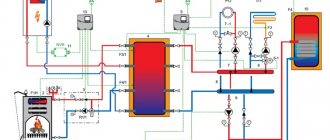
The expansion tank (expansomat) is an important element of the heating system, equalizing pressure indicator and maintenance volume of the heating medium during its thermal expansion and contraction.
Before installing the device, it is necessary to correctly calculate its volume.
Odnoklassniki
Possible problems
First, let's look at the consequences of incorrectly calculating the expansion tank for a closed heating system. Perhaps you also have an unusable reservoir for your system, and you do not even know about it. If the volume of the tank has been calculated correctly, there will always be a stable pressure in the circuit. It doesn't matter if your system is open or closed, the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating both types is similar, since the principle of their operation is approximately the same. The bottom line is that the water in the pipes acts as a heat carrier.
That is, it carries heat around the entire circuit and gives it away through radiators and pipe walls. Thanks to this, the room becomes warm. In this case, the amount of water always changes. After it heats up, there is more of it, and after it cools down - less. It is impossible to squeeze water mechanically, which means that you need to temporarily remove its excess from the circuit. And it is necessary in such quantities that the pressure in the system is always kept at the required level, without drops. So we come to the main thing - these are pressure drops.
If pressure drops occur in the circuit, these are the first bells of malfunction. This may be due to the incorrectly calculated volume of the expansion tank for the heating system.
Calculation of the volume of the coolant in pipes and boiler
The starting point for calculating the technical characteristics of the components is the calculation of the volume of water in the heating system. In fact, it is the sum of the capacity of all elements, from the boiler heat exchanger to the batteries.
How to calculate the volume of the heating system yourself, without the involvement of specialists or the use of special programs? To do this, you need a layout of the components and their overall characteristics. The total capacity of the system will be determined by these parameters.
The volume of water in the pipeline
A significant part of the water is located in pipelines. They occupy a large part in the heat supply scheme. How to calculate the volume of the coolant in the heating system, and what pipe characteristics do you need to know for this? The most important of these is the diameter of the line. It is he who will determine the capacity of the water in the pipes. To calculate, it is enough to take data from the table.
Pipes of various diameters can be used in the heating system. This is especially true for collector circuits. Therefore, the volume of water in the heating system is calculated using the following formula:
Vtot = Vtr1 * Ltr1 + Vtr2 * Ltr2 + Vtr2 * Ltr2 ...
Where Vtot
- total water capacity in pipelines, l,
Vtr
- the volume of the coolant in 1 lm. pipes of a certain diameter,
Ltr
- the total length of the line with a given section.
For plastic pipes, the diameter is calculated according to the dimensions of the outer walls, and for metal pipes - according to the inner ones. This can be significant for long-distance thermal systems.
Calculation of the volume of the heating boiler
The correct volume of the heating boiler can only be found from the data of the technical passport. Each model of this heater has its own unique characteristics, which are often not repeated.
The floor standing boiler can be large. This is especially true for solid fuel models.In fact, the coolant does not occupy the entire volume of the heating boiler, but only a small part of it. All liquid is located in a heat exchanger - a structure required to transfer thermal energy from the fuel combustion zone to water.
If the instruction from the heating equipment has been lost, the approximate capacity of the heat exchanger can be taken for miscalculations. It depends on the power and boiler model:
- Floor standing models can hold from 10 to 25 liters of water. On average, a 24 kW solid fuel boiler contains about 20 liters in a heat exchanger. coolant;
- Wall-mounted gas ones are less spacious - from 3 to 7 liters.
Taking into account the parameters for calculating the volume of the coolant in the heating system, the capacity of the boiler heat exchanger can be neglected. This indicator varies from 1% to 3% of the total heat supply of a private house.
Without periodic cleaning of the heating, the cross-section of pipes and the bore diameter of the batteries are reduced. This affects the actual capacity of the heating system.
How do the drops occur?
Possible options:
- increase;
- lowering.
Both processes are interconnected. An increase in pressure in the circuit means that the coolant has nowhere to go after it has increased in volume. One of the reasons, not the only one, may be the incorrect calculation of the expansion tank for closed-type heating. How does this happen in practice? Take, for example, a circuit containing one hundred liters of coolant:
- there is one hundred liters of cold liquid in the system;
- the boiler turns on and heats the coolant;
- the water expands and it becomes no longer a hundred, but approximately one hundred and five liters;
- excess liquid must go somewhere. For this, an expansion tank is installed in the circuit;
- after the coolant cooled down, it was not enough in the circuit, as part of it squeezed out into the tank. Accordingly, the water must be returned to the pipes, which happens if everything is fine.
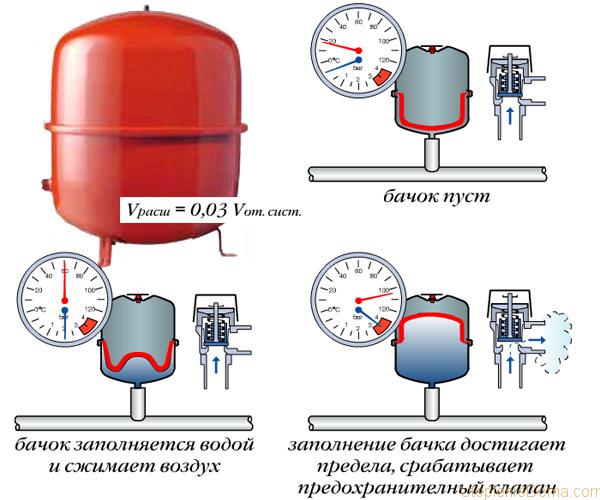

Pressure drops
If the volume of the expansion tank for a closed heating system is less than necessary, then all the liquid that does not fit will be removed to the outside. Special valves are provided in the circuit that release the coolant if the pressure rises to a critical level. Modern boilers are also equipped with such valves. This is a prerequisite for the safe operation of heating. An increase in pressure can even lead to an explosion. Imagine the consequences when the pipes simply burst and hot water flies in all directions. In addition to the fact that you can get injured from a shock, such an emergency threatens to burns to people and animals nearby.
Later, after cooling down, the water decreases in volume. The liquid from the tank is forced back into the pipes, but the coolant is still not enough. This is because the withdrawn water did not return to the outside, it left irrevocably. As a result, the pressure in the circuit drops sharply. This leads to the following results:
- stopping the boiler. Heaters have a certain minimum pressure threshold at which it can operate. If this value is not maintained, it simply cannot turn on, the automation does not allow it to be done;
- defrosting the system. If the stopping of the heating equipment occurred in the winter, and you are not at home, a serious accident may occur. The system will freeze in a few hours, depending on the level of thermal insulation of your home;
- the need for recharge. It is necessary to add the missing amount of water to the circuit.
These are the results of gross errors made when calculating the expansion tank for heating, or if you relied on a tank built into the boiler.
Modern boilers have built-in tanks, the volume of which is often insufficient. Be sure to take this fact into account and, if necessary, install additional tanks.
It also happens that the tank is completely filled, the pressure continues to rise, but does not reach the critical level. The pressure gauge needle balances on the verge of the operating maximum of the circuit, while everything is functioning. Such cases are countless. People very often ask questions about such differences. Of course, such processes worry them, since they are not the norm. With such increases, the circuit operates under extreme conditions, which leads to its early wear. Also, such processes adversely affect the boiler, and it costs money and is not small.
How to calculate the volume of an expansion tank for closed-type heating
The heating system of a private house must be equipped with all the elements necessary for proper operation.
Attempts to do without any "unimportant" devices lead to emergency situations requiring serious repair and restoration.
Moreover, even the complete presence of the necessary parts of the circuit will not provide a regular mode of operation if they are selected incorrectly and do not suit their characteristics.
All units must be carefully calculated and selected according to the data obtained.
The expansion tank is an element of protection of the system against rupture in case of exceeding the permissible pressure.
Staying without heating in winter is a serious problem (read about repairing and diagnosing plumbing violations in the bathroom here).
Therefore, the reliable and correct operation of the expansion tank is of vital importance.
Volume selection
Let's consider separately how to calculate an expansion tank for heating sealed and open types. Since the design and principle of operation of such tanks are completely different, although both perform the same function.


Open tank
The dimensions of the expansion tank for an open heating system, by and large, determine its volume, since the design of such a tank is quite simple. It is made from sheet metal. It has a hole through which the coolant enters the inside and goes back into the pipes. They can also be equipped with an overflow hole through which excess water is discharged into the drain.
It happens that an automatic make-up is brought into the tank. But the main thing is how the expansion tank in the heating system is calculated, or rather, its volume. Let's take the same system with one hundred liters of water. After heating, the liquid will increase by five percent, maybe more, depending on the temperature in the circuit. It turns out that the volume of the expansion tank for this open heating system should be at least five liters, preferably more. And the calculation of the expansion tank for the heating system is reduced to the following algorithm:
- five liters is the expansion of the water;
- a couple of liters should always be in the tank - this is to prevent air from entering the circuit;
- three liters must be made in reserve.
Based on the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank for heating, it receives ten liters. By the way, this is the simplest and most common selection method - ten percent of the amount of water in the circuit.
The easiest way to calculate the volume of an expansion tank for heating is to calculate a tenth of the total amount of coolant. This is a value with the necessary margin, at which everything will work like clockwork.
For closed systems, in addition to the simple, popular, method for calculating the volume of the expansion tank of the heating system, there are more accurate methods. To take advantage of them, you need to know several values. These include:
- how much the volume of water (RH) increases when heated. Answer: five percent. The value has been rounded to the nearest whole number without fractions for convenience. If an anti-freeze liquid circulates in your circuit, then this value will be higher;
- how much water is in the circuit (VC). Such data should already be available from the design stage.Since the selection of the heater is based on this value. If it so happens that you do not know how many liters there are, all that remains is to measure. The first thing that comes to mind is to completely drain all the liquid from the circuit and refill it. The number of liters can be measured in buckets, or you can use a special counter that is installed on the stream;
- what is the maximum pressure the circuit and the boiler (DK) are designed for. This value can be read on the heater documents, or on the heater itself. It is unlikely that it will happen that there are neither documents nor information on the boiler body. But if it really happened, then the Internet will help you;
- what is the pressure in the air chamber of the expansion tank (DB). This is also indicated in the technical documentation.
To calculate how much volume of the expansion tank is needed for heating, a simple mathematical calculation should be performed:
OV x VK x (DK + 1) / DK - DB
Based on the results of calculating the capacity of the expansion tank for heating, you will receive an accurate value. The question of the expediency of such complex calculations remains open. Undoubtedly, according to the results of this formula for calculating the expansion tank of the heating system, a lower value will be obtained than according to the results of the "folk" method. But a larger margin of error is not an error. If the tank is larger than what you need, it's okay, you just need to set it up correctly.
Types of expansion tanks
As you know, for heating private housing, different principles of coolant supply can be applied - natural and forced circulation. For each type of system, its own modifications of the expansion tank are used:
- Open. In infrastructure with natural circulation, the additional tank is installed at the highest point and is in the form of an open tank. The pressure in the pipes is equal to atmospheric, and air bubbles are removed through the tank and, if necessary, water is topped up.
- Closed. If a pump is installed in the heating main to circulate the coolant, a sealed metal cylinder with compressed air acts as an expansion tank. Excess coolant is supplied to the tank when heated, and when the temperature drops, the air pressure displaces the liquid back.
A closed expansion tank offers significant advantages over an open one. Its installation can be carried out in any convenient place, the absence of contact with the atmosphere protects the inner space of pipes and radiators from corrosion and penetration of dirt and small debris. However, the final decision on the choice of the type of expansion tank is usually dictated by the implementation scheme of the heating system as a whole, and not by these important, but not decisive advantages.
To what level to pump the air chamber
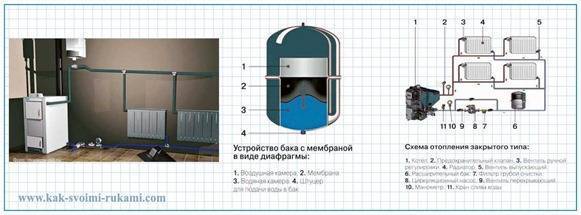
It is important to correctly adjust the expansion tank for closed heating. The calculation of the capacity is, of course, a serious aspect, but even if it is done correctly, the tank can still work in an inappropriate way. To deal with this, let's briefly dwell on its design. It consists of two compartments with a rubber gasket between them. There is no connection between cameras. There is a nipple in the air compartment.
During operation, water fills the volume of the tank chamber, while the membrane is stretched. If the pressure in the air chamber is too high, it will simply prevent the elastic from deforming. As a result, the tank does not work. The air chamber must be two tenths of an atmosphere less than the operating pressure of the boiler. Alternatively, use the manufacturer's recommendations for customization.
Why do you need an expansion tank for heating
For the normal functioning of the heating system and stable circulation of the coolant through all its elements, a stable pressure is required. Its sharp jumps lead to a violation of the hydraulic regime and malfunctioning of individual units.To avoid this, an expansion tank is provided in the system. Its task is to compensate for the change in the volume of the coolant (water or antifreeze) caused by a change in its temperature, and to reduce the possibility of water hammer. The change in the volume of the coolant is also affected by its composition and, accordingly, the temperature coefficient. When using water, the value of this coefficient is on average 4%, in the case of antifreeze, for example ethylene glycol, from 4.4 to 4.8% (depending on the concentration of glycol in the antifreeze). It is the expansion tank that is the very container where the excess coolant is dumped in order to maintain the required pressure in the network.
Depending on the type of heating system (open or closed), different expansion tanks are used. Immediately, we note that an open system (it is also called a system with natural circulation - self-flowing) is rarely used in new houses, it can be found mainly in old buildings.

(no votes yet)