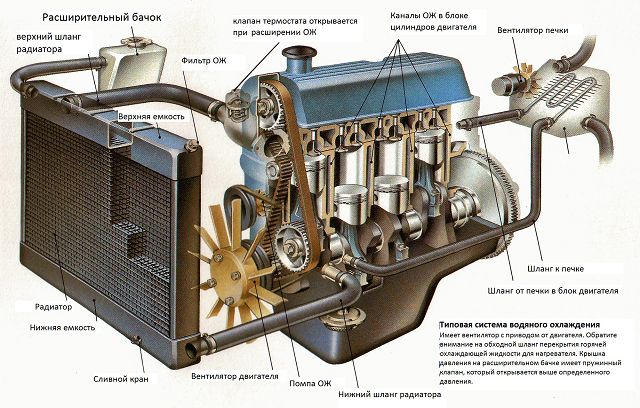
The expansion tanks used today have fundamentally the same design, which is simple. This is a container with a volume of no more than 3 - 5 liters, the shape of which is optimized for placement in the engine compartment of a car. Currently, the most common are tanks made of translucent white plastic, however, metal products are also presented on the market (as a rule, for old domestic cars VAZ, GAZ and some trucks). Several elements are made in the tank:
- Filler neck closed with steam and air valves;
- Fitting for connecting the hose from the engine cooling radiator;
- Optionally - a fitting for connecting a hose from a thermostat;
- Optionally - a fitting for connecting a hose from the interior heater radiator;
- Optional - a neck for installing a coolant level sensor.
Thus, in any tank there must be a filler neck with a plug and a fitting for connecting a hose from the main cooling radiator of the power unit. This hose is called a steam hose, because hot coolant and steam are discharged from the radiator through it. With this configuration, the choke is located at the lowest point of the tank. This is the simplest solution, however, compensation for coolant leaks is carried out through the radiator, which in some cases reduces the efficiency of the cooling system.
In many tanks, a hose is additionally used to connect to the thermostat, in this case the steam outlet hose is connected to the nipple in the upper part of the tank (on one of its side walls), and the nipple for connecting to the heater radiator has the same position. And the hose going to the thermostat is removed from the fitting at the lowest point of the tank. This design provides better filling of the cooling system with the working fluid from the reservoir; in general, the system works more efficiently and reliably.
Almost all modern expansion tanks use a liquid level sensor built into a specially designed throat. Most often, this is a signaling device of the simplest design, which notifies of a critical decrease in the coolant level, but, unlike the fuel level sensor, does not inform about the current amount of fluid in the system. The sensor is connected to a corresponding indicator on the car dashboard.
The expansion tank plug, like the main radiator plug, has built-in valves: steam (high pressure) to relieve pressure when the coolant is too hot, and air to equalize the pressure in the system when it cools. These are ordinary spring-loaded valves that are triggered when a certain pressure inside the tank is reached - when the pressure rises, the steam valve is squeezed out, when the pressure is lowered, the air valve. The valves can be located separately or combined into a single structure.
The reservoir is installed in the engine compartment not far from the radiator and is connected to it and to other components by means of rubber hoses of various cross-sections. The reservoir is slightly raised above the radiator (usually its middle line coincides with the upper level of the radiator), which ensures free flow of liquid (by gravity) from the reservoir into the radiator and / or into the thermostat housing. The reservoir and the radiator form a system of communicating vessels, therefore, the liquid level in the radiator can also be estimated from the liquid level in the reservoir. For control, a scale or separate marks with indicators "Min" and "Max" can be applied to the tank body.
Expansion tanks for power steering systems and hydraulics have a similar design, however, they are made only of metal, since they work under high pressure. Also, there are no level sensors and marks in these parts, but the plug is necessarily equipped with valves to equalize the pressure in the system in different modes. The hoses are connected with special tips, sometimes with threaded fittings.
About malfunctions and tank repair
During the operation of the machine, the following breakdowns of the expansion tank may occur;
- contamination or failure of the plug bypass valve;
- rupture of the tank body;
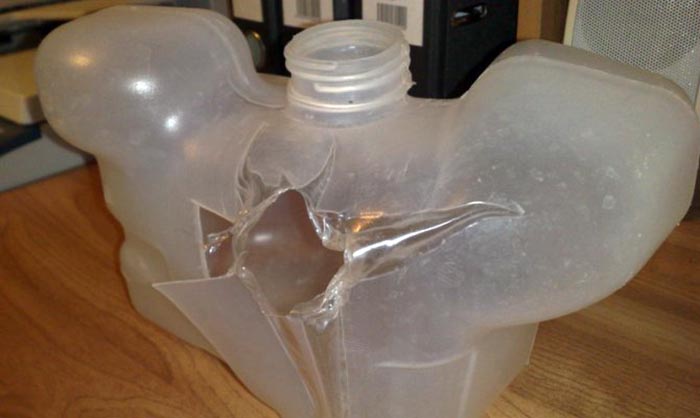


The wall of the tank bursts at too high pressure from the inside
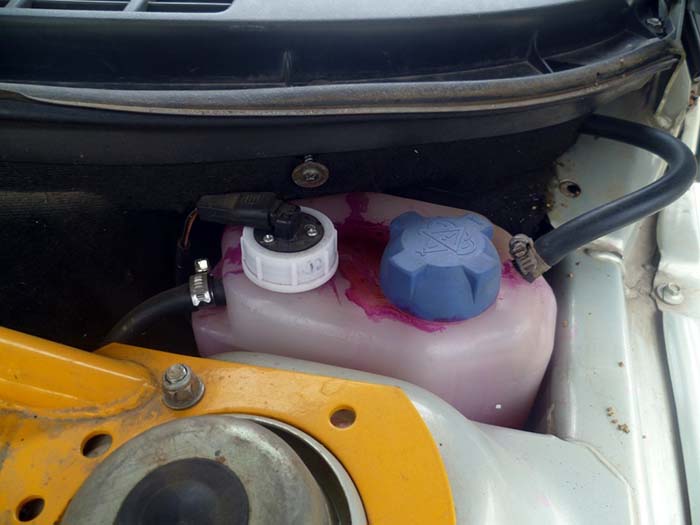


Leakage of the lid is characterized by the appearance of multi-colored streaks on the body
Most motorists, when a valve or body breaks down, simply change the part to a new one. This is justified by the lack of time for repairs and the cheapness of these spare parts. Although, if desired, the burst plastic of the tank can be sealed, and the lid can be disassembled and cleaned.
Leaks from under the cork occur with a loose fit or due to the design features of the container.For example, on VAZ 2110 cars, the jet from the upper small fitting connected to the radiator hits directly into the throat, which causes a leak. The way of elimination is the installation of a more perfect reservoir from "Priora".
Video: tank housing repair
The expansion tank of a car is considered one of the most reliable parts. Often they serve the entire life of the car, especially on foreign cars. In order not to have to change the container ahead of time, it is recommended to periodically check the condition of the valve in the lid. If it is in order, then the plastic of the vessel will not burst from high pressure.
A car engine, like any internal combustion engine, heats up during operation, so it needs to be constantly cooled. Cooling systems are designed for this purpose. According to the principle of operation, they are of two types: liquid and air. The most widespread are the first ones, although they are more complex constructively. Air vents, with their simplicity, are much more prone to overheating.
Since all engines today work with liquid cooling, in the engine compartment of any car there is a small container made of translucent plastic with a lid, designed for pouring antifreeze. This is the expansion tank of the engine cooling system. For different engines, the volume of the expansion tank ranges from 1.5 to 8 liters.