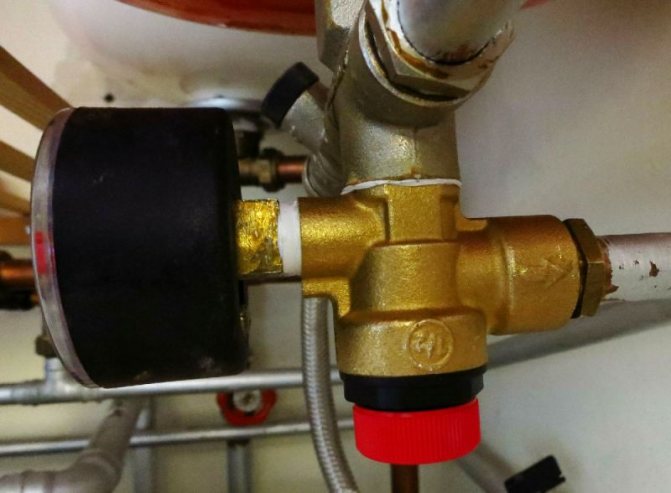
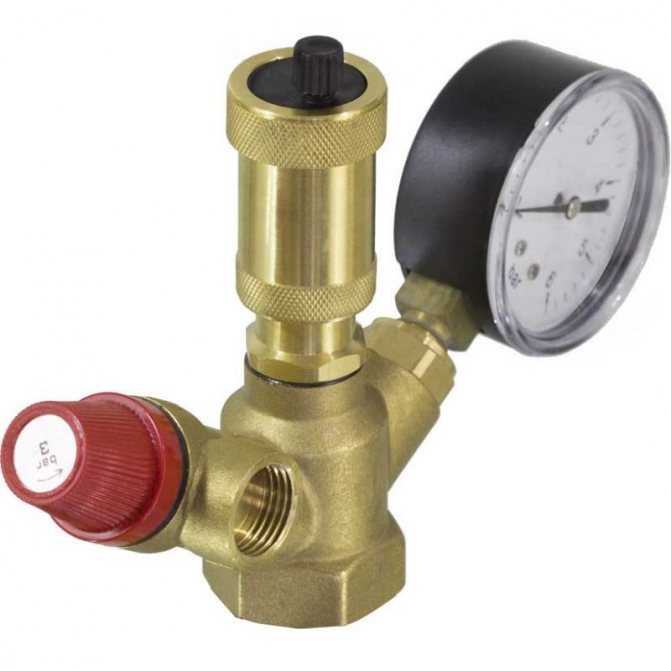
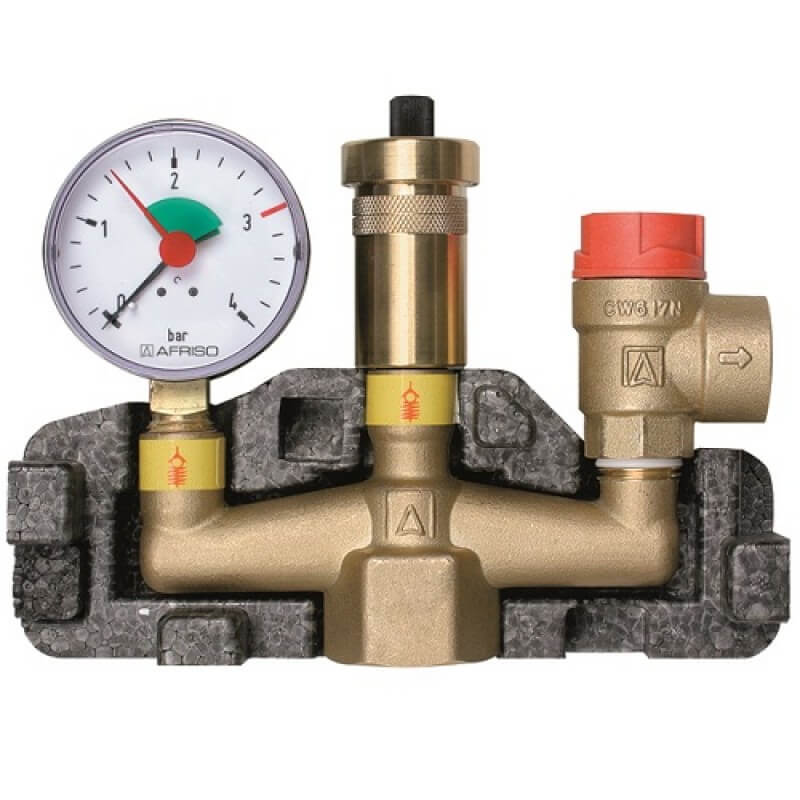
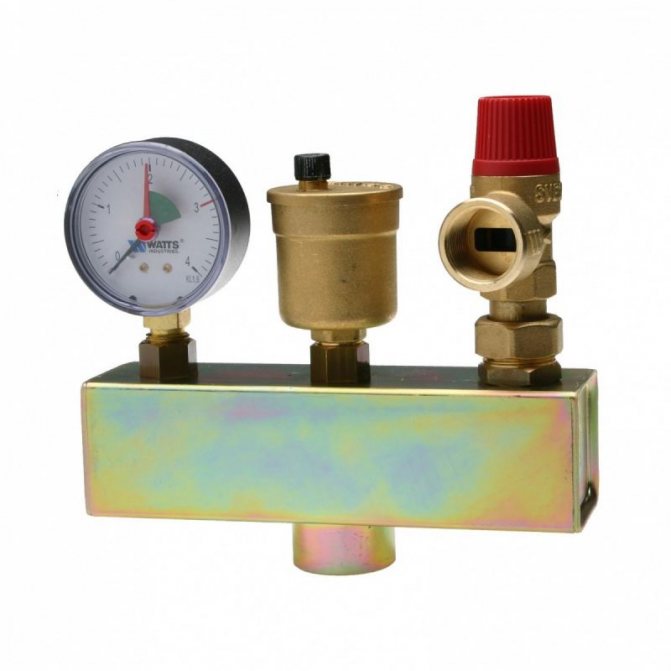
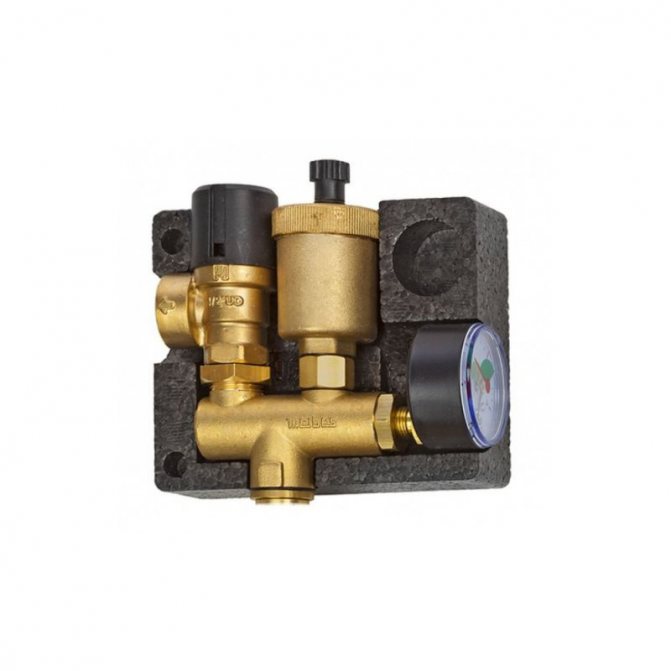
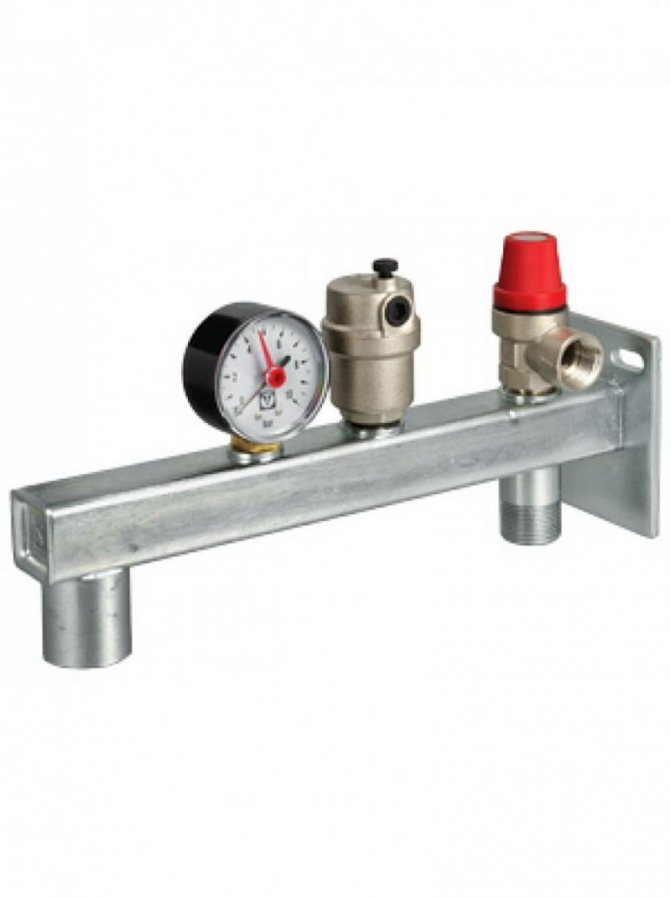
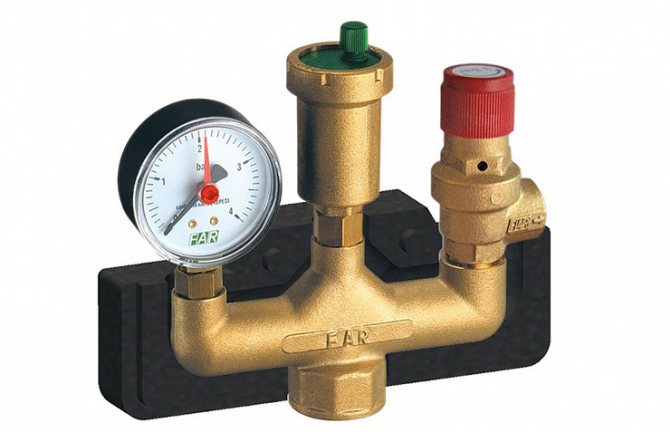
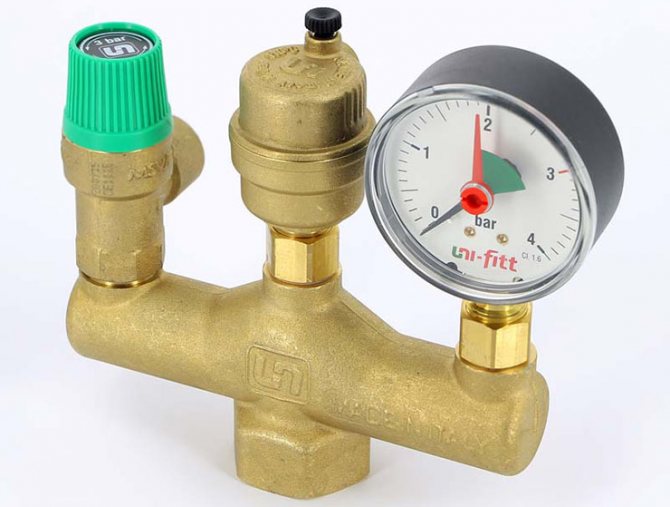
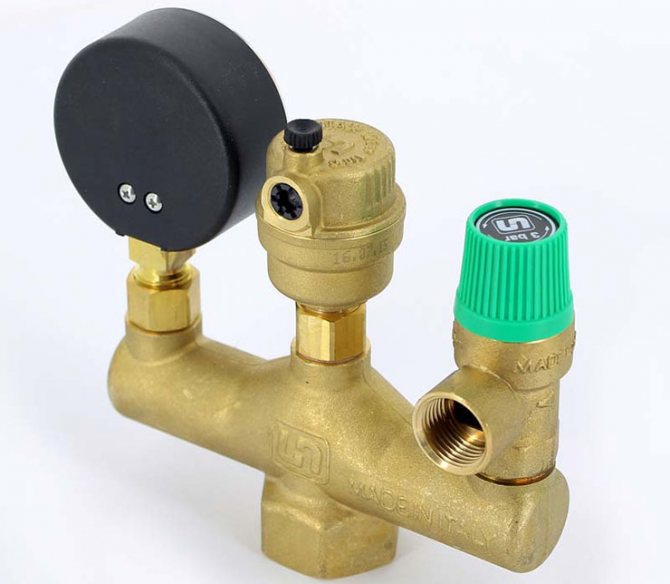
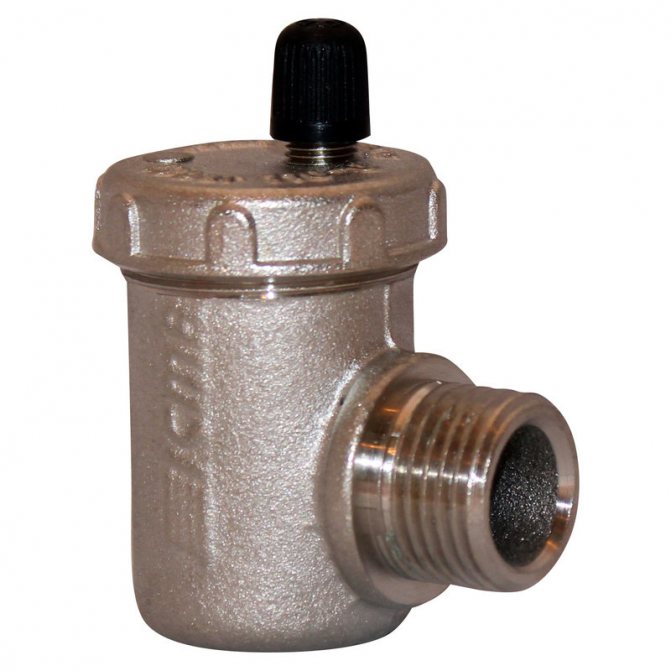
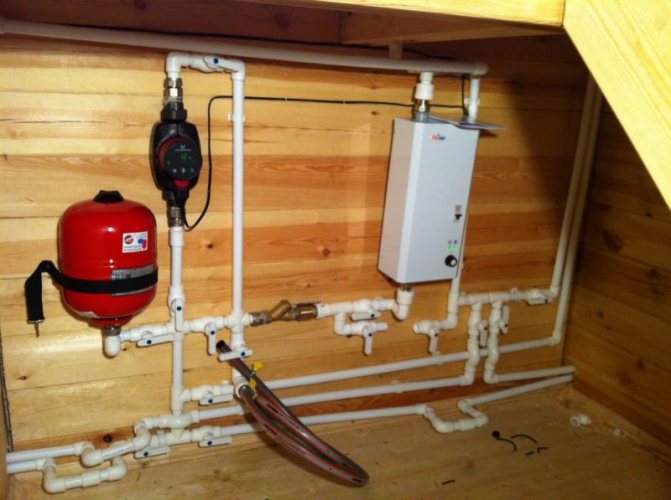
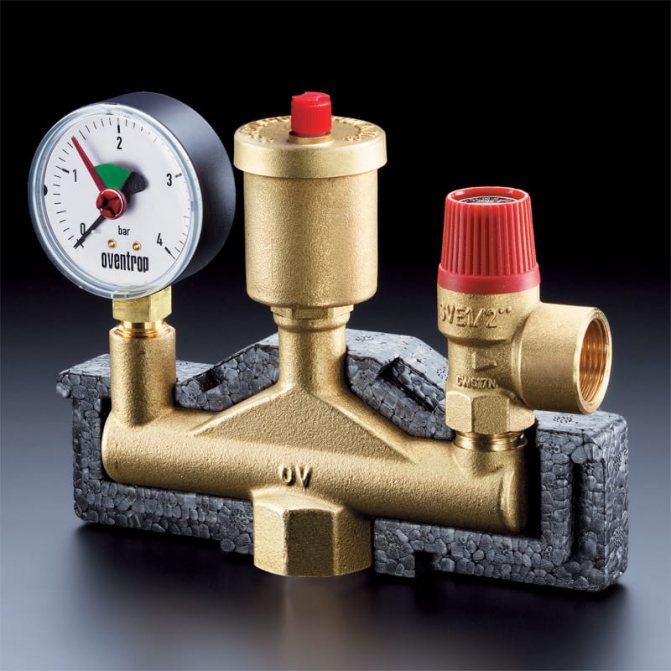
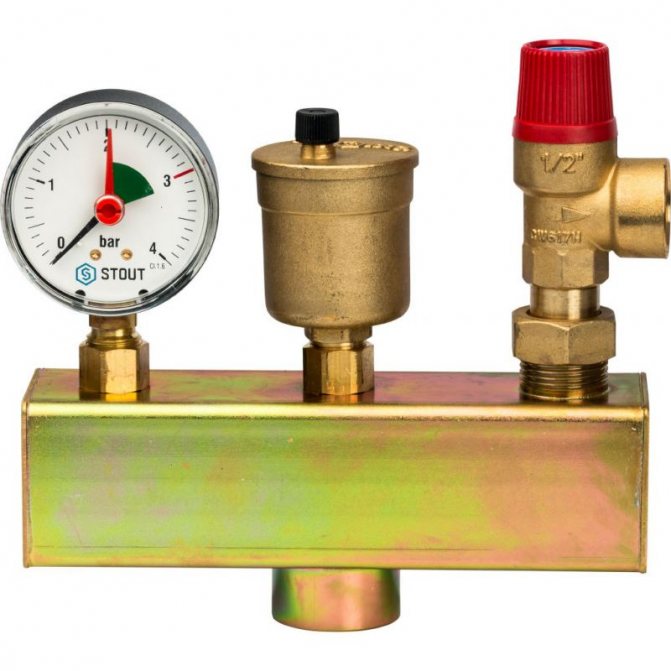
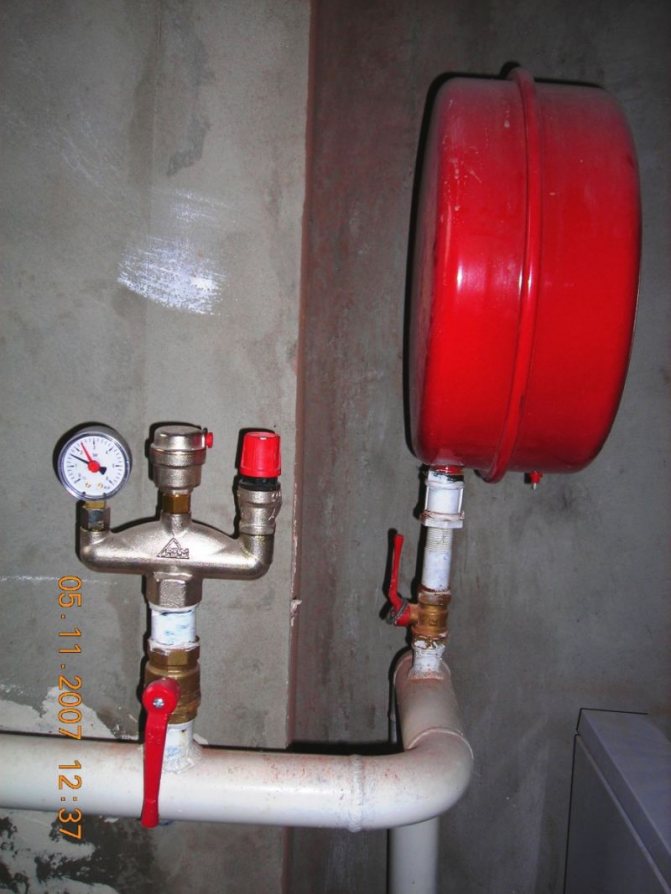
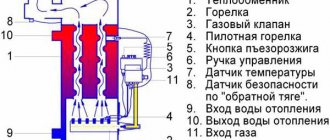
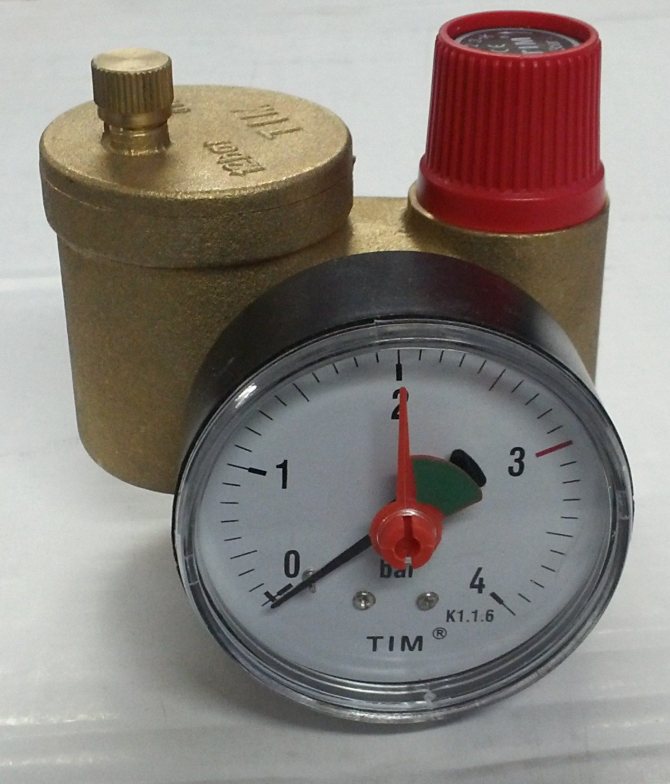
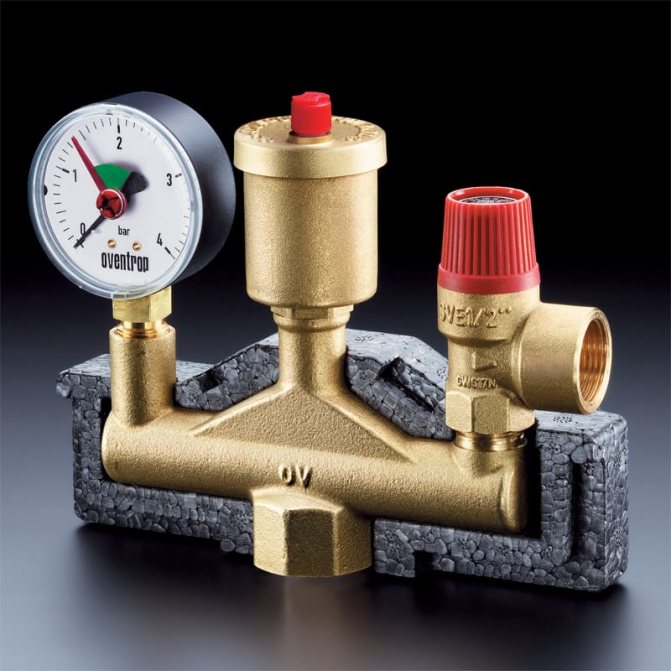
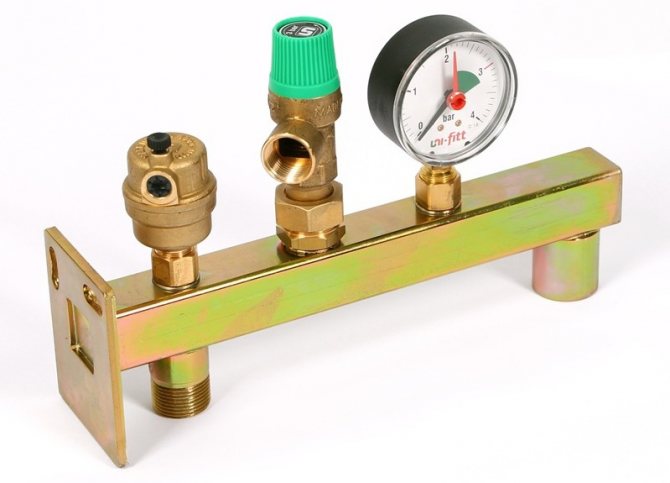
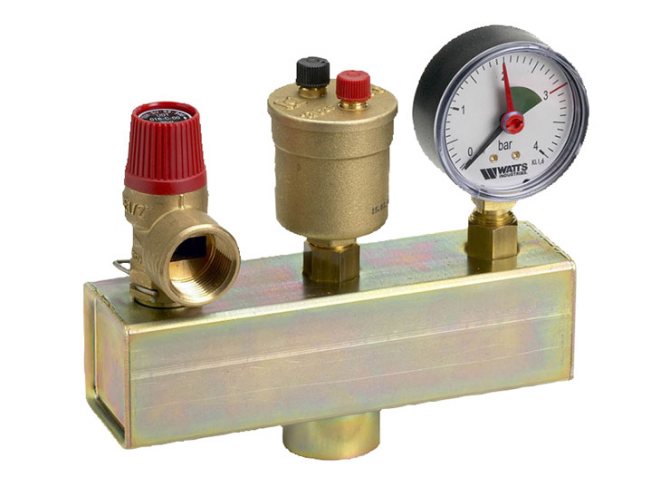
Boiler safety group - a set of safety elements designed to protect heating systems from exceeding the maximum permissible operating pressure and venting air from them.
It is a compact device consisting of a steel console on which are placed: a pressure gauge, an automatic air vent and a safety valve.
The pressure gauge allows you to monitor the operating pressure in the system, the air vent removes air plugs, the safety valve releases the coolant in the event of overpressure.
Principle of operation
If an open expansion tank is installed in the boiler equipment system, then the installation of a safety group is not required - the pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric, and an excessive amount of air leaves the system through the tank.
The safety group for the heating boiler works according to a very simple scheme, when each unit is responsible for maintaining the norms of the given indicators:
- The main job of an air vent is to release air that enters the pipes during operation.
- The safety valve prevents significant pressure readings in the heat generator.
- Thanks to the pressure gauge, the owner of a private house will be able to regulate the pressure level while filling the pipeline with a coolant, as well as later during the operation of the boiler.
All modules are a single link and are located in a special case - a collector.
Security groups "Teplodar"
manufactures safety groups for solid fuel boilers. We offer ready-made sets of devices assembled on brass manifolds. Each element is checked for compliance with the declared characteristics, which guarantees the development of all protective functions. We offer groups for heating systems with operating pressures of 2, 2.5 and 3 bar. They are equipped with pressure gauges with a measuring range of 0-4 bar. The diameter of the connecting sleeve is 1 “.
In the catalog you can select a safety group for any KUPPER model, as well as for solid fuel boilers from other manufacturers. You can get advice on the selection and configuration of devices from the manager by phone.
Varieties
Let's consider the types of security groups. They differ:
Outward appearance: classic - in the photo above, compact - in the photo below:

The presence of thermal insulation: there are models with and without insulation:
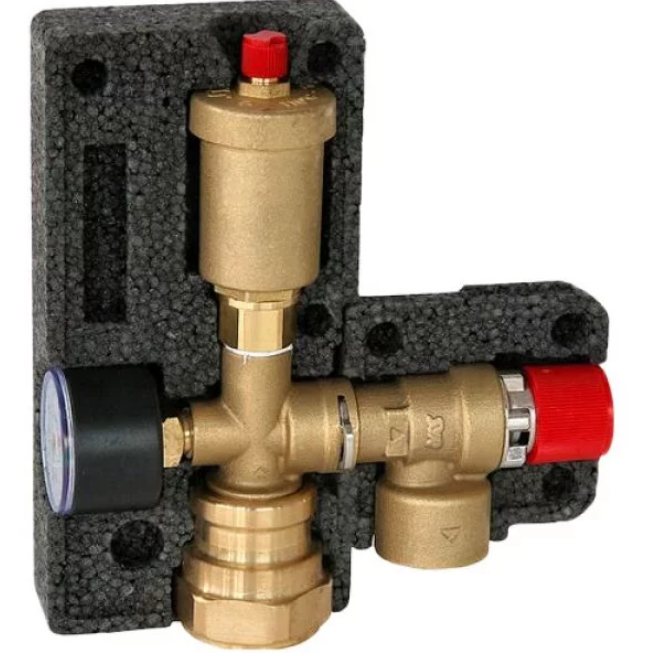


Installation method: to the pipeline (all of the above models) or to the wall:
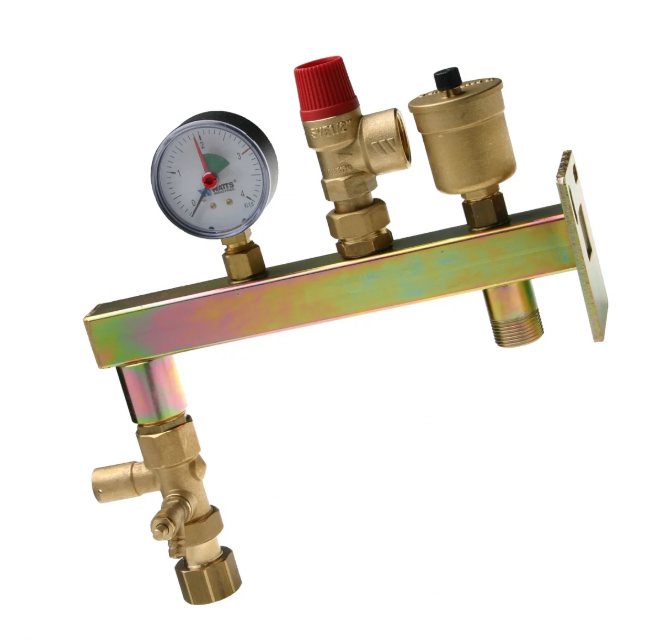


Boiler safety group WATTS GAG / KAV with wall console. By the way, on the left side of this boiler safety group, fittings are preinstalled for connecting an expansion tank (models up to 33 liters are well suited)
Maximum boiler power: most often the following sizes are found up to 50 kW, up to 100 kW, up to 200 kW:
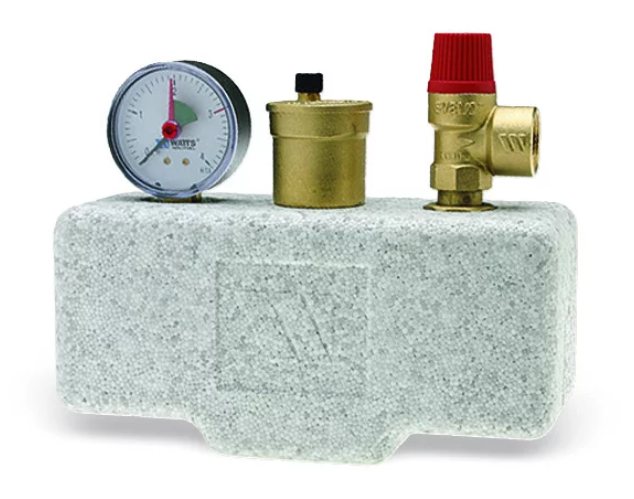


Boiler safety group WATTS KSG 30 / 25M-ISO insulated for boilers up to 200 kW
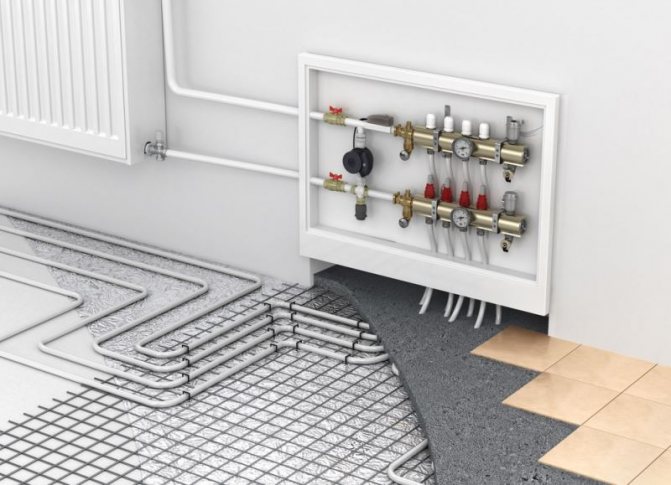
Circulation pump
The circulation pump ensures the operability of the closed heating system. Its capacity depends on many factors: the material and diameter of the pipes, the number and type of radiators, the presence of shut-off and thermostatic valves, the length of the pipes, the operating mode of the equipment, etc. In order not to go into the intricacies of calculating power, the circulation pump can be selected from the table. Select the nearest higher value for the heated area or the planned heat output of the system, in the corresponding line in the first columns find the required characteristics.
You can select the parameters of the circulation pump according to the table
In the second column, we find the power (what volume of the coolant he is able to pump in an hour), in the third - the pressure (resistance of the system), which he is able to overcome.
When choosing a circulation pump in a store, it is advisable not to save money. The entire system depends on its performance. Therefore, it is better not to save money and choose a trusted manufacturer. If you decide to buy unknown equipment, you need to somehow check it for noise levels. This indicator is especially critical if the heating unit is installed in a residential area.
Strapping scheme
As mentioned earlier, circulation pumps are installed mainly in the return pipeline. Previously, this requirement was mandatory, today it is only a wish. The materials used in the production can withstand heating up to 90 ° C, but it is still better not to risk it.
In systems that can also work with natural circulation, during installation, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of removing or replacing the pump without the need to drain the coolant, as well as to be able to work without a pump. For this, a bypass is installed - a bypass path through which the coolant can flow if necessary. In this case, the installation diagram of the circulation pump is shown in the photo below.
Installation of a circulation pump with bypass
In closed systems with forced circulation, the bypass is not needed - it is inoperative without a pump. But two ball valves on both sides and an inlet filter are needed. Ball valves make it possible, if necessary, to remove the device for maintenance, repair or replacement. A mud filter prevents clogging. Sometimes, as an additional element of reliability, a check valve is also placed between the filter and the ball valve, which will prevent the movement of the coolant in the opposite direction.
Diagram of connection (piping) of a circulation pump to a closed-type heating system
Device device
As a rule, the grounds for disrupting the normal functioning of a closed-type boiler are an increase in pressure or a significant overflow of the pipeline with a heat carrier, that is, water.
The heat exchanger is the first section in the boiler that reacts to these deviations, and therefore it quickly fails.
To avoid these malfunctions in the heating system, a safety group for boilers is used.
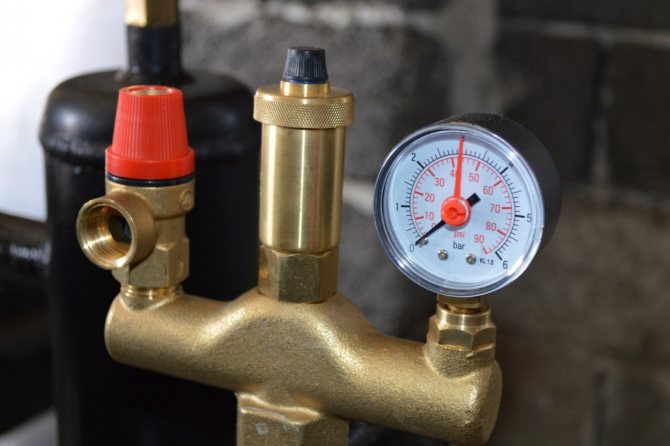


With the help of this block, the required pressure of the coolant in the pipes and radiator batteries is achieved.
During excessive pressure readings, the excess heated water is discharged.
Various abnormal situations occurring, for example, excessive heating of the heating boiler, increase the pressure in the pipeline.
During strong heating, the water begins to expand, the closed water heating system is not designed for this - there is no additional reserve here.
The result of increased pressure is a breakdown of boiler equipment or a rupture of the pipeline. In order to regulate the pressure and, during a potential threat, reduce it to the required value, it will be necessary to install a boiler safety group.
The design consists of the following elements: safety valve, pressure gauge and automatic air vent. All of these devices are housed in a metal housing with threaded connections.
Air vent


Most often, the automatic air vent for boiler safety systems is made of brass.
Air bubbles in the heating system are formed for the following reasons:
- poor quality seals or failure of old ones;
- initial filling of the heating line with water with air bubbles;
- incorrect installation or incorrect commissioning of the heating system;
- water make-up;
- blockage or deposits on the pipes.
The water entering the heating circuit contains a large amount of air, which, when heated, expands and creates plugs.
Due to their formation, the pressure increases, and the speed of movement of the heat carrier decreases.
Therefore, it is advisable to install an automatic valve for air discharge, which is characterized by ease of use - it does not require human participation in the adjustment.
The principle of operation of this device will completely depend on its design.
Typically an automatic valve includes a valve and a duct. The first element controls the discharge of an excessive amount of air. If there is no significant liquid head in the pipes, the float is in the raised position and the valve is in the closed position.
During the formation of a plug, the float is lowered, and the rocker arm opens the outlet valve - this is how air is released from the heating pipes. After releasing excess air, the float returns to its original position and the valve closes.
Where to install the safety box?
In the case of a wall-mounted heating boiler, you do not have to worry about anything at all, since the manufacturer has already taken care of everything: the safety group is already on the back wall or inside the device itself.


But for floor-standing boilers, the blocks should be purchased separately and installed with your own hands. Where exactly? On the supply pipe, in the maximum proximity to the heat generator (that is, no further than 100-150 centimeters from it). As for the pressure gauge, it must be installed so that all of its readings are clearly visible. It is also necessary that the working fluid that flows out of the safety valve be clearly visible, which should also be known before starting installation work.
Installation features
First, you need to briefly talk about shut-off ball valves (later you will find out why exactly). When arranging the heating system, care must be taken that if any of the elements breaks down, it can be easily replaced or, alternatively, repaired, and without draining the coolant from the entire system. It is for this purpose that ball valves are installed.


Let's say the battery has leaked. In this case, you just need to close the shut-off valves - before and after the battery - and then remove the battery itself. The heating system will then continue to function, which is extremely important if it is cold enough outside. In the absence of such taps, you will have to drain all the working fluid from the line. This will require a lot of effort and time, and, more importantly, the system will not work at this time.
Note! It is recommended to install such taps on all heating devices: on the circulation pump, on the batteries, and on the membrane tank, etc.
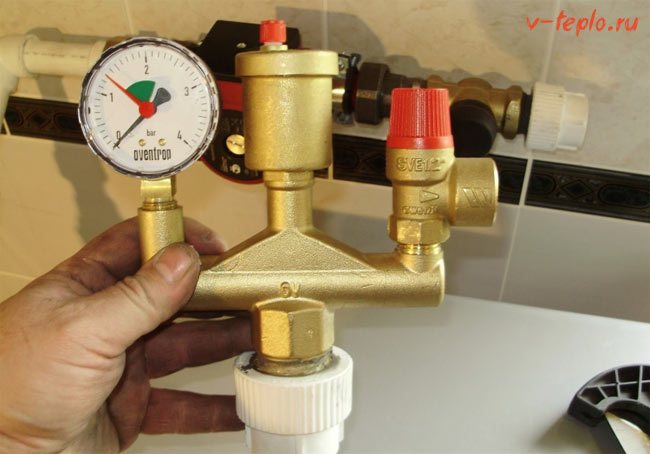


And now we have a security group directly in the heating system. Below is a brief instruction from which you will learn in which order the unit should be installed.
Step 1.
The safety group should be placed on the supply pipe, no further than 100-150 centimeters from the heating boiler.
Step 2.
Without the required knowledge, many, when installing this device, put cut-off taps between it and the heat generator, or, as an option, directly on the group itself. Their explanation looks like this: if the boiler fails, then it can be easily fixed or replaced. Below are two options for improper installation of shut-off valves.
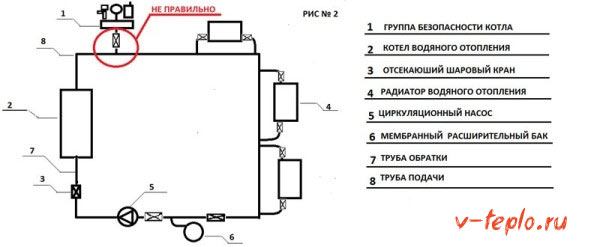

In each of the examples, the taps are installed incorrectly, and if the heat generator fails, then the seller will refuse you a guarantee, since the device was not installed as needed. With this kind of valve arrangement, the risk of overheating the system increases, which can lead to boiler breakdown.
Step 3.
When properly installed, the cranes should be located behind the safety group. This is correct, and in this case no one will refuse a guarantee.
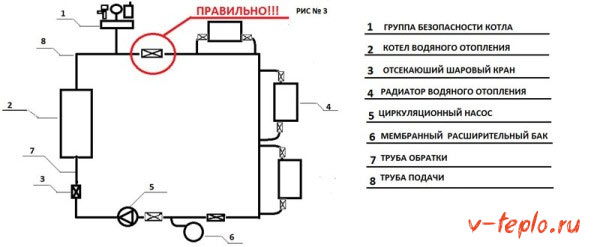

Video - How to connect a security group
How to choose?


Choosing the right model is not difficult, you need to look at:
- Maximum allowable system power (kW) for which the node is designed. Usually it is 44, 50 or 55 kW. If the system has less power - great, if more - you need to look for a more durable option.
- Pressure relief valve. As a rule, valves with a fixed value - 1.5 bar, 3 bar, 4 or 6 bar - are installed in ready-made assemblies. The response pressure should correspond to the maximum permissible operating pressure of the most vulnerable element of heating systems - usually a steel boiler heat exchanger, rated at 2 or 3 bar. Safety valves for 2 bar, despite sufficient demand, are difficult to find on sale, a way out of the situation is to assemble the assembly with your own hands by purchasing a safety valve and other elements separately (see below for more on this).
- Working temperature - this is the permissible temperature of the coolant, in almost all modern models it is in the range of -10 ° C - 110 ° C, which is more than enough.
- Coolant compatibility - if antifreeze is used as a heat carrier instead of water.
- Threaded connection diameter - it can be 1 ", 1/2" or 1.4 "in diameter. You can pick up a knot that does not match the thread diameter, but then you have to take care of the selection of the adapter, which is not always easy.
It is important to pay attention to the material of manufacture, galvanized steel or stainless steel is a good, but not the best option.
Brass products are more expensive, but more durable, wear-resistant and even more resistant to corrosion.
The material of manufacture is not always indicated in the characteristics, in addition, the collector can be made of steel, and the rest of the elements - of brass.
Brass can be distinguished by its characteristic monochromatic, matt color (bronze-gold or silver, depending on the alloy).
The use of antifreeze in the heating system
It turns out that a safety group for heating is not always needed, but at the request of the homeowner it can be installed in any system and serve as a safety net. For example, heat generators that burn natural gas and diesel fuel, as well as run on electricity, do not need additional protection.
But solid fuel heat sources have great inertia and cannot stop right away. Even automated pellet boilers take a little time to burn fuel that has got into the combustion zone. Imagine a furnace full of burning wood? The thermostat or controller will cut off the air instantly when the temperature in the jacket rises, but the process will not stop immediately.
To reduce the negative impact of low temperatures on radiators and pipelines, antifreeze is used for the home heating system. Antifreeze usually contains ethylene glycol. It is poisonous and you need to beware of getting this substance on open skin and, especially, in the eyes. Antifreeze vapors, which are formed under the influence of high temperatures and can be released to the outside in the presence of a small leak, are also harmful.
Of course, for antifreeze for a heating system, the price may differ depending on the composition of the product and the manufacturer. But still, the use of antifreeze in heating devices will cost more than using ordinary distilled water. True, in some cases, the use of antifreeze liquid is simply necessary to ensure the safe and proper operation of the entire heat supply system.


Many people have a question: is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system of a house?
You can use such an anti-freeze liquid, but you should know a number of rules and observe safety requirements. Sometimes car antifreeze is used for the heating system.
In this case, it is important to take into account some of the features of the heating system operation:
- antifreeze is more viscous than distilled water. Therefore, if a circulation pump is used, it will have to be changed to a more powerful unit;
- the degree of fluidity is quite high. A small microcrack or a loose connection is enough for the antifreeze for heating the house to begin to penetrate into the room. Therefore, you need to monitor the tightness of the structure, and instead of rubber gaskets, it is better to use paronite;
- the rate of heating water with antifreeze is slightly lower. This feature should be taken into account when choosing the temperature mode for the operation of the heating system;
- it is impossible to use antifreeze in the heating system of a house in a concentrated form. The product must be diluted with water.
Thus, many modern models of heating systems are equipped with a safety unit. But if this module is missing, then you should install it additionally. This protective mechanism reduces the likelihood of air pockets and regulates the pressure in the system. To avoid a negative effect on pipes of low temperatures, antifreeze is used. All this allows you to extend the service life of heating devices and make their work better and more efficient.
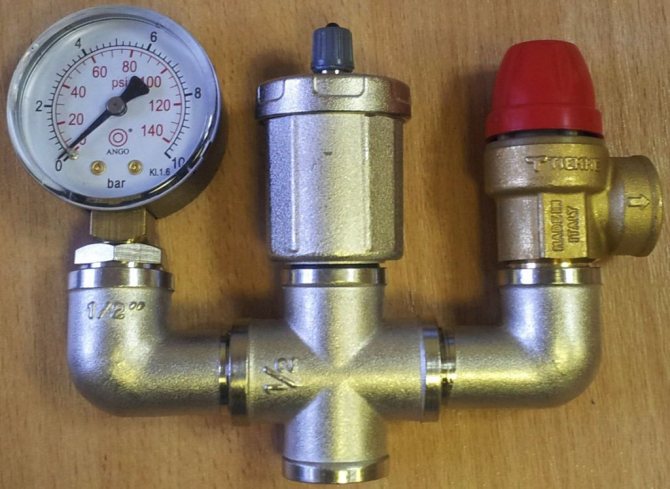
Self assembly
A correctly assembled safety group should be in the shape of a trident so that the air vent is in the middle, directly above the connection for the safety group.
So the air will flow into it guaranteed, without any obstacles.
A homemade security team includes the following elements:
- pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve;
- 2 steel or brass elbows at 90 ° with external and internal threads (the diameter is matched to the thread diameter of the modules and the cross);
- 1 steel or brass crosspiece;
- 1 coupling / nipple for connecting the assembly of the finished unit with the tee of the heating system;
- tow or silicone for sealing joints (FUM tape is not recommended, since it deforms at temperatures above 70-80 ° C).
We connect the elements in accordance with the photo below, connect to the heating system and check the operability:


Popular manufacturers and prices
Heating safety groups are produced by different manufacturers. Several firms have gained the greatest popularity, their brand is recognizable. They are often recommended by installers for heating private houses.
| Manufacturer | Average market price, rub. |
| ARS | from 1308 to 1422 |
| Fado | 2330 |
| Buderus | from 2965 to 3320 (depending on modification) |
| Watts | from 2625 to 5650 |
The range of prices is small. If we estimate the cost of the elements that make up the home heating system, then we can see that the price of the security group will be less than 1%. Taking into account the installation of all these devices, the price will be even lower.
The safety group for heating is an important and necessary element of the heating system, which, at a relatively low price, will reduce the risks during operation in the winter.
Related videos:
Heating connection
The whole process of connecting the safety group to the heating system consists in a threaded connection to the vertical pipe previously allocated for it (diameter of the thread of the pipe = thread diameter of the safety group) and in checking the operability of its modules.
An example of installing a safety group is shown in the diagram below:
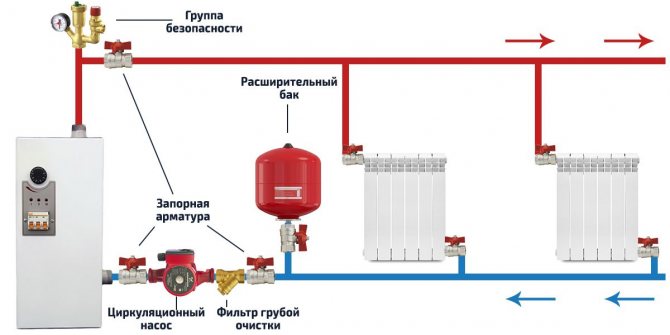

After the tight connection, you need to check the operation of the air vent by forcibly opening it: turning the valve handle (upper cap) until it clicks. We leave the air vent open.
For the period of filling the system with coolant, it is better to close the automatic air vent.A drain pipe must be put on the relief valve, leading either to the floor (into a prepared container) or to the sewer.
In the first case, the consequences of the accident will be visible; when you drain into the sewer, you may not know about what happened.
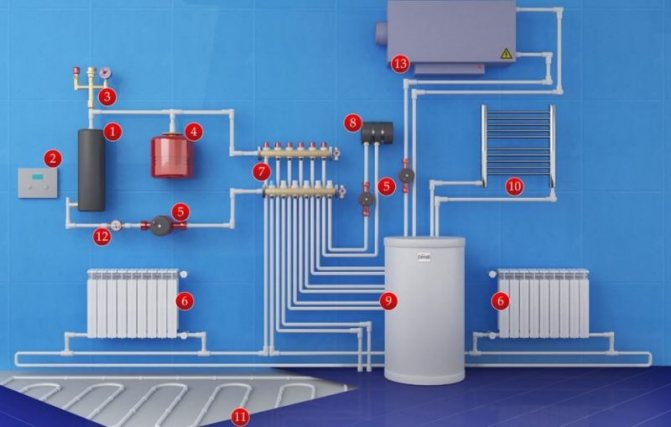
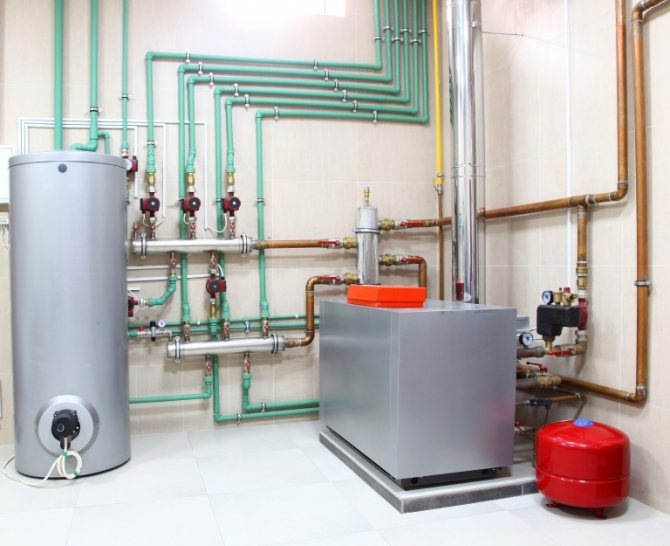
Closed heat supply system - what is it
As you know, in any heating system of a private house there is an expansion tank. This is a container that contains some weaning of the coolant. This tank is required to compensate for thermal expansion under various operating conditions. By design, expansion tanks are open and closed, respectively, and heating systems are called open and closed.
Closed two-pipe heating system
In recent years, it is the closed heating circuit that has become more and more popular. First, it is automated and works without human intervention for a long time. Secondly, any type of coolant can be used in it, including antifreeze (it evaporates from open tanks). Thirdly, the pressure is kept constant, which makes it possible to use any household appliances in a private house. There are a few more pluses that relate to wiring and operation:
- There is no direct contact of the coolant with air, therefore, there is no (or almost no) incoherent oxygen, which is a powerful oxidizing agent. This means that the heating elements will not oxidize, which will increase their service life.
- The closed-type expansion tank is placed anywhere, usually not far from the boiler (wall-mounted gas boilers come immediately with expansion tanks). An open-type tank should be in the attic, and these are additional pipes, as well as insulation measures so that heat does not "leak" through the roof.
- In a closed system, there are automatic air vents, so there is no airing.
In general, a closed heating system is considered more convenient. Its main drawback is volatility. The movement of the coolant is provided by a circulation pump (forced circulation), and it does not work without electricity. Natural circulation in closed systems can be organized, but this is difficult - flow regulation is required using the thickness of the pipes. This is a rather complicated calculation, because it is often believed that a closed heating system works only with a pump.
To reduce volatility and increase the reliability of heating, uninterruptible power supply units with batteries and / or small generators are installed, which will provide emergency power supply.
Maintenance
- It is advisable to check the status of all modules of the security group every 2-3 months.
- The safety valve must be cleaned every 6 months to prevent leaks and contamination. To do this, open it by turning the valve cap in the direction of the arrow.
- After 5-7 operations, it is recommended to replace the safety valve due to wear of the spring, which can lead to leakage and operation at lower pressure values in the system.
Operating principle
All work on the installation of a safety group in a closed heating system must be carried out by highly qualified specialists. Only they will be able to correctly connect the devices and configure them properly. If everything is done correctly, then the security group will work on the following principle:
- An emergency situation arises in the heating system. In this case, the movement of the coolant stops and the pressure begins to rise rapidly.
- Part of the steam goes to the automatic air vent. A special float is built inside it, which catches even the smallest air bubbles.
- Once this has happened, the float goes down and opens the valve.
- The steam is discharged to the outside and quickly reduces the pressure in the installation.
- If the air vent could not cope with the pressure on its own and its indicator continues to grow, then the safety valve is triggered.
- It opens and drains the coolant until the pressure returns to normal.


If any emergency occurs, the security team will protect you and your heating
Structural elements
The heating safety group diagram provides for the use of all structural elements. Otherwise, the unit will not function properly, which can lead to various breakdowns and accidents.
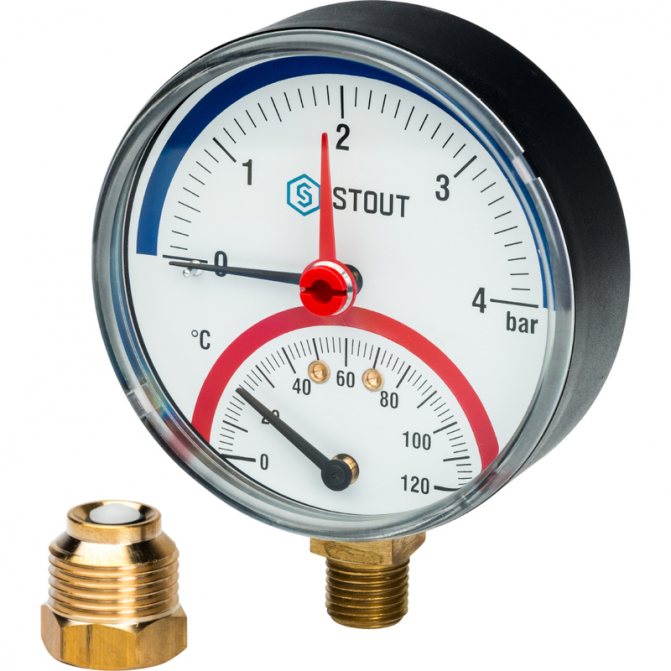
Accurate pressure gauge
This device is designed to measure pressure (in atmospheres or bar) and give immediate results. For this, a scale is graduated on the manometer and there are two arrows. One of them shows the pressure in the heating system, and the second shows the limit value, which is set during adjustment.
The device can measure any pressure between 4 and 10 bar. These indicators are quite enough, since the standard value can vary within the following ranges:
- For pipelines of heating systems installed in apartment buildings - 1.5 bar.
- In country one-story buildings - from 2 to 3 bars.
Mayevsky crane
An automatic air vent must be installed in the heating security system of a private house and city apartment. This is best done at the highest possible height. This feature is due to the fact that the air is lighter than the coolant. It moves upward and accumulates there, preventing the equipment from working properly.
Air can appear due to the following factors:
- Poor quality rubber seals or premature wear.
- The first start-up of the installation and filling the pipes with a coolant.
- Corrosion formation inside the instrument lines.
- Incorrect installation or failure to comply with the tightness conditions.
- Water make-up.


Such a faucet protects your heating system from the ingress of various dirt
The Mayevsky crane is designed in such a way that the smallest particles of dirt cannot get into the air chamber. The air vent is assembled from the following parts:
- case with a lid;
- jet;
- float;
- spool;
- holder;
- body and valve o-rings;
- bung;
- spring.
Safety valve
During the operation of the heating system, the increase in the volume of the coolant is compensated by an expansion tank, which is mounted over the heating devices and pipes. The user independently sets the desired outlet temperature, which leads to a change in the liquid level in the expansion tank.
In most cases, the performance of this unit remains effective for a long time. With wear and tear, the likelihood of some kind of breakdown increases. It is absolutely impossible to determine the problem visually, since its root is hidden inside the pipeline. Such a malfunction will lead to a rapid increase in pressure and destruction of the components of the heating system. To combat this phenomenon, a safety valve is used. It is installed together with other parts of the safety group and protects the device from damage. In addition, the owner of the dwelling will see a liquid discharge, which will confirm that there is a problem.
Before starting operation, the safety valve must be checked for functionality. This can be done as follows:
- The handle, which is located at the top, turns in the indicated direction and opens the water.
- Then the same actions are done in the opposite direction.
- If liquid still flows out, then it is necessary to open and close the safety valve several times in a row.
- If the performed manipulations did not give the desired result, then the valve is broken and must be replaced with a new one.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1.How to assemble a safety group for heating with your own hands:
Video # 2. Installation rules for the security module:
Video # 3. Connecting the safety assembly to a polypropylene supply pipe:
Many are sure that the protective assembly belongs to ordinary devices and its installation is optional. However, a negligent attitude towards this issue will not be able to protect the heating unit and the heating system itself from rupture as a result of a sharp jump in pressure, which is quite common in a closed circuit.
Please write comments, ask questions, post a photo on the topic of the article in the block below. Tell us how you equipped the heating circuit with a safety group. share useful information that may be useful to site visitors.
A safety group for heating with an expansion vessel is a set of elements that protect the heating system from exceeding the permissible maximum pressure value. Also, air is removed through it.