Necessary properties and requirements for the shell for pipe insulation

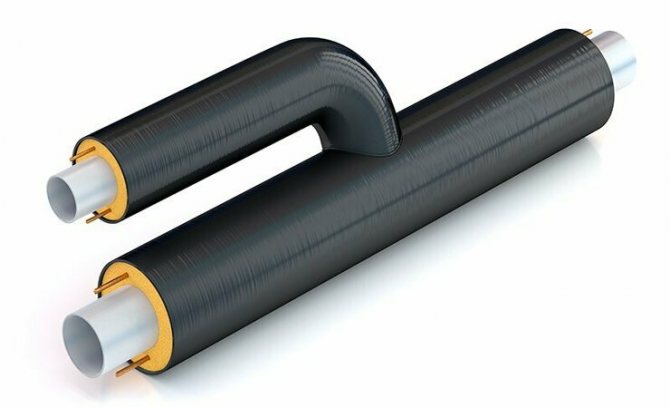
Insulation shell with a lock for fastening on a pipe
The shell for pipes is a cylinder, notched on one side, or segments that are fastened together according to the groove-comb principle. Insulation without grooves can be fixed with clamps, wire, glue. After fixing, a protective casing is formed on the pipe surface.
Shaped elements are provided for insulating tees, branches, bends, abutment angles. To connect the shell along the length, use a separate shaped element - a sleeve.
Such communication protection does not insulate, but avoids heat dissipation or heating due to high ambient temperatures.
The shell must correspond to the diameter of the pipeline on which it will be mounted. The material from which the insulation is made must be resistant to low and high temperatures.
The main requirements for thermal insulation for pipes:
- long service life;
- easy installation;
- insignificant thermal conductivity;
- resistance to mechanical stress;
- protection against burns in case of accidental touch;
- biological and chemical passivity;
- the ability to maintain a constant coolant temperature.
Different materials have different characteristics from each other. Taking into account the conditions in which the insulation will be installed, it is possible to choose a shell for pipes with suitable parameters.
How to properly insulate pipes with expanded polystyrene
The most difficult work on insulation is the insulation of large-diameter pipes; at your site, this procedure can be carried out independently using a foam sheath. The work is carried out in the following order:
- A trench is dug along the route of the pipeline location at the middle mark of the level of soil freezing (you can get the necessary data from the Internet using special maps for different areas, depending on the soil).
- Sand is poured into the ditch with a layer thickness of 10 - 20 cm.
- The condition of the pipes is checked - they must be dry, moisture under the insulation can lead to their corrosion, and installation must also be done in dry weather. The surface of metal pipes is treated with anti-corrosion material.
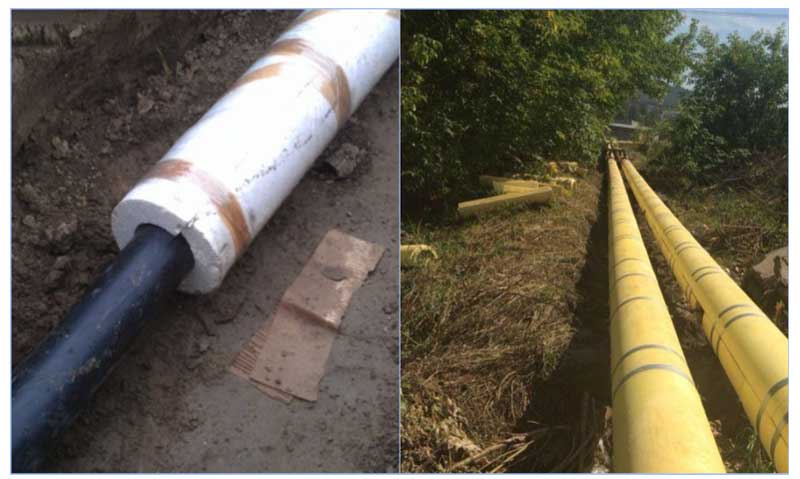


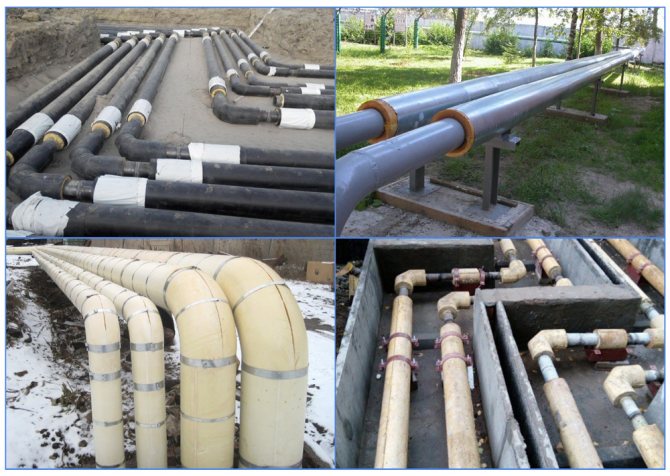
Fig. 7 Insulation with shells - method of installation on pipelines
- The assembled pipeline system is laid on the bottom of the pit in such a way that there is a gap in the lower part for the thickness of the shell.
- A pre-purchased shell, corresponding to the diameter of the pipe, is installed in such a way that parts of one half are tightly connected to the others. When installing, it is better to carry out the work together - one person will tightly squeeze the segments, and the other will fix them with tape. During installation, you can use glue, but the process will take much more time, it will be economically unprofitable, and the connection itself will be impossible to disassemble later.
- It is better to cut corner joints at the installation site using a conventional wood hacksaw.
- After installing the shell, its surface is covered with a special protective coating that is supplied in the kit. If it is absent, the casing can be covered with polyethylene foil.
- After installation, the trench is covered with sand 10 - 20 cm above the level of the pipeline, then the surface is leveled with earth.
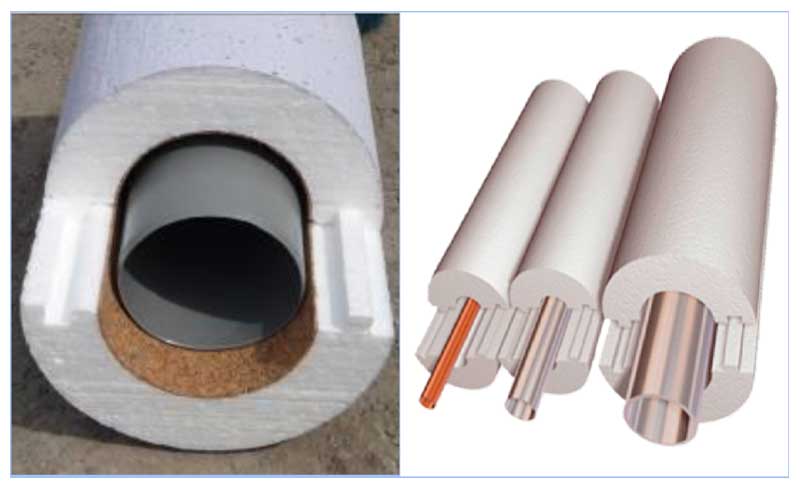


Fig. 8 An example of the use of polystyrene foam shells for pipe insulation
Insulating materials for the manufacture of shells


The shell material is selected depending on the operating conditions of the pipes
The range of modern insulating materials fully complies with the listed requirements. Shells for pipe insulation are made from the following materials:
- polyurethane foam;
- expanded polystyrene;
- basalt insulation;
- foamed polyethylene;
- synthetic rubber.
Insulation is insulated in order to protect against mechanical damage and increase the efficiency of insulation:
- foil;
- fiberglass and fiberglass;
- galvanized and stainless steel.
Polyurethane foam
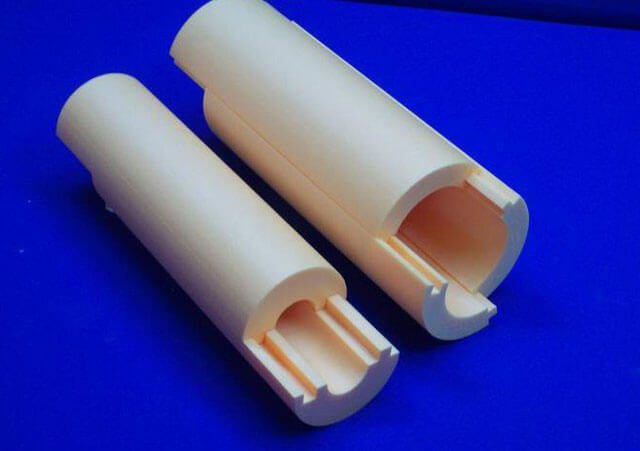


Polyurethane foam does not absorb water, therefore it is used for underground utilities
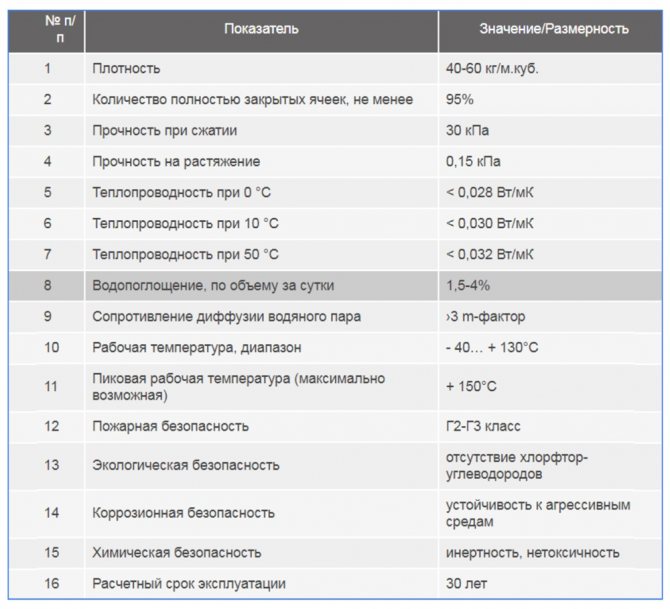
Polyurethane foam is a material with a fine-bubble closed-cell structure. It contains approximately 95% closed cells. PPU shell for pipes has the following technical characteristics:
- low thermal conductivity (0.037-0.042 W / m2 * K);
- high density (40-60 kg / m3);
- does not absorb water (1.5-3%);
- operating temperature range: -180 ° C to + 130 ° C.
Before installing the PPU shell for pipe insulation, the steel pipeline must be treated with anti-corrosion compounds, because the condensate formed due to the temperature difference remains under the shell and causes corrosion.
Fixation with the help of additional elements leads to the formation of seams, due to the presence of which heat loss increases. In order to seamlessly join the segments, polyurethane glue is used; it is recommended to fill the free space with polyurethane foam.
Expanded polystyrene
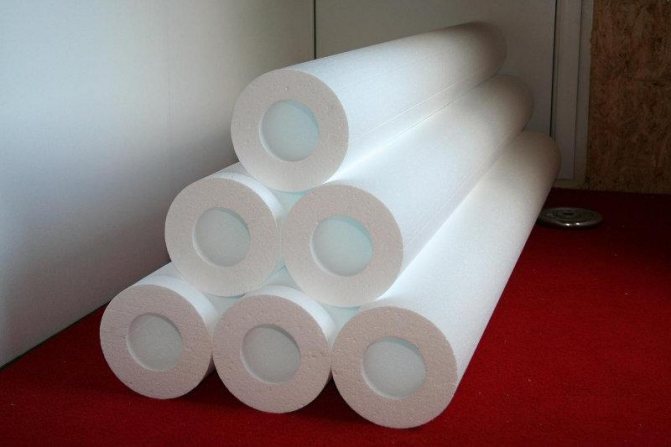


Styrofoam cannot be used without isolation from sunlight
The polystyrene foam shell is used mainly for warming ventilation, water supply, sewer pipelines located in the ground, since the material has low resistance to ultraviolet radiation. It causes destruction of the structure. When insulating above-ground communications, it is necessary to wrap the shell or paint with something.
Benefits:
- does not absorb moisture;
- shows resistance to biochemical effects;
- withstands significant static load.
Disadvantages of Styrofoam:
- fire hazardous;
- not resistant to mechanical stress.
The working temperature range of expanded polystyrene is from -50 ° C to + 80 ° C.
Basalt insulation
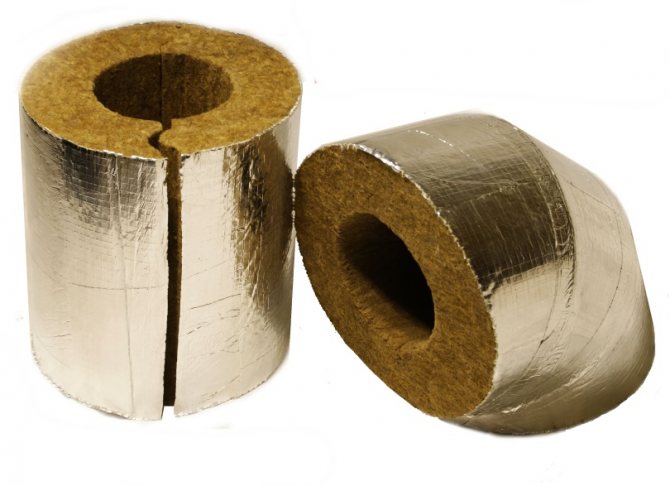


Basalt wool is not used for insulating pipes located in the ground
It is recommended to use basalt shells for insulation of the external pipeline. Its main disadvantage is high water absorption, which cannot be compensated even with the help of hydrophobic impregnations. Once wet, the shell completely loses its thermal insulation properties. Operating temperature range: -40 ° C to + 74 ° C.
Benefits:
- light weight;
- Fire safety;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- environmental friendliness;
- biological resistance.
Disadvantages: used only for insulation of plastic pipes.
It is recommended to glue the seams of the basalt wool shell with reinforced tape or construction tape, and then paint.
Foamed polyethylene
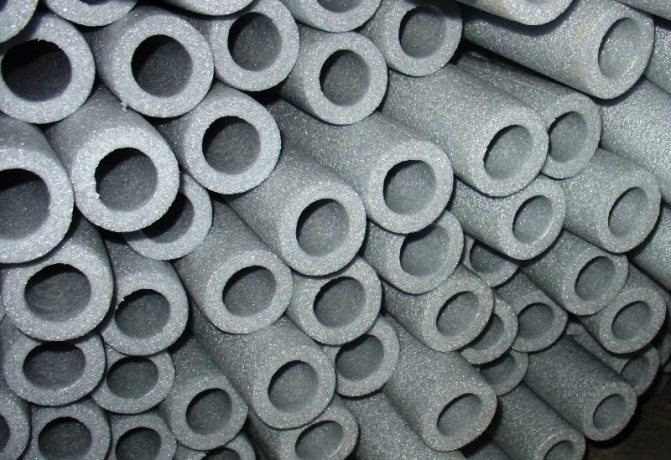


Foamed polyethylene does not absorb moisture
A polyethylene foam shell is a flexible and lightweight material in the form of a cylinder 1.2 or 2 m long with a slot. The operating temperature range varies from -40 ° C to + 95 ° C. Due to the special plasticity of the material, it is recommended to fix it with plastic or metal tightening clamps.
Benefits:
- relatively low price;
- has the properties of a steam, noise and heat insulator;
- resistance to aggressive environment;
- protects against the development of corrosion;
- environmental friendliness.
Disadvantages: Absorbs moisture.
Due to the high degree of water absorption, it is necessary to waterproof the shell from foamed polyethylene.
Synthetic rubber


Synthetic rubber is not afraid of moisture and ultraviolet radiation, suitable for any communications
Synthetic rubber is superior to many materials in its performance characteristics. The insulating shell made of this material is produced in the form of cylinders with a longitudinal cut, which can be mounted by putting the casing on the pipeline and gluing along the cut.
Benefits:
- UV resistance;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- the minimum level of water absorption;
- effective insulation;
- vapor tightness;
- long service life;
- resistance to mechanical stress.
In order to improve its appearance, the insulation is painted with paint.
Features of each
As materials do not claim to be versatile, each has installation and operation features that determine the scope of their application.
Styrofoam
Insulation for PPU, PPS pipes has structural locks for reliable connection and exclusion of the formation of cold bridges. PPU shell is recommended for thermal insulation of networks laid in the ground. Insulation made of PPP, PU foam for pipes is characterized by low resistance to sunlight. In direct sunlight, the structure of the thermal insulation is destroyed. The shell made of polyurethane foam has zero moisture absorption, high biochemical stability, and extreme fire hazard.
The shell of PPU, PPP can withstand a large static load, without shrinking under the weight of the earth, while maintaining thermal insulation properties.
When laying outside, it is recommended to protect the polyurethane foam insulation from ultraviolet radiation by painting or wrapping.
cold lock
Basalt based
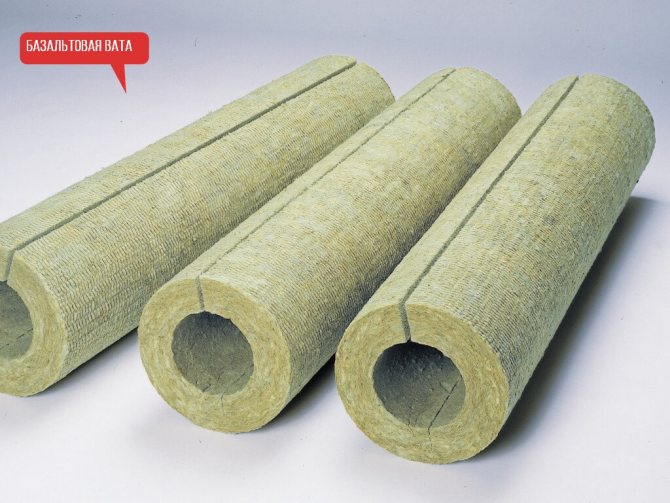


Basalt wool shell
Heat-insulating basalt shells are most expedient to use when insulating an external pipeline. The main argument confirming this is excessive water absorption of the material. Saturation with water leads to a complete loss of thermal insulation properties. It is restored only after the basalt fiber has completely dried. The use of hydrophobic impregnations does not significantly affect this indicator.
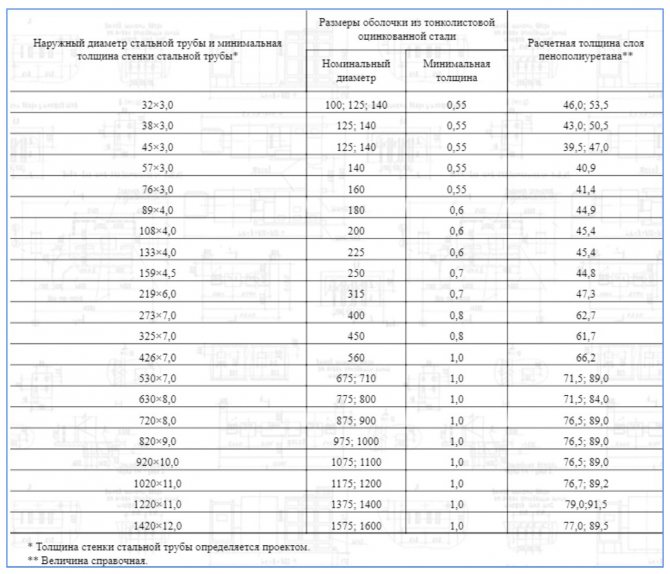
Dimensions and diameters


The size and thickness of the insulation layer is selected depending on the operating conditions
The shell is used for thermal insulation of aboveground and underground utilities. The protective cover is formed of two or more segments connected to each other. The larger the shell diameter, the more segments. The shell of a soft and flexible material, such as polyethylene foam, can be made in the form of a cylinder with a longitudinal cut. Shells of relatively dense material for small pipe diameters up to 2 inches are composed of semi-cylindrical segments. If the pipe diameter is 2 to 3 inches, the segments are narrower than 3. For larger diameter pipes, shells consisting of quarter-circle segments are suitable.
The inside diameter of the shell must match the outside diameter of the pipe.
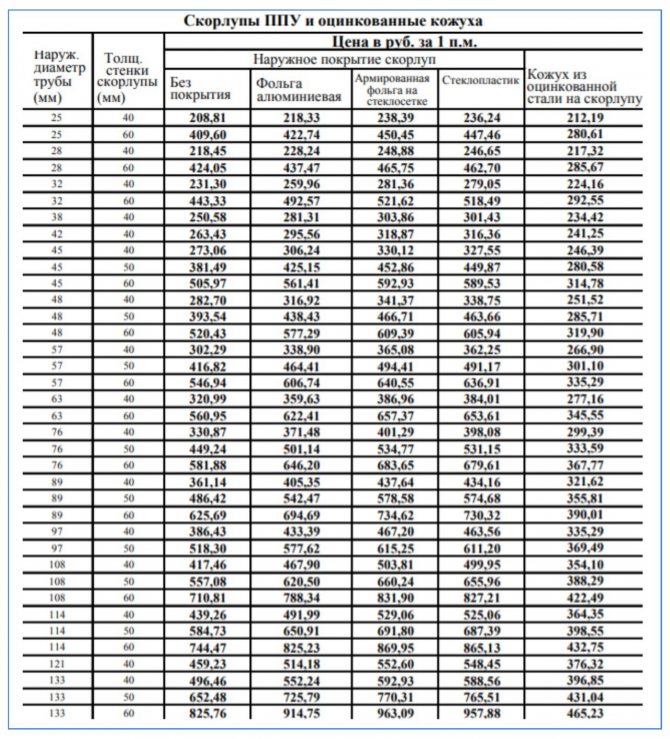
The thickness of the insulation from which the shell is made varies from 9 to 90 mm. Insulation with a larger diameter and thickness will cost more. According to this parameter, the shell is selected taking into account the requirements for the effectiveness of thermal insulation.
Lengthwise dimensions also range from 1 to 2 m. The latter characteristic is determined by the ease of transportation, manufacture and installation.
Methods of obtaining and types of coatings
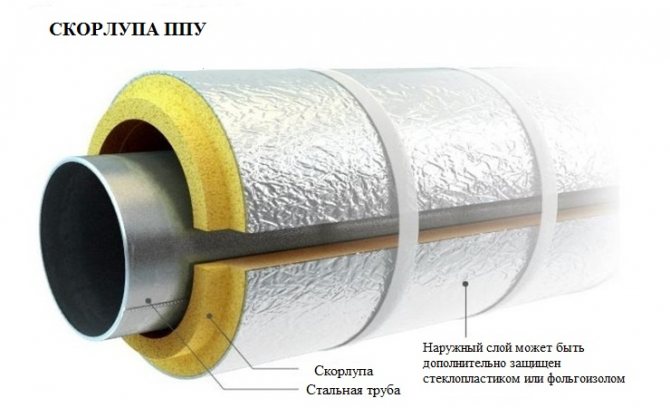
For the needs of industrial and civil construction, new heating mains are manufactured so-called. pre-insulated pipes. At the same time, the prepared polyurethane foam fills the space between the insulated object and a special formwork with a larger diameter. The result is a finished product, on the surface of which a protective polyurethane foam layer is already applied.
PU foam shells are manufactured in accordance with industry standards and specifications. Depending on the operating parameters defined by the area of application and the pumped media, they are produced in two types:
| Brand | Temperature range, ° C |
| CT1 | from 100 to 120 |
| CT2 | from 100 to 150 |
Polyurethane foam shell can be produced without coating or have a protective layer: foil, fiberglass, glassine, galvanized steel, which depends on the operational and strength characteristics of the structure. Shells without additional protection with a casing are used indoors or serve as the bottom layer of insulating "pies".
The main types of thermal insulation coatings for pipes:
- Foil (foilopergamine). It is used indoors and to protect internal communications. Not suitable for heating mains with channelless or duct laying.
- Reinforced foil (armafol). Recommended for economical insulation of both indoor and outdoor networks. Protects from the effects of precipitation in conditions of significant temperature changes.
- Moisture resistant or fiberglass. Suitable for all types of outdoor air piping. Provides a durable outer insulating layer, reliably protects against UV rays. Withstands mechanical loads and is considered optimal in terms of strength properties.
- Glassine (bituminous paper). The roofing material is resistant to ultraviolet light, but is inferior to fiberglass in strength.
- Galvanized steel casing. It is used for main networks of open laying, technological lines, gas and oil transportation systems. Serves both ultraviolet and anti-vandal protection, and the cost is even preferable to fiberglass.
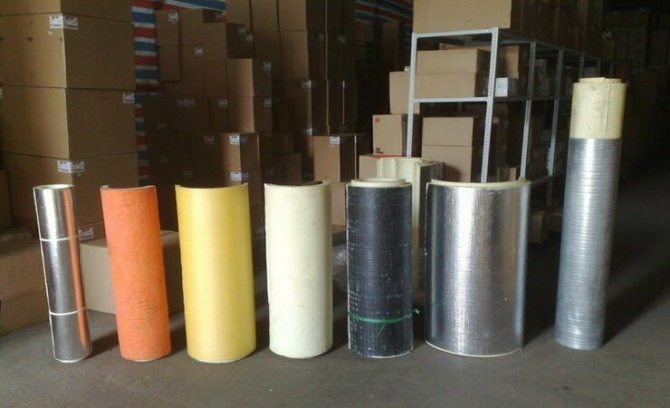


The variability of insulation will help to ensure the required quality and reduce your costs
Polyurethane foam shell for pipes withstands more than 1,000 freezing cycles without changing consumer properties. And if you follow the recommendations for transportation and storage, it allows you to increase the service life of technological communications.
Advantages of shells for pipe insulation

PPU shell is easily mounted, is not afraid of high and low temperatures, but needs shelter from ultraviolet radiation
Polyurethane foam shell is most suitable for pipe insulation. This insulation has a number of advantages:
- multiple use;
- resistance to mechanical, biological, chemical, atmospheric influences due to high density and chemical composition, including resistance to rodents and pests;
- durability;
- easy and quick installation at any temperature;
- possibility of installation without the use of additional fasteners;
- environmental friendliness;
- quick dismantling if necessary to repair a section of the pipeline;
- use in the insulation of underground and aboveground communications;
- does not make the structure heavier;
- shows inertness to fungi and mold;
- light weight;
- insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- noise insulation properties.
At a pipeline temperature above + 150 ° C, the insulation cokes. In addition, it collapses under the influence of ultraviolet rays, therefore, a prerequisite for warming overhead communications is the presence of a protective coating.
Physical and mechanical properties of uncoated products (PPU shells)
| Indicator name | Norm for the brand | |
| CT1 | ST2 | |
| Apparent density, kg / m3 | 30 to 50 | St. 60 to 80 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W / (m K), no more | 0,030 | 0,035 |
| Tensile strength, MPa, not less | — | 0,4 |
| The number of closed pores,% not less | — | 85 |
| Water absorption in 7 days, cm3 / m2, no more | 200 | 250 |
| Vicat heat resistance, оС, not less (at a load of 1 kg) | 120 | 150 |
| Flammability group (according to SNiP) | G4 | G4 |
Basics of installation and operation
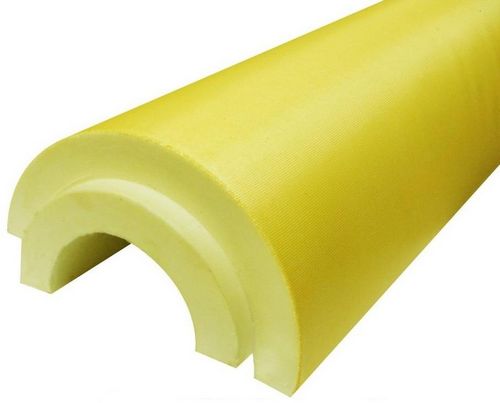


The joints should be coated with glue to reduce heat loss.
Before installing the shell, the pipes must be inspected to exclude the risk of leaks. Then the pipeline should be cleaned from traces of corrosion and primed twice.
Insulation segments should be installed with an offset of the longitudinal seams by 5-10 cm. For the insulation quality to be higher, the joints should be glued with foil or ordinary tape.
Having closed the pipeline with a protective casing, the insulation should be fixed with clamps, wire or steel tape. Then, on top of the shell, if there is no factory protective coating, roofing material, fiberglass or roofing paper are wrapped. The protection is also secured with plastic or metal clamps. The joints are coated with glue to reduce heat loss.
Together, in an 8-hour working day, you can insulate up to 150 m of the pipeline.
Installation nuances
First of all, when installing the shell, it is necessary to determine the diameter of the pipeline - in order to be able to select the appropriate shell diameter.
If it is larger than that of the pipe, the insulation will dangle on it. If it is larger, the insulation will have gaps: the shell segments simply will not converge.
To fasten the segments (we will consider this particular option, and not the whole shell - it is the most relevant), the following can be used:
- Wire - in this case, the applied thermal insulation is wrapped around it.
- Glue - joints (both longitudinal and transverse) are lubricated and glued.
- Groove - the halves are connected with a latch. Adjacent segments - can be connected either with a snap or with glue.
- Duct tape.
The first option is good because it allows you to get a detachable connection: if necessary, you can simply unwind the wire, get a "bare" pipeline, and after completing the inspection (or work), put the insulation back.
The glued segments will only have to be cut. However, they can then be glued together, but the quality of the connection will already be significantly lower. And every extra gap is a cold bridge.
A groove connection is suitable where there are no difficult conditions, and there is no need for a maximally sealed structure. The same is with the adhesive tape: it allows you to reliably fasten the heat-insulating segments, eliminating the gap, it is easily and quickly removed, allowing you to dismantle the casing, but it will not withstand difficult conditions.
Shell use (video)
Stages of work
Thermal insulation of this type is mounted as follows:
- The pipeline is stripped of old and unnecessary insulation (if used and not required).
- Measurement of the areas that need to be insulated.
- The number of shell segments is calculated.
- Insulation is mounted from one “barrier” (it can be a flange, turn, joint, reinforcement) to another.
- Each segment is fixed in the chosen way (glue, groove, wire, or their combination).
- If several fastening methods are used (for example - groove and tape, or groove, glue and tape, or any other combination) - the second (third, fourth) fastening tool is used.
- Each segment is installed so that its transverse joint (cut) does not coincide with the joint of the adjacent one.
- If surface protection is used, it is installed and joints are sealed.
- If necessary, the areas that could not be insulated with a shell are insulated separately (in other ways: with a heating cable, roll materials, spraying, paint).
Scope of application


Insulation of sewer and water pipes reduces the risk of plastic rupture in winter
A shell for insulating pipes made of polyurethane foam or other material is used to maintain a constant temperature of the medium circulating inside the pipeline, to protect people from burns at high or low pipe temperatures. This material is used for insulation:
- sewer pipes;
- cooling lines;
- hot and cold water supply networks;
- chemical synthesis systems;
- pipelines in the oil and gas industry.
The high speed and ease of installation distinguish the shell from the insulation materials of a different form factor. Due to the high efficiency of insulation, environmental friendliness, ease of use, the shell for pipe insulation is popular in the field of public and private construction, industry.
Expanded polystyrene casings
If we compare the shell for pipes made of expanded polystyrene (foam) with a product made of polyethylene, then the technical characteristics of the second are inferior to the first.
Due to its rigid structure, the PU foam shell almost does not absorb moisture. The operating temperature range is -50 ° C + 80 ° C. Composite elements are connected by a lock or lockless method.
Such material is used for the installation of sewer pipes, water supply, ventilation. It is used when the branches of the highways are laid directly in the ground.
Foam cylinder in two halves
Advantages and disadvantages
The benefits of using shells include:
- comparative cheapness (compared to using a heating cable), the possibility of insulating both newly created and already functioning lines, ease of installation and the absence of the need for a large "arsenal" of tools.
There are also disadvantages:
- the need to accurately select the diameter of the shell for the diameter of the pipe (while roll insulation does not require this); difficulty when passing pipe sections in the wall; difficulty when passing bends, branches, diameter transitions; inability to insulate flange sections, the location of filters, valves, return fittings ; the presence of seams (longitudinal and transverse), which remain after joining the shell segments.
Materials used
The key parameters of any heat insulator depend on what kind of material it is. The main characteristic is thermal conductivity, so we will make a list of heaters, taking into account only:
Mineral wool galvanized shell on the pipeline
- Polyurethane foam (PPU) - up to 0.03 W / mK. Expanded polystyrene (foam) - about 0.045 Extruded polystyrene foam - about 0.035-0.04. Mineral wool and "related" materials (basalt, stone, glass wool) - about 0.045. Foamed rubber shell - about 0.04 Crosslinked polyethylene - about 0.035-0.04.
In case of possible contact with moisture, you should also take into account how well the insulation tolerates it. From the above list, only mineral wool products do not "like" moisture too much, which begins to cake and can crumble.
1.1 Styrofoam shell
A shell made of polystyrene (expanded polystyrene) for thermal insulation is made of rigid materials and is produced in the form of two halves of the same size, which can have two docking systems: a locking system, and, accordingly, a lockless one. The advantages of this insulation material are as follows:
- High thermal characteristics; The material does not absorb moisture at all; A fairly large range of permissible operating temperature (from -50 to +70 degrees Celsius).
The foam shell also has one significant drawback, namely the high price for relatively small volumes of material.
1.4Foam polyethylene shell
This thermal insulation material is produced in the form of a cylinder, which has a special slot for ease of use and installation. Among the advantages of this heat-insulating material, the most important should be noted:
- Greater flexibility of the material; The ability to install the product on pipelines of different diameters (versatility); Relatively large range of operating temperatures (from -40 to +95 degrees Celsius).
However, this heat-insulating material is not without its drawbacks, and the most significant of them are as follows:
- The material absorbs moisture, therefore, after its installation, additional installation of waterproofing is required; The need to create an attachment on the surface of the pipeline. As a rule, scotch tape is used for this, which, in addition to fastening, is also an impromptu waterproofing layer.