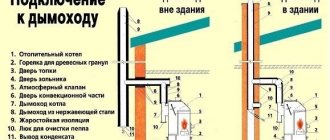
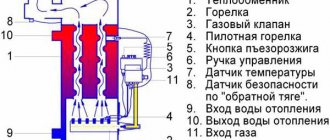
When designing and assembling a heating system in your home, safety should always be the main criterion. Whatever the type and design of the system, you should still protect yourself from any emergency situations, because in case of any breakdowns, expensive repairs will suffer, and maybe the health of the residents, which should not be allowed. The safety group for a heating boiler is a necessary and indispensable component, which has long been produced ready-assembled, standardized and thought out to the smallest detail. It is only necessary to determine the characteristics of the unit for a specific heating system and install it taking into account all the rules and requirements.

Self-assembly steps
The safety group for the heating system can be assembled by yourself. This will take a lot of time and money. If everything is done correctly, the unit will work perfectly and protect the equipment from breakdowns, as well as emergencies.
Connection rules
Before proceeding with the independent installation of the security unit, you need to study the advice of professionals in detail. They will help beginners avoid a lot of mistakes and make a truly reliable design.
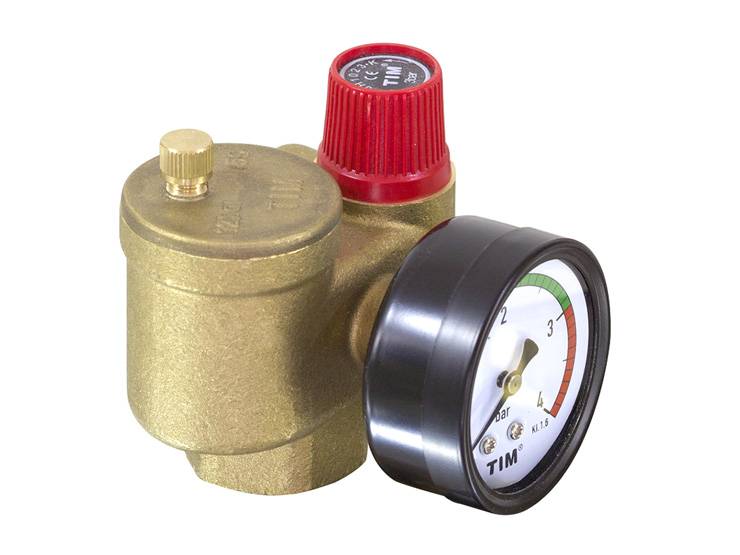


Do not forget to follow strictly the instructions when connecting a security group
General Connection Tips:
- It is best to install the protective block on the supply pipe located at the outlet of the device.
- The unit can be placed at a distance of at least 50 centimeters from the heat source.
- On the section of the pipeline where the protective device is mounted, there should be no extraneous parts (tees with a branch, taps).
- Professionals do not recommend installing a safety group on metal-plastic or polypropylene pipes, as they can deform under the influence of heated air. The best option would be to use a metal piece.
- The automatic air vent can only be fixed in an upright position.
- A flexible hose can be connected to the safety valve through which excess liquid can flow into the bottle or onto the floor.
Selection and purchase of components
Ready-made safety blocks are quite expensive, so it is best to purchase separate components. This little trick can help cut costs in half.
When choosing parts, you should adhere to the following tips:
- Don't buy the cheapest safety valves made in China. Such products will quickly fail and will not relieve pressure.
- All gauges of Asian origin give incorrect readings. This is due to the poor quality of materials and incorrect calibration.
- It is better not to use an angle type air vent, as it creates additional resistance to the escaping steam.
- The safety valve should be selected based on the operating pressure of the installed boiler. This information can be found in the technical data sheet that accompanies the device.
- It is better to choose a crosspiece from high quality brass.
Among the items must be:
- adjustable wrench;
- gas keys;
- fitting;
- crosspiece;
- adapters;
- squares with external and internal thread;
- any material for sealing joints (sanitary flax, special tapes, etc.);
- sealant.
Operating procedure
Once all the preparatory steps have been completed, you can start assembling the safety unit. This work is done in a few simple steps:
Plumbing linen is neatly wound on the thread of the squares
In this case, it is important to lay the material evenly, without gaps. For better fixing of the joint, a thin layer of sealant is applied. The elbows are attached to the crosspiece with a wrench. Then a pressure gauge, a Mayevsky valve and a safety valve are mounted. If they have different diameters, then use suitable adapters. All joints are carefully sealed with a sealant. The protective block is tested for functionality
During the check, detected leaks and other defects are eliminated.
Connection to the heating system
First of all, it is necessary to correctly determine the place of installation of the security group.
There are certain requirements that must be met:
- it should be a horizontal section of the pipeline next to the heat generator;
- on the supply line after the boiler;
- some boilers provide for the installation of a safety block directly on the unit itself; for this, there is a special connector on top of the heat generator;
- the distance from the heater to the protective block should not exceed 1.5 meters, less is possible;
- for a pipe running vertically upward from the boiler, for example, to the next floor, it is necessary to equip a branch. This is done with the help of a corner so that the safety group can be positioned in a horizontal plane and the units are looking "heads up";
- for a very powerful boiler, it may be necessary to equip another protective unit.
A very important rule to be followed is that no shut-off valves are installed between the safety group and the boiler. It would be advisable to install a protective block before the first shut-off valve located on the line.
It is worth checking the performance of the safety valve in a timely manner. This procedure is performed using the following method - after installation, open the cap in the direction indicated by the arrow on the device.
After installing the protective device, it is necessary to check the correct operation of all modules. To start operating the air vent, you will need to unscrew the top cap and release the air. The lid is now returned to its original position, but the device should remain ajar.
Connection to the heating system
Before connecting the boiler safety group, it is necessary to correctly determine the installation location. In this case, there are some rules that must be followed by all means:
- This should be the horizontal part of the pipes near the heat generator at the water outlet after the boiler.
- In certain boilers, it is possible to install a protective block on the device itself, for which a connector is provided in the upper part of the heat generator.
- The distance from the boiler to the protection unit must be at least 2 m.
- For pipes that are directed upwards from the boiler equipment, for example, to the second floor, you need to branch off. This is done with a corner so that the protective block can be positioned horizontally.
- For fairly powerful boiler equipment, an additional protection unit may be required.
Another important requirement: no locking devices are installed between the boiler and the protective block. In this case, it is more expedient to install the protective group up to the first shut-off valve, which is located on the circuit
It is necessary to make sure in time that the safety valve is working: after installation, simply open the cap in the direction indicated on the arrow of the device.
After installing the protective group, you need to make sure that all units are working correctly. Before starting the operation of the air vent, it is necessary to unscrew the top cover and bleed the air. Then the cap is returned to its original state, but the device must be ajar.
Most people believe that the protective group is an ordinary device, and its connection is optional.But negligence in this matter will not protect the boiler equipment and the heating system itself from rupture if the pressure changes strongly, which is not uncommon in a closed circuit.
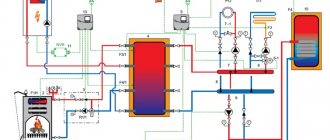
Combined heating scheme VALTEC
We would like to draw your attention to an example of a modern energy efficient heating system based on VALTEC equipment. It is designed for a country house or any other object with an autonomous heat source (boiler, etc.). The scheme provides for the combined use of traditional radiators and underfloor heating. This combination of technologies, as well as the applied automation make it possible to provide a high level of comfort at optimal costs for the purchase of equipment and its operation. The diagram uses and displays components from the current VALTEC assortment.
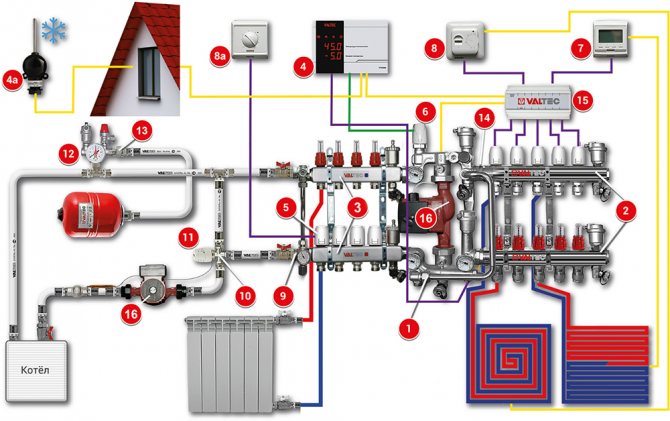

| № | vendor code | Name | Manufacturer |
| 1 | VT.COMBI.S | Pump-mixing unit | VALTEC |
| 2 | VTC.596EMNX | Collector block with flow meters | VALTEC |
| 3 | VTC.586EMNX | Collector block made of stainless steel become | VALTEC |
| 4 | VT.K200.M | Weather-compensated controller | VALTEC |
| 4a | VT.K200.M | Outside temperature sensor | VALTEC |
| 5 | VT.TE3040 | Electrothermal servo drive | VALTEC |
| 6 | VT.TE3061 | Analog servo | VALTEC |
| 7 | VT.AC709 | Electronic room chronothermostat with floor temperature sensor | VALTEC |
| 8a | VT.AC601 | Room thermostat | VALTEC |
| 8 | VT.AC602 | Room thermostat with underfloor heating sensor | VALTEC |
| 9 | VT.0667T | Bypass with by-pass valve for circulating with closed loops | VALTEC |
| 10 | VT.MR03 | Three-way mixing valve for maintaining the return temperature | VALTEC |
| 11 | VT.5012 | Thermal head with remote attachment sensor | VALTEC |
| 12 | VT.460 | Security group | VALTEC |
| 13 | VT.538 | Squeegee-cutter | VALTEC |
| 14 | VT.0606 | Double manifold nipple | VALTEC |
| 15 | VT.ZC6 | Communicator | VALTEC |
| 16 | VT.VRS | Circulation pump | VALTEC |
Explanations for the diagram:
The use of the VALTEC COMBIMIX pump-mixing unit allows to link high-temperature circuits (heat source and radiator heating) and underfloor heating circuits with a low coolant temperature into a single system.
The distribution of coolant flows is organized using VALTEC VTc 594 (radiator heating) and VTc 596 (floor heating) manifold blocks.
The distribution of the high-temperature heating system and the heating circuits are made of VALTEC metal-plastic pipes. The pipelines were installed using press fittings of the VTm 200 series; connection to manifolds - compression manifold fittings for metal-plastic pipes VT 4420.
Underfloor heating operation is controlled by a VALTEC K100 controller with a weather compensation function. Due to this, the temperature of the water in the underfloor heating circuits changes depending on the outside temperature, which guarantees savings in energy resources used for heating. The control signal from the controller is fed to the analog electrothermal servo drive of the control valve of the COMBIMIX assembly.
Thermal comfort in rooms with underfloor heating is maintained by a room thermostat VT AC 602 and a chronothermostat VT AC 709, equipped with air and floor temperature sensors. Through electrothermal drives, these automation modules control valves on the return manifold of the VTc 596 unit.
A thermostat with a remote temperature sensor VT AC 6161 is used as a safety thermostat. It stops the circulation pump of the COMBIMIX unit in case of exceeding the set maximum temperature of the heating agent in the supply to the underfloor heating circuits.
The heat transfer of the radiators is regulated by the room thermostat VT AC 601, which controls the valves of the VTc 594 manifold block using electrothermal servo drives.
The heat source circuit is equipped with a boiler safety group, a diaphragm expansion vessel, VALTEC non-return and drain valves.
Ball valves of the VALTEC BASE series were used as shut-off valves.
The main types of heating safety groups
The configuration of safety blocks, as noted above, can be very diverse.There is, for example, this option.

Or here's another option, in which all the elements are enclosed in a single body.

A few more options.


Many other options for performing a security group are on sale, but external indicators in this case do not matter, since the principle of operation is the same for all of them. To choose one or another model should, we repeat, according to the pressure indicator for which the pressure gauge and the safety valve are designed.
Now, having dealt with the main types of groups, we will get acquainted with popular manufacturers and the approximate cost of such products.
Choice
It is important to select a security group that exactly matches the characteristics of the assembled heating system. Each element of the group, pressure gauge, safety valve and air vent has its own technical and operational characteristics, which must exactly match the requirements of the heating project


Manufacturers offer ready-made solutions and assemblies of a security group based on the most common options for heating a house, for various boilers and wiring methods.
Before proceeding with the selection, you should carefully read the technical manual for your boiler. If it is a wall-mounted gas or electric boiler, then it already has a safety group, moreover, fully coordinated with its parameters, therefore it is not necessary to duplicate it. In the case of floor-standing boilers, solid fuel, stoves and fireplaces with a water circuit, there is no built-in equipment and piping in most cases. Read about how to choose a heating boiler here.
All elements of the security group are fixed on a single console. This is actually a pipe with prepared triplets for connecting equipment and two taps for connection to the heating circuit.
When choosing, you should clarify:
- Diameter for connection pipes (1 ’, ¾’, ½ ’).
- Connection option (corner, bottom, side, etc.), from which side the pipes should be brought to the safety group, and how exactly it should be oriented.
In any case, the air vent is mounted at the top of the group. So it should remain connected. Below it is a pressure gauge and a safety valve. This is done so that the air accumulating in the air chamber does not affect the readings of the pressure gauge and the operation of the explosion valve.
Safety console material: nickel, stainless steel, bronze, cast iron.
Cast iron is used only for high-pressure and efficient heating systems with a large cross-section of pipes on the wiring. These are mainly collective industrial boiler houses. For a private house, it is better to choose from nickel or stainless steel. In this case, the console and equipment can simply be covered by an external black cast iron casing for additional protection.
Pressure gauge
Two main characteristics:
- permissible measuring range (upper and lower limit);
- accuracy of measurement and indication of readings (scale and error).
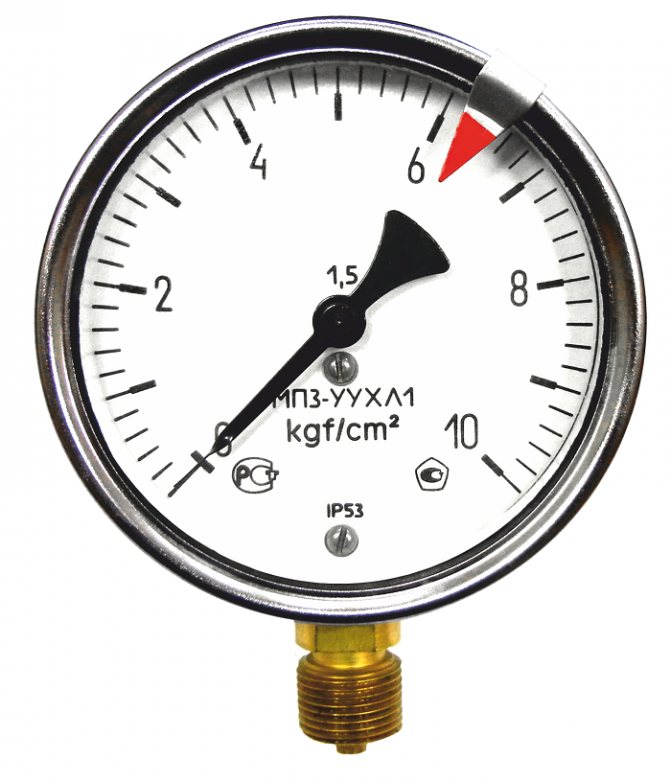


The measuring range must overlap with a margin of 0.5-1 bar the nominal pressure in the system and the permissible deviations during operation.
For example, for heating, a nominal pressure of 3 atm is taken. The permissible downward deviation will be equal to 1.5 atmospheres. A decrease below 1.5 atm will be considered a signal for an emergency. The upper limit will be 4.5-5 atm, after which the safety valve must inevitably work. Accordingly, the range of the pressure gauge should be from 1 to 5-6 atm. It is desirable that the scale be as accurate as possible and with an indication of the areas of attention. In this case, the scale is conventionally divided into 3-4 zones, marked with color markers, so that even with a cursory glance, you can react to any deviations.
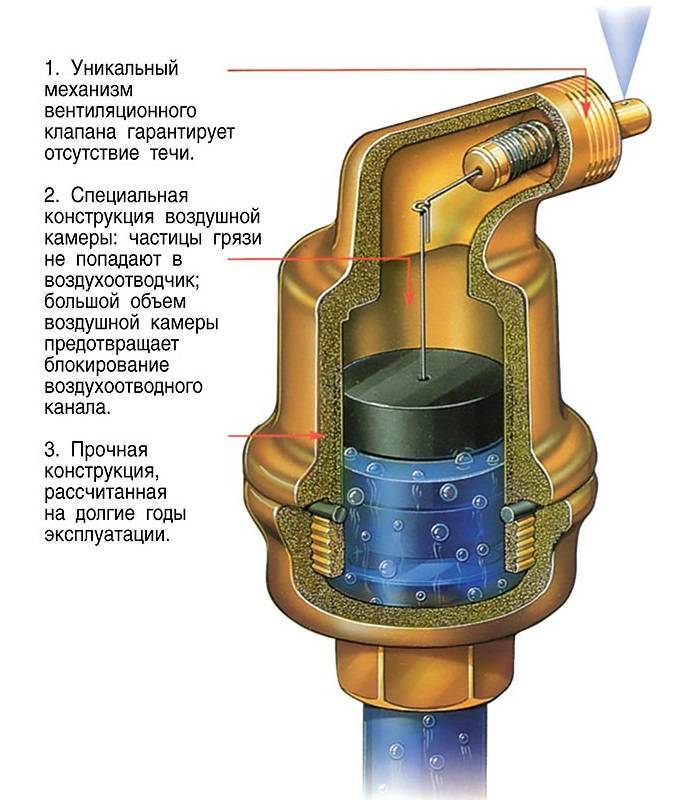
Air vent
It is characterized by the operating pressure in the system and the response parameters.Nearly all automatic valves are adjustable for optimum pressure and response conditions. If you set the control knob to the minimum position, then at the slightest accumulation of air, the valve will be triggered. At maximum setting, the valve operates less frequently, but accumulates more air. It is difficult to say which setting will be more appropriate. It is easier to leave the factory settings unchanged if the heating system is installed independently.

Safety valve
The main parameter of the valve is the response pressure. The upper limit of the pressure in the circuit, upon reaching which the valve opens and discharges part of the coolant. It is for this characteristic that you should choose a security group in the first place. The response pressure can only be adjusted within a small range.
It is useful to clarify in advance how the safety group is installed and to determine how and in which direction the valve discharges water. The discharge connection must be oriented away from the main equipment and the heating boiler. It is necessary to pick up a hose for draining into the sewer.


Popular models rating
Among the companies that produce safety valves for boiler rooms, two manufacturers are especially popular. We will consider their products:
Watts Security Team
manufactures a wide range of heating system elements, including safety groups of the KSG series for heating boilers. The line includes models on steel, cast brass or cast iron console, standard and compact. Some units are equipped with protective heat-insulating casings.
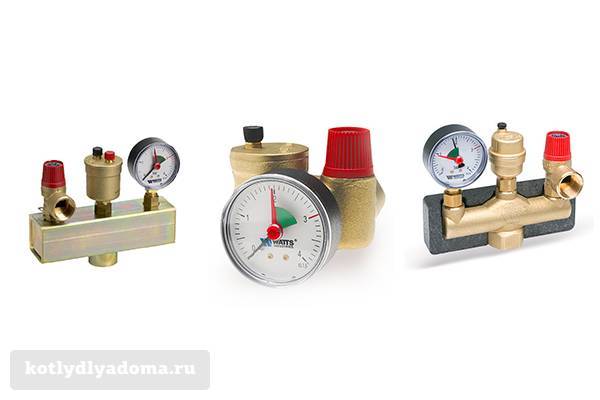


Photo 2: Safety groups "Watts" KSG series for heating boilers
All models of the Watts KSG series have a 3 bar pressure relief valve. The connection to the heating system is made through a 1 ”hole with a female thread. The model range is designed to work with hot water boilers with power from 50 to 200 kW. Prices for the Watts KSG model range from 2,000 to 6,000 rubles.
Valtec Security Team
It is also a popular manufacturer of protective fittings for heating systems among consumers. It produces safety groups for both boilers (VT 460) and expansion vessels (VT 495) mounted on a hollow console with wall mounting.
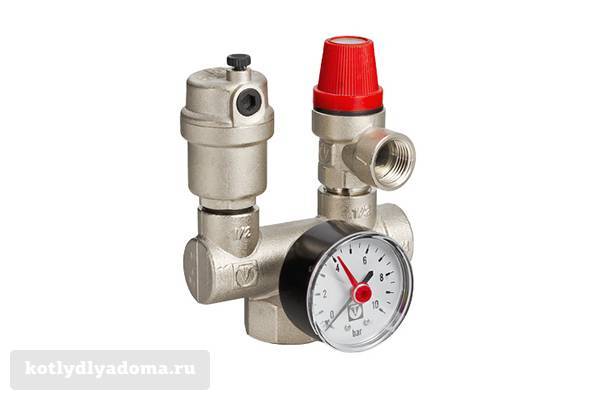


Photo 3: Safety group "Valtec" VT 460 for heating boilers
Safety group "Valtec" VT 460 is made in a compact brass body and is designed for boilers, boilers and hot water systems. The model is designed to work with household heating devices with a power of up to 44 kW and a maximum pressure of 3 bar, for example, such as the Motor Sich wood-fired heating boiler. On average, such a device can be bought for 1,700 rubles.
As you can see, the prices for safety fittings are far from low, so many people make them with their own hands. This process is not at all complicated, so it is quite possible to assemble a security group on your own at home.
valtec vt.460.0.0


Estimated cost: 1450 rubles.
Complete safety group for heating systems up to 44 kW. The safety valve and pressure gauge are designed to operate with a nominal pressure of up to 10 bar. A distinctive feature of the assembly is the presence of an additional ¾ ”expansion tank connection. The main line connection is made through a 1 ”female thread.
Conditions for boiler room equipment
- Conditions for boiler room equipment and devices for the heating system
- Approximate heating scheme
The trend towards a constant rise in the cost of conventional fuels and some conditions under which it is not possible to use traditional types of energy (natural gas, electricity), leads to the search for alternative fuels for heating systems in buildings. Installation of heating systems based on a solid fuel boiler in a private house or on industrial premises solves many problems. For example, with the high cost of delivery or the inability to carry out natural gas or profiling woodworking production, solid fuel is a priority type for heating premises.Quite often, heating systems based on a solid fuel boiler are used to heat private houses, cottages and summer cottages. This type of heating has an advantage in enterprises in hard-to-reach areas where there is no gas pipeline, as well as in industries related to the processing of wood, the waste of which can be used as fuel.


A solid fuel boiler is used for heating private houses and in enterprises where it is not possible to supply gas.
Solid fuels include wood, including firewood, wood waste and shavings, peat braces, coal and coal dust. Modern solid fuel boilers have an efficiency of about 80%, such a high level is achieved with the help of automatic control of fuel combustion in the tank. Such conditions make it possible to extend the combustion process of wood fuel up to 12 hours, and high-quality coal - up to 20 hours.
The design of solid fuel boilers is created in such a way as to maximize the heat produced. Energy efficiency is achieved with a water sleeve that absorbs heat from the system along its entire length, double boiler walls, through which air passes before entering the combustion chamber, and high-quality thermal insulation around the boiler.
Making a security group at home
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to make such a group with their own hands? It is possible, but for this you need to separately purchase each of the elements, and then connect them by means of adapters, tees, and so on. The body of the block can be welded from pieces of fittings and pipes made of polypropylene - it will cost much less than the “store” version made of brass.


At the same time, do not forget that the polypropylene safety group can be installed only in those lines where the temperature of the working fluid is low (for example, in the "warm floor" system), but in no case in the batteries! This is because if the liquid heats up to 95 degrees, it will lead to the destruction of polypropylene, and the consequences of this can be the most unpredictable.
Video - Security Group
Self assembly
During the manufacture of the safety unit, there should be no difficulties. To start the process, you need to prepare the following tools and materials:
- pressure gauge;
- relief valve;
- wrench and gas wrench;
- air vent;
- two squares;
- crosspiece;
- fitting;
- sanitary flax;
- sealant;
- adapters.
The squares are screwed into the crosspiece. For a tight connection, sanitary flax is wound on the thread, evenly distributing it over the surface. A small layer of sealant must be applied on top. Then, using a key, the squares are screwed into the crosspiece perpendicular to each other.
Then you need to install an air vent, a safety valve and a pressure gauge. If parts have different thread sizes, adapters are used. After the final assembly of all elements, the operation of the product must be tested under pressure - the unit must not leak, and all parts must be in working position.
We assemble the security unit ourselves
There should be no difficulties in the manufacture of the safety unit.
To start the process, you will need to prepare the following modules and tools:
- relief valve;
- pressure gauge;
- air vent;
- wrench;
- gas keys;
- two elbows with external and internal threaded connections;
- fitting;
- crosspiece;
- adapters;
- sealant;
- sanitary flax for sealing and sealing joints.
Initially, the elbows must be screwed into the crosspiece. For a tight fit, linen strands are screwed onto the thread in a clockwise direction, while the distribution of the seal over the surface should be the same.
A thin layer of sealant is applied on top of the threads. Next, using a wrench, the squares are screwed into the crosspiece perpendicular to one another.
Now you need to install a pressure gauge, a safety valve and an air vent. If parts have different diameters, appropriate adapters are used. After the final assembly of all modules, the operation of the mechanism must be checked under pressure - the device should not leak, and all parts should be in working order.
How to choose a safety group for a boiler
To make it more convenient to perceive, I will make recommendations for choosing in the form of a list:
- First, find out what pressure the capacity of your boiler is designed for. Otherwise, you risk making yourself a flood or explosion at home.
- Thread diameter - if you have a conventional storage water heater, then you need a group with a 1/2 inch diameter. On indirect heating boilers, it will be 3/4.
- The presence of a drain connection - many models of the groups are made with a threaded connection for connecting a sewer corrugation or come with a siphon in the kit, as shown in the figure above.
- Additional opportunities - manufacturers like to please customers with all kinds of "buns" such as shut-off valves and pressure gauges.
- Material - GBB should be made of brass. Do not consider other materials.
- The manufacturer is your business. I like European quality specimens more.
What the heating system security group consists of
The safety group for the heating system consists of a housing on which three instruments are installed: a pressure gauge, a safety valve and an automatic air vent:


Safety group for heating: from left to right - safety valve, automatic air vent, pressure gauge
Let's consider these devices separately.
Safety valve
The purpose of the safety valve is to protect the heating system from too much pressure.
The safety valve is designed for a certain pressure and when this pressure is exceeded, it works, that is, it releases the excess.
In fact, the expansion tank is responsible for compensating for excess pressure in the heating system: water expands when heated - its excess is displaced into the expansion tank, which keeps the pressure in the system constant, and the system is intact. In this case, the total amount of coolant in the entire heating system remains the same.
But it happens that the expansion tank did not work for some reason. For such a nuisance, a safety valve is installed through which excess water is discharged from the system. So that the water does not flow out to the floor, we attach the tube to the thread on the side and bring this tube into the sewer.
Conclusion: sewage in the boiler room is very desirable.
And further:
important! Antifreeze must not be disposed of down the drain!
There is a handle on top of the safety valve (red, similar to a water tap valve). With the help of this handle, we check the performance of the safety valve. The performance of the valve is checked very simply: turn the handle in the direction indicated by the arrow - water has flowed, released the handle - it has stopped flowing, which means that the valve is working properly, we can sleep peacefully. If the water continues to leak, open and close a second time, the third ... usually the flow stops.
But if the valve stubbornly does not hold water, you will have to replace it. And the faster, the better, because its performance is important.
The coolant through the safety valve may leak due to a loose fit of the valve in the seat (for the uninitiated it sounds like delirium, but it is).
They produce safety valves designed for different pressures, you need to select them based on the pressure for which our boiler is designed. For the heating system of a private house, we buy a valve for 3 atm.
Let's say there is no safety group on sale with the required valve. Then we buy the listed devices separately and assemble the security unit with our own hands.
Pressure gauge
A pressure gauge is a device for monitoring the pressure in a heating system.
Like safety valves, there are pressure gauges designed for different pressures, you need to select such that it is convenient for them to use: one glance at the device should be enough to determine its readings, without any calculations.
Conclusion: since the pressure in the heating system of a private house should be between 2 and 3 atm., Then the pressure gauge is chosen no more than 4 atm .:
There are two arrows in the manometer: red - control, black - working. Red is set manually to the desired mark (as a rule, 2 atm., For floor-standing boilers it is no longer recommended, but in general, we specify in the boiler passport). If, during heating operation, the working arrow deviates further than the red one - alarm! Something "flew"!
Automatic air vent
The entire safety group is placed on top of the boiler due to the air vent: it must be at the highest point where air bubbles rush.
Read more about this device in the article about the purpose, device and installation of an automatic air vent.
Group device
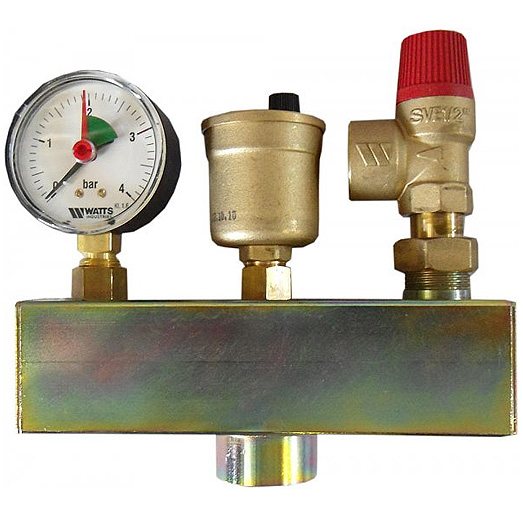


Any safety group for heating consists of three elements installed on one inlet connection (console). Looking from left to right: pressure gauge (pressure sensor); excess air removal device, emergency discharge valve (safety valve). On more expensive models, additional elements are installed - temperature meters and a mixing unit.
Below you can find out about each element in more detail.
Air vent
Typically, the heating system operates at high temperatures. Due to the heating of the liquid in the pipes, various kinds of gases are released. To prevent the formation of high pressure in the system, as well as to ensure better thermal conductivity, an air vent is used. This mechanism removes from the system any gas generated during the operation of the equipment. In addition, the liquid in the heating system can react with aluminum parts of the equipment, which in turn leads to an active chemical reaction with a significant formation of gaseous substances. Also, the automatic removal of gases and air from the system will prevent the appearance of air locks.
System safety valve
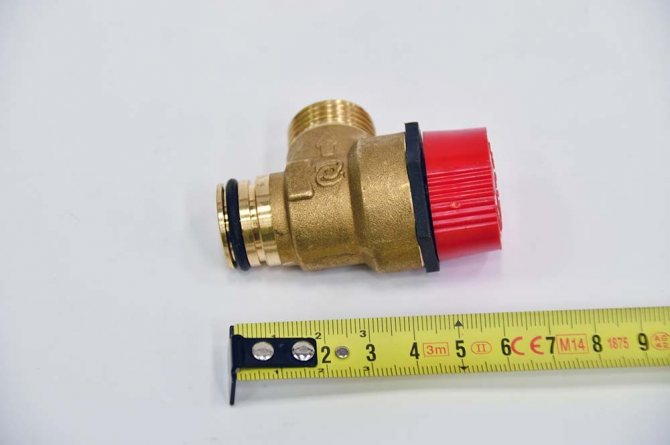


The operation of the heating system is always associated with the risk of high pressure in the system. Under significant load, the weakest element of the system fails. To prevent such a situation, a safety valve is provided in the boiler safety group. This element is set to a certain pressure, when this threshold is exceeded, it is triggered. The valve opens and an excess portion of fluid is expelled from the system, thereby normalizing the pressure. The fuse is an essential element in protecting equipment against damage caused by overpressure.
Pressure gauge
A pressure gauge is used to adjust the pressure in the heating main, as well as to visually display this parameter. In private houses, a device designed for pressures up to 3 atmospheres is mainly used. The pressure parameters of this device should be 1 unit higher than the boiler itself. The pressure gauge display consists of 2 arrows, one of them indicates the working pressure, the other (red) - critical. It is by adjusting the red arrow that the pressure limit in the heating safety group is set.
Collector
The arrangement of the group is realized on a special part, which is usually made in the form of a trident. An air duct is connected in the middle of the collector. This allows the air and system to be evacuated without obstruction. The rest of the elements of the group are located on the sides.
What is included in the heating system security group


The composition of the classic security group.
The safety group consists of three elements connected by a manifold (a technical element that breaks the flow into several parallel branches).
Automatic air vent
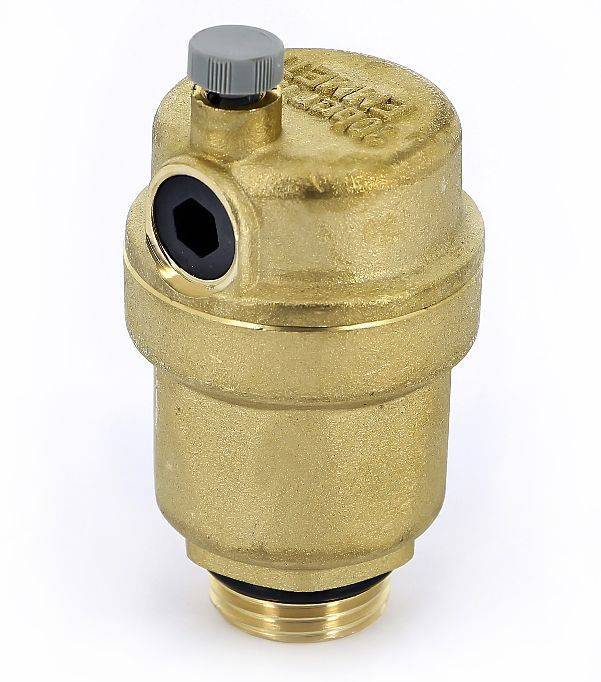


The automatic air valve is designed to discharge air masses from the heating system. An earlier alternative is Mayevsky's manual taps on radiators. The air in the pipes and radiators of the heating system slows down the heating and circulation rate of the coolant, reduces efficiency, and when heated above 90 ° C, it seriously increases the pressure, which can lead to damage and depressurization of the heating system.
Air can appear even with proper and careful use of CO. The most common reasons are:
- initial filling of the heating system with a coolant with air admission;
- the release of air bubbles when heating water used as a heat carrier above 90 ° C;
- improper use of the make-up tap;
- wear of elements and assemblies of the heating system, which violates its tightness.
The automatic air vent does not require adjustment or human intervention. As soon as air is formed in the system, it enters the duct of the air vent. The float located in this cylindrical channel is lowered, lowering the closing rod: the valve opens and bleeds all air from the channel.
Pressure gauge
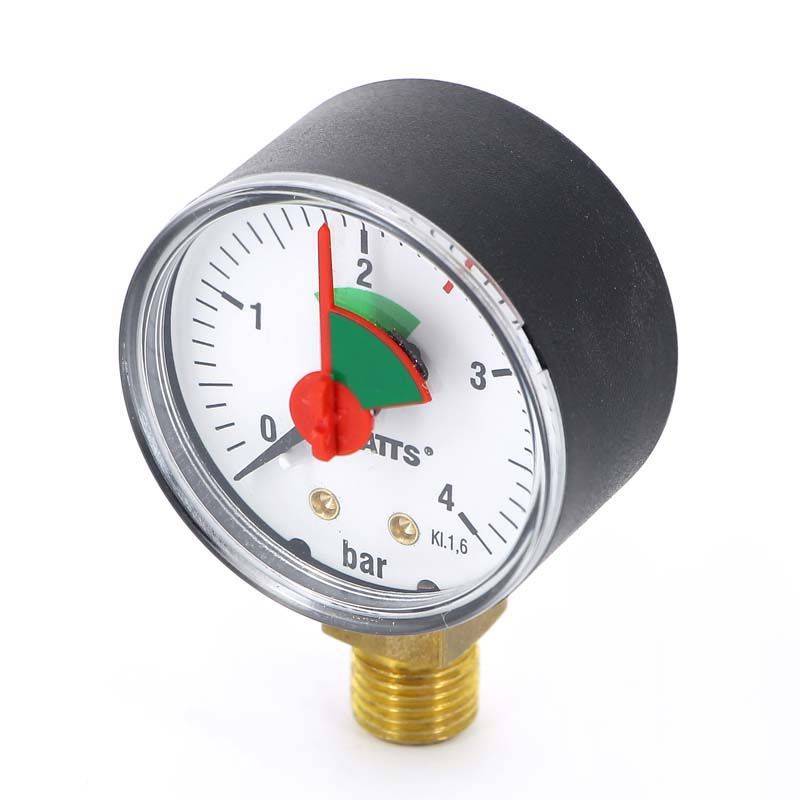


The purpose of the pressure gauge is to display the exact pressure inside the heating system to monitor indicators. Typically, bars are used as units. Having adjusted a certain level of pressure, looking at the pressure gauge, you can make sure that the system is working properly, all units are completely sealed, and other elements of the safety group perform their functions.
Safety relief valve
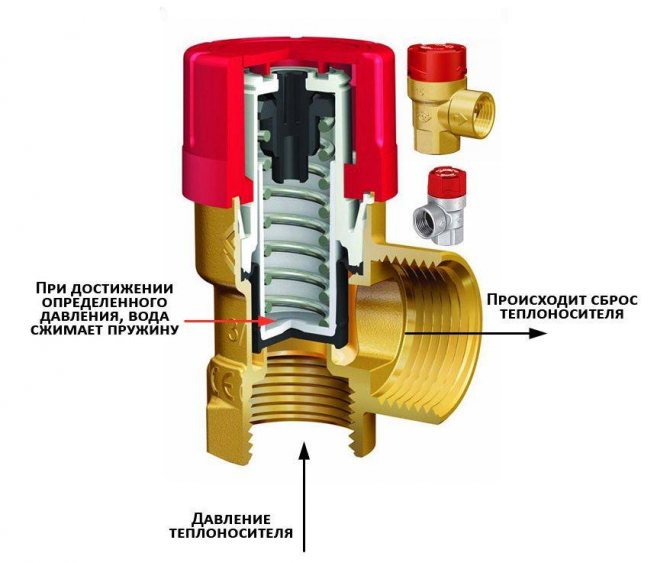

The principle of operation of a spring-loaded safety valve designed for an individual heating system.
The safety valve provides automatic release of air, steam or heat carrier when a critical point is reached, thereby freeing up space in the system for further expansion of the heat carrier. An increase in pressure in the heating system can be caused not only by the formation of air (which the air vent can handle), but also by the expansion of the coolant itself during strong heating, which can lead to damage and leakage.
If radiators and pipes usually can withstand a pressure of 7-9 bar without problems, then the most vulnerable element of the heating system is the boiler heat exchanger, often designed for 3 or even 2 bar.
It is according to the maximum allowable working pressure that the safety valve is selected: there are models designed for a specific pressure and models with an adjustable value, which is set during installation and adjustment. The most common and best in terms of price-quality ratio is the spring mechanism, and it is this mechanism that is used in almost all variants of security groups.
The principle of operation of a spring-loaded safety valve is to balance the pressure inside the system and the downforce of the valve spring:
- from the inside, the coolant exerts pressure on the valve gate;
- on the other hand, the spool is pressed by the stem, on which the spring presses, thereby holding the valve in the closed position;
- as soon as the pressure in the system exceeds the critical value, it outweighs the downforce of the spring and the valve opens slightly, bleeding off excess air, steam or coolant;
- as soon as the pressure drops below the critical level, the spring force is sufficient to move the valve to its original closed position.
Assigning a security group
In closed heating systems, protection performs the following tasks:
- Discharge of excess air from the heating system.Airing of the system occurs for the following reasons: filling of the system; use of defective or worn out seals; corrosion inside pipes; improper installation of equipment and valves. Heating of water is also important, since the oxygen in it begins to expand, which entails an increase in pressure.
- Protection against a critical increase in pressure in the system. A critical increase in pressure in the system can occur for the following reasons: excess of the rate of the volume of the coolant due to an automatic failure; a sharp rise in temperature in the system. A safety relief valve is used to prevent explosion.
- Control and regulation of pressure using a measuring device. A safety pressure gauge is used for these needs. The main requirement for a pressure gauge is measurement accuracy. Therefore, timely verification is a prerequisite for the operation of the heating system.
The installation of the boiler safety group will assist in these tasks.
Structural elements
The heating safety group diagram provides for the use of all structural elements. Otherwise, the unit will not function properly, which can lead to various breakdowns and accidents.
Accurate pressure gauge
This device is designed to measure pressure (in atmospheres or bar) and give immediate results. For this, a scale is graduated on the manometer and there are two arrows. One of them shows the pressure in the heating system, and the second shows the limit value, which is set during adjustment.
- For pipelines of heating systems installed in apartment buildings - 1.5 bar.
- In country one-story buildings - from 2 to 3 bars.
Mayevsky crane
An automatic air vent must be installed in the heating security system of a private house and city apartment. This is best done at the highest possible height. This feature is due to the fact that the air is lighter than the coolant. It moves upward and accumulates there, preventing the equipment from working properly.
Read the same: how to properly release air from the heating battery.
Air can appear due to the following factors:
- Poor quality rubber seals or premature wear.
- The first start-up of the installation and filling the pipes with a coolant.
- Corrosion formation inside the instrument lines.
- Incorrect installation or failure to comply with the tightness conditions.
- Water make-up.


Such a faucet protects your heating system from the ingress of various dirt
The Mayevsky crane is designed in such a way that the smallest particles of dirt cannot get into the air chamber. The air vent is assembled from the following parts:
- case with a lid;
- jet;
- float;
- spool;
- holder;
- body and valve o-rings;
- bung;
- spring.