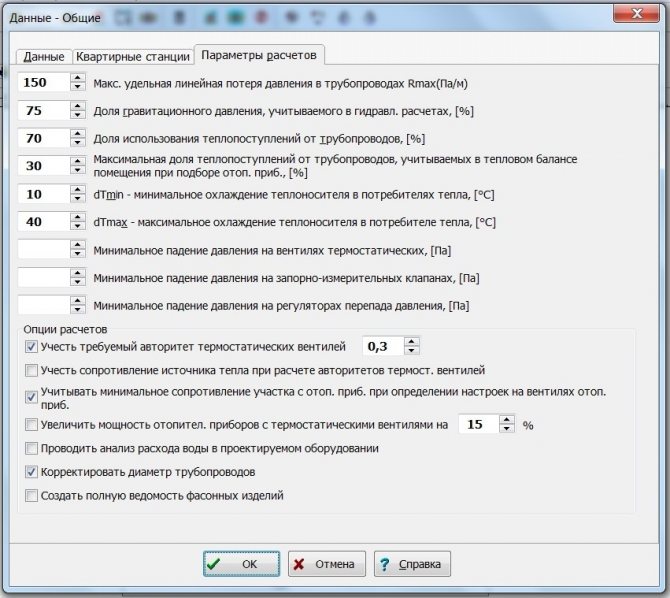
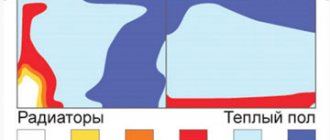
Modern private houses are most often built taking into account the fact that even at the design stage, a warm floor is provided as a main or additional source of heating. In any case, the advantage of houses with underfloor heating is obvious - they are more comfortable and warm. It is important to understand that the underfloor heating system must first be calculated - especially for the water system. The project of a warm floor allows you to foresee the power of the system, correctly arrange all the components, and calculate the amount of material. A lot of nuances will be taken into account when developing a project: the area of the room and the calculated heat loss in it, the type of pipes, the material of the finish coating and the method of installation of the system itself, as well as much more, without which a high-quality installation is impossible.

A properly designed underfloor heating project guarantees the durability and high-quality operation of the heating system
Where to begin
Among all the variety of technologies for underfloor heating (electric, infrared and others), the water system is especially popular. It is durable and reliable, but without a preliminary correct calculation there is a possibility of an increase in installation costs and a decrease in the operational properties of the system.


Water heat-insulated floor
The project of a water heating system can be developed as one of the items in the design documentation for a house. You can also order it separately or do it yourself. Some companies specializing in the installation of a water heated floor independently carry out a preliminary design of the system.
The project will be required even with an independent installation of a water-heated floor. This will allow you to purchase material and fittings in the required quantity, and perform the installation itself in a short time, without being distracted by calculations and alterations.
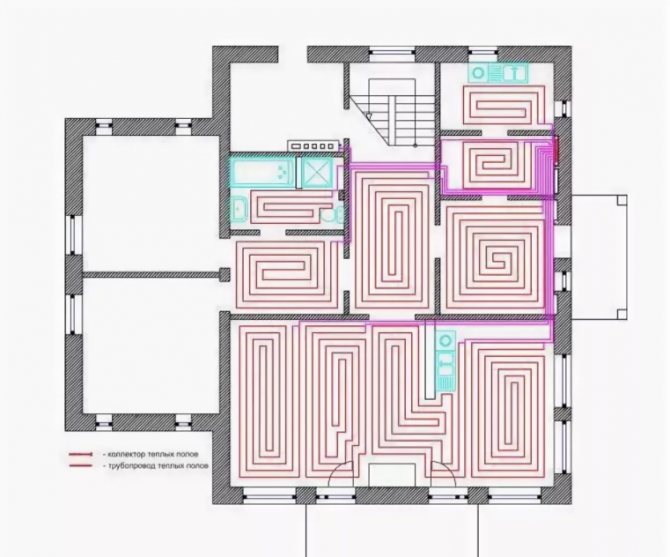

Layout and connection diagram in a private house
To draw up a project, you will need to have and record the following data:
- Floor plan of the building.
- Material of external walls and windows with doors.
- Desired indoor temperature.
- Information about where the risers and bends are located inside the building.
- Furniture layout plan.
Knowing the listed nuances of the room, they first perform the thermal calculation, and then proceed to drawing up the installation diagram.
Now on the construction market there are several types of "warm floors". They differ in the type of coolant and work efficiency. How to choose a warm floor? Let's tell in our article.
The sequence of design and calculation of a water-heated floor
A couple of lines about what awaits us in the design and further calculation of the warm floor. In what order is this done? Here in this one:
- Collect data on the object (house) in which it is planned to make water heated floors.
- Sketch a sketch (plan) of the house. Put on this sketch all the data collected in the previous step. This sketch with data will be needed to calculate the heat loss.
- Calculate the heat loss of the house or the room (if there is only one) where we want warm floors. This is necessary in order to know what heat output our warm floor should have, whether it is generally advisable to make a warm floor - whether it can heat the room / house. Or would it be smarter to skip this idea and install radiators? Or maybe - if the theme of a water-heated floor still persistently asks for embodiment - it will be necessary to make a warm floor + radiators.
- Carry out a hydraulic calculation of the water floor heating system. This is necessary to select the power of the circulation pump.
- To sum up the results of the calculations, to think again if it is worth the candle, maybe something needs to be changed in the project. then repeat everything from any of the above points. And repeat until the results of the calculations suit us.
And now - later in this article and in the next few articles - each point is detailed.
Documentation
Before proceeding with the installation of the system, it is necessary to have a plan of the heating system and a list of necessary materials and equipment.
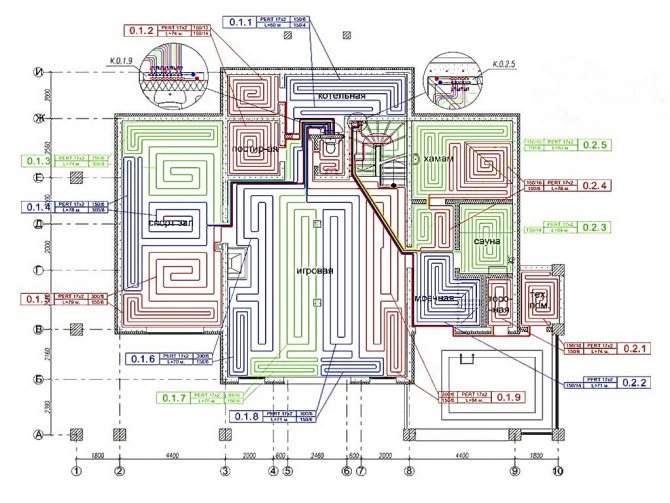

Warm floor plan
The plan structure includes the following data:
- On the location of heating devices.
- A diagram showing the location of the pipes, the distance between them, their diameter and the length of each straight section.
- Information about the required power of each radiator and their locations.
- Thermal calculation of the water floor heating system.
Requirements for the premises
Installation of a warm floor with a water heat carrier does not cause problems in houses with an autonomous heating system. If the room is in an apartment building, you must carry out a special examination to install this system. She must prove that the heating structure will not cause any disruption in the operation of the building's communications. For this, individual floor heating, floor heating wiring must be arranged, and a heat meter in the apartment must also be connected. If the apartment is located on the first floor of a multi-storey building, the water-heated floor must be connected to the return riser of the heating system.
Underfloor heating is installed in rooms that are properly prepared for installation. Requirements for them include:
- completed markings of the floor level;
- completed internal plastering works;
- the presence of doors, windows;
- derived points of connection of water, as well as sewerage and electricity;
- clean and even floor surface;
- reliable waterproofing of the base.
Materials (edit)
In the process of designing a water underfloor heating system, a list of materials is drawn up. Conditionally, they can be divided into components of the system itself and raw materials for creating a screed.
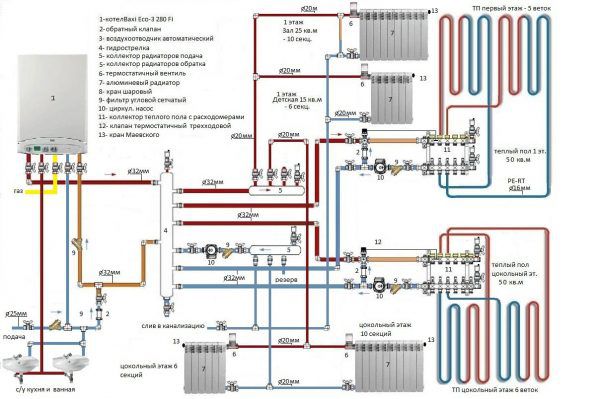

The main elements in a heating system with an additional heat source in the form of a warm floor
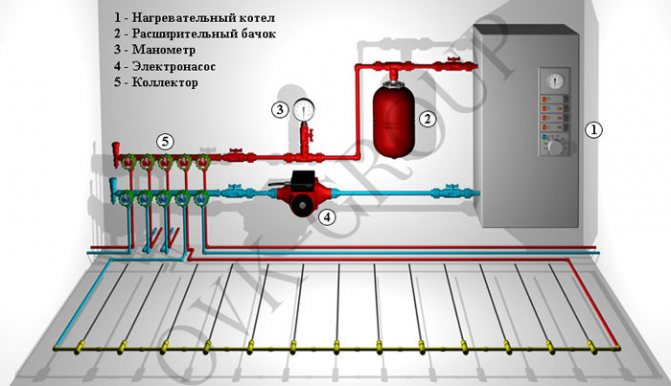
Components of a warm water floor are:
- A heat boiler that heats the heating medium in the absence of a central heating system.
- Built-in boiler or separately located pump for pumping water into the system.
- Pipes for the movement of the coolant.
- A collector is installed to distribute water through the pipes.
- The collector is placed in a special cabinet, and you will also need to purchase splitters for distributing cold and hot, valves, fittings, ball. You will also need to provide for an emergency drainage of water and air removal from the pipes.
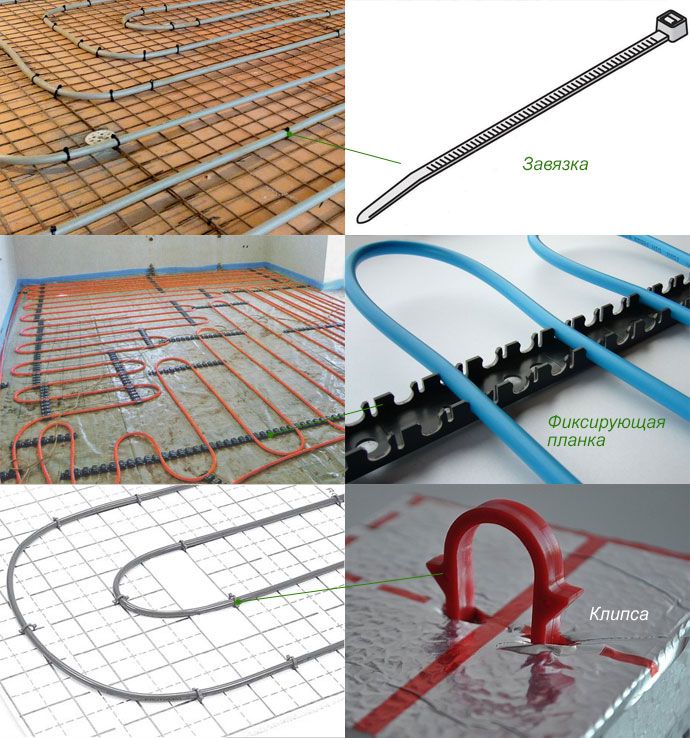

Pipe fastening methods
The list of materials depends on the method of installation of the system - wet (screed) or dry (using mats with bosses, eg).
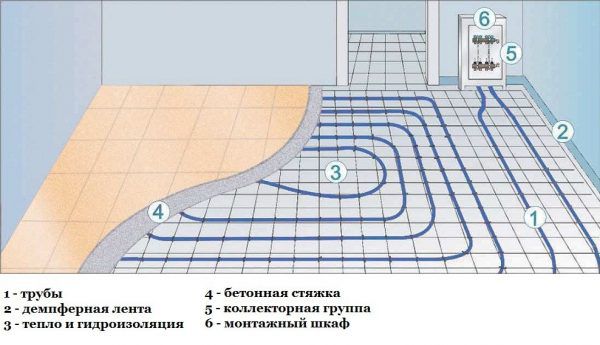

The principle of connecting a warm floor
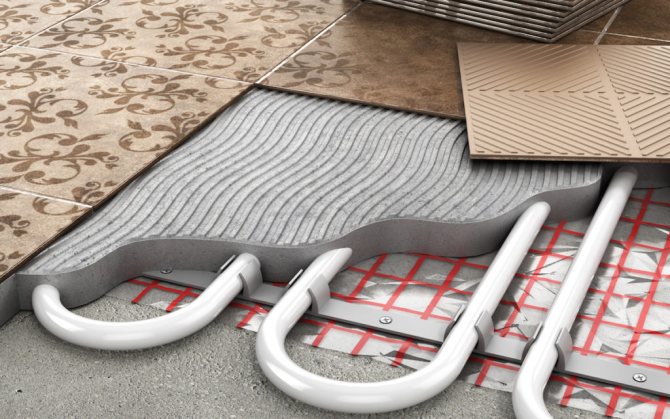
In the first case, a reflective layer is laid along a rough screed, reinforced mesh and pipes are fixed. After that, a finishing screed is poured onto which the finishing flooring will subsequently be laid.


Pipes can be laid with boss mats and thermoplastics that effectively reflect heat
In the second case, the pipes are fixed in a given position using special mats with bosses and thermoplates with a groove, where the pipe is laid. This method is relevant for rooms with old or weak floors.
How to choose the length of the pipe
One loop (loop) can have a certain maximum length depending on the diameter of the pipe used. With a pipe diameter of 16 mm, the maximum loop length is from 70 to 90 m, with a 17 mm diameter, the loop length varies from 90 to 100 m, if the pipe diameter is 20 mm, then one loop can have a length of up to 120 m.
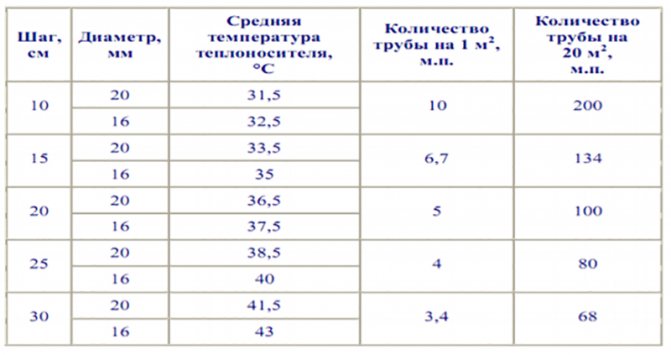

Calculation of the number of pipes, taking into account the main criteria
The dependence of the loop length on the diameter is due to the fact that pipes of different diameters have different hydraulic resistance and heat load. Less hydraulic resistance is observed in pipes with a large diameter.
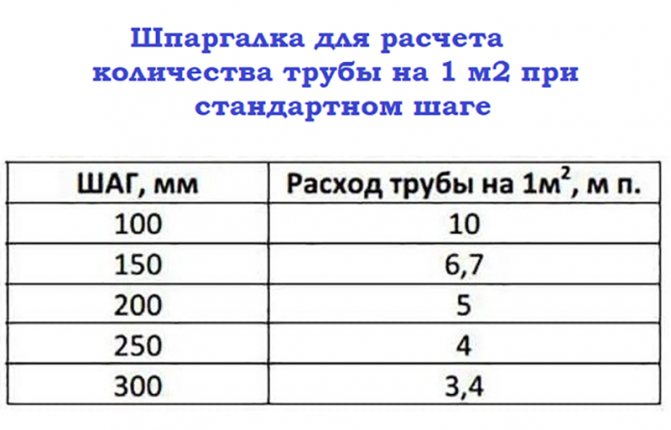

Calculation depending on the laying step
Note! In a small room, it is enough to mount one circuit that does not go beyond the maximum permissible length values. But if the room is large, then it is better to mount two circuits than to exceed the recommended optimal pipe length.
It is also worth considering that in fact, when installing the system, it is necessary to use pipes of the diameter for which the calculation was made in the project. You can make calculations for pipes of different diameters and choose the right option at this stage, and not later, choosing the right material empirically.
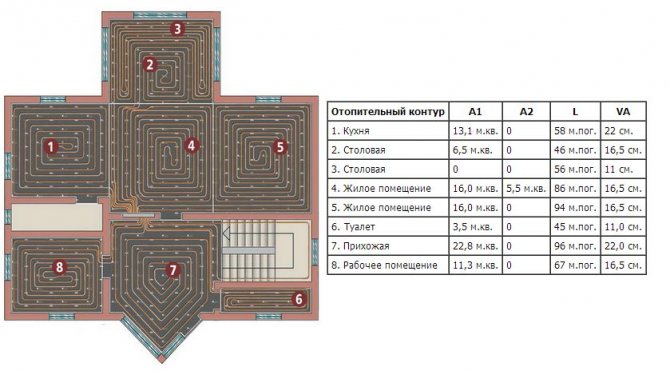

Calculation of the length of the contours for various rooms
When laying several contours, it is necessary that their lengths coincide as much as possible. The length of the contour is the length of the entire pipe, that is, it starts from the collector. It is clear that in the course of work it is not always possible to achieve the same length of the contours, but it is necessary to strive to ensure that the difference between the lengths does not exceed 10 m.


Specialist recommendations
The area of the room affects the way the contours are laid. Where it is less, when laying pipes between the turns, a smaller step is provided. Alternatively, to heat a small room with minimal heat loss (hallway, bathroom), you can use the return pipe of the adjacent loop.
How to choose a pipe laying step
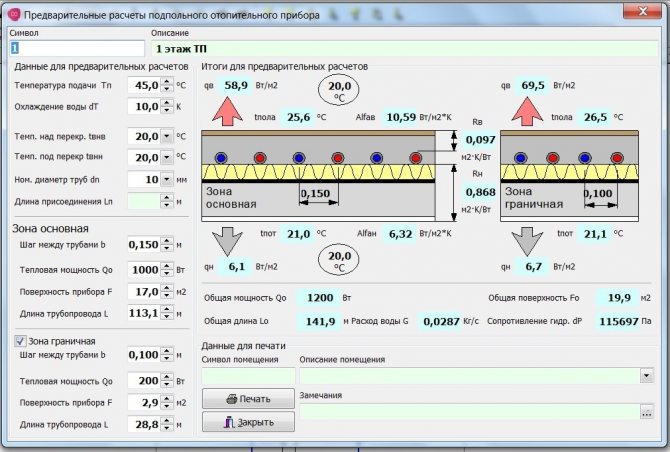
The distance between adjacent pipe coils (pitch) is 15-30 cm. In this range, the values are multiples of 5, i.e. 15, 20, 25.30. For large rooms such as gyms, the pitch can be 30 - 45 cm. Near a large window or outside wall, the pitch is 10 cm. These areas are called edge zones.
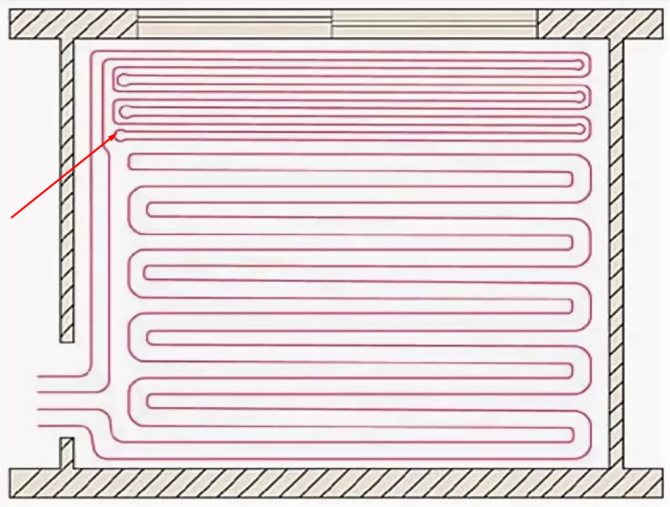

Laying pipes in the edge zone (by the window)
Various factors influence the choice of the pipe laying step: heat load, the purpose of the room, the length of the circuit, the material of the finished floor and other nuances. Concerning:
- For edge zones, the optimal number of rows is 6, the laying step is 10-15 cm.
- For central areas: 20 - 30 cm.
- For bathrooms, the step is 10 - 15 cm, but you should be prepared for the fact that, due to the need to bypass the plumbing equipment, the step may not be the same.
- If the finishing coating has high thermal conductivity (tile or marble tiles, porcelain stoneware), then the distance between the turns is 20 cm.
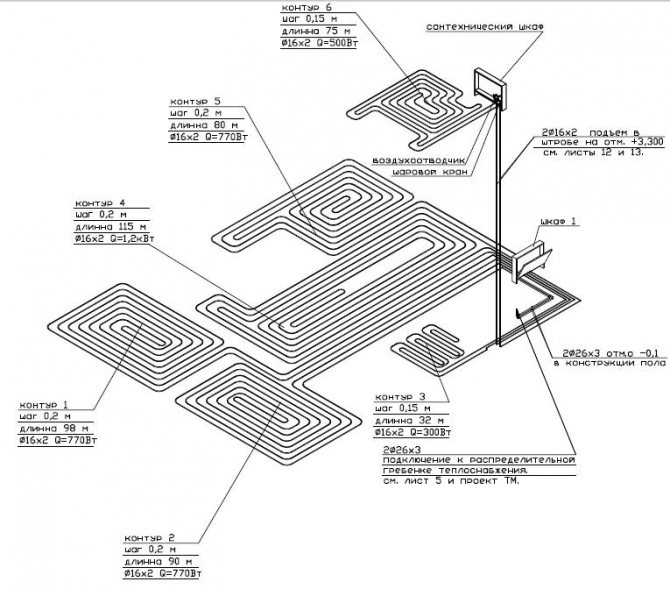

Calculations of the main parameters for contours of different lengths
Note! In practice, it is not always possible to adhere to these recommendations. According to experienced craftsmen, the best option is a step in the marginal zone - 10 cm, in the center - 15 cm. These are the values at which the system will work.
How to choose a pipe diameter
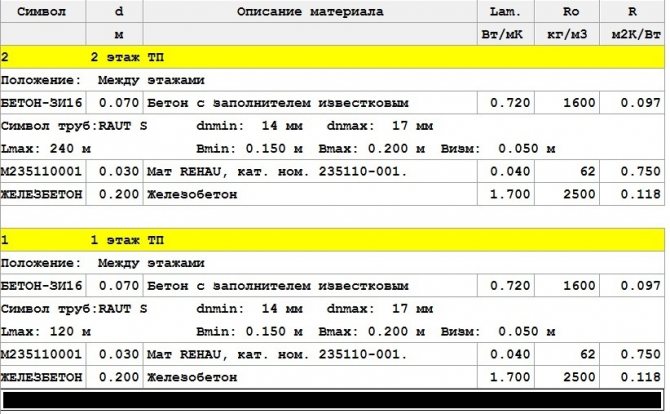
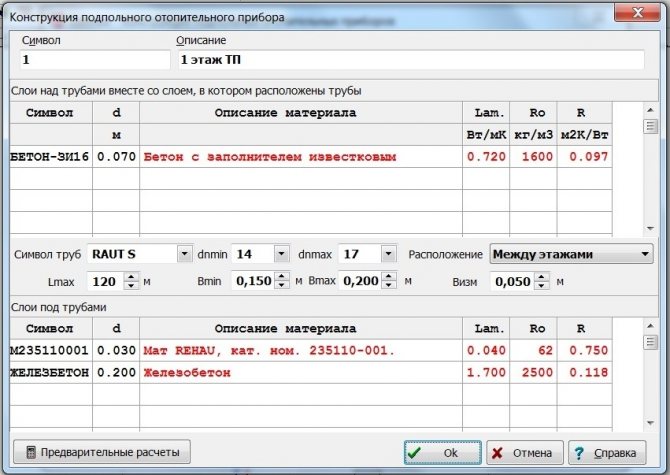
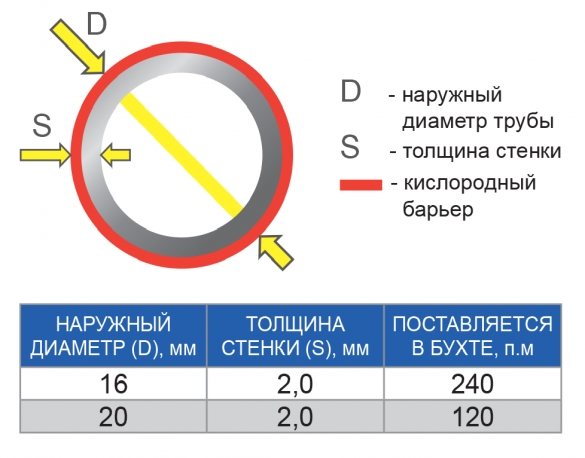
For residential premises, the area of which starts from 50 m², the best option would be pipes with a diameter of 16 mm. The height of the screed from the top of the tube is 5 cm.

Pipe diameter specifications
It is this diameter that allows you to comply with the conditions for laying pipes with a step of 15 - 20 cm.This applies even to houses with good thermal insulation, where the pipe laying step should not exceed 15 cm.For private houses, these parameters are optimal in terms of ease of installation, cost of materials and volume of coolant.


Performance properties of pipes for underfloor heating
Pipes with a diameter of 18 mm, due to their larger volume, lead to unnecessary costs, including for related materials (fittings, etc.).

The advantages of pipes specially designed for underfloor heating are obvious
Accordingly, for pipes with a diameter of 20 mm, even more energy will be required to heat the coolant. In addition, laying with a snake with a step of 15 cm is not realistic, due to the impossibility of bending a pipe of this diameter to the required radius. As a result, the laying step will be larger, the heat in the room will be less, and this is at a significantly increased cost of the heat carrier. Pipes of this diameter are used in public premises with a thick screed.

Properties affecting styling quality
Pipe material
Different pipe materials have a direct impact on the correct operation of the system.
Table 1. Varieties of material
| Type of material | Positive traits | disadvantages |
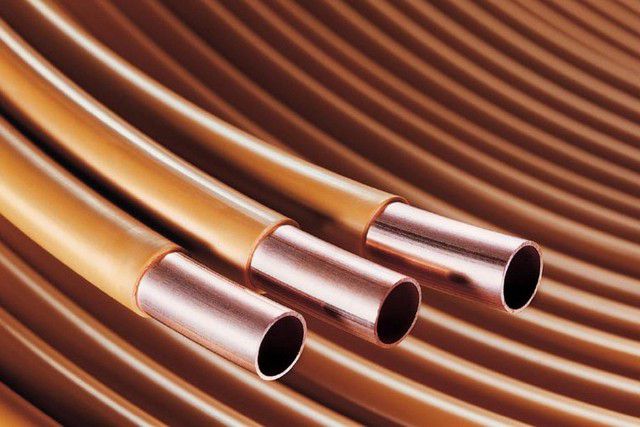
Copper | 1. The material conducts heat well. 2. Copper is highly resistant to corrosion. 3. The material has a long service life. 4. Copper possesses a unique plasticity, which allows pipes to bend along a rather small radius. 5. The walls are characterized by high mechanical strength and high resistance to temperature extremes. 6. The outer polymer coating protects the copper from negative external influences. | 1. Laying copper pipes requires skill in working with such a material. 2. The need to use special equipment. 3. High material cost. |
Stainless steel (corrugated pipes) | 1. Excellent flexibility. 2. Resistance to fracture. 3. High mechanical resistance. 4. High resistance to temperature changes. 5. A wide range of high quality fittings that allow joining pipes in a long circuit. | High price. |
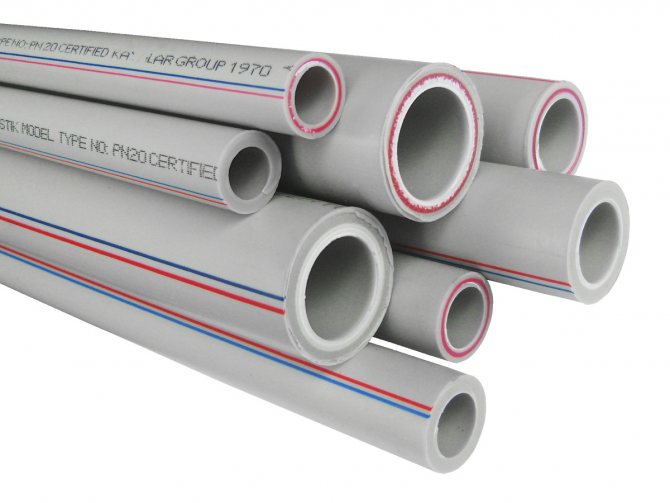
Polypropylene | 1. Simple installation. 2. Low cost. 3. Suitable for supplying heating medium from the boiler to the collector. | 1. Low plasticity. 2. Short length. 3. Forming the contour produces many welds that are potential leaks. 4. Low thermal conductivity. 5. High level of thermal expansion. |
XLPE | 1. High strength of the material 2. Tight connection of the circuits. 3. Ability to create a contour of any length. | Large bending radius. |
How long should the pipes for a water-heated floor be?
The maximum length of one circuit (loop) depends on the diameter of the pipes used:
- with a diameter of 16 mm - 70 ... 90 meters;
- with a diameter of 17 mm - 90 ... 100 m;
- with a diameter of 20 mm - 120 m.
The difference in lengths is due to the different flow resistance and heat load of pipes of different diameters. Well, it is clear: the thicker the pipe, the less hydraulic resistance (resistance to fluid flow) in it.
Usually one circuit heats one room. But if the area of the room is large, the length of the circuit turns out to be more than optimal, then it is better to make two circuits per room than to lay a pipe that is too long.
If, when designing and calculating, one pipe diameter is taken, and then another is mounted, then the hydraulics of the system will be different. So all experiments are better and correctly allowed at the design and calculation stage, compare the results, choose the best one and follow it.
If two or more circuits fit in a room, you need to strive to ensure that their lengths are the same (the entire pipe is considered to be the length of the circuit, starting from the collector, and not only that part of it that is directly in the heated room itself).
Of course, in practice, it is impossible to fit the length perfectly, but you need to strive for this and the difference should be no more than 10 m!
The premises in the house, as you know, have a different area. To lay as many meters of pipe in a smaller room as in a larger one, you need to take a smaller step between the turns.
If the room is small and the heat loss from it is not large (toilet, hallway), then you can combine the circuits, heat from the return pipe of the adjacent circuit.
What else needs to be taken into account in the process of designing a warm floor
In the process of developing a project for a warm floor system, it is recommended to perform a schematic drawing with a designation of pipe laying, basic dimensions, distances and indents, furniture placement.


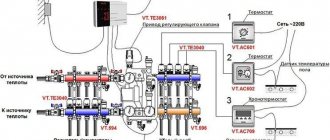
Collector group
You should also choose the material of the finishing (top) coating. To do this, you can familiarize yourself with our article... In it, we will consider the most suitable topcoats.
At the design stage, the type of coolant is determined: in 70% of cases, water is used, since it is the most accessible and cheapest substance. Its only drawback is its reaction to temperature changes, as a result of which there is a change in the physical properties of water.

Floor cake with pipes in a screed
Antifreeze based on ethylene glycol or propylene glycol with special additives that reduce the chemical and physical activity of fluids is often used as a heat carrier for underfloor heating. In any case, the type of coolant must be taken into account precisely at the design stage, since its properties form the basis for hydraulic calculations.


Antifreeze as a coolant
You will also need to take into account the following nuances:
- One contour fits into one room.
- To place the collector, the center of the house is chosen. If this is not possible, then to adjust the uniformity of the coolant flow through the circuits of different lengths, flow meters are used, which are installed on the manifold.
- The number of circuits connected to one collector depends on their length. So, with a circuit length of 90 m or more, no more than 9 circuits can be connected to one collector, and with a circuit length of 60 - 80 m - up to 11 loops.
- If there are several collectors, each has its own pump.
- When choosing a mixing unit (mixing module), it is important to take into account the length of the circuit pipe.
- A more accurate calculation will be based not only on data on heat loss in the room, but also on information about the flow of heat from household equipment and appliances, from the ceiling, if a heated floor is also installed on the upper floor. This is relevant when calculating for a multi-storey building, which is conducted from the upper floors to the lower ones.
- For the first and basement floors, the thickness of the insulation is taken at least 5 cm, for higher floors - at least 3 cm. The insulation on the second floor is used to exclude heat loss through the concrete base.
- If the pressure loss in the circuit exceeds 15 kPa, and the optimal value is 13 kPa, it is necessary to change the flow rate of the coolant downward. You can fit several smaller contours in the room.
- The minimum allowable flow rate of the heating agent in one loop is 28-30 l / h. If this value is higher, then the loops are combined. The low flow rate of the coolant leads to the fact that it cools down without having passed the entire length of the circuit, which indicates the inoperability of the system. To fix the minimum value of the coolant flow rate in each loop, a flow meter (control valve) installed on the manifold is used.


Connecting pipes to the manifold
What is the temperature of the coolant in the water underfloor heating system?
The supply water temperature should be between 40 and 55 degrees. The maximum temperature of the coolant at the entrance to the water floor heating system should not exceed +60 degrees.
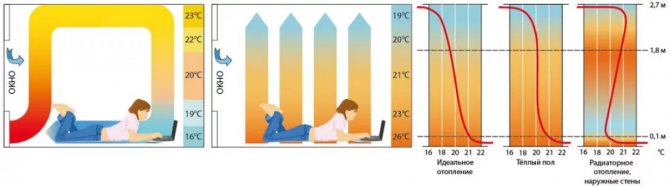
The temperature difference of the coolant between the supply and return pipelines is optimal 5. 15 degrees. Less than five degrees is not recommended due to the greatly increasing flow rate of the coolant through the circuit, which leads to large head losses. More than fifteen degrees is not recommended due to a noticeable temperature drop in the surface of the floor itself (under the windows we can have 27 degrees, at the end of the contour 22 degrees, such a large drop is not comfortable).The optimum temperature drop is 10 degrees. Recommended temperatures at the inlet / outlet of the loops: 55/45 degrees, 50/40 degrees, 45/35 degrees, 40/30 degrees.
If a heat pumping unit is used as a heat source (although this is a great rarity), then it is advisable to take the temperature of the supply coolant into the heating circuit 40 degrees. In all other cases, you can use any other supply temperature in the above range.
The role of a water floor as a main or additional source of heat
A warm floor in a room as a heating system can perform an additional or main function. As an additional system, underfloor heating affects the surface comfort of the floor covering. In this case, the main source of heat is traditional heating radiators. The thermostatic principle of regulation is used to maintain the temperature of the coolant.


Combined heating system
To compensate for heat losses in the room and protect it from temperature changes outside, when the water floor is the main source of heat, it is possible to control the level of heating of the coolant. The warmer it is outside, the lower the temperature of the coolant should be and vice versa.
In fact, a warm floor is a low-temperature type of heating system and, theoretically, the required temperature of the coolant can be obtained by setting the boiler to minimum heating. However, a conventional boiler, tuned to a low-temperature range, is characterized by a sharp decrease in efficiency and from the economic point of view, such a system becomes unprofitable.


Mixing unit
In this regard, there are other ways. For example, the use of a modern heat generator supplying a heat carrier heated to +30 - 50 degrees. When such a boiler is equipped with a circulation pump, each circuit has a heating medium of the same temperature, due to which the most economically efficient process of heating a house with a "warm floor" system is carried out.
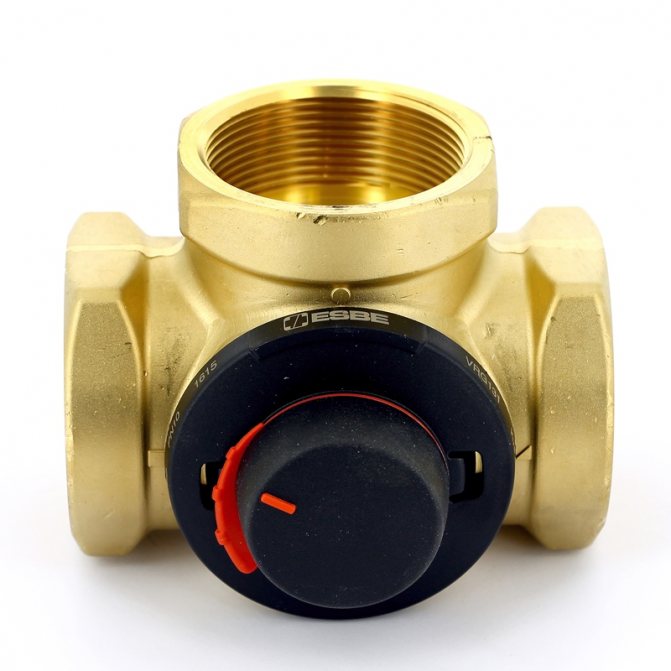


Three-way mixing valve
If the boiler is not equipped with the function of low-temperature operation, then a three-way mixing valve can be used, and the required temperature can be obtained by equipping the mixing unit with a thermostat.
Note! When installing a combined floor covering, for example, made of wood and ceramic tiles, a separate contour is laid under each material, since each of the materials differs in terms of thermal conductivity. The water in the circuits will have different temperatures to create an even heating of a room with such a floor.
It should also be borne in mind that some types of finishing materials are not suitable for a water floor and can be mounted in tandem with film or cable electrical heating systems.


Infrared film for underfloor heating
Additional conditions to be taken into account when designing underfloor heating
- The possibility of combined heating (warm floor + radiators) - in case of large heat loss in the room; the same can be said about water underfloor heating from a solid fuel boiler. This must be determined in advance, because mixing units will have to be used to separate heating circuits with different coolant temperatures.
- Possibility of heating bathrooms in summer with electric heating. (The boiler will not work in the summer, but perhaps someone has a desire or need to heat the bathroom in the summer.)
- How the room temperature will be regulated. Either by the temperature of each room, or by the temperature of the supply water at the inlet to the heating "comb". All this you need to know in order to determine the location of the sensors in the premises.
What affects the operation of a warm water floor
How to ensure that the warm floor really was and creates a comfortable temperature for the floor covering.Often, due to the long circuit length, a high pressure drop value is observed.
For the correct operation of the system in a house with several floors, a separate low-power pump is installed at each level, or one high-power pump is connected to the collector.
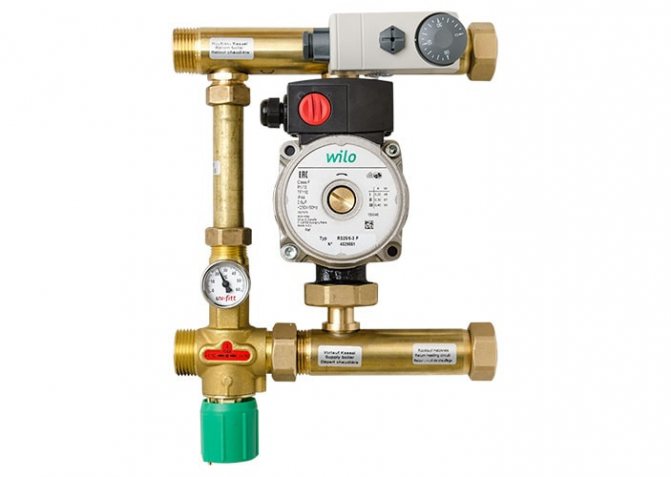


Pump group
When choosing a pump, take into account the calculated data, the volume of the coolant and the pressure. However, it is worth remembering that to determine the level of hydraulic resistance, it is not enough to know the length of the pipe. You will need to take into account the diameter of the pipes, valves, splitters, the laying pattern and main bends. More accurate calculations are obtained using a special computer program into which the main indicators are entered.
Alternatively, it is possible to use standard equipment with already known technical characteristics. The hydraulics of the system, by maneuvering its parameters, is adjusted to the characteristics of the pump.
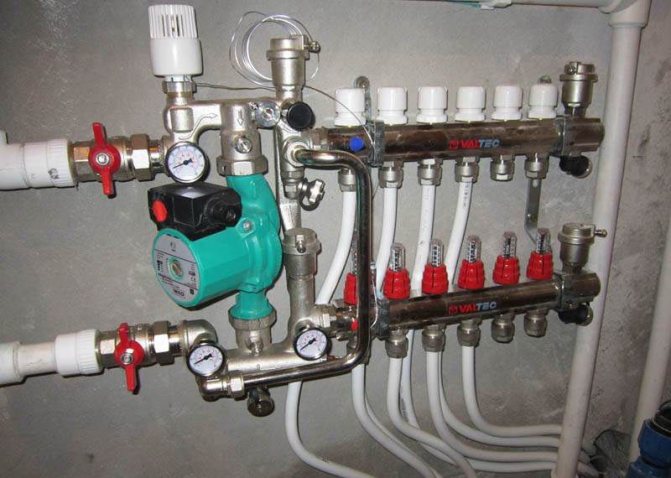


Collector with installed pump
What should be the diameter of the pipes from the boiler to the collector?
The task is to connect one, two or more floor heating collectors.
Almost every underfloor heating collector has a 1 inch (25 mm) thread for connecting to the main line - it does not matter whether it is internal or external.
There are collectors with thread per inch and a quarter, but this is for large industrial or public institutions where a pipe of a larger diameter will be used, so you do NOT need to take such collectors for a private house.
It makes no sense to initially narrow or "widen" the diameters of the main pipes (that is, supplying the coolant from the boiler), but it makes sense to take the same diameter as the collector inlet, that is, 1 inch. For a polypropylene pipe, this is 32 mm in diameter (this is the outer one, and the inner one is just 25 mm). For a metal-plastic pipe, this is a diameter of 26 mm. For copper - 28 mm. These are standard pipe options. But if there are doubts about the number of circuits, then the diameter of the main pipes can be increased by one size (40, 32 and 32 mm for polypropylene, metal-plastic and copper pipes, respectively; an adapter is required to go 1 inch).
Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) have the same dimensions with metal-plastic ones in wall thickness and diameters.
Heat distribution: features
Since the area of the premises in the house is different, the contours also have different lengths, therefore it is necessary to ensure the same hydraulic pressure in all parts of the system. It should be borne in mind that the pump is a constant.
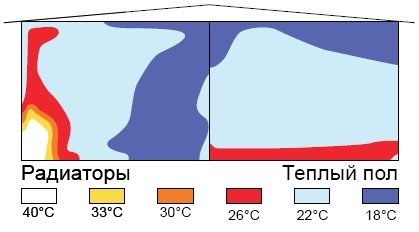

Distribution of heat from different sources
The supply of the same volume of water to the circuits of each length leads to the fact that in the longer one the coolant cools faster and at the outlet its temperature will differ from the coolant of the shorter profile. As a result, the floor surface will warm up unevenly - somewhere overheating will be observed, but somewhere on the contrary, the coating will be cold.

The advantage of using underfloor heating
Due to the high hydraulic resistance, the coolant may not enter at all into a long circuit, since it will move into shorter circuits with less resistance. To prevent this from happening, the system is equipped with a distribution manifold, which allows you to maintain a balance of supply and uniform heating of the coolant in each loop.
How to calculate the number of pipes
At the design stage, after all the calculations have been made, it is possible to understand how many pipes in running meters may be required. This will allow you to estimate the cost of the material.
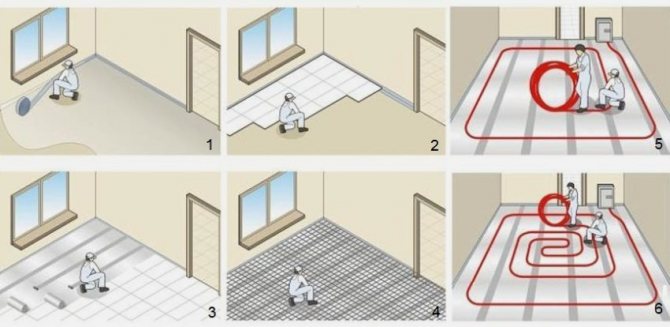

The main stages of installation
So, with a room area of 12 m², the air temperature should correspond to + 20 degrees. The width of the edge sections along the walls with furniture should be 30 cm.If one wall is 6 m long, and the other two are 2, then the working area of the system can be calculated using the following formula: 12 - 0.3 * (6 + 2 + 2) = 9 m².
Note! The pitch and diameter of the pipes depends on the level of heat loss. The smaller they are, the larger or smaller the pipe diameter is.
When determining heat loss in a room, the glazing area, the characteristics of the insulation used in the enclosing structures, and the height of the room are taken into account. The value obtained varies in the range from 20 to 300 W / m², depending on the thermal efficiency of the structures and the glass units used, the thickness of the walls and the number of openings.
Underfloor heating is a serious cost item for renovation, so it is important to calculate exactly how much and what materials will be needed. To ease your labor costs, we have prepared a special instruction telling you how to calculate the warm floor - water or electric. Online calculators are included. And in the article "What is needed for a warm floor?" you will find a complete list of everything you may need during installation.
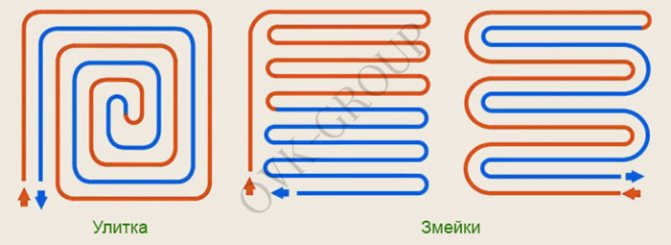
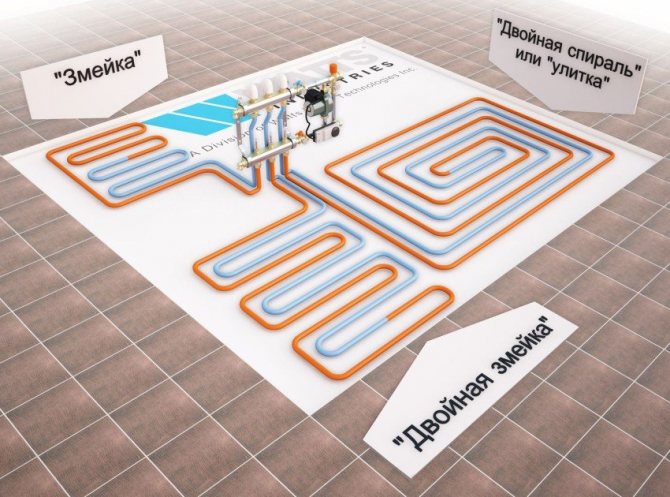
Popular pipe laying schemes and their features
The main schemes for laying pipes with a coolant include "snake" and "spiral", and other laying options based on them are often used, for example, a "snake" without edge zones.
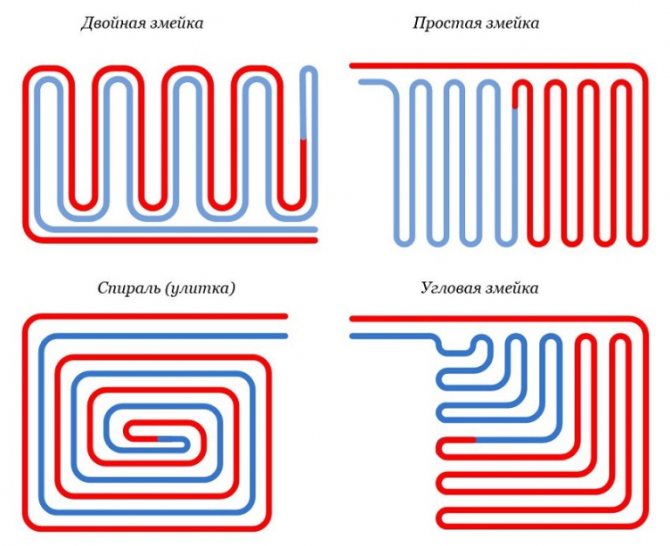

Common styling methods
"Snake" is a convenient option, which can be easily fitted in a small area, but the pipes are heated unevenly in this case. Therefore, pipes are laid along the wall, characterized by large heat losses, which are located closer to the collector (at the beginning) and warm up better.


The pipe-laying step according to this scheme should not be more than 30 cm, otherwise the flooring will have an uneven temperature - the heat will be felt over the pipes, and the cold between them. The distance between the extreme pipes is made 20 cm or less.
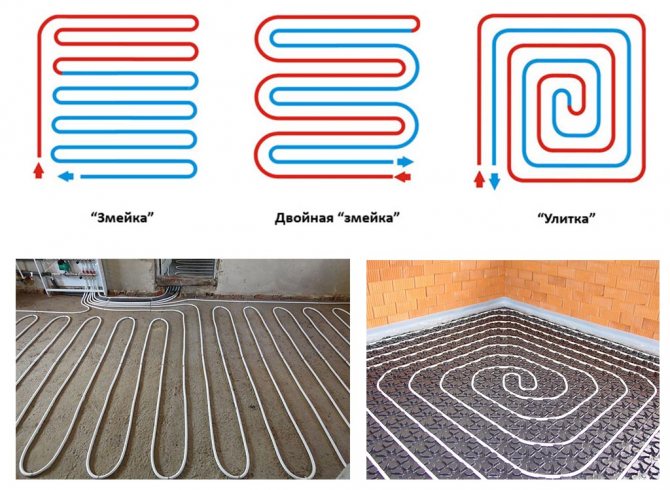

"Snake" and "spiral" - the best ways to form a contour
Note! So that when laying pipes according to the "snake" scheme, the heating of the floor surface is still uniform, a second (reverse) snake is laid.
The "spiral" scheme is characterized by such a laying method in which the supply and return pipes are placed parallel to each other. Due to this, the issue of uneven heating of the floor is solved, and the temperature above both pipes is approximately equal.

Styling options
The spiral type of installation is most relevant for large rooms, with the distance between the pipes being 20 cm.
Necessary calculations before installation
The basic calculations of warm water floors are based on the operation scheme: light heating of the floor covering to create a comfortable atmosphere or full heating of the room. To calculate and design a warm floor, the following room characteristics are used:
- Area.
- Floor height.
- Materials used in construction.
- Room glazing type, incl. window profile and type of glass unit.
- Features of the local climate (including minimum values of air temperature).
- The presence or absence of additional heating sources.
- Indoor air temperature.
- Floor thickness.
- Floor type.
- The presence or absence of base insulation.
- The shape of the room.
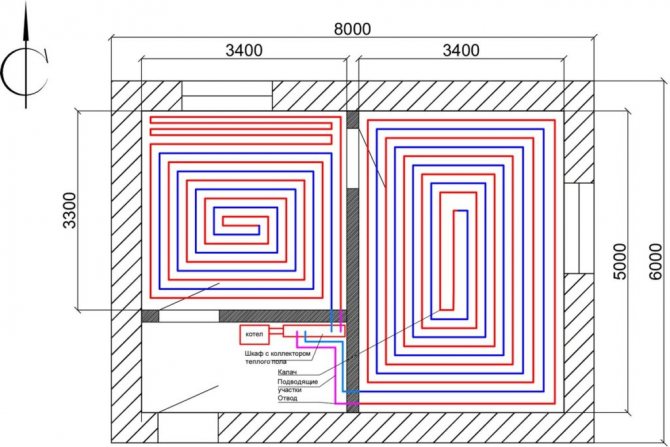

An example of a calculation for a private house before installing the pipeline along the length and width of the room. Installation of two circuits in different rooms with connection to a cabinet with a manifold.
During the calculation, the length, diameter, pipe pitch, length of the water floor contour, as well as the required pump characteristics are determined:
| Desired calculation | Calculation method |
| Pipe calculation | The area of the room is divided by the pipe step size, multiplied by a factor of 1.1, then the required length from the collector to the floor is added to the obtained value. |
| Water circuit length | The maximum length is 100 meters. For large rooms, two or more contours are laid. |
| Pipe laying step | The thicker the flooring and the lower the air temperature in winter, the smaller the pipe pitch. The laying interval is 100, 150 or 200 mm. |
| Calculation of the pump head | It is best to choose a variable power pump.Formula: the hydraulic resistance of a running meter of the tube is multiplied by the length of the largest circuit, the power reserve is added and divided by 1000. |
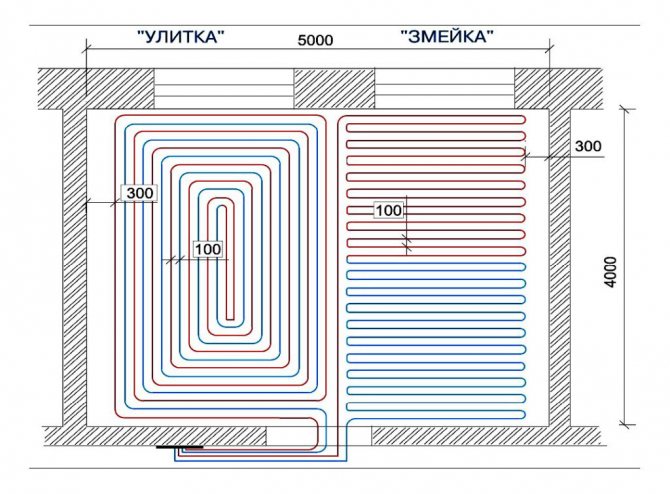

Calculations of the pipe laying step, observing the required distance to the walls. For different types of laying ("snail" and "snake") the pitch between the tubes should be the same, in this case - 100 mm.
Miscalculations will lead to an inefficient use of materials, a significant investment of time, effort and finance, up to the dismantling of the floor covering and screed.
Installation of underfloor heating: features
One of the design stages includes the creation of an installation scheme, which will subsequently need to be adhered to when performing work directly on the site.
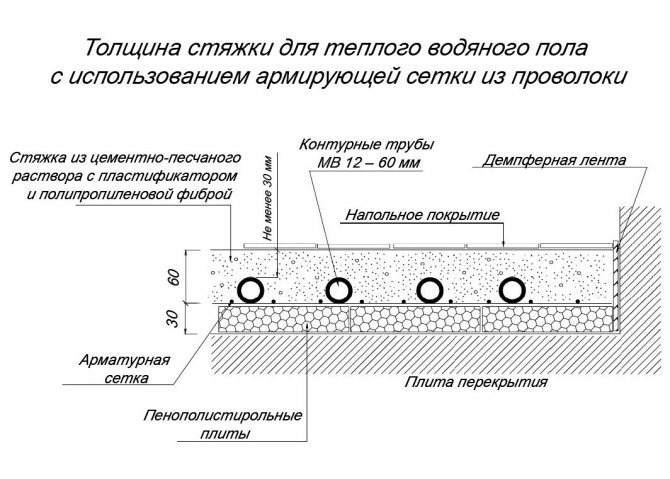

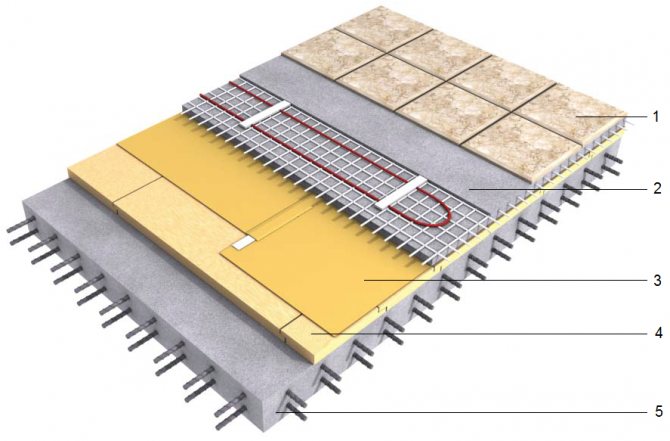
Floor cake with pipes inside the screed - optimal thickness
The following points should be reflected in the installation diagram:
- A plan for dividing the base surface into several sections. This stage cannot be ignored when pouring a screed over a large area, since thermal expansion in this case leads to its destruction. The division into separate sections allows the formation of expansion joints between them. In this case, one section should not exceed 40 m², and the rooms of the L and U-shaped configuration are divided into sections, regardless of their area.


Principle of laying on mats
- In the installation diagram, there should be a reference to the presence of expansion joints, which are filled with a damper tape, elements from extruded polystyrene foam or expanded polyethylene. Inside the seam, the pipes are placed in a casing, for example in a corrugation.
- The project specifies the way in which the pipes will be laid - this will allow purchasing the necessary material in a certain amount. They also reflect the way the screed is installed - wet, semi-dry or dry.
- They calculate the temperature of the pipes - this will help to determine the final floor material, the manufacturer of which indicates the compatibility of the material with the "warm floor" system and its permissible heating. So, the parquet can be heated up to 25 degrees - no more.


Screed laying principle
Prices for warm floors Caleo
warm floors Caleo
Video - 5 key rules for installing a water heated floor
Pipe installation process
Designing a water-heated floor is not complete without laying out the pipe system.
As a material in this case, you can use:
- polyethylene. This material is characterized by high density, which also affects the strength indicators. Pipes made of polyethylene are difficult to bend, which also helps to minimize cracks;
- metal-plastic. The level of heat transfer from such a material is slightly higher than that of its opponent, which has a positive effect on the level of heating of the entire room.


As for general tips for laying a pipe system, the layout of a warm water floor should be carried out in accordance with the following recommendations:
- If the room itself is cold, the pipe system should be laid more tightly. The distance between the pipes along the outer walls should be less than in the center.
- It is also recommended to retreat from the wall 15 cm, and also keep in mind that the minimum to show the location of the pipes relative to each other should be 10 cm, and the maximum - 30 cm.
- The total length of the system should not exceed 100 meters, as this will lead to a decrease in efficiency (about